为了缓解「力扣嘉年华」期间的人流压力,组委会在活动期间开设了一些交通专线。path[i] = [a, b] 表示有一条从地点 a通往地点 b 的 单向 交通专线。
若存在一个地点,满足以下要求,我们则称之为 交通枢纽:
- 所有地点(除自身外)均有一条 单向 专线 直接 通往该地点;
- 该地点不存在任何 通往其他地点 的单向专线。
请返回交通专线的 交通枢纽。若不存在,则返回 -1。
注意:
- 对于任意一个地点,至少被一条专线连通。
示例 1:
输入:
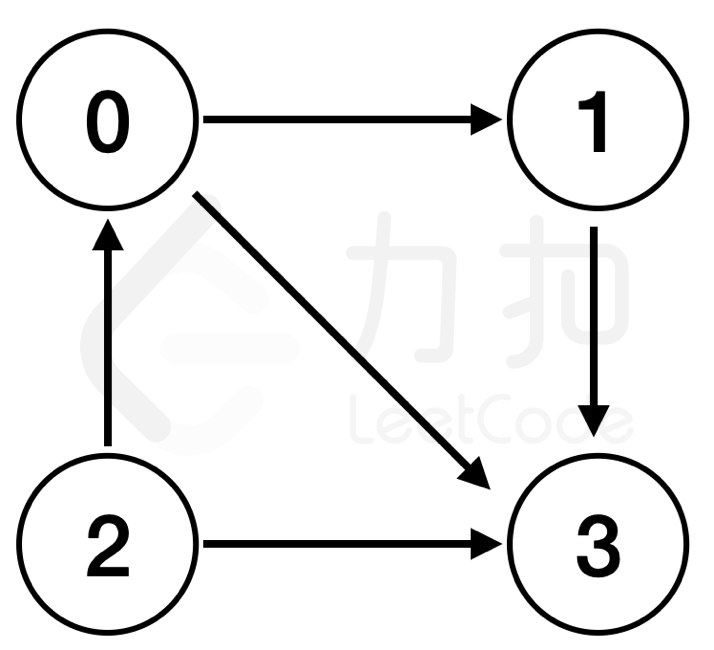
path = [[0,1],[0,3],[1,3],[2,0],[2,3]]输出:
3解释:如下图所示: 地点
0,1,2各有一条通往地点3的交通专线, 且地点3不存在任何通往其他地点的交通专线。
示例 2:
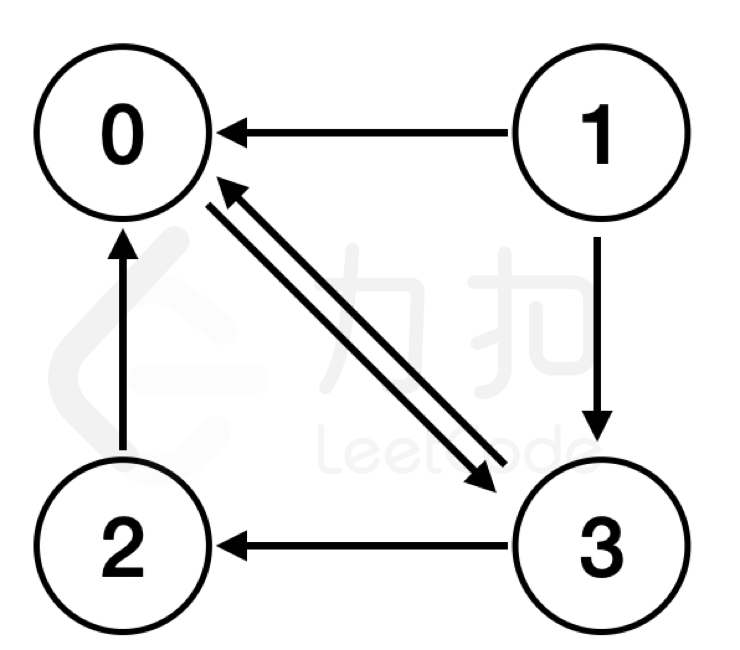
输入:
path = [[0,3],[1,0],[1,3],[2,0],[3,0],[3,2]]输出:
-1
提示:
1 <= path.length <= 10000 <= path[i][0], path[i][1] <= 1000path[i][0]与path[i][1]不相等
方法一:统计入度和出度
我们创建两个数组
接下来,遍历每个节点
否则遍历结束,返回
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def transportationHub(self, path: List[List[int]]) -> int:
ind = Counter()
outd = Counter()
s = set()
vis = set()
for a, b in path:
if (a, b) in vis:
continue
vis.add((a, b))
s.add(a)
s.add(b)
outd[a] += 1
ind[b] += 1
for c in s:
if ind[c] == len(s) - 1 and outd[c] == 0:
return c
return -1class Solution {
public int transportationHub(int[][] path) {
int[] ind = new int[1001];
int[] outd = new int[1001];
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] p : path) {
int a = p[0], b = p[1];
if (vis.add(a * 1000 + b)) {
s.add(a);
s.add(b);
ind[b]++;
outd[a]++;
}
}
for (int c : s) {
if (ind[c] == s.size() - 1 && outd[c] == 0) {
return c;
}
}
return -1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int transportationHub(vector<vector<int>>& path) {
int ind[1001]{};
int outd[1001]{};
unordered_set<int> s;
unordered_set<int> vis;
for (auto& p : path) {
int a = p[0], b = p[1];
if (vis.count(a * 1000 + b)) {
continue;
}
vis.insert(a * 1000 + b);
s.insert(a);
s.insert(b);
ind[b]++;
outd[a]++;
}
for (int c : s) {
if (ind[c] == s.size() - 1 && outd[c] == 0) {
return c;
}
}
return -1;
}
};func transportationHub(path [][]int) int {
ind := [1001]int{}
outd := [1001]int{}
s := map[int]struct{}{}
vis := map[int]bool{}
for _, p := range path {
a, b := p[0], p[1]
if vis[a*1000+b] {
continue
}
vis[a*1000+b] = true
s[a] = struct{}{}
s[b] = struct{}{}
outd[a]++
ind[b]++
}
for c := range s {
if ind[c] == len(s)-1 && outd[c] == 0 {
return c
}
}
return -1
}function transportationHub(path: number[][]): number {
const ind: number[] = new Array(1001).fill(0);
const outd: number[] = new Array(1001).fill(0);
const s: Set<number> = new Set();
const vis: Set<number> = new Set();
for (const [a, b] of path) {
if (vis.has(a * 1000 + b)) {
continue;
}
vis.add(a * 1000 + b);
s.add(a);
s.add(b);
ind[b]++;
outd[a]++;
}
for (const c of s) {
if (ind[c] === s.size - 1 && outd[c] === 0) {
return c;
}
}
return -1;
}