= new Set(nums);
+ for (let i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; i++) {
+ pos.delete(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.add(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ const ans = [...pos];
+ ans.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..6e2f1b8e8cd6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+# [2766. Relocate Marbles](https://leetcode.com/problems/relocate-marbles)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums representing the initial positions of some marbles. You are also given two 0-indexed integer arrays moveFrom and moveTo of equal length.
+
+Throughout moveFrom.length steps, you will change the positions of the marbles. On the ith step, you will move all marbles at position moveFrom[i] to position moveTo[i].
+
+After completing all the steps, return the sorted list of occupied positions.
+
+Notes:
+
+
+ - We call a position occupied if there is at least one marble in that position.
+ - There may be multiple marbles in a single position.
+
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,6,7,8], moveFrom = [1,7,2], moveTo = [2,9,5]
+Output: [5,6,8,9]
+Explanation: Initially, the marbles are at positions 1,6,7,8.
+At the i = 0th step, we move the marbles at position 1 to position 2. Then, positions 2,6,7,8 are occupied.
+At the i = 1st step, we move the marbles at position 7 to position 9. Then, positions 2,6,8,9 are occupied.
+At the i = 2nd step, we move the marbles at position 2 to position 5. Then, positions 5,6,8,9 are occupied.
+At the end, the final positions containing at least one marbles are [5,6,8,9].
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,1,3,3], moveFrom = [1,3], moveTo = [2,2]
+Output: [2]
+Explanation: Initially, the marbles are at positions [1,1,3,3].
+At the i = 0th step, we move all the marbles at position 1 to position 2. Then, the marbles are at positions [2,2,3,3].
+At the i = 1st step, we move all the marbles at position 3 to position 2. Then, the marbles are at positions [2,2,2,2].
+Since 2 is the only occupied position, we return [2].
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= moveFrom.length <= 105moveFrom.length == moveTo.length1 <= nums[i], moveFrom[i], moveTo[i] <= 109- The test cases are generated such that there is at least a marble in
moveFrom[i] at the moment we want to apply the ith move.
+
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Hash Table**
+
+Let's use a hash table $pos$ to record all stone positions. Initially, $pos$ contains all elements of $nums$. Then we iterate through $moveFrom$ and $moveTo$. Each time, we remove $moveFrom[i]$ from $pos$ and add $moveTo[i]$ to $pos$. Finally, we sort the elements in $pos$ and return.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$ and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of array $nums$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def relocateMarbles(
+ self, nums: List[int], moveFrom: List[int], moveTo: List[int]
+ ) -> List[int]:
+ pos = set(nums)
+ for f, t in zip(moveFrom, moveTo):
+ pos.remove(f)
+ pos.add(t)
+ return sorted(pos)
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public List relocateMarbles(int[] nums, int[] moveFrom, int[] moveTo) {
+ Set pos = new HashSet<>();
+ for (int x : nums) {
+ pos.add(x);
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; ++i) {
+ pos.remove(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.add(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ List ans = new ArrayList<>(pos);
+ ans.sort((a, b) -> a - b);
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector relocateMarbles(vector& nums, vector& moveFrom, vector& moveTo) {
+ unordered_set pos(nums.begin(), nums.end());
+ for (int i = 0; i < moveFrom.size(); ++i) {
+ pos.erase(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.insert(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ vector ans(pos.begin(), pos.end());
+ sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func relocateMarbles(nums []int, moveFrom []int, moveTo []int) (ans []int) {
+ pos := map[int]bool{}
+ for _, x := range nums {
+ pos[x] = true
+ }
+ for i, f := range moveFrom {
+ t := moveTo[i]
+ pos[f] = false
+ pos[t] = true
+ }
+ for x, ok := range pos {
+ if ok {
+ ans = append(ans, x)
+ }
+ }
+ sort.Ints(ans)
+ return
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function relocateMarbles(
+ nums: number[],
+ moveFrom: number[],
+ moveTo: number[],
+): number[] {
+ const pos: Set = new Set(nums);
+ for (let i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; i++) {
+ pos.delete(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.add(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ const ans = [...pos];
+ ans.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..4a5c76c1462dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector relocateMarbles(vector& nums, vector& moveFrom, vector& moveTo) {
+ unordered_set pos(nums.begin(), nums.end());
+ for (int i = 0; i < moveFrom.size(); ++i) {
+ pos.erase(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.insert(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ vector ans(pos.begin(), pos.end());
+ sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..4b6dfb8c05f4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+func relocateMarbles(nums []int, moveFrom []int, moveTo []int) (ans []int) {
+ pos := map[int]bool{}
+ for _, x := range nums {
+ pos[x] = true
+ }
+ for i, f := range moveFrom {
+ t := moveTo[i]
+ pos[f] = false
+ pos[t] = true
+ }
+ for x, ok := range pos {
+ if ok {
+ ans = append(ans, x)
+ }
+ }
+ sort.Ints(ans)
+ return
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e6971726c6a76
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution {
+ public List relocateMarbles(int[] nums, int[] moveFrom, int[] moveTo) {
+ Set pos = new HashSet<>();
+ for (int x : nums) {
+ pos.add(x);
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; ++i) {
+ pos.remove(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.add(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ List ans = new ArrayList<>(pos);
+ ans.sort((a, b) -> a - b);
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..4fc9bdb369593
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+class Solution:
+ def relocateMarbles(
+ self, nums: List[int], moveFrom: List[int], moveTo: List[int]
+ ) -> List[int]:
+ pos = set(nums)
+ for f, t in zip(moveFrom, moveTo):
+ pos.remove(f)
+ pos.add(t)
+ return sorted(pos)
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..5166165cfcbe7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate Marbles/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+function relocateMarbles(
+ nums: number[],
+ moveFrom: number[],
+ moveTo: number[],
+): number[] {
+ const pos: Set = new Set(nums);
+ for (let i = 0; i < moveFrom.length; i++) {
+ pos.delete(moveFrom[i]);
+ pos.add(moveTo[i]);
+ }
+ const ans = [...pos];
+ ans.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ return ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..64aace8848ecf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,292 @@
+# [2767. 将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-string-into-minimum-beautiful-substrings)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个二进制字符串 s ,你需要将字符串分割成一个或者多个 子字符串 ,使每个子字符串都是 美丽 的。
+
+如果一个字符串满足以下条件,我们称它是 美丽 的:
+
+
+ - 它不包含前导 0 。
+ - 它是
5 的幂的 二进制 表示。
+
+
+请你返回分割后的子字符串的 最少 数目。如果无法将字符串 s 分割成美丽子字符串,请你返回 -1 。
+
+子字符串是一个字符串中一段连续的字符序列。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+输入:s = "1011"
+输出:2
+解释:我们可以将输入字符串分成 ["101", "1"] 。
+- 字符串 "101" 不包含前导 0 ,且它是整数 51 = 5 的二进制表示。
+- 字符串 "1" 不包含前导 0 ,且它是整数 50 = 1 的二进制表示。
+最少可以将 s 分成 2 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+输入:s = "111"
+输出:3
+解释:我们可以将输入字符串分成 ["1", "1", "1"] 。
+- 字符串 "1" 不包含前导 0 ,且它是整数 50 = 1 的二进制表示。
+最少可以将 s 分成 3 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+输入:s = "0"
+输出:-1
+解释:无法将给定字符串分成任何美丽子字符串。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 15s[i] 要么是 '0' 要么是 '1' 。
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:记忆化搜索**
+
+题目中需要判断一个字符串是否是 $5$ 的幂的二进制表示,因此,我们不妨先预处理出所有 $5$ 的幂的数字,记录在哈希表 $ss$ 中。
+
+接下来,我们设计一个函数 $dfs(i)$,表示从字符串 $s$ 的第 $i$ 个字符开始,到字符串末尾的最少分割次数。那么答案就是 $dfs(0)$。
+
+函数 $dfs(i)$ 的计算方法如下:
+
+- 如果 $i \geq n$,表示已经处理完了所有字符,那么答案就是 $0$;
+- 如果 $s[i] = 0$,表示当前字符串包含前导 $0$,不符合美丽字符串的定义,因此答案是无穷大;
+- 否则,我们从 $i$ 开始枚举子字符串的结束位置 $j$,用 $x$ 表示子字符串 $s[i..j]$ 的十进制值,如果 $x$ 在哈希表 $ss$ 中,那么我们就可以将 $s[i..j]$ 作为一个美丽子字符串,此时答案就是 $1 + dfs(j + 1)$。我们需要枚举所有可能的 $j$,并取所有答案中的最小值。
+
+为了避免重复计算,我们可以使用记忆化搜索的方法。
+
+在主函数中,我们首先预处理出所有 $5$ 的幂的数字,然后调用 $dfs(0)$,如果返回值为无穷大,那么说明无法将字符串 $s$ 分割成美丽子字符串,答案返回 $-1$,否则返回 $dfs(0)$ 的值。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是字符串 $s$ 的长度。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def minimumBeautifulSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i >= n:
+ return 0
+ if s[i] == "0":
+ return inf
+ x = 0
+ ans = inf
+ for j in range(i, n):
+ x = x << 1 | int(s[j])
+ if x in ss:
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(s)
+ x = 1
+ ss = {x}
+ for i in range(n):
+ x *= 5
+ ss.add(x)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans == inf else ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private String s;
+ private Set ss = new HashSet<>();
+ private int n;
+
+ public int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(String s) {
+ n = s.length();
+ this.s = s;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s.charAt(i) == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s.charAt(j) - '0');
+ if (ss.contains(x)) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(string s) {
+ unordered_set ss;
+ int n = s.size();
+ long long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.insert(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s[j] - '0');
+ if (ss.count(x)) {
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s string) int {
+ ss := map[int]bool{}
+ n := len(s)
+ x := 1
+ f := make([]int, n+1)
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
+ ss[x] = true
+ x *= 5
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i >= n {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if s[i] == '0' {
+ return n + 1
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1
+ x := 0
+ for j := i; j < n; j++ {
+ x = x<<1 | int(s[j]-'0')
+ if ss[x] {
+ f[i] = min(f[i], 1+dfs(j+1))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans > n {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s: string): number {
+ const ss: Set = new Set();
+ const n = s.length;
+ const f: number[] = new Array(n).fill(-1);
+ for (let i = 0, x = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] === '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1;
+ for (let j = i, x = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = (x << 1) | (s[j] === '1' ? 1 : 0);
+ if (ss.has(x)) {
+ f[i] = Math.min(f[i], 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..9f1b243c139ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,285 @@
+# [2767. Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-string-into-minimum-beautiful-substrings)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+Given a binary string s, partition the string into one or more substrings such that each substring is beautiful.
