-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 92
tasks 223-232 #62
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
tasks 223-232 #62
Changes from all commits
809222b
17c614d
55739af
4d8e267
1d6b845
aa4dd98
129a20e
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Jump to
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ | ||
| package g0201_0300.s0223_rectangle_area; | ||
|
|
||
| @SuppressWarnings("java:S107") | ||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public int computeArea(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e, int f, int g, int h) { | ||
| long left = Math.max(a, e); | ||
| long right = Math.min(c, g); | ||
| long top = Math.min(d, h); | ||
| long bottom = Math.max(b, f); | ||
|
|
||
| long area = (right - left) * (top - bottom); | ||
| // if not overlaping, either of these two will be non-posittive | ||
| // if right - left = 0, are will automtically be 0 as well | ||
| if (right - left < 0 || top - bottom < 0) { | ||
| area = 0; | ||
| } | ||
| return (int) ((c - a) * (d - b) + (g - e) * (h - f) - area); | ||
| } | ||
| } |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ | ||
| 223\. Rectangle Area | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| Given the coordinates of two **rectilinear** rectangles in a 2D plane, return _the total area covered by the two rectangles_. | ||
|
|
||
| The first rectangle is defined by its **bottom-left** corner `(ax1, ay1)` and its **top-right** corner `(ax2, ay2)`. | ||
|
|
||
| The second rectangle is defined by its **bottom-left** corner `(bx1, by1)` and its **top-right** corner `(bx2, by2)`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** ax1 = -3, ay1 = 0, ax2 = 3, ay2 = 4, bx1 = 0, by1 = -1, bx2 = 9, by2 = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 45 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** ax1 = -2, ay1 = -2, ax2 = 2, ay2 = 2, bx1 = -2, by1 = -2, bx2 = 2, by2 = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 16 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= ax1, ay1, ax2, ay2, bx1, by1, bx2, by2 <= 10<sup>4</sup></code> |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,46 @@ | ||
| package g0201_0300.s0224_basic_calculator; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| int i = 0; | ||
|
|
||
| public int calculate(String s) { | ||
| char[] ca = s.toCharArray(); | ||
|
|
||
| return helper(ca); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int helper(char[] ca) { | ||
|
|
||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. The empty line may be removed. |
||
| int num = 0; | ||
| int prenum = 0; | ||
| boolean isPlus = true; | ||
| for (; i < ca.length; i++) { | ||
| char c = ca[i]; | ||
| if (c != ' ') { | ||
| if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { | ||
| if (num == 0) { | ||
| num = (c - '0'); | ||
| } else { | ||
| num = num * 10 + c - '0'; | ||
| } | ||
| } else if (c == '+') { | ||
| prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); | ||
| isPlus = true; | ||
| num = 0; | ||
| } else if (c == '-') { | ||
| prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); | ||
| num = 0; | ||
| isPlus = false; | ||
| } else if (c == '(') { | ||
| i++; | ||
| prenum += helper(ca) * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); | ||
| isPlus = true; | ||
| num = 0; | ||
| } else if (c == ')') { | ||
| return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ | ||
| 224\. Basic Calculator | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| Given a string `s` representing a valid expression, implement a basic calculator to evaluate it, and return _the result of the evaluation_. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note:** You are **not** allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = "1 + 1" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = " 2-1 + 2 " | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 23 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= s.length <= 3 * 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `s` consists of digits, `'+'`, `'-'`, `'('`, `')'`, and `' '`. | ||
| * `s` represents a valid expression. | ||
| * `'+'` is **not** used as a unary operation (i.e., `"+1"` and `"+(2 + 3)"` is invalid). | ||
| * `'-'` could be used as a unary operation (i.e., `"-1"` and `"-(2 + 3)"` is valid). | ||
| * There will be no two consecutive operators in the input. | ||
| * Every number and running calculation will fit in a signed 32-bit integer. |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ | ||
| package g0201_0300.s0225_implement_stack_using_queues; | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.LinkedList; | ||
| import java.util.Queue; | ||
|
|
||
| public class MyStack { | ||
| Queue<Integer> queueOne; | ||
| Queue<Integer> queueTwo; | ||
| int top; | ||
|
|
||
| /** Initialize your data structure here. */ | ||
| public MyStack() { | ||
| queueOne = new LinkedList<>(); | ||
| queueTwo = new LinkedList<>(); | ||
| top = 0; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| /** Push element x onto stack. */ | ||
| public void push(int x) { | ||
| queueOne.add(x); | ||
| top = x; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ | ||
| public int pop() { | ||
| while (queueOne.size() > 1) { | ||
| int val = queueOne.remove(); | ||
| top = val; | ||
| queueTwo.add(val); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| int popValue = queueOne.remove(); | ||
| queueOne.addAll(queueTwo); | ||
| queueTwo.clear(); | ||
|
|
||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. The empty line may be removed. |
||
