给你一个点数组 points 和一个表示角度的整数 angle ,你的位置是 location ,其中 location = [posx, posy] 且 points[i] = [xi, yi] 都表示 X-Y 平面上的整数坐标。
最开始,你面向东方进行观测。你 不能 进行移动改变位置,但可以通过 自转 调整观测角度。换句话说,posx 和 posy 不能改变。你的视野范围的角度用 angle 表示, 这决定了你观测任意方向时可以多宽。设 d 为你逆时针自转旋转的度数,那么你的视野就是角度范围 [d - angle/2, d + angle/2] 所指示的那片区域。
对于每个点,如果由该点、你的位置以及从你的位置直接向东的方向形成的角度 位于你的视野中 ,那么你就可以看到它。
同一个坐标上可以有多个点。你所在的位置也可能存在一些点,但不管你的怎么旋转,总是可以看到这些点。同时,点不会阻碍你看到其他点。
返回你能看到的点的最大数目。
示例 1:
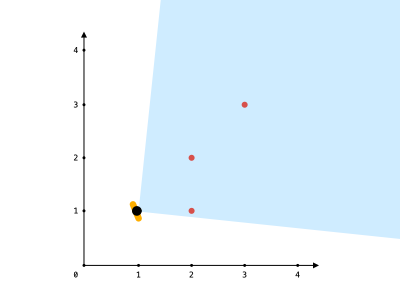
输入:points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,3]], angle = 90, location = [1,1] 输出:3 解释:阴影区域代表你的视野。在你的视野中,所有的点都清晰可见,尽管 [2,2] 和 [3,3]在同一条直线上,你仍然可以看到 [3,3] 。
示例 2:
输入:points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,4],[1,1]], angle = 90, location = [1,1] 输出:4 解释:在你的视野中,所有的点都清晰可见,包括你所在位置的那个点。
示例 3:
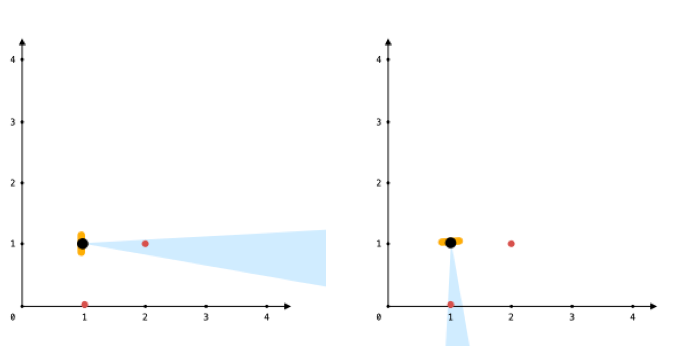
输入:points = [[1,0],[2,1]], angle = 13, location = [1,1] 输出:1 解释:如图所示,你只能看到两点之一。
提示:
1 <= points.length <= 105points[i].length == 2location.length == 20 <= angle < 3600 <= posx, posy, xi, yi <= 100
根据题目我们得知,需要求出在视角范围 [d - angle/2, d + angle / 2] 范围内覆盖的最多点的数量。视角可以转换为相对于 location (x, y) 的极角。
可以排除与 location 重合的点,将剩下的所有点 p 的坐标 (xi, yi) 转换为相对于 (x, y) 的极角。可以利用 atan2 函数,atan2 返回值范围是 [−π,π],覆盖范围是 2π。
求出极角后,按照大小进行排序。因为可以循环,所以把整个数组所有元素加上 2π 接在数组后面。
接下来利用双指针找出覆盖最多点的区间即可。最后返回时,要把重合的点加上。
class Solution:
def visiblePoints(
self, points: List[List[int]], angle: int, location: List[int]
) -> int:
v = []
x, y = location
same = 0
for xi, yi in points:
if xi == x and yi == y:
same += 1
else:
v.append(atan2(yi - y, xi - x))
v.sort()
n = len(v)
v += [deg + 2 * pi for deg in v]
t = angle * pi / 180
mx = max((bisect_right(v, v[i] + t) - i for i in range(n)), default=0)
return mx + sameclass Solution {
public int visiblePoints(List<List<Integer>> points, int angle, List<Integer> location) {
List<Double> v = new ArrayList<>();
int x = location.get(0), y = location.get(1);
int same = 0;
for (List<Integer> p : points) {
int xi = p.get(0), yi = p.get(1);
if (xi == x && yi == y) {
++same;
continue;
}
v.add(Math.atan2(yi - y, xi - x));
}
Collections.sort(v);
int n = v.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
v.add(v.get(i) + 2 * Math.PI);
}
int mx = 0;
Double t = angle * Math.PI / 180;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < 2 * n; ++j) {
while (i < j && v.get(j) - v.get(i) > t) {
++i;
}
mx = Math.max(mx, j - i + 1);
}
return mx + same;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int visiblePoints(vector<vector<int>>& points, int angle, vector<int>& location) {
vector<double> v;
int x = location[0], y = location[1];
int same = 0;
for (auto& p : points) {
int xi = p[0], yi = p[1];
if (xi == x && yi == y)
++same;
else
v.emplace_back(atan2(yi - y, xi - x));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int n = v.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) v.emplace_back(v[i] + 2 * M_PI);
int mx = 0;
double t = angle * M_PI / 180;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < 2 * n; ++j) {
while (i < j && v[j] - v[i] > t) ++i;
mx = max(mx, j - i + 1);
}
return mx + same;
}
};func visiblePoints(points [][]int, angle int, location []int) int {
same := 0
v := []float64{}
for _, p := range points {
if p[0] == location[0] && p[1] == location[1] {
same++
} else {
v = append(v, math.Atan2(float64(p[1]-location[1]), float64(p[0]-location[0])))
}
}
sort.Float64s(v)
for _, deg := range v {
v = append(v, deg+2*math.Pi)
}
mx := 0
t := float64(angle) * math.Pi / 180
for i, j := 0, 0; j < len(v); j++ {
for i < j && v[j]-v[i] > t {
i++
}
mx = max(mx, j-i+1)
}
return same + mx
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}