diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index c86501d0598..b5e832382ec 100755
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,6 +1,9 @@
-推荐你通过在线阅读网站进行阅读,体验更好,速度更快!地址:[javaguide.cn](https://javaguide.cn/)。
+# JavaGuide
-[ ](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
+> I recommend reading through online reading websites for a better experience and faster speed!
+> 📚 Address: [javaguide.cn](https://javaguide.cn/)
+
+[
](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
+> I recommend reading through online reading websites for a better experience and faster speed!
+> 📚 Address: [javaguide.cn](https://javaguide.cn/)
+
+[ ](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
@@ -10,437 +13,129 @@
-> - **面试专版**:准备 Java 面试的小伙伴可以考虑面试专版:**[《Java 面试指北 》](./docs/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)** (质量很高,专为面试打造,配合 JavaGuide 食用)。
-> - **知识星球**:专属面试小册/一对一交流/简历修改/专属求职指南,欢迎加入 **[JavaGuide 知识星球](./docs/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)**(点击链接即可查看星球的详细介绍,一定确定自己真的需要再加入)。
-> - **使用建议** :有水平的面试官都是顺着项目经历挖掘技术问题。一定不要死记硬背技术八股文!详细的学习建议请参考:[JavaGuide 使用建议](./docs/javaguide/use-suggestion.md)。
-> - **求个Star**:如果觉得 JavaGuide 的内容对你有帮助的话,还请点个免费的 Star,这是对我最大的鼓励,感谢各位一起同行,共勉!Github 地址:[https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide) 。
-> - **转载须知**:以下所有文章如非文首说明为转载皆为 JavaGuide 原创,转载请在文首注明出处。如发现恶意抄袭/搬运,会动用法律武器维护自己的权益。让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境!
+---
+
+> - **Interview Special Edition**: Preparing for Java interviews? Check out the Interview Special Edition: **[Java Interview Guide](./docs/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)** — high quality and tailored for interview prep, meant to be used alongside JavaGuide.
+> - **Knowledge Planet**: For exclusive interview booklets, one-on-one communication, resume help, and job-seeking guidance, consider joining **[JavaGuide Knowledge Planet](./docs/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)**.
+> - **Usage Suggestions**: Don't memorize jargon! Interviewers care about real-world application. Check out our [Usage Suggestions](./docs/javaguide/use-suggestion.md).
+> - **Request a Star**: If JavaGuide helps you, please ⭐ the project — it means a lot! GitHub: [https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide)
+> - **Reprint Notice**: All articles are original unless otherwise noted. Please include a source link when sharing. Unauthorized use may result in legal action.
-

+

 -
-每种方式都有各自的优势,根据实际场景选择最合适的才是王道。下面再对这三种方式做一个简单的对比,以供大家实际开发中选择正确的存放时间的数据类型:
-
-| 类型 | 存储空间 | 日期格式 | 日期范围 | 是否带时区信息 |
-| ------------ | -------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------- |
-| DATETIME | 5~8 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1000-01-01 00:00:00[.000000] ~ 9999-12-31 23:59:59[.999999] | 否 |
-| TIMESTAMP | 4~7 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1970-01-01 00:00:01[.000000] ~ 2038-01-19 03:14:07[.999999] | 是 |
-| 数值型时间戳 | 4 字节 | 全数字如 1578707612 | 1970-01-01 00:00:01 之后的时间 | 否 |
-
-**选择建议小结:**
-
-- `TIMESTAMP` 的核心优势在于其内建的时区处理能力。数据库负责 UTC 存储和基于会话时区的自动转换,简化了需要处理多时区应用的开发。如果应用需要处理多时区,或者希望数据库能自动管理时区转换,`TIMESTAMP` 是自然的选择(注意其时间范围限制,也就是 2038 年问题)。
-- 如果应用场景不涉及时区转换,或者希望应用程序完全控制时区逻辑,并且需要表示 2038 年之后的时间,`DATETIME` 是更稳妥的选择。
-- 如果极度关注比较性能,或者需要频繁跨系统传递时间数据,并且可以接受可读性的牺牲(或总是在应用层转换),数值时间戳是一个强大的选项。
-
-
+Insert a
diff --git a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
index 52ad40f4a47..46b60051291 100644
--- a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
+++ b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
@@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
---
-title: MySQL事务隔离级别详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of MySQL Transaction Isolation Levels
+category: Database
tag:
- MySQL
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [guang19](https://github.com/guang19) 共同完成。
+> This article is co-authored by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [guang19](https://github.com/guang19).
-关于事务基本概览的介绍,请看这篇文章的介绍:[MySQL 常见知识点&面试题总结](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-事务)
+For an overview of transactions, please refer to this article: [Summary of Common MySQL Knowledge Points & Interview Questions](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-%E4%BA%8B%E5%8A%A1)
-## 事务隔离级别总结
+## Summary of Transaction Isolation Levels
-SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别:
+The SQL standard defines four isolation levels:
-- **READ-UNCOMMITTED(读取未提交)** :最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读。
-- **READ-COMMITTED(读取已提交)** :允许读取并发事务已经提交的数据,可以阻止脏读,但是幻读或不可重复读仍有可能发生。
-- **REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)** :对同一字段的多次读取结果都是一致的,除非数据是被本身事务自己所修改,可以阻止脏读和不可重复读,但幻读仍有可能发生。
-- **SERIALIZABLE(可串行化)** :最高的隔离级别,完全服从 ACID 的隔离级别。所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。
+- **READ-UNCOMMITTED**: The lowest isolation level, allowing reading of uncommitted data changes, which may lead to dirty reads, phantom reads, or non-repeatable reads.
+- **READ-COMMITTED**: Allows reading of data that has been committed by concurrent transactions, preventing dirty reads, but phantom reads or non-repeatable reads may still occur.
+- **REPEATABLE-READ**: Ensures that multiple reads of the same field yield consistent results unless the data is modified by the transaction itself. It prevents dirty reads and non-repeatable reads, but phantom reads may still occur.
+- **SERIALIZABLE**: The highest isolation level, fully compliant with the ACID isolation level. All transactions are executed sequentially, preventing any interference between transactions, meaning this level can prevent dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads.
----
+______________________________________________________________________
-| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
-| :--------------: | :--: | :--------: | :--: |
-| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
-| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
-| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
-| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
+| Isolation Level | Dirty Read | Non-repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
+| :--------------: | :--------: | :-----------------: | :----------: |
+| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
+| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
+| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
+| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
-MySQL InnoDB 存储引擎的默认支持的隔离级别是 **REPEATABLE-READ(可重读)**。我们可以通过`SELECT @@tx_isolation;`命令来查看,MySQL 8.0 该命令改为`SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
+The default isolation level supported by the MySQL InnoDB storage engine is **REPEATABLE-READ**. We can check this using the command `SELECT @@tx_isolation;`, which in MySQL 8.0 has changed to `SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
```sql
MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
@@ -38,78 +38,34 @@ MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
```
-从上面对 SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别的介绍可以看出,标准的 SQL 隔离级别定义里,REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)是不可以防止幻读的。
+From the introduction above regarding the four isolation levels defined by the SQL standard, it can be seen that the standard SQL isolation level definition does not prevent phantom reads for REPEATABLE-READ.
-但是!InnoDB 实现的 REPEATABLE-READ 隔离级别其实是可以解决幻读问题发生的,主要有下面两种情况:
+However! The REPEATABLE-READ isolation level implemented by InnoDB can actually resolve the issue of phantom reads, mainly in the following two situations:
-- **快照读**:由 MVCC 机制来保证不出现幻读。
-- **当前读**:使用 Next-Key Lock 进行加锁来保证不出现幻读,Next-Key Lock 是行锁(Record Lock)和间隙锁(Gap Lock)的结合,行锁只能锁住已经存在的行,为了避免插入新行,需要依赖间隙锁。
+- **Snapshot Read**: Ensured by the MVCC mechanism to prevent phantom reads.
+- **Current Read**: Uses Next-Key Lock for locking to prevent phantom reads. Next-Key Lock is a combination of row locks (Record Lock) and gap locks (Gap Lock). Row locks can only lock existing rows, and to prevent the insertion of new rows, gap locks are relied upon.
-因为隔离级别越低,事务请求的锁越少,所以大部分数据库系统的隔离级别都是 **READ-COMMITTED** ,但是你要知道的是 InnoDB 存储引擎默认使用 **REPEATABLE-READ** 并不会有任何性能损失。
+Since lower isolation levels require fewer locks for transaction requests, most database systems use **READ-COMMITTED** as the default isolation level. However, it is important to note that the InnoDB storage engine's default use of **REPEATABLE-READ** does not incur any performance loss.
-InnoDB 存储引擎在分布式事务的情况下一般会用到 SERIALIZABLE 隔离级别。
+In distributed transactions, the InnoDB storage engine generally uses the SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
-《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎(第 2 版)》7.7 章这样写到:
+Chapter 7.7 of "MySQL Internals: InnoDB Storage Engine (2nd Edition)" states:
-> InnoDB 存储引擎提供了对 XA 事务的支持,并通过 XA 事务来支持分布式事务的实现。分布式事务指的是允许多个独立的事务资源(transactional resources)参与到一个全局的事务中。事务资源通常是关系型数据库系统,但也可以是其他类型的资源。全局事务要求在其中的所有参与的事务要么都提交,要么都回滚,这对于事务原有的 ACID 要求又有了提高。另外,在使用分布式事务时,InnoDB 存储引擎的事务隔离级别必须设置为 SERIALIZABLE。
+> The InnoDB storage engine provides support for XA transactions and uses XA transactions to support the implementation of distributed transactions. Distributed transactions allow multiple independent transactional resources to participate in a global transaction. Transactional resources are typically relational database systems, but can also include other types of resources. A global transaction requires that all participating transactions either commit or roll back, which raises the original ACID requirements for transactions. Additionally, when using distributed transactions, the transaction isolation level of the InnoDB storage engine must be set to SERIALIZABLE.
-## 实际情况演示
+## Practical Demonstration
-在下面我会使用 2 个命令行 MySQL ,模拟多线程(多事务)对同一份数据的脏读问题。
+Below, I will use two MySQL command line instances to simulate the dirty read problem with multiple threads (multiple transactions) on the same data.
-MySQL 命令行的默认配置中事务都是自动提交的,即执行 SQL 语句后就会马上执行 COMMIT 操作。如果要显式地开启一个事务需要使用命令:`START TRANSACTION`。
+In the default configuration of the MySQL command line, transactions are automatically committed, meaning that after executing an SQL statement, a COMMIT operation is immediately performed. To explicitly start a transaction, the command `START TRANSACTION` is used.
-我们可以通过下面的命令来设置隔离级别。
+We can set the isolation level using the following command:
```sql
SET [SESSION|GLOBAL] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL [READ UNCOMMITTED|READ COMMITTED|REPEATABLE READ|SERIALIZABLE]
```
-我们再来看一下我们在下面实际操作中使用到的一些并发控制语句:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` |`BEGIN`:显式地开启一个事务。
-- `COMMIT`:提交事务,使得对数据库做的所有修改成为永久性。
-- `ROLLBACK`:回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的修改。
-
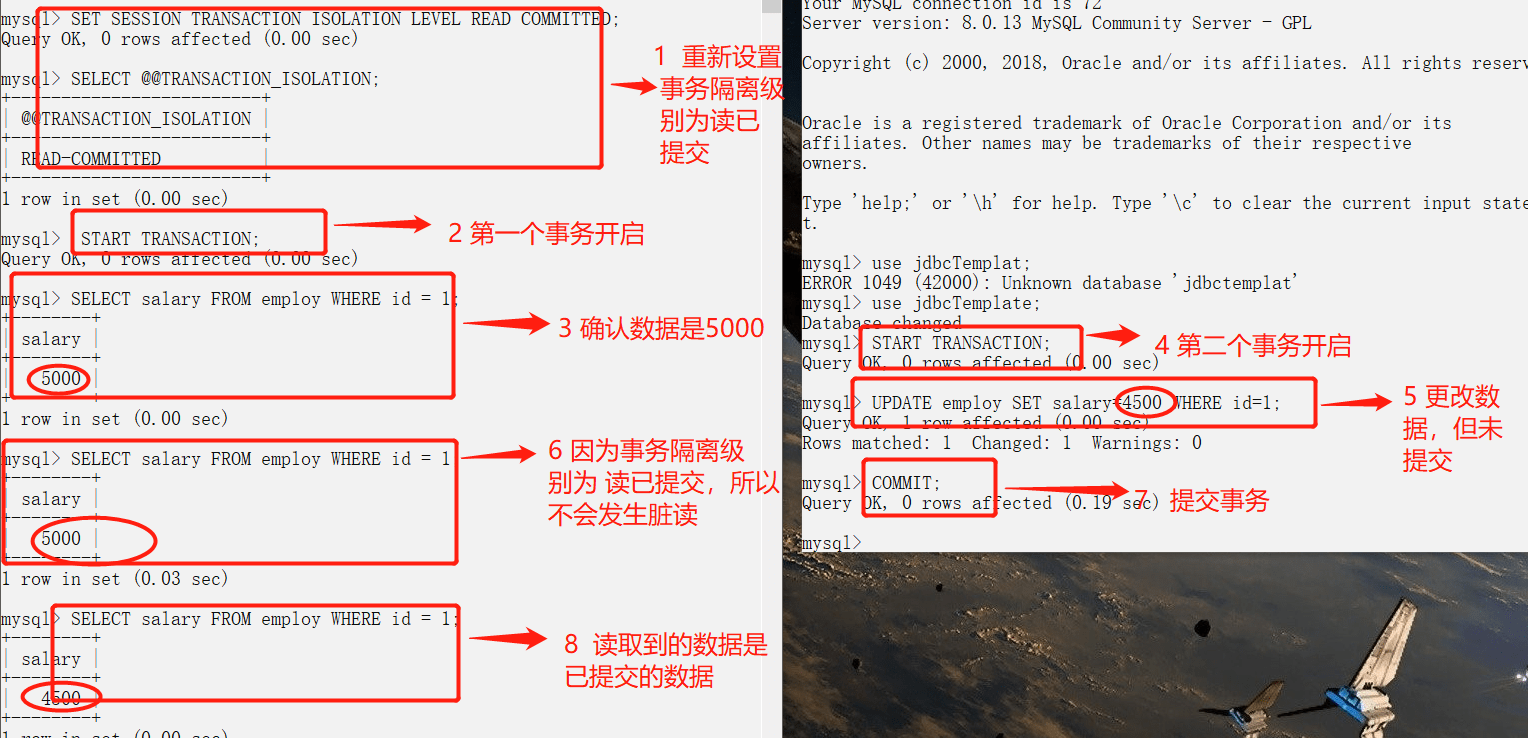
-### 脏读(读未提交)
-
-![]()
-
-### 避免脏读(读已提交)
-
-
-
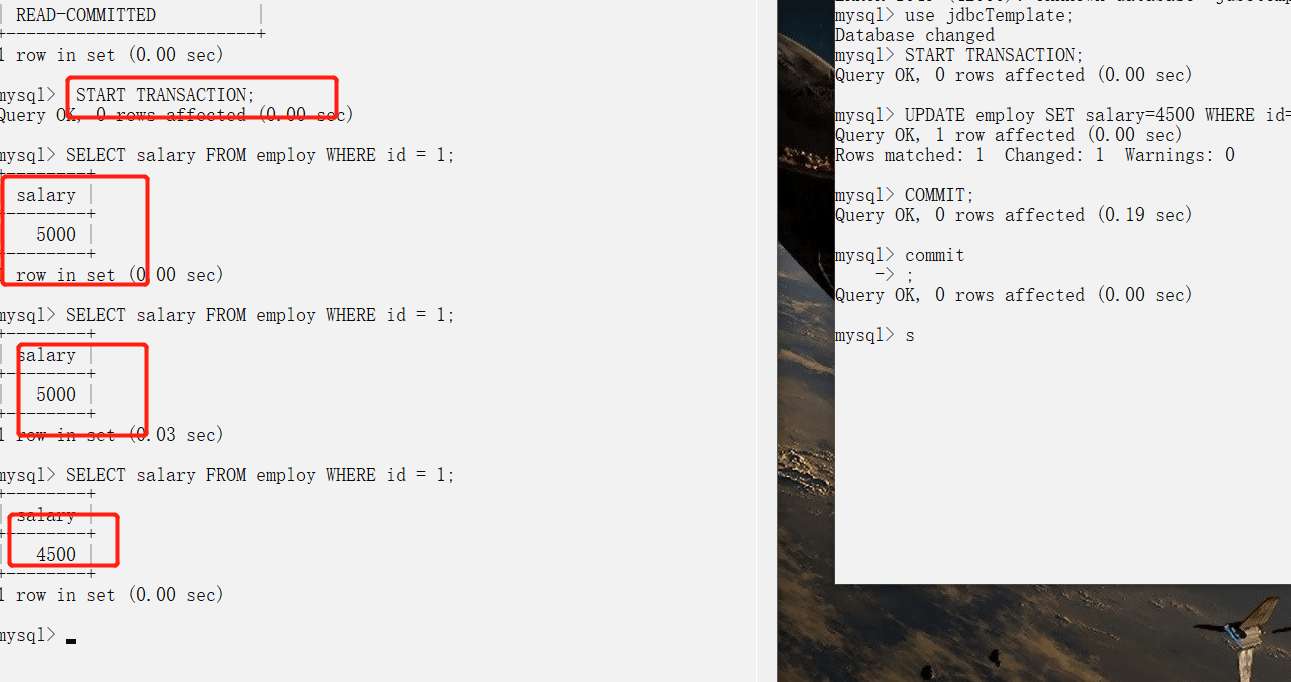
-### 不可重复读
-
-还是刚才上面的读已提交的图,虽然避免了读未提交,但是却出现了,一个事务还没有结束,就发生了 不可重复读问题。
-
-
-
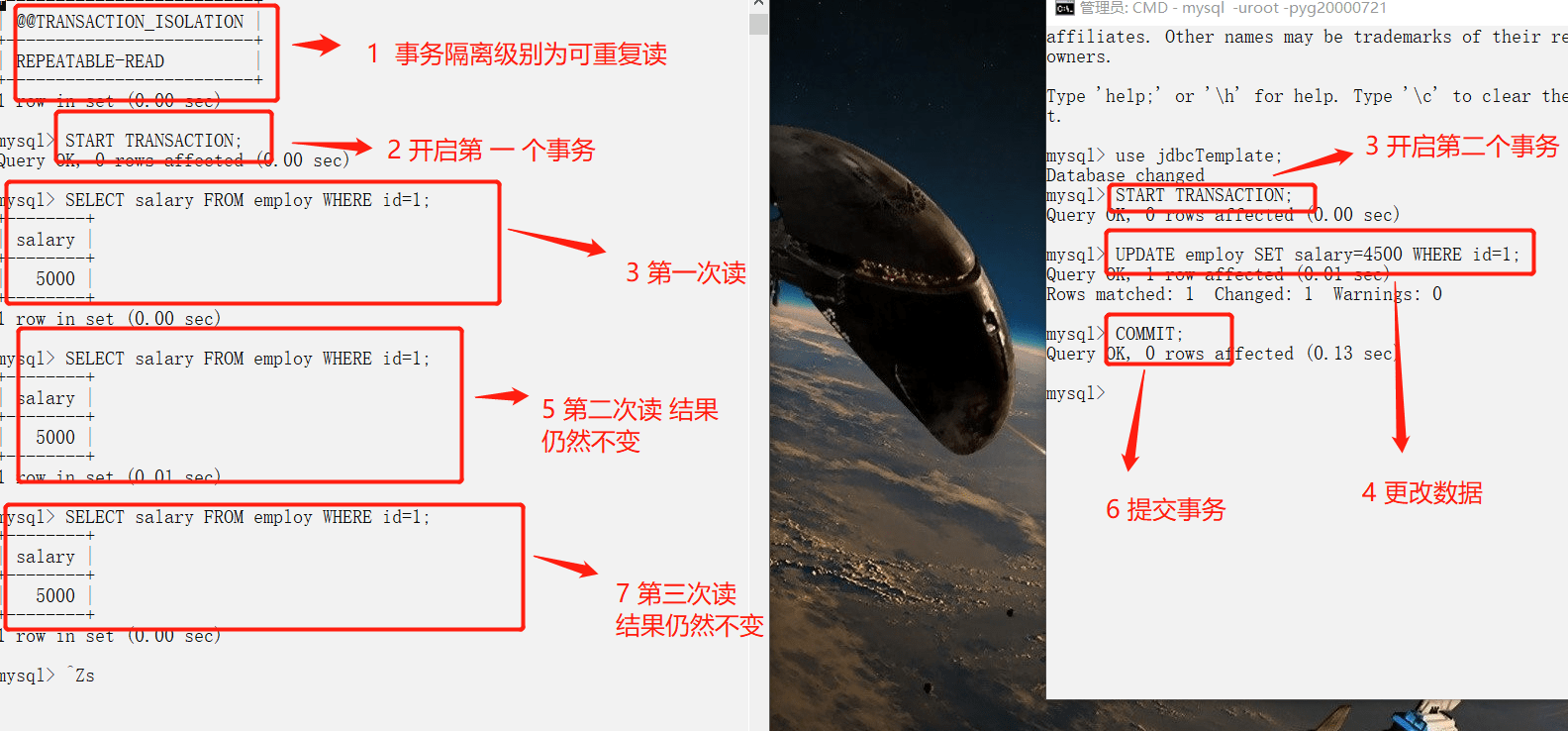
-### 可重复读
-
-
-
-### 幻读
-
-#### 演示幻读出现的情况
-
-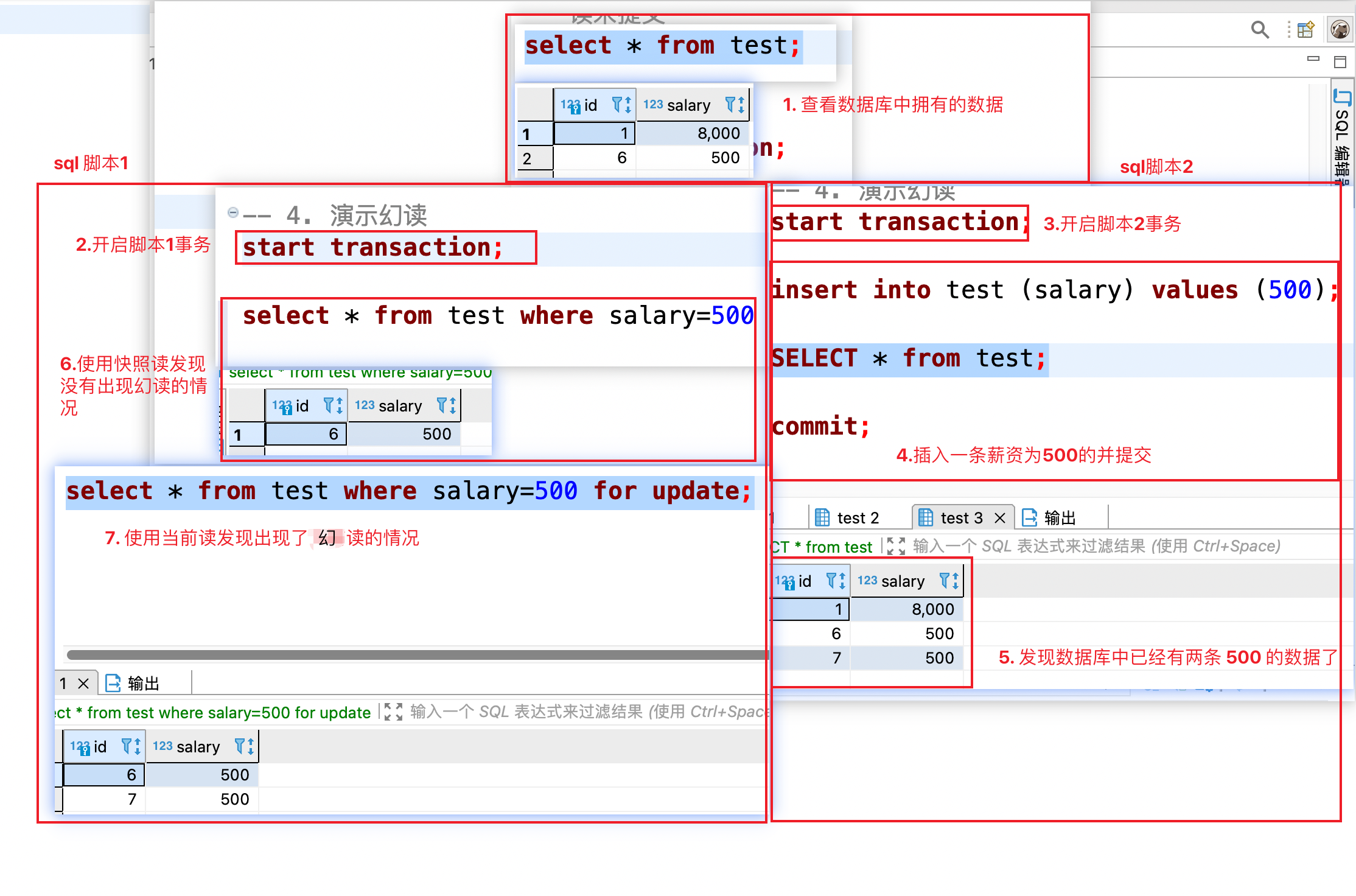
-
-SQL 脚本 1 在第一次查询工资为 500 的记录时只有一条,SQL 脚本 2 插入了一条工资为 500 的记录,提交之后;SQL 脚本 1 在同一个事务中再次使用当前读查询发现出现了两条工资为 500 的记录这种就是幻读。
-
-#### 解决幻读的方法
-
-解决幻读的方式有很多,但是它们的核心思想就是一个事务在操作某张表数据的时候,另外一个事务不允许新增或者删除这张表中的数据了。解决幻读的方式主要有以下几种:
-
-1. 将事务隔离级别调整为 `SERIALIZABLE` 。
-2. 在可重复读的事务级别下,给事务操作的这张表添加表锁。
-3. 在可重复读的事务级别下,给事务操作的这张表添加 `Next-key Lock(Record Lock+Gap Lock)`。
-
-### 参考
-
-- 《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎》
--
-- [Mysql 锁:灵魂七拷问](https://tech.youzan.com/seven-questions-about-the-lock-of-MySQL/)
-- [Innodb 中的事务隔离级别和锁的关系](https://tech.meituan.com/2014/08/20/innodb-lock.html)
+Next, let's look at some concurrency control statements we will use in the practical operations below:
-
+- `START TRANSACTION` | `BEGIN`: Explicitly starts a transaction.
+- \`COMMIT
diff --git a/docs/database/nosql.md b/docs/database/nosql.md
index d5ca59698bd..17bf3fa7070 100644
--- a/docs/database/nosql.md
+++ b/docs/database/nosql.md
@@ -1,61 +1,61 @@
---
-title: NoSQL基础知识总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of NoSQL Fundamentals
+category: Database
tag:
- NoSQL
- MongoDB
- Redis
---
-## NoSQL 是什么?
+## What is NoSQL?
-NoSQL(Not Only SQL 的缩写)泛指非关系型的数据库,主要针对的是键值、文档以及图形类型数据存储。并且,NoSQL 数据库天生支持分布式,数据冗余和数据分片等特性,旨在提供可扩展的高可用高性能数据存储解决方案。
+NoSQL (Not Only SQL) refers to non-relational databases that primarily target key-value, document, and graph data storage. Moreover, NoSQL databases naturally support distributed features, data redundancy, and data partitioning, aiming to provide scalable, high-availability, and high-performance data storage solutions.
-一个常见的误解是 NoSQL 数据库或非关系型数据库不能很好地存储关系型数据。NoSQL 数据库可以存储关系型数据—它们与关系型数据库的存储方式不同。
+A common misconception is that NoSQL databases or non-relational databases cannot store relational data well. NoSQL databases can store relational data—they just have a different storage method compared to relational databases.
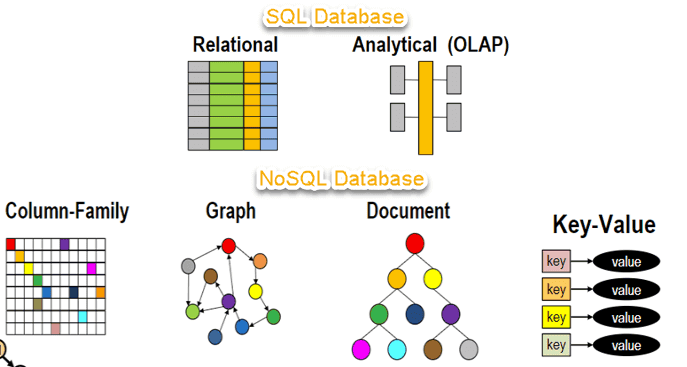
-NoSQL 数据库代表:HBase、Cassandra、MongoDB、Redis。
+Examples of NoSQL databases include: HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB, Redis.
-## SQL 和 NoSQL 有什么区别?
+## What are the differences between SQL and NoSQL?
