diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..57c8e23e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0223_rectangle_area;
+
+@SuppressWarnings("java:S107")
+public class Solution {
+ public int computeArea(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e, int f, int g, int h) {
+ long left = Math.max(a, e);
+ long right = Math.min(c, g);
+ long top = Math.min(d, h);
+ long bottom = Math.max(b, f);
+
+ long area = (right - left) * (top - bottom);
+ // if not overlaping, either of these two will be non-posittive
+ // if right - left = 0, are will automtically be 0 as well
+ if (right - left < 0 || top - bottom < 0) {
+ area = 0;
+ }
+ return (int) ((c - a) * (d - b) + (g - e) * (h - f) - area);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e7d26fed3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+223\. Rectangle Area
+
+Medium
+
+Given the coordinates of two **rectilinear** rectangles in a 2D plane, return _the total area covered by the two rectangles_.
+
+The first rectangle is defined by its **bottom-left** corner `(ax1, ay1)` and its **top-right** corner `(ax2, ay2)`.
+
+The second rectangle is defined by its **bottom-left** corner `(bx1, by1)` and its **top-right** corner `(bx2, by2)`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** ax1 = -3, ay1 = 0, ax2 = 3, ay2 = 4, bx1 = 0, by1 = -1, bx2 = 9, by2 = 2
+
+**Output:** 45
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** ax1 = -2, ay1 = -2, ax2 = 2, ay2 = 2, bx1 = -2, by1 = -2, bx2 = 2, by2 = 2
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -104 <= ax1, ay1, ax2, ay2, bx1, by1, bx2, by2 <= 104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..08cc07d89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0224_basic_calculator;
+
+public class Solution {
+ int i = 0;
+
+ public int calculate(String s) {
+ char[] ca = s.toCharArray();
+
+ return helper(ca);
+ }
+
+ public int helper(char[] ca) {
+
+ int num = 0;
+ int prenum = 0;
+ boolean isPlus = true;
+ for (; i < ca.length; i++) {
+ char c = ca[i];
+ if (c != ' ') {
+ if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
+ if (num == 0) {
+ num = (c - '0');
+ } else {
+ num = num * 10 + c - '0';
+ }
+ } else if (c == '+') {
+ prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1);
+ isPlus = true;
+ num = 0;
+ } else if (c == '-') {
+ prenum += num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1);
+ num = 0;
+ isPlus = false;
+ } else if (c == '(') {
+ i++;
+ prenum += helper(ca) * (isPlus ? 1 : -1);
+ isPlus = true;
+ num = 0;
+ } else if (c == ')') {
+ return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return prenum + num * (isPlus ? 1 : -1);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..cc42fe44b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+224\. Basic Calculator
+
+Hard
+
+Given a string `s` representing a valid expression, implement a basic calculator to evaluate it, and return _the result of the evaluation_.
+
+**Note:** You are **not** allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "1 + 1"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = " 2-1 + 2 "
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)"
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
+* `s` consists of digits, `'+'`, `'-'`, `'('`, `')'`, and `' '`.
+* `s` represents a valid expression.
+* `'+'` is **not** used as a unary operation (i.e., `"+1"` and `"+(2 + 3)"` is invalid).
+* `'-'` could be used as a unary operation (i.e., `"-1"` and `"-(2 + 3)"` is valid).
+* There will be no two consecutive operators in the input.
+* Every number and running calculation will fit in a signed 32-bit integer.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3fd24fcd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStack.java
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0225_implement_stack_using_queues;
+
+import java.util.LinkedList;
+import java.util.Queue;
+
+public class MyStack {
+ Queue queueOne;
+ Queue queueTwo;
+ int top;
+
+ /** Initialize your data structure here. */
+ public MyStack() {
+ queueOne = new LinkedList<>();
+ queueTwo = new LinkedList<>();
+ top = 0;
+ }
+
+ /** Push element x onto stack. */
+ public void push(int x) {
+ queueOne.add(x);
+ top = x;
+ }
+
+ /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
+ public int pop() {
+ while (queueOne.size() > 1) {
+ int val = queueOne.remove();
+ top = val;
+ queueTwo.add(val);
+ }
+
+ int popValue = queueOne.remove();
+ queueOne.addAll(queueTwo);
+ queueTwo.clear();
+
+ return popValue;
+ }
+
+ /** Get the top element. */
+ public int top() {
+ return top;
+ }
+
+ /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
+ public boolean empty() {
+ return queueOne.isEmpty();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1fffa214a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+225\. Implement Stack using Queues
+
+Easy
+
+Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (`push`, `top`, `pop`, and `empty`).
