| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
Design an algorithm to encode an N-ary tree into a binary tree and decode the binary tree to get the original N-ary tree. An N-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than N children. Similarly, a binary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than 2 children. There is no restriction on how your encode/decode algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that an N-ary tree can be encoded to a binary tree and this binary tree can be decoded to the original N-nary tree structure.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See following example).
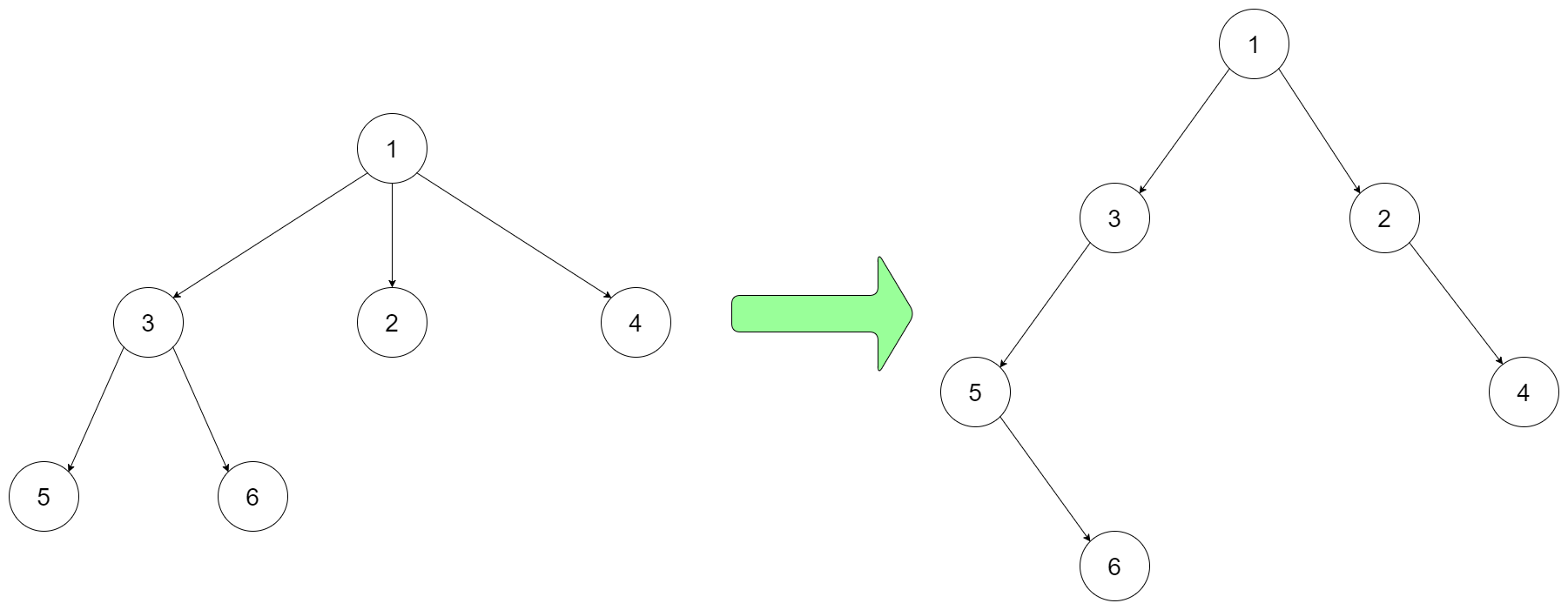
For example, you may encode the following 3-ary tree to a binary tree in this way:
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Note that the above is just an example which might or might not work. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 104- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000 - Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your encode and decode algorithms should be stateless.
We can point the left pointer of the binary tree to the first child of the N-ary tree and the right pointer of the binary tree to the next sibling node of the N-ary tree.
The time complexity is
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: Optional[int] = None, children: Optional[List['Node']] = None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
"""
class Codec:
# Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
def encode(self, root: "Optional[Node]") -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
node = TreeNode(root.val)
if not root.children:
return node
left = self.encode(root.children[0])
node.left = left
for child in root.children[1:]:
left.right = self.encode(child)
left = left.right
return node
# Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
def decode(self, data: Optional[TreeNode]) -> "Optional[Node]":
if data is None:
return None
node = Node(data.val, [])
if data.left is None:
return node
left = data.left
while left:
node.children.append(self.decode(left))
left = left.right
return node
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# codec = Codec()
# codec.decode(codec.encode(root))/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Codec {
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root.val);
if (root.children == null || root.children.isEmpty()) {
return node;
}
TreeNode left = encode(root.children.get(0));
node.left = left;
for (int i = 1; i < root.children.size(); i++) {
left.right = encode(root.children.get(i));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode data) {
if (data == null) {
return null;
}
Node node = new Node(data.val, new ArrayList<>());
if (data.left == null) {
return node;
}
TreeNode left = data.left;
while (left != null) {
node.children.add(decode(left));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.decode(codec.encode(root));/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
TreeNode* encode(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(root->val);
if (root->children.empty()) {
return node;
}
TreeNode* left = encode(root->children[0]);
node->left = left;
for (int i = 1; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
left->right = encode(root->children[i]);
left = left->right;
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
Node* decode(TreeNode* data) {
if (data == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
Node* node = new Node(data->val, vector<Node*>());
if (data->left == nullptr) {
return node;
}
TreeNode* left = data->left;
while (left != nullptr) {
node->children.push_back(decode(left));
left = left->right;
}
return node;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.decode(codec.encode(root));/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() *Codec {
return &Codec{}
}
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
func (this *Codec) encode(root *Node) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
node := &TreeNode{Val: root.Val}
if len(root.Children) == 0 {
return node
}
left := this.encode(root.Children[0])
node.Left = left
for i := 1; i < len(root.Children); i++ {
left.Right = this.encode(root.Children[i])
left = left.Right
}
return node
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
func (this *Codec) decode(data *TreeNode) *Node {
if data == nil {
return nil
}
node := &Node{Val: data.Val, Children: []*Node{}}
if data.Left == nil {
return node
}
left := data.Left
for left != nil {
node.Children = append(node.Children, this.decode(left))
left = left.Right
}
return node
}
/**
* Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* bst := obj.encode(root);
* ans := obj.decode(bst);
*//**
* Definition for _Node.
* class _Node {
* val: number
* children: _Node[]
*
* constructor(v: number) {
* this.val = v;
* this.children = [];
* }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
class Codec {
constructor() {}
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
serialize(root: _Node | null): TreeNode | null {
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
const node = new TreeNode(root.val);
if (root.children.length === 0) {
return node;
}
let left: TreeNode | null = this.serialize(root.children[0]);
node.left = left;
for (let i = 1; i < root.children.length; i++) {
if (left) {
left.right = this.serialize(root.children[i]);
left = left.right;
}
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree back to an n-ary tree.
deserialize(root: TreeNode | null): _Node | null {
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
const node = new _Node(root.val);
if (root.left === null) {
return node;
}
let left: TreeNode | null = root.left;
while (left !== null) {
node.children.push(this.deserialize(left));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));