-| | SQL 数据库 | NoSQL 数据库 |
-| :----------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| 数据存储模型 | 结构化存储,具有固定行和列的表格 | 非结构化存储。文档:JSON 文档,键值:键值对,宽列:包含行和动态列的表,图:节点和边 |
-| 发展历程 | 开发于 1970 年代,重点是减少数据重复 | 开发于 2000 年代后期,重点是提升可扩展性,减少大规模数据的存储成本 |
-| 例子 | Oracle、MySQL、Microsoft SQL Server、PostgreSQL | 文档:MongoDB、CouchDB,键值:Redis、DynamoDB,宽列:Cassandra、 HBase,图表:Neo4j、 Amazon Neptune、Giraph |
-| ACID 属性 | 提供原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性 (ACID) 属性 | 通常不支持 ACID 事务,为了可扩展、高性能进行了权衡,少部分支持比如 MongoDB 。不过,MongoDB 对 ACID 事务 的支持和 MySQL 还是有所区别的。 |
-| 性能 | 性能通常取决于磁盘子系统。要获得最佳性能,通常需要优化查询、索引和表结构。 | 性能通常由底层硬件集群大小、网络延迟以及调用应用程序来决定。 |
-| 扩展 | 垂直(使用性能更强大的服务器进行扩展)、读写分离、分库分表 | 横向(增加服务器的方式横向扩展,通常是基于分片机制) |
-| 用途 | 普通企业级的项目的数据存储 | 用途广泛比如图数据库支持分析和遍历连接数据之间的关系、键值数据库可以处理大量数据扩展和极高的状态变化 |
-| 查询语法 | 结构化查询语言 (SQL) | 数据访问语法可能因数据库而异 |
+| | SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases |
+| :------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| Data Storage Model | Structured storage with tables that have fixed rows and columns | Unstructured storage. Documents: JSON documents, Key-Value: Key-Value pairs, Wide Column: Tables with rows and dynamic columns, Graph: Nodes and edges |
+| Development History | Developed in the 1970s, focusing on reducing data duplication | Developed in the late 2000s, focusing on improving scalability and reducing storage costs for massive amounts of data |
+| Examples | Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL | Documents: MongoDB, CouchDB; Key-Value: Redis, DynamoDB; Wide Column: Cassandra, HBase; Graph: Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, Giraph |
+| ACID Properties | Provides Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID) properties | Generally does not support ACID transactions, making trade-offs for scalability and high performance; some, like MongoDB, support them, but differently than MySQL. |
+| Performance | Performance typically depends on the disk subsystem. To achieve optimal performance, optimizing queries, indexes, and table structures is often necessary. | Performance is usually determined by the size of the underlying hardware cluster, network latency, and the application calling. |
+| Scalability | Vertical (scaling up using more powerful servers), read-write separation, database sharding | Horizontal (scaling out by adding servers, usually based on sharding mechanisms) |
+| Use Cases | Data storage for typical enterprise-level projects | Wide-ranging uses, for example, graph databases support analysis and traversing relationships between connected data; key-value databases can handle massive data scaling and extreme state changes. |
+| Query Language | Structured Query Language (SQL) | Data access syntax may vary by database |
-## NoSQL 数据库有什么优势?
+## What are the advantages of NoSQL databases?
-NoSQL 数据库非常适合许多现代应用程序,例如移动、Web 和游戏等应用程序,它们需要灵活、可扩展、高性能和功能强大的数据库以提供卓越的用户体验。
+NoSQL databases are particularly suitable for many modern applications, such as mobile, web, and gaming applications, which require flexible, scalable, high-performance, and powerful databases to provide excellent user experiences.
-- **灵活性:** NoSQL 数据库通常提供灵活的架构,以实现更快速、更多的迭代开发。灵活的数据模型使 NoSQL 数据库成为半结构化和非结构化数据的理想之选。
-- **可扩展性:** NoSQL 数据库通常被设计为通过使用分布式硬件集群来横向扩展,而不是通过添加昂贵和强大的服务器来纵向扩展。
-- **高性能:** NoSQL 数据库针对特定的数据模型和访问模式进行了优化,这与尝试使用关系数据库完成类似功能相比可实现更高的性能。
-- **强大的功能:** NoSQL 数据库提供功能强大的 API 和数据类型,专门针对其各自的数据模型而构建。
+- **Flexibility:** NoSQL databases often provide flexible architectures for faster and more iterative development. Their flexible data models make NoSQL databases ideal for semi-structured and unstructured data.
+- **Scalability:** NoSQL databases are generally designed to scale horizontally by utilizing distributed hardware clusters rather than vertically scaling by adding expensive and powerful servers.
+- **High Performance:** NoSQL databases are optimized for specific data models and access patterns, achieving higher performance compared to trying to accomplish similar functions with a relational database.
+- **Powerful Features:** NoSQL databases offer powerful APIs and data types designed specifically for their respective data models.
-## NoSQL 数据库有哪些类型?
+## What types of NoSQL databases are there?
-NoSQL 数据库主要可以分为下面四种类型:
+NoSQL databases can primarily be divided into the following four types:
-- **键值**:键值数据库是一种较简单的数据库,其中每个项目都包含键和值。这是极为灵活的 NoSQL 数据库类型,因为应用可以完全控制 value 字段中存储的内容,没有任何限制。Redis 和 DynanoDB 是两款非常流行的键值数据库。
-- **文档**:文档数据库中的数据被存储在类似于 JSON(JavaScript 对象表示法)对象的文档中,非常清晰直观。每个文档包含成对的字段和值。这些值通常可以是各种类型,包括字符串、数字、布尔值、数组或对象等,并且它们的结构通常与开发者在代码中使用的对象保持一致。MongoDB 就是一款非常流行的文档数据库。
-- **图形**:图形数据库旨在轻松构建和运行与高度连接的数据集一起使用的应用程序。图形数据库的典型使用案例包括社交网络、推荐引擎、欺诈检测和知识图形。Neo4j 和 Giraph 是两款非常流行的图形数据库。
-- **宽列**:宽列存储数据库非常适合需要存储大量的数据。Cassandra 和 HBase 是两款非常流行的宽列存储数据库。
+- **Key-Value:** Key-value databases are a simpler type of database where each item consists of a key and a value. This is a very flexible type of NoSQL database because applications have complete control over the content stored in the value field, with no restrictions. Redis and DynamoDB are two popular key-value databases.
+- **Document:** Data in document databases is stored in documents resembling JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) objects, which are very clear and intuitive. Each document contains paired fields and values. These values can typically be of various types, including strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or objects, and their structure often aligns with the objects developers use in code. MongoDB is a very popular document database.
+- **Graph:** Graph databases are designed to make it easy to build and run applications that work with highly connected datasets. Typical use cases for graph databases include social networks, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and knowledge graphs. Neo4j and Giraph are two well-known graph databases.
+- **Wide Column:** Wide-column store databases are well-suited for scenarios requiring the storage of massive amounts of data. Cassandra and HBase are two popular wide-column storage databases.
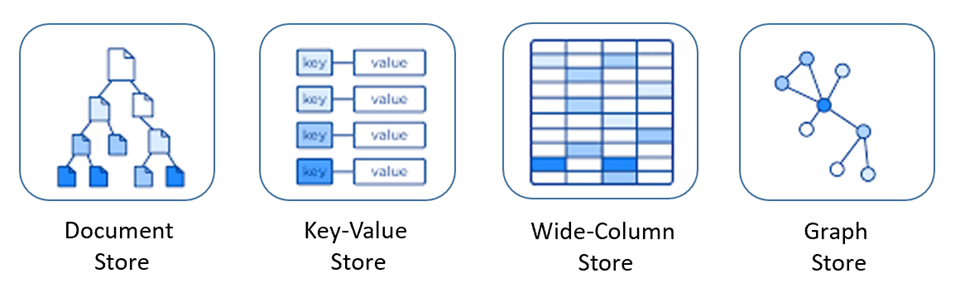
-下面这张图片来源于 [微软的官方文档 | 关系数据与 NoSQL 数据](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/relational-vs-nosql-data)。
+The image below is sourced from [Microsoft's official documentation | Relational Data vs. NoSQL Data](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/relational-vs-nosql-data).
-
+
-## 参考
+## References
-- NoSQL 是什么?- MongoDB 官方文档:
-- 什么是 NoSQL? - AWS:
-- NoSQL vs. SQL Databases - MongoDB 官方文档:
+- What is NoSQL? - MongoDB Official Documentation:
+- What is NoSQL? - AWS:
+- NoSQL vs. SQL Databases - MongoDB Official Documentation:
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md b/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
index 7ad88958704..ce2d47640e9 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
@@ -1,118 +1,87 @@
---
-title: 3种常用的缓存读写策略详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 3 Common Cache Read/Write Strategies
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-看到很多小伙伴简历上写了“**熟练使用缓存**”,但是被我问到“**缓存常用的 3 种读写策略**”的时候却一脸懵逼。
+I've seen many friends list "**proficient in using cache**" on their resumes, but when I ask them about the "**3 common read/write strategies for cache**," they often look confused.
-在我看来,造成这个问题的原因是我们在学习 Redis 的时候,可能只是简单写了一些 Demo,并没有去关注缓存的读写策略,或者说压根不知道这回事。
+In my opinion, this issue arises because when we learn Redis, we might only write some simple demos without paying attention to cache read/write strategies, or we might not even be aware of them.
-但是,搞懂 3 种常见的缓存读写策略对于实际工作中使用缓存以及面试中被问到缓存都是非常有帮助的!
+However, understanding the 3 common cache read/write strategies is very helpful for using cache in real work and for interview questions about cache!
-**下面介绍到的三种模式各有优劣,不存在最佳模式,根据具体的业务场景选择适合自己的缓存读写模式。**
+**The three patterns introduced below each have their pros and cons; there is no best pattern. Choose a cache read/write pattern that suits your specific business scenario.**
-### Cache Aside Pattern(旁路缓存模式)
+### Cache Aside Pattern
-**Cache Aside Pattern 是我们平时使用比较多的一个缓存读写模式,比较适合读请求比较多的场景。**
+**The Cache Aside Pattern is a commonly used cache read/write pattern, particularly suitable for scenarios with a high volume of read requests.**
-Cache Aside Pattern 中服务端需要同时维系 db 和 cache,并且是以 db 的结果为准。
+In the Cache Aside Pattern, the server needs to maintain both the database (db) and the cache, with the db results being the authoritative source.
-下面我们来看一下这个策略模式下的缓存读写步骤。
+Let's take a look at the steps for reading and writing cache under this strategy.
-**写**:
+**Write:**
-- 先更新 db
-- 然后直接删除 cache 。
+- First, update the db.
+- Then, delete the cache directly.
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解写的步骤。
+Here’s a simple diagram to help you understand the writing steps.

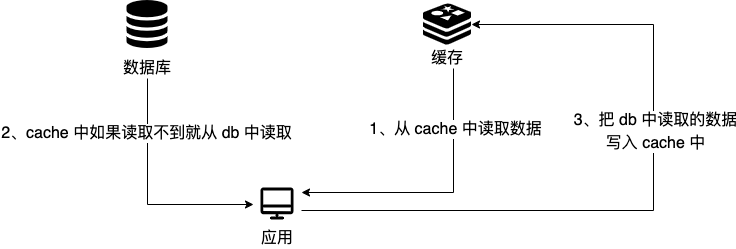
-**读** :
+**Read:**
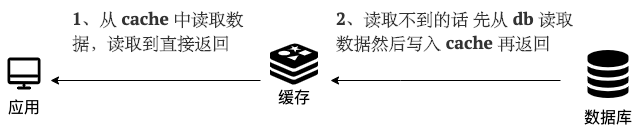
-- 从 cache 中读取数据,读取到就直接返回
-- cache 中读取不到的话,就从 db 中读取数据返回
-- 再把数据放到 cache 中。
+- Read data from the cache; if found, return it directly.
+- If not found in the cache, read the data from the db and return it.
+- Then, place the data into the cache.
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解读的步骤。
+Here’s a simple diagram to help you understand the reading steps.
-你仅仅了解了上面这些内容的话是远远不够的,我们还要搞懂其中的原理。
+If you only understand the above content, it is far from enough; we also need to grasp the underlying principles.
-比如说面试官很可能会追问:“**在写数据的过程中,可以先删除 cache ,后更新 db 么?**”
+For example, the interviewer might follow up with: "**During the data writing process, can we delete the cache first and then update the db?**"
-**答案:** 那肯定是不行的!因为这样可能会造成 **数据库(db)和缓存(Cache)数据不一致**的问题。
+**Answer:** Absolutely not! Because this could lead to the problem of **inconsistency between the database (db) and the cache.**
-举例:请求 1 先写数据 A,请求 2 随后读数据 A 的话,就很有可能产生数据不一致性的问题。
+For instance: If request 1 writes data A first, and request 2 subsequently reads data A, it is very likely to cause data inconsistency.
-这个过程可以简单描述为:
+This process can be simply described as:
-> 请求 1 先把 cache 中的 A 数据删除 -> 请求 2 从 db 中读取数据->请求 1 再把 db 中的 A 数据更新
+> Request 1 deletes data A from the cache -> Request 2 reads data from the db -> Request 1 updates data A in the db.
-当你这样回答之后,面试官可能会紧接着就追问:“**在写数据的过程中,先更新 db,后删除 cache 就没有问题了么?**”
+After you answer this, the interviewer might immediately ask: "**During the data writing process, is it okay to update the db first and then delete the cache?**"
-**答案:** 理论上来说还是可能会出现数据不一致性的问题,不过概率非常小,因为缓存的写入速度是比数据库的写入速度快很多。
+**Answer:** Theoretically, there could still be a problem with data inconsistency, but the probability is very low because the write speed of the cache is much faster than that of the database.
-举例:请求 1 先读数据 A,请求 2 随后写数据 A,并且数据 A 在请求 1 请求之前不在缓存中的话,也有可能产生数据不一致性的问题。
+For example: If request 1 reads data A first, and request 2 subsequently writes data A, and data A is not in the cache before request 1, there could still be a problem with data inconsistency.
-这个过程可以简单描述为:
+This process can be simply described as:
-> 请求 1 从 db 读数据 A-> 请求 2 更新 db 中的数据 A(此时缓存中无数据 A ,故不用执行删除缓存操作 ) -> 请求 1 将数据 A 写入 cache
+> Request 1 reads data A from the db -> Request 2 updates data A in the db (at this point, there is no data A in the cache, so no cache deletion is needed) -> Request 1 writes data A into the cache.
-现在我们再来分析一下 **Cache Aside Pattern 的缺陷**。
+Now let's analyze the **deficiencies of the Cache Aside Pattern**.
-**缺陷 1:首次请求数据一定不在 cache 的问题**
+**Deficiency 1: The issue that the first request for data is definitely not in the cache.**
-解决办法:可以将热点数据可以提前放入 cache 中。
+Solution: Hot data can be preloaded into the cache.
-**缺陷 2:写操作比较频繁的话导致 cache 中的数据会被频繁被删除,这样会影响缓存命中率 。**
+**Deficiency 2: Frequent write operations can lead to data being frequently deleted from the cache, which affects the cache hit rate.**
-解决办法:
+Solutions:
-- 数据库和缓存数据强一致场景:更新 db 的时候同样更新 cache,不过我们需要加一个锁/分布式锁来保证更新 cache 的时候不存在线程安全问题。
-- 可以短暂地允许数据库和缓存数据不一致的场景:更新 db 的时候同样更新 cache,但是给缓存加一个比较短的过期时间,这样的话就可以保证即使数据不一致的话影响也比较小。
+- For scenarios requiring strong consistency between the database and cache: Update the cache when updating the db, but we need to add a lock/distributed lock to ensure thread safety when updating the cache.
+- For scenarios where temporary inconsistency between the database and cache is acceptable: Update the cache when updating the db, but set a relatively short expiration time for the cache, which can ensure that even if data is inconsistent, the impact is minimal.
-### Read/Write Through Pattern(读写穿透)
+### Read/Write Through Pattern
-Read/Write Through Pattern 中服务端把 cache 视为主要数据存储,从中读取数据并将数据写入其中。cache 服务负责将此数据读取和写入 db,从而减轻了应用程序的职责。
+In the Read/Write Through Pattern, the server treats the cache as the primary data store, reading data from it and writing data into it. The cache service is responsible for reading and writing this data to the db, thereby reducing the responsibilities of the application.
-这种缓存读写策略小伙伴们应该也发现了在平时在开发过程中非常少见。抛去性能方面的影响,大概率是因为我们经常使用的分布式缓存 Redis 并没有提供 cache 将数据写入 db 的功能。
+This cache read/write strategy is also rarely seen in our development process. Aside from performance impacts, it is likely because the distributed cache we often use, Redis, does not provide the functionality for the cache to write data to the db.
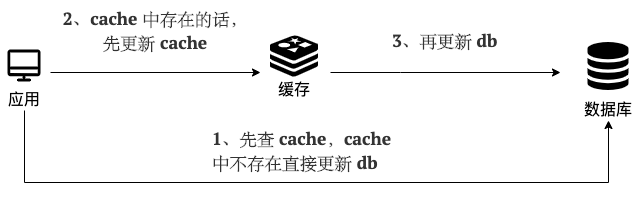
-**写(Write Through):**
+**Write (Write Through):**
-- 先查 cache,cache 中不存在,直接更新 db。
-- cache 中存在,则先更新 cache,然后 cache 服务自己更新 db(**同步更新 cache 和 db**)。
-
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解写的步骤。
-
-
-
-**读(Read Through):**
-
-- 从 cache 中读取数据,读取到就直接返回 。
-- 读取不到的话,先从 db 加载,写入到 cache 后返回响应。
-
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解读的步骤。
-
-
-
-Read-Through Pattern 实际只是在 Cache-Aside Pattern 之上进行了封装。在 Cache-Aside Pattern 下,发生读请求的时候,如果 cache 中不存在对应的数据,是由客户端自己负责把数据写入 cache,而 Read Through Pattern 则是 cache 服务自己来写入缓存的,这对客户端是透明的。
-
-和 Cache Aside Pattern 一样, Read-Through Pattern 也有首次请求数据一定不再 cache 的问题,对于热点数据可以提前放入缓存中。
-
-### Write Behind Pattern(异步缓存写入)
-
-Write Behind Pattern 和 Read/Write Through Pattern 很相似,两者都是由 cache 服务来负责 cache 和 db 的读写。
-
-但是,两个又有很大的不同:**Read/Write Through 是同步更新 cache 和 db,而 Write Behind 则是只更新缓存,不直接更新 db,而是改为异步批量的方式来更新 db。**
-
-很明显,这种方式对数据一致性带来了更大的挑战,比如 cache 数据可能还没异步更新 db 的话,cache 服务可能就就挂掉了。
-
-这种策略在我们平时开发过程中也非常非常少见,但是不代表它的应用场景少,比如消息队列中消息的异步写入磁盘、MySQL 的 Innodb Buffer Pool 机制都用到了这种策略。
-
-Write Behind Pattern 下 db 的写性能非常高,非常适合一些数据经常变化又对数据一致性要求没那么高的场景,比如浏览量、点赞量。
-
-
+- First, check the cache; if it does not exist, directly update the db.
+- If it exists in the cache, first update the cache, then the
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md b/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
index 391e5bec82d..b82a91c1d3d 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: 缓存基础常见面试题总结(付费)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Interview Questions on Cache Basics (Paid)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-**缓存基础** 相关的面试题为我的 [知识星球](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)中。
+Interview questions related to **cache basics** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md) (click the link to view detailed introduction and joining method), and have been organized into [“Java Interview Guide”](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md).

diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
index e3ef2efd04c..480596dd84b 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: Redis集群详解(付费)
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Clusters (Paid)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-**Redis 集群** 相关的面试题为我的 [知识星球](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)中。
+The interview questions related to **Redis Clusters** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md) (click the link for a detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled in [《Java Interview Guide》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md).
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
index 9aec17fc0cc..62342697a2d 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
@@ -1,146 +1,144 @@
---
-title: Redis常见阻塞原因总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Blocking Reasons in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-> 本文整理完善自: ,作者:阿 Q 说代码
+> This article is compiled and perfected from: , author: A Q Talks Code
-这篇文章会详细总结一下可能导致 Redis 阻塞的情况,这些情况也是影响 Redis 性能的关键因素,使用 Redis 的时候应该格外注意!
+This article will summarize in detail the situations that may cause Redis blocking, which are also key factors affecting Redis performance. Care should be taken when using Redis!
-## O(n) 命令
+## O(n) Commands
-Redis 中的大部分命令都是 O(1)时间复杂度,但也有少部分 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令,例如:
+Most commands in Redis have an O(1) time complexity, but there are also a few commands with O(n) time complexity, such as:
-- `KEYS *`:会返回所有符合规则的 key。
-- `HGETALL`:会返回一个 Hash 中所有的键值对。
-- `LRANGE`:会返回 List 中指定范围内的元素。
-- `SMEMBERS`:返回 Set 中的所有元素。
-- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`:计算多个 Set 的交集/并集/差集。
+- `KEYS *`: Returns all keys that match the rules.
+- `HGETALL`: Returns all key-value pairs in a Hash.
+- `LRANGE`: Returns elements within a specified range in a List.
+- `SMEMBERS`: Returns all elements in a Set.
+- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`: Calculates the intersection/union/difference of multiple Sets.
- ……
-由于这些命令时间复杂度是 O(n),有时候也会全表扫描,随着 n 的增大,执行耗时也会越长,从而导致客户端阻塞。不过, 这些命令并不是一定不能使用,但是需要明确 N 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
+Due to the O(n) time complexity of these commands, sometimes a full table scan occurs. As n increases, the execution time will also increase, leading to client blocking. However, these commands are not entirely unusable, but the value of N needs to be clarified. If there is a need for traversal, `HSCAN`, `SSCAN`, or `ZSCAN` can be used instead.
-除了这些 O(n)时间复杂度的命令可能会导致阻塞之外, 还有一些时间复杂度可能在 O(N) 以上的命令,例如:
+In addition to these O(n) time complexity commands that may cause blocking, there are also commands with time complexities potentially greater than O(N), such as:
-- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`:返回指定 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量, m 为返回的元素数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`:移除 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围/指定 score 范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量, m 被删除元素的数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
+- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`: Returns all elements within a specified ranking range in a Sorted Set. The time complexity is O(log(n)+m), where n is the total number of elements and m is the number of elements returned. When m and n are relatively large, the time complexity O(n) is smaller.
+- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`: Removes all elements within a specified ranking range/specified score range in a Sorted Set. The time complexity is O(log(n)+m), where n is the total number of elements and m is the number of deleted elements. When m and n are relatively large, the time complexity O(n) is smaller.
- ……
-## SAVE 创建 RDB 快照
+## SAVE Creating RDB Snapshots
-Redis 提供了两个命令来生成 RDB 快照文件:
+Redis provides two commands to generate RDB snapshot files:
-- `save` : 同步保存操作,会阻塞 Redis 主线程;
-- `bgsave` : fork 出一个子进程,子进程执行,不会阻塞 Redis 主线程,默认选项。
+- `save`: Synchronously saves operations and blocks the Redis main thread.
+- `bgsave`: Forks a child process to execute, which does not block the Redis main thread, the default option.
-默认情况下,Redis 默认配置会使用 `bgsave` 命令。如果手动使用 `save` 命令生成 RDB 快照文件的话,就会阻塞主线程。
+By default, Redis will use the `bgsave` command. If you manually use the `save` command to generate RDB snapshot files, it will block the main thread.
## AOF
-### AOF 日志记录阻塞
+### AOF Log Record Blocking
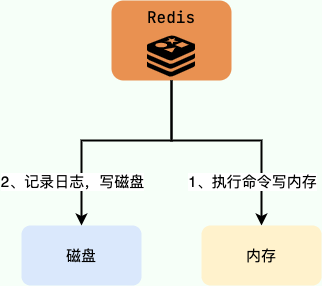
-Redis AOF 持久化机制是在执行完命令之后再记录日志,这和关系型数据库(如 MySQL)通常都是执行命令之前记录日志(方便故障恢复)不同。
+Redis's AOF persistence mechanism records logs after executing commands, differing from relational databases (like MySQL), which usually log before executing commands for recovery purposes.
-
+
-**为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志呢?**
+**Why record logs after executing commands?**
-- 避免额外的检查开销,AOF 记录日志不会对命令进行语法检查;
-- 在命令执行完之后再记录,不会阻塞当前的命令执行。
+- To avoid extra checking overhead, AOF log recording does not perform syntax checking on commands.
+- Logging after command execution does not block the current command execution.
-这样也带来了风险(我在前面介绍 AOF 持久化的时候也提到过):
+This also brings risks (which I mentioned when introducing AOF persistence):
-- 如果刚执行完命令 Redis 就宕机会导致对应的修改丢失;
-- **可能会阻塞后续其他命令的执行(AOF 记录日志是在 Redis 主线程中进行的)**。
+- If Redis crashes right after executing a command, the corresponding modifications may be lost.
+- **It may block the execution of subsequent commands (AOF log recording is conducted in the Redis main thread).**
-### AOF 刷盘阻塞
+### AOF Flush Blocking
-开启 AOF 持久化后每执行一条会更改 Redis 中的数据的命令,Redis 就会将该命令写入到 AOF 缓冲区 `server.aof_buf` 中,然后再根据 `appendfsync` 配置来决定何时将其同步到硬盘中的 AOF 文件。
+After enabling AOF persistence, every command that changes data in Redis will write that command to the AOF buffer `server.aof_buf`, and then according to the `appendfsync` configuration, it decides when to synchronize it to the AOF file on the hard disk.
-在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式( `fsync`策略),它们分别是:
+There are three different AOF persistence methods (fsync strategy) in Redis's configuration file:
-1. `appendfsync always`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后,后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)立即会调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件(刷盘),`fsync` 完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低 Redis 的性能(`write` + `fsync`)。
-2. `appendfsync everysec`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,由后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)每秒钟调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用)同步一次 AOF 文件(`write`+`fsync`,`fsync`间隔为 1 秒)
-3. `appendfsync no`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,让操作系统决定何时进行同步,Linux 下一般为 30 秒一次(`write`但不`fsync`,`fsync` 的时机由操作系统决定)。
+1. `appendfsync always`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation, after which the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) immediately calls the `fsync` function to sync the AOF file (flush). After `fsync` completes, the thread returns; this will severely decrease Redis's performance (write + fsync).
+1. `appendfsync everysec`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation and immediately returns, with the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) calling the `fsync` function once every second to sync the AOF file (write + fsync, the fsync interval is 1 second).
+1. `appendfsync no`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation and immediately returns, allowing the operating system to decide when to sync, which is usually once every 30 seconds on Linux (write but no fsync; the timing of fsync is determined by the operating system).
-当后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件时,需要等待,直到写入完成。当磁盘压力太大的时候,会导致 `fsync` 操作发生阻塞,主线程调用 `write` 函数时也会被阻塞。`fsync` 完成后,主线程执行 `write` 才能成功返回。
+When the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) calls the `fsync` function to sync the AOF file, it needs to wait until the writing is complete. When there is too much disk pressure, blocking may occur during the `fsync` operation, and the main thread calling `write` will also be blocked. The main thread can only return successfully after `fsync` completes.
-关于 AOF 工作流程的详细介绍可以查看:[Redis 持久化机制详解](./redis-persistence.md),有助于理解 AOF 刷盘阻塞。
+For a detailed introduction to the AOF workflow, you can refer to: [Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanism](./redis-persistence.md), which helps understand AOF flush blocking.
-### AOF 重写阻塞
+### AOF Rewrite Blocking
-1. fork 出一条子线程来将文件重写,在执行 `BGREWRITEAOF` 命令时,Redis 服务器会维护一个 AOF 重写缓冲区,该缓冲区会在子线程创建新 AOF 文件期间,记录服务器执行的所有写命令。
-2. 当子线程完成创建新 AOF 文件的工作之后,服务器会将重写缓冲区中的所有内容追加到新 AOF 文件的末尾,使得新的 AOF 文件保存的数据库状态与现有的数据库状态一致。
-3. 最后,服务器用新的 AOF 文件替换旧的 AOF 文件,以此来完成 AOF 文件重写操作。
+1. A child thread is forked to rewrite the file. When executing the `BGREWRITEAOF` command, the Redis server maintains an AOF rewrite buffer that records all write commands executed by the server during the child thread's creation of the new AOF file.
+1. After the child thread completes the task of creating the new AOF file, the server appends all content from the rewrite buffer to the end of the new AOF file, ensuring that the new AOF file preserves the database state consistent with the existing database state.
+1. Finally, the server replaces the old AOF file with the new AOF file to complete the AOF file rewrite operation.
-阻塞就是出现在第 2 步的过程中,将缓冲区中新数据写到新文件的过程中会产生**阻塞**。
+Blocking occurs during the process of step 2 when writing new data from the buffer to the new file, causing a **block**.
-相关阅读:[Redis AOF 重写阻塞问题分析](https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1633077)。
+For further reading: [Analysis of Redis AOF Rewrite Blocking Issues](https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1633077).
-## 大 Key
+## Big Key
-如果一个 key 对应的 value 所占用的内存比较大,那这个 key 就可以看作是 bigkey。具体多大才算大呢?有一个不是特别精确的参考标准:
+If the value corresponding to a key occupies a large amount of memory, that key can be considered a big key. What exactly counts as large? There is a rather imprecise reference standard:
-- string 类型的 value 超过 1MB
-- 复合类型(列表、哈希、集合、有序集合等)的 value 包含的元素超过 5000 个(对于复合类型的 value 来说,不一定包含的元素越多,占用的内存就越多)。
+- String-type values exceeding 1MB.
+- Composite types (lists, hashes, sets, sorted sets, etc.) whose values contain more than 5000 elements (for composite types, having more elements does not necessarily mean occupying more memory).
-大 key 造成的阻塞问题如下:
+The blocking issues caused by big keys are as follows:
-- 客户端超时阻塞:由于 Redis 执行命令是单线程处理,然后在操作大 key 时会比较耗时,那么就会阻塞 Redis,从客户端这一视角看,就是很久很久都没有响应。
-- 引发网络阻塞:每次获取大 key 产生的网络流量较大,如果一个 key 的大小是 1 MB,每秒访问量为 1000,那么每秒会产生 1000MB 的流量,这对于普通千兆网卡的服务器来说是灾难性的。
-- 阻塞工作线程:如果使用 del 删除大 key 时,会阻塞工作线程,这样就没办法处理后续的命令。
+- Client timeout blocking: Since Redis executes commands in a single-threaded manner, operations on big keys can be time-consuming, causing Redis to block, resulting in the client not responding for an extended period.
