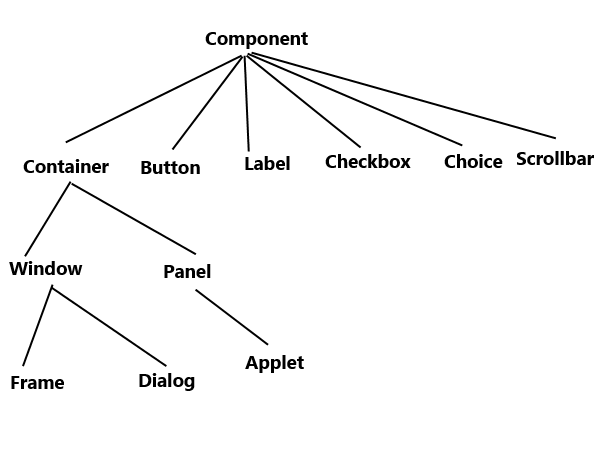
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Component add (Component ComponentRef);
void remove(Component ComponentRef);void removeAll(); +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Checkbox is a control that is used to turn an option on or off.Label associated with each check box that describes what option the box represents.Checkbox by clicking on it.## Constructors:
+ 1. Checkbox() throws HeadlessException
+ 2. Checkbox(String str) throws HeadlessException
+ 3. Checkbox(String str, boolean on) throws HeadlessException
+ 4. Checkbox(String str, boolean on, CheckboxGroup cbGroup) throws HeadlessException
+ 5. Checkbox(String str, CheckboxGroup cbGroup, boolean on) throws HeadlessException
## Methods
+ 1. boolean getState();
+ 2. void setState(boolean on);
+ 3. String getLabel();
+ 4. void setLabel(String str);
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Component that contains a label and that generates an event when it is pressed. Push buttons are objects of type button. Button defines these two constructors:## Constructors
+ 1. public Button()
+ 2. public Button(String buttonLabel) throws headless Exception;
## Public Methods
+ 1. public String getLabel();
+ - Get the label of this button instance.
public void setLabel(String btnlabel);Set the label of this button instance.
+public void setEnable(boolean enable);
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ CheckboxGroup();
Checkbox getSelectedCheckbox(); void setSelectedCheckbox(Checkbox which); +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ++Same as Select in HTML + - The
+Choiceclass is used to create a pop-up list of items from which user may choose. + - Only one item can be chosen.
## Constructors:
+ Choice();
## Methods:
+ 1. void add(String name);
+ 2. String getSelectedItem();
+ 3. int getSelectedIndex();
+ 4. int getItemCount();
+ 5. void select(String name);
+ 6. String getItem(int index);
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Also called javafx JFx
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Label and it contains a String, which it displays.Label() throws HeadLessExceptionLabel(String str) throws HeadLessException // The string is left justified.Label(String str, int how) throws HeadLessException // label.LEFT, label.RIGHT i. void setText(String str);
+ii. String getText();
+iii. void setAlignment(int how);
+iv. int getAlignment();
Label name = new Label("Arjun");
+ name.setText("Another Arjun");
+ String myNameWas = name.getText();
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ GridBagLayout class is flexible Layout manager that aligns components vertically and horizontally and the components of different size.GridBagLayout object maintains a dynamic, rectangular grid of cells.GridBagLayout is associated with an instance of GridBagConstraints.void setConstraints(Component c, GridBagConstraints cons);
+1.GridBagLayout();
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ a. GridLayout()
+b. GridLayout(int rows, int cols)
+c. GridLayout(int rows, int cols, int hgap, int vgap)
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ BorderLayout()BorderLayout(int hgap, int vgap)add(new Button("North"), BorderLayout.WEST)
+ add("North", new Button("West") ) +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ CardLayout () CardLayout (int hgap, int vgap) void first (Container deck) void last (Container deck) void next (Container deck) void previous (Container deck) void show (Container deck, String cardName)  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ## Constructors
+ 1. FlowLayout()
+ 2. FlowLayout(int align)
+ 3. FlowLayout(int align, int hgape, int vgape)
## FlowLayout Alignments
+FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, FlowLayout.CENTER
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ LayoutManager are provided to arrange GUI components on a container for presentation purpose.Container object has a LayoutManager interface.LayoutManager interfacesetLayout() method.setLayout() is made, then the default layout manager is used that is FlowLayout.## Types of LayoutManager
+ 1. FlowLayout
+ 2. BorderLayout
+ 3. GridLayout
+ 4. CardLayout
+ 5. GridBagLayout
### Two ways to create a Frame in AWT :
+ 1. By extending Frame Class. (Inheritance)
+ 2. By creating the object of Frame class. (Association)
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ List class provides a compact, multiple-choice scrolling selection list.## Constructors
+ 1. List() throws HeadlessException
+ 2. List(int numRows) throws HeadlessException
+ 3. List( int numRows, boolean multipleSelect) throws HeadlessException
++numRows number of rows will be visible, if false, then only one item may be selected.
