| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请你构造一个下标从 0 开始、大小为 m x n 的字符串矩阵 res ,用以表示树的 格式化布局 。构造此格式化布局矩阵需要遵循以下规则:
- 树的 高度 为
height,矩阵的行数m应该等于height + 1。 - 矩阵的列数
n应该等于2height+1 - 1。 - 根节点 需要放置在 顶行 的 正中间 ,对应位置为
res[0][(n-1)/2]。 - 对于放置在矩阵中的每个节点,设对应位置为
res[r][c],将其左子节点放置在res[r+1][c-2height-r-1],右子节点放置在res[r+1][c+2height-r-1]。 - 继续这一过程,直到树中的所有节点都妥善放置。
- 任意空单元格都应该包含空字符串
""。
返回构造得到的矩阵 res 。
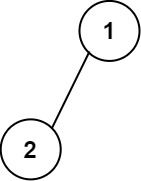
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2] 输出: [["","1",""], ["2","",""]]
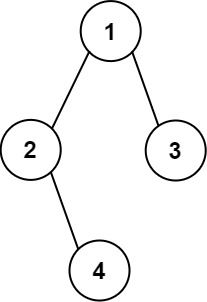
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,4] 输出: [["","","","1","","",""], ["","2","","","","3",""], ["","","4","","","",""]]
提示:
- 树中节点数在范围
[1, 210]内 -99 <= Node.val <= 99- 树的深度在范围
[1, 10]内
先通过 DFS 求二叉树的高度 0 开始),然后根据
根据 ans,然后 DFS 遍历二叉树,依次在每个位置填入二叉树节点值(字符串形式)即可。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def printTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[str]]:
def height(root):
if root is None:
return -1
return 1 + max(height(root.left), height(root.right))
def dfs(root, r, c):
if root is None:
return
ans[r][c] = str(root.val)
dfs(root.left, r + 1, c - 2 ** (h - r - 1))
dfs(root.right, r + 1, c + 2 ** (h - r - 1))
h = height(root)
m, n = h + 1, 2 ** (h + 1) - 1
ans = [[""] * n for _ in range(m)]
dfs(root, 0, (n - 1) // 2)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
String[][] res = new String[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(res[i], "");
}
dfs(root, res, h, 0, (n - 1) / 2);
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] t : res) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(t));
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, String[][] res, int h, int r, int c) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res[r][c] = String.valueOf(root.val);
dfs(root.left, res, h, r + 1, c - (1 << (h - r - 1)));
dfs(root.right, res, h, r + 1, c + (1 << (h - r - 1)));
}
private int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
return 1 + Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> printTree(TreeNode* root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
vector<vector<string>> ans(m, vector<string>(n, ""));
dfs(root, ans, h, 0, (n - 1) / 2);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<vector<string>>& ans, int h, int r, int c) {
if (!root) return;
ans[r][c] = to_string(root->val);
dfs(root->left, ans, h, r + 1, c - pow(2, h - r - 1));
dfs(root->right, ans, h, r + 1, c + pow(2, h - r - 1));
}
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return -1;
return 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right));
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func printTree(root *TreeNode) [][]string {
var height func(root *TreeNode) int
height = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return -1
}
return 1 + max(height(root.Left), height(root.Right))
}
h := height(root)
m, n := h+1, (1<<(h+1))-1
ans := make([][]string, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]string, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = ""
}
}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, r, c int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, r, c int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
ans[r][c] = strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
dfs(root.Left, r+1, c-int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1))))
dfs(root.Right, r+1, c+int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1))))
}
dfs(root, 0, (n-1)/2)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function printTree(root: TreeNode | null): string[][] {
const getHeight = (root: TreeNode | null, h: number) => {
if (root == null) {
return h - 1;
}
return Math.max(getHeight(root.left, h + 1), getHeight(root.right, h + 1));
};
const height = getHeight(root, 0);
const m = height + 1;
const n = 2 ** (height + 1) - 1;
const res: string[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n).fill(''));
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, i: number, j: number) => {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
const { val, left, right } = root;
res[i][j] = val + '';
dfs(left, i + 1, j - 2 ** (height - i - 1));
dfs(right, i + 1, j + 2 ** (height - i - 1));
};
dfs(root, 0, (n - 1) >>> 1);
return res;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn get_height(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, h: u32) -> u32 {
if let Some(node) = root {
let node = node.borrow();
return Self::get_height(&node.left, h + 1).max(Self::get_height(&node.right, h + 1));
