-
示例 1:
+
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2]
@@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ tags:
解释:经过一次 move 操作,数组将变为 [1, 2, 3]。
-
示例 2:
+
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,1,2,1,7]
diff --git a/solution/0900-0999/0945.Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique/README_EN.md b/solution/0900-0999/0945.Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique/README_EN.md
index 54526c5199143..5bb44f951e300 100644
--- a/solution/0900-0999/0945.Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0900-0999/0945.Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique/README_EN.md
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ tags:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,2,1,7]
Output: 6
Explanation: After 6 moves, the array could be [3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 7].
-It can be shown with 5 or less moves that it is impossible for the array to have all unique values.
+It can be shown that it is impossible for the array to have all unique values with 5 or less moves.
diff --git a/solution/1000-1099/1039.Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon/README_EN.md b/solution/1000-1099/1039.Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon/README_EN.md
index 34e695ae0722b..dc5f2cece7f3d 100644
--- a/solution/1000-1099/1039.Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1000-1099/1039.Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon/README_EN.md
@@ -19,37 +19,51 @@ tags:
-
You have a convex n-sided polygon where each vertex has an integer value. You are given an integer array values where values[i] is the value of the ith vertex (i.e., clockwise order).
+
You have a convex n-sided polygon where each vertex has an integer value. You are given an integer array values where values[i] is the value of the ith vertex in clockwise order.
-
You will triangulate the polygon into n - 2 triangles. For each triangle, the value of that triangle is the product of the values of its vertices, and the total score of the triangulation is the sum of these values over all n - 2 triangles in the triangulation.
+
Polygon triangulation is a process where you divide a polygon into a set of triangles and the vertices of each triangle must also be vertices of the original polygon. Note that no other shapes other than triangles are allowed in the division. This process will result in n - 2 triangles.
-
Return the smallest possible total score that you can achieve with some triangulation of the polygon.
+
You will triangulate the polygon. For each triangle, the weight of that triangle is the product of the values at its vertices. The total score of the triangulation is the sum of these weights over all n - 2 triangles.
+
+
Return the minimum possible score that you can achieve with some triangulation of the polygon.
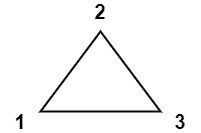
Example 1:
-
-
-Input: values = [1,2,3]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The polygon is already triangulated, and the score of the only triangle is 6.
-
+
+

+
+
+
Input: values = [1,2,3]
+
+
Output: 6
+
+
Explanation: The polygon is already triangulated, and the score of the only triangle is 6.
+
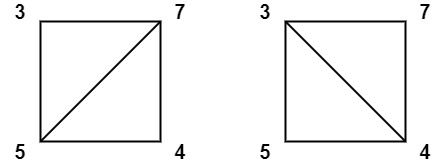
Example 2:
-
-
-Input: values = [3,7,4,5]
-Output: 144
-Explanation: There are two triangulations, with possible scores: 3*7*5 + 4*5*7 = 245, or 3*4*5 + 3*4*7 = 144.
-The minimum score is 144.
-
+
+

+
+
+
Input: values = [3,7,4,5]
+
+
Output: 144
+
+
Explanation: There are two triangulations, with possible scores: 3*7*5 + 4*5*7 = 245, or 3*4*5 + 3*4*7 = 144.
+The minimum score is 144.
+
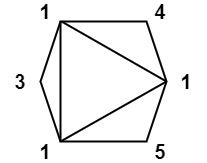
Example 3:
-
-
-Input: values = [1,3,1,4,1,5]
-Output: 13
-Explanation: The minimum score triangulation has score 1*1*3 + 1*1*4 + 1*1*5 + 1*1*1 = 13.
-
+
+

+
+
+
Input: values = [1,3,1,4,1,5]
+
+
Output: 13
+
+
Explanation: The minimum score triangulation is 1*1*3 + 1*1*4 + 1*1*5 + 1*1*1 = 13.
+
Constraints:
diff --git a/solution/1300-1399/1330.Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value/README_EN.md b/solution/1300-1399/1330.Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value/README_EN.md
index d392ca046cf87..b6c4724709a74 100644
--- a/solution/1300-1399/1330.Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1300-1399/1330.Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value/README_EN.md
@@ -46,8 +46,9 @@ tags:
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 1042 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104-105 <= nums[i] <= 105- The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit integer.
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1437.Check If All 1's Are at Least Length K Places Away/README.md b/solution/1400-1499/1437.Check If All 1's Are at Least Length K Places Away/README.md
index 5101aa1ecd885..283ab683fde28 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1437.Check If All 1's Are at Least Length K Places Away/README.md
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1437.Check If All 1's Are at Least Length K Places Away/README.md
@@ -18,44 +18,34 @@ tags:
-
给你一个由若干 0 和 1 组成的数组 nums 以及整数 k。如果所有 1 都至少相隔 k 个元素,则返回 True ;否则,返回 False 。
+
给你一个由若干 0 和 1 组成的数组 nums 以及整数 k。如果所有 1 都至少相隔 k 个元素,则返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
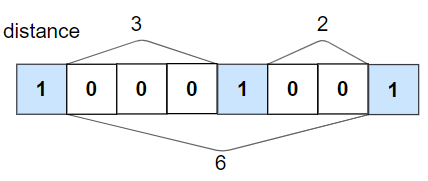
示例 1:
-
+

-
输入:nums = [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], k = 2
+
+输入:nums = [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], k = 2
输出:true
解释:每个 1 都至少相隔 2 个元素。
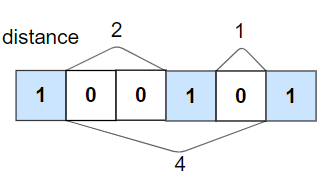
示例 2:
-
+
-输入:nums = [1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 2
+
+输入:nums = [1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 2
输出:false
解释:第二个 1 和第三个 1 之间只隔了 1 个元素。
-示例 3:
-
-输入:nums = [1,1,1,1,1], k = 0
-输出:true
-
-
-示例 4:
-
-输入:nums = [0,1,0,1], k = 1
-输出:true
-
-
提示:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums.length <= 1050 <= k <= nums.lengthnums[i] 的值为 0 或 1
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1796.Second Largest Digit in a String/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1796.Second Largest Digit in a String/README_EN.md
index 67ff0b8189661..e14a18628a512 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1796.Second Largest Digit in a String/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1796.Second Largest Digit in a String/README_EN.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ tags:
1 <= s.length <= 500s consists of only lowercase English letters and/or digits.s consists of only lowercase English letters and digits.