+
+A string is beautiful if:
+
+
+ - It doesn't contain leading zeros.
+ - It's the binary representation of a number that is a power of
5.
+
+
+Return the minimum number of substrings in such partition. If it is impossible to partition the string s into beautiful substrings, return -1.
+
+A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: s = "1011"
+Output: 2
+Explanation: We can paritition the given string into ["101", "1"].
+- The string "101" does not contain leading zeros and is the binary representation of integer 51 = 5.
+- The string "1" does not contain leading zeros and is the binary representation of integer 50 = 1.
+It can be shown that 2 is the minimum number of beautiful substrings that s can be partitioned into.
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: s = "111"
+Output: 3
+Explanation: We can paritition the given string into ["1", "1", "1"].
+- The string "1" does not contain leading zeros and is the binary representation of integer 50 = 1.
+It can be shown that 3 is the minimum number of beautiful substrings that s can be partitioned into.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: s = "0"
+Output: -1
+Explanation: We can not partition the given string into beautiful substrings.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 15s[i] is either '0' or '1'.
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Memoization Search**
+
+Since the problem requires us to judge whether a string is the binary representation of a power of $5$, we might as well first preprocess all the powers of $5$ and record them in a hash table $ss$.
+
+Next, we design a function $dfs(i)$, which indicates the minimum number of cuts from the $i$-th character of the string $s$ to the end of the string. Then the answer is $dfs(0)$.
+
+The calculation method of function $dfs(i)$ is as follows:
+
+- If $i \geq n$, it means that all the characters have been processed, and the answer is $0$;
+- If $s[i] = 0$, it means that the current string contains leading $0$, which does not conform to the definition of a beautiful string, so the answer is infinite;
+- Otherwise, we enumerate the end position $j$ of the substring from $i$, and use $x$ to represent the decimal value of the substring $s[i..j]$. If $x$ is in the hash table $ss$, then we can take $s[i..j]$ as a beautiful substring, and the answer is $1 + dfs(j + 1)$. We need to enumerate all possible $j$ and take the minimum value of all answers.
+
+In order to avoid repeated calculation, we can use the method of memory search.
+
+In the main function, we first preprocess all the powers of $5$, and then call $dfs(0)$. If the return value is infinite, it means that the string $s$ cannot be divided into beautiful substrings, and the answer returns $-1$, otherwise, return the value of $dfs(0)$.
+
+Time complexity $O(n^2)$, space complexity $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the length of string $s$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def minimumBeautifulSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i >= n:
+ return 0
+ if s[i] == "0":
+ return inf
+ x = 0
+ ans = inf
+ for j in range(i, n):
+ x = x << 1 | int(s[j])
+ if x in ss:
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(s)
+ x = 1
+ ss = {x}
+ for i in range(n):
+ x *= 5
+ ss.add(x)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans == inf else ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private String s;
+ private Set ss = new HashSet<>();
+ private int n;
+
+ public int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(String s) {
+ n = s.length();
+ this.s = s;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s.charAt(i) == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s.charAt(j) - '0');
+ if (ss.contains(x)) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(string s) {
+ unordered_set ss;
+ int n = s.size();
+ long long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.insert(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s[j] - '0');
+ if (ss.count(x)) {
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s string) int {
+ ss := map[int]bool{}
+ n := len(s)
+ x := 1
+ f := make([]int, n+1)
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
+ ss[x] = true
+ x *= 5
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i >= n {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if s[i] == '0' {
+ return n + 1
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1
+ x := 0
+ for j := i; j < n; j++ {
+ x = x<<1 | int(s[j]-'0')
+ if ss[x] {
+ f[i] = min(f[i], 1+dfs(j+1))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans > n {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s: string): number {
+ const ss: Set = new Set();
+ const n = s.length;
+ const f: number[] = new Array(n).fill(-1);
+ for (let i = 0, x = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] === '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1;
+ for (let j = i, x = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = (x << 1) | (s[j] === '1' ? 1 : 0);
+ if (ss.has(x)) {
+ f[i] = Math.min(f[i], 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..ba948729da767
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(string s) {
+ unordered_set ss;
+ int n = s.size();
+ long long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.insert(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s[j] - '0');
+ if (ss.count(x)) {
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..80fa08b131958
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+func minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s string) int {
+ ss := map[int]bool{}
+ n := len(s)
+ x := 1
+ f := make([]int, n+1)
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
+ ss[x] = true
+ x *= 5
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i >= n {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if s[i] == '0' {
+ return n + 1
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1
+ x := 0
+ for j := i; j < n; j++ {
+ x = x<<1 | int(s[j]-'0')
+ if ss[x] {
+ f[i] = min(f[i], 1+dfs(j+1))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans > n {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..b3d7df9056f68
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private String s;
+ private Set ss = new HashSet<>();
+ private int n;
+
+ public int minimumBeautifulSubstrings(String s) {
+ n = s.length();
+ this.s = s;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ long x = 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i >= n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s.charAt(i) == '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ long x = 0;
+ int ans = n + 1;
+ for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = x << 1 | (s.charAt(j) - '0');
+ if (ss.contains(x)) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..ae0cb9715fb88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+class Solution:
+ def minimumBeautifulSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i >= n:
+ return 0
+ if s[i] == "0":
+ return inf
+ x = 0
+ ans = inf
+ for j in range(i, n):
+ x = x << 1 | int(s[j])
+ if x in ss:
+ ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j + 1))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(s)
+ x = 1
+ ss = {x}
+ for i in range(n):
+ x *= 5
+ ss.add(x)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans == inf else ans
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..8b381256bf149
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+function minimumBeautifulSubstrings(s: string): number {
+ const ss: Set = new Set();
+ const n = s.length;
+ const f: number[] = new Array(n).fill(-1);
+ for (let i = 0, x = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
