| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
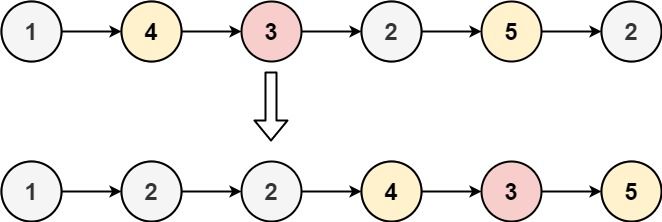
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3 输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2 输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 200]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
我们创建两个链表
时间复杂度
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
l = ListNode()
r = ListNode()
tl, tr = l, r
while head:
if head.val < x:
tl.next = head
tl = tl.next
else:
tr.next = head
tr = tr.next
head = head.next
tr.next = None
tl.next = r.next
return l.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode l = new ListNode();
ListNode r = new ListNode();
ListNode tl = l, tr = r;
for (; head != null; head = head.next) {
if (head.val < x) {
tl.next = head;
tl = tl.next;
} else {
tr.next = head;
tr = tr.next;
}
}
tr.next = null;
tl.next = r.next;
return l.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
ListNode* l = new ListNode();
ListNode* r = new ListNode();
ListNode* tl = l;
ListNode* tr = r;
for (; head; head = head->next) {
if (head->val < x) {
tl->next = head;
tl = tl->next;
} else {
tr->next = head;
tr = tr->next;
}
}
tr->next = nullptr;
tl->next = r->next;
return l->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func partition(head *ListNode, x int) *ListNode {
l, r := &ListNode{}, &ListNode{}
tl, tr := l, r
for ; head != nil; head = head.Next {
if head.Val < x {
tl.Next = head
tl = tl.Next
} else {
tr.Next = head
tr = tr.Next
}
}
tr.Next = nil
tl.Next = r.Next
return l.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function partition(head: ListNode | null, x: number): ListNode | null {
const [l, r] = [new ListNode(), new ListNode()];
let [tl, tr] = [l, r];
for (; head; head = head.next) {
if (head.val < x) {
tl.next = head;
tl = tl.next;
} else {
tr.next = head;
tr = tr.next;
}
}
tr.next = null;
tl.next = r.next;
return l.next;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn partition(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, x: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut l = ListNode::new(0);
let mut r = ListNode::new(0);
let mut tl = &mut l;
let mut tr = &mut r;
let mut current = head;
while let Some(mut node) = current {
current = node.next.take();
if node.val < x {
tl.next = Some(node);
tl = tl.next.as_mut().unwrap();
} else {
tr.next = Some(node);
tr = tr.next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
}
tr.next = None;
tl.next = r.next;
l.next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} x
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var partition = function (head, x) {
const [l, r] = [new ListNode(), new ListNode()];
let [tl, tr] = [l, r];
for (; head; head = head.next) {
if (head.val < x) {
tl.next = head;
tl = tl.next;
} else {
tr.next = head;
tr = tr.next;
}
}
tr.next = null;
tl.next = r.next;
return l.next;
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode l = new ListNode();
ListNode r = new ListNode();
ListNode tl = l, tr = r;
for (; head != null; head = head.next) {
if (head.val < x) {
tl.next = head;
tl = tl.next;
} else {
tr.next = head;
tr = tr.next;
}
}
tr.next = null;
tl.next = r.next;
return l.next;
}
}