+
## Methods
+ 1. void add(String name);
+ 2. void add(String name , int index);
+ 3. String getSelectedItem()
+ - for single selection
+ 5. int getSelectedIndex()
+ 6. String[] getSelectedItems()
+ - for multiple selection
+ 8. int[] getSelectedIndexes()
+ 9. int getItemCount();
+ 10. void select(int index);
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Scrollbar is used to select continuous values between a specified minimum and maximum.# Constructors
+ 1. Scrollbar() throws HeadlessException
+ 2. Scrollbar(int style) throws HeadlessException
+- Style includes Scrollbar.VERTICAL and Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL.
Scrollbar(int style, int thumbSize, int min, int max) throws HeadlessException# Methods:
+ 1. void setValues(int initialValue, int thumbSize, int min, int max);
+ 2. int getValue()
+ 3. void setValue(int newValue)
+ 4. int getMinimum()
+ 5. int getMaximum()
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ++Sub class of
+TextComponent
TextArea.## Constructors
+ 1. TextArea() throws HeadlessException
+ 2. TextArea(int numLines, int numChars) throws HeadlessException
+ 3. TextArea(String str) throws HeadlessException
+ 4. TextArea(Stirng str, int numLines, numChars) throws HeadlessException
+ 5. TextArea(String str, int numLines,int numChars, int sBars) throws HeadlessException
++Here, numLines represents rows and numChars represents number of columns. sBars is Scroll Bar to use scrollbar in the TextArea.
+
SCROLLBARS_BOTH, SCROLLBARS_NONE, SCROLLBARS_HORIZONTAL_ONLY, SCROLLBARS_VERTICAL_ONLY
Public Methods:
+ 1. String getText()
+ 2. void setText()
+ 3. String getSelectedText()
+ 4. void select(int startIndex, int endIndex)
+ 5. boolean isEditable()
+ 6. void setEditable( boolean canEdit)
++These methods are defined by
+TextComponent
+TextComponentclass is the superclass ofTextFieldandTextArea
+So, bothTextFieldandTextAreacan use these methods.
TextArea adds the following editing methods:
+ 1. void append(String str)
+ - The append() method appends the strings specified by str to the end of the current text.
void insert(String str , int index)insert() method inserts the string passed in str at the specified index.
void replaceRange(String sr, int startIndex , int endIndex)
replaceRange() replaces the characters from startIndex to endIndex-1, with the replacement text passed in str. +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ The TextField class implements a single line text entry area ususally called an edit control.
TextField allow the user to enter strings and to edit the text using the arrow keys, cut and paste keys and mouse selection.
## Constructors
+ 1. public TextField(String initialText, int columns)
+ - Construct a TextField instance with the given initial text string with the number of column
public TextField(String strText);Set the text display text on this TextField instance
+public TextField(int columns);
## Public Methods
+ 1. boolean isEditable()
public String getText();Get the current text on this TextField instance
+public void setText(String strText)
Set this display text on this TextField instance
+public void setEditable(boolean editable);
Set the TextField to editable (read/ write) or non editable (read- only)
+void setEchoChar(char ch)
If ch is 0, then normal echoing is restored.
+TextField password = new TextField();
+password.setEchoChar("*")
boolean echoCharIsSet();
Return ture or false whether the TextField is set with some char
+char getEchoChar();
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ++1992, Open Database Connectivity
+
++ + +1997, Java Database Connectivity +- Support any database +- Support any platform +- Only for Java language +- Developed by Sun Microsystems.
+
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ | Statement | +Prepared Statement | +
|---|---|
| At the time of creating Statement object, we are not required to provide any query | +At the time of creating Prepared Object, we have to provide SQL Query compulsary which can be send to the database and will be compiled. | +
Statemnt st = con.createStatement(); |
+PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(query); |
+
| Hence, Statement object is not associated with any query and we can use for multiple queries. | +Hence, Prepared Statement is associated with any query. | +
| Whenever, we are using execute method, everytime query will be compiled. | +Whenever, we are using execute method, query won't be compiled every time. | +
| Statement object can work only for static queries. | +Work for Static and Dynamic Queries | +
| Relatively, performance is low. | +Relatively, performance is high. | +
| Chance of SQL Injection | +No Chance of SQL Injection | +
| Inserting data value and large object is difficult. | +Insering data value and large object is easy. | +
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ++Progress Direct Software Company introduced Type-5 driver but is not industry standard driver.
+
++ODBC Supports all programming languages.