| return popValue; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| /** Get the top element. */ | ||
| public int top() { | ||
| return top; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ | ||
| public boolean empty() { | ||
| return queueOne.isEmpty(); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,33 @@ | ||
| 225\. Implement Stack using Queues | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (`push`, `top`, `pop`, and `empty`). | ||
|
|
||
| Implement the `MyStack` class: | ||
|
|
||
| * `void push(int x)` Pushes element x to the top of the stack. | ||
| * `int pop()` Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it. | ||
| * `int top()` Returns the element on the top of the stack. | ||
| * `boolean empty()` Returns `true` if the stack is empty, `false` otherwise. | ||
|
|
||
| **Notes:** | ||
|
|
||
| * You must use **only** standard operations of a queue, which means that only `push to back`, `peek/pop from front`, `size` and `is empty` operations are valid. | ||
| * Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input** \["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"\] \[\[\], \[1\], \[2\], \[\], \[\], \[\]\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \[null, null, null, 2, 2, false\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // return 2 myStack.pop(); // return 2 myStack.empty(); // return False | ||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. It may be changed with the ident format. |
||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= x <= 9` | ||
| * At most `100` calls will be made to `push`, `pop`, `top`, and `empty`. | ||
| * All the calls to `pop` and `top` are valid. | ||
|
|
||
| **Follow-up:** Can you implement the stack using only one queue? | ||
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ | ||
| package g0201_0300.s0226_invert_binary_tree; | ||
|
|
||
| import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { | ||
| if (root == null) { | ||
| return null; | ||
| } | ||
| TreeNode temp = root.left; | ||
| root.left = invertTree(root.right); | ||
| root.right = invertTree(temp); | ||
| return root; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | ||
| 226\. Invert Binary Tree | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| Given the `root` of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return _its root_. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** root = \[4,2,7,1,3,6,9\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \[4,7,2,9,6,3,1\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| 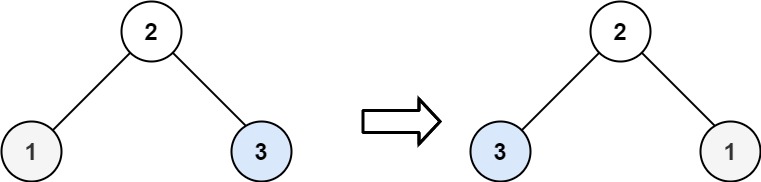 | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** root = \[2,1,3\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \[2,3,1\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** root = \[\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \[\] | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`. | ||
| * `-100 <= Node.val <= 100` |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,44 @@ | ||
| package g0201_0300.s0227_basic_calculator_ii; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public int calculate(String s) { | ||
| int sum = 0; | ||
| int tempSum = 0; | ||
| int num = 0; | ||
| char lastSign = '+'; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { | ||
| char c = s.charAt(i); | ||
| if (Character.isDigit(c)) { | ||
| num = num * 10 + c - '0'; | ||
| } | ||
| // i == s.length() - 1 will make sure that after last num is | ||
| // made and there is nothing to read anything from 's', the final computation is done | ||
| if (i == s.length() - 1 || !Character.isDigit(c) && c != ' ') { | ||
| switch (lastSign) { | ||
| case '+': | ||
| sum += tempSum; | ||
| tempSum = num; | ||
| break; | ||
| case '-': | ||
| sum += tempSum; | ||
| tempSum = -num; | ||
| break; | ||
| case '*': | ||
| tempSum *= num; | ||
| break; | ||
| case '/': | ||
| if (num != 0) { | ||
| tempSum /= num; | ||
| } | ||
| break; | ||
| default: | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| lastSign = c; | ||
| num = 0; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| sum += tempSum; // finally, add tempSum to sum | ||
| return sum; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,37 @@ | ||
| 227\. Basic Calculator II | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| Given a string `s` which represents an expression, _evaluate this expression and return its value_. | ||
|
|
||
| The integer division should truncate toward zero. | ||
|
|
||
| You may assume that the given expression is always valid. All intermediate results will be in the range of <code>[-2<sup>31</sup>, 2<sup>31</sup> - 1]</code>. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note:** You are not allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = "3+2\*2" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 7 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = " 3/2 " | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = " 3+5 / 2 " | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 5 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= s.length <= 3 * 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `s` consists of integers and operators `('+', '-', '*', '/')` separated by some number of spaces. | ||
| * `s` represents **a valid expression**. | ||
| * All the integers in the expression are non-negative integers in the range <code>[0, 2<sup>31</sup> - 1]</code>. | ||
| * The answer is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit integer**. |
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
The empty line may be removed.