diff --git a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README.md b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README.md
index 907de5036c28b..b7dc7b03596aa 100644
--- a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README.md
+++ b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README.md
@@ -314,7 +314,7 @@ function getDirections(root: TreeNode | null, startValue: number, destValue: num
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null, x: number, path: string[]): boolean => {
@@ -370,7 +370,7 @@ var getDirections = function (root, startValue, destValue) {
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node, x, path) => {
diff --git a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README_EN.md b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README_EN.md
index 58782483df639..41a9811d4e980 100644
--- a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/README_EN.md
@@ -310,7 +310,7 @@ function getDirections(root: TreeNode | null, startValue: number, destValue: num
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null, x: number, path: string[]): boolean => {
@@ -366,7 +366,7 @@ var getDirections = function (root, startValue, destValue) {
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node, x, path) => {
diff --git a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.js b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.js
index cf11074f0553b..c6ca93d60610d 100644
--- a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.js
+++ b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.js
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ var getDirections = function (root, startValue, destValue) {
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node, x, path) => {
diff --git a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.ts b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.ts
index 5c028830da797..fa2f24e5d72b9 100644
--- a/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/2000-2099/2096.Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another/Solution.ts
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ function getDirections(root: TreeNode | null, startValue: number, destValue: num
const left = lca(node.left, p, q);
const right = lca(node.right, p, q);
- return left && right ? node : (left ?? right);
+ return left && right ? node : left ?? right;
};
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null, x: number, path: string[]): boolean => {
diff --git a/solution/2200-2299/2244.Minimum Rounds to Complete All Tasks/README_EN.md b/solution/2200-2299/2244.Minimum Rounds to Complete All Tasks/README_EN.md
index 17bc5c86bb95e..f2b793a6f44c6 100644
--- a/solution/2200-2299/2244.Minimum Rounds to Complete All Tasks/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2200-2299/2244.Minimum Rounds to Complete All Tasks/README_EN.md
@@ -55,6 +55,9 @@ It can be shown that all the tasks cannot be completed in fewer than 4 rounds, s
1 <= tasks[i] <= 109
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 2870: Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Empty.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/2300-2399/2324.Product Sales Analysis IV/README.md b/solution/2300-2399/2324.Product Sales Analysis IV/README.md
index e0ce6c0c0ccc7..b87a1e626e225 100644
--- a/solution/2300-2399/2324.Product Sales Analysis IV/README.md
+++ b/solution/2300-2399/2324.Product Sales Analysis IV/README.md
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ Product 表:
- 在产品 3 上花费 7 * 15 = 105。
用户101在产品3上花的钱最多。
用户 102:
- - 在产品 1 上花费 (9 + 7)* 10 = 150
+ - 在产品 1 上花费 (9 + 6)* 10 = 150
- 在产品 2 上花费 6 * 25 = 150
- 在产品 3 上花费 10 * 15 = 150。
用户 102 在产品 1、2、3 上花的钱最多。
diff --git a/solution/2300-2399/2397.Maximum Rows Covered by Columns/README_EN.md b/solution/2300-2399/2397.Maximum Rows Covered by Columns/README_EN.md
index 082f5951418e2..e8104a8827abe 100644
--- a/solution/2300-2399/2397.Maximum Rows Covered by Columns/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2300-2399/2397.Maximum Rows Covered by Columns/README_EN.md
@@ -22,43 +22,56 @@ tags:
-
You are given a 0-indexed m x n binary matrix matrix and an integer numSelect, which denotes the number of distinct columns you must select from matrix.
+
You are given an m x n binary matrix matrix and an integer numSelect.
-
Let us consider s = {c1, c2, ...., cnumSelect} as the set of columns selected by you. A row row is covered by s if:
+
Your goal is to select exactly numSelect distinct columns from matrix such that you cover as many rows as possible.
+
+
A row is considered covered if all the 1's in that row are also part of a column that you have selected. If a row does not have any 1s, it is also considered covered.
+
+
More formally, let us consider selected = {c1, c2, ...., cnumSelect} as the set of columns selected by you. A row i is covered by selected if:
- - For each cell
matrix[row][col] (0 <= col <= n - 1) where matrix[row][col] == 1, col is present in s or,
- - No cell in
row has a value of 1.
+ - For each cell where
matrix[i][j] == 1, the column j is in selected.
+ - Or, no cell in row
i has a value of 1.
-
You need to choose numSelect columns such that the number of rows that are covered is maximized.
-
-
Return the maximum number of rows that can be covered by a set of numSelect columns.
+
Return the maximum number of rows that can be covered by a set of numSelect columns.
