(此题是 交互式问题 )
在用笛卡尔坐标系表示的二维海平面上,有一些船。每一艘船都在一个整数点上,且每一个整数点最多只有 1 艘船。
有一个函数 Sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft) ,输入参数为右上角和左下角两个点的坐标,当且仅当这两个点所表示的矩形区域(包含边界)内至少有一艘船时,这个函数才返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
给你矩形的右上角 topRight 和左下角 bottomLeft 的坐标,请你返回此矩形内船只的数目。题目保证矩形内 至多只有 10 艘船。
调用函数 hasShips 超过400次 的提交将被判为 错误答案(Wrong Answer) 。同时,任何尝试绕过评测系统的行为都将被取消比赛资格。
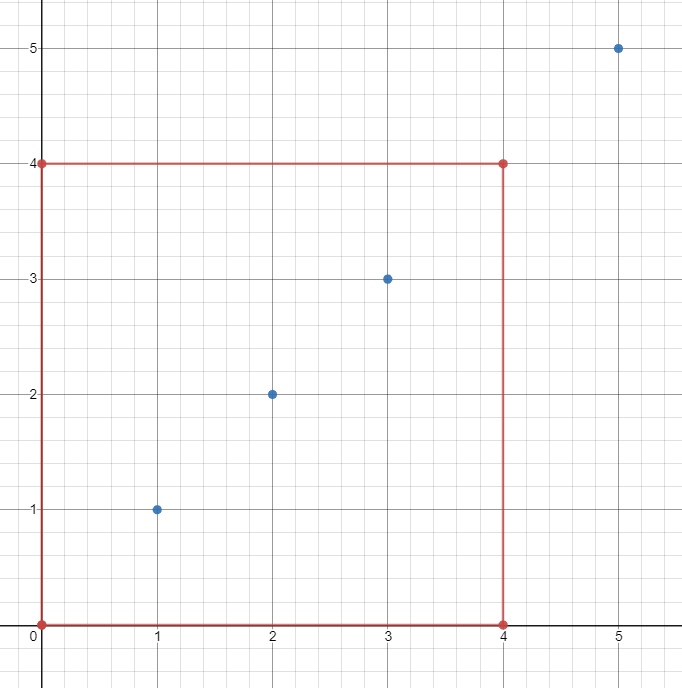
示例 1:
输入: ships = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[5,5]], topRight = [4,4], bottomLeft = [0,0] 输出:3 解释:在 [0,0] 到 [4,4] 的范围内总共有 3 艘船。
示例 2:
输入:ans = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]], topRight = [1000,1000], bottomLeft = [0,0] 输出:3
提示:
ships数组只用于评测系统内部初始化。你必须“蒙着眼睛”解决这个问题。你无法得知ships的信息,所以只能通过调用hasShips接口来求解。0 <= bottomLeft[0] <= topRight[0] <= 10000 <= bottomLeft[1] <= topRight[1] <= 1000topRight != bottomLeft
由于矩形内最多只有
时间复杂度
# """
# This is Sea's API interface.
# You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
# """
# class Sea:
# def hasShips(self, topRight: 'Point', bottomLeft: 'Point') -> bool:
#
# class Point:
# def __init__(self, x: int, y: int):
# self.x = x
# self.y = y
class Solution:
def countShips(self, sea: "Sea", topRight: "Point", bottomLeft: "Point") -> int:
def dfs(topRight, bottomLeft):
x1, y1 = bottomLeft.x, bottomLeft.y
x2, y2 = topRight.x, topRight.y
if x1 > x2 or y1 > y2:
return 0
if not sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft):
return 0
if x1 == x2 and y1 == y2:
return 1
midx = (x1 + x2) >> 1
midy = (y1 + y2) >> 1
a = dfs(topRight, Point(midx + 1, midy + 1))
b = dfs(Point(midx, y2), Point(x1, midy + 1))
c = dfs(Point(midx, midy), bottomLeft)
d = dfs(Point(x2, midy), Point(midx + 1, y1))
return a + b + c + d
return dfs(topRight, bottomLeft)/**
* // This is Sea's API interface.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class Sea {
* public boolean hasShips(int[] topRight, int[] bottomLeft);
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countShips(Sea sea, int[] topRight, int[] bottomLeft) {
int x1 = bottomLeft[0], y1 = bottomLeft[1];
int x2 = topRight[0], y2 = topRight[1];
if (x1 > x2 || y1 > y2) {
return 0;
}
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) {
return 0;
}
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
return 1;
}
int midx = (x1 + x2) >> 1;
int midy = (y1 + y2) >> 1;
int a = countShips(sea, topRight, new int[] {midx + 1, midy + 1});
int b = countShips(sea, new int[] {midx, y2}, new int[] {x1, midy + 1});
int c = countShips(sea, new int[] {midx, midy}, bottomLeft);
int d = countShips(sea, new int[] {x2, midy}, new int[] {midx + 1, y1});
return a + b + c + d;
}
}/**
* // This is Sea's API interface.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class Sea {
* public:
* bool hasShips(vector<int> topRight, vector<int> bottomLeft);
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countShips(Sea sea, vector<int> topRight, vector<int> bottomLeft) {
int x1 = bottomLeft[0], y1 = bottomLeft[1];
int x2 = topRight[0], y2 = topRight[1];
if (x1 > x2 || y1 > y2) {
return 0;
}
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) {
return 0;
}
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
return 1;
}
int midx = (x1 + x2) >> 1;
int midy = (y1 + y2) >> 1;
int a = countShips(sea, topRight, {midx + 1, midy + 1});
int b = countShips(sea, {midx, y2}, {x1, midy + 1});
int c = countShips(sea, {midx, midy}, bottomLeft);
int d = countShips(sea, {x2, midy}, {midx + 1, y1});
return a + b + c + d;
}
};/**
* // This is Sea's API interface.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* type Sea struct {
* func hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft []int) bool {}
* }
*/
func countShips(sea Sea, topRight, bottomLeft []int) int {
x1, y1 := bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]
x2, y2 := topRight[0], topRight[1]
if x1 > x2 || y1 > y2 {
return 0
}
if !sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft) {
return 0
}
if x1 == x2 && y1 == y2 {
return 1
}
midx := (x1 + x2) >> 1
midy := (y1 + y2) >> 1
a := countShips(sea, topRight, []int{midx + 1, midy + 1})
b := countShips(sea, []int{midx, y2}, []int{x1, midy + 1})
c := countShips(sea, []int{midx, midy}, bottomLeft)
d := countShips(sea, []int{x2, midy}, []int{midx + 1, y1})
return a + b + c + d
}/**
* // This is the Sea's API interface.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class Sea {
* hasShips(topRight: number[], bottomLeft: number[]): boolean {}
* }
*/
function countShips(sea: Sea, topRight: number[], bottomLeft: number[]): number {
const [x1, y1] = bottomLeft;
const [x2, y2] = topRight;
if (x1 > x2 || y1 > y2 || !sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) {
return 0;
}
if (x1 === x2 && y1 === y2) {
return 1;
}
const midx = (x1 + x2) >> 1;
const midy = (y1 + y2) >> 1;
const a = countShips(sea, topRight, [midx + 1, midy + 1]);
const b = countShips(sea, [midx, y2], [x1, midy + 1]);
const c = countShips(sea, [midx, midy], bottomLeft);
const d = countShips(sea, [x2, midy], [midx + 1, y1]);
return a + b + c + d;
}