+- Causing network blocking: The network traffic generated when retrieving big keys is relatively large. If a key's size is 1MB and the access frequency is 1000 per second, it will generate 1000MB of traffic per second, which is disastrous for a typical gigabit network card server.
+- Blocking worker threads: If deleting a big key using del, it will block worker threads, preventing subsequent commands from being processed.
-### 查找大 key
+### Finding Big Keys
-当我们在使用 Redis 自带的 `--bigkeys` 参数查找大 key 时,最好选择在从节点上执行该命令,因为主节点上执行时,会**阻塞**主节点。
+When using Redis's built-in `--bigkeys` parameter to find big keys, it is best to execute the command on a slave node, as executing it on the master node will **block** the master node.
-- 我们还可以使用 SCAN 命令来查找大 key;
+- We can also use the SCAN command to find big keys;
+- Analyzing RDB files to identify big keys requires that Redis is using RDB persistence. There are tools available online:
+ - redis-rdb-tools: A Python tool for analyzing Redis RDB snapshot files.
+ - rdb_bigkeys: A Go tool for analyzing Redis RDB snapshot files, which performs better.
-- 通过分析 RDB 文件来找出 big key,这种方案的前提是 Redis 采用的是 RDB 持久化。网上有现成的工具:
+### Deleting Big Keys
-- - redis-rdb-tools:Python 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具
- - rdb_bigkeys:Go 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具,性能更好。
+The essence of the delete operation is to free the memory space occupied by key-value pairs.
-### 删除大 key
+Freeing memory is just the first step. To manage memory space more efficiently, when an application releases memory, **the operating system needs to insert the released memory blocks into a linked list of free memory blocks** for subsequent management and reallocation. This process itself requires some time and can **block** the current application that is freeing memory.
-删除操作的本质是要释放键值对占用的内存空间。
+Therefore, if a large amount of memory is released at once, the time required for managing the linked list of free memory blocks will increase, consequently causing blocking in the Redis main thread. If the main thread becomes blocked, all other requests may timeout, leading to increasing timeouts that can exhaust Redis connections and generate various exceptions.
-释放内存只是第一步,为了更加高效地管理内存空间,在应用程序释放内存时,**操作系统需要把释放掉的内存块插入一个空闲内存块的链表**,以便后续进行管理和再分配。这个过程本身需要一定时间,而且会**阻塞**当前释放内存的应用程序。
+When deleting big keys, it is recommended to use batch deletions and asynchronous deletions.
-所以,如果一下子释放了大量内存,空闲内存块链表操作时间就会增加,相应地就会造成 Redis 主线程的阻塞,如果主线程发生了阻塞,其他所有请求可能都会超时,超时越来越多,会造成 Redis 连接耗尽,产生各种异常。
+## Clearing the Database
-删除大 key 时建议采用分批次删除和异步删除的方式进行。
+Clearing the database is similar to the deletion of big keys; `flushdb` and `flushall` involve the deletion and release of all key-value pairs, which are also blocking points in Redis.
-## 清空数据库
+## Cluster Expansion
-清空数据库和上面 bigkey 删除也是同样道理,`flushdb`、`flushall` 也涉及到删除和释放所有的键值对,也是 Redis 的阻塞点。
+Redis clusters can dynamically scale up and down nodes. This process is currently semi-automated and requires manual intervention.
-## 集群扩容
+During the expansion or contraction, data migration is needed. Redis ensures the consistency of migration; all migration operations are synchronous.
-Redis 集群可以进行节点的动态扩容缩容,这一过程目前还处于半自动状态,需要人工介入。
+During migration, both ends of Redis will enter a blocking state for varying durations. For small keys, this time can be negligible, but if a key's memory usage is too large, it can trigger failover within the cluster, causing unnecessary switching.
-在扩缩容的时候,需要进行数据迁移。而 Redis 为了保证迁移的一致性,迁移所有操作都是同步操作。
+## Swap
-执行迁移时,两端的 Redis 均会进入时长不等的阻塞状态,对于小 Key,该时间可以忽略不计,但如果一旦 Key 的内存使用过大,严重的时候会触发集群内的故障转移,造成不必要的切换。
+**What is Swap?** Swap refers to the exchange, and in Linux, Swap is often called memory swapping or swap partition. Similar to virtual memory in Windows, it solves memory shortages by virtualizing some hard disk space to be used as memory. Thus, the purpose of the Swap partition is to sacrifice hard disk space to increase memory and address the issue of insufficient or overloaded VPS memory.
-## Swap(内存交换)
+Swap can be very detrimental to Redis. One important premise for Redis to ensure high performance is that all data exists in memory. If the operating system swaps out some of the memory used by Redis to the hard disk, the read and write speeds of memory and hard disk differ by several orders of magnitude, leading to a drastic decline in Redis performance after the swap.
-**什么是 Swap?** Swap 直译过来是交换的意思,Linux 中的 Swap 常被称为内存交换或者交换分区。类似于 Windows 中的虚拟内存,就是当内存不足的时候,把一部分硬盘空间虚拟成内存使用,从而解决内存容量不足的情况。因此,Swap 分区的作用就是牺牲硬盘,增加内存,解决 VPS 内存不够用或者爆满的问题。
+Here are methods to check if Redis is experiencing Swap:
-Swap 对于 Redis 来说是非常致命的,Redis 保证高性能的一个重要前提是所有的数据在内存中。如果操作系统把 Redis 使用的部分内存换出硬盘,由于内存与硬盘的读写速度差几个数量级,会导致发生交换后的 Redis 性能急剧下降。
-
-识别 Redis 发生 Swap 的检查方法如下:
-
-1、查询 Redis 进程号
+1. Query the Redis process ID
```bash
redis-cli -p 6383 info server | grep process_id
process_id: 4476
```
-2、根据进程号查询内存交换信息
+2. Check memory swap information based on the process ID
```bash
cat /proc/4476/smaps | grep Swap
@@ -152,27 +150,27 @@ Swap: 0kB
.....
```
-如果交换量都是 0KB 或者个别的是 4KB,则正常。
+If the swap amounts are all 0KB or a few are 4KB, it is normal.
-预防内存交换的方法:
+Methods to prevent memory swapping:
-- 保证机器充足的可用内存
-- 确保所有 Redis 实例设置最大可用内存(maxmemory),防止极端情况 Redis 内存不可控的增长
-- 降低系统使用 swap 优先级,如`echo 10 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness`
+- Ensure ample available memory on the machine.
+- Ensure all Redis instances set a maximum available memory (maxmemory) to prevent uncontrolled growth of Redis memory in extreme situations.
+- Lower the system's swap priority, such as `echo 10 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness`.
-## CPU 竞争
+## CPU Competition
-Redis 是典型的 CPU 密集型应用,不建议和其他多核 CPU 密集型服务部署在一起。当其他进程过度消耗 CPU 时,将严重影响 Redis 的吞吐量。
+Redis is a typical CPU-intensive application and should not be deployed alongside other multi-core CPU-intensive services. When other processes excessively consume CPU, it will severely affect Redis's throughput.
-可以通过`redis-cli --stat`获取当前 Redis 使用情况。通过`top`命令获取进程对 CPU 的利用率等信息 通过`info commandstats`统计信息分析出命令不合理开销时间,查看是否是因为高算法复杂度或者过度的内存优化问题。
+You can use `redis-cli --stat` to get the current Redis usage. The `top` command can be used to get information on processes' CPU utilization, and `info commandstats` can provide statistics to analyze unreasonable command overhead, checking if it is due to high algorithm complexity or excessive memory optimization issues.
-## 网络问题
+## Network Issues
-连接拒绝、网络延迟,网卡软中断等网络问题也可能会导致 Redis 阻塞。
+Connection refusals, network delays, software interrupts on network cards, and other network issues might also lead to Redis blocking.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Redis 阻塞的 6 大类场景分析与总结:
-- Redis 开发与运维笔记-Redis 的噩梦-阻塞:
+- Analysis and Summary of 6 Major Scenarios of Redis Blocking:
+- Redis Development and Operation Notes - The Nightmare of Redis - Blocking:
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
index 9dfb0c3eaa5..0e7d5a4d03f 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
@@ -1,69 +1,69 @@
---
-title: Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 5 Basic Data Types in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis常见数据类型
+ content: Common data types in Redis
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis基础数据类型总结:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)
+ content: Summary of Redis basic data types: String, List, Set, Hash, Zset
---
-Redis 共有 5 种基本数据类型:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)。
+Redis has a total of 5 basic data types: String, List, Set, Hash, and Zset.
-这 5 种数据类型是直接提供给用户使用的,是数据的保存形式,其底层实现主要依赖这 8 种数据结构:简单动态字符串(SDS)、LinkedList(双向链表)、Dict(哈希表/字典)、SkipList(跳跃表)、Intset(整数集合)、ZipList(压缩列表)、QuickList(快速列表)。
+These 5 data types are directly provided for user use and represent the form of data storage. Their underlying implementation mainly relies on these 8 data structures: Simple Dynamic Strings (SDS), LinkedList, Dict (hash table/dictionary), SkipList, Intset (integer set), ZipList (compressed list), and QuickList.
-Redis 5 种基本数据类型对应的底层数据结构实现如下表所示:
+The underlying data structure implementations corresponding to the 5 basic data types in Redis are shown in the table below:
| String | List | Hash | Set | Zset |
| :----- | :--------------------------- | :------------ | :----------- | :---------------- |
-| SDS | LinkedList/ZipList/QuickList | Dict、ZipList | Dict、Intset | ZipList、SkipList |
+| SDS | LinkedList/ZipList/QuickList | Dict, ZipList | Dict, Intset | ZipList, SkipList |
-Redis 3.2 之前,List 底层实现是 LinkedList 或者 ZipList。 Redis 3.2 之后,引入了 LinkedList 和 ZipList 的结合 QuickList,List 的底层实现变为 QuickList。从 Redis 7.0 开始, ZipList 被 ListPack 取代。
+Before Redis 3.2, the underlying implementation of List was LinkedList or ZipList. After Redis 3.2, QuickList, a combination of LinkedList and ZipList, was introduced, and the underlying implementation of List changed to QuickList. Starting from Redis 7.0, ZipList has been replaced by ListPack.
-你可以在 Redis 官网上找到 Redis 数据类型/结构非常详细的介绍:
+You can find a very detailed introduction to Redis data types/structures on the official Redis website:
- [Redis Data Structures](https://redis.com/redis-enterprise/data-structures/)
- [Redis Data types tutorial](https://redis.io/docs/manual/data-types/data-types-tutorial/)
-未来随着 Redis 新版本的发布,可能会有新的数据结构出现,通过查阅 Redis 官网对应的介绍,你总能获取到最靠谱的信息。
+In the future, with the release of new versions of Redis, new data structures may appear. By consulting the corresponding introductions on the Redis official website, you can always obtain the most reliable information.
-## String(字符串)
+## String
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-String 是 Redis 中最简单同时也是最常用的一个数据类型。
+String is the simplest and most commonly used data type in Redis.
-String 是一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。
+String is a binary-safe data type that can be used to store any type of data, such as strings, integers, floating-point numbers, images (base64 encoding or decoding of images or image paths), and serialized objects.
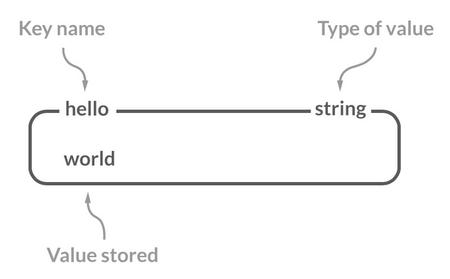
-虽然 Redis 是用 C 语言写的,但是 Redis 并没有使用 C 的字符串表示,而是自己构建了一种 **简单动态字符串**(Simple Dynamic String,**SDS**)。相比于 C 的原生字符串,Redis 的 SDS 不光可以保存文本数据还可以保存二进制数据,并且获取字符串长度复杂度为 O(1)(C 字符串为 O(N)),除此之外,Redis 的 SDS API 是安全的,不会造成缓冲区溢出。
+Although Redis is written in C, it does not use C's string representation but instead constructs a **Simple Dynamic String** (SDS). Compared to C's native strings, Redis's SDS can not only store text data but also binary data, and the complexity of obtaining the string length is O(1) (C strings are O(N)). In addition, Redis's SDS API is safe and does not cause buffer overflows.
-### 常用命令
+### Common Commands
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------- | -------------------------------- |
-| SET key value | 设置指定 key 的值 |
-| SETNX key value | 只有在 key 不存在时设置 key 的值 |
-| GET key | 获取指定 key 的值 |
-| MSET key1 value1 key2 value2 …… | 设置一个或多个指定 key 的值 |
-| MGET key1 key2 ... | 获取一个或多个指定 key 的值 |
-| STRLEN key | 返回 key 所储存的字符串值的长度 |
-| INCR key | 将 key 中储存的数字值增一 |
-| DECR key | 将 key 中储存的数字值减一 |
-| EXISTS key | 判断指定 key 是否存在 |
-| DEL key(通用) | 删除指定的 key |
-| EXPIRE key seconds(通用) | 给指定 key 设置过期时间 |
+| Command | Description |
+| -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------- |
+| SET key value | Set the value of the specified key |
+| SETNX key value | Set the value of the key only if it does not exist |
+| GET key | Get the value of the specified key |
+| MSET key1 value1 key2 value2 ... | Set the values of one or more specified keys |
+| MGET key1 key2 ... | Get the values of one or more specified keys |
+| STRLEN key | Return the length of the string value stored at key |
+| INCR key | Increment the numeric value stored at key by one |
+| DECR key | Decrement the numeric value stored at key by one |
+| EXISTS key | Determine if the specified key exists |
+| DEL key (general) | Delete the specified key |
+| EXPIRE key seconds (general) | Set an expiration time for the specified key |
-更多 Redis String 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
+For more Redis String commands and detailed usage guides, please refer to the corresponding introduction on the Redis official website: .
-**基本操作**:
+**Basic Operations**:
```bash
> SET key value
@@ -80,424 +80,22 @@ OK
(nil)
```
-**批量设置**:
+**Batch Setting**:
```bash
> MSET key1 value1 key2 value2
OK
-> MGET key1 key2 # 批量获取多个 key 对应的 value
+> MGET key1 key2 # Batch get the values corresponding to multiple keys
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
```
-**计数器(字符串的内容为整数的时候可以使用):**
+**Counter (when the content of the string is an integer)**:
```bash
> SET number 1
OK
-> INCR number # 将 key 中储存的数字值增一
+> INCR number # Increment the numeric value stored at key by one
(integer) 2
> GET number
-"2"
-> DECR number # 将 key 中储存的数字值减一
-(integer) 1
-> GET number
-"1"
-```
-
-**设置过期时间(默认为永不过期)**:
-
-```bash
-> EXPIRE key 60
-(integer) 1
-> SETEX key 60 value # 设置值并设置过期时间
-OK
-> TTL key
-(integer) 56
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要存储常规数据的场景**
-
-- 举例:缓存 Session、Token、图片地址、序列化后的对象(相比较于 Hash 存储更节省内存)。
-- 相关命令:`SET`、`GET`。
-
-**需要计数的场景**
-
-- 举例:用户单位时间的请求数(简单限流可以用到)、页面单位时间的访问数。
-- 相关命令:`SET`、`GET`、 `INCR`、`DECR` 。
-
-**分布式锁**
-
-利用 `SETNX key value` 命令可以实现一个最简易的分布式锁(存在一些缺陷,通常不建议这样实现分布式锁)。
-
-## List(列表)
-
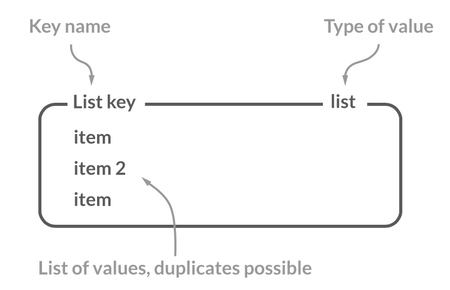
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 List 其实就是链表数据结构的实现。我在 [线性数据结构 :数组、链表、栈、队列](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/linear-data-structure.html) 这篇文章中详细介绍了链表这种数据结构,我这里就不多做介绍了。
-
-许多高级编程语言都内置了链表的实现比如 Java 中的 `LinkedList`,但是 C 语言并没有实现链表,所以 Redis 实现了自己的链表数据结构。Redis 的 List 的实现为一个 **双向链表**,即可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了部分额外的内存开销。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
-| RPUSH key value1 value2 ... | 在指定列表的尾部(右边)添加一个或多个元素 |
-| LPUSH key value1 value2 ... | 在指定列表的头部(左边)添加一个或多个元素 |
-| LSET key index value | 将指定列表索引 index 位置的值设置为 value |
-| LPOP key | 移除并获取指定列表的第一个元素(最左边) |
-| RPOP key | 移除并获取指定列表的最后一个元素(最右边) |
-| LLEN key | 获取列表元素数量 |
-| LRANGE key start end | 获取列表 start 和 end 之间 的元素 |
-
-更多 Redis List 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
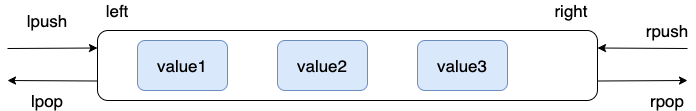
-**通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP`实现队列**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList value1
-(integer) 1
-> RPUSH myList value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> LPOP myList
-"value1"
-> LRANGE myList 0 1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value3"
-> LRANGE myList 0 -1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value3"
-```
-
-**通过 `RPUSH/RPOP`或者`LPUSH/LPOP` 实现栈**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList2 value1 value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> RPOP myList2 # 将 list的最右边的元素取出
-"value3"
-```
-
-我专门画了一个图方便大家理解 `RPUSH` , `LPOP` , `lpush` , `RPOP` 命令:
-
-
-
-**通过 `LRANGE` 查看对应下标范围的列表元素**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList value1 value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> LRANGE myList 0 1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> LRANGE myList 0 -1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-3) "value3"
-```
-
-通过 `LRANGE` 命令,你可以基于 List 实现分页查询,性能非常高!
-
-**通过 `LLEN` 查看链表长度**:
-
-```bash
-> LLEN myList
-(integer) 3
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**信息流展示**
-
-- 举例:最新文章、最新动态。
-- 相关命令:`LPUSH`、`LRANGE`。
-
-**消息队列**
-
-`List` 可以用来做消息队列,只是功能过于简单且存在很多缺陷,不建议这样做。
-
-相对来说,Redis 5.0 新增加的一个数据结构 `Stream` 更适合做消息队列一些,只是功能依然非常简陋。和专业的消息队列相比,还是有很多欠缺的地方比如消息丢失和堆积问题不好解决。
-
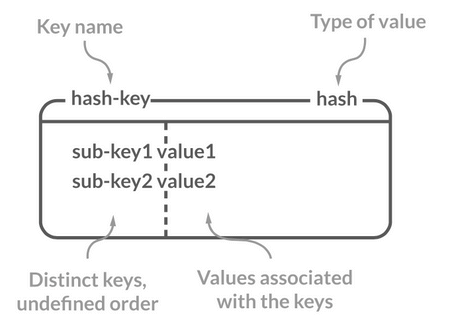
-## Hash(哈希)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 Hash 是一个 String 类型的 field-value(键值对) 的映射表,特别适合用于存储对象,后续操作的时候,你可以直接修改这个对象中的某些字段的值。
-
-Hash 类似于 JDK1.8 前的 `HashMap`,内部实现也差不多(数组 + 链表)。不过,Redis 的 Hash 做了更多优化。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ----------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
-| HSET key field value | 设置指定哈希表中指定字段的值 |
-| HSETNX key field value | 只有指定字段不存在时设置指定字段的值 |
-| HMSET key field1 value1 field2 value2 ... | 同时将一个或多个 field-value (域-值)对设置到指定哈希表中 |
-| HGET key field | 获取指定哈希表中指定字段的值 |
-| HMGET key field1 field2 ... | 获取指定哈希表中一个或者多个指定字段的值 |
-| HGETALL key | 获取指定哈希表中所有的键值对 |
-| HEXISTS key field | 查看指定哈希表中指定的字段是否存在 |
-| HDEL key field1 field2 ... | 删除一个或多个哈希表字段 |
-| HLEN key | 获取指定哈希表中字段的数量 |
-| HINCRBY key field increment | 对指定哈希中的指定字段做运算操作(正数为加,负数为减) |
-
-更多 Redis Hash 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**模拟对象数据存储**:
-
-```bash
-> HMSET userInfoKey name "guide" description "dev" age 24
-OK
-> HEXISTS userInfoKey name # 查看 key 对应的 value中指定的字段是否存在。
-(integer) 1
-> HGET userInfoKey name # 获取存储在哈希表中指定字段的值。
-"guide"
-> HGET userInfoKey age
-"24"
-> HGETALL userInfoKey # 获取在哈希表中指定 key 的所有字段和值
-1) "name"
-2) "guide"
-3) "description"
-4) "dev"
-5) "age"
-6) "24"
-> HSET userInfoKey name "GuideGeGe"
-> HGET userInfoKey name
-"GuideGeGe"
-> HINCRBY userInfoKey age 2
-(integer) 26
```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**对象数据存储场景**
-
-- 举例:用户信息、商品信息、文章信息、购物车信息。
-- 相关命令:`HSET` (设置单个字段的值)、`HMSET`(设置多个字段的值)、`HGET`(获取单个字段的值)、`HMGET`(获取多个字段的值)。
-
-## Set(集合)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 Set 类型是一种无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。当你需要存储一个列表数据,又不希望出现重复数据时,Set 是一个很好的选择,并且 Set 提供了判断某个元素是否在一个 Set 集合内的重要接口,这个也是 List 所不能提供的。
-
-你可以基于 Set 轻易实现交集、并集、差集的操作,比如你可以将一个用户所有的关注人存在一个集合中,将其所有粉丝存在一个集合。这样的话,Set 可以非常方便的实现如共同关注、共同粉丝、共同喜好等功能。这个过程也就是求交集的过程。
-
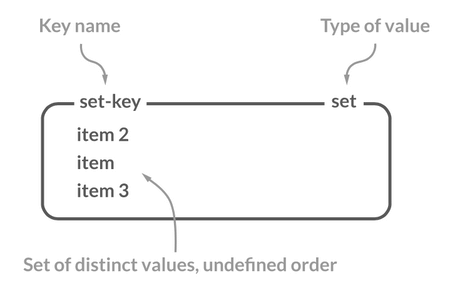
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------- |
-| SADD key member1 member2 ... | 向指定集合添加一个或多个元素 |
-| SMEMBERS key | 获取指定集合中的所有元素 |
-| SCARD key | 获取指定集合的元素数量 |
-| SISMEMBER key member | 判断指定元素是否在指定集合中 |
-| SINTER key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的交集 |
-| SINTERSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的交集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SUNION key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的并集 |
-| SUNIONSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的并集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SDIFF key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的差集 |
-| SDIFFSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的差集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SPOP key count | 随机移除并获取指定集合中一个或多个元素 |
-| SRANDMEMBER key count | 随机获取指定集合中指定数量的元素 |
-
-更多 Redis Set 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> SADD mySet value1 value2
-(integer) 2
-> SADD mySet value1 # 不允许有重复元素,因此添加失败
-(integer) 0
-> SMEMBERS mySet
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> SCARD mySet
-(integer) 2
-> SISMEMBER mySet value1
-(integer) 1
-> SADD mySet2 value2 value3
-(integer) 2
-```
-
-- `mySet` : `value1`、`value2` 。
-- `mySet2`:`value2`、`value3` 。
-
-**求交集**:
-
-```bash
-> SINTERSTORE mySet3 mySet mySet2
-(integer) 1
-> SMEMBERS mySet3
-1) "value2"
-```
-
-**求并集**:
-
-```bash
-> SUNION mySet mySet2
-1) "value3"
-2) "value2"
-3) "value1"
-```
-
-**求差集**:
-
-```bash
-> SDIFF mySet mySet2 # 差集是由所有属于 mySet 但不属于 A 的元素组成的集合
-1) "value1"
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要存放的数据不能重复的场景**
-
-- 举例:网站 UV 统计(数据量巨大的场景还是 `HyperLogLog`更适合一些)、文章点赞、动态点赞等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SCARD`(获取集合数量) 。
-
-
-
-**需要获取多个数据源交集、并集和差集的场景**
-
-- 举例:共同好友(交集)、共同粉丝(交集)、共同关注(交集)、好友推荐(差集)、音乐推荐(差集)、订阅号推荐(差集+交集) 等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SINTER`(交集)、`SINTERSTORE` (交集)、`SUNION` (并集)、`SUNIONSTORE`(并集)、`SDIFF`(差集)、`SDIFFSTORE` (差集)。
-
-
-
-**需要随机获取数据源中的元素的场景**
-
-- 举例:抽奖系统、随机点名等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SPOP`(随机获取集合中的元素并移除,适合不允许重复中奖的场景)、`SRANDMEMBER`(随机获取集合中的元素,适合允许重复中奖的场景)。
-
-## Sorted Set(有序集合)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Sorted Set 类似于 Set,但和 Set 相比,Sorted Set 增加了一个权重参数 `score`,使得集合中的元素能够按 `score` 进行有序排列,还可以通过 `score` 的范围来获取元素的列表。有点像是 Java 中 `HashMap` 和 `TreeSet` 的结合体。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| ZADD key score1 member1 score2 member2 ... | 向指定有序集合添加一个或多个元素 |
-| ZCARD KEY | 获取指定有序集合的元素数量 |
-| ZSCORE key member | 获取指定有序集合中指定元素的 score 值 |
-| ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有有序集合的交集存储在 destination 中,对相同元素对应的 score 值进行 SUM 聚合操作,numkeys 为集合数量 |
-| ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 求并集,其它和 ZINTERSTORE 类似 |
-| ZDIFFSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 求差集,其它和 ZINTERSTORE 类似 |
-| ZRANGE key start end | 获取指定有序集合 start 和 end 之间的元素(score 从低到高) |
-| ZREVRANGE key start end | 获取指定有序集合 start 和 end 之间的元素(score 从高到底) |
-| ZREVRANK key member | 获取指定有序集合中指定元素的排名(score 从大到小排序) |
-
-更多 Redis Sorted Set 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> ZADD myZset 2.0 value1 1.0 value2
-(integer) 2
-> ZCARD myZset
-2
-> ZSCORE myZset value1
-2.0
-> ZRANGE myZset 0 1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value1"
-> ZREVRANGE myZset 0 1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> ZADD myZset2 4.0 value2 3.0 value3
-(integer) 2
-
-```
-
-- `myZset` : `value1`(2.0)、`value2`(1.0) 。
-- `myZset2`:`value2` (4.0)、`value3`(3.0) 。
-
-**获取指定元素的排名**:
-
-```bash
-> ZREVRANK myZset value1
-0
-> ZREVRANK myZset value2
-1
-```
-
-**求交集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZINTERSTORE myZset3 2 myZset myZset2
-1
-> ZRANGE myZset3 0 1 WITHSCORES
-value2
-5
-```
-
-**求并集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZUNIONSTORE myZset4 2 myZset myZset2
-3
-> ZRANGE myZset4 0 2 WITHSCORES
-value1
-2
-value3
-3
-value2
-5
-```
-
-**求差集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZDIFF 2 myZset myZset2 WITHSCORES
-value1
-2
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要随机获取数据源中的元素根据某个权重进行排序的场景**
-
-- 举例:各种排行榜比如直播间送礼物的排行榜、朋友圈的微信步数排行榜、王者荣耀中的段位排行榜、话题热度排行榜等等。
-- 相关命令:`ZRANGE` (从小到大排序)、 `ZREVRANGE` (从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK` (指定元素排名)。
-
-
-
-[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 的「技术面试题篇」就有一篇文章详细介绍如何使用 Sorted Set 来设计制作一个排行榜。
-
-
-
-**需要存储的数据有优先级或者重要程度的场景** 比如优先级任务队列。
-
-- 举例:优先级任务队列。
-- 相关命令:`ZRANGE` (从小到大排序)、 `ZREVRANGE` (从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK` (指定元素排名)。
-
-## 总结
-
-| 数据类型 | 说明 |
-| -------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| String | 一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。 |
-| List | Redis 的 List 的实现为一个双向链表,即可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了部分额外的内存开销。 |
-| Hash | 一个 String 类型的 field-value(键值对) 的映射表,特别适合用于存储对象,后续操作的时候,你可以直接修改这个对象中的某些字段的值。 |
-| Set | 无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。 |
-| Zset | 和 Set 相比,Sorted Set 增加了一个权重参数 `score`,使得集合中的元素能够按 `score` 进行有序排列,还可以通过 `score` 的范围来获取元素的列表。有点像是 Java 中 `HashMap` 和 `TreeSet` 的结合体。 |
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis Data Structures: 。
-- Redis Commands: 。
-- Redis Data types tutorial: 。
-- Redis 存储对象信息是用 Hash 还是 String :
-
-
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
index 9e5fbcee59b..835b5f8b8be 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
@@ -1,48 +1,48 @@
---
-title: Redis 3 种特殊数据类型详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 3 Special Data Types in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis常见数据类型
+ content: Common data types in Redis
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis特殊数据类型总结:HyperLogLogs(基数统计)、Bitmap (位存储)、Geospatial (地理位置)。
+ content: Summary of Redis special data types: HyperLogLogs (cardinality statistics), Bitmap (bit storage), Geospatial (geolocation).
---
-除了 5 种基本的数据类型之外,Redis 还支持 3 种特殊的数据类型:Bitmap、HyperLogLog、GEO。
+In addition to the 5 basic data types, Redis also supports 3 special data types: Bitmap, HyperLogLog, and GEO.
