城市的 天际线 是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。给你所有建筑物的位置和高度,请返回 由这些建筑物形成的 天际线 。
每个建筑物的几何信息由数组 buildings 表示,其中三元组 buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti] 表示:
lefti是第i座建筑物左边缘的x坐标。righti是第i座建筑物右边缘的x坐标。heighti是第i座建筑物的高度。
你可以假设所有的建筑都是完美的长方形,在高度为 0 的绝对平坦的表面上。
天际线 应该表示为由 “关键点” 组成的列表,格式 [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...] ,并按 x 坐标 进行 排序 。关键点是水平线段的左端点。列表中最后一个点是最右侧建筑物的终点,y 坐标始终为 0 ,仅用于标记天际线的终点。此外,任何两个相邻建筑物之间的地面都应被视为天际线轮廓的一部分。
注意:输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如 [...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...] 是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
示例 1:
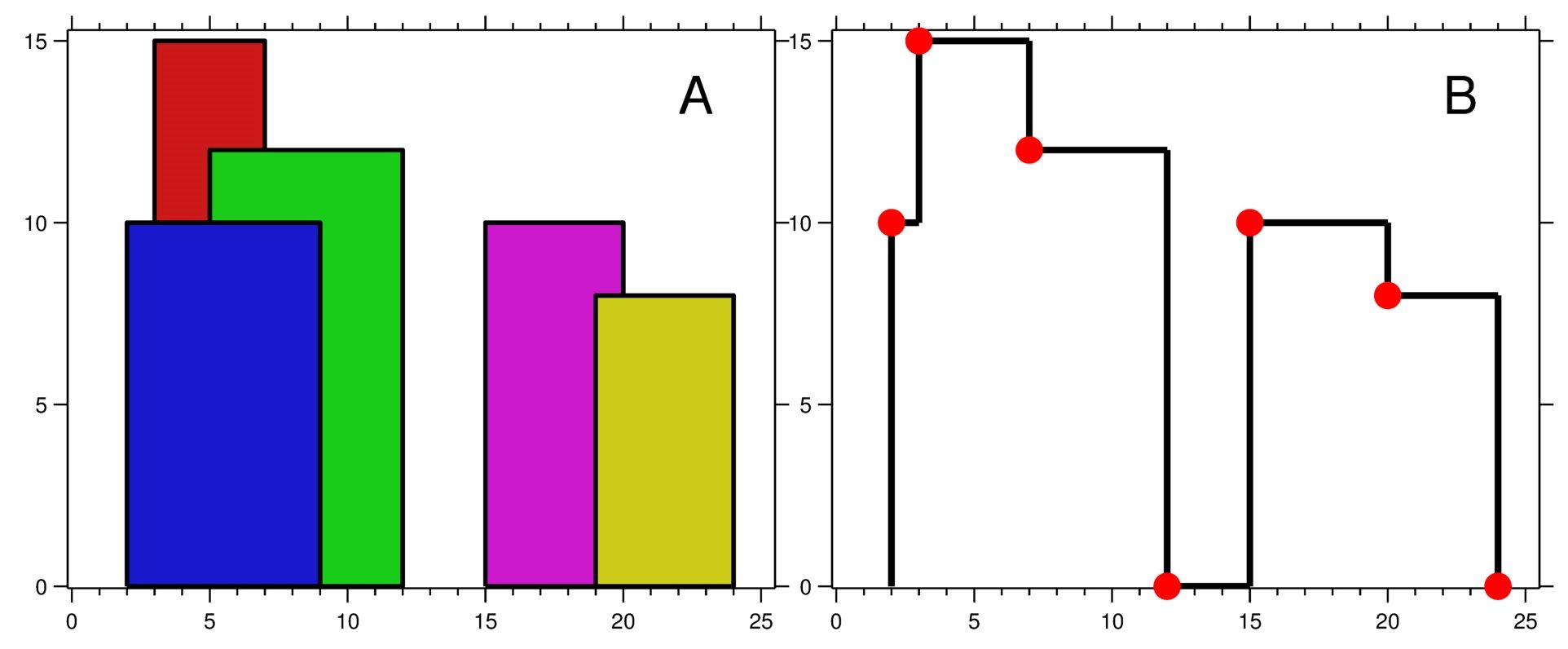
输入:buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]] 输出:[[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]] 解释: 图 A 显示输入的所有建筑物的位置和高度, 图 B 显示由这些建筑物形成的天际线。图 B 中的红点表示输出列表中的关键点。
示例 2:
输入:buildings = [[0,2,3],[2,5,3]] 输出:[[0,3],[5,0]]
提示:
1 <= buildings.length <= 1040 <= lefti < righti <= 231 - 11 <= heighti <= 231 - 1buildings按lefti非递减排序
方法一:扫描线+优先队列
记录下所有建筑物的左右边界线,升序排序之后得到序列 lines。对于每一个边界线 lines[i],找出所有包含 lines[i] 的建筑物,并确保建筑物的左边界小于等于 lines[i],右边界大于 lines[i],则这些建筑物中高度最高的建筑物的高度就是该线轮廓点的高度。可以使用建筑物的高度构建优先队列(大根堆),同时需要注意高度相同的轮廓点需要合并为一个。
from queue import PriorityQueue
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
skys, lines, pq = [], [], PriorityQueue()
for build in buildings:
lines.extend([build[0], build[1]])
lines.sort()
city, n = 0, len(buildings)
for line in lines:
while city < n and buildings[city][0] <= line:
pq.put([-buildings[city][2], buildings[city]
[0], buildings[city][1]])
city += 1
while not pq.empty() and pq.queue[0][2] <= line:
pq.get()
high = 0
if not pq.empty():
high = -pq.queue[0][0]
if len(skys) > 0 and skys[-1][1] == high:
continue
skys.append([line, high])
return skystype Matrix struct{ left, right, height int }
type Queue []Matrix