+

++Written in C, C++
+
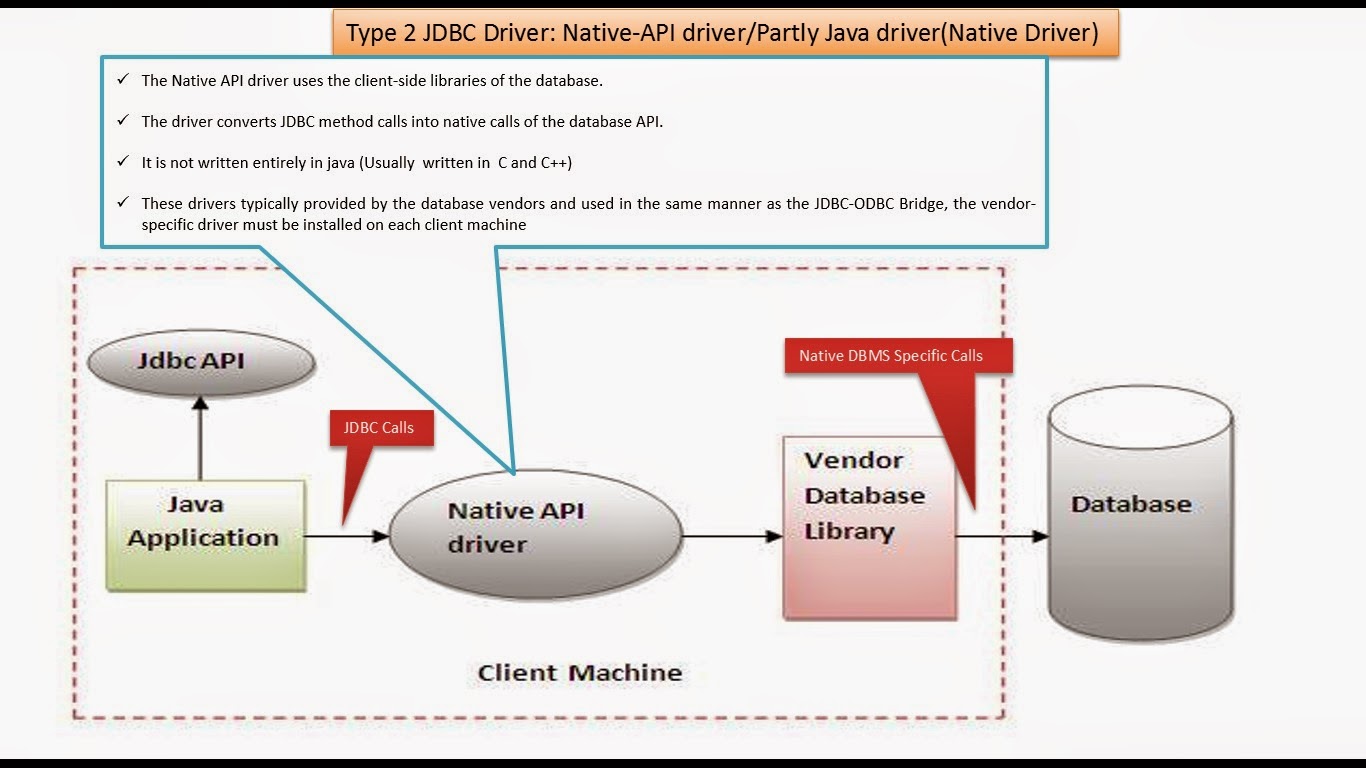
++Three tiers
+
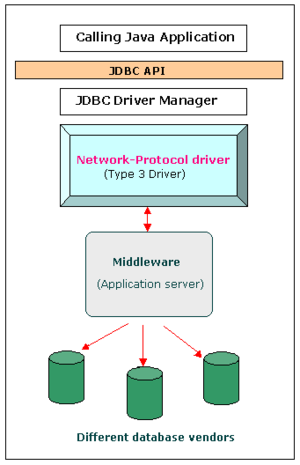

++See in copy.
+
| Property | +Type 1 | +Type 2 | +Type 3 | +Type 4 | +
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion | +From JDBC Calls to ODBC Call | +From JDBC Calls to Native Library Call | +From JDBC Calls to Middleware Server Call | +From JDBC Calls to Database specific Call | +
| Implemented In | +Only Java | +Java and Native Langiages like C, C++ | +Only Java | +Only Java | +
| Architecture | +2 Tier | +2 Tier | +3 Tier | +2 Tier | +
| Platform Independent | +No | +No | +Yes | +Yes | +
| Database Independent | +Yes | +No | +Yes | +No | +
| Thick or Thin | +Thick | +Thick | +Thick | +Thin | +
| Also Known As | +JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver | +Native API-Partly Driver or Native Driver | +All Java Net Protocol Driver or Network Protocol Driver or Middleware Driver | +Pure Java Driver or Native Protocol or Thin Driver | +
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 
Load and Register driver class.
+Class.forName("Oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");
Establish Conection
+Connection con = Driver.Manager.getConnection( url , DbUsername , DbPassword ) ;
Statement st = con.createStatement();Result rs = st.executeQuery("Select * from employees");Process Result from ResultSet
+while(rs.next())
+{
+ System.out.Println(rs.getInt(1));
+}
+Close connection
+ con.close();
 +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ CREATE TABLE, ALTER, DROPSELECTALTER, PASSWORD, GRANT ACCESSINSERT, DELETE, UPDATESTART AUDITCOMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT++Returns Result Set
+
++Returns Numeric Value
+
executeQuery()To execute SELECT queries.
public result executeQuery(String sqlQuery) throws SQLException
+Eg:
+Result rs = st.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM employess");
+while(rs.next()){
+ System.out.println(" ID : " rs.getInt(1));
+}
+executeUpdate()
public int executeUpdate(String sqlQuery) throws SQLException Eg:
+ int affectedRow = st.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO employees(`id`) VALUES ('1')");
+Returns the afftected rows.
