给你一个有根节点 root 的二叉树,返回它 最深的叶节点的最近公共祖先 。
回想一下:
- 叶节点 是二叉树中没有子节点的节点
- 树的根节点的 深度 为
0,如果某一节点的深度为d,那它的子节点的深度就是d+1 - 如果我们假定
A是一组节点S的 最近公共祖先,S中的每个节点都在以A为根节点的子树中,且A的深度达到此条件下可能的最大值。
示例 1:
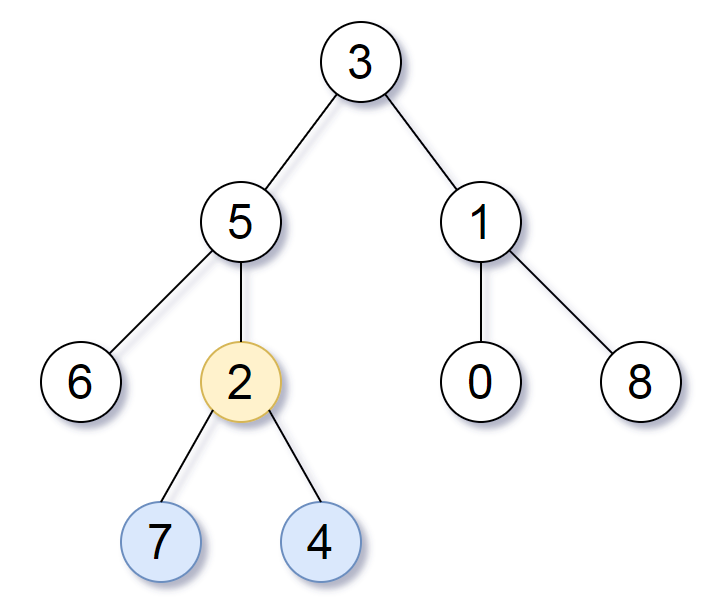
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] 输出:[2,7,4] 解释:我们返回值为 2 的节点,在图中用黄色标记。 在图中用蓝色标记的是树的最深的节点。 注意,节点 6、0 和 8 也是叶节点,但是它们的深度是 2 ,而节点 7 和 4 的深度是 3 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1] 解释:根节点是树中最深的节点,它是它本身的最近公共祖先。
示例 3:
输入:root = [0,1,3,null,2] 输出:[2] 解释:树中最深的叶节点是 2 ,最近公共祖先是它自己。
提示:
- 树中的节点数将在
[1, 1000]的范围内。 0 <= Node.val <= 1000- 每个节点的值都是 独一无二 的。
注意:本题与力扣 865 重复:https://leetcode.cn/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
我们设计一个函数
- 如果
为空,则返回二元组 ; - 否则,我们递归调用
和 ,得到二元组 和 。如果 ,则 的最深公共祖先节点为 ,深度为 ;如果 ,则 的最深公共祖先节点为 ,深度为 ;如果 ,则 的最深公共祖先节点为 ,深度为 。
我们在主函数中调用
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def lcaDeepestLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return None, 0
l, d1 = dfs(root.left)
r, d2 = dfs(root.right)
if d1 > d2:
return l, d1 + 1
if d1 < d2:
return r, d2 + 1
return root, d1 + 1
return dfs(root)[0]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lcaDeepestLeaves(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root).getKey();
}
private Pair<TreeNode, Integer> dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new Pair<>(null, 0);
}
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> l = dfs(root.left);
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> r = dfs(root.right);
int d1 = l.getValue(), d2 = r.getValue();
if (d1 > d2) {
return new Pair<>(l.getKey(), d1 + 1);
}
if (d1 < d2) {
return new Pair<>(r.getKey(), d2 + 1);
}
return new Pair<>(root, d1 + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lcaDeepestLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root).first;
}
pair<TreeNode*, int> dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return {nullptr, 0};
}
auto [l, d1] = dfs(root->left);
auto [r, d2] = dfs(root->right);
if (d1 > d2) {
return {l, d1 + 1};
}
if (d1 < d2) {
return {r, d2 + 1};
}
return {root, d1 + 1};
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
type pair struct {
first *TreeNode
second int
}
func lcaDeepestLeaves(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
var dfs func(root *TreeNode) pair
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) pair {
if root == nil {
return pair{nil, 0}
}
l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right)
d1, d2 := l.second, r.second
if d1 > d2 {
return pair{l.first, d1 + 1}
}
if d1 < d2 {
return pair{r.first, d2 + 1}
}
return pair{root, d1 + 1}
}
return dfs(root).first
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function lcaDeepestLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): [TreeNode | null, number] => {
if (root === null) {
return [null, 0];
}
const [l, d1] = dfs(root.left);
const [r, d2] = dfs(root.right);
if (d1 > d2) {
return [l, d1 + 1];
}
if (d1 < d2) {
return [r, d2 + 1];
}
return [root, d1 + 1];
};
return dfs(root)[0];
}