Given the root of a binary tree, construct a 0-indexed m x n string matrix res that represents a formatted layout of the tree. The formatted layout matrix should be constructed using the following rules:
- The height of the tree is
heightand the number of rowsmshould be equal toheight + 1. - The number of columns
nshould be equal to2height+1 - 1. - Place the root node in the middle of the top row (more formally, at location
res[0][(n-1)/2]). - For each node that has been placed in the matrix at position
res[r][c], place its left child atres[r+1][c-2height-r-1]and its right child atres[r+1][c+2height-r-1]. - Continue this process until all the nodes in the tree have been placed.
- Any empty cells should contain the empty string
"".
Return the constructed matrix res.
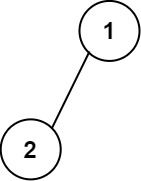
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [["","1",""], ["2","",""]]
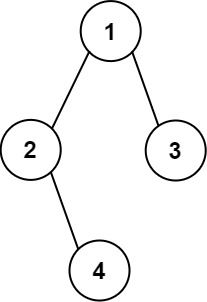
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4] Output: [["","","","1","","",""], ["","2","","","","3",""], ["","","4","","","",""]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 210]. -99 <= Node.val <= 99- The depth of the tree will be in the range
[1, 10].
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def printTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[str]]:
def height(root):
if root is None:
return -1
return 1 + max(height(root.left), height(root.right))
def dfs(root, r, c):
if root is None:
return
ans[r][c] = str(root.val)
dfs(root.left, r + 1, c - 2 ** (h - r - 1))
dfs(root.right, r + 1, c + 2 ** (h - r - 1))
h = height(root)
m, n = h + 1, 2 ** (h + 1) - 1
ans = [[""] * n for _ in range(m)]
dfs(root, 0, (n - 1) // 2)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
String[][] res = new String[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(res[i], "");
}
dfs(root, res, h, 0, (n - 1) / 2);
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] t : res) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(t));
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, String[][] res, int h, int r, int c) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res[r][c] = String.valueOf(root.val);
dfs(root.left, res, h, r + 1, c - (1 << (h - r - 1)));
dfs(root.right, res, h, r + 1, c + (1 << (h - r - 1)));
}
private int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
return 1 + Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> printTree(TreeNode* root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
vector<vector<string>> ans(m, vector<string>(n, ""));
dfs(root, ans, h, 0, (n - 1) / 2);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<vector<string>>& ans, int h, int r, int c) {
if (!root) return;
ans[r][c] = to_string(root->val);
dfs(root->left, ans, h, r + 1, c - pow(2, h - r - 1));
dfs(root->right, ans, h, r + 1, c + pow(2, h - r - 1));
}
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return -1;
return 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right));
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func printTree(root *TreeNode) [][]string {
var height func(root *TreeNode) int
height = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return -1
}
return 1 + max(height(root.Left), height(root.Right))
}
h := height(root)
m, n := h+1, (1<<(h+1))-1
ans := make([][]string, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]string, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = ""
}
}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, r, c int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, r, c int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
ans[r][c] = strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
dfs(root.Left, r+1, c-int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1))))
dfs(root.Right, r+1, c+int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1))))
}
dfs(root, 0, (n-1)/2)
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}