-## Bitmap (位图)
+## Bitmap
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-根据官网介绍:
+According to the official website:
> Bitmaps are not an actual data type, but a set of bit-oriented operations defined on the String type which is treated like a bit vector. Since strings are binary safe blobs and their maximum length is 512 MB, they are suitable to set up to 2^32 different bits.
>
-> Bitmap 不是 Redis 中的实际数据类型,而是在 String 类型上定义的一组面向位的操作,将其视为位向量。由于字符串是二进制安全的块,且最大长度为 512 MB,它们适合用于设置最多 2^32 个不同的位。
+> Bitmap is not an actual data type in Redis, but a set of bit-oriented operations defined on the String type, treated as a bit vector. Since strings are binary safe blobs and their maximum length is 512 MB, they are suitable for setting up to 2^32 different bits.
-Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap, 只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身 。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。
+Bitmaps store continuous binary numbers (0 and 1). With Bitmap, only one bit is needed to represent the value or state of a corresponding element, where the key is the element itself. We know that 8 bits can form one byte, so Bitmap can greatly save storage space.
-你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。
+You can think of Bitmap as an array that stores binary numbers (0 and 1), where each element's index is called an offset.
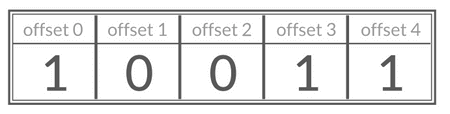
-### 常用命令
+### Common Commands
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| SETBIT key offset value | 设置指定 offset 位置的值 |
-| GETBIT key offset | 获取指定 offset 位置的值 |
-| BITCOUNT key start end | 获取 start 和 end 之间值为 1 的元素个数 |
-| BITOP operation destkey key1 key2 ... | 对一个或多个 Bitmap 进行运算,可用运算符有 AND, OR, XOR 以及 NOT |
+| Command | Description |
+| ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| SETBIT key offset value | Set the value at the specified offset position |
+| GETBIT key offset | Get the value at the specified offset position |
+| BITCOUNT key start end | Get the number of elements with a value of 1 between start and end |
+| BITOP operation destkey key1 key2 ... | Perform operations on one or more Bitmaps, with operators AND, OR, XOR, and NOT |
-**Bitmap 基本操作演示**:
+**Basic Bitmap Operations Demonstration**:
```bash
-# SETBIT 会返回之前位的值(默认是 0)这里会生成 7 个位
+# SETBIT will return the previous value of the bit (default is 0), generating 7 bits
> SETBIT mykey 7 1
(integer) 0
> SETBIT mykey 7 0
@@ -53,174 +53,35 @@ Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap, 只需
(integer) 0
> SETBIT mykey 8 1
(integer) 0
-# 通过 bitcount 统计被被设置为 1 的位的数量。
+# Count the number of bits set to 1 using bitcount.
> BITCOUNT mykey
(integer) 2
```
-### 应用场景
+### Application Scenarios
-**需要保存状态信息(0/1 即可表示)的场景**
+**Scenarios that require saving state information (0/1 can represent)**
-- 举例:用户签到情况、活跃用户情况、用户行为统计(比如是否点赞过某个视频)。
-- 相关命令:`SETBIT`、`GETBIT`、`BITCOUNT`、`BITOP`。
+- Example: User sign-in status, active user status, user behavior statistics (e.g., whether a user has liked a certain video).
+- Related commands: `SETBIT`, `GETBIT`, `BITCOUNT`, `BITOP`.
-## HyperLogLog(基数统计)
+## HyperLogLog
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-HyperLogLog 是一种有名的基数计数概率算法 ,基于 LogLog Counting(LLC)优化改进得来,并不是 Redis 特有的,Redis 只是实现了这个算法并提供了一些开箱即用的 API。
+HyperLogLog is a well-known probabilistic algorithm for cardinality counting, optimized from LogLog Counting (LLC). It is not unique to Redis; Redis simply implements this algorithm and provides some out-of-the-box APIs.
-Redis 提供的 HyperLogLog 占用空间非常非常小,只需要 12k 的空间就能存储接近`2^64`个不同元素。这是真的厉害,这就是数学的魅力么!并且,Redis 对 HyperLogLog 的存储结构做了优化,采用两种方式计数:
+The HyperLogLog provided by Redis occupies a very small space, requiring only 12k of space to store nearly `2^64` different elements. This is truly impressive; this is the charm of mathematics! Additionally, Redis has optimized the storage structure of HyperLogLog, using two counting methods:
-- **稀疏矩阵**:计数较少的时候,占用空间很小。
-- **稠密矩阵**:计数达到某个阈值的时候,占用 12k 的空间。
+- **Sparse Matrix**: When the count is low, it occupies very little space.
+- **Dense Matrix**: When the count reaches a certain threshold, it occupies 12k of space.
-Redis 官方文档中有对应的详细说明:
+The official Redis documentation provides detailed explanations:

-基数计数概率算法为了节省内存并不会直接存储元数据,而是通过一定的概率统计方法预估基数值(集合中包含元素的个数)。因此, HyperLogLog 的计数结果并不是一个精确值,存在一定的误差(标准误差为 `0.81%` )。
+The cardinality counting probabilistic algorithm does not directly store metadata to save memory; instead, it estimates the cardinality value (the number of elements in the set) through certain probabilistic statistical methods. Therefore, the counting result of HyperLogLog is not an exact value and has a certain margin of error (standard error is `0.81%`).

-HyperLogLog 的使用非常简单,但原理非常复杂。HyperLogLog 的原理以及在 Redis 中的实现可以看这篇文章:[HyperLogLog 算法的原理讲解以及 Redis 是如何应用它的](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903785744056333) 。
-
-再推荐一个可以帮助理解 HyperLogLog 原理的工具:[Sketch of the Day: HyperLogLog — Cornerstone of a Big Data Infrastructure](http://content.research.neustar.biz/blog/hll.html) 。
-
-除了 HyperLogLog 之外,Redis 还提供了其他的概率数据结构,对应的官方文档地址: 。
-
-### 常用命令
-
-HyperLogLog 相关的命令非常少,最常用的也就 3 个。
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ----------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| PFADD key element1 element2 ... | 添加一个或多个元素到 HyperLogLog 中 |
-| PFCOUNT key1 key2 | 获取一个或者多个 HyperLogLog 的唯一计数。 |
-| PFMERGE destkey sourcekey1 sourcekey2 ... | 将多个 HyperLogLog 合并到 destkey 中,destkey 会结合多个源,算出对应的唯一计数。 |
-
-**HyperLogLog 基本操作演示**:
-
-```bash
-> PFADD hll foo bar zap
-(integer) 1
-> PFADD hll zap zap zap
-(integer) 0
-> PFADD hll foo bar
-(integer) 0
-> PFCOUNT hll
-(integer) 3
-> PFADD some-other-hll 1 2 3
-(integer) 1
-> PFCOUNT hll some-other-hll
-(integer) 6
-> PFMERGE desthll hll some-other-hll
-"OK"
-> PFCOUNT desthll
-(integer) 6
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**数量巨大(百万、千万级别以上)的计数场景**
-
-- 举例:热门网站每日/每周/每月访问 ip 数统计、热门帖子 uv 统计。
-- 相关命令:`PFADD`、`PFCOUNT` 。
-
-## Geospatial (地理位置)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Geospatial index(地理空间索引,简称 GEO) 主要用于存储地理位置信息,基于 Sorted Set 实现。
-
-通过 GEO 我们可以轻松实现两个位置距离的计算、获取指定位置附近的元素等功能。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| GEOADD key longitude1 latitude1 member1 ... | 添加一个或多个元素对应的经纬度信息到 GEO 中 |
-| GEOPOS key member1 member2 ... | 返回给定元素的经纬度信息 |
-| GEODIST key member1 member2 M/KM/FT/MI | 返回两个给定元素之间的距离 |
-| GEORADIUS key longitude latitude radius distance | 获取指定位置附近 distance 范围内的其他元素,支持 ASC(由近到远)、DESC(由远到近)、Count(数量) 等参数 |
-| GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius distance | 类似于 GEORADIUS 命令,只是参照的中心点是 GEO 中的元素 |
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> GEOADD personLocation 116.33 39.89 user1 116.34 39.90 user2 116.35 39.88 user3
-3
-> GEOPOS personLocation user1
-116.3299986720085144
-39.89000061669732844
-> GEODIST personLocation user1 user2 km
-1.4018
-```
-
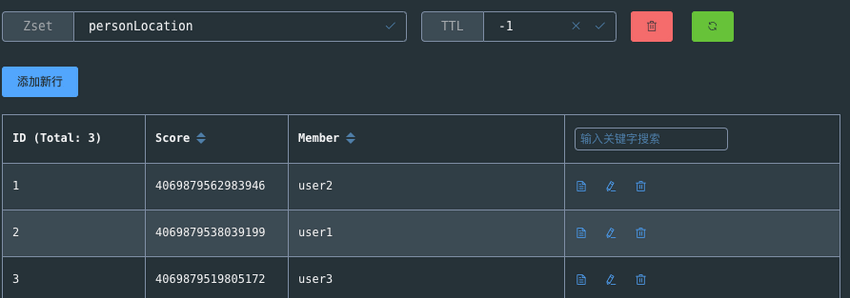
-通过 Redis 可视化工具查看 `personLocation` ,果不其然,底层就是 Sorted Set。
-
-GEO 中存储的地理位置信息的经纬度数据通过 GeoHash 算法转换成了一个整数,这个整数作为 Sorted Set 的 score(权重参数)使用。
-
-
-
-**获取指定位置范围内的其他元素**:
-
-```bash
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 3 km
-user3
-user1
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 2 km
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 5 km
-user3
-user1
-user2
-> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER personLocation user1 5 km
-user3
-user1
-user2
-> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER personLocation user1 2 km
-user1
-user2
-```
-
-`GEORADIUS` 命令的底层原理解析可以看看阿里的这篇文章:[Redis 到底是怎么实现“附近的人”这个功能的呢?](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903966061363207) 。
-
-**移除元素**:
-
-GEO 底层是 Sorted Set ,你可以对 GEO 使用 Sorted Set 相关的命令。
-
-```bash
-> ZREM personLocation user1
-1
-> ZRANGE personLocation 0 -1
-user3
-user2
-> ZSCORE personLocation user2
-4069879562983946
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要管理使用地理空间数据的场景**
-
-- 举例:附近的人。
-- 相关命令: `GEOADD`、`GEORADIUS`、`GEORADIUSBYMEMBER` 。
-
-## 总结
-
-| 数据类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| Bitmap | 你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。通过 Bitmap, 只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身 。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。 |
-| HyperLogLog | Redis 提供的 HyperLogLog 占用空间非常非常小,只需要 12k 的空间就能存储接近`2^64`个不同元素。不过,HyperLogLog 的计数结果并不是一个精确值,存在一定的误差(标准误差为 `0.81%` )。 |
-| Geospatial index | Geospatial index(地理空间索引,简称 GEO) 主要用于存储地理位置信息,基于 Sorted Set 实现。 |
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis Data Structures: 。
-- 《Redis 深度历险:核心原理与应用实践》1.6 四两拨千斤——HyperLogLog
-- 布隆过滤器,位图,HyperLogLog:
-
-
+Using HyperLogLog is very simple, but the principle is quite complex. You can read this article for an explanation of the principle of HyperLogLog and how it is applied in Redis: \[Explanation of the Principle of HyperLogLog Algorithm and How Redis Applies It\](https://juejin.cn/post/684490378574
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
index 35f9304321f..acfebfbb9d6 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
@@ -1,82 +1,82 @@
---
-title: 如何基于Redis实现延时任务
-category: 数据库
+title: How to Implement Delayed Tasks Based on Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-基于 Redis 实现延时任务的功能无非就下面两种方案:
+The functionality of implementing delayed tasks based on Redis consists of the following two solutions:
-1. Redis 过期事件监听
-2. Redisson 内置的延时队列
+1. Redis Expiration Event Listening
+1. Built-in Delayed Queue in Redisson
-面试的时候,你可以先说自己考虑了这两种方案,但最后发现 Redis 过期事件监听这种方案存在很多问题,因此你最终选择了 Redisson 内置的 DelayedQueue 这种方案。
+During the interview, you can first mention that you considered these two solutions, but ultimately found that the Redis expiration event listening approach has many issues, which led you to choose the built-in DelayedQueue in Redisson.
-这个时候面试官可能会追问你一些相关的问题,我们后面会提到,提前准备就好了。
+At this point, the interviewer may ask you some related questions, which we will cover later, so it's good to prepare in advance.
-另外,除了下面介绍到的这些问题之外,Redis 相关的常见问题建议你都复习一遍,不排除面试官会顺带问你一些 Redis 的其他问题。
+Additionally, besides the issues mentioned below, it is recommended that you review all common issues related to Redis, as the interviewer may also ask some other questions about Redis.
-### Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能的原理?
+### What is the Principle of Implementing Delayed Task Functionality through Redis Expiration Event Listening?
-Redis 2.0 引入了发布订阅 (pub/sub) 功能。在 pub/sub 中,引入了一个叫做 **channel(频道)** 的概念,有点类似于消息队列中的 **topic(主题)**。
+Redis 2.0 introduced the publish/subscribe (pub/sub) feature. In pub/sub, a concept called **channel** is introduced, which is somewhat similar to **topic** in message queues.
-pub/sub 涉及发布者(publisher)和订阅者(subscriber,也叫消费者)两个角色:
+pub/sub involves two roles: publisher and subscriber (also known as consumers):
-- 发布者通过 `PUBLISH` 投递消息给指定 channel。
-- 订阅者通过`SUBSCRIBE`订阅它关心的 channel。并且,订阅者可以订阅一个或者多个 channel。
+- The publisher delivers messages to a specified channel using `PUBLISH`.
+- Subscribers subscribe to the channels of their interest using `SUBSCRIBE`, and they can subscribe to one or more channels.
-
+
-在 pub/sub 模式下,生产者需要指定消息发送到哪个 channel 中,而消费者则订阅对应的 channel 以获取消息。
+In the pub/sub model, the producer needs to specify which channel the message is sent to, while consumers subscribe to the corresponding channel to receive messages.
-Redis 中有很多默认的 channel,这些 channel 是由 Redis 本身向它们发送消息的,而不是我们自己编写的代码。其中,`__keyevent@0__:expired` 就是一个默认的 channel,负责监听 key 的过期事件。也就是说,当一个 key 过期之后,Redis 会发布一个 key 过期的事件到`__keyevent@__:expired`这个 channel 中。
+Redis has many default channels, which are messages sent by Redis itself rather than our own code. One of them, `__keyevent@0__:expired`, is a default channel responsible for listening to the expiration events of keys. This means that when a key expires, Redis will publish an expiration event to the channel `__keyevent@__:expired`.
-我们只需要监听这个 channel,就可以拿到过期的 key 的消息,进而实现了延时任务功能。
+We only need to listen to this channel to receive messages about expired keys, thus achieving the delayed task functionality.
-这个功能被 Redis 官方称为 **keyspace notifications** ,作用是实时监控 Redis 键和值的变化。
+This feature is officially referred to as **keyspace notifications** by Redis, which serves to monitor changes in Redis keys and values in real-time.
-### Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能有什么缺陷?
+### What Are the Defects of Implementing Delayed Task Functionality through Redis Expiration Event Listening?
-**1、时效性差**
+**1. Poor Timeliness**
-官方文档的一段介绍解释了时效性差的原因,地址: 。
+A paragraph in the official documentation explains the reason for poor timeliness, reference: .
-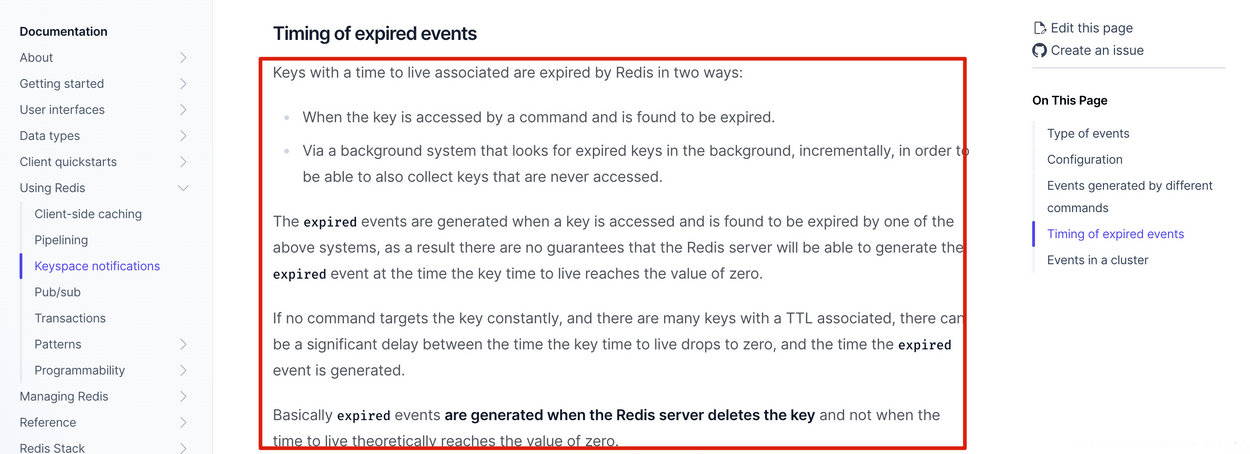
+
-这段话的核心是:过期事件消息是在 Redis 服务器删除 key 时发布的,而不是一个 key 过期之后就会就会直接发布。
+The core of this statement is that expiration event messages are published when the Redis server deletes the key, not immediately when a key expires.
-我们知道常用的过期数据的删除策略就两个:
+We know there are two common strategies for deleting expired data:
-1. **惰性删除**:只会在取出 key 的时候才对数据进行过期检查。这样对 CPU 最友好,但是可能会造成太多过期 key 没有被删除。
-2. **定期删除**:每隔一段时间抽取一批 key 执行删除过期 key 操作。并且,Redis 底层会通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对 CPU 时间的影响。
+1. **Lazy Deletion**: It only checks for expiration when the key is accessed. This is friendly to the CPU but may result in many expired keys not being deleted.
+1. **Periodic Deletion**: A batch of keys is randomly selected to execute the deletion of expired keys at intervals. Moreover, Redis limits the duration and frequency of deletion operations to reduce the impact on CPU time.
-定期删除对内存更加友好,惰性删除对 CPU 更加友好。两者各有千秋,所以 Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 。
+Periodic deletion is more memory-friendly, while lazy deletion is more CPU-friendly. Each has its advantages, which is why Redis adopts **periodic deletion combined with lazy/eager deletion**.
-因此,就会存在我设置了 key 的过期时间,但到了指定时间 key 还未被删除,进而没有发布过期事件的情况。
+Therefore, there might be scenarios where I set an expiration time for a key, but the key has not been deleted by the specified time and thus did not publish an expiration event.
-**2、丢消息**
+**2. Message Loss**
-Redis 的 pub/sub 模式中的消息并不支持持久化,这与消息队列不同。在 Redis 的 pub/sub 模式中,发布者将消息发送给指定的频道,订阅者监听相应的频道以接收消息。当没有订阅者时,消息会被直接丢弃,在 Redis 中不会存储该消息。
+Messages in Redis's pub/sub mode do not support persistence, which is different from message queues. In Redis's pub/sub mode, the publisher sends messages to a specified channel, and subscribers listen to the corresponding channel to receive messages. When there are no subscribers, messages are directly discarded and will not be stored in Redis.
-**3、多服务实例下消息重复消费**
+**3. Message Duplicate Consumption in Multiple Service Instances**
-Redis 的 pub/sub 模式目前只有广播模式,这意味着当生产者向特定频道发布一条消息时,所有订阅相关频道的消费者都能够收到该消息。
+Redis's pub/sub mode currently only supports broadcasting, which means that when a producer publishes a message to a specific channel, all consumers listening to that channel can receive it.
-这个时候,我们需要注意多个服务实例重复处理消息的问题,这会增加代码开发量和维护难度。
+In this case, we need to be aware of the issue of multiple service instances processing messages repeatedly, which increases both code development and maintenance difficulty.
-### Redisson 延迟队列原理是什么?有什么优势?
+### What Is the Principle of Redisson Delayed Queue? What Are Its Advantages?
-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,比如多种分布式锁的实现、延时队列。
+Redisson is an open-source Redis client for the Java language, providing many out-of-the-box features, such as various implementations of distributed locks and delayed queues.
-我们可以借助 Redisson 内置的延时队列 RDelayedQueue 来实现延时任务功能。
+We can use Redisson's built-in delayed queue RDelayedQueue to implement the delayed task functionality.
-Redisson 的延迟队列 RDelayedQueue 是基于 Redis 的 SortedSet 来实现的。SortedSet 是一个有序集合,其中的每个元素都可以设置一个分数,代表该元素的权重。Redisson 利用这一特性,将需要延迟执行的任务插入到 SortedSet 中,并给它们设置相应的过期时间作为分数。
+Redisson's delayed queue RDelayedQueue is implemented based on Redis's SortedSet. SortedSet is an ordered collection where each element can have a score set that represents the weight of that element. Redisson uses this feature to insert tasks that need to be executed with a delay into the SortedSet and sets their corresponding expiration time as the score.
-Redisson 定期使用 `zrangebyscore` 命令扫描 SortedSet 中过期的元素,然后将这些过期元素从 SortedSet 中移除,并将它们加入到就绪消息列表中。就绪消息列表是一个阻塞队列,有消息进入就会被消费者监听到。这样做可以避免消费者对整个 SortedSet 进行轮询,提高了执行效率。
+Redisson periodically uses the `zrangebyscore` command to scan for expired elements in the SortedSet, then removes these expired elements from the SortedSet and adds them to the ready message list. The ready message list is a blocking queue that consumers can listen to when new messages enter. This avoids consumers polling the entire SortedSet, thereby improving execution efficiency.
-相比于 Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能,这种方式具备下面这些优势:
+Compared to the Redis expiration event listening method for implementing delayed tasks, this approach has the following advantages:
-1. **减少了丢消息的可能**:DelayedQueue 中的消息会被持久化,即使 Redis 宕机了,根据持久化机制,也只可能丢失一点消息,影响不大。当然了,你也可以使用扫描数据库的方法作为补偿机制。
-2. **消息不存在重复消费问题**:每个客户端都是从同一个目标队列中获取任务的,不存在重复消费的问题。
+1. **Reduced Possibility of Message Loss**: Messages in the DelayedQueue are persisted, so even if Redis crashes, based on the persistence mechanism, only a small number of messages may be lost, which has a minimal impact. Of course, you can also use database scanning as a compensation mechanism.
+1. **No Duplicate Consumption Issue**: Every client retrieves tasks from the same target queue, eliminating the issue of duplicate consumption.
-跟 Redisson 内置的延时队列相比,消息队列可以通过保障消息消费的可靠性、控制消息生产者和消费者的数量等手段来实现更高的吞吐量和更强的可靠性,实际项目中首选使用消息队列的延时消息这种方案。
+Compared to Redisson's built-in delayed queue, message queues can achieve higher throughput and stronger reliability by ensuring message consumption reliability and controlling the number of message producers and consumers, making delayed messages in message queues the preferred solution in practical projects.
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
index cb2da7476d1..97a731c3291 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
@@ -1,37 +1,37 @@
---
-title: Redis内存碎片详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Memory Fragmentation
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-## 什么是内存碎片?
+## What is Memory Fragmentation?
-你可以将内存碎片简单地理解为那些不可用的空闲内存。
+You can simply understand memory fragmentation as the unusable free memory.
-举个例子:操作系统为你分配了 32 字节的连续内存空间,而你存储数据实际只需要使用 24 字节内存空间,那这多余出来的 8 字节内存空间如果后续没办法再被分配存储其他数据的话,就可以被称为内存碎片。
+For example, if the operating system allocates a continuous memory space of 32 bytes for you, but you only need to use 24 bytes of that space to store data, then the extra 8 bytes of memory, if it cannot be allocated for other data later, can be referred to as memory fragmentation.
-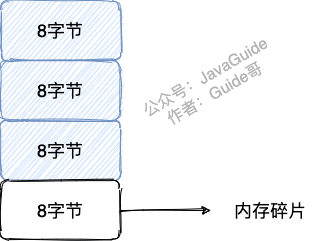
+
-Redis 内存碎片虽然不会影响 Redis 性能,但是会增加内存消耗。
+Although Redis memory fragmentation does not affect Redis performance, it does increase memory consumption.
-## 为什么会有 Redis 内存碎片?
+## Why Does Redis Memory Fragmentation Occur?
-Redis 内存碎片产生比较常见的 2 个原因:
+There are two common reasons for Redis memory fragmentation:
-**1、Redis 存储数据的时候向操作系统申请的内存空间可能会大于数据实际需要的存储空间。**
+**1. The memory space requested by Redis from the operating system when storing data may be larger than the actual storage space needed.**
-以下是这段 Redis 官方的原话:
+Here is the original statement from the Redis official documentation:
> To store user keys, Redis allocates at most as much memory as the `maxmemory` setting enables (however there are small extra allocations possible).
-Redis 使用 `zmalloc` 方法(Redis 自己实现的内存分配方法)进行内存分配的时候,除了要分配 `size` 大小的内存之外,还会多分配 `PREFIX_SIZE` 大小的内存。
+When Redis allocates memory using the `zmalloc` method (a memory allocation method implemented by Redis itself), it not only allocates memory of size `size`, but also allocates additional memory of size `PREFIX_SIZE`.
-`zmalloc` 方法源码如下(源码地址:
+The source code for the `zmalloc` method is as follows (source link: ):
```java
void *zmalloc(size_t size) {
- // 分配指定大小的内存
+ // Allocate memory of the specified size
void *ptr = malloc(size+PREFIX_SIZE);
if (!ptr) zmalloc_oom_handler(size);
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOC_SIZE
@@ -45,80 +45,39 @@ void *zmalloc(size_t size) {
}
```
-另外,Redis 可以使用多种内存分配器来分配内存( libc、jemalloc、tcmalloc),默认使用 [jemalloc](https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc),而 jemalloc 按照一系列固定的大小(8 字节、16 字节、32 字节……)来分配内存的。jemalloc 划分的内存单元如下图所示:
+Additionally, Redis can use various memory allocators to allocate memory (libc, jemalloc, tcmalloc), with the default being [jemalloc](https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc), which allocates memory based on a series of fixed sizes (8 bytes, 16 bytes, 32 bytes, etc.). The memory units allocated by jemalloc are shown in the following diagram:
-
+
-当程序申请的内存最接近某个固定值时,jemalloc 会给它分配相应大小的空间,就比如说程序需要申请 17 字节的内存,jemalloc 会直接给它分配 32 字节的内存,这样会导致有 15 字节内存的浪费。不过,jemalloc 专门针对内存碎片问题做了优化,一般不会存在过度碎片化的问题。
+When the memory requested by the program is closest to a fixed value, jemalloc allocates the corresponding size of space. For example, if the program requests 17 bytes of memory, jemalloc will allocate 32 bytes, resulting in a waste of 15 bytes of memory. However, jemalloc has been optimized specifically for memory fragmentation issues, so excessive fragmentation is generally not a problem.
-**2、频繁修改 Redis 中的数据也会产生内存碎片。**
+**2. Frequent modifications to data in Redis can also lead to memory fragmentation.**
-当 Redis 中的某个数据删除时,Redis 通常不会轻易释放内存给操作系统。
+When a piece of data in Redis is deleted, Redis typically does not readily release memory back to the operating system.
-这个在 Redis 官方文档中也有对应的原话:
+This is also mentioned in the official Redis documentation:
-文档地址: 。
+Documentation link: .
-## 如何查看 Redis 内存碎片的信息?
+## How to Check Redis Memory Fragmentation Information?
-使用 `info memory` 命令即可查看 Redis 内存相关的信息。下图中每个参数具体的含义,Redis 官方文档有详细的介绍: 。
+You can use the `info memory` command to view Redis memory-related information. The specific meanings of each parameter in the following image are detailed in the Redis official documentation: .
-Redis 内存碎片率的计算公式:`mem_fragmentation_ratio` (内存碎片率)= `used_memory_rss` (操作系统实际分配给 Redis 的物理内存空间大小)/ `used_memory`(Redis 内存分配器为了存储数据实际申请使用的内存空间大小)
+The formula for calculating Redis memory fragmentation ratio: `mem_fragmentation_ratio` (memory fragmentation ratio) = `used_memory_rss` (the actual physical memory space allocated to Redis by the operating system) / `used_memory` (the actual memory space requested by the Redis memory allocator for storing data).
-也就是说,`mem_fragmentation_ratio` (内存碎片率)的值越大代表内存碎片率越严重。
+In other words, a larger value of `mem_fragmentation_ratio` indicates a more serious memory fragmentation issue.
-一定不要误认为`used_memory_rss` 减去 `used_memory`值就是内存碎片的大小!!!这不仅包括内存碎片,还包括其他进程开销,以及共享库、堆栈等的开销。
+Do not mistakenly think that the value of `used_memory_rss` minus `used_memory` is the size of memory fragmentation!!! This includes not only memory fragmentation but also overhead from other processes, as well as shared libraries, stacks, etc.
-很多小伙伴可能要问了:“多大的内存碎片率才是需要清理呢?”。
+Many may ask, "What level of memory fragmentation ratio requires cleanup?"
-通常情况下,我们认为 `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` 的话才需要清理内存碎片。 `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` 意味着你使用 Redis 存储实际大小 2G 的数据需要使用大于 3G 的内存。
+Generally, we consider that a `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` indicates the need to clean up memory fragmentation. A `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` means that you need more than 3G of memory to store an actual size of 2G of data in Redis.
-如果想要快速查看内存碎片率的话,你还可以通过下面这个命令:
+If you want to quickly check the memory fragmentation ratio, you can use the following command:
```bash
-> redis-cli -p 6379 info | grep mem_fragmentation_ratio
-```
-
-另外,内存碎片率可能存在小于 1 的情况。这种情况我在日常使用中还没有遇到过,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看这篇文章 [故障分析 | Redis 内存碎片率太低该怎么办?- 爱可生开源社区](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/drlDvp7bfq5jt2M5pTqJCw) 。
-
-## 如何清理 Redis 内存碎片?