+ ss.add(x);
+ x *= 5;
+ }
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (s[i] === '0') {
+ return n + 1;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = n + 1;
+ for (let j = i, x = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ x = (x << 1) | (s[j] === '1' ? 1 : 0);
+ if (ss.has(x)) {
+ f[i] = Math.min(f[i], 1 + dfs(j + 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..00d94386a8028
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+# [2768. 黑格子的数目](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-black-blocks)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你两个整数 m 和 n ,表示一个下标从 0 开始的 m x n 的网格图。
+
+给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数矩阵 coordinates ,其中 coordinates[i] = [x, y] 表示坐标为 [x, y] 的格子是 黑色的 ,所有没出现在 coordinates 中的格子都是 白色的。
+
+一个块定义为网格图中 2 x 2 的一个子矩阵。更正式的,对于左上角格子为 [x, y] 的块,其中 0 <= x < m - 1 且 0 <= y < n - 1 ,包含坐标为 [x, y] ,[x + 1, y] ,[x, y + 1] 和 [x + 1, y + 1] 的格子。
+
+请你返回一个下标从 0 开始长度为 5 的整数数组 arr ,arr[i] 表示恰好包含 i 个 黑色 格子的块的数目。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+
+输入:m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0]]
+输出:[3,1,0,0,0]
+解释:网格图如下:
+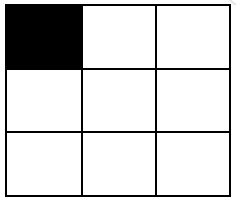 +只有 1 个块有一个黑色格子,这个块是左上角为 [0,0] 的块。
+其他 3 个左上角分别为 [0,1] ,[1,0] 和 [1,1] 的块都有 0 个黑格子。
+所以我们返回 [3,1,0,0,0] 。
+
+只有 1 个块有一个黑色格子,这个块是左上角为 [0,0] 的块。
+其他 3 个左上角分别为 [0,1] ,[1,0] 和 [1,1] 的块都有 0 个黑格子。
+所以我们返回 [3,1,0,0,0] 。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+输入:m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,2]]
+输出:[0,2,2,0,0]
+解释:网格图如下:
+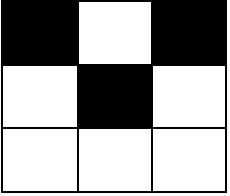 +有 2 个块有 2 个黑色格子(左上角格子分别为 [0,0] 和 [0,1])。
+左上角为 [1,0] 和 [1,1] 的两个块,都有 1 个黑格子。
+所以我们返回 [0,2,2,0,0] 。
+
+有 2 个块有 2 个黑色格子(左上角格子分别为 [0,0] 和 [0,1])。
+左上角为 [1,0] 和 [1,1] 的两个块,都有 1 个黑格子。
+所以我们返回 [0,2,2,0,0] 。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 2 <= m <= 1052 <= n <= 1050 <= coordinates.length <= 104coordinates[i].length == 20 <= coordinates[i][0] < m0 <= coordinates[i][1] < ncoordinates 中的坐标对两两互不相同。
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:哈希表计数**
+
+对于每个 $2 \times 2$ 的子矩阵,我们可以用其左上角的坐标 $(x, y)$ 来表示它。
+
+而对于每个黑格子 $(x, y)$,它对 $4$ 个子矩阵的贡献为 $1$,即矩阵 $(x - 1, y - 1)$, $(x - 1, y)$, $(x, y - 1)$, $(x, y)$。
+
+因此,我们遍历所有的黑格子,然后累计每个子矩阵中黑格子的个数,记录在哈希表 $cnt$ 中。
+
+最后,我们遍历 $cnt$ 中的所有值(大于 $0$),统计其出现的次数,记录在答案数组 $ans$ 中,而 $ans[0]$ 则表示没有黑格子的子矩阵的个数,值为 $(m - 1) \times (n - 1) - \sum_{i = 1}^4 ans[i]$。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(l)$,空间复杂度 $O(l)$,其中 $l$ 为 $coordinates$ 的长度。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def countBlackBlocks(
+ self, m: int, n: int, coordinates: List[List[int]]
+ ) -> List[int]:
+ cnt = Counter()
+ for x, y in coordinates:
+ for a, b in pairwise((0, 0, -1, -1, 0)):
+ i, j = x + a, y + b
+ if 0 <= i < m - 1 and 0 <= j < n - 1:
+ cnt[(i, j)] += 1
+ ans = [0] * 5
+ for x in cnt.values():
+ ans[x] += 1
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1) - len(cnt.values())
+ return ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public long[] countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, int[][] coordinates) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>(coordinates.length);
+ int[] dirs = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (var e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ cnt.merge(1L * i * n + j, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ long[] ans = new long[5];
+ ans[0] = (m - 1L) * (n - 1);
+ for (int x : cnt.values()) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, vector>& coordinates) {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ int dirs[5] = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (auto& e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ ++cnt[1LL * i * n + j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ vector ans(5);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1LL) * (n - 1);
+ for (auto& [_, x] : cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func countBlackBlocks(m int, n int, coordinates [][]int) []int64 {
+ cnt := map[int64]int{}
+ dirs := [5]int{0, 0, -1, -1, 0}
+ for _, e := range coordinates {
+ x, y := e[0], e[1]
+ for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
+ i, j := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
+ if i >= 0 && i < m-1 && j >= 0 && j < n-1 {
+ cnt[int64(i*n+j)]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ans := make([]int64, 5)
+ ans[0] = int64((m - 1) * (n - 1))
+ for _, x := range cnt {
+ ans[x]++
+ ans[0]--
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function countBlackBlocks(
+ m: number,
+ n: number,
+ coordinates: number[][],
+): number[] {
+ const cnt: Map = new Map();
+ const dirs: number[] = [0, 0, -1, -1, 0];
+ for (const [x, y] of coordinates) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ const [i, j] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ const key = i * n + j;
+ cnt.set(key, (cnt.get(key) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(5).fill(0);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1);
+ for (const [_, x] of cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..ba8d5c905476e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,204 @@
+# [2768. Number of Black Blocks](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-black-blocks)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given two integers m and n representing the dimensions of a 0-indexed m x n grid.
+
+You are also given a 0-indexed 2D integer matrix coordinates, where coordinates[i] = [x, y] indicates that the cell with coordinates [x, y] is colored black. All cells in the grid that do not appear in coordinates are white.
+
+A block is defined as a 2 x 2 submatrix of the grid. More formally, a block with cell [x, y] as its top-left corner where 0 <= x < m - 1 and 0 <= y < n - 1 contains the coordinates [x, y], [x + 1, y], [x, y + 1], and [x + 1, y + 1].
+
+Return a 0-indexed integer array arr of size 5 such that arr[i] is the number of blocks that contains exactly i black cells.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0]]
+Output: [3,1,0,0,0]
+Explanation: The grid looks like this:
+ +There is only 1 block with one black cell, and it is the block starting with cell [0,0].
+The other 3 blocks start with cells [0,1], [1,0] and [1,1]. They all have zero black cells.
+Thus, we return [3,1,0,0,0].
+
+There is only 1 block with one black cell, and it is the block starting with cell [0,0].
+The other 3 blocks start with cells [0,1], [1,0] and [1,1]. They all have zero black cells.
+Thus, we return [3,1,0,0,0].
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: m = 3, n = 3, coordinates = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,2]]
+Output: [0,2,2,0,0]
+Explanation: The grid looks like this:
+ +There are 2 blocks with two black cells (the ones starting with cell coordinates [0,0] and [0,1]).
+The other 2 blocks have starting cell coordinates of [1,0] and [1,1]. They both have 1 black cell.
+Therefore, we return [0,2,2,0,0].
+
+There are 2 blocks with two black cells (the ones starting with cell coordinates [0,0] and [0,1]).
+The other 2 blocks have starting cell coordinates of [1,0] and [1,1]. They both have 1 black cell.
+Therefore, we return [0,2,2,0,0].
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 2 <= m <= 1052 <= n <= 1050 <= coordinates.length <= 104coordinates[i].length == 20 <= coordinates[i][0] < m0 <= coordinates[i][1] < n- It is guaranteed that
coordinates contains pairwise distinct coordinates.
+
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Hash Table**
+
+For each $2 \times 2$ submatrix, we can use its upper-left corner coordinate $(x, y)$ to represent it.