+execute()SELECT and NON-SELECT operations.SQL query until run-time, we can use execute().booleanSELECT QuerySELECT Querypublic boolean execute (String query) throws SQLExceptionEg:
+ boolean b = st.execute(Dynamically provide SQLQuery);
+ if(b == true) {
+ ResultSet rs = st.getResultSet();
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ int rowCount = st.getUpdateCount();
+ }
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ <html>
+
+<head>
+ <title>Passing Parameter to Applet</title>
+</head>
+
+<body>
+ <applet code="ParamDemo.java" height = "300" width = "300">
+ <param name="fontName" value="Comic Sans MS">
+ <param name="fontSize" value="40">
+ <param name="leadingfontName" value="14.80">
+ <param name="active" value="true">
+ </applet>
+</body>
+
+</html>
+import java.applet.*;
+import java.awt.*;
+
+// Following HTML chunk will pass parameter to Applet. This is comment for Java Compiler but not for appletviewer, so altering the attribute of parameter never compell to recompile again.
+
+/*/
+ <applet code = "ParamDemo" height = "500" width = "500">
+ <param name = "fontName" value = "Comic Sans MS">
+ <param name = "fontSize" value = "40">
+ <param name = "leading" value = "14.80">
+ <param name = "active" value = "true">
+ </applet>
+*/
+public class ParamDemo extends Applet {
+ String fontName;
+ String param;
+ int fontSize;
+ float leading;
+ boolean active;
+
+ public void init() {
+
+ // Param is not used here because to get the String value and again to pass to String, no temp variable (param) is needed.
+ fontName = getParameter("fontName");
+ if (fontName == null) {
+ fontName = "Not Specified";
+ }
+
+ // Param is used as temporary String variable which retrieves the parameter passed.
+
+ param = getParameter("fontSize");
+ try {
+ if (param != null) {
+ fontSize = Integer.parseInt(param); // Converts the number in String to Integer data type.
+ } else {
+ fontSize = 0;
+ }
+ } catch (NumberFormatException exc) {
+ fontSize = 0;
+ }
+
+ param = getParameter("leading");
+ try {
+ if (param != null) {
+ leading = Float.valueOf(param).floatValue(); // Converts the number in String to Float data type.
+ } else {
+ leading = 0f;
+ }
+ } catch (NumberFormatException exc) {
+ leading = 0f;
+ }
+ param = getParameter("active");
+ if (param != null) {
+ active = Boolean.valueOf(param).booleanValue(); // Converts the boolean value in String to Boolean data type.
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void paint(Graphics graphicsObject) {
+ graphicsObject.drawString("Font Name : " + fontName, 100, 50);
+ graphicsObject.drawString("Font Size : " + fontName, 100, 60);
+ graphicsObject.drawString("Leading : " + leading, 100, 70);
+ graphicsObject.drawString("Active : " + active, 100, 80);
+ }
+
+}
+/* This shows the available fonts in Host Computer. */
+
+/* <applet code = "AvailableFonts" height ="300" width = "300" ></applet> */
+
+import java.awt.*;
+import java.applet.*;
+
+public class AvailableFonts extends Applet {
+ public void paint(Graphics g) {
+ String message = ""; // Initialize string to empty first.
+ String fontLists[];
+ /* I don't get the below line. */
+ GraphicsEnvironment ge = GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
+ fontLists = ge.getAvailableFontFamilyNames();
+ for (String fontList : fontLists) {
+ message += fontList + "\n ";
+ g.drawString(message, 10, 20);
+ }
+ }
+}
+import java.awt.*;
+import java.applet.*;
+
+// This HTML chunk is for passing parameter to appletviewer.
+
+/*
+ <applet code = "Introduction" height = "200" width = "500">
+ <param name = "fontName" value = "Tahoma">
+ <param name = "fontSize" value = "16">
+ <param name = "title" value = "Introduction">
+ <param name = "message" value = " >> I read in Gandaki College of Information and Science.">
+ </applet>
+*/
+
+public class CustomFont extends Applet{
+ String param;
+ String fontName;
+ String title;
+ String message;
+ int fontSize;
+
+ // We are defining our custom font. So, font object is created.
+ Font myFont;
+
+
+ public void init()
+ {
+
+ fontName = getParameter("fontName");
+ if(fontName == null)
+ {
+ fontName = "TimesRoman";
+ }
+
+ title = getParameter("title");
+ if(title == null)
+ {
+ title = "Untitled";
+ }
+
+ message = getParameter("message");
+ if(message == null)
+ {
+ message = "Write your description here.";
+ }
+
+ param = getParameter("fontSize");
+ try{
+ if(param != null)
+ {
+ fontSize = Integer.parseInt(param);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ fontSize = 10; // parameter pass garyo tara integer parse vayena vane
+ }
+ }catch(NumberFormatException exc)
+ {
+ fontSize = 15; // Parameter nai pass garena vane chahi yo run huncha
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void paint(Graphics g)
+ {
+ // Font object Syntax : Font(font_name, Font.font_type, font_size);
+
+ myFont = new Font(fontName,Font.BOLD,fontSize);
+ g.setFont(myFont); // Setting the defined font for this object.
+ setBackground(Color.red); // Setting background color.
+ setForeground(Color.white); // Setting foreground color.
+
+ g.drawString(title,20,50);
+ myFont = new Font(fontName,Font.PLAIN,fontSize); // Defining new font-style for displaying message.
+ g.setFont(myFont); // Setting the new font.
