A cinema has n rows of seats, numbered from 1 to n and there are ten seats in each row, labelled from 1 to 10 as shown in the figure above.
Given the array reservedSeats containing the numbers of seats already reserved, for example, reservedSeats[i] = [3,8] means the seat located in row 3 and labelled with 8 is already reserved.
Return the maximum number of four-person groups you can assign on the cinema seats. A four-person group occupies four adjacent seats in one single row. Seats across an aisle (such as [3,3] and [3,4]) are not considered to be adjacent, but there is an exceptional case on which an aisle split a four-person group, in that case, the aisle split a four-person group in the middle, which means to have two people on each side.
Example 1:
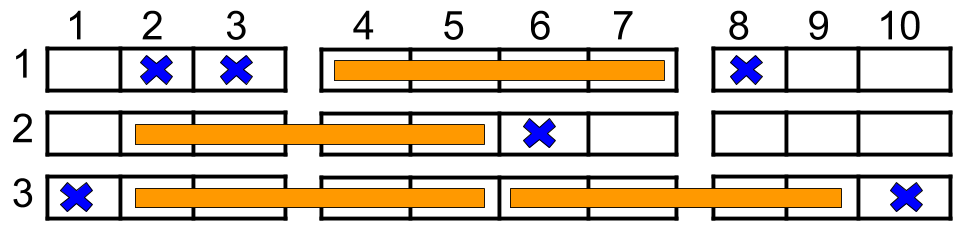
Input: n = 3, reservedSeats = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,8],[2,6],[3,1],[3,10]] Output: 4 Explanation: The figure above shows the optimal allocation for four groups, where seats mark with blue are already reserved and contiguous seats mark with orange are for one group.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, reservedSeats = [[2,1],[1,8],[2,6]] Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, reservedSeats = [[4,3],[1,4],[4,6],[1,7]] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^91 <= reservedSeats.length <= min(10*n, 10^4)reservedSeats[i].length == 21 <= reservedSeats[i][0] <= n1 <= reservedSeats[i][1] <= 10- All
reservedSeats[i]are distinct.
class Solution:
def maxNumberOfFamilies(self, n: int, reservedSeats: List[List[int]]) -> int:
d = defaultdict(int)
for i, j in reservedSeats:
d[i] |= 1 << (10 - j)
masks = (0b0111100000, 0b0000011110, 0b0001111000)
ans = (n - len(d)) * 2
for x in d.values():
for mask in masks:
if (x & mask) == 0:
x |= mask
ans += 1
return ansclass Solution {
public int maxNumberOfFamilies(int n, int[][] reservedSeats) {
Map<Integer, Integer> d = new HashMap<>();
for (var e : reservedSeats) {
int i = e[0], j = e[1];
d.merge(i, 1 << (10 - j), (x, y) -> x | y);
}
int[] masks = {0b0111100000, 0b0000011110, 0b0001111000};
int ans = (n - d.size()) * 2;
for (int x : d.values()) {
for (int mask : masks) {
if ((x & mask) == 0) {
x |= mask;
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxNumberOfFamilies(int n, vector<vector<int>>& reservedSeats) {
unordered_map<int, int> d;
for (auto& e : reservedSeats) {
int i = e[0], j = e[1];
d[i] |= 1 << (10 - j);
}
int masks[3] = {0b0111100000, 0b0000011110, 0b0001111000};
int ans = (n - d.size()) * 2;
for (auto& [_, x] : d) {
for (int& mask : masks) {
if ((x & mask) == 0) {
x |= mask;
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func maxNumberOfFamilies(n int, reservedSeats [][]int) int {
d := map[int]int{}
for _, e := range reservedSeats {
i, j := e[0], e[1]
d[i] |= 1 << (10 - j)
}
ans := (n - len(d)) * 2
masks := [3]int{0b0111100000, 0b0000011110, 0b0001111000}
for _, x := range d {
for _, mask := range masks {
if x&mask == 0 {
x |= mask
ans++
}
}
}
return ans
}function maxNumberOfFamilies(n: number, reservedSeats: number[][]): number {
const d: Map<number, number> = new Map();
for (const [i, j] of reservedSeats) {
d.set(i, (d.get(i) ?? 0) | (1 << (10 - j)));
}
let ans = (n - d.size) << 1;
const masks = [0b0111100000, 0b0000011110, 0b0001111000];
for (let [_, x] of d) {
for (const mask of masks) {
if ((x & mask) === 0) {
x |= mask;
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}