| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
This question is about implementing a basic elimination algorithm for Candy Crush.
Given an m x n integer array board representing the grid of candy where board[i][j] represents the type of candy. A value of board[i][j] == 0 represents that the cell is empty.
The given board represents the state of the game following the player's move. Now, you need to restore the board to a stable state by crushing candies according to the following rules:
- If three or more candies of the same type are adjacent vertically or horizontally, crush them all at the same time - these positions become empty.
- After crushing all candies simultaneously, if an empty space on the board has candies on top of itself, then these candies will drop until they hit a candy or bottom at the same time. No new candies will drop outside the top boundary.
- After the above steps, there may exist more candies that can be crushed. If so, you need to repeat the above steps.
- If there does not exist more candies that can be crushed (i.e., the board is stable), then return the current board.
You need to perform the above rules until the board becomes stable, then return the stable board.
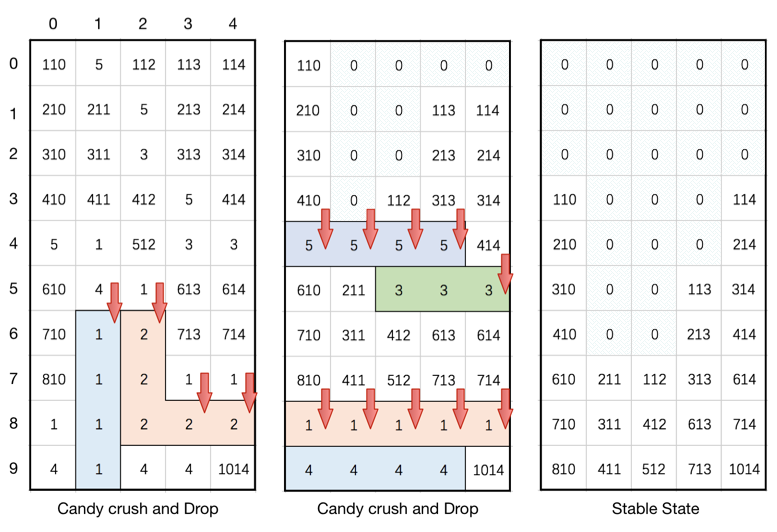
Example 1:
Input: board = [[110,5,112,113,114],[210,211,5,213,214],[310,311,3,313,314],[410,411,412,5,414],[5,1,512,3,3],[610,4,1,613,614],[710,1,2,713,714],[810,1,2,1,1],[1,1,2,2,2],[4,1,4,4,1014]] Output: [[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[110,0,0,0,114],[210,0,0,0,214],[310,0,0,113,314],[410,0,0,213,414],[610,211,112,313,614],[710,311,412,613,714],[810,411,512,713,1014]]
Example 2:
Input: board = [[1,3,5,5,2],[3,4,3,3,1],[3,2,4,5,2],[2,4,4,5,5],[1,4,4,1,1]] Output: [[1,3,0,0,0],[3,4,0,5,2],[3,2,0,3,1],[2,4,0,5,2],[1,4,3,1,1]]
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length3 <= m, n <= 501 <= board[i][j] <= 2000
We can traverse the matrix row by row and column by column to find three consecutive identical elements and mark them as negative numbers. If marking is successful, we need to move the elements in the matrix down until no elements can move down.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def candyCrush(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
run = True
while run:
run = False
for i in range(m):
for j in range(2, n):
if board[i][j] and abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i][j - 1]) == abs(
board[i][j - 2]
):
run = True
board[i][j] = board[i][j - 1] = board[i][j - 2] = -abs(
board[i][j]
)
for j in range(n):
for i in range(2, m):
if board[i][j] and abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i - 1][j]) == abs(
board[i - 2][j]
):
run = True
board[i][j] = board[i - 1][j] = board[i - 2][j] = -abs(
board[i][j]
)
if run:
for j in range(n):
k = m - 1
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
if board[i][j] > 0:
board[k][j] = board[i][j]
k -= 1
while k >= 0:
board[k][j] = 0
k -= 1
return boardclass Solution {
public int[][] candyCrush(int[][] board) {
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
boolean run = true;
while (run) {
run = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 2; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != 0 && Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i][j - 1])
&& Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i][j - 2])) {
run = true;
int val = Math.abs(board[i][j]);
board[i][j] = board[i][j - 1] = board[i][j - 2] = -val;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 2; i < m; i++) {
if (board[i][j] != 0 && Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i - 1][j])
&& Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i - 2][j])) {
run = true;
int val = Math.abs(board[i][j]);
board[i][j] = board[i - 1][j] = board[i - 2][j] = -val;
}
}
}
if (run) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int k = m - 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][j] > 0) {
board[k][j] = board[i][j];
k--;
}
}
while (k >= 0) {
board[k][j] = 0;
k--;
}
}
}
}
return board;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> candyCrush(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
bool run = true;
while (run) {
run = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - 2; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] != 0 && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i][j + 1]) && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i][j + 2])) {
run = true;
board[i][j] = board[i][j + 1] = board[i][j + 2] = -abs(board[i][j]);
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int i = 0; i < m - 2; ++i) {
if (board[i][j] != 0 && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i + 1][j]) && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i + 2][j])) {
run = true;
board[i][j] = board[i + 1][j] = board[i + 2][j] = -abs(board[i][j]);
}
}
}
if (run) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int curr = m - 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (board[i][j] > 0) {
board[curr][j] = board[i][j];
--curr;
}
}
while (curr > -1) {
board[curr][j] = 0;
--curr;
}
}
}
}
return board;
}
};func candyCrush(board [][]int) [][]int {
m := len(board)
n := len(board[0])
run := true
for run {
run = false
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 2; j < n; j++ {
if board[i][j] != 0 && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i][j-1]) && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i][j-2]) {
run = true
val := abs(board[i][j])
board[i][j] = -val
board[i][j-1] = -val
board[i][j-2] = -val
}
}
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
for i := 2; i < m; i++ {
if board[i][j] != 0 && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i-1][j]) && abs(board[i][j]) == abs(board[i-2][j]) {
run = true
val := abs(board[i][j])
board[i][j] = -val
board[i-1][j] = -val
board[i-2][j] = -val
}
}
}
if run {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
k := m - 1
for i := m - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
if board[i][j] > 0 {
board[k][j] = board[i][j]
k--
}
}
for k >= 0 {
board[k][j] = 0
k--
}
}
}
}
return board
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}function candyCrush(board: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = board.length;
const n = board[0].length;
let run = true;
while (run) {
run = false;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 2; j < n; j++) {
if (
board[i][j] !== 0 &&
Math.abs(board[i][j]) === Math.abs(board[i][j - 1]) &&
Math.abs(board[i][j]) === Math.abs(board[i][j - 2])
) {
run = true;
const val = Math.abs(board[i][j]);
board[i][j] = board[i][j - 1] = board[i][j - 2] = -val;
}
}
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (let i = 2; i < m; i++) {
if (
board[i][j] !== 0 &&
Math.abs(board[i][j]) === Math.abs(board[i - 1][j]) &&
Math.abs(board[i][j]) === Math.abs(board[i - 2][j])
) {
run = true;
const val = Math.abs(board[i][j]);
board[i][j] = board[i - 1][j] = board[i - 2][j] = -val;
}
}
}
if (run) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
let k = m - 1;
for (let i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (board[i][j] > 0) {
board[k][j] = board[i][j];
k--;
}
}
while (k >= 0) {
board[k][j] = 0;
k--;
}
}
}
}
return board;
}