| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例 1:
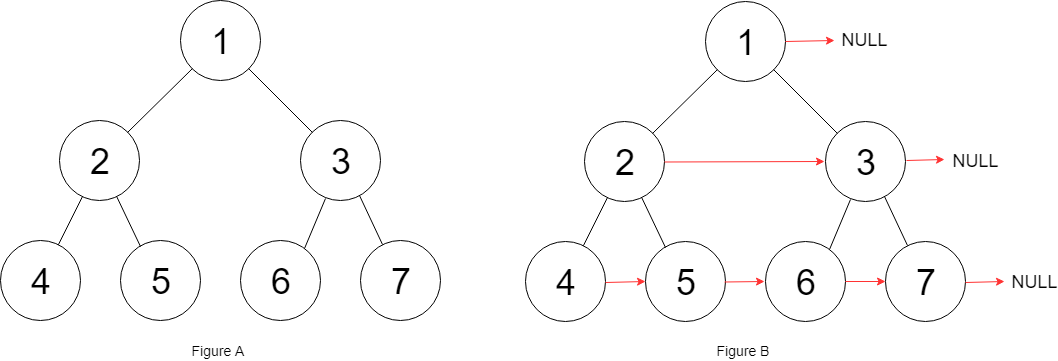
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#] 解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化的输出按层序遍历排列,同一层节点由 next 指针连接,'#' 标志着每一层的结束。
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 212 - 1]范围内 -1000 <= node.val <= 1000
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
使用队列进行层序遍历,每次遍历一层时,将当前层的节点按顺序连接起来。
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: "Optional[Node]") -> "Optional[Node]":
if root is None:
return root
q = deque([root])
while q:
p = None
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
if p:
p.next = node
p = node
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
return root/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Deque<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node p = null;
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
Node node = q.poll();
if (p != null) {
p.next = node;
}
p = node;
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) {
return root;
}
queue<Node*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* p = nullptr;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
Node* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (p) {
p->next = node;
}
p = node;
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Left *Node
* Right *Node
* Next *Node
* }
*/
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
q := []*Node{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
var p *Node
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if p != nil {
p.Next = node
}
p = node
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}/**
* Definition for Node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* left: Node | null
* right: Node | null
* next: Node | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: Node, right?: Node, next?: Node) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
if (root == null || root.left == null) {
return root;
}
const { left, right, next } = root;
left.next = right;
if (next != null) {
right.next = next.left;
}
connect(left);
connect(right);
return root;
}使用递归进行前序遍历,每次遍历到一个节点时,将其左右子节点按顺序连接起来。
具体地,我们设计一个函数
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
def dfs(left, right):
if left is None or right is None:
return
left.next = right
dfs(left.left, left.right)
dfs(left.right, right.left)
dfs(right.left, right.right)
if root:
dfs(root.left, root.right)
return root/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
dfs(root.left, root.right);
}
return root;
}
private void dfs(Node left, Node right) {
if (left == null || right == null) {
return;
}
left.next = right;
dfs(left.left, left.right);
dfs(left.right, right.left);
dfs(right.left, right.right);
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
function<void(Node*, Node*)> dfs = [&](Node* left, Node* right) {
if (!left || !right) {
return;
}
left->next = right;
dfs(left->left, left->right);
dfs(left->right, right->left);
dfs(right->left, right->right);
};
if (root) {
dfs(root->left, root->right);
}
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Left *Node
* Right *Node
* Next *Node
* }
*/
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
var dfs func(*Node, *Node)
dfs = func(left, right *Node) {
if left == nil || right == nil {
return
}
left.Next = right
dfs(left.Left, left.Right)
dfs(left.Right, right.Left)
dfs(right.Left, right.Right)
}
if root != nil {
dfs(root.Left, root.Right)
}
return root
}/**
* Definition for Node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* left: Node | null
* right: Node | null
* next: Node | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: Node, right?: Node, next?: Node) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
const queue = [root];
while (queue.length !== 0) {
const n = queue.length;
let pre = null;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.next = pre;
pre = node;
const { left, right } = node;
left && queue.push(right, left);
}
}
return root;
}