+
+For each black cell $(x, y)$, its contribution to the 4 submatrices is $1$, namely the matrices $(x - 1, y - 1)$, $(x - 1, y)$, $(x, y - 1)$, $(x, y)$.
+
+Therefore, we traverse all the black cells, and then accumulate the number of black cells in each submatrix, recorded in the hash table $cnt$.
+
+Finally, we traverse all the values in $cnt$ (greater than $0$), count the number of times they appear, and record them in the answer array $ans$, while $ans[0]$ represents the number of submatrices without black cells, the value is $(m - 1) \times (n - 1) - \sum_{i = 1}^4 ans[i]$.
+
+Time complexity $O(l)$, space complexity $O(l)$, where $l$ is the length of $coordinates$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def countBlackBlocks(
+ self, m: int, n: int, coordinates: List[List[int]]
+ ) -> List[int]:
+ cnt = Counter()
+ for x, y in coordinates:
+ for a, b in pairwise((0, 0, -1, -1, 0)):
+ i, j = x + a, y + b
+ if 0 <= i < m - 1 and 0 <= j < n - 1:
+ cnt[(i, j)] += 1
+ ans = [0] * 5
+ for x in cnt.values():
+ ans[x] += 1
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1) - len(cnt.values())
+ return ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public long[] countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, int[][] coordinates) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>(coordinates.length);
+ int[] dirs = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (var e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ cnt.merge(1L * i * n + j, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ long[] ans = new long[5];
+ ans[0] = (m - 1L) * (n - 1);
+ for (int x : cnt.values()) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, vector>& coordinates) {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ int dirs[5] = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (auto& e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ ++cnt[1LL * i * n + j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ vector ans(5);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1LL) * (n - 1);
+ for (auto& [_, x] : cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func countBlackBlocks(m int, n int, coordinates [][]int) []int64 {
+ cnt := map[int64]int{}
+ dirs := [5]int{0, 0, -1, -1, 0}
+ for _, e := range coordinates {
+ x, y := e[0], e[1]
+ for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
+ i, j := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
+ if i >= 0 && i < m-1 && j >= 0 && j < n-1 {
+ cnt[int64(i*n+j)]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ans := make([]int64, 5)
+ ans[0] = int64((m - 1) * (n - 1))
+ for _, x := range cnt {
+ ans[x]++
+ ans[0]--
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function countBlackBlocks(
+ m: number,
+ n: number,
+ coordinates: number[][],
+): number[] {
+ const cnt: Map = new Map();
+ const dirs: number[] = [0, 0, -1, -1, 0];
+ for (const [x, y] of coordinates) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ const [i, j] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ const key = i * n + j;
+ cnt.set(key, (cnt.get(key) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(5).fill(0);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1);
+ for (const [_, x] of cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..cb086480cb754
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, vector>& coordinates) {
+ unordered_map cnt;
+ int dirs[5] = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (auto& e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ ++cnt[1LL * i * n + j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ vector ans(5);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1LL) * (n - 1);
+ for (auto& [_, x] : cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..fc5b23b025e92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+func countBlackBlocks(m int, n int, coordinates [][]int) []int64 {
+ cnt := map[int64]int{}
+ dirs := [5]int{0, 0, -1, -1, 0}
+ for _, e := range coordinates {
+ x, y := e[0], e[1]
+ for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
+ i, j := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
+ if i >= 0 && i < m-1 && j >= 0 && j < n-1 {
+ cnt[int64(i*n+j)]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ans := make([]int64, 5)
+ ans[0] = int64((m - 1) * (n - 1))
+ for _, x := range cnt {
+ ans[x]++
+ ans[0]--
+ }
+ return ans
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..f6b2dd91d20ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+class Solution {
+ public long[] countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, int[][] coordinates) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>(coordinates.length);
+ int[] dirs = {0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
+ for (var e : coordinates) {
+ int x = e[0], y = e[1];
+ for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ int i = x + dirs[k], j = y + dirs[k + 1];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ cnt.merge(1L * i * n + j, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ long[] ans = new long[5];
+ ans[0] = (m - 1L) * (n - 1);
+ for (int x : cnt.values()) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..683f49ea30e02
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution:
+ def countBlackBlocks(
+ self, m: int, n: int, coordinates: List[List[int]]
+ ) -> List[int]:
+ cnt = Counter()
+ for x, y in coordinates:
+ for a, b in pairwise((0, 0, -1, -1, 0)):
+ i, j = x + a, y + b
+ if 0 <= i < m - 1 and 0 <= j < n - 1:
+ cnt[(i, j)] += 1
+ ans = [0] * 5
+ for x in cnt.values():
+ ans[x] += 1
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1) - len(cnt.values())
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..650e14bed1e85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+function countBlackBlocks(
+ m: number,
+ n: number,
+ coordinates: number[][],
+): number[] {
+ const cnt: Map = new Map();
+ const dirs: number[] = [0, 0, -1, -1, 0];
+ for (const [x, y] of coordinates) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
+ const [i, j] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
+ if (i >= 0 && i < m - 1 && j >= 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ const key = i * n + j;
+ cnt.set(key, (cnt.get(key) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(5).fill(0);
+ ans[0] = (m - 1) * (n - 1);
+ for (const [_, x] of cnt) {
+ ++ans[x];
+ --ans[0];
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-44656-am.png b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-44656-am.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..d1670e76c4172
Binary files /dev/null and b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-44656-am.png differ
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-45018-am.png b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-45018-am.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..dd26ba65984f1
Binary files /dev/null and b/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number of Black Blocks/images/screen-shot-2023-06-18-at-45018-am.png differ
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..9e20a29bd59a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+# [2769. 找出最大的可达成数字](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-maximum-achievable-number)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你两个整数 num 和 t 。
+
+如果整数 x 可以在执行下述操作不超过 t 次的情况下变为与 num 相等,则称其为 可达成数字 :
+
+
+ - 每次操作将
x 的值增加或减少 1 ,同时可以选择将 num 的值增加或减少 1 。
+
+
+返回所有可达成数字中的最大值。可以证明至少存在一个可达成数字。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+输入:num = 4, t = 1
+输出:6
+解释:最大可达成数字是 x = 6 ,执行下述操作可以使其等于 num :
+- x 减少 1 ,同时 num 增加 1 。此时,x = 5 且 num = 5 。
+可以证明不存在大于 6 的可达成数字。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+输入:num = 3, t = 2
+输出:7
+解释:最大的可达成数字是 x = 7 ,执行下述操作可以使其等于 num :
+- x 减少 1 ,同时 num 增加 1 。此时,x = 6 且 num = 4 。
+- x 减少 1 ,同时 num 增加 1 。此时,x = 5 且 num = 5 。
+可以证明不存在大于 7 的可达成数字。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:数学**
+
+我们注意到,每次操作可以将 $x$ 减少 $1$,同时将 $num$ 增加 $1$,这样 $x$ 和 $num$ 的差值就会减少 $2$,而最多可以操作 $t$ 次,所以最大可达成数字为 $num + t \times 2$。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(1)$,空间复杂度 $O(1)$。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def theMaximumAchievableX(self, num: int, t: int) -> int:
+ return num + t * 2
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func theMaximumAchievableX(num int, t int) int {
+ return num + t*2
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function theMaximumAchievableX(num: number, t: number): number {
+ return num + t * 2;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..86af5160f2036
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+# [2769. Find the Maximum Achievable Number](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-maximum-achievable-number)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given two integers, num and t.
+
+An integer x is called achievable if it can become equal to num after applying the following operation no more than t times:
+
+
+ - Increase or decrease
x by 1, and simultaneously increase or decrease num by 1.
+
+
+Return the maximum possible achievable number. It can be proven that there exists at least one achievable number.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: num = 4, t = 1
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The maximum achievable number is x = 6; it can become equal to num after performing this operation:
+1- Decrease x by 1, and increase num by 1. Now, x = 5 and num = 5.
+It can be proven that there is no achievable number larger than 6.
+
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: num = 3, t = 2
+Output: 7
+Explanation: The maximum achievable number is x = 7; after performing these operations, x will equal num:
+1- Decrease x by 1, and increase num by 1. Now, x = 6 and num = 4.
+2- Decrease x by 1, and increase num by 1. Now, x = 5 and num = 5.