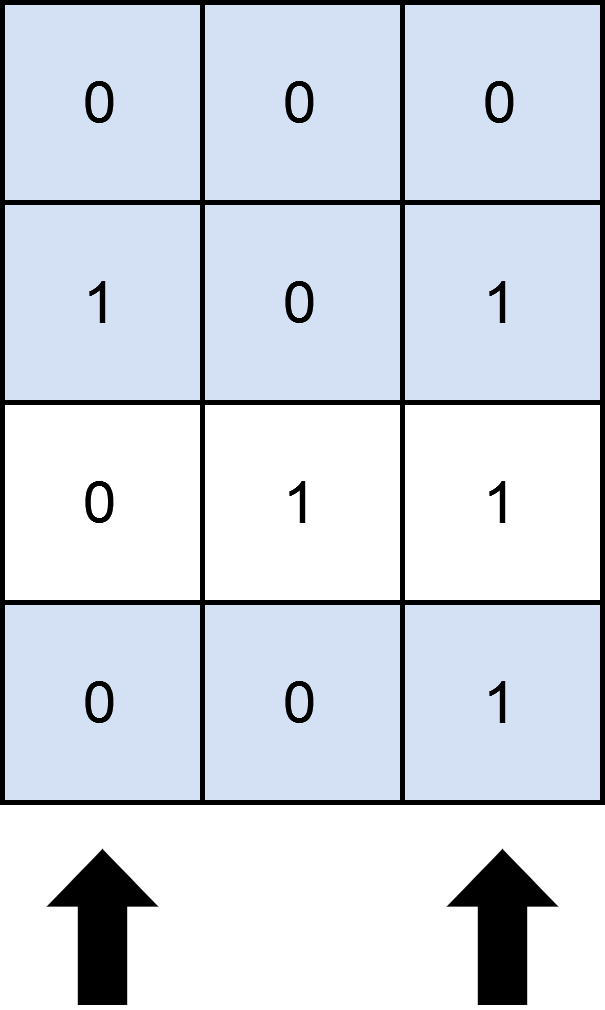
Example 1:
-
-
-Input: matrix = [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]], numSelect = 2
-Output: 3
-Explanation: One possible way to cover 3 rows is shown in the diagram above.
-We choose s = {0, 2}.
-- Row 0 is covered because it has no occurrences of 1.
-- Row 1 is covered because the columns with value 1, i.e. 0 and 2 are present in s.
-- Row 2 is not covered because matrix[2][1] == 1 but 1 is not present in s.
-- Row 3 is covered because matrix[2][2] == 1 and 2 is present in s.
-Thus, we can cover three rows.
-Note that s = {1, 2} will also cover 3 rows, but it can be shown that no more than three rows can be covered.
-
+
+

+
+
+
Input: matrix = [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]], numSelect = 2
+
+
Output: 3
+
+
Explanation:
+
+
One possible way to cover 3 rows is shown in the diagram above.
+We choose s = {0, 2}.
+- Row 0 is covered because it has no occurrences of 1.
+- Row 1 is covered because the columns with value 1, i.e. 0 and 2 are present in s.
+- Row 2 is not covered because matrix[2][1] == 1 but 1 is not present in s.
+- Row 3 is covered because matrix[2][2] == 1 and 2 is present in s.
+Thus, we can cover three rows.
+Note that s = {1, 2} will also cover 3 rows, but it can be shown that no more than three rows can be covered.
+
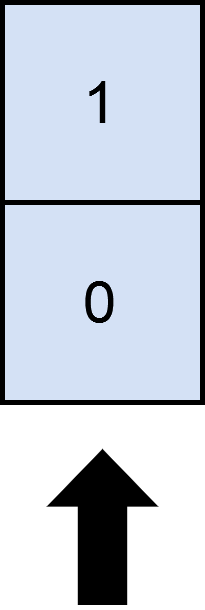
Example 2:
-
-
-Input: matrix = [[1],[0]], numSelect = 1
-Output: 2
-Explanation: Selecting the only column will result in both rows being covered since the entire matrix is selected.
-Therefore, we return 2.
-
+
+

+
+
+
Input: matrix = [[1],[0]], numSelect = 1
+
+
Output: 2
+
+
Explanation:
+
+
Selecting the only column will result in both rows being covered since the entire matrix is selected.
+
Constraints:
diff --git a/solution/2400-2499/2410.Maximum Matching of Players With Trainers/README_EN.md b/solution/2400-2499/2410.Maximum Matching of Players With Trainers/README_EN.md
index 30b237f79e30f..eee7b8f4ad56b 100644
--- a/solution/2400-2499/2410.Maximum Matching of Players With Trainers/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2400-2499/2410.Maximum Matching of Players With Trainers/README_EN.md
@@ -58,6 +58,9 @@ Each player can only be matched with one trainer, so the maximum answer is 1.
1 <= players[i], trainers[j] <= 109
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 445: Assign Cookies.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README.md b/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README.md
index 7995ffa41a767..9fc8015c56440 100644
--- a/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README.md
+++ b/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README.md
@@ -56,6 +56,10 @@ tags:
1 <= time <= 1000
+
+
+
注意:本题与 3178.找出 K 秒后拿着球的孩子 一致。
+
## 解法
diff --git a/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README_EN.md b/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README_EN.md
index e8c4d48d2a36b..52b220b3b8715 100644
--- a/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2500-2599/2582.Pass the Pillow/README_EN.md
@@ -53,6 +53,9 @@ After two seconds, the 3
rd person is holding the pillow.
