| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1358 |
Weekly Contest 269 Q2 |
|
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
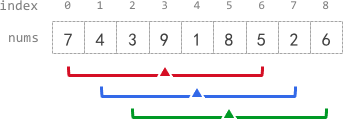
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index. - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37. Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4. - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4. - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 Output: [100000] Explanation: - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000. avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 Output: [-1] Explanation: - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
The number of elements in a subarray with radius
We create an answer array
Next, we first check whether nums. If it is, we directly return the answer array.
Otherwise, we calculate the sum nums, and assign the quotient of
Then, we start traversing the array nums from
Finally, we return the answer array.
The time complexity is nums. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is
class Solution:
def getAverages(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
k = k << 1 | 1
n = len(nums)
ans = [-1] * n
if k > n:
return ans
s = sum(nums[:k])
j = k // 2
ans[j] = s // k
for i in range(k, n):
j += 1
s += nums[i] - nums[i - k]
ans[j] = s // k
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] getAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
k = k << 1 | 1;
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
if (k > n) {
return ans;
}
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
s += nums[i];
}
int j = k / 2;
ans[j] = (int) (s / k);
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i] - nums[i - k];
ans[++j] = (int) (s / k);
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
k = k << 1 | 1;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n, -1);
if (k > n) {
return ans;
}
long long s = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + k, 0LL);
int j = k / 2;
ans[j] = s / k;
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i] - nums[i - k];
ans[++j] = s / k;
}
return ans;
}
};func getAverages(nums []int, k int) []int {
k = k<<1 | 1
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int, n)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = -1
}
if k > n {
return ans
}
s := 0
for _, x := range nums[:k] {
s += x
}
j := k >> 1
ans[j] = s / k
for i := k; i < n; i++ {
s += nums[i] - nums[i-k]
j++
ans[j] = s / k
}
return ans
}function getAverages(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
k = (k << 1) | 1;
const n = nums.length;
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1);
if (k > n) {
return ans;
}
let s = nums.slice(0, k).reduce((acc, cur) => acc + cur, 0);
let j = k >> 1;
ans[j] = Math.floor(s / k);
for (let i = k; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i] - nums[i - k];
ans[++j] = Math.floor(s / k);
}
return ans;
}We maintain a window of size
Like Solution 1, we create an answer array
Next, we traverse the array nums, add the value of
Finally, we return the answer array.
The time complexity is nums. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is
class Solution:
def getAverages(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
s = 0
ans = [-1] * len(nums)
for i, v in enumerate(nums):
s += v
if i >= k * 2:
ans[i - k] = s // (k * 2 + 1)
s -= nums[i - k * 2]
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] getAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i];
if (i >= k * 2) {
ans[i - k] = (int) (s / (k * 2 + 1));
s -= nums[i - k * 2];
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n, -1);
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i];
if (i >= k * 2) {
ans[i - k] = s / (k * 2 + 1);
s -= nums[i - k * 2];
}
}
return ans;
}
};func getAverages(nums []int, k int) []int {
ans := make([]int, len(nums))
s := 0
for i, v := range nums {
ans[i] = -1
s += v
if i >= k*2 {
ans[i-k] = s / (k*2 + 1)
s -= nums[i-k*2]
}
}
return ans
}function getAverages(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
const n = nums.length;
const ans: number[] = new Array(n).fill(-1);
let s = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
s += nums[i];
if (i >= k * 2) {
ans[i - k] = Math.floor(s / (k * 2 + 1));
s -= nums[i - k * 2];
}
}
return ans;
}