+It can be proven that there is no achievable number larger than 7.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Mathematics**
+
+Notice that every time we can decrease $x$ by $1$ and increase $num$ by $1$, the difference between $x$ and $num$ will decrease by $2$, and we can do this operation at most $t$ times, so the maximum reachable number is $num + t \times 2$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(1)$, and the space complexity is $O(1)$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def theMaximumAchievableX(self, num: int, t: int) -> int:
+ return num + t * 2
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func theMaximumAchievableX(num int, t int) int {
+ return num + t*2
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function theMaximumAchievableX(num: number, t: number): number {
+ return num + t * 2;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c91e4160ffe69
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..0924a9cb73e48
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+func theMaximumAchievableX(num int, t int) int {
+ return num + t*2
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..80dc6b9700303
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+class Solution {
+ public int theMaximumAchievableX(int num, int t) {
+ return num + t * 2;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..f39d38f49db32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+class Solution:
+ def theMaximumAchievableX(self, num: int, t: int) -> int:
+ return num + t * 2
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..8d4f251ecc950
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+function theMaximumAchievableX(num: number, t: number): number {
+ return num + t * 2;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..3c98ee3d2d10e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
+# [2770. 达到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-number-of-jumps-to-reach-the-last-index)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个下标从 0 开始、由 n 个整数组成的数组 nums 和一个整数 target 。
+
+你的初始位置在下标 0 。在一步操作中,你可以从下标 i 跳跃到任意满足下述条件的下标 j :
+
+
+ 0 <= i < j < n-target <= nums[j] - nums[i] <= target
+
+返回到达下标 n - 1 处所需的 最大跳跃次数 。
+
+如果无法到达下标 n - 1 ,返回 -1 。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+输入:nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 2
+输出:3
+解释:要想以最大跳跃次数从下标 0 到下标 n - 1 ,可以按下述跳跃序列执行操作:
+- 从下标 0 跳跃到下标 1 。
+- 从下标 1 跳跃到下标 3 。
+- 从下标 3 跳跃到下标 5 。
+可以证明,从 0 到 n - 1 的所有方案中,不存在比 3 步更长的跳跃序列。因此,答案是 3 。
+
+示例 2:
+
+输入:nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 3
+输出:5
+解释:要想以最大跳跃次数从下标 0 到下标 n - 1 ,可以按下述跳跃序列执行操作:
+- 从下标 0 跳跃到下标 1 。
+- 从下标 1 跳跃到下标 2 。
+- 从下标 2 跳跃到下标 3 。
+- 从下标 3 跳跃到下标 4 。
+- 从下标 4 跳跃到下标 5 。
+可以证明,从 0 到 n - 1 的所有方案中,不存在比 5 步更长的跳跃序列。因此,答案是 5 。
+
+示例 3:
+
+输入:nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 0
+输出:-1
+解释:可以证明不存在从 0 到 n - 1 的跳跃序列。因此,答案是 -1 。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 2 <= nums.length == n <= 1000-109 <= nums[i] <= 1090 <= target <= 2 * 109
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:记忆化搜索**
+
+对于每个位置 $i$,我们考虑向后搜索能跳到的位置 $j$,如果满足 $|nums[i] - nums[j]| \leq target$,那么我们就可以从 $i$ 跳到 $j$,并且从 $j$ 开始继续向后搜索。
+
+因此,我们设计一个函数 $dfs(i)$,表示从位置 $i$ 开始跳跃到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数。那么答案就是 $dfs(0)$。
+
+函数 $dfs(i)$ 的计算过程如下:
+
+- 如果 $i = n - 1$,那么我们已经到达了末尾下标,不需要跳跃,因此返回 $0$;
+- 否则,我们需要枚举从位置 $i$ 开始能跳到的位置 $j$,并计算从 $j$ 开始跳跃到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数,那么 $dfs(i)$ 就等于所有 $dfs(j)$ 中的最大值加 $1$。如果不存在从 $i$ 开始能跳到的位置 $j$,那么 $dfs(i) = -\infty$。
+
+为了避免重复计算,我们可以使用记忆化搜索。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组的长度。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maximumJumps(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i == n - 1:
+ return 0
+ ans = -inf
+ for j in range(i + 1, n):
+ if abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target:
+ ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(j))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans < 0 else ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private int[] nums;
+ private int n;
+ private int target;
+
+ public int maximumJumps(int[] nums, int target) {
+ n = nums.length;
+ this.target = target;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ int ans = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maximumJumps(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func maximumJumps(nums []int, target int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ f := make([]int, n)
+ for i := range f {
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i == n-1 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30)
+ for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
+ if abs(nums[i]-nums[j]) <= target {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1+dfs(j))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans < 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func abs(x int) int {
+ if x < 0 {
+ return -x
+ }
+ return x
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function maximumJumps(nums: number[], target: number): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const f: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1);
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (let j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = Math.max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..845023fb16733
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
+# [2770. Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-jumps-to-reach-the-last-index)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers and an integer target.
+
+You are initially positioned at index 0. In one step, you can jump from index i to any index j such that:
+
+
+ 0 <= i < j < n-target <= nums[j] - nums[i] <= target
+
+Return the maximum number of jumps you can make to reach index n - 1.
+
+If there is no way to reach index n - 1, return -1.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 2
+Output: 3
+Explanation: To go from index 0 to index n - 1 with the maximum number of jumps, you can perform the following jumping sequence:
+- Jump from index 0 to index 1.
+- Jump from index 1 to index 3.
+- Jump from index 3 to index 5.
+It can be proven that there is no other jumping sequence that goes from 0 to n - 1 with more than 3 jumps. Hence, the answer is 3.
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 3
+Output: 5
+Explanation: To go from index 0 to index n - 1 with the maximum number of jumps, you can perform the following jumping sequence:
+- Jump from index 0 to index 1.
+- Jump from index 1 to index 2.
+- Jump from index 2 to index 3.
+- Jump from index 3 to index 4.
+- Jump from index 4 to index 5.
+It can be proven that there is no other jumping sequence that goes from 0 to n - 1 with more than 5 jumps. Hence, the answer is 5.
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,3,6,4,1,2], target = 0
+Output: -1
+Explanation: It can be proven that there is no jumping sequence that goes from 0 to n - 1. Hence, the answer is -1.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 2 <= nums.length == n <= 1000-109 <= nums[i] <= 1090 <= target <= 2 * 109
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Memoization**
+
+For each position $i$, we consider to jump to position $j$ which satisfies $|nums[i] - nums[j]| \leq target$. Then we can jump from $i$ to $j$, and continue to jump from $j$ to the end.
+
+Therefore, we design a function $dfs(i)$, which represents the maximum number of jumps needed to jump to the end index starting from position $i$. Then the answer is $dfs(0)$.
+
+The calculation process of function $dfs(i)$ is as follows:
+
+- If $i = n - 1$, then we have reached the end index and no jumps are required, so return $0$;
+- Otherwise, we need to enumerate the positions $j$ that can be jumped from position $i$, and calculate the maximum number of jumps needed to jump to the end index starting from $j$, then $dfs(i)$ is equal to the maximum value of all $dfs(j)$ plus $1$. If there is no position $j$ that can be jumped from $i$, then $dfs(i) = -\infty$.
+
+To avoid duplicate calculations, we can use memoization.