+
+Implement the `MyStack` class:
+
+* `void push(int x)` Pushes element x to the top of the stack.
+* `int pop()` Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.
+* `int top()` Returns the element on the top of the stack.
+* `boolean empty()` Returns `true` if the stack is empty, `false` otherwise.
+
+**Notes:**
+
+* You must use **only** standard operations of a queue, which means that only `push to back`, `peek/pop from front`, `size` and `is empty` operations are valid.
+* Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** \["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"\] \[\[\], \[1\], \[2\], \[\], \[\], \[\]\]
+
+**Output:** \[null, null, null, 2, 2, false\]
+
+**Explanation:** MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // return 2 myStack.pop(); // return 2 myStack.empty(); // return False
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= x <= 9`
+* At most `100` calls will be made to `push`, `pop`, `top`, and `empty`.
+* All the calls to `pop` and `top` are valid.
+
+**Follow-up:** Can you implement the stack using only one queue?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4d25041af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0226_invert_binary_tree;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return null;
+ }
+ TreeNode temp = root.left;
+ root.left = invertTree(root.right);
+ root.right = invertTree(temp);
+ return root;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..733b6955f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+226\. Invert Binary Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return _its root_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[4,2,7,1,3,6,9\]
+
+**Output:** \[4,7,2,9,6,3,1\]
+
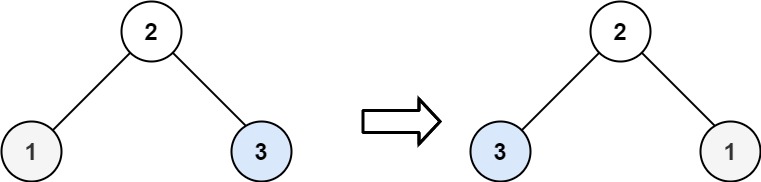
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[2,1,3\]
+
+**Output:** \[2,3,1\]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = \[\]
+
+**Output:** \[\]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7e513e9db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0227_basic_calculator_ii;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int calculate(String s) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ int tempSum = 0;
+ int num = 0;
+ char lastSign = '+';
+ for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
+ char c = s.charAt(i);
+ if (Character.isDigit(c)) {
+ num = num * 10 + c - '0';
+ }
+ // i == s.length() - 1 will make sure that after last num is
+ // made and there is nothing to read anything from 's', the final computation is done
+ if (i == s.length() - 1 || !Character.isDigit(c) && c != ' ') {
+ switch (lastSign) {
+ case '+':
+ sum += tempSum;
+ tempSum = num;
+ break;
+ case '-':
+ sum += tempSum;
+ tempSum = -num;
+ break;
+ case '*':
+ tempSum *= num;
+ break;
+ case '/':
+ if (num != 0) {
+ tempSum /= num;
+ }
+ break;
+ default:
+ break;
+ }
+ lastSign = c;
+ num = 0;
+ }
+ }
+ sum += tempSum; // finally, add tempSum to sum
+ return sum;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..41b92c3a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+227\. Basic Calculator II
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s` which represents an expression, _evaluate this expression and return its value_.
+
+The integer division should truncate toward zero.
+
+You may assume that the given expression is always valid. All intermediate results will be in the range of [-231, 231 - 1].
+
+**Note:** You are not allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as `eval()`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "3+2\*2"
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = " 3/2 "
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = " 3+5 / 2 "
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
+* `s` consists of integers and operators `('+', '-', '*', '/')` separated by some number of spaces.