+ g.drawString(message,20,80);
+ }
+}
+import java.applet.*;
+import java.awt.*;
+
+/*
+ <applet code = "Flag" width = "500" height = "500"></applet>
+*/
+
+public class Flag extends Applet {
+
+ static Color NEPALIFLAG = new Color(221, 12, 39); // Defines custom color
+
+ public void paint(Graphics flag) {
+
+ // Figure starts from (210,10)
+
+ // For upper traingle
+ int upperTriangleX[] = { 210, 360, 210 }; // +150 for upper triangle
+ int upperTriangleY[] = { 10, 160, 160 };
+ // g.drawPolygon(upperTriangleX,upperTriangleY,3); // Also can be drawn like
+ // this.
+ Polygon upperTriangle = new Polygon(upperTriangleX, upperTriangleY, 3);
+ flag.drawPolygon(upperTriangle);
+ flag.setColor(NEPALIFLAG); // Setting color of our brave Gorkha Soldiers Blood
+ flag.fillPolygon(upperTriangle);
+
+ // For lower traingle
+ int lowerTriangleX[] = { 210, 390, 210 }; // +180 for lower triangle
+ int lowerTriangleY[] = { 160, 340, 340 };
+ Polygon lowerTriangle = new Polygon(lowerTriangleX, lowerTriangleY, 3);
+ flag.drawPolygon(lowerTriangle);
+ flag.setColor(NEPALIFLAG);
+ flag.fillPolygon(lowerTriangle);
+
+ // For standing rod
+ int rodX[] = { 207, 210, 210, 207 };
+ int rodY[] = { 7, 7, 500, 498 };
+ Polygon rod = new Polygon(rodX, rodY, 4);
+ flag.drawPolygon(rod);
+ flag.setColor(Color.black);
+ flag.fillPolygon(rod);
+
+ // For borders
+ int borderX[] = { 210, 210, 360, 210, 390, 210, 210, 396, 216, 366 }; // 3 units
+ int borderY[] = { 7, 10, 160, 160, 340, 340, 343, 343, 163, 163 };
+ Polygon border = new Polygon(borderX, borderY, 10);
+ flag.drawPolygon(border);
+ flag.setColor(Color.blue);
+ flag.fillPolygon(border);
+
+ // For moon
+ // One Oval overlaps other Oval to form a Crescent moon; I was unable to learn
+ // drawArc() at this moment.
+
+ flag.setColor(Color.white);
+ flag.fillOval(240, 100, 30, 30); // Synatx : fillOval(int xPosition, int yPosition, width, height)
+ flag.setColor(NEPALIFLAG);
+ flag.fillOval(240, 91, 30, 30);
+
+ // For star
+ int starX[] = { 240, 250, 255, 260, 270, 265, 270, 260, 255, 250, 240, 245 };
+ int starY[] = { 260, 260, 250, 260, 260, 270, 280, 280, 290, 280, 280, 270 }; // Starting is 240
+ Polygon star = new Polygon(starX, starY, 12);
+ flag.drawPolygon(star);
+ flag.setColor(Color.white);
+ flag.fillPolygon(star);
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ There are two ways to run an applet :
+To execute the applet by HTML file, create an applet and compile it. After that create an html file and place the applet code in HTML file. Now click the HTML file.
+//HelloApplet.java
+import java.applet.Applet;
+import java.awt.Graphics;
+public class HelloApplet extends Applet{
+ public void paint(Graphics g){
+ g.drawString("welcome",150,150);
+ }
+
+}
+++Note:
+
Class must be public because its object is created by Java Plugin software that resides on the browser. +HelloApplet.html
+<html>
+ <title>Applet's Demonstration</title>
+ <body>
+ <applet code="HelloApplet.class" width="300" height="300">
+ </applet>
+ </body>
+</html>
+To execute the applet by appletviewer tool, create an applet that contains applet tag in comment and compile it. After that run it by: appletviewer HelloApplet.java. Now HTML file is not required but it is for testing purpose only.
+//HelloApplet.java
+import java.applet.Applet;
+import java.awt.Graphics;
+public class HelloApplet extends Applet{
+ public void paint(Graphics g){
+ g.drawString("welcome to applet",150,150);
+ }
+}
+To execute the applet by appletviewer tool, write in command prompt:
+ c:\>javac HelloApplet.java
+ c:\>appletviewer HelloApplet.java
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Java will allow the applet to load the data holding the HTML file that started the applet (theDocumentBase) and the directory from which class file was loaded (codeBase). Both documentBase and codeBase return directories as URL object respectively.
+blue.jpg.