func (q Queue) Len() int { return len(q) }
func (q Queue) Top() Matrix { return q[0] }
func (q Queue) Swap(i, j int) { q[i], q[j] = q[j], q[i] }
func (q Queue) Less(i, j int) bool { return q[i].height > q[j].height }
func (q *Queue) Push(x interface{}) { *q = append(*q, x.(Matrix)) }
func (q *Queue) Pop() interface{} {
old, x := *q, (*q)[len(*q)-1]
*q = old[:len(old)-1]
return x
}
func getSkyline(buildings [][]int) [][]int {
skys, lines, pq := make([][]int, 0), make([]int, 0), &Queue{}
heap.Init(pq)
for _, v := range buildings {
lines = append(lines, v[0], v[1])
}
sort.Ints(lines)
city, n := 0, len(buildings)
for _, line := range lines {
// 将所有符合条件的矩形加入队列
for ; city < n && buildings[city][0] <= line && buildings[city][1] > line; city++ {
v := Matrix{left: buildings[city][0], right: buildings[city][1], height: buildings[city][2]}
heap.Push(pq, v)
}
// 从队列移除不符合条件的矩形
for pq.Len() > 0 && pq.Top().right <= line {
heap.Pop(pq)
}
high := 0
// 队列为空说明是最右侧建筑物的终点,其轮廓点为 (line, 0)
if pq.Len() != 0 {
high = pq.Top().height
}
// 如果该点高度和前一个轮廓点一样的话,直接忽略
if len(skys) > 0 && skys[len(skys)-1][1] == high {
continue
}
skys = append(skys, []int{line, high})
}
return skys
}class Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
set<int> poss;
map<int, int> m;
for (auto v : buildings) {
poss.insert(v[0]);
poss.insert(v[1]);
}
int i = 0;
for (int pos : poss)
m.insert(pair<int, int>(pos, i++));
vector<int> highs(m.size(), 0);
for (auto v : buildings) {
const int b = m[v[0]], e = m[v[1]];
for (int i = b; i < e; ++i)
highs[i] = max(highs[i], v[2]);
}
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
vector<int> mm(poss.begin(), poss.end());
for (int i = 0; i < highs.size(); ++i) {
if (highs[i] != highs[i + 1])
res.push_back(pair<int, int>(mm[i], highs[i]));
else {
const int start = i;
res.push_back(pair<int, int>(mm[start], highs[i]));
while (highs[i] == highs[i + 1])
++i;
}
}
return res;
}
};