diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d92d46734
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount;
+
+// #Easy #Array #Sorting #Greedy #2022_06_07_Time_2_ms_(97.50%)_Space_41.4_MB_(99.04%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int minimumCost(int[] cost) {
+ Arrays.sort(cost);
+ int size = 0;
+ int sum = 0;
+ for (int i = cost.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ size++;
+ if (size % 3 != 0) {
+ sum += cost[i];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return sum;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/readme.md b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e8b5c994a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+2144\. Minimum Cost of Buying Candies With Discount
+
+Easy
+
+A shop is selling candies at a discount. For **every two** candies sold, the shop gives a **third** candy for **free**.
+
+The customer can choose **any** candy to take away for free as long as the cost of the chosen candy is less than or equal to the **minimum** cost of the two candies bought.
+
+* For example, if there are `4` candies with costs `1`, `2`, `3`, and `4`, and the customer buys candies with costs `2` and `3`, they can take the candy with cost `1` for free, but not the candy with cost `4`.
+
+Given a **0-indexed** integer array `cost`, where `cost[i]` denotes the cost of the ith candy, return _the **minimum cost** of buying **all** the candies_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** cost = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** We buy the candies with costs 2 and 3, and take the candy with cost 1 for free.
+
+The total cost of buying all candies is 2 + 3 = 5. This is the **only** way we can buy the candies.
+
+Note that we cannot buy candies with costs 1 and 3, and then take the candy with cost 2 for free.
+
+The cost of the free candy has to be less than or equal to the minimum cost of the purchased candies.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** cost = [6,5,7,9,2,2]
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Explanation:** The way in which we can get the minimum cost is described below:
+
+- Buy candies with costs 9 and 7
+
+- Take the candy with cost 6 for free
+
+- We buy candies with costs 5 and 2
+
+- Take the last remaining candy with cost 2 for free
+
+Hence, the minimum cost to buy all candies is 9 + 7 + 5 + 2 = 23.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** cost = [5,5]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:** Since there are only 2 candies, we buy both of them. There is not a third candy we can take for free.
+
+Hence, the minimum cost to buy all candies is 5 + 5 = 10.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= cost.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= cost[i] <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6d4ce7fd2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Prefix_Sum #2022_06_07_Time_7_ms_(36.03%)_Space_111.3_MB_(13.23%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int numberOfArrays(int[] diff, int lower, int upper) {
+ int n = diff.length;
+ if (lower == upper) {
+ for (int j : diff) {
+ if (j != 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ int max = -(int) 1e9;
+ int min = (int) 1e9;
+ int[] hidden = new int[n + 1];
+ hidden[0] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ hidden[i] = hidden[i - 1] + diff[i - 1];
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (hidden[i] > max) {
+ max = hidden[i];
+ }
+ if (hidden[i] < min) {
+ min = hidden[i];
+ }
+ }
+ int low = lower - min;
+ int high = upper - max;
+ if (low > high) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ return (high - low) + 1;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/readme.md b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6c5ac5c41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+2145\. Count the Hidden Sequences
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a **0-indexed** array of `n` integers `differences`, which describes the **differences** between each pair of **consecutive** integers of a **hidden** sequence of length `(n + 1)`. More formally, call the hidden sequence `hidden`, then we have that `differences[i] = hidden[i + 1] - hidden[i]`.
+
+You are further given two integers `lower` and `upper` that describe the **inclusive** range of values `[lower, upper]` that the hidden sequence can contain.
+
+* For example, given `differences = [1, -3, 4]`, `lower = 1`, `upper = 6`, the hidden sequence is a sequence of length `4` whose elements are in between `1` and `6` (**inclusive**).
+ * `[3, 4, 1, 5]` and `[4, 5, 2, 6]` are possible hidden sequences.
+ * `[5, 6, 3, 7]` is not possible since it contains an element greater than `6`.
+ * `[1, 2, 3, 4]` is not possible since the differences are not correct.
