| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
2298 |
第 317 场周赛 Q4 |
|
给你一棵 二叉树 的根节点 root ,树中有 n 个节点。每个节点都可以被分配一个从 1 到 n 且互不相同的值。另给你一个长度为 m 的数组 queries 。
你必须在树上执行 m 个 独立 的查询,其中第 i 个查询你需要执行以下操作:
- 从树中 移除 以
queries[i]的值作为根节点的子树。题目所用测试用例保证queries[i]不 等于根节点的值。
返回一个长度为 m 的数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是执行第 i 个查询后树的高度。
注意:
- 查询之间是独立的,所以在每个查询执行后,树会回到其 初始 状态。
- 树的高度是从根到树中某个节点的 最长简单路径中的边数 。
示例 1:
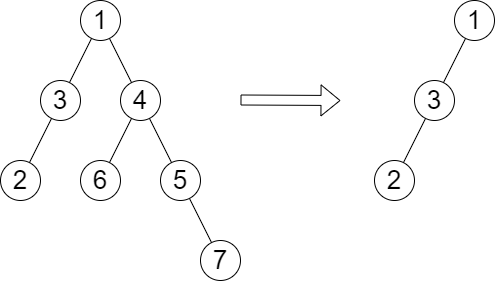
输入:root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4] 输出:[2] 解释:上图展示了从树中移除以 4 为根节点的子树。 树的高度是 2(路径为 1 -> 3 -> 2)。
示例 2:
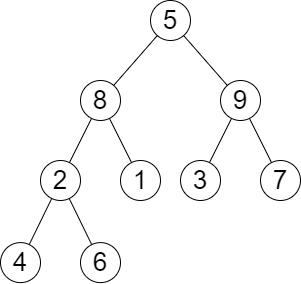
输入:root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8] 输出:[3,2,3,2] 解释:执行下述查询: - 移除以 3 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 3(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4)。 - 移除以 2 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 2(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 1)。 - 移除以 4 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 3(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6)。 - 移除以 8 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 2(路径为 5 -> 9 -> 3)。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目是
n 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- 树中的所有值 互不相同
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
我们先通过一次 DFS 遍历的深度,存放在哈希表
然后我们设计一个函数
root表示当前节点;depth表示当前节点的深度;rest表示删除当前节点后,树的高度。
函数的计算逻辑如下:
如果节点为空,直接返回。否则,我们将 depth 加 rest 保存在 res 中。
接着递归遍历左右子树。
递归左子树前,我们计算从根节点到当前节点右子树最深节点的就,即 rest 比较,取较大值作为左子树的 rest。
递归右子树前,我们计算从根节点到当前节点左子树最深节点的就,即 rest 比较,取较大值作为右子树的 rest。
最后返回每个查询节点对应的结果值即可。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:
def f(root):
if root is None:
return 0
l, r = f(root.left), f(root.right)
d[root] = 1 + max(l, r)
return d[root]
def dfs(root, depth, rest):
if root is None:
return
depth += 1
res[root.val] = rest
dfs(root.left, depth, max(rest, depth + d[root.right]))
dfs(root.right, depth, max(rest, depth + d[root.left]))
d = defaultdict(int)
f(root)
res = [0] * (len(d) + 1)
dfs(root, -1, 0)
return [res[v] for v in queries]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<TreeNode, Integer> d = new HashMap<>();
private int[] res;
public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {
f(root);
res = new int[d.size() + 1];
d.put(null, 0);
dfs(root, -1, 0);
int m = queries.length;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans[i] = res[queries[i]];
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, int rest) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
++depth;
res[root.val] = rest;
dfs(root.left, depth, Math.max(rest, depth + d.get(root.right)));
dfs(root.right, depth, Math.max(rest, depth + d.get(root.left)));
}
private int f(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = f(root.left), r = f(root.right);
d.put(root, 1 + Math.max(l, r));
return d.get(root);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> d;
function<int(TreeNode*)> f = [&](TreeNode* root) -> int {
if (!root) return 0;
int l = f(root->left), r = f(root->right);
d[root] = 1 + max(l, r);
return d[root];
};
f(root);
vector<int> res(d.size() + 1);
function<void(TreeNode*, int, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int depth, int rest) {
if (!root) return;
++depth;
res[root->val] = rest;
dfs(root->left, depth, max(rest, depth + d[root->right]));
dfs(root->right, depth, max(rest, depth + d[root->left]));
};
dfs(root, -1, 0);
vector<int> ans;
for (int v : queries) ans.emplace_back(res[v]);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func treeQueries(root *TreeNode, queries []int) (ans []int) {
d := map[*TreeNode]int{}
var f func(*TreeNode) int
f = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
l, r := f(root.Left), f(root.Right)
d[root] = 1 + max(l, r)
return d[root]
}
f(root)
res := make([]int, len(d)+1)
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, depth, rest int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
depth++
res[root.Val] = rest
dfs(root.Left, depth, max(rest, depth+d[root.Right]))
dfs(root.Right, depth, max(rest, depth+d[root.Left]))
}
dfs(root, -1, 0)
for _, v := range queries {
ans = append(ans, res[v])
}
return
}