-
-Redis4.0-RC3 版本以后自带了内存整理,可以避免内存碎片率过大的问题。
-
-直接通过 `config set` 命令将 `activedefrag` 配置项设置为 `yes` 即可。
-
-```bash
-config set activedefrag yes
-```
-
-具体什么时候清理需要通过下面两个参数控制:
-
-```bash
-# 内存碎片占用空间达到 500mb 的时候开始清理
-config set active-defrag-ignore-bytes 500mb
-# 内存碎片率大于 1.5 的时候开始清理
-config set active-defrag-threshold-lower 50
-```
-
-通过 Redis 自动内存碎片清理机制可能会对 Redis 的性能产生影响,我们可以通过下面两个参数来减少对 Redis 性能的影响:
-
-```bash
-# 内存碎片清理所占用 CPU 时间的比例不低于 20%
-config set active-defrag-cycle-min 20
-# 内存碎片清理所占用 CPU 时间的比例不高于 50%
-config set active-defrag-cycle-max 50
-```
-
-另外,重启节点可以做到内存碎片重新整理。如果你采用的是高可用架构的 Redis 集群的话,你可以将碎片率过高的主节点转换为从节点,以便进行安全重启。
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis 官方文档:
-- Redis 核心技术与实战 - 极客时间 - 删除数据后,为什么内存占用率还是很高?:
-- Redis 源码解析——内存分配:< 源码解析——内存管理>
-
-
+> redis-cli -p 637
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
index c17fe7db316..1929e74c349 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
@@ -1,217 +1,74 @@
---
-title: Redis持久化机制详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanisms
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis持久化机制详解
+ content: Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanisms
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:快照(snapshotting,RDB)、只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)、RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)。
+ content: One important difference between Redis and Memcached is that Redis supports persistence, and it supports three types of persistence methods: snapshots (snapshotting, RDB), append-only files (append-only file, AOF), and hybrid persistence of RDB and AOF (new in Redis 4.0).
---
-使用缓存的时候,我们经常需要对内存中的数据进行持久化也就是将内存中的数据写入到硬盘中。大部分原因是为了之后重用数据(比如重启机器、机器故障之后恢复数据),或者是为了做数据同步(比如 Redis 集群的主从节点通过 RDB 文件同步数据)。
+When using caching, we often need to persist data in memory, which means writing the data in memory to disk. The main reasons are to reuse data later (for example, to recover data after restarting the machine or after a machine failure) or to synchronize data (for example, Redis cluster master-slave nodes synchronize data through RDB files).
-Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:
+One important difference between Redis and Memcached is that Redis supports persistence, and it supports three types of persistence methods:
-- 快照(snapshotting,RDB)
-- 只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)
-- RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)
+- Snapshots (snapshotting, RDB)
+- Append-only files (append-only file, AOF)
+- Hybrid persistence of RDB and AOF (new in Redis 4.0)
-官方文档地址: 。
+Official documentation link: .

-## RDB 持久化
+## RDB Persistence
-### 什么是 RDB 持久化?
+### What is RDB Persistence?
-Redis 可以通过创建快照来获得存储在内存里面的数据在 **某个时间点** 上的副本。Redis 创建快照之后,可以对快照进行备份,可以将快照复制到其他服务器从而创建具有相同数据的服务器副本(Redis 主从结构,主要用来提高 Redis 性能),还可以将快照留在原地以便重启服务器的时候使用。
+Redis can create snapshots to obtain a copy of the data stored in memory at **a certain point in time**. After Redis creates a snapshot, it can back it up, copy the snapshot to other servers to create replicas with the same data (the Redis master-slave structure, mainly used to improve Redis performance), or keep the snapshot in place for use when restarting the server.
-快照持久化是 Redis 默认采用的持久化方式,在 `redis.conf` 配置文件中默认有此下配置:
+Snapshot persistence is the default persistence method used by Redis, and the following configuration is present by default in the `redis.conf` configuration file:
```clojure
-save 900 1 #在900秒(15分钟)之后,如果至少有1个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 900 1 # After 900 seconds (15 minutes), if at least 1 key has changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
-save 300 10 #在300秒(5分钟)之后,如果至少有10个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 300 10 # After 300 seconds (5 minutes), if at least 10 keys have changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
-save 60 10000 #在60秒(1分钟)之后,如果至少有10000个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 60 10000 # After 60 seconds (1 minute), if at least 10000 keys have changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
```
-### RDB 创建快照时会阻塞主线程吗?
+### Does RDB Block the Main Thread When Creating Snapshots?
-Redis 提供了两个命令来生成 RDB 快照文件:
+Redis provides two commands to generate RDB snapshot files:
-- `save` : 同步保存操作,会阻塞 Redis 主线程;
-- `bgsave` : fork 出一个子进程,子进程执行,不会阻塞 Redis 主线程,默认选项。
+- `save`: A synchronous save operation that blocks the Redis main thread;
+- `bgsave`: Forks a child process to execute, which does not block the Redis main thread, the default option.
-> 这里说 Redis 主线程而不是主进程的主要是因为 Redis 启动之后主要是通过单线程的方式完成主要的工作。如果你想将其描述为 Redis 主进程,也没毛病。
+> Here, we refer to the Redis main thread rather than the main process mainly because Redis primarily completes its main work in a single-threaded manner after startup. If you want to describe it as the Redis main process, that is also acceptable.
-## AOF 持久化
+## AOF Persistence
-### 什么是 AOF 持久化?
+### What is AOF Persistence?
-与快照持久化相比,AOF 持久化的实时性更好。默认情况下 Redis 没有开启 AOF(append only file)方式的持久化(Redis 6.0 之后已经默认是开启了),可以通过 `appendonly` 参数开启:
+Compared to snapshot persistence, AOF persistence has better real-time performance. By default, Redis does not enable AOF (append-only file) persistence (it has been enabled by default since Redis 6.0), and it can be enabled through the `appendonly` parameter:
```bash
appendonly yes
```
-开启 AOF 持久化后每执行一条会更改 Redis 中的数据的命令,Redis 就会将该命令写入到 AOF 缓冲区 `server.aof_buf` 中,然后再写入到 AOF 文件中(此时还在系统内核缓存区未同步到磁盘),最后再根据持久化方式( `fsync`策略)的配置来决定何时将系统内核缓存区的数据同步到硬盘中的。
+After enabling AOF persistence, every command that modifies data in Redis will write that command to the AOF buffer `server.aof_buf`, and then write it to the AOF file (at this point, it is still in the system kernel cache and has not been synchronized to disk). Finally, it decides when to synchronize the data in the system kernel cache to the hard disk based on the persistence method (`fsync` strategy) configuration.
-只有同步到磁盘中才算持久化保存了,否则依然存在数据丢失的风险,比如说:系统内核缓存区的数据还未同步,磁盘机器就宕机了,那这部分数据就算丢失了。
+Only when synchronized to disk is it considered persistently saved; otherwise, there is still a risk of data loss. For example, if the data in the system kernel cache has not been synchronized and the disk machine crashes, that portion of data will be lost.
-AOF 文件的保存位置和 RDB 文件的位置相同,都是通过 `dir` 参数设置的,默认的文件名是 `appendonly.aof`。
+The AOF file's save location is the same as that of the RDB file, both set by the `dir` parameter, and the default filename is `appendonly.aof`.
-### AOF 工作基本流程是怎样的?
+### What is the Basic Workflow of AOF?
-AOF 持久化功能的实现可以简单分为 5 步:
+The implementation of AOF persistence can be simply divided into 5 steps:
-1. **命令追加(append)**:所有的写命令会追加到 AOF 缓冲区中。
-2. **文件写入(write)**:将 AOF 缓冲区的数据写入到 AOF 文件中。这一步需要调用`write`函数(系统调用),`write`将数据写入到了系统内核缓冲区之后直接返回了(延迟写)。注意!!!此时并没有同步到磁盘。
-3. **文件同步(fsync)**:AOF 缓冲区根据对应的持久化方式( `fsync` 策略)向硬盘做同步操作。这一步需要调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用), `fsync` 针对单个文件操作,对其进行强制硬盘同步,`fsync` 将阻塞直到写入磁盘完成后返回,保证了数据持久化。
-4. **文件重写(rewrite)**:随着 AOF 文件越来越大,需要定期对 AOF 文件进行重写,达到压缩的目的。
-5. **重启加载(load)**:当 Redis 重启时,可以加载 AOF 文件进行数据恢复。
-
-> Linux 系统直接提供了一些函数用于对文件和设备进行访问和控制,这些函数被称为 **系统调用(syscall)**。
-
-这里对上面提到的一些 Linux 系统调用再做一遍解释:
-
-- `write`:写入系统内核缓冲区之后直接返回(仅仅是写到缓冲区),不会立即同步到硬盘。虽然提高了效率,但也带来了数据丢失的风险。同步硬盘操作通常依赖于系统调度机制,Linux 内核通常为 30s 同步一次,具体值取决于写出的数据量和 I/O 缓冲区的状态。
-- `fsync`:`fsync`用于强制刷新系统内核缓冲区(同步到到磁盘),确保写磁盘操作结束才会返回。
-
-AOF 工作流程图如下:
-
-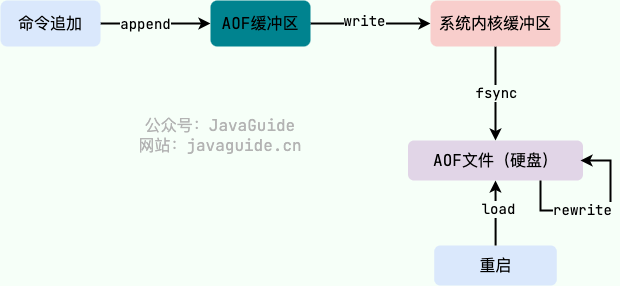
-
-### AOF 持久化方式有哪些?
-
-在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式( `fsync`策略),它们分别是:
-
-1. `appendfsync always`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后,后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)立即会调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件(刷盘),`fsync` 完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低 Redis 的性能(`write` + `fsync`)。
-2. `appendfsync everysec`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,由后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)每秒钟调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用)同步一次 AOF 文件(`write`+`fsync`,`fsync`间隔为 1 秒)
-3. `appendfsync no`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,让操作系统决定何时进行同步,Linux 下一般为 30 秒一次(`write`但不`fsync`,`fsync` 的时机由操作系统决定)。
-
-可以看出:**这 3 种持久化方式的主要区别在于 `fsync` 同步 AOF 文件的时机(刷盘)**。
-
-为了兼顾数据和写入性能,可以考虑 `appendfsync everysec` 选项 ,让 Redis 每秒同步一次 AOF 文件,Redis 性能受到的影响较小。而且这样即使出现系统崩溃,用户最多只会丢失一秒之内产生的数据。当硬盘忙于执行写入操作的时候,Redis 还会优雅的放慢自己的速度以便适应硬盘的最大写入速度。
-
-从 Redis 7.0.0 开始,Redis 使用了 **Multi Part AOF** 机制。顾名思义,Multi Part AOF 就是将原来的单个 AOF 文件拆分成多个 AOF 文件。在 Multi Part AOF 中,AOF 文件被分为三种类型,分别为:
-
-- BASE:表示基础 AOF 文件,它一般由子进程通过重写产生,该文件最多只有一个。
-- INCR:表示增量 AOF 文件,它一般会在 AOFRW 开始执行时被创建,该文件可能存在多个。
-- HISTORY:表示历史 AOF 文件,它由 BASE 和 INCR AOF 变化而来,每次 AOFRW 成功完成时,本次 AOFRW 之前对应的 BASE 和 INCR AOF 都将变为 HISTORY,HISTORY 类型的 AOF 会被 Redis 自动删除。
-
-Multi Part AOF 不是重点,了解即可,详细介绍可以看看阿里开发者的[Redis 7.0 Multi Part AOF 的设计和实现](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/467217082) 这篇文章。
-
-**相关 issue**:[Redis 的 AOF 方式 #783](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/783)。
-
-### AOF 为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志?
-
-关系型数据库(如 MySQL)通常都是执行命令之前记录日志(方便故障恢复),而 Redis AOF 持久化机制是在执行完命令之后再记录日志。
-
-
-
-**为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志呢?**
-
-- 避免额外的检查开销,AOF 记录日志不会对命令进行语法检查;
-- 在命令执行完之后再记录,不会阻塞当前的命令执行。
-
-这样也带来了风险(我在前面介绍 AOF 持久化的时候也提到过):
-
-- 如果刚执行完命令 Redis 就宕机会导致对应的修改丢失;
-- 可能会阻塞后续其他命令的执行(AOF 记录日志是在 Redis 主线程中进行的)。
-
-### AOF 重写了解吗?
-
-当 AOF 变得太大时,Redis 能够在后台自动重写 AOF 产生一个新的 AOF 文件,这个新的 AOF 文件和原有的 AOF 文件所保存的数据库状态一样,但体积更小。
-
-
-
-> AOF 重写(rewrite) 是一个有歧义的名字,该功能是通过读取数据库中的键值对来实现的,程序无须对现有 AOF 文件进行任何读入、分析或者写入操作。
-
-由于 AOF 重写会进行大量的写入操作,为了避免对 Redis 正常处理命令请求造成影响,Redis 将 AOF 重写程序放到子进程里执行。
-
-AOF 文件重写期间,Redis 还会维护一个 **AOF 重写缓冲区**,该缓冲区会在子进程创建新 AOF 文件期间,记录服务器执行的所有写命令。当子进程完成创建新 AOF 文件的工作之后,服务器会将重写缓冲区中的所有内容追加到新 AOF 文件的末尾,使得新的 AOF 文件保存的数据库状态与现有的数据库状态一致。最后,服务器用新的 AOF 文件替换旧的 AOF 文件,以此来完成 AOF 文件重写操作。
-
-开启 AOF 重写功能,可以调用 `BGREWRITEAOF` 命令手动执行,也可以设置下面两个配置项,让程序自动决定触发时机:
-
-- `auto-aof-rewrite-min-size`:如果 AOF 文件大小小于该值,则不会触发 AOF 重写。默认值为 64 MB;
-- `auto-aof-rewrite-percentage`:执行 AOF 重写时,当前 AOF 大小(aof_current_size)和上一次重写时 AOF 大小(aof_base_size)的比值。如果当前 AOF 文件大小增加了这个百分比值,将触发 AOF 重写。将此值设置为 0 将禁用自动 AOF 重写。默认值为 100。
-
-Redis 7.0 版本之前,如果在重写期间有写入命令,AOF 可能会使用大量内存,重写期间到达的所有写入命令都会写入磁盘两次。
-
-Redis 7.0 版本之后,AOF 重写机制得到了优化改进。下面这段内容摘自阿里开发者的[从 Redis7.0 发布看 Redis 的过去与未来](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RnoPPL7jiFSKkx3G4p57Pg) 这篇文章。
-
-> AOF 重写期间的增量数据如何处理一直是个问题,在过去写期间的增量数据需要在内存中保留,写结束后再把这部分增量数据写入新的 AOF 文件中以保证数据完整性。可以看出来 AOF 写会额外消耗内存和磁盘 IO,这也是 Redis AOF 写的痛点,虽然之前也进行过多次改进但是资源消耗的本质问题一直没有解决。
->
-> 阿里云的 Redis 企业版在最初也遇到了这个问题,在内部经过多次迭代开发,实现了 Multi-part AOF 机制来解决,同时也贡献给了社区并随此次 7.0 发布。具体方法是采用 base(全量数据)+inc(增量数据)独立文件存储的方式,彻底解决内存和 IO 资源的浪费,同时也支持对历史 AOF 文件的保存管理,结合 AOF 文件中的时间信息还可以实现 PITR 按时间点恢复(阿里云企业版 Tair 已支持),这进一步增强了 Redis 的数据可靠性,满足用户数据回档等需求。
-
-**相关 issue**:[Redis AOF 重写描述不准确 #1439](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1439)。
-
-### AOF 校验机制了解吗?
-
-纯 AOF 模式下,Redis 不会对整个 AOF 文件使用校验和(如 CRC64),而是通过逐条解析文件中的命令来验证文件的有效性。如果解析过程中发现语法错误(如命令不完整、格式错误),Redis 会终止加载并报错,从而避免错误数据载入内存。
-
-在 **混合持久化模式**(Redis 4.0 引入)下,AOF 文件由两部分组成:
-
-- **RDB 快照部分**:文件以固定的 `REDIS` 字符开头,存储某一时刻的内存数据快照,并在快照数据末尾附带一个 CRC64 校验和(位于 RDB 数据块尾部、AOF 增量部分之前)。
-- **AOF 增量部分**:紧随 RDB 快照部分之后,记录 RDB 快照生成后的增量写命令。这部分增量命令以 Redis 协议格式逐条记录,无整体或全局校验和。
-
-RDB 文件结构的核心部分如下:
-
-| **字段** | **解释** |
-| ----------------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
-| `"REDIS"` | 固定以该字符串开始 |
-| `RDB_VERSION` | RDB 文件的版本号 |
-| `DB_NUM` | Redis 数据库编号,指明数据需要存放到哪个数据库 |
-| `KEY_VALUE_PAIRS` | Redis 中具体键值对的存储 |
-| `EOF` | RDB 文件结束标志 |
-| `CHECK_SUM` | 8 字节确保 RDB 完整性的校验和 |
-
-Redis 启动并加载 AOF 文件时,首先会校验文件开头 RDB 快照部分的数据完整性,即计算该部分数据的 CRC64 校验和,并与紧随 RDB 数据之后、AOF 增量部分之前存储的 CRC64 校验和值进行比较。如果 CRC64 校验和不匹配,Redis 将拒绝启动并报告错误。
-
-RDB 部分校验通过后,Redis 随后逐条解析 AOF 部分的增量命令。如果解析过程中出现错误(如不完整的命令或格式错误),Redis 会停止继续加载后续命令,并报告错误,但此时 Redis 已经成功加载了 RDB 快照部分的数据。
-
-## Redis 4.0 对于持久化机制做了什么优化?
-
-由于 RDB 和 AOF 各有优势,于是,Redis 4.0 开始支持 RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(默认关闭,可以通过配置项 `aof-use-rdb-preamble` 开启)。
-
-如果把混合持久化打开,AOF 重写的时候就直接把 RDB 的内容写到 AOF 文件开头。这样做的好处是可以结合 RDB 和 AOF 的优点, 快速加载同时避免丢失过多的数据。当然缺点也是有的, AOF 里面的 RDB 部分是压缩格式不再是 AOF 格式,可读性较差。
-
-官方文档地址:
-
-
-
-## 如何选择 RDB 和 AOF?
-
-关于 RDB 和 AOF 的优缺点,官网上面也给了比较详细的说明[Redis persistence](https://redis.io/docs/manual/persistence/),这里结合自己的理解简单总结一下。
-
-**RDB 比 AOF 优秀的地方**:
-
-- RDB 文件存储的内容是经过压缩的二进制数据, 保存着某个时间点的数据集,文件很小,适合做数据的备份,灾难恢复。AOF 文件存储的是每一次写命令,类似于 MySQL 的 binlog 日志,通常会比 RDB 文件大很多。当 AOF 变得太大时,Redis 能够在后台自动重写 AOF。新的 AOF 文件和原有的 AOF 文件所保存的数据库状态一样,但体积更小。不过, Redis 7.0 版本之前,如果在重写期间有写入命令,AOF 可能会使用大量内存,重写期间到达的所有写入命令都会写入磁盘两次。
-- 使用 RDB 文件恢复数据,直接解析还原数据即可,不需要一条一条地执行命令,速度非常快。而 AOF 则需要依次执行每个写命令,速度非常慢。也就是说,与 AOF 相比,恢复大数据集的时候,RDB 速度更快。
-
-**AOF 比 RDB 优秀的地方**:
-
-- RDB 的数据安全性不如 AOF,没有办法实时或者秒级持久化数据。生成 RDB 文件的过程是比较繁重的, 虽然 BGSAVE 子进程写入 RDB 文件的工作不会阻塞主线程,但会对机器的 CPU 资源和内存资源产生影响,严重的情况下甚至会直接把 Redis 服务干宕机。AOF 支持秒级数据丢失(取决 fsync 策略,如果是 everysec,最多丢失 1 秒的数据),仅仅是追加命令到 AOF 文件,操作轻量。
-- RDB 文件是以特定的二进制格式保存的,并且在 Redis 版本演进中有多个版本的 RDB,所以存在老版本的 Redis 服务不兼容新版本的 RDB 格式的问题。
-- AOF 以一种易于理解和解析的格式包含所有操作的日志。你可以轻松地导出 AOF 文件进行分析,你也可以直接操作 AOF 文件来解决一些问题。比如,如果执行`FLUSHALL`命令意外地刷新了所有内容后,只要 AOF 文件没有被重写,删除最新命令并重启即可恢复之前的状态。
-
-**综上**:
-
-- Redis 保存的数据丢失一些也没什么影响的话,可以选择使用 RDB。
-- 不建议单独使用 AOF,因为时不时地创建一个 RDB 快照可以进行数据库备份、更快的重启以及解决 AOF 引擎错误。
-- 如果保存的数据要求安全性比较高的话,建议同时开启 RDB 和 AOF 持久化或者开启 RDB 和 AOF 混合持久化。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- Redis persistence - Redis 官方文档:
-- The difference between AOF and RDB persistence:
-- Redis AOF 持久化详解 - 程序员历小冰:
-- Redis RDB 与 AOF 持久化 · Analyze:
-
-
+1. **Command Append (append)**: All write commands are appended to the AOF buffer.
+1. **File Write (write)**: The data in the AOF buffer is written to the AOF file. This step requires calling the `write` function (system call), and `write` returns directly after writing the data to the system kernel buffer (delayed write). Note!!! At this point, it has not been synchronized to disk.
+1. \*\*File Synchron
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
index 7102985b9a5..ead2803acfb 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
@@ -1,874 +1,57 @@
---
-title: Redis常见面试题总结(上)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Redis Interview Questions (Part 1)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: Redis基础,Redis常见数据结构,Redis线程模型,Redis内存管理,Redis事务,Redis性能优化
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 一篇文章总结Redis常见的知识点和面试题,涵盖Redis基础、Redis常见数据结构、Redis线程模型、Redis内存管理、Redis事务、Redis性能优化等内容。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Redis Basics, Common Redis Data Structures, Redis Thread Model, Redis Memory Management, Redis Transactions, Redis Performance Optimization
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: An article summarizing common knowledge points and interview questions about Redis, covering Redis basics, common data structures, thread model, memory management, transactions, performance optimization, and more.
---
-## Redis 基础
+## Redis Basics
-### 什么是 Redis?
+### What is Redis?
-[Redis](https://redis.io/) (**RE**mote **DI**ctionary **S**erver)是一个基于 C 语言开发的开源 NoSQL 数据库(BSD 许可)。与传统数据库不同的是,Redis 的数据是保存在内存中的(内存数据库,支持持久化),因此读写速度非常快,被广泛应用于分布式缓存方向。并且,Redis 存储的是 KV 键值对数据。
+[Redis](https://redis.io/) (**RE**mote **DI**ctionary **S**erver) is an open-source NoSQL database developed in C language (BSD license). Unlike traditional databases, Redis stores data in memory (in-memory database, supports persistence), which allows for very fast read and write speeds, making it widely used in distributed caching. Additionally, Redis stores data as key-value pairs (KV).
-为了满足不同的业务场景,Redis 内置了多种数据类型实现(比如 String、Hash、Sorted Set、Bitmap、HyperLogLog、GEO)。并且,Redis 还支持事务、持久化、Lua 脚本、发布订阅模型、多种开箱即用的集群方案(Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster)。
+To meet different business scenarios, Redis has built-in implementations of various data types (such as String, Hash, Sorted Set, Bitmap, HyperLogLog, GEO). Furthermore, Redis supports transactions, persistence, Lua scripting, a publish-subscribe model, and various out-of-the-box clustering solutions (Redis Sentinel, Redis Cluster).
-
+
-Redis 没有外部依赖,Linux 和 OS X 是 Redis 开发和测试最多的两个操作系统,官方推荐生产环境使用 Linux 部署 Redis。
+Redis has no external dependencies, and Linux and OS X are the two operating systems where Redis is developed and tested the most. The official recommendation is to deploy Redis in a production environment using Linux.
-个人学习的话,你可以自己本机安装 Redis 或者通过 Redis 官网提供的[在线 Redis 环境](https://try.redis.io/)(少部分命令无法使用)来实际体验 Redis。
+For personal learning, you can install Redis on your local machine or use the [online Redis environment](https://try.redis.io/) provided by the Redis official website (some commands may not be available) to experience Redis in practice.
-全世界有非常多的网站使用到了 Redis,[techstacks.io](https://techstacks.io/) 专门维护了一个[使用 Redis 的热门站点列表](https://techstacks.io/tech/redis),感兴趣的话可以看看。
+Many websites around the world use Redis, and [techstacks.io](https://techstacks.io/) maintains a [list of popular sites using Redis](https://techstacks.io/tech/redis). If you're interested, you can take a look.
-### Redis 为什么这么快?
+### Why is Redis so fast?
-Redis 内部做了非常多的性能优化,比较重要的有下面 4 点:
+Redis has implemented many performance optimizations internally, with the following four points being particularly important:
-1. **纯内存操作 (Memory-Based Storage)** :这是最主要的原因。Redis 数据读写操作都发生在内存中,访问速度是纳秒级别,而传统数据库频繁读写磁盘的速度是毫秒级别,两者相差数个数量级。
-2. **高效的 I/O 模型 (I/O Multiplexing & Single-Threaded Event Loop)** :Redis 使用单线程事件循环配合 I/O 多路复用技术,让单个线程可以同时处理多个网络连接上的 I/O 事件(如读写),避免了多线程模型中的上下文切换和锁竞争问题。虽然是单线程,但结合内存操作的高效性和 I/O 多路复用,使得 Redis 能轻松处理大量并发请求(Redis 线程模型会在后文中详细介绍到)。
-3. **优化的内部数据结构 (Optimized Data Structures)** :Redis 提供多种数据类型(如 String, List, Hash, Set, Sorted Set 等),其内部实现采用高度优化的编码方式(如 ziplist, quicklist, skiplist, hashtable 等)。Redis 会根据数据大小和类型动态选择最合适的内部编码,以在性能和空间效率之间取得最佳平衡。
-4. **简洁高效的通信协议 (Simple Protocol - RESP)** :Redis 使用的是自己设计的 RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) 协议。这个协议实现简单、解析性能好,并且是二进制安全的。客户端和服务端之间通信的序列化/反序列化开销很小,有助于提升整体的交互速度。
+1. **Memory-Based Storage**: This is the primary reason. Redis read and write operations occur in memory, with access speeds at the nanosecond level, while traditional databases frequently read and write to disk at the millisecond level, resulting in several orders of magnitude difference.
+1. **Efficient I/O Model (I/O Multiplexing & Single-Threaded Event Loop)**: Redis uses a single-threaded event loop combined with I/O multiplexing technology, allowing a single thread to handle multiple I/O events (such as read and write) on multiple network connections simultaneously, avoiding context switching and lock contention issues in multi-threaded models. Although it is single-threaded, the efficiency of memory operations and I/O multiplexing allows Redis to easily handle a large number of concurrent requests (the Redis thread model will be introduced in detail later).
+1. **Optimized Internal Data Structures**: Redis provides various data types (such as String, List, Hash, Set, Sorted Set, etc.), and its internal implementation uses highly optimized encoding methods (such as ziplist, quicklist, skiplist, hashtable, etc.). Redis dynamically selects the most suitable internal encoding based on data size and type to achieve the best balance between performance and space efficiency.
+1. **Simple and Efficient Communication Protocol (Simple Protocol - RESP)**: Redis uses its own designed RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) protocol. This protocol is simple to implement, has good parsing performance, and is binary safe. The serialization/deserialization overhead for communication between the client and server is minimal, which helps improve overall interaction speed.
-> 下面这张图片总结的挺不错的,分享一下,出自 [Why is Redis so fast?](https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1498703822528544770)。
+> The image below summarizes this well, shared from [Why is Redis so fast?](https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1498703822528544770).

-那既然都这么快了,为什么不直接用 Redis 当主数据库呢?主要是因为内存成本太高,并且 Redis 提供的数据持久化仍然有数据丢失的风险。
+Since Redis is so fast, why not use it as the primary database? The main reason is that memory costs are too high, and the data persistence provided by Redis still carries the risk of data loss.
-### 除了 Redis,你还知道其他分布式缓存方案吗?
+### Besides Redis, do you know other distributed caching solutions?
-如果面试中被问到这个问题的话,面试官主要想看看:
+If asked this question in an interview, the interviewer mainly wants to see:
-1. 你在选择 Redis 作为分布式缓存方案时,是否是经过严谨的调研和思考,还是只是因为 Redis 是当前的“热门”技术。
-2. 你在分布式缓存方向的技术广度。
+1. Whether your choice of Redis as a distributed caching solution was based on rigorous research and thought, or just because Redis is currently a "hot" technology.
+1. Your breadth of knowledge in distributed caching technologies.
-如果你了解其他方案,并且能解释为什么最终选择了 Redis(更进一步!),这会对你面试表现加分不少!