+
+Return _the number of **possible** hidden sequences there are._ If there are no possible sequences, return `0`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** differences = [1,-3,4], lower = 1, upper = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The possible hidden sequences are:
+
+- [3, 4, 1, 5]
+
+- [4, 5, 2, 6]
+
+Thus, we return 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** differences = [3,-4,5,1,-2], lower = -4, upper = 5
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The possible hidden sequences are:
+
+- [-3, 0, -4, 1, 2, 0]
+
+- [-2, 1, -3, 2, 3, 1]
+
+- [-1, 2, -2, 3, 4, 2]
+
+- [0, 3, -1, 4, 5, 3]
+
+Thus, we return 4.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** differences = [4,-7,2], lower = 3, upper = 6
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** There are no possible hidden sequences. Thus, we return 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == differences.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* -105 <= differences[i] <= 105
+* -105 <= lower <= upper <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a48633bab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Sorting #Breadth_First_Search #Matrix #Heap_Priority_Queue
+// #2022_06_07_Time_81_ms_(88.84%)_Space_65.7_MB_(99.30%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import java.util.LinkedList;
+import java.util.List;
+import java.util.Queue;
+
+public class Solution {
+ static class Item {
+ int row;
+ int col;
+ int dist;
+ int price;
+
+ public Item(int row, int col, int dist, int price) {
+ this.row = row;
+ this.col = col;
+ this.dist = dist;
+ this.price = price;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public List> highestRankedKItems(
+ int[][] grid, int[] pricing, int[] start, int k) {
+ int n = grid.length;
+ int m = grid[0].length;
+ Queue bfs = new LinkedList<>();
+ LinkedList- items = new LinkedList<>();
+
+ bfs.add(start);
+ if (grid[start[0]][start[1]] >= pricing[0] && grid[start[0]][start[1]] <= pricing[1]) {
+ items.add(new Item(start[0], start[1], 0, grid[start[0]][start[1]]));
+ }
+ grid[start[0]][start[1]] = -1;
+
+ int distance = 0;
+ while (!bfs.isEmpty()) {
+ int size = bfs.size();
+ distance++;
+ while (size-- > 0) {
+ int[] loc = bfs.poll();
+ int[] dirX = {0, 1, -1, 0};
+ int[] dirY = {-1, 0, 0, 1};
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int newX = loc[0] + dirX[i];
+ int newY = loc[1] + dirY[i];
+ if (newX < 0
+ || newX >= n
+ || newY < 0
+ || newY >= m
+ || grid[newX][newY] == -1
+ || grid[newX][newY] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (grid[newX][newY] >= pricing[0] && grid[newX][newY] <= pricing[1]) {
+ items.add(new Item(newX, newY, distance, grid[newX][newY]));
+ }
+ grid[newX][newY] = -1;
+ bfs.add(new int[] {newX, newY});
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ items.sort(
+ (a, b) -> {
+ int distDiff = a.dist - b.dist;
+ if (distDiff == 0) {
+ int priceDiff = a.price - b.price;
+ if (priceDiff == 0) {
+ int rowDiff = a.row - b.row;
+ if (rowDiff == 0) {
+ return a.col - b.col;
+ }
+ return rowDiff;
+ }
+ return priceDiff;
+ }
+ return distDiff;
+ });
+ List> ans = new LinkedList<>();
+ while (k-- > 0 && !items.isEmpty()) {
+ Item item = items.poll();
+ ans.add(Arrays.asList(item.row, item.col));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/readme.md b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4f7c79184
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+2146\. K Highest Ranked Items Within a Price Range
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a **0-indexed** 2D integer array `grid` of size `m x n` that represents a map of the items in a shop. The integers in the grid represent the following:
+
+* `0` represents a wall that you cannot pass through.
+* `1` represents an empty cell that you can freely move to and from.
+* All other positive integers represent the price of an item in that cell. You may also freely move to and from these item cells.
+
+It takes `1` step to travel between adjacent grid cells.
+
+You are also given integer arrays `pricing` and `start` where `pricing = [low, high]` and `start = [row, col]` indicates that you start at the position `(row, col)` and are interested only in items with a price in the range of `[low, high]` (**inclusive**). You are further given an integer `k`.
+
+You are interested in the **positions** of the `k` **highest-ranked** items whose prices are **within** the given price range. The rank is determined by the **first** of these criteria that is different:
+
+1. Distance, defined as the length of the shortest path from the `start` (**shorter** distance has a higher rank).
+2. Price (**lower** price has a higher rank, but it must be **in the price range**).
+3. The row number (**smaller** row number has a higher rank).
+4. The column number (**smaller** column number has a higher rank).
+
+Return _the_ `k` _highest-ranked items within the price range **sorted** by their rank (highest to lowest)_. If there are fewer than `k` reachable items within the price range, return _**all** of them_.
