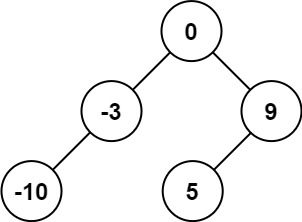
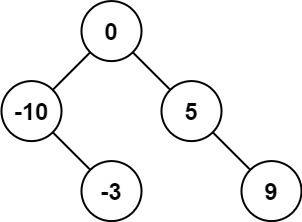
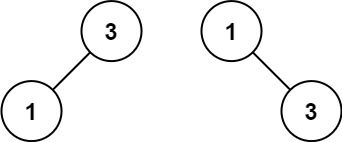
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted: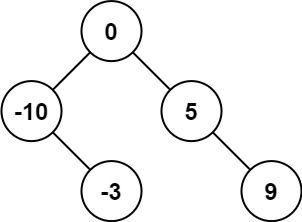
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3] Output: [3,1] Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
We design a recursive function nums. This function returns the root node of the constructed binary search tree.
The execution process of the function
- If
, it means the current array is empty, return null. - If
, take the element with the index in the array as the root node of the current binary search tree, where represents rounding down . - Recursively construct the left subtree of the current binary search tree, whose root node value is the element with the index
in the array, and the node values of the left subtree are all within the index range of the array. - Recursively construct the right subtree of the current binary search tree, whose root node value is the element with the index
in the array, and the node values of the right subtree are all within the index range of the array. - Return the root node of the current binary search tree.
The answer is the return value of the function
The time complexity is nums.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def dfs(l, r):
if l > r:
return None
mid = (l + r) >> 1
left = dfs(l, mid - 1)
right = dfs(mid + 1, r)
return TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right)
return dfs(0, len(nums) - 1)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int[] nums;
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode dfs(int l, int r) {
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
TreeNode left = dfs(l, mid - 1);
TreeNode right = dfs(mid + 1, r);
return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
function<TreeNode*(int, int)> dfs = [&](int l, int r) -> TreeNode* {
if (l > r) {
return nullptr;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
auto left = dfs(l, mid - 1);
auto right = dfs(mid + 1, r);
return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right);
};
return dfs(0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
var dfs func(int, int) *TreeNode
dfs = func(l, r int) *TreeNode {
if l > r {
return nil
}
mid := (l + r) >> 1
left, right := dfs(l, mid-1), dfs(mid+1, r)
return &TreeNode{nums[mid], left, right}
}
return dfs(0, len(nums)-1)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sortedArrayToBST(nums: number[]): TreeNode | null {
const n = nums.length;
if (n === 0) {
return null;
}
const mid = n >> 1;
return new TreeNode(
nums[mid],
sortedArrayToBST(nums.slice(0, mid)),
sortedArrayToBST(nums.slice(mid + 1)),
);
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
fn to_bst(nums: &Vec<i32>, start: usize, end: usize) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if start >= end {
return None;
}
let mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
Some(
Rc::new(
RefCell::new(TreeNode {
val: nums[mid],
left: Self::to_bst(nums, start, mid),
right: Self::to_bst(nums, mid + 1, end),
})
)
)
}
pub fn sorted_array_to_bst(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
Self::to_bst(&nums, 0, nums.len())
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {
const dfs = (l, r) => {
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
const left = dfs(l, mid - 1);
const right = dfs(mid + 1, r);
return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right);
};
return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
};