1 <= time <= 1000
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 3178: Find the Child Who Has the Ball After K Seconds.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum Length of Semi-Decreasing Subarrays/README.md b/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum Length of Semi-Decreasing Subarrays/README.md
index c12c29a77c75f..95efc548c5ea2 100644
--- a/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum Length of Semi-Decreasing Subarrays/README.md
+++ b/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum Length of Semi-Decreasing Subarrays/README.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ tags:
-# [2863. 最长半递减数组 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-length-of-semi-decreasing-subarrays)
+# [2863. 最长半递减子数组的长度 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-length-of-semi-decreasing-subarrays)
[English Version](/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum%20Length%20of%20Semi-Decreasing%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README.md b/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README.md
index 485a5227c4a58..936540edc060a 100644
--- a/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README.md
+++ b/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README.md
@@ -20,25 +20,9 @@ tags:
-
给你一个长度为 n 下标从 0 开始的整数数组 maxHeights 。
+
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 heights 表示 n 座连续的塔中砖块的数量。你的任务是移除一些砖块来形成一个 山脉状 的塔排列。在这种布置中,塔高度先是非递减,有一个或多个连续塔达到最大峰值,然后非递增排列。
-
你的任务是在坐标轴上建 n 座塔。第 i 座塔的下标为 i ,高度为 heights[i] 。
-
-
如果以下条件满足,我们称这些塔是 美丽 的:
-
-
- 1 <= heights[i] <= maxHeights[i]heights 是一个 山脉 数组。
-
-
如果存在下标 i 满足以下条件,那么我们称数组 heights 是一个 山脉 数组:
-
-
- - 对于所有
0 < j <= i ,都有 heights[j - 1] <= heights[j]
- - 对于所有
i <= k < n - 1 ,都有 heights[k + 1] <= heights[k]
-
-
-
请你返回满足 美丽塔 要求的方案中,高度和的最大值 。
+
返回满足山脉状塔排列的方案中,高度和的最大值 。
@@ -47,31 +31,22 @@ tags:
输入:maxHeights = [5,3,4,1,1]
输出:13
-解释:和最大的美丽塔方案为 heights = [5,3,3,1,1] ,这是一个美丽塔方案,因为:
-- 1 <= heights[i] <= maxHeights[i]
-- heights 是个山脉数组,峰值在 i = 0 处。
-13 是所有美丽塔方案中的最大高度和。
+
解释:我们移除一些砖块来形成 heights = [5,3,3,1,1],峰值位于下标 0。
+
示例 2:
输入:maxHeights = [6,5,3,9,2,7]
输出:22
-解释: 和最大的美丽塔方案为 heights = [3,3,3,9,2,2] ,这是一个美丽塔方案,因为:
-- 1 <= heights[i] <= maxHeights[i]
-- heights 是个山脉数组,峰值在 i = 3 处。
-22 是所有美丽塔方案中的最大高度和。
+
解释:我们移除一些砖块来形成 heights = [3,3,3,9,2,2],峰值位于下标 3。
示例 3:
输入:maxHeights = [3,2,5,5,2,3]
输出:18
-解释:和最大的美丽塔方案为 heights = [2,2,5,5,2,2] ,这是一个美丽塔方案,因为:
-- 1 <= heights[i] <= maxHeights[i]
-- heights 是个山脉数组,最大值在 i = 2 处。
-注意,在这个方案中,i = 3 也是一个峰值。
-18 是所有美丽塔方案中的最大高度和。
+解释:我们移除一些砖块来形成 heights = [2,2,5,5,2,2],峰值位于下标 2 或 3。
@@ -79,8 +54,8 @@ tags:
提示:
- 1 <= n == maxHeights <= 1031 <= maxHeights[i] <= 1091 <= n == heights.length <= 1031 <= heights[i] <= 109
diff --git a/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README_EN.md b/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README_EN.md
index 31a88be1f7c49..6c4dc7470cb1d 100644
--- a/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful Towers I/README_EN.md
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ tags:
Constraints:
- 1 <= n == heights <= 1031 <= n == heights.length <= 1031 <= heights[i] <= 109
diff --git a/solution/2800-2899/2866.Beautiful Towers II/README_EN.md b/solution/2800-2899/2866.Beautiful Towers II/README_EN.md
index 8a3cf4f983c4f..d95835f8ff7dd 100644
--- a/solution/2800-2899/2866.Beautiful Towers II/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2800-2899/2866.Beautiful Towers II/README_EN.md
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ It can be shown that there exists no other beautiful configuration with a sum of
Constraints:
- 1 <= n == maxHeights <= 1051 <= n == maxHeights.length <= 1051 <= maxHeights[i] <= 109
diff --git a/solution/2800-2899/2870.Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Empty/README_EN.md b/solution/2800-2899/2870.Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Empty/README_EN.md
index 53a497127b369..84c19f104e062 100644
--- a/solution/2800-2899/2870.Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Empty/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2800-2899/2870.Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Empty/README_EN.md
@@ -62,6 +62,9 @@ It can be shown that we cannot make the array empty in less than 4 operations.
1 <= nums[i] <= 106
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 2244: Minimum Rounds to Complete All Tasks.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/3000-3099/3054.Binary Tree Nodes/README_EN.md b/solution/3000-3099/3054.Binary Tree Nodes/README_EN.md
index 9493460c1ea71..8e378f287d40e 100644
--- a/solution/3000-3099/3054.Binary Tree Nodes/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/3000-3099/3054.Binary Tree Nodes/README_EN.md
@@ -72,10 +72,13 @@ Tree table:
+---+-------+
Explanation:
- Node 5 is the root node since it has no parent node.
-- Nodes 1, 3, 6, and 8 are leaf nodes because they don't have any child nodes.
-- Nodes 2, 4, and 7 are inner nodes as they serve as parents to some of the nodes in the structure.
+- Nodes 1, 3, 6, and 9 are leaf nodes because they don't have any child nodes.
+- Nodes 2, and 8 are inner nodes as they serve as parents to some of the nodes in the structure.