+
+Time complexity $O(n^2)$, space complexity $O(n)$. where $n$ is the length of array.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maximumJumps(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i == n - 1:
+ return 0
+ ans = -inf
+ for j in range(i + 1, n):
+ if abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target:
+ ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(j))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans < 0 else ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private int[] nums;
+ private int n;
+ private int target;
+
+ public int maximumJumps(int[] nums, int target) {
+ n = nums.length;
+ this.target = target;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ int ans = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maximumJumps(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func maximumJumps(nums []int, target int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ f := make([]int, n)
+ for i := range f {
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i == n-1 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30)
+ for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
+ if abs(nums[i]-nums[j]) <= target {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1+dfs(j))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans < 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func abs(x int) int {
+ if x < 0 {
+ return -x
+ }
+ return x
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function maximumJumps(nums: number[], target: number): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const f: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1);
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (let j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = Math.max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c51b8bab266e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maximumJumps(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ int f[n];
+ memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
+ function dfs = [&](int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c9bf869ee4532
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+func maximumJumps(nums []int, target int) int {
+ n := len(nums)
+ f := make([]int, n)
+ for i := range f {
+ f[i] = -1
+ }
+ var dfs func(int) int
+ dfs = func(i int) int {
+ if i == n-1 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if f[i] != -1 {
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30)
+ for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
+ if abs(nums[i]-nums[j]) <= target {
+ f[i] = max(f[i], 1+dfs(j))
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i]
+ }
+ ans := dfs(0)
+ if ans < 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func abs(x int) int {
+ if x < 0 {
+ return -x
+ }
+ return x
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..7f0b7e6bea499
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+class Solution {
+ private Integer[] f;
+ private int[] nums;
+ private int n;
+ private int target;
+
+ public int maximumJumps(int[] nums, int target) {
+ n = nums.length;
+ this.target = target;
+ this.nums = nums;
+ f = new Integer[n];
+ int ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i) {
+ if (i == n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] != null) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ int ans = -(1 << 30);
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i] = ans;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..033458007450b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution:
+ def maximumJumps(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
+ @cache
+ def dfs(i: int) -> int:
+ if i == n - 1:
+ return 0
+ ans = -inf
+ for j in range(i + 1, n):
+ if abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target:
+ ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(j))
+ return ans
+
+ n = len(nums)
+ ans = dfs(0)
+ return -1 if ans < 0 else ans
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..0d80c65977d31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+function maximumJumps(nums: number[], target: number): number {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const f: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1);
+ const dfs = (i: number): number => {
+ if (i === n - 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (f[i] !== -1) {
+ return f[i];
+ }
+ f[i] = -(1 << 30);
+ for (let j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
+ if (Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= target) {
+ f[i] = Math.max(f[i], 1 + dfs(j));
+ }
+ }
+ return f[i];
+ };
+ const ans = dfs(0);
+ return ans < 0 ? -1 : ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..66e2b1fed08d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
+# [2771. 构造最长非递减子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-non-decreasing-subarray-from-two-arrays)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你两个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,长度均为 n 。
+
+让我们定义另一个下标从 0 开始、长度为 n 的整数数组,nums3 。对于范围 [0, n - 1] 的每个下标 i ,你可以将 nums1[i] 或 nums2[i] 的值赋给 nums3[i] 。
+
+你的任务是使用最优策略为 nums3 赋值,以最大化 nums3 中 最长非递减子数组 的长度。
+
+以整数形式表示并返回 nums3 中 最长非递减 子数组的长度。
+
+注意:子数组 是数组中的一个连续非空元素序列。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+输入:nums1 = [2,3,1], nums2 = [1,2,1]
+输出:2
+解释:构造 nums3 的方法之一是:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums2[1], nums2[2]] => [2,2,1]
+从下标 0 开始到下标 1 结束,形成了一个长度为 2 的非递减子数组 [2,2] 。
+可以证明 2 是可达到的最大长度。
+
+示例 2:
+
+输入:nums1 = [1,3,2,1], nums2 = [2,2,3,4]
+输出:4
+解释:构造 nums3 的方法之一是:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums2[1], nums2[2], nums2[3]] => [1,2,3,4]
+整个数组形成了一个长度为 4 的非递减子数组,并且是可达到的最大长度。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+输入:nums1 = [1,1], nums2 = [2,2]
+输出:2
+解释:构造 nums3 的方法之一是:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums1[1]] => [1,1]
+整个数组形成了一个长度为 2 的非递减子数组,并且是可达到的最大长度。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= nums1.length == nums2.length == n <= 1051 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 109
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:动态规划**
+
+我们定义两个变量 $f$ 和 $g$,分别表示当前位置的最长非递减子数组长度,其中 $f$ 表示以 $nums1$ 元素为结尾的最长非递减子数组长度,而 $g$ 表示以 $nums2$ 元素为结尾的最长非递减子数组长度。初始时 $f = g = 1$,初始答案 $ans = 1$。
+
+接下来,我们在 $i \in [1, n)$ 的范围内遍历数组元素,对于每个 $i$,我们定义两个变量 $ff$ 和 $gg$,分别表示以 $nums1[i]$ 和 $nums2[i]$ 元素为结尾的最长非递减子数组长度,初始化时 $ff = gg = 1$。
+
+我们可以通过 $f$ 和 $g$ 的值来计算出 $ff$ 和 $gg$ 的值:
+
+- 如果 $nums1[i] \ge nums1[i - 1]$,那么 $ff = max(ff, f + 1)$;
+- 如果 $nums1[i] \ge nums2[i - 1]$,那么 $ff = max(ff, g + 1)$;
+- 如果 $nums2[i] \ge nums1[i - 1]$,那么 $gg = max(gg, f + 1)$;
+- 如果 $nums2[i] \ge nums2[i - 1]$,那么 $gg = max(gg, g + 1)$。
+
+然后,我们更新 $f = ff$ 和 $g = gg$,并将 $ans$ 更新为 $max(ans, f, g)$。
+
+遍历结束后,我们返回 $ans$ 即可。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是数组的长度。空间复杂度 $O(1)$。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxNonDecreasingLength(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
+ n = len(nums1)
+ f = g = 1
+ ans = 1
+ for i in range(1, n):
+ ff = gg = 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1)
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1)
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, f, g)
+ return ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int maxNonDecreasingLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.length;
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, Math.max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maxNonDecreasingLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.size();
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) int {
+ n := len(nums1)
+ f, g, ans := 1, 1, 1
+ for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
+ ff, gg := 1, 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, g+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, g+1)
+ }
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g))
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums1.length;
+ let [f, g, ans] = [1, 1, 1];
+ for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ let [ff, gg] = [1, 1];
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, f, g);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..0d84a441a1e30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
+# [2771. Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-non-decreasing-subarray-from-two-arrays)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given two 0-indexed integer arrays nums1 and nums2 of length n.
+
+Let's define another 0-indexed integer array, nums3, of length n. For each index i in the range [0, n - 1], you can assign either nums1[i] or nums2[i] to nums3[i].
+
+Your task is to maximize the length of the longest non-decreasing subarray in nums3 by choosing its values optimally.
+
+Return an integer representing the length of the longest non-decreasing subarray in nums3.
+
+Note: A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: nums1 = [2,3,1], nums2 = [1,2,1]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: One way to construct nums3 is:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums2[1], nums2[2]] => [2,2,1].
+The subarray starting from index 0 and ending at index 1, [2,2], forms a non-decreasing subarray of length 2.
+We can show that 2 is the maximum achievable length.
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: nums1 = [1,3,2,1], nums2 = [2,2,3,4]
+Output: 4
+Explanation: One way to construct nums3 is:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums2[1], nums2[2], nums2[3]] => [1,2,3,4].
+The entire array forms a non-decreasing subarray of length 4, making it the maximum achievable length.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: nums1 = [1,1], nums2 = [2,2]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: One way to construct nums3 is:
+nums3 = [nums1[0], nums1[1]] => [1,1].
+The entire array forms a non-decreasing subarray of length 2, making it the maximum achievable length.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= nums1.length == nums2.length == n <= 1051 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 109
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1:Dynamic Programming**
+
+We define two variables $f$ and $g$, which represent the longest non-decreasing subarray length at the current position, where $f$ represents the longest non-decreasing subarray length ending in the $nums1$ element, and $g$ represents the longest non-decreasing subarray length ending in the $nums2$ element. At the beginning, $f = g = 1$, and the initial answer $ans = 1$.
+
+Next, we traverse the array elements in the range of $i \in [1, n)$, for each $i$, we define two variables $ff$ and $gg$, which represent the longest non-decreasing subarray length ending in the $nums1[i]$ and $nums2[i]$ element, respectively, and initialize $ff = gg = 1$.
+
+We can calculate the value of $ff$ and $gg$ from the values of $f$ and $g$:
+
+- If $nums1[i] \ge nums1[i - 1]$, then $ff = max(ff, f + 1)$;
+- If $nums1[i] \ge nums2[i - 1]$, then $ff = max(ff, g + 1)$;
+- If $nums2[i] \ge nums1[i - 1]$, then $gg = max(gg, f + 1)$;
+- If $nums2[i] \ge nums2[i - 1]$, then $gg = max(gg, g + 1)$.