-
-下面简单聊聊常见的分布式缓存技术选型。
-
-分布式缓存的话,比较老牌同时也是使用的比较多的还是 **Memcached** 和 **Redis**。不过,现在基本没有看过还有项目使用 **Memcached** 来做缓存,都是直接用 **Redis**。
-
-Memcached 是分布式缓存最开始兴起的那会,比较常用的。后来,随着 Redis 的发展,大家慢慢都转而使用更加强大的 Redis 了。
-
-有一些大厂也开源了类似于 Redis 的分布式高性能 KV 存储数据库,例如,腾讯开源的 [**Tendis**](https://github.com/Tencent/Tendis)。Tendis 基于知名开源项目 [RocksDB](https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb) 作为存储引擎 ,100% 兼容 Redis 协议和 Redis4.0 所有数据模型。关于 Redis 和 Tendis 的对比,腾讯官方曾经发过一篇文章:[Redis vs Tendis:冷热混合存储版架构揭秘](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/MeYkfOIdnU6LYlsGb24KjQ),可以简单参考一下。
-
-不过,从 Tendis 这个项目的 Github 提交记录可以看出,Tendis 开源版几乎已经没有被维护更新了,加上其关注度并不高,使用的公司也比较少。因此,不建议你使用 Tendis 来实现分布式缓存。
-
-目前,比较业界认可的 Redis 替代品还是下面这两个开源分布式缓存(都是通过碰瓷 Redis 火的):
-
-- [Dragonfly](https://github.com/dragonflydb/dragonfly):一种针对现代应用程序负荷需求而构建的内存数据库,完全兼容 Redis 和 Memcached 的 API,迁移时无需修改任何代码,号称全世界最快的内存数据库。
-- [KeyDB](https://github.com/Snapchat/KeyDB):Redis 的一个高性能分支,专注于多线程、内存效率和高吞吐量。
-
-不过,个人还是建议分布式缓存首选 Redis,毕竟经过了这么多年的考验,生态非常优秀,资料也很全面!
-
-PS:篇幅问题,我这并没有对上面提到的分布式缓存选型做详细介绍和对比,感兴趣的话,可以自行研究一下。
-
-### 说一下 Redis 和 Memcached 的区别和共同点
-
-现在公司一般都是用 Redis 来实现缓存,而且 Redis 自身也越来越强大了!不过,了解 Redis 和 Memcached 的区别和共同点,有助于我们在做相应的技术选型的时候,能够做到有理有据!
-
-**共同点**:
-
-1. 都是基于内存的数据库,一般都用来当做缓存使用。
-2. 都有过期策略。
-3. 两者的性能都非常高。
-
-**区别**:
-
-1. **数据类型**:Redis 支持更丰富的数据类型(支持更复杂的应用场景)。Redis 不仅仅支持简单的 k/v 类型的数据,同时还提供 list、set、zset、hash 等数据结构的存储;而 Memcached 只支持最简单的 k/v 数据类型。
-2. **数据持久化**:Redis 支持数据的持久化,可以将内存中的数据保持在磁盘中,重启的时候可以再次加载进行使用;而 Memcached 把数据全部存在内存之中。也就是说,Redis 有灾难恢复机制,而 Memcached 没有。
-3. **集群模式支持**:Memcached 没有原生的集群模式,需要依靠客户端来实现往集群中分片写入数据;而 Redis 自 3.0 版本起是原生支持集群模式的。
-4. **线程模型**:Memcached 是多线程、非阻塞 IO 复用的网络模型;而 Redis 使用单线程的多路 IO 复用模型(Redis 6.0 针对网络数据的读写引入了多线程)。
-5. **特性支持**:Redis 支持发布订阅模型、Lua 脚本、事务等功能,而 Memcached 不支持。并且,Redis 支持更多的编程语言。
-6. **过期数据删除**:Memcached 过期数据的删除策略只用了惰性删除,而 Redis 同时使用了惰性删除与定期删除。
-
-相信看了上面的对比之后,我们已经没有什么理由可以选择使用 Memcached 来作为自己项目的分布式缓存了。
-
-### 为什么要用 Redis?
-
-**1、访问速度更快**
-
-传统数据库数据保存在磁盘,而 Redis 基于内存,内存的访问速度比磁盘快很多。引入 Redis 之后,我们可以把一些高频访问的数据放到 Redis 中,这样下次就可以直接从内存中读取,速度可以提升几十倍甚至上百倍。
-
-**2、高并发**
-
-一般像 MySQL 这类的数据库的 QPS 大概都在 4k 左右(4 核 8g),但是使用 Redis 缓存之后很容易达到 5w+,甚至能达到 10w+(就单机 Redis 的情况,Redis 集群的话会更高)。
-
-> QPS(Query Per Second):服务器每秒可以执行的查询次数;
-
-由此可见,直接操作缓存能够承受的数据库请求数量是远远大于直接访问数据库的,所以我们可以考虑把数据库中的部分数据转移到缓存中去,这样用户的一部分请求会直接到缓存这里而不用经过数据库。进而,我们也就提高了系统整体的并发。
-
-**3、功能全面**
-
-Redis 除了可以用作缓存之外,还可以用于分布式锁、限流、消息队列、延时队列等场景,功能强大!
-
-### 为什么用 Redis 而不用本地缓存呢?
-
-| 特性 | 本地缓存 | Redis |
-| ------------ | ------------------------------------ | -------------------------------- |
-| 数据一致性 | 多服务器部署时存在数据不一致问题 | 数据一致 |
-| 内存限制 | 受限于单台服务器内存 | 独立部署,内存空间更大 |
-| 数据丢失风险 | 服务器宕机数据丢失 | 可持久化,数据不易丢失 |
-| 管理维护 | 分散,管理不便 | 集中管理,提供丰富的管理工具 |
-| 功能丰富性 | 功能有限,通常只提供简单的键值对存储 | 功能丰富,支持多种数据结构和功能 |
-
-### 常见的缓存读写策略有哪些?
-
-关于常见的缓存读写策略的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[3 种常用的缓存读写策略详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.html)。
-
-### 什么是 Redis Module?有什么用?
-
-Redis 从 4.0 版本开始,支持通过 Module 来扩展其功能以满足特殊的需求。这些 Module 以动态链接库(so 文件)的形式被加载到 Redis 中,这是一种非常灵活的动态扩展功能的实现方式,值得借鉴学习!
-
-我们每个人都可以基于 Redis 去定制化开发自己的 Module,比如实现搜索引擎功能、自定义分布式锁和分布式限流。
-
-目前,被 Redis 官方推荐的 Module 有:
-
-- [RediSearch](https://github.com/RediSearch/RediSearch):用于实现搜索引擎的模块。
-- [RedisJSON](https://github.com/RedisJSON/RedisJSON):用于处理 JSON 数据的模块。
-- [RedisGraph](https://github.com/RedisGraph/RedisGraph):用于实现图形数据库的模块。
-- [RedisTimeSeries](https://github.com/RedisTimeSeries/RedisTimeSeries):用于处理时间序列数据的模块。
-- [RedisBloom](https://github.com/RedisBloom/RedisBloom):用于实现布隆过滤器的模块。
-- [RedisAI](https://github.com/RedisAI/RedisAI):用于执行深度学习/机器学习模型并管理其数据的模块。
-- [RedisCell](https://github.com/brandur/redis-cell):用于实现分布式限流的模块。
-- ……
-
-关于 Redis 模块的详细介绍,可以查看官方文档:。
-
-## Redis 应用
-
-### Redis 除了做缓存,还能做什么?
-
-- **分布式锁**:通过 Redis 来做分布式锁是一种比较常见的方式。通常情况下,我们都是基于 Redisson 来实现分布式锁。关于 Redis 实现分布式锁的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock.html)。
-- **限流**:一般是通过 Redis + Lua 脚本的方式来实现限流。如果不想自己写 Lua 脚本的话,也可以直接利用 Redisson 中的 `RRateLimiter` 来实现分布式限流,其底层实现就是基于 Lua 代码+令牌桶算法。
-- **消息队列**:Redis 自带的 List 数据结构可以作为一个简单的队列使用。Redis 5.0 中增加的 Stream 类型的数据结构更加适合用来做消息队列。它比较类似于 Kafka,有主题和消费组的概念,支持消息持久化以及 ACK 机制。
-- **延时队列**:Redisson 内置了延时队列(基于 Sorted Set 实现的)。
-- **分布式 Session**:利用 String 或者 Hash 数据类型保存 Session 数据,所有的服务器都可以访问。
-- **复杂业务场景**:通过 Redis 以及 Redis 扩展(比如 Redisson)提供的数据结构,我们可以很方便地完成很多复杂的业务场景,比如通过 Bitmap 统计活跃用户、通过 Sorted Set 维护排行榜、通过 HyperLogLog 统计网站 UV 和 PV。
-- ……
-
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现分布式锁?
-
-关于 Redis 实现分布式锁的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.html)。
-
-### Redis 可以做消息队列么?
-
-> 实际项目中使用 Redis 来做消息队列的非常少,毕竟有更成熟的消息队列中间件可以用。
-
-先说结论:**可以是可以,但不建议使用 Redis 来做消息队列。和专业的消息队列相比,还是有很多欠缺的地方。**
-
-**Redis 2.0 之前,如果想要使用 Redis 来做消息队列的话,只能通过 List 来实现。**
-
-通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP` 即可实现简易版消息队列:
-
-```bash
-# 生产者生产消息
-> RPUSH myList msg1 msg2
-(integer) 2
-> RPUSH myList msg3
-(integer) 3
-# 消费者消费消息
-> LPOP myList
-"msg1"
-```
-
-不过,通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP` 这样的方式存在性能问题,我们需要不断轮询去调用 `RPOP` 或 `LPOP` 来消费消息。当 List 为空时,大部分的轮询的请求都是无效请求,这种方式大量浪费了系统资源。
-
-因此,Redis 还提供了 `BLPOP`、`BRPOP` 这种阻塞式读取的命令(带 B-Blocking 的都是阻塞式),并且还支持一个超时参数。如果 List 为空,Redis 服务端不会立刻返回结果,它会等待 List 中有新数据后再返回或者是等待最多一个超时时间后返回空。如果将超时时间设置为 0 时,即可无限等待,直到弹出消息
-
-```bash
-# 超时时间为 10s
-# 如果有数据立刻返回,否则最多等待10秒
-> BRPOP myList 10
-null
-```
-
-**List 实现消息队列功能太简单,像消息确认机制等功能还需要我们自己实现,最要命的是没有广播机制,消息也只能被消费一次。**
-
-**Redis 2.0 引入了发布订阅 (pub/sub) 功能,解决了 List 实现消息队列没有广播机制的问题。**
-
-
-
-pub/sub 中引入了一个概念叫 **channel(频道)**,发布订阅机制的实现就是基于这个 channel 来做的。
-
-pub/sub 涉及发布者(Publisher)和订阅者(Subscriber,也叫消费者)两个角色:
-
-- 发布者通过 `PUBLISH` 投递消息给指定 channel。
-- 订阅者通过`SUBSCRIBE`订阅它关心的 channel。并且,订阅者可以订阅一个或者多个 channel。
-
-我们这里启动 3 个 Redis 客户端来简单演示一下:
-
-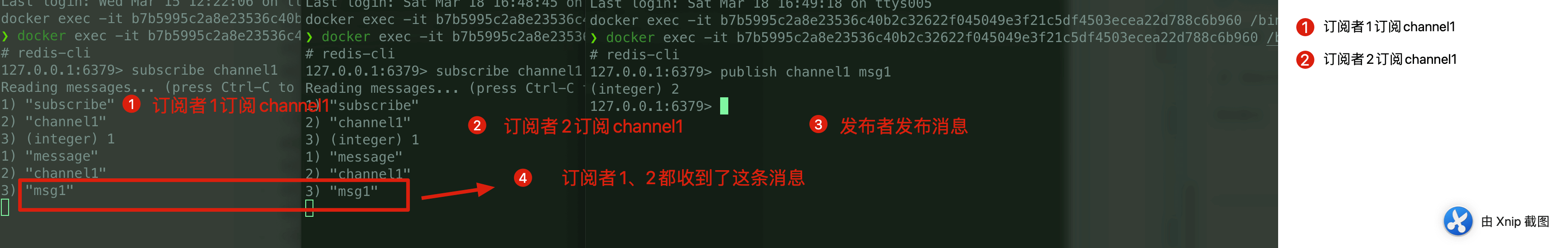
-
-pub/sub 既能单播又能广播,还支持 channel 的简单正则匹配。不过,消息丢失(客户端断开连接或者 Redis 宕机都会导致消息丢失)、消息堆积(发布者发布消息的时候不会管消费者的具体消费能力如何)等问题依然没有一个比较好的解决办法。
-
-为此,Redis 5.0 新增加的一个数据结构 `Stream` 来做消息队列。`Stream` 支持:
-
-- 发布 / 订阅模式;
-- 按照消费者组进行消费(借鉴了 Kafka 消费者组的概念);
-- 消息持久化( RDB 和 AOF);
-- ACK 机制(通过确认机制来告知已经成功处理了消息);
-- 阻塞式获取消息。
-
-`Stream` 的结构如下:
-
-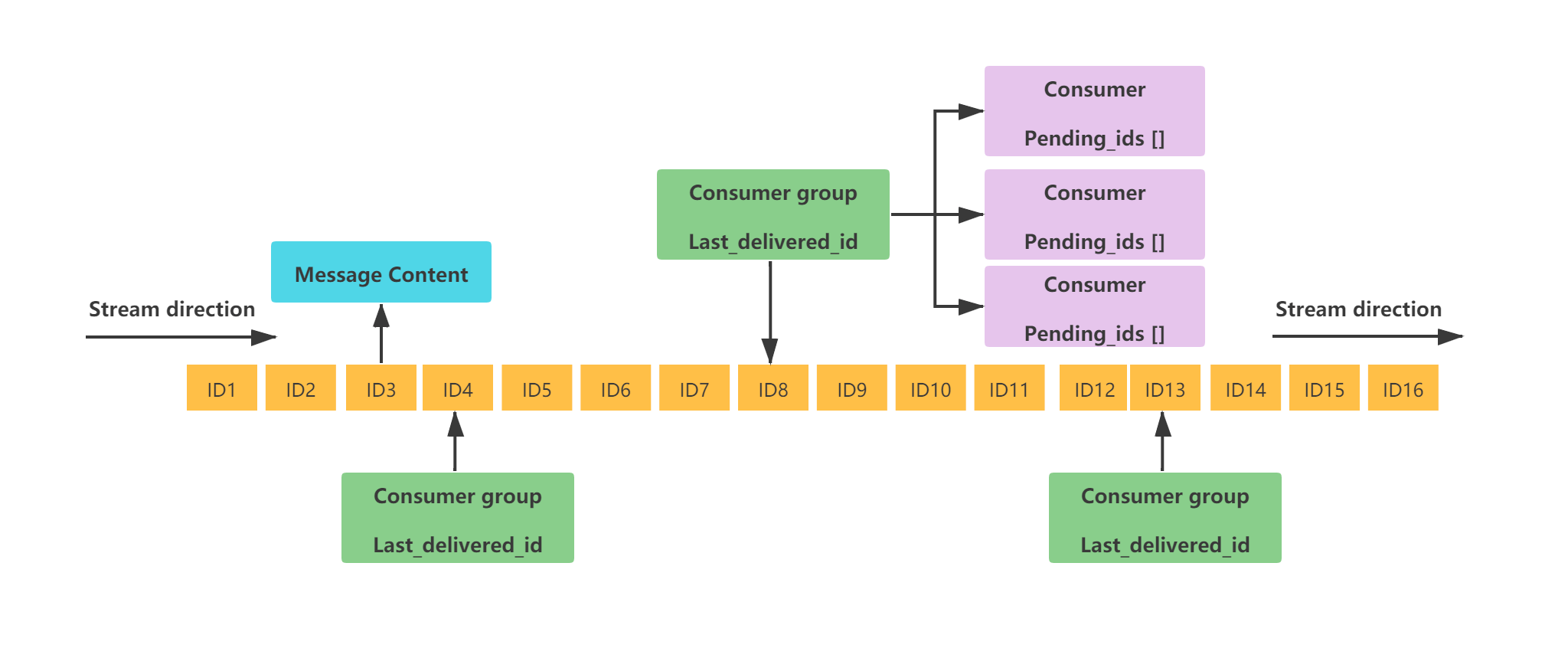
-
-这是一个有序的消息链表,每个消息都有一个唯一的 ID 和对应的内容。ID 是一个时间戳和序列号的组合,用来保证消息的唯一性和递增性。内容是一个或多个键值对(类似 Hash 基本数据类型),用来存储消息的数据。
-
-这里再对图中涉及到的一些概念,进行简单解释:
-
-- `Consumer Group`:消费者组用于组织和管理多个消费者。消费者组本身不处理消息,而是再将消息分发给消费者,由消费者进行真正的消费。
-- `last_delivered_id`:标识消费者组当前消费位置的游标,消费者组中任意一个消费者读取了消息都会使 last_delivered_id 往前移动。
-- `pending_ids`:记录已经被客户端消费但没有 ack 的消息的 ID。
-
-下面是`Stream` 用作消息队列时常用的命令:
-
-- `XADD`:向流中添加新的消息。
-- `XREAD`:从流中读取消息。
-- `XREADGROUP`:从消费组中读取消息。
-- `XRANGE`:根据消息 ID 范围读取流中的消息。
-- `XREVRANGE`:与 `XRANGE` 类似,但以相反顺序返回结果。
-- `XDEL`:从流中删除消息。
-- `XTRIM`:修剪流的长度,可以指定修建策略(`MAXLEN`/`MINID`)。
-- `XLEN`:获取流的长度。
-- `XGROUP CREATE`:创建消费者组。
-- `XGROUP DESTROY`:删除消费者组。
-- `XGROUP DELCONSUMER`:从消费者组中删除一个消费者。
-- `XGROUP SETID`:为消费者组设置新的最后递送消息 ID。
-- `XACK`:确认消费组中的消息已被处理。
-- `XPENDING`:查询消费组中挂起(未确认)的消息。
-- `XCLAIM`:将挂起的消息从一个消费者转移到另一个消费者。
-- `XINFO`:获取流(`XINFO STREAM`)、消费组(`XINFO GROUPS`)或消费者(`XINFO CONSUMERS`)的详细信息。
-
-`Stream` 使用起来相对要麻烦一些,这里就不演示了。
-
-总的来说,`Stream` 已经可以满足一个消息队列的基本要求了。不过,`Stream` 在实际使用中依然会有一些小问题不太好解决,比如在 Redis 发生故障恢复后不能保证消息至少被消费一次。
-
-综上,和专业的消息队列相比,使用 Redis 来实现消息队列还是有很多欠缺的地方,比如消息丢失和堆积问题不好解决。因此,我们通常建议不要使用 Redis 来做消息队列,你完全可以选择市面上比较成熟的一些消息队列,比如 RocketMQ、Kafka。不过,如果你就是想要用 Redis 来做消息队列的话,那我建议你优先考虑 `Stream`,这是目前相对最优的 Redis 消息队列实现。
-
-相关阅读:[Redis 消息队列发展历程 - 阿里开发者 - 2022](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gCUT5TcCQRAxYkTJfTRjJw)。
-
-### Redis 可以做搜索引擎么?
-
-Redis 是可以实现全文搜索引擎功能的,需要借助 **RediSearch**,这是一个基于 Redis 的搜索引擎模块。
-
-RediSearch 支持中文分词、聚合统计、停用词、同义词、拼写检查、标签查询、向量相似度查询、多关键词搜索、分页搜索等功能,算是一个功能比较完善的全文搜索引擎了。
-
-相比较于 Elasticsearch 来说,RediSearch 主要在下面两点上表现更优异一些:
-
-1. 性能更优秀:依赖 Redis 自身的高性能,基于内存操作(Elasticsearch 基于磁盘)。
-2. 较低内存占用实现快速索引:RediSearch 内部使用压缩的倒排索引,所以可以用较低的内存占用来实现索引的快速构建。
-
-对于小型项目的简单搜索场景来说,使用 RediSearch 来作为搜索引擎还是没有问题的(搭配 RedisJSON 使用)。
-
-对于比较复杂或者数据规模较大的搜索场景,还是不太建议使用 RediSearch 来作为搜索引擎,主要是因为下面这些限制和问题:
-
-1. 数据量限制:Elasticsearch 可以支持 PB 级别的数据量,可以轻松扩展到多个节点,利用分片机制提高可用性和性能。RedisSearch 是基于 Redis 实现的,其能存储的数据量受限于 Redis 的内存容量,不太适合存储大规模的数据(内存昂贵,扩展能力较差)。
-2. 分布式能力较差:Elasticsearch 是为分布式环境设计的,可以轻松扩展到多个节点。虽然 RedisSearch 支持分布式部署,但在实际应用中可能会面临一些挑战,如数据分片、节点间通信、数据一致性等问题。
-3. 聚合功能较弱:Elasticsearch 提供了丰富的聚合功能,而 RediSearch 的聚合功能相对较弱,只支持简单的聚合操作。
-4. 生态较差:Elasticsearch 可以轻松和常见的一些系统/软件集成比如 Hadoop、Spark、Kibana,而 RedisSearch 则不具备该优势。
-
-Elasticsearch 适用于全文搜索、复杂查询、实时数据分析和聚合的场景,而 RediSearch 适用于快速数据存储、缓存和简单查询的场景。
-
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现延时任务?
-
-> 类似的问题:
->
-> - 订单在 10 分钟后未支付就失效,如何用 Redis 实现?
-> - 红包 24 小时未被查收自动退还,如何用 Redis 实现?
-
-基于 Redis 实现延时任务的功能无非就下面两种方案:
-
-1. Redis 过期事件监听。
-2. Redisson 内置的延时队列。
-
-Redis 过期事件监听存在时效性较差、丢消息、多服务实例下消息重复消费等问题,不被推荐使用。
-
-Redisson 内置的延时队列具备下面这些优势:
-
-1. **减少了丢消息的可能**:DelayedQueue 中的消息会被持久化,即使 Redis 宕机了,根据持久化机制,也只可能丢失一点消息,影响不大。当然了,你也可以使用扫描数据库的方法作为补偿机制。
-2. **消息不存在重复消费问题**:每个客户端都是从同一个目标队列中获取任务的,不存在重复消费的问题。
-
-关于 Redis 实现延时任务的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[如何基于 Redis 实现延时任务?](./redis-delayed-task.md)。
-
-## Redis 数据类型
-
-关于 Redis 5 种基础数据类型和 3 种特殊数据类型的详细介绍请看下面这两篇文章以及 [Redis 官方文档](https://redis.io/docs/data-types/):
-
-- [Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.html)
-- [Redis 3 种特殊数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.html)
-
-### Redis 常用的数据类型有哪些?
-
-Redis 中比较常见的数据类型有下面这些:
-
-- **5 种基础数据类型**:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)。
-- **3 种特殊数据类型**:HyperLogLog(基数统计)、Bitmap (位图)、Geospatial (地理位置)。
-
-除了上面提到的之外,还有一些其他的比如 [Bloom filter(布隆过滤器)](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/bloom-filter.html)、Bitfield(位域)。
-
-### String 的应用场景有哪些?
-
-String 是 Redis 中最简单同时也是最常用的一个数据类型。它是一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。
-
-String 的常见应用场景如下:
-
-- 常规数据(比如 Session、Token、序列化后的对象、图片的路径)的缓存;
-- 计数比如用户单位时间的请求数(简单限流可以用到)、页面单位时间的访问数;
-- 分布式锁(利用 `SETNX key value` 命令可以实现一个最简易的分布式锁);
-- ……
-
-关于 String 的详细介绍请看这篇文章:[Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.html)。
-
-### String 还是 Hash 存储对象数据更好呢?
-
-简单对比一下二者:
-
-- **对象存储方式**:String 存储的是序列化后的对象数据,存放的是整个对象,操作简单直接。Hash 是对对象的每个字段单独存储,可以获取部分字段的信息,也可以修改或者添加部分字段,节省网络流量。如果对象中某些字段需要经常变动或者经常需要单独查询对象中的个别字段信息,Hash 就非常适合。
-- **内存消耗**:Hash 通常比 String 更节省内存,特别是在字段较多且字段长度较短时。Redis 对小型 Hash 进行优化(如使用 ziplist 存储),进一步降低内存占用。
-- **复杂对象存储**:String 在处理多层嵌套或复杂结构的对象时更方便,因为无需处理每个字段的独立存储和操作。
-- **性能**:String 的操作通常具有 O(1) 的时间复杂度,因为它存储的是整个对象,操作简单直接,整体读写的性能较好。Hash 由于需要处理多个字段的增删改查操作,在字段较多且经常变动的情况下,可能会带来额外的性能开销。
-
-总结:
-
-- 在绝大多数情况下,**String** 更适合存储对象数据,尤其是当对象结构简单且整体读写是主要操作时。
-- 如果你需要频繁操作对象的部分字段或节省内存,**Hash** 可能是更好的选择。
-
-### String 的底层实现是什么?
-
-Redis 是基于 C 语言编写的,但 Redis 的 String 类型的底层实现并不是 C 语言中的字符串(即以空字符 `\0` 结尾的字符数组),而是自己编写了 [SDS](https://github.com/antirez/sds)(Simple Dynamic String,简单动态字符串)来作为底层实现。
-
-SDS 最早是 Redis 作者为日常 C 语言开发而设计的 C 字符串,后来被应用到了 Redis 上,并经过了大量的修改完善以适合高性能操作。
-
-Redis7.0 的 SDS 的部分源码如下():
-
-```c
-/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
- * However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
- uint8_t len; /* used */
- uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
- uint16_t len; /* used */
- uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
- uint32_t len; /* used */
- uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
- uint64_t len; /* used */
- uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-```
-
-通过源码可以看出,SDS 共有五种实现方式:SDS_TYPE_5(并未用到)、SDS_TYPE_8、SDS_TYPE_16、SDS_TYPE_32、SDS_TYPE_64,其中只有后四种实际用到。Redis 会根据初始化的长度决定使用哪种类型,从而减少内存的使用。
-
-| 类型 | 字节 | 位 |
-| -------- | ---- | --- |
-| sdshdr5 | < 1 | <8 |
-| sdshdr8 | 1 | 8 |
-| sdshdr16 | 2 | 16 |
-| sdshdr32 | 4 | 32 |
-| sdshdr64 | 8 | 64 |
-
-对于后四种实现都包含了下面这 4 个属性:
-
-- `len`:字符串的长度也就是已经使用的字节数。
-- `alloc`:总共可用的字符空间大小,alloc-len 就是 SDS 剩余的空间大小。
-- `buf[]`:实际存储字符串的数组。
-- `flags`:低三位保存类型标志。
-
-SDS 相比于 C 语言中的字符串有如下提升:
-
-1. **可以避免缓冲区溢出**:C 语言中的字符串被修改(比如拼接)时,一旦没有分配足够长度的内存空间,就会造成缓冲区溢出。SDS 被修改时,会先根据 len 属性检查空间大小是否满足要求,如果不满足,则先扩展至所需大小再进行修改操作。
-2. **获取字符串长度的复杂度较低**:C 语言中的字符串的长度通常是经过遍历计数来实现的,时间复杂度为 O(n)。SDS 的长度获取直接读取 len 属性即可,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
-3. **减少内存分配次数**:为了避免修改(增加/减少)字符串时,每次都需要重新分配内存(C 语言的字符串是这样的),SDS 实现了空间预分配和惰性空间释放两种优化策略。当 SDS 需要增加字符串时,Redis 会为 SDS 分配好内存,并且根据特定的算法分配多余的内存,这样可以减少连续执行字符串增长操作所需的内存重分配次数。当 SDS 需要减少字符串时,这部分内存不会立即被回收,会被记录下来,等待后续使用(支持手动释放,有对应的 API)。
-4. **二进制安全**:C 语言中的字符串以空字符 `\0` 作为字符串结束的标识,这存在一些问题,像一些二进制文件(比如图片、视频、音频)就可能包括空字符,C 字符串无法正确保存。SDS 使用 len 属性判断字符串是否结束,不存在这个问题。
-
-🤐 多提一嘴,很多文章里 SDS 的定义是下面这样的:
-
-```c
-struct sdshdr {
- unsigned int len;
- unsigned int free;
- char buf[];
-};
-```
-
-这个也没错,Redis 3.2 之前就是这样定义的。后来,由于这种方式的定义存在问题,`len` 和 `free` 的定义用了 4 个字节,造成了浪费。Redis 3.2 之后,Redis 改进了 SDS 的定义,将其划分为了现在的 5 种类型。
-
-### 购物车信息用 String 还是 Hash 存储更好呢?
-
-由于购物车中的商品频繁修改和变动,购物车信息建议使用 Hash 存储:
-
-- 用户 id 为 key
-- 商品 id 为 field,商品数量为 value
-
-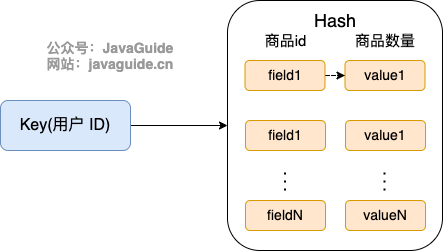
-
-那用户购物车信息的维护具体应该怎么操作呢?
-
-- 用户添加商品就是往 Hash 里面增加新的 field 与 value;
-- 查询购物车信息就是遍历对应的 Hash;
-- 更改商品数量直接修改对应的 value 值(直接 set 或者做运算皆可);
-- 删除商品就是删除 Hash 中对应的 field;
-- 清空购物车直接删除对应的 key 即可。
-
-这里只是以业务比较简单的购物车场景举例,实际电商场景下,field 只保存一个商品 id 是没办法满足需求的。
-
-### 使用 Redis 实现一个排行榜怎么做?
-
-Redis 中有一个叫做 `Sorted Set`(有序集合)的数据类型经常被用在各种排行榜的场景,比如直播间送礼物的排行榜、朋友圈的微信步数排行榜、王者荣耀中的段位排行榜、话题热度排行榜等等。
-
-相关的一些 Redis 命令:`ZRANGE`(从小到大排序)、`ZREVRANGE`(从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK`(指定元素排名)。
-
-
-
-[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 的「技术面试题篇」就有一篇文章详细介绍如何使用 Sorted Set 来设计制作一个排行榜,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
-
-
-
-### Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+ 树?
