Given the head of a linked list, find all the values that appear more than once in the list and delete the nodes that have any of those values.
Return the linked list after the deletions.
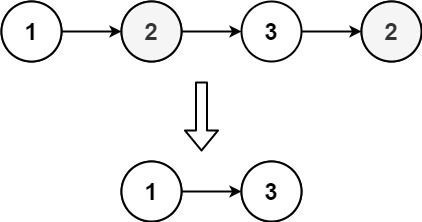
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,2] Output: [1,3] Explanation: 2 appears twice in the linked list, so all 2's should be deleted. After deleting all 2's, we are left with [1,3].
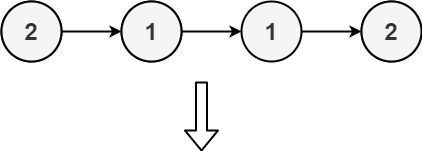
Example 2:
Input: head = [2,1,1,2] Output: [] Explanation: 2 and 1 both appear twice. All the elements should be deleted.
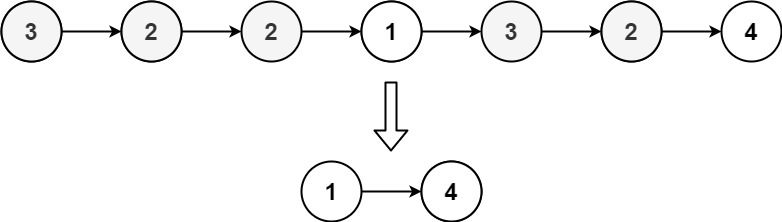
Example 3:
Input: head = [3,2,2,1,3,2,4] Output: [1,4] Explanation: 3 appears twice and 2 appears three times. After deleting all 3's and 2's, we are left with [1,4].
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105] 1 <= Node.val <= 105
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicatesUnsorted(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cnt = Counter()
cur = head
while cur:
cnt[cur.val] += 1
cur = cur.next
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
pre, cur = dummy, head
while cur:
if cnt[cur.val] > 1:
pre.next = cur.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicatesUnsorted(ListNode head) {
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
cnt.put(cur.val, cnt.getOrDefault(cur.val, 0) + 1);
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode pre = dummy, cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
if (cnt.get(cur.val) > 1) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicatesUnsorted(ListNode* head) {
unordered_map<int, int> cnt;
for (ListNode* cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next) {
cnt[cur->val]++;
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode *pre = dummy, *cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next) {
if (cnt[cur->val] > 1) {
pre->next = cur->next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func deleteDuplicatesUnsorted(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
cnt := map[int]int{}
for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next {
cnt[cur.Val]++
}
dummy := &ListNode{0, head}
for pre, cur := dummy, head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next {
if cnt[cur.Val] > 1 {
pre.Next = cur.Next
} else {
pre = cur
}
}
return dummy.Next
}