+import java.awt.*;
+import java.applet.*;
+/*
+ <applet code = "DisplayImage" height = "400" width = "400"></applet>
+*/
+
+public class DisplayImage extends Applet {
+
+ public Image picture;
+
+ public void init() {
+ picture = getImage(getDocumentBase(), "blue.jpg");
+ }
+
+ public void paint(Graphics g){
+ g.drawImage(picture,30,30,this);
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ java.applet.Applet.main() methodAWT) to provide the graphical user interface (GUI).JApplet classJApplet which inherits Applet.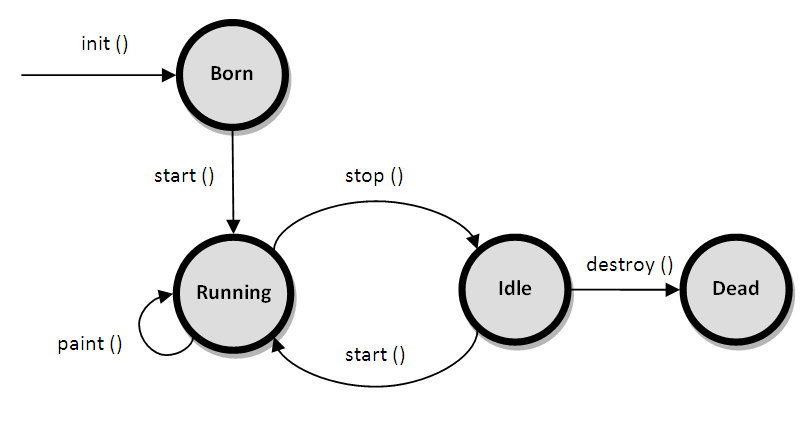
init()start()paint()
+Whenever an applet is terminated, the following sequence of methods calls takes place.stop()destroy()init()The init( ) method is the first method to be called. This is where you should initialize variables. This method is called only once during the run time of your applet.
start()
The start( ) method is called after init( ). It is also called to restart an applet after it has been stopped. Whereas init( ) is called once—the first time an applet is loaded—start( ) is called each time an applet’s HTML document is displayed onscreen. So, if a user leaves a web page and comes back, the applet resumes execution at start( ).
paint()
The paint( ) method is called each time an AWT-based applet’s output must be redrawn. This situation can occur for several reasons. Whatever the applet must redraw its output, paint( ) method is called. The paint( ) method has one parameter of type Graphics.
stop()
The stop( ) method is called when a web browser leaves the HTML document containing the applet—when it goes to another page, for example. When stop( ) is called, the applet is probably running. You should use stop( ) to suspend threads that don’t need to run when the applet is not visible. You can restart them when start( ) is called if the user returns to the page.
destroy()
destroy( ) method is called when the environment determines that your applet needs to be removed completely from memory. At this point, you should free up any resources the applet may be using. The stop( ) method is always called before destroy( ).Syntax :
+ <applet
+ [codebase = codebaseURL]
+ code = appletFile
+ [alt = alternateText]
+ [name = appletInstanceName]
+ width = pixels
+ height = pixels
+ [align = alignment]
+ [vspace = pixels]
+ [hspace = pixels]
+ >
+
+ [< PARAM NAME = attributeName VALUE = AttributeValue>] >> Important for Exam 💯
+ [HTML Displayed in the absence of Java]
+
+ </applet>
+Note : [ ] ⏩ Optional
+getParameter( ) import java.applet.*;
+import java.awt.*;
+
+/*
+ <applet code = "LifeCycle.class" height = "300" width = "300">
+
+ </applet>
+*/
+
+public class LifeCycle extends Applet{
+ String message = "";
+
+ public void init(Graphics graphicsObject){
+ message += "Inside Init() ";
+ graphicsObject.drawString(message, 100, 120);
+ }
+
+ public void start() {
+ message += "Inside Start() ";
+ }
+
+ public void paint(Graphics graphicsObject) {
+ message += "Inside Paint() ";
+ graphicsObject.drawString(message, 100, 120);
+ }
+
+ public void stop() {
+ message += "Inside Stop() ";
+ }
+
+ public void destroy() {
+ message += "Inside Destroy() ";
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ An applet can play an audio file represented by the AudioClip interface in the java.applet package. The AudioClip interface has three methods, including :
+public void play() − Plays the audio clip one time, from the beginning.
+public void loop() − Causes the audio clip to replay continually.
+public void stop() − Stops playing the audio clip.
+To obtain an AudioClip object, you must invoke the getAudioClip() method of the Applet class. The getAudioClip() method returns immediately, whether or not the URL resolves to an actual audio file. The audio file is not downloaded until an attempt is made to play the audio clip.
sample.wav.
+import java.awt.*;
+import java.net.*; // For URL objects
+import java.applet.*;
+
+/*
+ <applet code = "PlayAudio" height = "400" width = "400">
+ <param name = "audioURL" value = "sample.wav">
+ </applet>
+
+*/
+
+// AppletContext is an environment (interface) which helps to communicate with outer-environment and deal with media files such as audio, image.
+
+public class PlayAudio extends Applet {
+ public AudioClip myMusic; // Defining a variable of data type AudioClip.
+ public AppletContext context;
+
+ public void init() {
+ context = this.getAppletContext();
+ String audioURL = this.getParameter("audioURL"); // This gets the parameter passed from applet.
+ if (audioURL == null) {
+ audioURL = "sample.wav"; // If no parameter is passed.
+ }
+
+ try {
+ URL myURL = new URL(this.getDocumentBase(), audioURL); // New URL object storing audio URL passed by user.
+ myMusic = context.getAudioClip(myURL);
+ // myMusic = this.getAudioClip(myURL); // Also can be done like this.
+ } catch (MalformedURLException exc) {
+ exc.printStackTrace();
+ context.showStatus("Couldn't load audio file."); // Showing status to the Browser status bar.
