| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
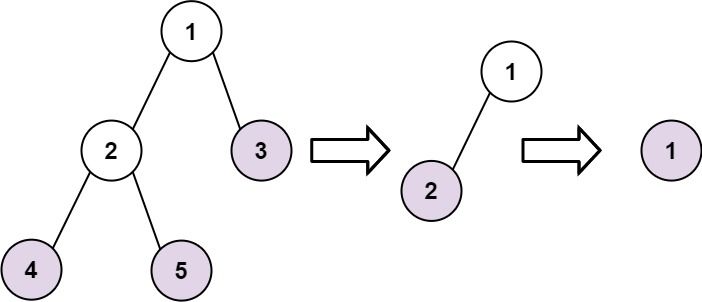
给你一棵二叉树的 root 节点,请按照以下方式收集树的节点:
- 收集所有的叶子节点。
- 移除所有的叶子节点。
- 重复以上步骤,直到树为空。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[[4,5,3],[2],[1]] 解释: [[3,5,4],[2],[1]] 和 [[3,4,5],[2],[1]] 也被视作正确答案,因为每一层返回元素的顺序不影响结果。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]]
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[1, 100]范围内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
我们可以使用深度优先搜索的方法,递归遍历二叉树,将每个节点的高度作为索引,将节点的值添加到对应索引的数组中。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
l, r = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right)
h = max(l, r)
if len(ans) == h:
ans.append([])
ans[h].append(root.val)
return h + 1
ans = []
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> findLeaves(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = dfs(root.left);
int r = dfs(root.right);
int h = Math.max(l, r);
if (ans.size() == h) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
ans.get(h).add(root.val);
return h + 1;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
function<int(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int l = dfs(root->left);
int r = dfs(root->right);
int h = max(l, r);
if (ans.size() == h) {
ans.push_back({});
}
ans[h].push_back(root->val);
return h + 1;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findLeaves(root *TreeNode) (ans [][]int) {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right)
h := max(l, r)
if len(ans) == h {
ans = append(ans, []int{})
}
ans[h] = append(ans[h], root.Val)
return h + 1
}
dfs(root)
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function findLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): number => {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
const l = dfs(root.left);
const r = dfs(root.right);
const h = Math.max(l, r);
if (ans.length === h) {
ans.push([]);
}
ans[h].push(root.val);
return h + 1;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public IList<IList<int>> FindLeaves(TreeNode root) {
var ans = new List<IList<int>>();
int Dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = Dfs(node.left);
int r = Dfs(node.right);
int h = Math.Max(l, r);
if (ans.Count == h) {
ans.Add(new List<int>());
}
ans[h].Add(node.val);
return h + 1;
}
Dfs(root);
return ans;
}
}