任务调度优化是计算机性能优化的关键任务之一。在任务众多时,不同的调度策略可能会得到不同的总体执行时间,因此寻求一个最优的调度方案是非常有必要的。
通常任务之间是存在依赖关系的,即对于某个任务,你需要先完成他的前导任务(如果非空),才能开始执行该任务。我们保证任务的依赖关系是一棵二叉树,其中 root 为根任务,root.left 和 root.right 为他的两个前导任务(可能为空),root.val 为其自身的执行时间。
在一个 CPU 核执行某个任务时,我们可以在任何时刻暂停当前任务的执行,并保留当前执行进度。在下次继续执行该任务时,会从之前停留的进度开始继续执行。暂停的时间可以不是整数。
现在,系统有两个 CPU 核,即我们可以同时执行两个任务,但是同一个任务不能同时在两个核上执行。给定这颗任务树,请求出所有任务执行完毕的最小时间。
示例 1:
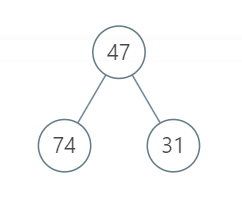
输入:root = [47, 74, 31]
输出:121
解释:根节点的左右节点可以并行执行31分钟,剩下的43+47分钟只能串行执行,因此总体执行时间是121分钟。
示例 2:
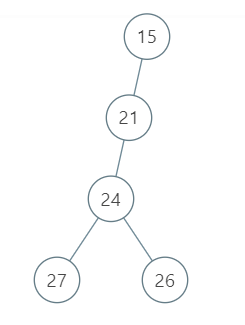
输入:root = [15, 21, null, 24, null, 27, 26]
输出:87
示例 3:
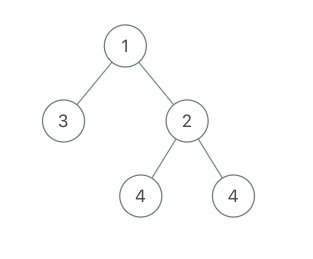
输入:root = [1,3,2,null,null,4,4]
输出:7.5
限制:
1 <= 节点数量 <= 10001 <= 单节点执行时间 <= 1000
class Solution:
def minimalExecTime(self, root: TreeNode) -> float:
def dfs(root: TreeNode) -> Tuple[int, int]:
if not root:
return 0, 0
s1, t1 = dfs(root.left)
s2, t2 = dfs(root.right)
return s1 + s2 + root.val, max(t1, t2, (s1 + s2) / 2) + root.val
return dfs(root)[1]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public double minimalExecTime(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root)[1];
}
private double[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new double[] {0, 0};
}
double[] left = dfs(root.left);
double[] right = dfs(root.right);
double s = left[0] + right[0] + root.val;
double t = Math.max(Math.max(left[1], right[1]), (left[0] + right[0]) / 2) + root.val;
return new double[] {s, t};
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
double minimalExecTime(TreeNode* root) {
function<pair<double, double>(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) -> pair<double, double> {
if (!root) {
return {0, 0};
}
auto [s1, t1] = dfs(root->left);
auto [s2, t2] = dfs(root->right);
double s = s1 + s2 + root->val;
double t = max({t1, t2, (s1 + s2) / 2}) + root->val;
return {s, t};
};
auto [_, t] = dfs(root);
return t;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func minimalExecTime(root *TreeNode) float64 {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) (float64, float64)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) (float64, float64) {
if root == nil {
return 0, 0
}
s1, t1 := dfs(root.Left)
s2, t2 := dfs(root.Right)
s := s1 + s2 + float64(root.Val)
t := math.Max(math.Max(t1, t2), (s1+s2)/2) + float64(root.Val)
return s, t
}
_, t := dfs(root)
return t
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function minimalExecTime(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): [number, number] => {
if (root === null) {
return [0, 0];
}
const [s1, t1] = dfs(root.left);
const [s2, t2] = dfs(root.right);
const s = s1 + s2 + root.val;
const t = Math.max(t1, t2, (s1 + s2) / 2) + root.val;
return [s, t];
};
return dfs(root)[1];
}