给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
示例 1:
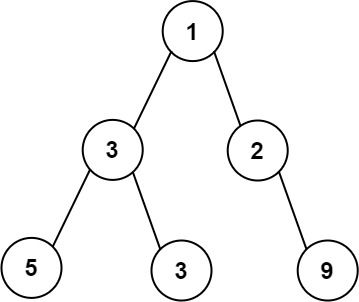
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] 输出:4 解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9) 。
示例 2:
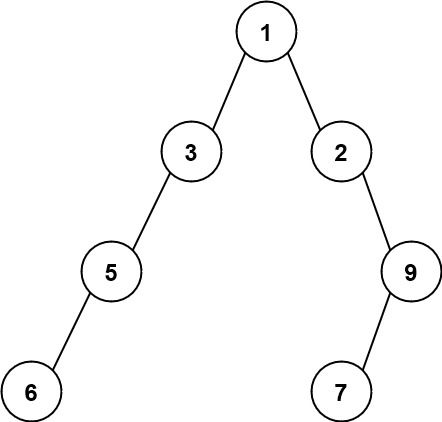
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7] 输出:7 解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7) 。
示例 3:
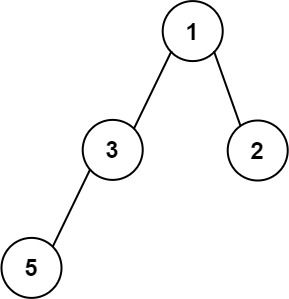
输入:root = [1,3,2,5] 输出:2 解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2) 。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[1, 3000] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
方法一:BFS
对节点进行编号,初始根节点编号为
对于一个编号为 i 的节点,它的左节点编号为 i<<1,右节点编号为 i<<1|1。
采用 BFS 进行层序遍历,求每层的宽度时,用该层的最大节点编号减去最小节点编号再加一即可。
时间复杂度
方法二:DFS
定义 dfs(root, depth, i) 表示从深度为 depth,且编号为 i 的节点 root 开始往下搜索。记录每一层最先访问到的节点的编号。访问到当前层其它节点时,求当前节点编号与当前层最小编号的差再加一,更新当前层的最大宽度。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
ans = 0
q = deque([(root, 1)])
while q:
ans = max(ans, q[-1][1] - q[0][1] + 1)
for _ in range(len(q)):
root, i = q.popleft()
if root.left:
q.append((root.left, i << 1))
if root.right:
q.append((root.right, i << 1 | 1))
return ans# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root, depth, i):
if root is None:
return
if len(t) == depth:
t.append(i)
else:
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, i - t[depth] + 1)
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, i << 1)
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, i << 1 | 1)
ans = 1
t = []
dfs(root, 0, 1)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
Deque<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new Pair<>(root, 1));
int ans = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
ans = Math.max(ans, q.peekLast().getValue() - q.peekFirst().getValue() + 1);
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
var p = q.pollFirst();
root = p.getKey();
int i = p.getValue();
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(new Pair<>(root.left, i << 1));
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(new Pair<>(root.right, i << 1 | 1));
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans = 1;
private List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0, 1);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (t.size() == depth) {
t.add(i);
} else {
ans = Math.max(ans, i - t.get(depth) + 1);
}
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, i << 1);
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, i << 1 | 1);
}
}i << 1 表示下一层的起点。计算下一层左右子树索引时,减去 i << 1,可以防止溢出。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q;
q.push({root, 1});
int ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
ans = max(ans, q.back().second - q.front().second + 1);
int i = q.front().second;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
root = p.first;
int j = p.second;
if (root->left) q.push({root->left, (j << 1) - (i << 1)});
if (root->right) q.push({root->right, (j << 1 | 1) - (i << 1)});
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> t;
int ans = 1;
using ull = unsigned long long;
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, 0, 1);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth, ull i) {
if (!root) return;
if (t.size() == depth) {
t.push_back(i);
} else {
ans = max(ans, (int) (i - t[depth] + 1));
}
dfs(root->left, depth + 1, i << 1);
dfs(root->right, depth + 1, i << 1 | 1);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func widthOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
q := []pair{{root, 1}}
ans := 0
for len(q) > 0 {
ans = max(ans, q[len(q)-1].i-q[0].i+1)
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
root = p.node
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, pair{root.Left, p.i << 1})
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, pair{root.Right, p.i<<1 | 1})
}
}
}
return ans
}
type pair struct {
node *TreeNode
i int
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func widthOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 1
t := []int{}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, depth, i int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, depth, i int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if len(t) == depth {
t = append(t, i)
} else {
ans = max(ans, i-t[depth]+1)
}
dfs(root.Left, depth+1, i<<1)
dfs(root.Right, depth+1, i<<1|1)
}
dfs(root, 0, 1)
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}