-
-这道面试题很多大厂比较喜欢问,难度还是有点大的。
-
-- 平衡树 vs 跳表:平衡树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)**。对于范围查询来说,平衡树也可以通过中序遍历的方式达到和跳表一样的效果。但是它的每一次插入或者删除操作都需要保证整颗树左右节点的绝对平衡,只要不平衡就要通过旋转操作来保持平衡,这个过程是比较耗时的。跳表诞生的初衷就是为了克服平衡树的一些缺点。跳表使用概率平衡而不是严格强制的平衡,因此,跳表中的插入和删除算法比平衡树的等效算法简单得多,速度也快得多。
-- 红黑树 vs 跳表:相比较于红黑树来说,跳表的实现也更简单一些,不需要通过旋转和染色(红黑变换)来保证黑平衡。并且,按照区间来查找数据这个操作,红黑树的效率没有跳表高。
-- B+ 树 vs 跳表:B+ 树更适合作为数据库和文件系统中常用的索引结构之一,它的核心思想是通过可能少的 IO 定位到尽可能多的索引来获得查询数据。对于 Redis 这种内存数据库来说,它对这些并不感冒,因为 Redis 作为内存数据库它不可能存储大量的数据,所以对于索引不需要通过 B+ 树这种方式进行维护,只需按照概率进行随机维护即可,节约内存。而且使用跳表实现 zset 时相较前者来说更简单一些,在进行插入时只需通过索引将数据插入到链表中合适的位置再随机维护一定高度的索引即可,也不需要像 B+ 树那样插入时发现失衡时还需要对节点分裂与合并。
-
-另外,我还单独写了一篇文章从有序集合的基本使用到跳表的源码分析和实现,让你会对 Redis 的有序集合底层实现的跳表有着更深刻的理解和掌握:[Redis 为什么用跳表实现有序集合](./redis-skiplist.md)。
-
-### Set 的应用场景是什么?
-
-Redis 中 `Set` 是一种无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。
-
-`Set` 的常见应用场景如下:
-
-- 存放的数据不能重复的场景:网站 UV 统计(数据量巨大的场景还是 `HyperLogLog` 更适合一些)、文章点赞、动态点赞等等。
-- 需要获取多个数据源交集、并集和差集的场景:共同好友(交集)、共同粉丝(交集)、共同关注(交集)、好友推荐(差集)、音乐推荐(差集)、订阅号推荐(差集+交集)等等。
-- 需要随机获取数据源中的元素的场景:抽奖系统、随机点名等等。
-
-### 使用 Set 实现抽奖系统怎么做?
-
-如果想要使用 `Set` 实现一个简单的抽奖系统的话,直接使用下面这几个命令就可以了:
-
-- `SADD key member1 member2 ...`:向指定集合添加一个或多个元素。
-- `SPOP key count`:随机移除并获取指定集合中一个或多个元素,适合不允许重复中奖的场景。
-- `SRANDMEMBER key count`:随机获取指定集合中指定数量的元素,适合允许重复中奖的场景。
-
-### 使用 Bitmap 统计活跃用户怎么做?
-
-Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap,只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。
-
-你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。
-
-
-
-如果想要使用 Bitmap 统计活跃用户的话,可以使用日期(精确到天)作为 key,然后用户 ID 为 offset,如果当日活跃过就设置为 1。
-
-初始化数据:
-
-```bash
-> SETBIT 20210308 1 1
-(integer) 0
-> SETBIT 20210308 2 1
-(integer) 0
-> SETBIT 20210309 1 1
-(integer) 0
-```
-
-统计 20210308~20210309 总活跃用户数:
-
-```bash
-> BITOP and desk1 20210308 20210309
-(integer) 1
-> BITCOUNT desk1
-(integer) 1
-```
-
-统计 20210308~20210309 在线活跃用户数:
-
-```bash
-> BITOP or desk2 20210308 20210309
-(integer) 1
-> BITCOUNT desk2
-(integer) 2
-```
-
-### 使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV 怎么做?
-
-使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV 主要需要用到下面这两个命令:
-
-- `PFADD key element1 element2 ...`:添加一个或多个元素到 HyperLogLog 中。
-- `PFCOUNT key1 key2`:获取一个或者多个 HyperLogLog 的唯一计数。
-
-1、将访问指定页面的每个用户 ID 添加到 `HyperLogLog` 中。
-
-```bash
-PFADD PAGE_1:UV USER1 USER2 ...... USERn
-```
-
-2、统计指定页面的 UV。
-
-```bash
-PFCOUNT PAGE_1:UV
-```
-
-## Redis 持久化机制(重要)
-
-Redis 持久化机制(RDB 持久化、AOF 持久化、RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化)相关的问题比较多,也比较重要,于是我单独抽了一篇文章来总结 Redis 持久化机制相关的知识点和问题:[Redis 持久化机制详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-persistence.html)。
-
-## Redis 线程模型(重要)
-
-对于读写命令来说,Redis 一直是单线程模型。不过,在 Redis 4.0 版本之后引入了多线程来执行一些大键值对的异步删除操作,Redis 6.0 版本之后引入了多线程来处理网络请求(提高网络 IO 读写性能)。
-
-### Redis 单线程模型了解吗?
-
-**Redis 基于 Reactor 模式设计开发了一套高效的事件处理模型**(Netty 的线程模型也基于 Reactor 模式,Reactor 模式不愧是高性能 IO 的基石),这套事件处理模型对应的是 Redis 中的文件事件处理器(file event handler)。由于文件事件处理器(file event handler)是单线程方式运行的,所以我们一般都说 Redis 是单线程模型。
-
-《Redis 设计与实现》有一段话是这样介绍文件事件处理器的,我觉得写得挺不错。
-
-> Redis 基于 Reactor 模式开发了自己的网络事件处理器:这个处理器被称为文件事件处理器(file event handler)。
->
-> - 文件事件处理器使用 I/O 多路复用(multiplexing)程序来同时监听多个套接字,并根据套接字目前执行的任务来为套接字关联不同的事件处理器。
-> - 当被监听的套接字准备好执行连接应答(accept)、读取(read)、写入(write)、关 闭(close)等操作时,与操作相对应的文件事件就会产生,这时文件事件处理器就会调用套接字之前关联好的事件处理器来处理这些事件。
->
-> **虽然文件事件处理器以单线程方式运行,但通过使用 I/O 多路复用程序来监听多个套接字**,文件事件处理器既实现了高性能的网络通信模型,又可以很好地与 Redis 服务器中其他同样以单线程方式运行的模块进行对接,这保持了 Redis 内部单线程设计的简单性。
-
-**既然是单线程,那怎么监听大量的客户端连接呢?**
-
-Redis 通过 **IO 多路复用程序** 来监听来自客户端的大量连接(或者说是监听多个 socket),它会将感兴趣的事件及类型(读、写)注册到内核中并监听每个事件是否发生。
-
-这样的好处非常明显:**I/O 多路复用技术的使用让 Redis 不需要额外创建多余的线程来监听客户端的大量连接,降低了资源的消耗**(和 NIO 中的 `Selector` 组件很像)。
-
-文件事件处理器(file event handler)主要是包含 4 个部分:
-
-- 多个 socket(客户端连接)
-- IO 多路复用程序(支持多个客户端连接的关键)
-- 文件事件分派器(将 socket 关联到相应的事件处理器)
-- 事件处理器(连接应答处理器、命令请求处理器、命令回复处理器)
-
-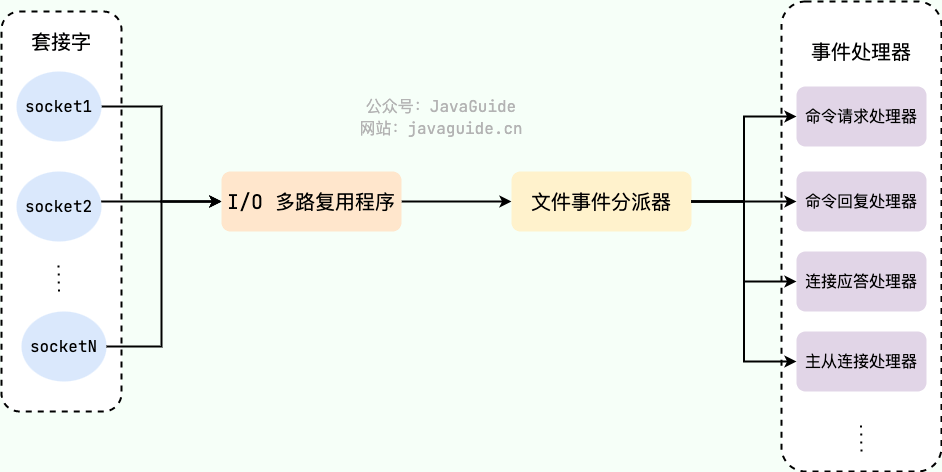
-
-相关阅读:[Redis 事件机制详解](http://remcarpediem.net/article/1aa2da89/)。
-
-### Redis6.0 之前为什么不使用多线程?
-
-虽然说 Redis 是单线程模型,但实际上,**Redis 在 4.0 之后的版本中就已经加入了对多线程的支持。**
-
-不过,Redis 4.0 增加的多线程主要是针对一些大键值对的删除操作的命令,使用这些命令就会使用主线程之外的其他线程来“异步处理”,从而减少对主线程的影响。
-
-为此,Redis 4.0 之后新增了几个异步命令:
-
-- `UNLINK`:可以看作是 `DEL` 命令的异步版本。
-- `FLUSHALL ASYNC`:用于清空所有数据库的所有键,不限于当前 `SELECT` 的数据库。
-- `FLUSHDB ASYNC`:用于清空当前 `SELECT` 数据库中的所有键。
-
-
-
-总的来说,直到 Redis 6.0 之前,Redis 的主要操作仍然是单线程处理的。
-
-**那 Redis6.0 之前为什么不使用多线程?** 我觉得主要原因有 3 点:
-
-- 单线程编程容易并且更容易维护;
-- Redis 的性能瓶颈不在 CPU,主要在内存和网络;
-- 多线程就会存在死锁、线程上下文切换等问题,甚至会影响性能。
-
-相关阅读:[为什么 Redis 选择单线程模型?](https://draveness.me/whys-the-design-redis-single-thread/)。
-
-### Redis6.0 之后为何引入了多线程?
-
-**Redis6.0 引入多线程主要是为了提高网络 IO 读写性能**,因为这个算是 Redis 中的一个性能瓶颈(Redis 的瓶颈主要受限于内存和网络)。
-
-虽然,Redis6.0 引入了多线程,但是 Redis 的多线程只是在网络数据的读写这类耗时操作上使用了,执行命令仍然是单线程顺序执行。因此,你也不需要担心线程安全问题。
-
-Redis6.0 的多线程默认是禁用的,只使用主线程。如需开启需要设置 IO 线程数 > 1,需要修改 redis 配置文件 `redis.conf`:
-
-```bash
-io-threads 4 #设置1的话只会开启主线程,官网建议4核的机器建议设置为2或3个线程,8核的建议设置为6个线程
-```
-
-另外:
-
-- io-threads 的个数一旦设置,不能通过 config 动态设置。
-- 当设置 ssl 后,io-threads 将不工作。
-
-开启多线程后,默认只会使用多线程进行 IO 写入 writes,即发送数据给客户端,如果需要开启多线程 IO 读取 reads,同样需要修改 redis 配置文件 `redis.conf`:
-
-```bash
-io-threads-do-reads yes
-```
-
-但是官网描述开启多线程读并不能有太大提升,因此一般情况下并不建议开启。
-
-相关阅读:
-
-- [Redis 6.0 新特性-多线程连环 13 问!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FZu3acwK6zrCBZQ_3HoUgw)
-- [Redis 多线程网络模型全面揭秘](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039223696)(推荐)
-
-### Redis 后台线程了解吗?
-
-我们虽然经常说 Redis 是单线程模型(主要逻辑是单线程完成的),但实际还有一些后台线程用于执行一些比较耗时的操作:
-
-- 通过 `bio_close_file` 后台线程来释放 AOF / RDB 等过程中产生的临时文件资源。
-- 通过 `bio_aof_fsync` 后台线程调用 `fsync` 函数将系统内核缓冲区还未同步到到磁盘的数据强制刷到磁盘(AOF 文件)。
-- 通过 `bio_lazy_free` 后台线程释放大对象(已删除)占用的内存空间.
-
-在`bio.h` 文件中有定义(Redis 6.0 版本,源码地址:):
-
-```java
-#ifndef __BIO_H
-#define __BIO_H
-
-/* Exported API */
-void bioInit(void);
-void bioCreateBackgroundJob(int type, void *arg1, void *arg2, void *arg3);
-unsigned long long bioPendingJobsOfType(int type);
-unsigned long long bioWaitStepOfType(int type);
-time_t bioOlderJobOfType(int type);
-void bioKillThreads(void);
-
-/* Background job opcodes */
-#define BIO_CLOSE_FILE 0 /* Deferred close(2) syscall. */
-#define BIO_AOF_FSYNC 1 /* Deferred AOF fsync. */
-#define BIO_LAZY_FREE 2 /* Deferred objects freeing. */
-#define BIO_NUM_OPS 3
-
-#endif
-```
-
-关于 Redis 后台线程的详细介绍可以查看 [Redis 6.0 后台线程有哪些?](https://juejin.cn/post/7102780434739626014) 这篇就文章。
-
-## Redis 内存管理
-
-### Redis 给缓存数据设置过期时间有什么用?
-
-一般情况下,我们设置保存的缓存数据的时候都会设置一个过期时间。为什么呢?
-
-内存是有限且珍贵的,如果不对缓存数据设置过期时间,那内存占用就会一直增长,最终可能会导致 OOM 问题。通过设置合理的过期时间,Redis 会自动删除暂时不需要的数据,为新的缓存数据腾出空间。
-
-Redis 自带了给缓存数据设置过期时间的功能,比如:
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> expire key 60 # 数据在 60s 后过期
-(integer) 1
-127.0.0.1:6379> setex key 60 value # 数据在 60s 后过期 (setex:[set] + [ex]pire)
-OK
-127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key # 查看数据还有多久过期
-(integer) 56
-```
-
-注意 ⚠️:Redis 中除了字符串类型有自己独有设置过期时间的命令 `setex` 外,其他方法都需要依靠 `expire` 命令来设置过期时间 。另外,`persist` 命令可以移除一个键的过期时间。
-
-**过期时间除了有助于缓解内存的消耗,还有什么其他用么?**
-
-很多时候,我们的业务场景就是需要某个数据只在某一时间段内存在,比如我们的短信验证码可能只在 1 分钟内有效,用户登录的 Token 可能只在 1 天内有效。
-
-如果使用传统的数据库来处理的话,一般都是自己判断过期,这样更麻烦并且性能要差很多。
-
-### Redis 是如何判断数据是否过期的呢?
-
-Redis 通过一个叫做过期字典(可以看作是 hash 表)来保存数据过期的时间。过期字典的键指向 Redis 数据库中的某个 key(键),过期字典的值是一个 long long 类型的整数,这个整数保存了 key 所指向的数据库键的过期时间(毫秒精度的 UNIX 时间戳)。
-
-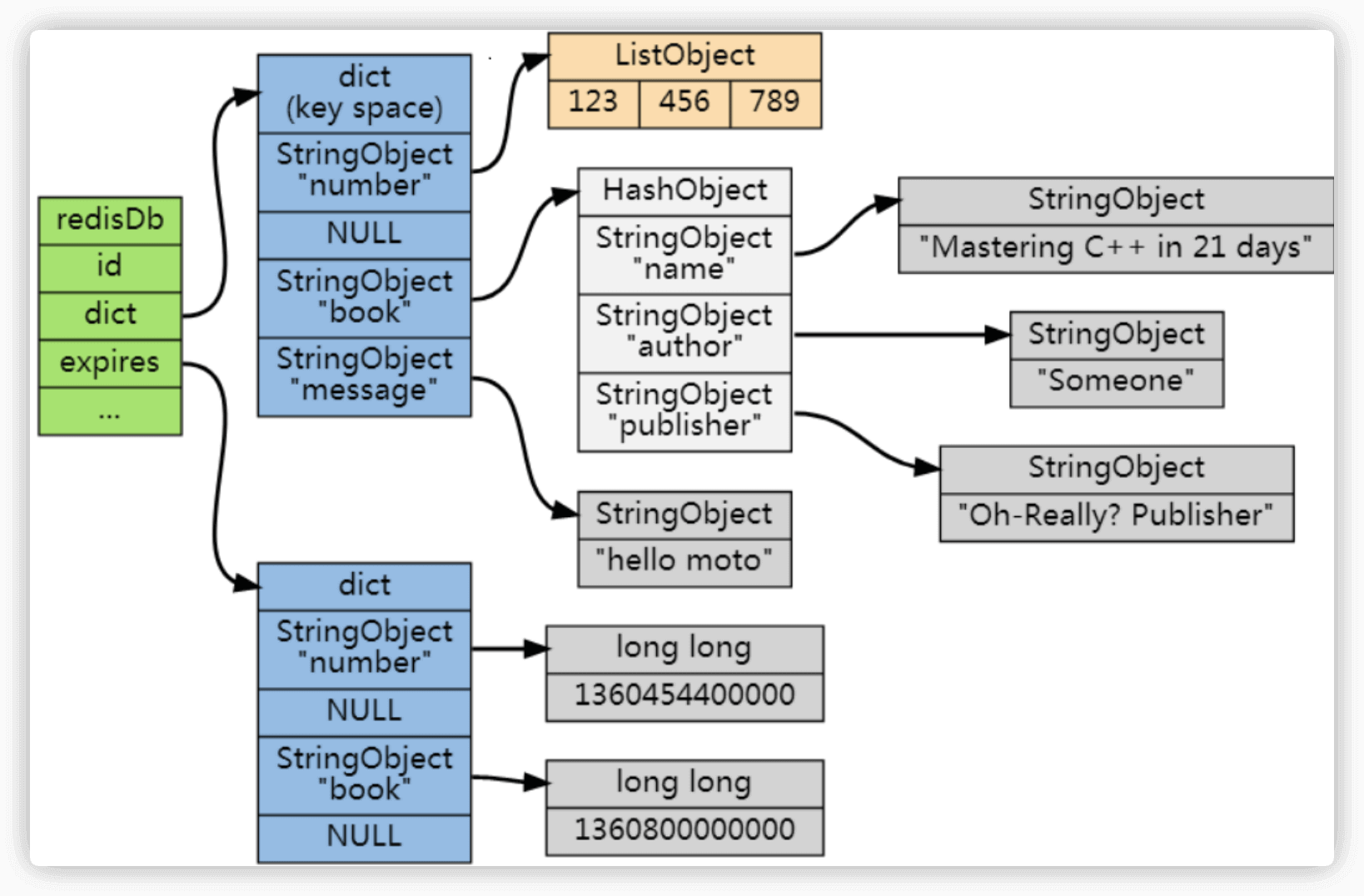
-
-过期字典是存储在 redisDb 这个结构里的:
-
-```c
-typedef struct redisDb {
- ...
-
- dict *dict; //数据库键空间,保存着数据库中所有键值对
- dict *expires // 过期字典,保存着键的过期时间
- ...
-} redisDb;
-```
-
-在查询一个 key 的时候,Redis 首先检查该 key 是否存在于过期字典中(时间复杂度为 O(1)),如果不在就直接返回,在的话需要判断一下这个 key 是否过期,过期直接删除 key 然后返回 null。
-
-### Redis 过期 key 删除策略了解么?
-
-如果假设你设置了一批 key 只能存活 1 分钟,那么 1 分钟后,Redis 是怎么对这批 key 进行删除的呢?
-
-常用的过期数据的删除策略就下面这几种:
-
-1. **惰性删除**:只会在取出/查询 key 的时候才对数据进行过期检查。这种方式对 CPU 最友好,但是可能会造成太多过期 key 没有被删除。
-2. **定期删除**:周期性地随机从设置了过期时间的 key 中抽查一批,然后逐个检查这些 key 是否过期,过期就删除 key。相比于惰性删除,定期删除对内存更友好,对 CPU 不太友好。
-3. **延迟队列**:把设置过期时间的 key 放到一个延迟队列里,到期之后就删除 key。这种方式可以保证每个过期 key 都能被删除,但维护延迟队列太麻烦,队列本身也要占用资源。
-4. **定时删除**:每个设置了过期时间的 key 都会在设置的时间到达时立即被删除。这种方法可以确保内存中不会有过期的键,但是它对 CPU 的压力最大,因为它需要为每个键都设置一个定时器。
-
-**Redis 采用的是那种删除策略呢?**
-
-Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 结合的策略,这也是大部分缓存框架的选择。定期删除对内存更加友好,惰性删除对 CPU 更加友好。两者各有千秋,结合起来使用既能兼顾 CPU 友好,又能兼顾内存友好。
-
-下面是我们详细介绍一下 Redis 中的定期删除具体是如何做的。
-
-Redis 的定期删除过程是随机的(周期性地随机从设置了过期时间的 key 中抽查一批),所以并不保证所有过期键都会被立即删除。这也就解释了为什么有的 key 过期了,并没有被删除。并且,Redis 底层会通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对 CPU 时间的影响。
-
-另外,定期删除还会受到执行时间和过期 key 的比例的影响:
-
-- 执行时间已经超过了阈值,那么就中断这一次定期删除循环,以避免使用过多的 CPU 时间。
-- 如果这一批过期的 key 比例超过一个比例,就会重复执行此删除流程,以更积极地清理过期 key。相应地,如果过期的 key 比例低于这个比例,就会中断这一次定期删除循环,避免做过多的工作而获得很少的内存回收。
-
-Redis 7.2 版本的执行时间阈值是 **25ms**,过期 key 比例设定值是 **10%**。
-
-```c
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 1000 /* Microseconds. */
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 25 /* Max % of CPU to use. */
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE 10 /* % of stale keys after which
- we do extra efforts. */
-```
-
-**每次随机抽查数量是多少?**
-
-`expire.c` 中定义了每次随机抽查的数量,Redis 7.2 版本为 20,也就是说每次会随机选择 20 个设置了过期时间的 key 判断是否过期。
-
-```c
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP 20 /* Keys for each DB loop. */
-```
-
-**如何控制定期删除的执行频率?**
-
-在 Redis 中,定期删除的频率是由 **hz** 参数控制的。hz 默认为 10,代表每秒执行 10 次,也就是每秒钟进行 10 次尝试来查找并删除过期的 key。
-
-hz 的取值范围为 1~500。增大 hz 参数的值会提升定期删除的频率。如果你想要更频繁地执行定期删除任务,可以适当增加 hz 的值,但这会增加 CPU 的使用率。根据 Redis 官方建议,hz 的值不建议超过 100,对于大部分用户使用默认的 10 就足够了。
-
-下面是 hz 参数的官方注释,我翻译了其中的重要信息(Redis 7.2 版本)。
-
-
-
-类似的参数还有一个 **dynamic-hz**,这个参数开启之后 Redis 就会在 hz 的基础上动态计算一个值。Redis 提供并默认启用了使用自适应 hz 值的能力,
-
-这两个参数都在 Redis 配置文件 `redis.conf` 中:
-
-```properties
-# 默认为 10
-hz 10
-# 默认开启
-dynamic-hz yes
-```
-
-多提一嘴,除了定期删除过期 key 这个定期任务之外,还有一些其他定期任务例如关闭超时的客户端连接、更新统计信息,这些定期任务的执行频率也是通过 hz 参数决定。
-
-**为什么定期删除不是把所有过期 key 都删除呢?**
-
-这样会对性能造成太大的影响。如果我们 key 数量非常庞大的话,挨个遍历检查是非常耗时的,会严重影响性能。Redis 设计这种策略的目的是为了平衡内存和性能。
-
-**为什么 key 过期之后不立马把它删掉呢?这样不是会浪费很多内存空间吗?**
-
-因为不太好办到,或者说这种删除方式的成本太高了。假如我们使用延迟队列作为删除策略,这样存在下面这些问题:
-
-1. 队列本身的开销可能很大:key 多的情况下,一个延迟队列可能无法容纳。
-2. 维护延迟队列太麻烦:修改 key 的过期时间就需要调整期在延迟队列中的位置,并且还需要引入并发控制。
-
-### 大量 key 集中过期怎么办?
-
-当 Redis 中存在大量 key 在同一时间点集中过期时,可能会导致以下问题:
-
-- **请求延迟增加**:Redis 在处理过期 key 时需要消耗 CPU 资源,如果过期 key 数量庞大,会导致 Redis 实例的 CPU 占用率升高,进而影响其他请求的处理速度,造成延迟增加。
-- **内存占用过高**:过期的 key 虽然已经失效,但在 Redis 真正删除它们之前,仍然会占用内存空间。如果过期 key 没有及时清理,可能会导致内存占用过高,甚至引发内存溢出。
-
-为了避免这些问题,可以采取以下方案:
-
-1. **尽量避免 key 集中过期**:在设置键的过期时间时尽量随机一点。
-2. **开启 lazy free 机制**:修改 `redis.conf` 配置文件,将 `lazyfree-lazy-expire` 参数设置为 `yes`,即可开启 lazy free 机制。开启 lazy free 机制后,Redis 会在后台异步删除过期的 key,不会阻塞主线程的运行,从而降低对 Redis 性能的影响。
-
-### Redis 内存淘汰策略了解么?
-
-> 相关问题:MySQL 里有 2000w 数据,Redis 中只存 20w 的数据,如何保证 Redis 中的数据都是热点数据?
-
-Redis 的内存淘汰策略只有在运行内存达到了配置的最大内存阈值时才会触发,这个阈值是通过 `redis.conf` 的 `maxmemory` 参数来定义的。64 位操作系统下,`maxmemory` 默认为 0,表示不限制内存大小。32 位操作系统下,默认的最大内存值是 3GB。
-
-你可以使用命令 `config get maxmemory` 来查看 `maxmemory` 的值。
-
-```bash
-> config get maxmemory
-maxmemory
-0
-```
-
-Redis 提供了 6 种内存淘汰策略:
-
-1. **volatile-lru(least recently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰。
-2. **volatile-ttl**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选将要过期的数据淘汰。
-3. **volatile-random**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中任意选择数据淘汰。
-4. **allkeys-lru(least recently used)**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中移除最近最少使用的数据淘汰。
-5. **allkeys-random**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中任意选择数据淘汰。
-6. **no-eviction**(默认内存淘汰策略):禁止驱逐数据,当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,新写入操作会报错。
-
-4.0 版本后增加以下两种:
-
-7. **volatile-lfu(least frequently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-8. **allkeys-lfu(least frequently used)**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中移除最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-
-`allkeys-xxx` 表示从所有的键值中淘汰数据,而 `volatile-xxx` 表示从设置了过期时间的键值中淘汰数据。
-
-`config.c` 中定义了内存淘汰策略的枚举数组:
-
-```c
-configEnum maxmemory_policy_enum[] = {
- {"volatile-lru", MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU},
- {"volatile-lfu", MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LFU},
- {"volatile-random",MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM},
- {"volatile-ttl",MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL},
- {"allkeys-lru",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU},
- {"allkeys-lfu",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LFU},
- {"allkeys-random",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM},
- {"noeviction",MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION},
- {NULL, 0}
-};
-```
-
-你可以使用 `config get maxmemory-policy` 命令来查看当前 Redis 的内存淘汰策略。
-
-```bash
-> config get maxmemory-policy
-maxmemory-policy
-noeviction
-```
-
-可以通过 `config set maxmemory-policy 内存淘汰策略` 命令修改内存淘汰策略,立即生效,但这种方式重启 Redis 之后就失效了。修改 `redis.conf` 中的 `maxmemory-policy` 参数不会因为重启而失效,不过,需要重启之后修改才能生效。
-
-```properties
-maxmemory-policy noeviction
-```
-
-关于淘汰策略的详细说明可以参考 Redis 官方文档:。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 开发与运维》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- 《Redis 核心原理与实战》
-- Redis 命令手册:
-- RedisSearch 终极使用指南,你值得拥有!:
-- WHY Redis choose single thread (vs multi threads): [https://medium.com/@jychen7/sharing-redis-single-thread-vs-multi-threads-5870bd44d153](https://medium.com/@jychen7/sharing-redis-single-thread-vs-multi-threads-5870bd44d153)
-
-
+If you are familiar with other solutions and can explain why you ultimately chose Redis (even better!), this will significantly enhance your interview performance
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
index 37ef43ea72a..9a391821bf5 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
@@ -1,34 +1,34 @@
---
-title: Redis常见面试题总结(下)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Redis Interview Questions (Part 2)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: Redis基础,Redis常见数据结构,Redis线程模型,Redis内存管理,Redis事务,Redis性能优化
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 一篇文章总结Redis常见的知识点和面试题,涵盖Redis基础、Redis常见数据结构、Redis线程模型、Redis内存管理、Redis事务、Redis性能优化等内容。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Redis Basics, Common Redis Data Structures, Redis Thread Model, Redis Memory Management, Redis Transactions, Redis Performance Optimization
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: An article summarizing common knowledge points and interview questions about Redis, covering Redis basics, common data structures, thread model, memory management, transactions, and performance optimization.
---
-## Redis 事务
+## Redis Transactions
-### 什么是 Redis 事务?
+### What is a Redis Transaction?
-你可以将 Redis 中的事务理解为:**Redis 事务提供了一种将多个命令请求打包的功能。然后,再按顺序执行打包的所有命令,并且不会被中途打断。**
+You can understand a transaction in Redis as: **Redis transactions provide a way to package multiple command requests together. Then, all the packaged commands are executed in order without being interrupted.**
-Redis 事务实际开发中使用的非常少,功能比较鸡肋,不要将其和我们平时理解的关系型数据库的事务混淆了。
+In actual development, Redis transactions are used very rarely, and their functionality is somewhat limited. Do not confuse them with transactions in relational databases as we usually understand them.