+* `s` represents **a valid expression**.
+* All the integers in the expression are non-negative integers in the range [0, 231 - 1].
+* The answer is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit integer**.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fac9db87d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0228_summary_ranges;
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public List summaryRanges(int[] nums) {
+ List ranges = new ArrayList<>();
+ if (nums.length == 0) {
+ return ranges;
+ }
+ int n = nums.length; // size of array
+ int a = nums[0]; // start of range
+ int b = a; // end of range
+
+ StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
+ // we need to make a decision if the next element
+ // will expand the range
+ // i starts at 1, not 0, because 1 is the next
+ // candidate for expanding the range
+ if (nums[i] != b + 1) {
+ // only when our next element does not expand the range
+ // do we add the range a->b to our list of ranges
+ strB.append(a);
+ if (a != b) {
+ strB.append("->").append(b);
+ }
+
+ ranges.add(strB.toString());
+ // since nums[i] is not accounted for by our range a->b
+ // because nums[i] is not b+1, we need to set a and b
+ // to this new range start point of bigger than b+1
+ // maybe it is b+2? b+3? b+4? all we know is it is not b+1
+ a = nums[i];
+ b = a;
+
+ // Reset string builder
+ strB.setLength(0);
+ } else {
+ b++; // if the next element expands our range we do so
+ }
+ }
+ // the only range that is not accounted for at this point is the last range
+ // if our a and b are not equal then we add the range accordingly
+ strB.append(a);
+ if (a != b) {
+ strB.append("->").append(b);
+ }
+ ranges.add(strB.toString());
+
+ return ranges;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..fecaac0ce
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+228\. Summary Ranges
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a **sorted unique** integer array `nums`.
+
+Return _the **smallest sorted** list of ranges that **cover all the numbers in the array exactly**_. That is, each element of `nums` is covered by exactly one of the ranges, and there is no integer `x` such that `x` is in one of the ranges but not in `nums`.
+
+Each range `[a,b]` in the list should be output as:
+
+* `"a->b"` if `a != b`
+* `"a"` if `a == b`
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[0,1,2,4,5,7\]
+
+**Output:** \["0->2","4->5","7"\]
+
+**Explanation:** The ranges are: \[0,2\] --> "0->2" \[4,5\] --> "4->5" \[7,7\] --> "7"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[0,2,3,4,6,8,9\]
+
+**Output:** \["0","2->4","6","8->9"\]
+
+**Explanation:** The ranges are: \[0,0\] --> "0" \[2,4\] --> "2->4" \[6,6\] --> "6" \[8,9\] --> "8->9"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[\]
+
+**Output:** \[\]
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[-1\]
+
+**Output:** \["-1"\]
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[0\]
+
+**Output:** \["0"\]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= nums.length <= 20`
+* -231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+* All the values of `nums` are **unique**.
+* `nums` is sorted in ascending order.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f0d9e50f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0229_majority_element_ii;
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public List majorityElement(int[] nums) {
+ List results = new ArrayList<>();
+ int len = nums.length;
+ int first = 0;
+ int second = 1;
+ int count1 = 0;
+ int count2 = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
+ int temp = nums[i];
+ if (temp == first) {
+ count1++;
+ } else if (temp == second) {
+ count2++;
+ } else if (count1 == 0) {
+ first = temp;
+ count1++;
+ } else if (count2 == 0) {
+ second = temp;
+ count2++;
+ } else {
+ count1--;
+ count2--;
+ }
+ }
+ count1 = 0;
+ count2 = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
+ // check both of them is bigger than n/3.Becasue we may have only one satisfying
+ // the demand.