}
h - 1
}
fn dfs(
root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
i: usize,
j: usize,
res: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>,
height: u32,
) {
if root.is_none() {
return;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
res[i][j] = node.val.to_string();
Self::dfs(
&node.left,
i + 1,
j - (2usize).pow(height - (i as u32) - 1),
res,
height,
);
Self::dfs(
&node.right,
i + 1,
j + (2usize).pow(height - (i as u32) - 1),
res,
height,
);
}
pub fn print_tree(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
let height = Self::get_height(&root, 0);
let m = (height + 1) as usize;
let n = (2usize).pow(height + 1) - 1;
let mut res = vec![vec![String::new(); n]; m];
Self::dfs(&root, 0, (n - 1) >> 1, &mut res, height);
res
}
}方法一中,我们是通过 DFS 来求二叉树的高度,我们也可以改成 BFS 的方式,逐层往下扩展,那么扩展的层数就是二叉树的高度。
同样,我们初始化结果列表 ans,然后 BFS 遍历二叉树,依次在每个位置填入二叉树节点值(字符串形式)即可。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def printTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[str]]:
def height(root):
q = deque([root])
h = -1
while q:
h += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
root = q.popleft()
if root.left:
q.append(root.left)
if root.right:
q.append(root.right)
return h
h = height(root)
m, n = h + 1, 2 ** (h + 1) - 1
ans = [[""] * n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque([(root, 0, (n - 1) // 2)])
while q:
node, r, c = q.popleft()
ans[r][c] = str(node.val)
if node.left:
q.append((node.left, r + 1, c - 2 ** (h - r - 1)))
if node.right:
q.append((node.right, r + 1, c + 2 ** (h - r - 1)))
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
String[][] res = new String[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(res[i], "");
}
Deque<Tuple> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new Tuple(root, 0, (n - 1) / 2));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Tuple p = q.pollFirst();
root = p.node;
int r = p.r, c = p.c;
res[r][c] = String.valueOf(root.val);
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(new Tuple(root.left, r + 1, c - (1 << (h - r - 1))));
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(new Tuple(root.right, r + 1, c + (1 << (h - r - 1))));
}
}
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] t : res) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(t));
}
return ans;
}
private int height(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
int h = -1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
++h;
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
root = q.pollFirst();
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(root.right);
}
}
}
return h;
}
}
class Tuple {
TreeNode node;
int r;
int c;
public Tuple(TreeNode node, int r, int c) {
this.node = node;
this.r = r;
this.c = c;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> printTree(TreeNode* root) {
int h = height(root);
int m = h + 1, n = (1 << (h + 1)) - 1;
vector<vector<string>> ans(m, vector<string>(n, ""));
queue<tuple<TreeNode*, int, int>> q;
q.push({root, 0, (n - 1) / 2});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
root = get<0>(p);
int r = get<1>(p), c = get<2>(p);
ans[r][c] = to_string(root->val);
if (root->left) q.push({root->left, r + 1, c - pow(2, h - r - 1)});
if (root->right) q.push({root->right, r + 1, c + pow(2, h - r - 1)});
}
return ans;
}
int height(TreeNode* root) {
int h = -1;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
++h;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if (root->left) q.push(root->left);
if (root->right) q.push(root->right);
}
}
return h;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func printTree(root *TreeNode) [][]string {
h := height(root)
m, n := h+1, (1<<(h+1))-1
ans := make([][]string, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]string, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = ""
}
}
q := []tuple{tuple{root, 0, (n - 1) / 2}}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
root := p.node
r, c := p.r, p.c
ans[r][c] = strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, tuple{root.Left, r + 1, c - int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1)))})
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, tuple{root.Right, r + 1, c + int(math.Pow(float64(2), float64(h-r-1)))})
}
}
return ans
}
func height(root *TreeNode) int {
h := -1
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
h++
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
root := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, root.Right)
}
}
}
return h
}
type tuple struct {
node *TreeNode
r int
c int
}