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 608: Tree Node.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README.md b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README.md
index adfa421aafb35..7970ae1d3e7ef 100644
--- a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README.md
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README.md
@@ -84,32 +84,203 @@ tags:
-### 方法一
+### 方法一:二分查找 + 双指针
+
+我们记数组 $\textit{nums}$ 的长度为 $n$,那么唯一性数组的长度为 $m = \frac{(1 + n) \times n}{2}$,而唯一性数组的中位数就是这 $m$ 个数中的第 $\frac{m + 1}{2}$ 小的数字。
+
+考虑唯一性数组中,有多少个数小于等于 $x$。随着 $x$ 的增大,只会有越来越多的数小于等于 $x$。这存在着单调性,因此,我们可以二分枚举 $x$,找到第一个 $x$,满足唯一性数组中小于等于 $x$ 的数的个数大于等于 $\frac{m + 1}{2}$,这个 $x$ 就是唯一性数组的中位数。
+
+我们定义二分查找的左边界 $l = 0$,右边界 $r = n$,然后进行二分查找,对于每个 $\textit{mid}$,我们检查唯一性数组中小于等于 $\textit{mid}$ 的数的个数是否大于等于 $\frac{m + 1}{2}$。我们通过函数 $\text{check}(mx)$ 来实现这一点。
+
+函数 $\text{check}(mx)$ 的实现思路如下:
+
+由于子数组越长,不同元素的个数越多,因此,我们可以利用双指针维护一个滑动窗口,使得窗口中的子数组的不同元素的个数不超过 $mx$。具体地,我们维护一个哈希表 $\textit{cnt}$,$\textit{cnt}[x]$ 表示窗口中元素 $x$ 的个数。我们使用两个指针 $l$ 和 $r$,其中 $l$ 表示窗口的左边界,而 $r$ 表示窗口的右边界。初始时 $l = r = 0$。
+
+我们枚举 $r$,对于每个 $r$,我们将 $\textit{nums}[r]$ 加入窗口中,并更新 $\textit{cnt}[\textit{nums}[r]]$。如果窗口中的不同元素的个数超过了 $mx$,我们需要将 $l$ 右移,直到窗口中的不同元素的个数不超过 $mx$。此时,右端点为 $r$,而左端点为 $[l,..r]$ 的子数组都是满足条件的,一共有 $r - l + 1$ 个子数组。我们将这个数量累加到 $k$ 中,如果 $k$ 大于等于 $\frac{m + 1}{2}$,那么说明唯一性数组中小于等于 $\textit{mid}$ 的数的个数大于等于 $\frac{m + 1}{2}$,我们返回 $\text{true}$,否则返回 $\text{false}$。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 为数组 $\textit{nums}$ 的长度。
#### Python3
```python
-
+class Solution:
+ def medianOfUniquenessArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ def check(mx: int) -> bool:
+ cnt = defaultdict(int)
+ k = l = 0
+ for r, x in enumerate(nums):
+ cnt[x] += 1
+ while len(cnt) > mx:
+ y = nums[l]
+ cnt[y] -= 1
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
+ cnt.pop(y)
+ l += 1
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m + 1) // 2:
+ return True
+ return False
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ m = (1 + n) * n // 2
+ return bisect_left(range(n), True, key=check)
```
#### Java
```java
-
+class Solution {
+ private long m;
+ private int[] nums;
+
+ public int medianOfUniquenessArray(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ m = (1L + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+
+ private boolean check(int mx) {
+ Map
cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ long k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < nums.length; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) == 0) {
+ cnt.remove(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
```
#### C++
```cpp
-
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int medianOfUniquenessArray(vector& nums) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ using ll = long long;
+ ll m = (1LL + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ auto check = [&](int mx) -> bool {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ ll k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ ++cnt[x];
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+};
```
#### Go
```go
+func medianOfUniquenessArray(nums []int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ m := (1 + n) * n / 2
+ return sort.Search(n, func(mx int) bool {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ l, k := 0, 0
+ for r, x := range nums {
+ cnt[x]++
+ for len(cnt) > mx {
+ y := nums[l]
+ cnt[y]--
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
+ delete(cnt, y)
+ }
+ l++
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m+1)/2 {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ })
+}
+```
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function medianOfUniquenessArray(nums: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const m = Math.floor(((1 + n) * n) / 2);
+ let [l, r] = [0, n];
+ const check = (mx: number): boolean => {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ let [l, k] = [0, 0];
+ for (let r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ const x = nums[r];
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ while (cnt.size > mx) {
+ const y = nums[l++];
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
+ if (cnt.get(y) === 0) {
+ cnt.delete(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= Math.floor((m + 1) / 2)) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+}
```
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README_EN.md b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README_EN.md
index fecdc83f62b45..21ef386e983eb 100644
--- a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/README_EN.md
@@ -80,32 +80,203 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Binary Search + Two Pointers
+
+Let the length of the array $\textit{nums}$ be $n$. The length of the uniqueness array is $m = \frac{(1 + n) \times n}{2}$, and the median of the uniqueness array is the $\frac{m + 1}{2}$-th smallest number among these $m$ numbers.
+
+Consider how many numbers in the uniqueness array are less than or equal to $x$. As $x$ increases, there will be more and more numbers less than or equal to $x$. This property is monotonic, so we can use binary search to enumerate $x$ and find the first $x$ such that the number of elements in the uniqueness array less than or equal to $x$ is greater than or equal to $\frac{m + 1}{2}$. This $x$ is the median of the uniqueness array.
+
+We define the left boundary of the binary search as $l = 0$ and the right boundary as $r = n$. Then we perform binary search. For each $\textit{mid}$, we check whether the number of elements in the uniqueness array less than or equal to $\textit{mid}$ is greater than or equal to $\frac{m + 1}{2}$. We achieve this through the function $\text{check}(mx)$.
+
+The implementation idea of the function $\text{check}(mx)$ is as follows:
+
+Since the longer the subarray, the more different elements it contains, we can use two pointers to maintain a sliding window such that the number of different elements in the window does not exceed $mx$. Specifically, we maintain a hash table $\textit{cnt}$, where $\textit{cnt}[x]$ represents the number of occurrences of element $x$ in the window. We use two pointers $l$ and $r$, where $l$ represents the left boundary of the window and $r$ represents the right boundary. Initially, $l = r = 0$.
+
+We enumerate $r$. For each $r$, we add $\textit{nums}[r]$ to the window and update $\textit{cnt}[\textit{nums}[r]]$. If the number of different elements in the window exceeds $mx$, we need to move $l$ to the right until the number of different elements in the window does not exceed $mx$. At this point, the subarrays with the right endpoint $r$ and left endpoints in the range $[l, .., r]$ all meet the condition, and there are $r - l + 1$ such subarrays. We accumulate this count into $k$. If $k$ is greater than or equal to $\frac{m + 1}{2}$, it means that the number of elements in the uniqueness array less than or equal to $\textit{mid}$ is greater than or equal to $\frac{m + 1}{2}$, and we return $\text{true}$; otherwise, we return $\text{false}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{nums}$.