+
+Then, we update $f = ff$ and $g = gg$, and update $ans$ to $max(ans, f, g)$.
+
+After the traversal is over, we return $ans$.
+
+Time complexity $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array. Space complexity $O(1)$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxNonDecreasingLength(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
+ n = len(nums1)
+ f = g = 1
+ ans = 1
+ for i in range(1, n):
+ ff = gg = 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1)
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1)
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, f, g)
+ return ans
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int maxNonDecreasingLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.length;
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, Math.max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maxNonDecreasingLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.size();
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) int {
+ n := len(nums1)
+ f, g, ans := 1, 1, 1
+ for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
+ ff, gg := 1, 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, g+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, g+1)
+ }
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g))
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums1.length;
+ let [f, g, ans] = [1, 1, 1];
+ for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ let [ff, gg] = [1, 1];
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, f, g);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..f114c072cd8a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int maxNonDecreasingLength(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.size();
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..aec6225903882
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+func maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) int {
+ n := len(nums1)
+ f, g, ans := 1, 1, 1
+ for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
+ ff, gg := 1, 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ ff = max(ff, g+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, f+1)
+ }
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i-1] {
+ gg = max(gg, g+1)
+ }
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, max(f, g))
+ }
+ return ans
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..f836a25d411e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+class Solution {
+ public int maxNonDecreasingLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
+ int n = nums1.length;
+ int f = 1, g = 1;
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ int ff = 1, gg = 1;
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, Math.max(f, g));
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e34ba2152edcb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+class Solution:
+ def maxNonDecreasingLength(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
+ n = len(nums1)
+ f = g = 1
+ ans = 1
+ for i in range(1, n):
+ ff = gg = 1
+ if nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, f + 1)
+ if nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ ff = max(ff, g + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, f + 1)
+ if nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]:
+ gg = max(gg, g + 1)
+ f, g = ff, gg
+ ans = max(ans, f, g)
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..b2ed0ae185eb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+function maxNonDecreasingLength(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number {
+ const n = nums1.length;
+ let [f, g, ans] = [1, 1, 1];
+ for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
+ let [ff, gg] = [1, 1];
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums1[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ ff = Math.max(ff, g + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums1[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, f + 1);
+ }
+ if (nums2[i] >= nums2[i - 1]) {
+ gg = Math.max(gg, g + 1);
+ }
+ f = ff;
+ g = gg;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, f, g);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README.md b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..9976857d6f30f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
+# [2772. 使数组中的所有元素都等于零](https://leetcode.cn/problems/apply-operations-to-make-all-array-elements-equal-to-zero)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums 和一个正整数 k 。
+
+你可以对数组执行下述操作 任意次 :
+
+
+ - 从数组中选出长度为
k 的 任一 子数组,并将子数组中每个元素都 减去 1 。
+
+
+如果你可以使数组中的所有元素都等于 0 ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
+
+子数组 是数组中的一个非空连续元素序列。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+输入:nums = [2,2,3,1,1,0], k = 3
+输出:true
+解释:可以执行下述操作:
+- 选出子数组 [2,2,3] ,执行操作后,数组变为 nums = [1,1,2,1,1,0] 。
+- 选出子数组 [2,1,1] ,执行操作后,数组变为 nums = [1,1,1,0,0,0] 。
+- 选出子数组 [1,1,1] ,执行操作后,数组变为 nums = [0,0,0,0,0,0] 。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+输入:nums = [1,3,1,1], k = 2
+输出:false
+解释:无法使数组中的所有元素等于 0 。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 106
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+**方法一:差分数组 + 前缀和**
+
+我们先考虑 $nums$ 的第一个元素 $nums[0]$:
+
+- 如果 $nums[0] = 0$,那么我们可以不用操作;
+- 如果 $nums[0] \gt 0$,那么我们需要对 $nums[0..k-1]$ 操作 $nums[0]$ 次,使得 $nums[0..k-1]$ 中的元素都减去 $nums[0]$,这样 $nums[0]$ 就变成了 $0$。
+
+对一段连续的元素同时进行加减操作,我们可以使用差分数组来维护这些操作,我们用 $d[i]$ 表示差分数组,对差分数组求前缀和,就可以得到每个位置的数值的变化量。
+
+因此,我们遍历 $nums$,对于每个元素 $nums[i]$,当前位置的变化量 $s = \sum_{j=0}^{i} d[j]$,我们将 $nums[i]$ 加上 $s$,就得到了当前 $nums[i]$ 的实际值。
+
+- 如果 $nums[i] = 0$,那么无须进行操作,直接跳过。
+- 如果 $nums[i]=0$,或者 $i + k \gt n$,说明经过前面的操作,$nums[i]$ 已经变成了负数,或者 $nums[i..i+k-1]$ 越界,那么无法使得 $nums$ 中的所有元素都等于 $0$,返回 `false`。否则,我们需要将 $[i..i+k-1]$ 这段区间的所有元素都减去 $nums[i]$,因此我们将 $s$ 减去 $nums[i]$,并将 $d[i+k]$ 加上 $nums[i]$。
+- 继续遍历下一个元素。
+
+遍历结束,说明可以使得 $nums$ 中的所有元素都等于 $0$,返回 `true`。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $nums$ 的长度。
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def checkArray(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> bool:
+ n = len(nums)
+ d = [0] * (n + 1)
+ s = 0
+ for i, x in enumerate(nums):
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0:
+ continue
+ if x < 0 or i + k > n:
+ return False
+ s -= x
+ d[i + k] += x
+ return True
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean checkArray(int[] nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[] d = new int[n + 1];
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool checkArray(vector& nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ vector d(n + 1);
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func checkArray(nums []int, k int) bool {
+ n := len(nums)
+ d := make([]int, n+1)
+ s := 0
+ for i, x := range nums {
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+ if x < 0 || i+k > n {
+ return false
+ }
+ s -= x
+ d[i+k] += x
+ }
+ return true
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function checkArray(nums: number[], k: number): boolean {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const d: number[] = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] === 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..f816d205ab87b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
+# [2772. Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero](https://leetcode.com/problems/apply-operations-to-make-all-array-elements-equal-to-zero)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and a positive integer k.
+
+You can apply the following operation on the array any number of times:
+
+
+ - Choose any subarray of size
k from the array and decrease all its elements by 1.
+
+
+Return true if you can make all the array elements equal to 0, or false otherwise.
+
+A subarray is a contiguous non-empty part of an array.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: nums = [2,2,3,1,1,0], k = 3
+Output: true
+Explanation: We can do the following operations:
+- Choose the subarray [2,2,3]. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,2,1,1,0].
+- Choose the subarray [2,1,1]. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,1,0,0,0].
+- Choose the subarray [1,1,1]. The resulting array will be nums = [0,0,0,0,0,0].
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,3,1,1], k = 2
+Output: false
+Explanation: It is not possible to make all the array elements equal to 0.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 106
+
+## Solutions
+
+**Solution 1: Difference Array + Prefix Sum**
+
+Let's first consider the first element $nums[0]$ of $nums$:
+
+- If $nums[0] = 0$, then we don't need to do anything;
+- If $nums[0] \gt 0$, then we need to operate $nums[0]$ times on $nums[0..k-1]$ to make the elements in $nums[0..k-1]$ all subtract $nums[0]$, so that $nums[0]$ becomes $0$.
+
+We can use difference array to maintain the operations on a segment of continuous elements. We use $d[i]$ to represent the difference array, and take the prefix sum of the difference array to get the variation amount of each position.
+
+Therefore, we traverse $nums$, for each element $nums[i]$, the current variation amount $s = \sum_{j=0}^{i} d[j]$ and we add $s$ to $nums[i]$ to get the actual value of $nums[i]$.
+
+- If $nums[i] = 0$, then we don't need to do anything, just skip.
+- If $nums[i]=0$ or $i + k \gt n$, it means that after the previous operation, $nums[i]$ has become negative, or $nums[i..i+k-1]$ out of bounds, so it is impossible to make all elements in $nums$ equal to $0$, then return `false`. Otherwise, we need to subtract $nums[i]$ from all elements in $[i..i+k-1]$, so we subtract $nums[i]$ from $s$ and add $nums[i]$ to $d[i+k]$.
+- Continue to traverse the next element.
+
+If the traversal is over, it means that we can make all elements in $nums$ equal to $0$, return `true`.