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void start() { // When Applet starts
+ if (myMusic != null) {
+ myMusic.loop();
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void stop() { // When Applet stop
+ if (myMusic != null) {
+ myMusic.stop();
+ }
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
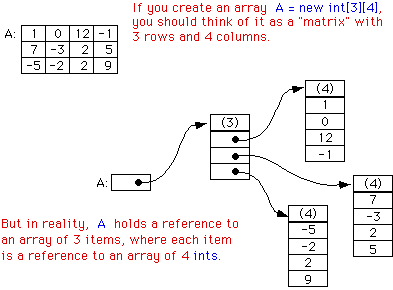
+ This representation of array shows how the memory blocks are allocated to the array. Value is not assigned to the memory blocks, though.
+
class ArrayRepresentation {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ // First the level of the array is pre-defined, and initial indearray of the
+ // array is mentioned in assignation.
+ int[][][] array = new int[2][][];
+
+ // First Level
+ array[0] = new int[3][];
+ array[1] = new int[2][];
+
+ // Second Level
+ array[0][0] = new int[1];
+ array[0][1] = new int[2];
+ array[0][2] = new int[3];
+
+ array[1][0] = new int[2];
+ array[1][1] = new int[2];
+
+ // In this way, the memory blocks are allocated and no memory leakage happens
+ // here.
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ This representation of array teaches how to allocate the memory block to the elements and assign the integer value to those memory blocks.
+
// Let's Experience 5D Array
+// www.github.com/thearjun/Java
+
+class ArrayRepresentation{
+ public static void main(String[] args){
+
+ // First Level
+ int[][][][][] array = new int [4][][][][];
+
+ // Second Level
+ array[0] = new int [1][][][];
+ array[1] = new int [1][][][];
+ array[2] = new int [1][][][];
+ array[3] = new int [3][][][];
+
+ // Third Level
+ array[0][0] = new int [2][][];
+ array[2][0] = new int [2][][];
+ array[3][0] = new int [1][][];
+
+ // Fourth Level
+ array[0][0][0] = new int [2][];
+ array[0][0][1] = new int [1][];
+
+ // Fifth Level
+ array[0][0][1][0] = new int [2];
+
+ // Value Assign for first level
+ array[0][0][0][0][0] = 1;
+ array[1][0][0][0][0] = 2;
+ array[2][0][0][0][0] = 3;
+ array[3][0][0][0][0] = 4;
+
+ // Value assign for second level
+ array[0][0][0][0][0] = 5;
+ array[1][0][0][0][0] = 13;
+ array[2][0][0][0][0] = 14;
+ array[3][0][0][0][0] = 18;
+ array[3][1][0][0][0] = 19;
+ array[3][2][0][0][0] = 20;
+
+ // Value assign for third level
+ array[0][0][0][0][0] = 6;
+ array[0][0][0][0][0] = 6;
+ array[2][0][0][0][0] = 15;
+ array[2][0][1][0][0] = 16;
+ array[3][0][0][0][0] = 17;
+
+ // Value assign for fourth level
+ array[0][0][0][0][0] = 8;
+ array[0][0][0][1][0] = 9;
+ array[0][0][1][0][0] = 10;
+
+ // Value assign for fifth level
+ array[0][0][1][0][0] = 11;
+ array[0][0][1][0][1] = 12;
+
+ // // Now we are printing the elements of array. We know that we haven't assigned 0 to any of those memory blocks, so we print the elements which are not zero.
+
+ // System.out.println("First Level Elements : [ ");
+ // for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
+ // System.out.println(array[i]+" ");
+
+ // // if(array[i]!=0){
+ // // System.out.println(array[i]+" ");
+ // // }
+ // }
+ // System.out.print("]");
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 
This method of declaring array is often referred as conventional way of declaring array.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ class Array{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ int days[];
+ days = new int[12];
+ for(int i = 0; i<12;i++){
+ days[i] = i;
+ }
+ for(int i = 0; i<12;i++){
+ System.out.println("Day : "+days[i]);
+ }
+ System.out.println(days.getClass().getName());
+ }
+}
+class AlternativeArrayDeclaration{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ /* Array can be declared like : type_name[] variable_name; for eg: public static void main(String[] args) */
+ int a1[] = new int[3];
+ int[] a2 = new int[2];
+
+ /* We can also declare multiple arrays at a time by this method. */
+
+ int [] a3,a4,a5 = new int [3];
+ /* which creates the three array variables of integer type */
+ }
+}
+class ArrayAssignment{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ int month[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
+ for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
+ System.out.println("Month : "+month[i]);
+ }
+ }
+}
+class Average{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ double marks[] = {40.6,30.5,90.3,20.8,87.5};
+ double result=0;
+
+ for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
+ result +=marks[i];
+ }
+ System.out.println("Percentage = "+result/5);
+ }
+}
+class TwoDimensionalArray{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ int nums[][] = new int[4][5];
+
+ int i,j,k=0;
+ for (i=0;i<4;i++){
+ for(j=0;j<5;j++){
+ nums[i][j] = k;
+ k++;
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (i=0;i<4;i++){
+ for(j=0;j<5;j++){
+ System.out.print(nums[i][j]+" "); /* Print doesn't gets printed in new line , but println does. Know the difference. */
+ }
+ System.out.println();
+ }
+ System.out.println(nums.getClass().getName()); // This returns the class name for corressponding array type.