+
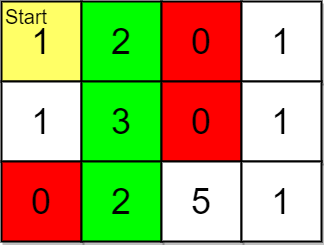
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,0,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,5], start = [0,0], k = 3
+
+**Output:** [[0,1],[1,1],[2,1]]
+
+**Explanation:** You start at (0,0).
+
+With a price range of [2,5], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (2,1) and (2,2).
+
+The ranks of these items are:
+
+- (0,1) with distance 1
+
+- (1,1) with distance 2
+
+- (2,1) with distance 3
+
+- (2,2) with distance 4
+
+Thus, the 3 highest ranked items in the price range are (0,1), (1,1), and (2,1).
+
+**Example 2:**
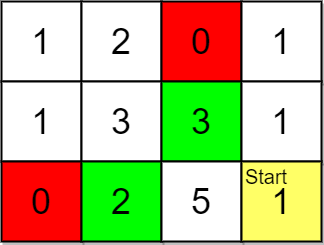
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,3,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,3], start = [2,3], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [[2,1],[1,2]]
+
+**Explanation:** You start at (2,3).
+
+With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (1,2) and (2,1).
+
+The ranks of these items are:
+
+- (2,1) with distance 2, price 2
+
+- (1,2) with distance 2, price 3
+
+- (1,1) with distance 3
+
+- (0,1) with distance 4
+
+Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (1,2).
+
+**Example 3:**
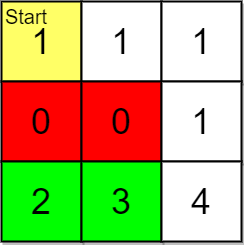
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,1],[2,3,4]], pricing = [2,3], start = [0,0], k = 3
+
+**Output:** [[2,1],[2,0]]
+
+**Explanation:** You start at (0,0).
+
+With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (2,0) and (2,1).
+
+The ranks of these items are:
+
+- (2,1) with distance 5
+
+- (2,0) with distance 6
+
+Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (2,0).
+
+ Note that k = 3 but there are only 2 reachable items within the price range.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+*
1 <= m, n <= 105
+* 1 <= m * n <= 105
+* 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
+* `pricing.length == 2`
+* 2 <= low <= high <= 105
+* `start.length == 2`
+* `0 <= row <= m - 1`
+* `0 <= col <= n - 1`
+* `grid[row][col] > 0`
+* `1 <= k <= m * n`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ba89aa032
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor;
+
+// #Hard #String #Dynamic_Programming #Math #2022_06_07_Time_54_ms_(62.96%)_Space_71.7_MB_(39.81%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int numberOfWays(String corridor) {
+ int seat = 0;
+ int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
+ for (int i = 0; i < corridor.length(); i++) {
+ if (corridor.charAt(i) == 'S') {
+ seat++;
+ }
+ }
+ if (seat == 0 || seat % 2 != 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ seat /= 2;
+ long curr = 0;
+ long ans = 1;
+ int i = 0;
+ while (corridor.charAt(i) != 'S') {
+ i++;
+ }
+ i++;
+ while (seat > 1) {
+ while (corridor.charAt(i) != 'S') {
+ i++;
+ }
+ i++;
+ while (corridor.charAt(i) != 'S') {
+ i++;
+ curr++;
+ }
+ curr++;
+ ans = (ans * curr) % mod;
+ curr = 0;
+ seat--;
+ i++;
+ }
+ return (int) ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/readme.md b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3e92db0d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+2147\. Number of Ways to Divide a Long Corridor
+
+Hard
+
+Along a long library corridor, there is a line of seats and decorative plants. You are given a **0-indexed** string `corridor` of length `n` consisting of letters `'S'` and `'P'` where each `'S'` represents a seat and each `'P'` represents a plant.
+
+One room divider has **already** been installed to the left of index `0`, and **another** to the right of index `n - 1`. Additional room dividers can be installed. For each position between indices `i - 1` and `i` (`1 <= i <= n - 1`), at most one divider can be installed.
+
+Divide the corridor into non-overlapping sections, where each section has **exactly two seats** with any number of plants. There may be multiple ways to perform the division. Two ways are **different** if there is a position with a room divider installed in the first way but not in the second way.
+
+Return _the number of ways to divide the corridor_. Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7. If there is no way, return `0`.
+
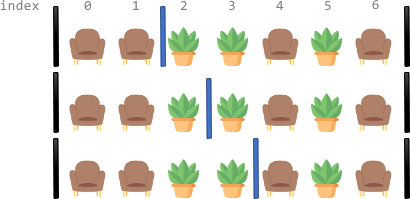
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** corridor = "SSPPSPS"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** There are 3 different ways to divide the corridor.