+
+Time complexity $O(n)$, space complexity $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the length of the array $nums$.
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def checkArray(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> bool:
+ n = len(nums)
+ d = [0] * (n + 1)
+ s = 0
+ for i, x in enumerate(nums):
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0:
+ continue
+ if x < 0 or i + k > n:
+ return False
+ s -= x
+ d[i + k] += x
+ return True
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean checkArray(int[] nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[] d = new int[n + 1];
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool checkArray(vector& nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ vector d(n + 1);
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+func checkArray(nums []int, k int) bool {
+ n := len(nums)
+ d := make([]int, n+1)
+ s := 0
+ for i, x := range nums {
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+ if x < 0 || i+k > n {
+ return false
+ }
+ s -= x
+ d[i+k] += x
+ }
+ return true
+}
+```
+
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function checkArray(nums: number[], k: number): boolean {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const d: number[] = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] === 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.cpp b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..627d91abac2ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool checkArray(vector& nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.size();
+ vector d(n + 1);
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.go b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..d2ac743e57eb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+func checkArray(nums []int, k int) bool {
+ n := len(nums)
+ d := make([]int, n+1)
+ s := 0
+ for i, x := range nums {
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+ if x < 0 || i+k > n {
+ return false
+ }
+ s -= x
+ d[i+k] += x
+ }
+ return true
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.java b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..08fbb770890db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+class Solution {
+ public boolean checkArray(int[] nums, int k) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[] d = new int[n + 1];
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.py b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..b209647ea018a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution:
+ def checkArray(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> bool:
+ n = len(nums)
+ d = [0] * (n + 1)
+ s = 0
+ for i, x in enumerate(nums):
+ s += d[i]
+ x += s
+ if x == 0:
+ continue
+ if x < 0 or i + k > n:
+ return False
+ s -= x
+ d[i + k] += x
+ return True
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.ts b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..5ae6f28a0565f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+function checkArray(nums: number[], k: number): boolean {
+ const n = nums.length;
+ const d: number[] = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ s += d[i];
+ nums[i] += s;
+ if (nums[i] === 0) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (nums[i] < 0 || i + k > n) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ s -= nums[i];
+ d[i + k] += nums[i];
+ }
+ return true;
+}
diff --git a/solution/CONTEST_README.md b/solution/CONTEST_README.md
index 536a2a7ecec2c..414735b195c75 100644
--- a/solution/CONTEST_README.md
+++ b/solution/CONTEST_README.md
@@ -22,6 +22,20 @@
## 往期竞赛
+#### 第 353 场周赛(2023-07-09 10:30, 90 分钟) 参赛人数 4112
+
+- [2769. 找出最大的可达成数字](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README.md)
+- [2770. 达到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README.md)
+- [2771. 构造最长非递减子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README.md)
+- [2772. 使数组中的所有元素都等于零](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README.md)
+
+#### 第 108 场双周赛(2023-07-08 22:30, 90 分钟) 参赛人数 2349
+
+- [2765. 最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
+- [2766. 重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
+- [2767. 将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
+- [2768. 黑格子的数目](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README.md)
+
#### 第 352 场周赛(2023-07-02 10:30, 90 分钟) 参赛人数 3437
- [2760. 最长奇偶子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2760.Longest%20Even%20Odd%20Subarray%20With%20Threshold/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md b/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
index b1d2ffc8e885a..4d918a07601b1 100644
--- a/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
@@ -25,6 +25,20 @@ Get your rating changes right after the completion of LeetCode contests, https:/
## Past Contests
+#### Weekly Contest 353
+
+- [2769. Find the Maximum Achievable Number](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README_EN.md)
+- [2770. Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README_EN.md)
+- [2771. Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README_EN.md)
+- [2772. Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README_EN.md)
+
+#### Biweekly Contest 108
+
+- [2765. Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
+- [2766. Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
+- [2767. Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
+- [2768. Number of Black Blocks](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README_EN.md)
+
#### Weekly Contest 352
- [2760. Longest Even Odd Subarray With Threshold](/solution/2700-2799/2760.Longest%20Even%20Odd%20Subarray%20With%20Threshold/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index 0d02096a67626..c2ca2d12ead56 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2775,6 +2775,14 @@
| 2762 | [不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md) | `队列`,`数组`,`有序集合`,`滑动窗口`,`单调队列`,`堆(优先队列)` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2763 | [所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`有序集合` | 困难 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2765 | [最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md) | | 简单 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
+| 2766 | [重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
+| 2767 | [将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
+| 2768 | [黑格子的数目](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
+| 2769 | [找出最大的可达成数字](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README.md) | | 简单 | 第 353 场周赛 |
+| 2770 | [达到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 353 场周赛 |
+| 2771 | [构造最长非递减子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 353 场周赛 |
+| 2772 | [使数组中的所有元素都等于零](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 353 场周赛 |
## 版权
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 7d78f36ebba0f..472695b202fe9 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2773,6 +2773,14 @@ Press Control+F(or Command+F on the
| 2762 | [Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Queue`,`Array`,`Ordered Set`,`Sliding Window`,`Monotonic Queue`,`Heap (Priority Queue)` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2763 | [Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Ordered Set` | Hard | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | | Medium | 🔒 |
+| 2765 | [Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md) | | Easy | Biweekly Contest 108 |
+| 2766 | [Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
+| 2767 | [Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
+| 2768 | [Number of Black Blocks](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
+| 2769 | [Find the Maximum Achievable Number](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README_EN.md) | | Easy | Weekly Contest 353 |
+| 2770 | [Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Weekly Contest 353 |
+| 2771 | [Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Weekly Contest 353 |
+| 2772 | [Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Weekly Contest 353 |
## Copyright
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index 7ecb7491ca819..9735ffc0dff56 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -2818,3 +2818,11 @@
- [2762.不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2763.所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+ - [2765.最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
+ - [2766.重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
+ - [2767.将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
+ - [2768.黑格子的数目](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README.md)
+ - [2769.找出最大的可达成数字](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README.md)
+ - [2770.达到末尾下标所需的最大跳跃次数](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README.md)
+ - [2771.构造最长非递减子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README.md)
+ - [2772.使数组中的所有元素都等于零](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 88609641d2b4f..2c79c36a9ffc4 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -2818,3 +2818,11 @@
- [2762.Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2763.Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+ - [2765.Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
+ - [2766.Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
+ - [2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
+ - [2768.Number of Black Blocks](/solution/2700-2799/2768.Number%20of%20Black%20Blocks/README_EN.md)
+ - [2769.Find the Maximum Achievable Number](/solution/2700-2799/2769.Find%20the%20Maximum%20Achievable%20Number/README_EN.md)
+ - [2770.Maximum Number of Jumps to Reach the Last Index](/solution/2700-2799/2770.Maximum%20Number%20of%20Jumps%20to%20Reach%20the%20Last%20Index/README_EN.md)
+ - [2771.Longest Non-decreasing Subarray From Two Arrays](/solution/2700-2799/2771.Longest%20Non-decreasing%20Subarray%20From%20Two%20Arrays/README_EN.md)
+ - [2772.Apply Operations to Make All Array Elements Equal to Zero](/solution/2700-2799/2772.Apply%20Operations%20to%20Make%20All%20Array%20Elements%20Equal%20to%20Zero/README_EN.md)
+只有 1 个块有一个黑色格子,这个块是左上角为 [0,0] 的块。 +其他 3 个左上角分别为 [0,1] ,[1,0] 和 [1,1] 的块都有 0 个黑格子。 +所以我们返回 [3,1,0,0,0] 。 +
+有 2 个块有 2 个黑色格子(左上角格子分别为 [0,0] 和 [0,1])。 +左上角为 [1,0] 和 [1,1] 的两个块,都有 1 个黑格子。 +所以我们返回 [0,2,2,0,0] 。 +
+There is only 1 block with one black cell, and it is the block starting with cell [0,0]. +The other 3 blocks start with cells [0,1], [1,0] and [1,1]. They all have zero black cells. +Thus, we return [3,1,0,0,0]. +
+There are 2 blocks with two black cells (the ones starting with cell coordinates [0,0] and [0,1]). +The other 2 blocks have starting cell coordinates of [1,0] and [1,1]. They both have 1 black cell. +Therefore, we return [0,2,2,0,0]. +