+ int temp = nums[i];
+ if (temp == first) {
+ count1++;
+ }
+ if (temp == second) {
+ count2++;
+ }
+ }
+ if (count1 > len / 3) {
+ results.add(first);
+ }
+ if (count2 > len / 3) {
+ results.add(second);
+ }
+ return results;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c7162c5e6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+229\. Majority Element II
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array of size `n`, find all elements that appear more than `⌊ n/3 ⌋` times.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[3,2,3\]
+
+**Output:** \[3\]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[1\]
+
+**Output:** \[1\]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[1,2\]
+
+**Output:** \[1,2\]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve the problem in linear time and in `O(1)` space?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d9ceb1120
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private int k;
+ int count = 0;
+ private int val;
+
+ public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
+ this.k = k;
+ count(root);
+ return val;
+ }
+
+ private void count(TreeNode node) {
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
+ count++;
+ if (count == k) {
+ this.val = node.val;
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ count(node.left);
+ }
+ count++;
+ if (count == k) {
+ this.val = node.val;
+ return;
+ }
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ count(node.right);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3532ff8fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+230\. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return _the_ kth _smallest value (**1-indexed**) of all the values of the nodes in the tree_.
+
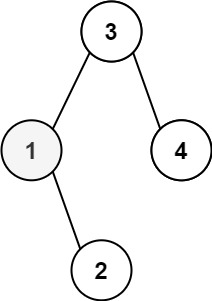
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[3,1,4,null,2\], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
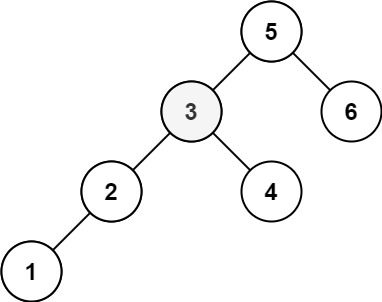
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = \[5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1\], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 104
+* 0 <= Node.val <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..db44acb4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0231_power_of_two;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
+ if (n <= 0) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ while (true) {
+ if (n == 1) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if (n % 2 == 1) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ n /= 2;
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d0e0841df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+231\. Power of Two
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer `n`, return _`true` if it is a power of two. Otherwise, return `false`_.
+
+An integer `n` is a power of two, if there exists an integer `x` such that n == 2x.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 20 = 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 16
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 24 = 16
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -231 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..999d50294
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueue.java
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks;
+
+import java.util.ArrayDeque;
+import java.util.Deque;
+
+public class MyQueue {
+ Deque left;
+ Deque right;
+ /** Initialize your data structure here. */
+ public MyQueue() {
+ left = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ right = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ }
+
+ /** Push element x to the back of queue. */
+ public void push(int x) {
+ while (!right.isEmpty()) {
+ left.add(right.pop());
+ }
+ left.add(x);
+ }
+
+ /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
+ public int pop() {
+ while (!left.isEmpty()) {
+ right.add(left.pop());
+ }
+ return right.pop();
+ }
+
+ /** Get the front element. */
+ public int peek() {
+ while (!left.isEmpty()) {
+ right.add(left.pop());
+ }
+ return right.peek();
+ }
+
+ /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
+ public boolean empty() {
+ return right.isEmpty() && left.isEmpty();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..975f4c91d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+232\. Implement Queue using Stacks
+
+Easy
+
+Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (`push`, `peek`, `pop`, and `empty`).
+
+Implement the `MyQueue` class:
+
+* `void push(int x)` Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
+* `int pop()` Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
+* `int peek()` Returns the element at the front of the queue.
+* `boolean empty()` Returns `true` if the queue is empty, `false` otherwise.
+
+**Notes:**
+
+* You must use **only** standard operations of a stack, which means only `push to top`, `peek/pop from top`, `size`, and `is empty` operations are valid.
+* Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** \["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"\] \[\[\], \[1\], \[2\], \[\], \[\], \[\]\]
+
+**Output:** \[null, null, null, 1, 1, false\]
+
+**Explanation:** MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: \[1\] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: \[1, 2\] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is \[2\] myQueue.empty(); // return false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= x <= 9`
+* At most `100` calls will be made to `push`, `pop`, `peek`, and `empty`.
+* All the calls to `pop` and `peek` are valid.