+ }
+}
+class DoubleTwoDArray{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ double nums[][]= {
+ {0.0,1.0,2.0},
+ {3.0,4.0,5.0},
+ {6.0,7.0,8,0}
+ }; /* Two declare a two dimensional array, the last braces should be ended with braces as like Class in C++ . */
+ for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
+ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
+ System.out.print(nums[i][j]+ " ");
+ }
+ System.out.println();
+ }
+ }
+}
+class TwoDArray{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ int nums[][] = new int[4][];
+ nums[0] = new int[1];
+ nums[1] = new int[2];
+ nums[2] = new int[3];
+ nums[3] = new int[4];
+ int k = 0;
+
+ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
+ for(int j=0;i<i+1;j++){
+ nums[i][j]=k;
+ k++;
+ }
+ }
+
+ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
+ for(int j=0;i<i+1;j++){
+ System.out.print(nums[i][j] + " ");
+ }
+ System.out.println();
+ }
+ }
+}
+class ThreeDimensionalArray{
+ public static void main(String args[]){
+ int nums[][][] = new int [3][3][3];
+ int l = 0;
+ for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
+ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
+ for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
+ nums[i][j][k] = l;
+ l++;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
+ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
+ for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
+ System.out.print(nums[i][j][k]+" ");
+ }
+ System.out.println();
+ }
+ System.out.println("\n");
+ }
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Java provides a data structure, the array, which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful to think of an array as a collection of variables of the same type.
+Array is indexed collection of fixed number of homogeneous data element.
+int[] x;
+int []x;
+int x[];
+int[6] x; ❌ // We cannot define size in declaration. So, we must specify in creation.
+
+String[] args; ✅ Best way
+String []args;
+String args[];
+int[][] x;
+int [][]x;
+int[] []x;
+int[] x[];
+int [][]x;
+int []x[];
+int[] x = new int[1000]; // fixed in size.
+int a[] = new int[5];//declaration and instantiation
+a[0] = 10;
+a[1] = 20;
+a[2] = 70;
+a[3] = 40;
+a[4] = 50;
+System.out.println(a.getClass().getName());
+| Array Type | +Corresponding Class Name | +
|---|---|
| int[ ] | +[ I | +
| int[ ][ ] | +[ [ I | +
| double[ ] | +[ D | +
| short[ ] | +[ S | +
| byte[ ] | +[ B | +
| boolean[ ] | +[ Z | +
| char[ ] | +[ C | +
| long[ ] | +[ J | +
int[] a,b; -> 1D Array
+int[] a[],b[]; -> 2D Array
+int[] []a,b[]; -> 2D,3D Array
+int[] a[]b; -> 2D Array
+int[] []a,b; -> 2D Array
+int[][]a, []b; ❌ // [ ] can be shared with all, if it comes before variable.
+
+int[]x = new int[]; // ❌ Size should be mentioned.
+int[]x = new int[0]; ✅
+int[]x = new int[-2]; // ✅ Runtime error; though compiled.
+
+byte b = 20;
+int[] x = new int[b];
+int[] x = new int['b']; // Character ASCII gets inputed.
+Follwing way, we can know more about the internal representation of Arrays.
+class InternalRepresentation {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ // Integer[] array = new Integer[2];
+ int[] array = new int[2];
+ int[][] twoDArray = new int[2][2];
+ double itsDouble[] = new double[2];
+ short itsShort[] = new short[2];
+ byte itsByte[] = new byte[2];
+ boolean itsBoolean[] = new boolean[2];
+ char itsChar[] = new char[2];
+ long itsLong[] = new long[2];
+ System.out.println("Array : " + array.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("2D Array : " + twoDArray.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Double : " + itsDouble.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Short : " + itsShort.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Byte : " + itsByte.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Boolean : " + itsBoolean.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Char : " + itsChar.getClass().getName());
+ System.out.println("Long : " + itsLong.getClass().getName());
+ // For every array type, corresponding class are available but not available in
+ // programming level.
+ }
+}
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 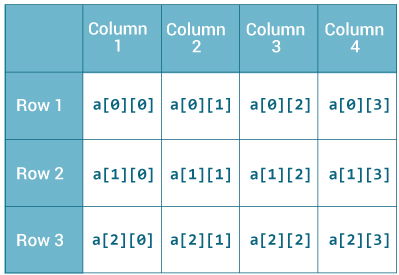
This type of array declaration is represented in matrix form. Memory wastage is most probable to happen in this scenario and manually unassigned blocks of memory are automatically assigned to zero.
+class MatrixRepresentation {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int[][] x = new int[4][4];
+ x[0][0] = 10;
+ x[0][1] = 12;
+ x[0][2] = 99;
+ x[0][3] = 89;
+ x[1][0] = 28;
+ x[1][1] = 67;
+ x[1][2] = 56;
+ x[2][0] = 80;
+ x[2][1] = 90;
+ x[3][0] = 90;
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
+ System.out.println("x[" + i + "][" + j + "] = " + x[i][j]);
+ }
+ System.out.println();
+ }
+ System.out.println("The unassigned block of memory are assigned to zero.");
+ }
+}
+This method of declaring array is often referred as conventional way of declaring array. +
class ConventionalWay{
+ public static void main(String[] args){
+ int[][] x = new int[4][3]; // The no of pairs of brackets represents the level of array i.e. dimensions.
+ }
+}
+\n {translation(\"search.result.term.missing\")}: {...missing}\n
\n }\n \n