#### Python3
```python
-
+class Solution:
+ def medianOfUniquenessArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ def check(mx: int) -> bool:
+ cnt = defaultdict(int)
+ k = l = 0
+ for r, x in enumerate(nums):
+ cnt[x] += 1
+ while len(cnt) > mx:
+ y = nums[l]
+ cnt[y] -= 1
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
+ cnt.pop(y)
+ l += 1
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m + 1) // 2:
+ return True
+ return False
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ m = (1 + n) * n // 2
+ return bisect_left(range(n), True, key=check)
```
#### Java
```java
-
+class Solution {
+ private long m;
+ private int[] nums;
+
+ public int medianOfUniquenessArray(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ m = (1L + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+
+ private boolean check(int mx) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ long k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < nums.length; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) == 0) {
+ cnt.remove(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
```
#### C++
```cpp
-
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int medianOfUniquenessArray(vector& nums) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ using ll = long long;
+ ll m = (1LL + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ auto check = [&](int mx) -> bool {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ ll k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ ++cnt[x];
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+};
```
#### Go
```go
+func medianOfUniquenessArray(nums []int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ m := (1 + n) * n / 2
+ return sort.Search(n, func(mx int) bool {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ l, k := 0, 0
+ for r, x := range nums {
+ cnt[x]++
+ for len(cnt) > mx {
+ y := nums[l]
+ cnt[y]--
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
+ delete(cnt, y)
+ }
+ l++
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m+1)/2 {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ })
+}
+```
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function medianOfUniquenessArray(nums: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const m = Math.floor(((1 + n) * n) / 2);
+ let [l, r] = [0, n];
+ const check = (mx: number): boolean => {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ let [l, k] = [0, 0];
+ for (let r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ const x = nums[r];
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ while (cnt.size > mx) {
+ const y = nums[l++];
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
+ if (cnt.get(y) === 0) {
+ cnt.delete(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= Math.floor((m + 1) / 2)) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+}
```
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.cpp b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..2bd4be3ebc1fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int medianOfUniquenessArray(vector& nums) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ using ll = long long;
+ ll m = (1LL + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ auto check = [&](int mx) -> bool {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ ll k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ ++cnt[x];
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.go b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..9df651e368a4d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+func medianOfUniquenessArray(nums []int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ m := (1 + n) * n / 2
+ return sort.Search(n, func(mx int) bool {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ l, k := 0, 0
+ for r, x := range nums {
+ cnt[x]++
+ for len(cnt) > mx {
+ y := nums[l]
+ cnt[y]--
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
+ delete(cnt, y)
+ }
+ l++
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m+1)/2 {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ })
+}
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.java b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..fc22bff7e0d36
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+class Solution {
+ private long m;
+ private int[] nums;
+
+ public int medianOfUniquenessArray(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ m = (1L + n) * n / 2;
+ int l = 0, r = n;
+ while (l < r) {
+ int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+
+ private boolean check(int mx) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ long k = 0;
+ for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < nums.length; ++r) {
+ int x = nums[r];
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ while (cnt.size() > mx) {
+ int y = nums[l++];
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) == 0) {
+ cnt.remove(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= (m + 1) / 2) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.py b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..98171a899ba3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+class Solution:
+ def medianOfUniquenessArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ def check(mx: int) -> bool:
+ cnt = defaultdict(int)
+ k = l = 0
+ for r, x in enumerate(nums):
+ cnt[x] += 1
+ while len(cnt) > mx:
+ y = nums[l]
+ cnt[y] -= 1
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
+ cnt.pop(y)
+ l += 1
+ k += r - l + 1
+ if k >= (m + 1) // 2:
+ return True
+ return False
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ m = (1 + n) * n // 2
+ return bisect_left(range(n), True, key=check)
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.ts b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..46819bf0e3b68
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3134.Find the Median of the Uniqueness Array/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+function medianOfUniquenessArray(nums: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const m = Math.floor(((1 + n) * n) / 2);
+ let [l, r] = [0, n];
+ const check = (mx: number): boolean => {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ let [l, k] = [0, 0];
+ for (let r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
+ const x = nums[r];
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ while (cnt.size > mx) {
+ const y = nums[l++];
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
+ if (cnt.get(y) === 0) {
+ cnt.delete(y);
+ }
+ }
+ k += r - l + 1;
+ if (k >= Math.floor((m + 1) / 2)) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ while (l < r) {
+ const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
+ if (check(mid)) {
+ r = mid;
+ } else {
+ l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+}
diff --git a/solution/3100-3199/3178.Find the Child Who Has the Ball After K Seconds/README_EN.md b/solution/3100-3199/3178.Find the Child Who Has the Ball After K Seconds/README_EN.md
index 0d987d1edfb04..d15216be24cfd 100644
--- a/solution/3100-3199/3178.Find the Child Who Has the Ball After K Seconds/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/3100-3199/3178.Find the Child Who Has the Ball After K Seconds/README_EN.md
@@ -155,6 +155,9 @@ tags:
1 <= k <= 50
+
+Note: This question is the same as 2582: Pass the Pillow.
