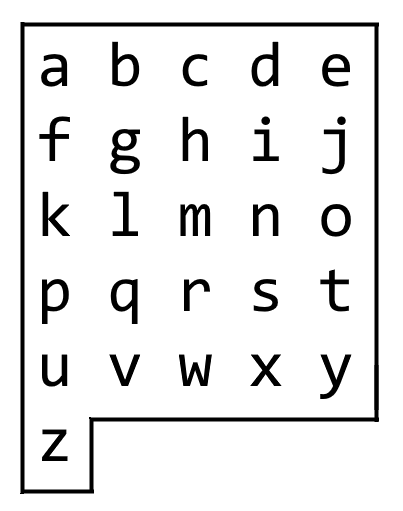
On an alphabet board, we start at position (0, 0), corresponding to character board[0][0].
Here, board = ["abcde", "fghij", "klmno", "pqrst", "uvwxy", "z"], as shown in the diagram below.
We may make the following moves:
'U'moves our position up one row, if the position exists on the board;'D'moves our position down one row, if the position exists on the board;'L'moves our position left one column, if the position exists on the board;'R'moves our position right one column, if the position exists on the board;'!'adds the characterboard[r][c]at our current position(r, c)to the answer.
(Here, the only positions that exist on the board are positions with letters on them.)
Return a sequence of moves that makes our answer equal to target in the minimum number of moves. You may return any path that does so.
Example 1:
Input: target = "leet" Output: "DDR!UURRR!!DDD!"
Example 2:
Input: target = "code" Output: "RR!DDRR!UUL!R!"
Constraints:
1 <= target.length <= 100targetconsists only of English lowercase letters.
class Solution:
def alphabetBoardPath(self, target: str) -> str:
i = j = 0
ans = []
for c in target:
v = ord(c) - ord("a")
x, y = v // 5, v % 5
while j > y:
j -= 1
ans.append("L")
while i > x:
i -= 1
ans.append("U")
while j < y:
j += 1
ans.append("R")
while i < x:
i += 1
ans.append("D")
ans.append("!")
return "".join(ans)class Solution {
public String alphabetBoardPath(String target) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < target.length(); ++k) {
int v = target.charAt(k) - 'a';
int x = v / 5, y = v % 5;
while (j > y) {
--j;
ans.append('L');
}
while (i > x) {
--i;
ans.append('U');
}
while (j < y) {
++j;
ans.append('R');
}
while (i < x) {
++i;
ans.append('D');
}
ans.append("!");
}
return ans.toString();
}
}class Solution {
public:
string alphabetBoardPath(string target) {
string ans;
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (char& c : target) {
int v = c - 'a';
int x = v / 5, y = v % 5;
while (j > y) {
--j;
ans += 'L';
}
while (i > x) {
--i;
ans += 'U';
}
while (j < y) {
++j;
ans += 'R';
}
while (i < x) {
++i;
ans += 'D';
}
ans += '!';
}
return ans;
}
};func alphabetBoardPath(target string) string {
ans := []byte{}
var i, j int
for _, c := range target {
v := int(c - 'a')
x, y := v/5, v%5
for j > y {
j--
ans = append(ans, 'L')
}
for i > x {
i--
ans = append(ans, 'U')
}
for j < y {
j++
ans = append(ans, 'R')
}
for i < x {
i++
ans = append(ans, 'D')
}
ans = append(ans, '!')
}
return string(ans)
}