+
+**Follow-up:** Can you implement the queue such that each operation is **[amortized](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amortized_analysis)** `O(1)` time complexity? In other words, performing `n` operations will take overall `O(n)` time even if one of those operations may take longer.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d8ee7570b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0223_rectangle_area/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0223_rectangle_area;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void rectangleArea() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().computeArea(-3, 0, 3, 4, 0, -1, 9, 2), equalTo(45));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a01a4e332
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0224_basic_calculator/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0224_basic_calculator;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void calculate() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().calculate("1 + 1"), equalTo(2));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStackTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStackTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3afac92e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0225_implement_stack_using_queues/MyStackTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0225_implement_stack_using_queues;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class MyStackTest {
+ @Test
+ public void stackUsingQueue() {
+ MyStack stack = new MyStack();
+ stack.push(1);
+ stack.push(2);
+ assertThat(stack.top, equalTo(2));
+
+ assertThat(stack.pop(), equalTo(2));
+
+ assertThat(stack.empty(), equalTo(false));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..61e0894e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0226_invert_binary_tree;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void invertTree() {
+ TreeNode leftBottomLeft = new TreeNode(1);
+ TreeNode leftBottomRight = new TreeNode(3);
+ TreeNode left = new TreeNode(2, leftBottomLeft, leftBottomRight);
+
+ TreeNode rightBottomLeft = new TreeNode(6);
+ TreeNode rightBottomRight = new TreeNode(9);
+ TreeNode right = new TreeNode(7, rightBottomLeft, rightBottomRight);
+
+ TreeNode root = new TreeNode(4, left, right);
+
+ TreeNode leftBottomLeftInverted = new TreeNode(9);
+ TreeNode leftBottomRightInverted = new TreeNode(6);
+ TreeNode leftInverted = new TreeNode(7, leftBottomLeftInverted, leftBottomRightInverted);
+
+ TreeNode rightBottomLeftInverted = new TreeNode(3);
+ TreeNode rightBottomRightInverted = new TreeNode(1);
+ TreeNode rightInverted = new TreeNode(2, rightBottomLeftInverted, rightBottomRightInverted);
+
+ TreeNode rootInverted = new TreeNode(4, leftInverted, rightInverted);
+
+ assertThat(new Solution().invertTree(root).toString(), equalTo(rootInverted.toString()));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..928c7ac7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0227_basic_calculator_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0227_basic_calculator_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void basicCalculatorII() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().calculate("3+2*2"), equalTo(7));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9dc31f3c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0228_summary_ranges/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0228_summary_ranges;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void summaryRanges() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().summaryRanges(new int[] {0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 7}),
+ equalTo(Arrays.asList("0->2", "4->5", "7")));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c4fe8039a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0229_majority_element_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0229_majority_element_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void majorityElement() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().majorityElement(new int[] {3, 2, 3}), equalTo(Arrays.asList(3)));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c2ce5ae55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+
+ @Test
+ public void kthSmallest() {
+ TreeNode rightBottomLeft = new TreeNode(2);
+ TreeNode left = new TreeNode(1, null, rightBottomLeft);
+
+ TreeNode right = new TreeNode(4);
+ TreeNode root = new TreeNode(3, left, right);
+
+ assertThat(new Solution().kthSmallest(root, 1), equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e8aefc324
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0231_power_of_two/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0231_power_of_two;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ public void isPowerOfTwo() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().isPowerOfTwo(1), equalTo(true));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueueTest.java b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueueTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c11c7ab24
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0201_0300/s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks/MyQueueTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g0201_0300.s0232_implement_queue_using_stacks;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.Test;
+
+public class MyQueueTest {
+ @Test
+ public void queueUsingStacks() {
+ MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
+ myQueue.push(1);
+ myQueue.push(2);
+
+ assertThat(myQueue.peek(), equalTo(1));
+ assertThat(myQueue.pop(), equalTo(1));
+ assertThat(myQueue.empty(), equalTo(false));
+ }
+}