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/3200-3299/3213.Construct String with Minimum Cost/README.md b/solution/3200-3299/3213.Construct String with Minimum Cost/README.md
index c32e43fe2fe81..131e340f019a6 100644
--- a/solution/3200-3299/3213.Construct String with Minimum Cost/README.md
+++ b/solution/3200-3299/3213.Construct String with Minimum Cost/README.md
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ tags:
设想一个空字符串 s。
-你可以执行以下操作任意次数(包括零次):
+你可以执行以下操作任意次数(包括 零 次):
- 选择一个在范围
[0, words.length - 1] 的索引 i。
diff --git a/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct String with Minimum Cost (Easy)/README.md b/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct String with Minimum Cost (Easy)/README.md
index fc855a4c5b4f8..b0128e3700177 100644
--- a/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct String with Minimum Cost (Easy)/README.md
+++ b/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct String with Minimum Cost (Easy)/README.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/3200-3299/3253.Co
-# [3253. 以最低成本构建字符串(简单) 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-string-with-minimum-cost-easy)
+# [3253. 最小代价构造字符串(简单) 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-string-with-minimum-cost-easy)
[English Version](/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct%20String%20with%20Minimum%20Cost%20%28Easy%29/README_EN.md)
@@ -14,51 +14,45 @@ edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/3200-3299/3253.Co
-给定字符串 target,一个字符串数组 words 以及一个整数数组 costs,两个数组长度相同。
+给你一个字符串 target、一个字符串数组 words 以及一个整数数组 costs,这两个数组长度相同。
-想象一个空字符串 s。
+设想一个空字符串 s。
-您可以执行以下操作任意次数(包括 零):
+你可以执行以下操作任意次数(包括 零 次):
- - 从范围
[0, words.length - 1] 中选择一个下标 i。
- - 将
words[i] 添加到 s。
- - 操作的开销为
costs[i]。
+ - 选择一个在范围
[0, words.length - 1] 的索引 i。
+ - 将
words[i] 追加到 s。
+ - 该操作的成本是
costs[i]。
-返回使 s 与 target 相等的 最小 开销。如果不可能做到,返回 -1。
+返回使 s 等于 target 的 最小 成本。如果不可能,返回 -1。
-示例 1:
+示例 1:
-
-
输入:target = "abcdef", words = ["abdef","abc","d","def","ef"], costs = [100,1,1,10,5]
+
输入: target = "abcdef", words = ["abdef","abc","d","def","ef"], costs = [100,1,1,10,5]
-
输出:7
+
输出: 7
解释:
-
通过执行以下操作可以实现最低开销:
-
- - 选择下标 1 然后以 1 的开销将
"abc" 添加到 s,得到 s = "abc"。
- - 选择下标 2 然后以 1 的开销将
"d" 添加到 s,得到 s = "abcd"。
- - 选择下标 4 然后以 5 的开销将
"ef" 添加到 s,得到 s = "abcdef"。
+ - 选择索引 1 并以成本 1 将
"abc" 追加到 s,得到 s = "abc"。
+ - 选择索引 2 并以成本 1 将
"d" 追加到 s,得到 s = "abcd"。
+ - 选择索引 4 并以成本 5 将
"ef" 追加到 s,得到 s = "abcdef"。
-
示例 2:
+示例 2:
-
-
输入:target = "aaaa", words = ["z","zz","zzz"], costs = [1,10,100]
+
输入: target = "aaaa", words = ["z","zz","zzz"], costs = [1,10,100]
-
输出:-1
+
输出: -1
解释:
-
不可能使 s 与 target 相等,所以我们返回 -1。
-
无法使 s 等于 target,因此返回 -1。
@@ -68,7 +62,7 @@ edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/3200-3299/3253.Co
1 <= target.length <= 20001 <= words.length == costs.length <= 501 <= words[i].length <= target.lengthtarget 和 words[i] 只包含小写英语字母。target 和 words[i] 仅由小写英文字母组成。1 <= costs[i] <= 105
diff --git a/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I/README.md b/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I/README.md
index 4970e3713dd40..25da724d491c6 100644
--- a/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I/README.md
+++ b/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I/README.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/3200-3299/3263.Co
-# [3263. Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-doubly-linked-list-to-array-i)
+# [3263. 将双链表转换为数组 I 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-doubly-linked-list-to-array-i)
[English Version](/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert%20Doubly%20Linked%20List%20to%20Array%20I/README_EN.md)
@@ -14,40 +14,42 @@ edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/3200-3299/3263.Co
-You are given the head of a doubly linked list, which contains nodes that have a next pointer and a previous pointer.
+给定一个 双链表 的 head 节点,其中的节点具有指向下一个节点的指针和上一个节点的指针。
-Return an integer array which contains the elements of the linked list in order.
+返回一个 按顺序 包含链表中元素的整数数组。
-Example 1:
+
+示例 1:
-
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,3,2,1]
+
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,3,2,1]
-
Output: [1,2,3,4,3,2,1]
+
输出:[1,2,3,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
+示例 2:
-
Input: head = [2,2,2,2,2]
+
输入:head = [2,2,2,2,2]
-
Output: [2,2,2,2,2]
+
输出:[2,2,2,2,2]
Example 3:
+示例 3:
-
Input: head = [3,2,3,2,3,2]
+
输入:head = [3,2,3,2,3,2]
-
Output: [3,2,3,2,3,2]
+
输出:[3,2,3,2,3,2]
-Constraints:
+
+提示:
- - The number of nodes in the given list is in the range
[1, 50].