+
+The black bars in the above image indicate the two room dividers already installed.
+
+Note that in each of the ways, **each** section has exactly **two** seats.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** corridor = "PPSPSP"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** There is only 1 way to divide the corridor, by not installing any additional dividers.
+
+Installing any would create some section that does not have exactly two seats.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** corridor = "S"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** There is no way to divide the corridor because there will always be a section that does not have exactly two seats.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == corridor.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `corridor[i]` is either `'S'` or `'P'`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ad352488c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements;
+
+// #Easy #Array #Sorting #2022_06_07_Time_0_ms_(100.00%)_Space_40.6_MB_(88.75%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int countElements(int[] a) {
+ int min = a[0];
+ int max = a[0];
+ int minocr = 1;
+ int maxocr = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < a.length; ++i) {
+ {
+ if (a[i] < min) {
+ min = a[i];
+ minocr = 1;
+ } else if (a[i] == min) {
+ minocr++;
+ }
+ }
+ {
+ if (a[i] > max) {
+ max = a[i];
+ maxocr = 1;
+ } else if (a[i] == max) {
+ maxocr++;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return (min == max) ? 0 : a.length - minocr - maxocr;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/readme.md b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a63eb17d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+2148\. Count Elements With Strictly Smaller and Greater Elements
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, return _the number of elements that have **both** a strictly smaller and a strictly greater element appear in_ `nums`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [11,7,2,15]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The element 7 has the element 2 strictly smaller than it and the element 11 strictly greater than it.
+
+Element 11 has element 7 strictly smaller than it and element 15 strictly greater than it.
+
+In total there are 2 elements having both a strictly smaller and a strictly greater element appear in `nums`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-3,3,3,90]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The element 3 has the element -3 strictly smaller than it and the element 90 strictly greater than it.
+
+Since there are two elements with the value 3, in total there are 2 elements having both a strictly smaller and a strictly greater element appear in `nums`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 100`
+* -105 <= nums[i] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e7b5cca73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2144_minimum_cost_of_buying_candies_with_discount;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minimumCost() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minimumCost(new int[] {1, 2, 3}), equalTo(5));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumCost2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minimumCost(new int[] {6, 5, 7, 9, 2, 2}), equalTo(23));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minimumCost3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minimumCost(new int[] {5, 5}), equalTo(10));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..91616dcaa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2145_count_the_hidden_sequences;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfArrays() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfArrays(new int[] {1, -3, 4}, 1, 6), equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfArrays2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfArrays(new int[] {3, -4, 5, 1, -2}, -4, 5), equalTo(4));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfArrays3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfArrays(new int[] {4, -7, 2}, 3, 6), equalTo(0));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..21d0079b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2146_k_highest_ranked_items_within_a_price_range;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void highestRankedKItems() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .highestRankedKItems(
+ new int[][] {{1, 2, 0, 1}, {1, 3, 0, 1}, {0, 2, 5, 1}},
+ new int[] {2, 5},
+ new int[] {0, 0},
+ 3),
+ equalTo(
+ Arrays.asList(
+ Arrays.asList(0, 1), Arrays.asList(1, 1), Arrays.asList(2, 1))));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void highestRankedKItems2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .highestRankedKItems(
+ new int[][] {{1, 2, 0, 1}, {1, 3, 3, 1}, {0, 2, 5, 1}},
+ new int[] {2, 3},
+ new int[] {2, 3},
+ 2),
+ equalTo(Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(2, 1), Arrays.asList(1, 2))));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void highestRankedKItems3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .highestRankedKItems(
+ new int[][] {{1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {2, 3, 4}},
+ new int[] {2, 3},
+ new int[] {0, 0},
+ 3),
+ equalTo(Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(2, 1), Arrays.asList(2, 0))));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d1ec69426
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2147_number_of_ways_to_divide_a_long_corridor;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfWays() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfWays("SSPPSPS"), equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfWays2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfWays("PPSPSP"), equalTo(1));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfWays3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().numberOfWays("S"), equalTo(0));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7ab85a652
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g2101_2200/s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g2101_2200.s2148_count_elements_with_strictly_smaller_and_greater_elements;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countElements() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countElements(new int[] {11, 7, 2, 15}), equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countElements2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countElements(new int[] {-3, 3, 3, 90}), equalTo(2));
+ }
+}