给定一颗二叉树的根节点 root ,返回满足条件:节点的值等于该节点所有子节点的值之和 的节点的数量。
一个节点 x 的 子节点 是指从节点 x 出发,到所有叶子节点路径上的节点。没有子节点的节点的子节点和视为 0 。
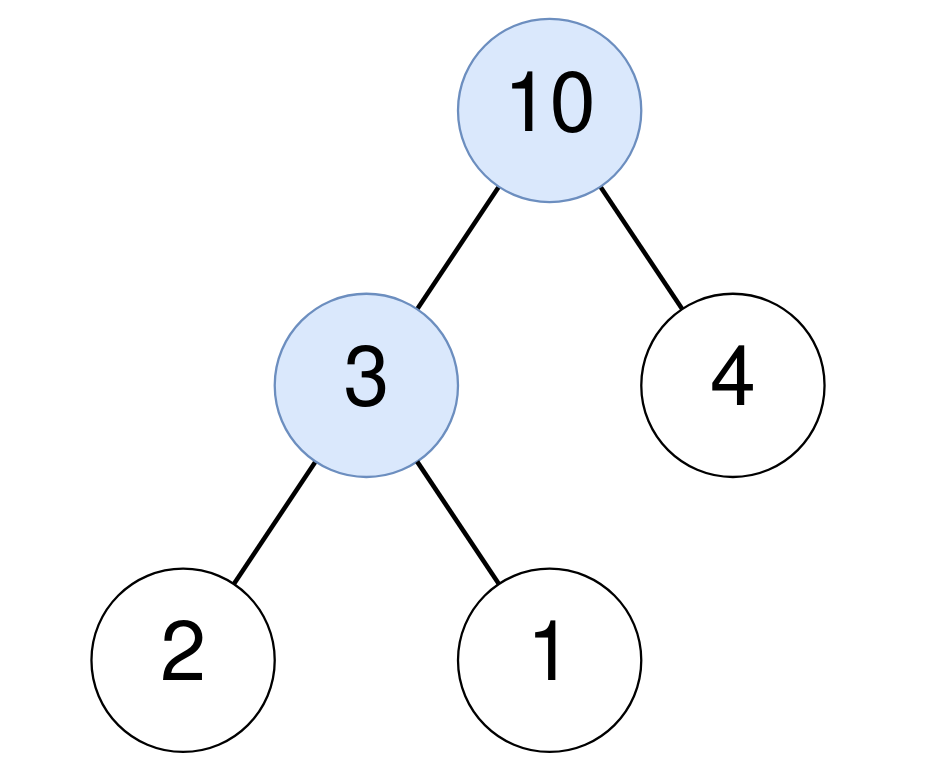
示例 1:
输入: root = [10,3,4,2,1] 输出: 2 解释: 对于值为10的节点: 其子节点之和为: 3+4+2+1 = 10。 对于值为3的节点:其子节点之和为: 2+1 = 3。
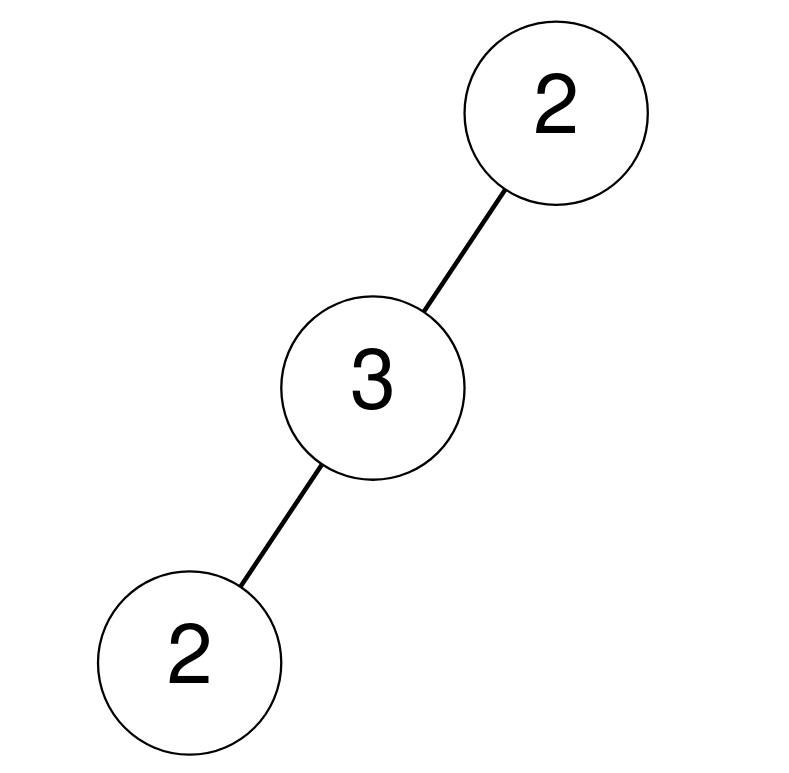
示例 2:
输入: root = [2,3,null,2,null] 输出: 0 解释: 没有节点满足其值等于子节点之和。
示例 3:
输入: root = [0] 输出: 1 解释: 对于值为0的节点:因为它没有子节点,所以自己点之和为0。
提示:
- 树中节点的数量范围:
[1, 105] 0 <= Node.val <= 105
我们设计一个函数
- 如果
$root$ 为空,返回$0$ ; - 否则,我们递归地计算
$root$ 的左子树和右子树的节点值之和,记为$l$ 和$r$ ;如果$l + r = root.val$ ,说明以$root$ 为根节点的子树满足条件,我们将答案加$1$ ;最后,返回$root.val + l + r$ 。
然后我们调用函数
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def equalToDescendants(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return 0
l, r = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right)
if l + r == root.val:
nonlocal ans
ans += 1
return root.val + l + r
ans = 0
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
public int equalToDescendants(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = dfs(root.left);
int r = dfs(root.right);
if (l + r == root.val) {
++ans;
}
return root.val + l + r;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int equalToDescendants(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
function<long long(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) -> long long {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
auto l = dfs(root->left);
auto r = dfs(root->right);
ans += l + r == root->val;
return root->val + l + r;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func equalToDescendants(root *TreeNode) (ans int) {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right)
if l+r == root.Val {
ans++
}
return root.Val + l + r
}
dfs(root)
return
}