+ - 给定链表中节点的数量在
[1, 50] 范围。
1 <= Node.val <= 50
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README.md b/solution/DATABASE_README.md
index 24636f820ef0a..d2e967ef985fe 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README.md
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@
| 0585 | [2016年的投资](/solution/0500-0599/0585.Investments%20in%202016/README.md) | `数据库` | 中等 | |
| 0586 | [订单最多的客户](/solution/0500-0599/0586.Customer%20Placing%20the%20Largest%20Number%20of%20Orders/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
| 0595 | [大的国家](/solution/0500-0599/0595.Big%20Countries/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
-| 0596 | [超过5名学生的课](/solution/0500-0599/0596.Classes%20More%20Than%205%20Students/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
+| 0596 | [超过 5 名学生的课](/solution/0500-0599/0596.Classes%20More%20Than%205%20Students/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
| 0597 | [好友申请 I:总体通过率](/solution/0500-0599/0597.Friend%20Requests%20I%20Overall%20Acceptance%20Rate/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | 🔒 |
| 0601 | [体育馆的人流量](/solution/0600-0699/0601.Human%20Traffic%20of%20Stadium/README.md) | `数据库` | 困难 | |
| 0602 | [好友申请 II :谁有最多的好友](/solution/0600-0699/0602.Friend%20Requests%20II%20Who%20Has%20the%20Most%20Friends/README.md) | `数据库` | 中等 | |
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index 3739034b935a7..5f31be654d5d4 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -606,7 +606,7 @@
| 0593 | [有效的正方形](/solution/0500-0599/0593.Valid%20Square/README.md) | `几何`,`数学` | 中等 | |
| 0594 | [最长和谐子序列](/solution/0500-0599/0594.Longest%20Harmonious%20Subsequence/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`计数`,`排序`,`滑动窗口` | 简单 | |
| 0595 | [大的国家](/solution/0500-0599/0595.Big%20Countries/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
-| 0596 | [超过5名学生的课](/solution/0500-0599/0596.Classes%20More%20Than%205%20Students/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
+| 0596 | [超过 5 名学生的课](/solution/0500-0599/0596.Classes%20More%20Than%205%20Students/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | |
| 0597 | [好友申请 I:总体通过率](/solution/0500-0599/0597.Friend%20Requests%20I%20Overall%20Acceptance%20Rate/README.md) | `数据库` | 简单 | 🔒 |
| 0598 | [区间加法 II](/solution/0500-0599/0598.Range%20Addition%20II/README.md) | `数组`,`数学` | 简单 | |
| 0599 | [两个列表的最小索引总和](/solution/0500-0599/0599.Minimum%20Index%20Sum%20of%20Two%20Lists/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`字符串` | 简单 | |
@@ -2873,7 +2873,7 @@
| 2860 | [让所有学生保持开心的分组方法数](/solution/2800-2899/2860.Happy%20Students/README.md) | `数组`,`枚举`,`排序` | 中等 | 第 363 场周赛 |
| 2861 | [最大合金数](/solution/2800-2899/2861.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Alloys/README.md) | `数组`,`二分查找` | 中等 | 第 363 场周赛 |
| 2862 | [完全子集的最大元素和](/solution/2800-2899/2862.Maximum%20Element-Sum%20of%20a%20Complete%20Subset%20of%20Indices/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`数论` | 困难 | 第 363 场周赛 |
-| 2863 | [最长半递减数组](/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum%20Length%20of%20Semi-Decreasing%20Subarrays/README.md) | `栈`,`数组`,`排序`,`单调栈` | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2863 | [最长半递减子数组的长度](/solution/2800-2899/2863.Maximum%20Length%20of%20Semi-Decreasing%20Subarrays/README.md) | `栈`,`数组`,`排序`,`单调栈` | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 2864 | [最大二进制奇数](/solution/2800-2899/2864.Maximum%20Odd%20Binary%20Number/README.md) | `贪心`,`数学`,`字符串` | 简单 | 第 364 场周赛 |
| 2865 | [美丽塔 I](/solution/2800-2899/2865.Beautiful%20Towers%20I/README.md) | `栈`,`数组`,`单调栈` | 中等 | 第 364 场周赛 |
| 2866 | [美丽塔 II](/solution/2800-2899/2866.Beautiful%20Towers%20II/README.md) | `栈`,`数组`,`单调栈` | 中等 | 第 364 场周赛 |
@@ -3263,7 +3263,7 @@
| 3250 | [单调数组对的数目 I](/solution/3200-3299/3250.Find%20the%20Count%20of%20Monotonic%20Pairs%20I/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`动态规划`,`组合数学`,`前缀和` | 困难 | 第 410 场周赛 |
| 3251 | [单调数组对的数目 II](/solution/3200-3299/3251.Find%20the%20Count%20of%20Monotonic%20Pairs%20II/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`动态规划`,`组合数学`,`前缀和` | 困难 | 第 410 场周赛 |
| 3252 | [英超积分榜排名 II](/solution/3200-3299/3252.Premier%20League%20Table%20Ranking%20II/README.md) | `数据库` | 中等 | 🔒 |
-| 3253 | [以最低成本构建字符串(简单)](/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct%20String%20with%20Minimum%20Cost%20%28Easy%29/README.md) | | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 3253 | [最小代价构造字符串(简单)](/solution/3200-3299/3253.Construct%20String%20with%20Minimum%20Cost%20%28Easy%29/README.md) | | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 3254 | [长度为 K 的子数组的能量值 I](/solution/3200-3299/3254.Find%20the%20Power%20of%20K-Size%20Subarrays%20I/README.md) | `数组`,`滑动窗口` | 中等 | 第 137 场双周赛 |
| 3255 | [长度为 K 的子数组的能量值 II](/solution/3200-3299/3255.Find%20the%20Power%20of%20K-Size%20Subarrays%20II/README.md) | `数组`,`滑动窗口` | 中等 | 第 137 场双周赛 |
| 3256 | [放三个车的价值之和最大 I](/solution/3200-3299/3256.Maximum%20Value%20Sum%20by%20Placing%20Three%20Rooks%20I/README.md) | `数组`,`动态规划`,`枚举`,`矩阵` | 困难 | 第 137 场双周赛 |
@@ -3273,7 +3273,7 @@
| 3260 | [找出最大的 N 位 K 回文数](/solution/3200-3299/3260.Find%20the%20Largest%20Palindrome%20Divisible%20by%20K/README.md) | `贪心`,`数学`,`字符串`,`动态规划`,`数论` | 困难 | 第 411 场周赛 |
| 3261 | [统计满足 K 约束的子字符串数量 II](/solution/3200-3299/3261.Count%20Substrings%20That%20Satisfy%20K-Constraint%20II/README.md) | `数组`,`字符串`,`二分查找`,`前缀和`,`滑动窗口` | 困难 | 第 411 场周赛 |
| 3262 | [查找重叠的班次](/solution/3200-3299/3262.Find%20Overlapping%20Shifts/README.md) | | 中等 | 🔒 |
-| 3263 | [Convert Doubly Linked List to Array I](/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert%20Doubly%20Linked%20List%20to%20Array%20I/README.md) | | 简单 | 🔒 |
+| 3263 | [将双链表转换为数组 I](/solution/3200-3299/3263.Convert%20Doubly%20Linked%20List%20to%20Array%20I/README.md) | | 简单 | 🔒 |
## 版权
 -
-
 -
-
 -
-


 -
-
 -
-