| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given the root of a binary tree where every node has a unique value and a target integer k, return the value of the nearest leaf node to the target k in the tree.
Nearest to a leaf means the least number of edges traveled on the binary tree to reach any leaf of the tree. Also, a node is called a leaf if it has no children.
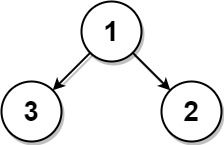
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,3,2], k = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: Either 2 or 3 is the nearest leaf node to the target of 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], k = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: The nearest leaf node is the root node itself.
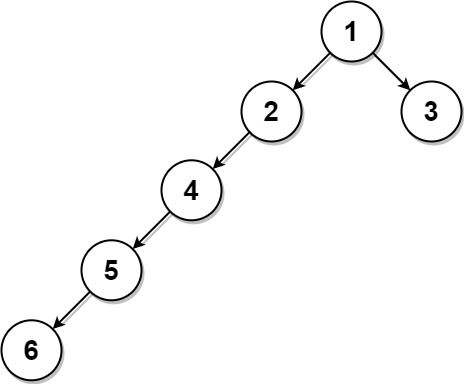
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5,null,6], k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: The leaf node with value 3 (and not the leaf node with value 6) is nearest to the node with value 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000- All the values of the tree are unique.
- There exist some node in the tree where
Node.val == k.
First, we use depth-first search to construct an undirected graph
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findClosestLeaf(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode], fa: Optional[TreeNode]):
if root:
g[root].append(fa)
g[fa].append(root)
dfs(root.left, root)
dfs(root.right, root)
g = defaultdict(list)
dfs(root, None)
q = deque(node for node in g if node and node.val == k)
vis = set(q)
while 1:
node = q.popleft()
if node:
if node.left == node.right:
return node.val
for nxt in g[node]:
if nxt not in vis:
vis.add(nxt)
q.append(nxt)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<TreeNode, List<TreeNode>> g = new HashMap<>();
public int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode root, int k) {
dfs(root, null);
Deque<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<TreeNode> vis = new HashSet<>(q.size());
for (TreeNode node : g.keySet()) {
if (node != null && node.val == k) {
vis.add(node);
q.offer(node);
break;
}
}
while (true) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node != null) {
if (node.left == node.right) {
return node.val;
}
for (TreeNode nxt : g.get(node)) {
if (vis.add(nxt)) {
q.offer(nxt);
}
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode fa) {
if (root != null) {
g.computeIfAbsent(root, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(fa);
g.computeIfAbsent(fa, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root);
dfs(root.left, root);
dfs(root.right, root);
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode* root, int k) {
unordered_map<TreeNode*, vector<TreeNode*>> g;
function<void(TreeNode*, TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, TreeNode* fa) {
if (root) {
g[root].push_back(fa);
g[fa].push_back(root);
dfs(root->left, root);
dfs(root->right, root);
}
};
dfs(root, nullptr);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
unordered_set<TreeNode*> vis;
for (auto& [node, _] : g) {
if (node && node->val == k) {
q.push(node);
vis.insert(node);
}
}
while (1) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (node) {
if (node->left == node->right) {
return node->val;
}
for (auto& nxt : g[node]) {
if (vis.count(nxt)) {
continue;
}
q.push(nxt);
vis.insert(nxt);
}
}
}
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findClosestLeaf(root *TreeNode, k int) int {
g := map[*TreeNode][]*TreeNode{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root, fa *TreeNode) {
if root != nil {
g[root] = append(g[root], fa)
g[fa] = append(g[fa], root)
dfs(root.Left, root)
dfs(root.Right, root)
}
}
dfs(root, nil)
q := []*TreeNode{}
vis := map[*TreeNode]bool{}
for node := range g {
if node != nil && node.Val == k {
q = append(q, node)
vis[node] = true
break
}
}
for {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if node != nil {
if node.Left == node.Right {
return node.Val
}
for _, nxt := range g[node] {
if !vis[nxt] {
vis[nxt] = true
q = append(q, nxt)
}
}
}
}
}