-除了不满足原子性和持久性之外,事务中的每条命令都会与 Redis 服务器进行网络交互,这是比较浪费资源的行为。明明一次批量执行多个命令就可以了,这种操作实在是看不懂。
+In addition to not satisfying atomicity and durability, each command in a transaction interacts with the Redis server over the network, which is a resource-wasting behavior. Clearly, multiple commands can be executed in a batch, so this operation is hard to understand.
-因此,Redis 事务是不建议在日常开发中使用的。
+Therefore, Redis transactions are not recommended for use in daily development.
-### 如何使用 Redis 事务?
+### How to Use Redis Transactions?
-Redis 可以通过 **`MULTI`、`EXEC`、`DISCARD` 和 `WATCH`** 等命令来实现事务(Transaction)功能。
+Redis can implement transaction functionality through commands like **`MULTI`, `EXEC`, `DISCARD`, and `WATCH`**.
```bash
> MULTI
@@ -42,15 +42,15 @@ QUEUED
2) "JavaGuide"
```
-[`MULTI`](https://redis.io/commands/multi) 命令后可以输入多个命令,Redis 不会立即执行这些命令,而是将它们放到队列,当调用了 [`EXEC`](https://redis.io/commands/exec) 命令后,再执行所有的命令。
+After the [`MULTI`](https://redis.io/commands/multi) command, you can input multiple commands. Redis will not execute these commands immediately but will queue them. When the [`EXEC`](https://redis.io/commands/exec) command is called, all commands are executed.
-这个过程是这样的:
+The process is as follows:
-1. 开始事务(`MULTI`);
-2. 命令入队(批量操作 Redis 的命令,先进先出(FIFO)的顺序执行);
-3. 执行事务(`EXEC`)。
+1. Start the transaction (`MULTI`);
+1. Queue commands (commands for batch operations on Redis are executed in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order);
+1. Execute the transaction (`EXEC`).
-你也可以通过 [`DISCARD`](https://redis.io/commands/discard) 命令取消一个事务,它会清空事务队列中保存的所有命令。
+You can also cancel a transaction using the [`DISCARD`](https://redis.io/commands/discard) command, which will clear all commands saved in the transaction queue.
```bash
> MULTI
@@ -63,10 +63,10 @@ QUEUED
OK
```
-你可以通过[`WATCH`](https://redis.io/commands/watch) 命令监听指定的 Key,当调用 `EXEC` 命令执行事务时,如果一个被 `WATCH` 命令监视的 Key 被 **其他客户端/Session** 修改的话,整个事务都不会被执行。
+You can use the [`WATCH`](https://redis.io/commands/watch) command to monitor a specified key. When the `EXEC` command is called to execute the transaction, if a key being monitored by the `WATCH` command is modified by **another client/session**, the entire transaction will not be executed.
```bash
-# 客户端 1
+# Client 1
> SET PROJECT "RustGuide"
OK
> WATCH PROJECT
@@ -76,21 +76,21 @@ OK
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
QUEUED
-# 客户端 2
-# 在客户端 1 执行 EXEC 命令提交事务之前修改 PROJECT 的值
+# Client 2
+# Modifies the value of PROJECT before Client 1 executes the EXEC command to submit the transaction
> SET PROJECT "GoGuide"
-# 客户端 1
-# 修改失败,因为 PROJECT 的值被客户端2修改了
+# Client 1
+# Modification fails because the value of PROJECT was changed by Client 2
> EXEC
(nil)
> GET PROJECT
"GoGuide"
```
-不过,如果 **WATCH** 与 **事务** 在同一个 Session 里,并且被 **WATCH** 监视的 Key 被修改的操作发生在事务内部,这个事务是可以被执行成功的(相关 issue:[WATCH 命令碰到 MULTI 命令时的不同效果](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1714))。
+However, if **WATCH** and **transaction** are in the same session, and the operation that modifies the monitored key occurs within the transaction, the transaction can be successfully executed (related issue: [Different Effects of WATCH Command When Encountering MULTI Command](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1714)).
-事务内部修改 WATCH 监视的 Key:
+Modifying the WATCH monitored key inside the transaction:
```bash
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ QUEUED
"JavaGuide3"
```
-事务外部修改 WATCH 监视的 Key:
+Modifying the WATCH monitored key outside the transaction:
```bash
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
@@ -130,670 +130,10 @@ QUEUED
(nil)
```
-Redis 官网相关介绍 [https://redis.io/topics/transactions](https://redis.io/topics/transactions) 如下:
+The official Redis website provides related information [https://redis.io/topics/transactions](https://redis.io/topics/transactions) as follows:
-
+
-### Redis 事务支持原子性吗?
+### Does Redis Transactions Support Atomicity?
-Redis 的事务和我们平时理解的关系型数据库的事务不同。我们知道事务具有四大特性:**1. 原子性**,**2. 隔离性**,**3. 持久性**,**4. 一致性**。
-
-1. **原子性(Atomicity)**:事务是最小的执行单位,不允许分割。事务的原子性确保动作要么全部完成,要么完全不起作用;
-2. **隔离性(Isolation)**:并发访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不被其他事务所干扰,各并发事务之间数据库是独立的;
-3. **持久性(Durability)**:一个事务被提交之后。它对数据库中数据的改变是持久的,即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响;
-4. **一致性(Consistency)**:执行事务前后,数据保持一致,多个事务对同一个数据读取的结果是相同的。
-
-Redis 事务在运行错误的情况下,除了执行过程中出现错误的命令外,其他命令都能正常执行。并且,Redis 事务是不支持回滚(roll back)操作的。因此,Redis 事务其实是不满足原子性的。
-
-Redis 官网也解释了自己为啥不支持回滚。简单来说就是 Redis 开发者们觉得没必要支持回滚,这样更简单便捷并且性能更好。Redis 开发者觉得即使命令执行错误也应该在开发过程中就被发现而不是生产过程中。
-
-
-
-**相关 issue**:
-
-- [issue#452: 关于 Redis 事务不满足原子性的问题](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/452)。
-- [Issue#491:关于 Redis 没有事务回滚?](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/491)。
-
-### Redis 事务支持持久性吗?
-
-Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:
-
-- 快照(snapshotting,RDB);
-- 只追加文件(append-only file,AOF);
-- RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)。
-
-与 RDB 持久化相比,AOF 持久化的实时性更好。在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式(`fsync` 策略),它们分别是:
-
-```bash
-appendfsync always #每次有数据修改发生时,都会调用fsync函数同步AOF文件,fsync完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低Redis的速度
-appendfsync everysec #每秒钟调用fsync函数同步一次AOF文件
-appendfsync no #让操作系统决定何时进行同步,一般为30秒一次
-```
-
-AOF 持久化的 `fsync` 策略为 no、everysec 时都会存在数据丢失的情况。always 下可以基本是可以满足持久性要求的,但性能太差,实际开发过程中不会使用。
-
-因此,Redis 事务的持久性也是没办法保证的。
-
-### 如何解决 Redis 事务的缺陷?
-
-Redis 从 2.6 版本开始支持执行 Lua 脚本,它的功能和事务非常类似。我们可以利用 Lua 脚本来批量执行多条 Redis 命令,这些 Redis 命令会被提交到 Redis 服务器一次性执行完成,大幅减小了网络开销。
-
-一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰。
-
-不过,如果 Lua 脚本运行时出错并中途结束,出错之后的命令是不会被执行的。并且,出错之前执行的命令是无法被撤销的,无法实现类似关系型数据库执行失败可以回滚的那种原子性效果。因此,**严格来说的话,通过 Lua 脚本来批量执行 Redis 命令实际也是不完全满足原子性的。**
-
-如果想要让 Lua 脚本中的命令全部执行,必须保证语句语法和命令都是对的。
-
-另外,Redis 7.0 新增了 [Redis functions](https://redis.io/docs/manual/programmability/functions-intro/) 特性,你可以将 Redis functions 看作是比 Lua 更强大的脚本。
-
-## Redis 性能优化(重要)
-
-除了下面介绍的内容之外,再推荐两篇不错的文章:
-
-- [你的 Redis 真的变慢了吗?性能优化如何做 - 阿里开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/nNEuYw0NlYGhuKKKKoWfcQ)。
-- [Redis 常见阻塞原因总结 - JavaGuide](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.html)。
-
-### 使用批量操作减少网络传输
-
-一个 Redis 命令的执行可以简化为以下 4 步:
-
-1. 发送命令;
-2. 命令排队;
-3. 命令执行;
-4. 返回结果。
-
-其中,第 1 步和第 4 步耗费时间之和称为 **Round Trip Time(RTT,往返时间)**,也就是数据在网络上传输的时间。
-
-使用批量操作可以减少网络传输次数,进而有效减小网络开销,大幅减少 RTT。
-
-另外,除了能减少 RTT 之外,发送一次命令的 socket I/O 成本也比较高(涉及上下文切换,存在 `read()` 和 `write()` 系统调用),批量操作还可以减少 socket I/O 成本。这个在官方对 pipeline 的介绍中有提到:。
-
-#### 原生批量操作命令
-
-Redis 中有一些原生支持批量操作的命令,比如:
-
-- `MGET`(获取一个或多个指定 key 的值)、`MSET`(设置一个或多个指定 key 的值)、
-- `HMGET`(获取指定哈希表中一个或者多个指定字段的值)、`HMSET`(同时将一个或多个 field-value 对设置到指定哈希表中)、
-- `SADD`(向指定集合添加一个或多个元素)
-- ……
-
-不过,在 Redis 官方提供的分片集群解决方案 Redis Cluster 下,使用这些原生批量操作命令可能会存在一些小问题需要解决。就比如说 `MGET` 无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上,`MGET`可能还是需要多次网络传输,原子操作也无法保证了。不过,相较于非批量操作,还是可以节省不少网络传输次数。
-
-整个步骤的简化版如下(通常由 Redis 客户端实现,无需我们自己再手动实现):
-
-1. 找到 key 对应的所有 hash slot;
-2. 分别向对应的 Redis 节点发起 `MGET` 请求获取数据;
-3. 等待所有请求执行结束,重新组装结果数据,保持跟入参 key 的顺序一致,然后返回结果。
-
-如果想要解决这个多次网络传输的问题,比较常用的办法是自己维护 key 与 slot 的关系。不过这样不太灵活,虽然带来了性能提升,但同样让系统复杂性提升。
-
-> Redis Cluster 并没有使用一致性哈希,采用的是 **哈希槽分区**,每一个键值对都属于一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)**。当客户端发送命令请求的时候,需要先根据 key 通过上面的计算公式找到的对应的哈希槽,然后再查询哈希槽和节点的映射关系,即可找到目标 Redis 节点。
->
-> 我在 [Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html) 这篇文章中详细介绍了 Redis Cluster 这部分的内容,感兴趣地可以看看。
-
-#### pipeline
-
-对于不支持批量操作的命令,我们可以利用 **pipeline(流水线)** 将一批 Redis 命令封装成一组,这些 Redis 命令会被一次性提交到 Redis 服务器,只需要一次网络传输。不过,需要注意控制一次批量操作的 **元素个数**(例如 500 以内,实际也和元素字节数有关),避免网络传输的数据量过大。
-
-与 `MGET`、`MSET` 等原生批量操作命令一样,pipeline 同样在 Redis Cluster 上使用会存在一些小问题。原因类似,无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上。如果想要使用的话,客户端需要自己维护 key 与 slot 的关系。
-
-原生批量操作命令和 pipeline 的是有区别的,使用的时候需要注意:
-
-- 原生批量操作命令是原子操作,pipeline 是非原子操作。
-- pipeline 可以打包不同的命令,原生批量操作命令不可以。
-- 原生批量操作命令是 Redis 服务端支持实现的,而 pipeline 需要服务端和客户端的共同实现。
-
-顺带补充一下 pipeline 和 Redis 事务的对比:
-
-- 事务是原子操作,pipeline 是非原子操作。两个不同的事务不会同时运行,而 pipeline 可以同时以交错方式执行。
-- Redis 事务中每个命令都需要发送到服务端,而 Pipeline 只需要发送一次,请求次数更少。
-
-> 事务可以看作是一个原子操作,但其实并不满足原子性。当我们提到 Redis 中的原子操作时,主要指的是这个操作(比如事务、Lua 脚本)不会被其他操作(比如其他事务、Lua 脚本)打扰,并不能完全保证这个操作中的所有写命令要么都执行要么都不执行。这主要也是因为 Redis 是不支持回滚操作。
-
-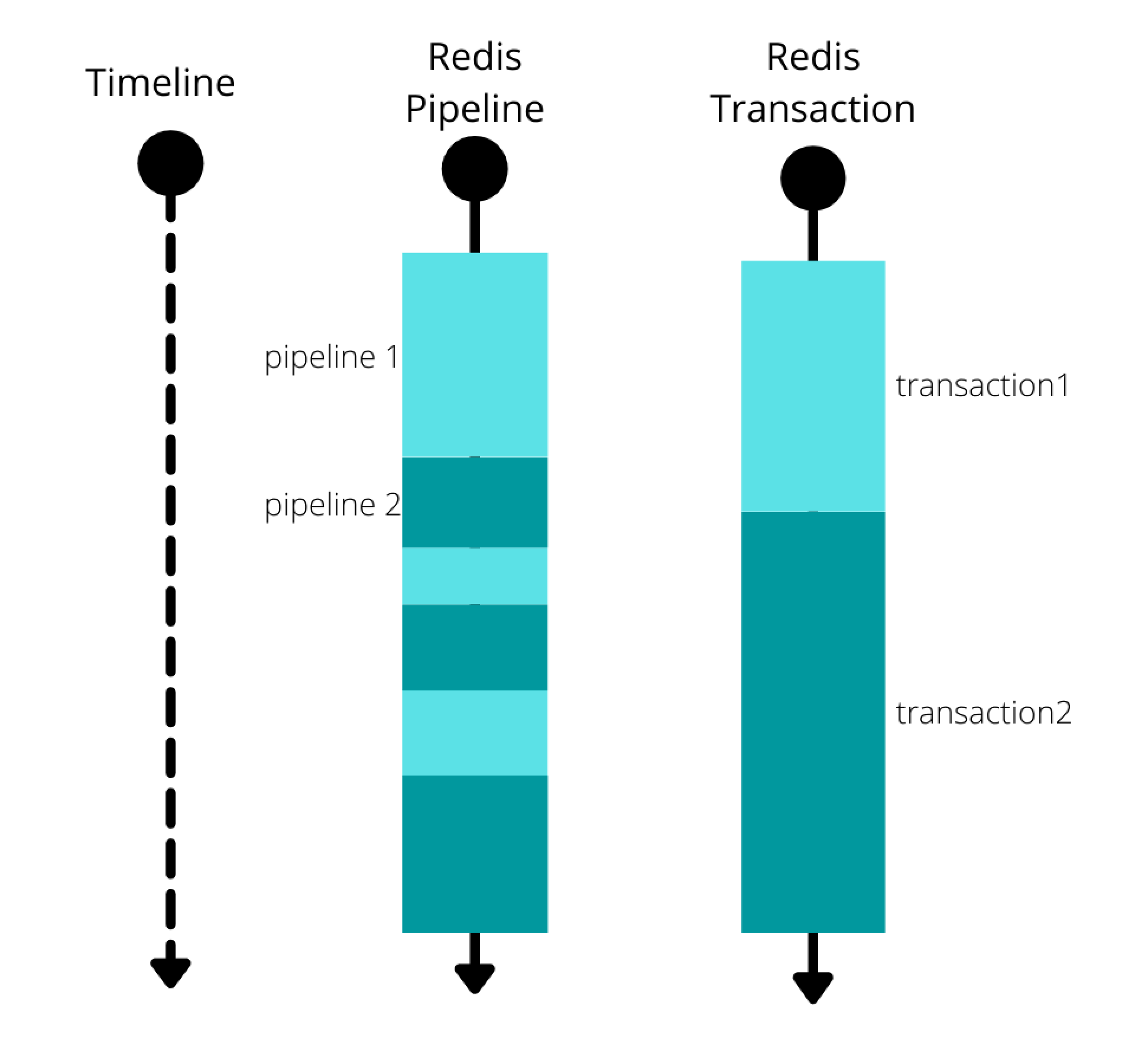
-
-另外,pipeline 不适用于执行顺序有依赖关系的一批命令。就比如说,你需要将前一个命令的结果给后续的命令使用,pipeline 就没办法满足你的需求了。对于这种需求,我们可以使用 **Lua 脚本**。
-
-#### Lua 脚本
-
-Lua 脚本同样支持批量操作多条命令。一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,可以看作是 **原子操作**。也就是说,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰,这是 pipeline 所不具备的。
-
-并且,Lua 脚本中支持一些简单的逻辑处理比如使用命令读取值并在 Lua 脚本中进行处理,这同样是 pipeline 所不具备的。
-
-不过, Lua 脚本依然存在下面这些缺陷:
-
-- 如果 Lua 脚本运行时出错并中途结束,之后的操作不会进行,但是之前已经发生的写操作不会撤销,所以即使使用了 Lua 脚本,也不能实现类似数据库回滚的原子性。
-- Redis Cluster 下 Lua 脚本的原子操作也无法保证了,原因同样是无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上。
-
-### 大量 key 集中过期问题
-
-我在前面提到过:对于过期 key,Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 策略。
-
-定期删除执行过程中,如果突然遇到大量过期 key 的话,客户端请求必须等待定期清理过期 key 任务线程执行完成,因为这个这个定期任务线程是在 Redis 主线程中执行的。这就导致客户端请求没办法被及时处理,响应速度会比较慢。
-
-**如何解决呢?** 下面是两种常见的方法:
-
-1. 给 key 设置随机过期时间。
-2. 开启 lazy-free(惰性删除/延迟释放)。lazy-free 特性是 Redis 4.0 开始引入的,指的是让 Redis 采用异步方式延迟释放 key 使用的内存,将该操作交给单独的子线程处理,避免阻塞主线程。
-
-个人建议不管是否开启 lazy-free,我们都尽量给 key 设置随机过期时间。
-
-### Redis bigkey(大 Key)
-
-#### 什么是 bigkey?
-
-简单来说,如果一个 key 对应的 value 所占用的内存比较大,那这个 key 就可以看作是 bigkey。具体多大才算大呢?有一个不是特别精确的参考标准:
-
-- String 类型的 value 超过 1MB
-- 复合类型(List、Hash、Set、Sorted Set 等)的 value 包含的元素超过 5000 个(不过,对于复合类型的 value 来说,不一定包含的元素越多,占用的内存就越多)。
-
-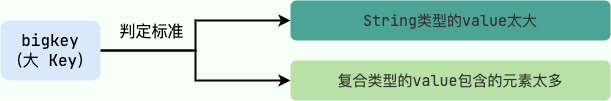
-
-#### bigkey 是怎么产生的?有什么危害?
-
-bigkey 通常是由于下面这些原因产生的:
-
-- 程序设计不当,比如直接使用 String 类型存储较大的文件对应的二进制数据。
-- 对于业务的数据规模考虑不周到,比如使用集合类型的时候没有考虑到数据量的快速增长。
-- 未及时清理垃圾数据,比如哈希中冗余了大量的无用键值对。
-
-bigkey 除了会消耗更多的内存空间和带宽,还会对性能造成比较大的影响。
-
-在 [Redis 常见阻塞原因总结](./redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md) 这篇文章中我们提到:大 key 还会造成阻塞问题。具体来说,主要体现在下面三个方面:
-
-1. 客户端超时阻塞:由于 Redis 执行命令是单线程处理,然后在操作大 key 时会比较耗时,那么就会阻塞 Redis,从客户端这一视角看,就是很久很久都没有响应。
-2. 网络阻塞:每次获取大 key 产生的网络流量较大,如果一个 key 的大小是 1 MB,每秒访问量为 1000,那么每秒会产生 1000MB 的流量,这对于普通千兆网卡的服务器来说是灾难性的。
-3. 工作线程阻塞:如果使用 del 删除大 key 时,会阻塞工作线程,这样就没办法处理后续的命令。
-
-大 key 造成的阻塞问题还会进一步影响到主从同步和集群扩容。
-
-综上,大 key 带来的潜在问题是非常多的,我们应该尽量避免 Redis 中存在 bigkey。
-
-#### 如何发现 bigkey?
-
-**1、使用 Redis 自带的 `--bigkeys` 参数来查找。**
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli -p 6379 --bigkeys
-
-# Scanning the entire keyspace to find biggest keys as well as
-# average sizes per key type. You can use -i 0.1 to sleep 0.1 sec
-# per 100 SCAN commands (not usually needed).
-
-[00.00%] Biggest string found so far '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' with 4437 bytes
-[00.00%] Biggest list found so far '"my-list"' with 17 items
-
--------- summary -------
-
-Sampled 5 keys in the keyspace!
-Total key length in bytes is 264 (avg len 52.80)
-
-Biggest list found '"my-list"' has 17 items
-Biggest string found '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' has 4437 bytes
-
-1 lists with 17 items (20.00% of keys, avg size 17.00)
-0 hashs with 0 fields (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-4 strings with 4831 bytes (80.00% of keys, avg size 1207.75)
-0 streams with 0 entries (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-0 sets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-0 zsets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00
-```
-
-从这个命令的运行结果,我们可以看出:这个命令会扫描(Scan)Redis 中的所有 key,会对 Redis 的性能有一点影响。并且,这种方式只能找出每种数据结构 top 1 bigkey(占用内存最大的 String 数据类型,包含元素最多的复合数据类型)。然而,一个 key 的元素多并不代表占用内存也多,需要我们根据具体的业务情况来进一步判断。
-
-在线上执行该命令时,为了降低对 Redis 的影响,需要指定 `-i` 参数控制扫描的频率。`redis-cli -p 6379 --bigkeys -i 3` 表示扫描过程中每次扫描后休息的时间间隔为 3 秒。
-
-**2、使用 Redis 自带的 SCAN 命令**
-
-`SCAN` 命令可以按照一定的模式和数量返回匹配的 key。获取了 key 之后,可以利用 `STRLEN`、`HLEN`、`LLEN` 等命令返回其长度或成员数量。
-
-| 数据结构 | 命令 | 复杂度 | 结果(对应 key) |
-| ---------- | ------ | ------ | ------------------ |
-| String | STRLEN | O(1) | 字符串值的长度 |
-| Hash | HLEN | O(1) | 哈希表中字段的数量 |
-| List | LLEN | O(1) | 列表元素数量 |
-| Set | SCARD | O(1) | 集合元素数量 |
-| Sorted Set | ZCARD | O(1) | 有序集合的元素数量 |
-
-对于集合类型还可以使用 `MEMORY USAGE` 命令(Redis 4.0+),这个命令会返回键值对占用的内存空间。
-
-**3、借助开源工具分析 RDB 文件。**
-
-通过分析 RDB 文件来找出 big key。这种方案的前提是你的 Redis 采用的是 RDB 持久化。
-
-网上有现成的代码/工具可以直接拿来使用:
-
-- [redis-rdb-tools](https://github.com/sripathikrishnan/redis-rdb-tools):Python 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具。
-- [rdb_bigkeys](https://github.com/weiyanwei412/rdb_bigkeys):Go 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具,性能更好。
-
-**4、借助公有云的 Redis 分析服务。**
-
-如果你用的是公有云的 Redis 服务的话,可以看看其是否提供了 key 分析功能(一般都提供了)。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持 bigkey 实时分析、发现,文档地址:。
-
-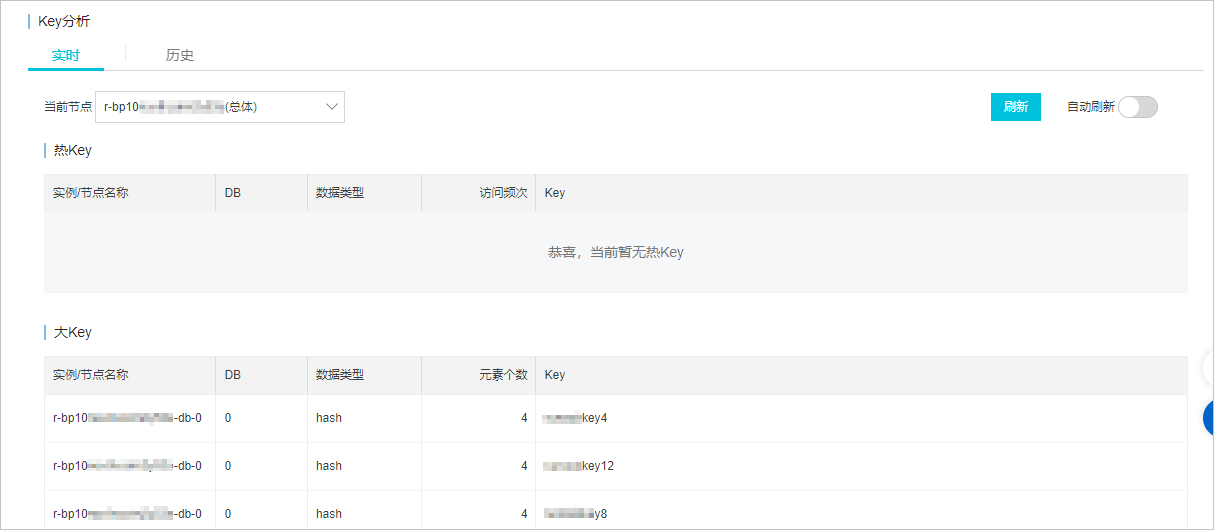
-
-#### 如何处理 bigkey?
-
-bigkey 的常见处理以及优化办法如下(这些方法可以配合起来使用):
-
-- **分割 bigkey**:将一个 bigkey 分割为多个小 key。例如,将一个含有上万字段数量的 Hash 按照一定策略(比如二次哈希)拆分为多个 Hash。
-- **手动清理**:Redis 4.0+ 可以使用 `UNLINK` 命令来异步删除一个或多个指定的 key。Redis 4.0 以下可以考虑使用 `SCAN` 命令结合 `DEL` 命令来分批次删除。
-- **采用合适的数据结构**:例如,文件二进制数据不使用 String 保存、使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV、Bitmap 保存状态信息(0/1)。
-- **开启 lazy-free(惰性删除/延迟释放)**:lazy-free 特性是 Redis 4.0 开始引入的,指的是让 Redis 采用异步方式延迟释放 key 使用的内存,将该操作交给单独的子线程处理,避免阻塞主线程。
-
-### Redis hotkey(热 Key)
-
-#### 什么是 hotkey?
-
-如果一个 key 的访问次数比较多且明显多于其他 key 的话,那这个 key 就可以看作是 **hotkey(热 Key)**。例如在 Redis 实例的每秒处理请求达到 5000 次,而其中某个 key 的每秒访问量就高达 2000 次,那这个 key 就可以看作是 hotkey。
-
-hotkey 出现的原因主要是某个热点数据访问量暴增,如重大的热搜事件、参与秒杀的商品。
-
-#### hotkey 有什么危害?
-
-处理 hotkey 会占用大量的 CPU 和带宽,可能会影响 Redis 实例对其他请求的正常处理。此外,如果突然访问 hotkey 的请求超出了 Redis 的处理能力,Redis 就会直接宕机。这种情况下,大量请求将落到后面的数据库上,可能会导致数据库崩溃。
-
-因此,hotkey 很可能成为系统性能的瓶颈点,需要单独对其进行优化,以确保系统的高可用性和稳定性。
-
-#### 如何发现 hotkey?
-
-**1、使用 Redis 自带的 `--hotkeys` 参数来查找。**
-
-Redis 4.0.3 版本中新增了 `hotkeys` 参数,该参数能够返回所有 key 的被访问次数。
-
-使用该方案的前提条件是 Redis Server 的 `maxmemory-policy` 参数设置为 LFU 算法,不然就会出现如下所示的错误。
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli -p 6379 --hotkeys
-
-# Scanning the entire keyspace to find hot keys as well as
-# average sizes per key type. You can use -i 0.1 to sleep 0.1 sec
-# per 100 SCAN commands (not usually needed).
-
-Error: ERR An LFU maxmemory policy is not selected, access frequency not tracked. Please note that when switching between policies at runtime LRU and LFU data will take some time to adjust.
-```
-
-Redis 中有两种 LFU 算法:
-
-1. **volatile-lfu(least frequently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-2. **allkeys-lfu(least frequently used)**:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在键空间中,移除最不经常使用的 key。
-
-以下是配置文件 `redis.conf` 中的示例:
-
-```properties
-# 使用 volatile-lfu 策略
-maxmemory-policy volatile-lfu
-
-# 或者使用 allkeys-lfu 策略
-maxmemory-policy allkeys-lfu
-```
-
-需要注意的是,`hotkeys` 参数命令也会增加 Redis 实例的 CPU 和内存消耗(全局扫描),因此需要谨慎使用。
-
-**2、使用 `MONITOR` 命令。**
-
-`MONITOR` 命令是 Redis 提供的一种实时查看 Redis 的所有操作的方式,可以用于临时监控 Redis 实例的操作情况,包括读写、删除等操作。
-
-由于该命令对 Redis 性能的影响比较大,因此禁止长时间开启 `MONITOR`(生产环境中建议谨慎使用该命令)。
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli
-127.0.0.1:6379> MONITOR
-OK
-1683638260.637378 [0 172.17.0.1:61516] "ping"
-1683638267.144236 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638268.941863 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638269.551671 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638270.646256 [0 172.17.0.1:61516] "ping"
-1683638270.849551 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638271.926945 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638274.276599 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet2"
-1683638276.327234 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-```
-
-在发生紧急情况时,我们可以选择在合适的时机短暂执行 `MONITOR` 命令并将输出重定向至文件,在关闭 `MONITOR` 命令后通过对文件中请求进行归类分析即可找出这段时间中的 hotkey。
-
-**3、借助开源项目。**
-
-京东零售的 [hotkey](https://gitee.com/jd-platform-opensource/hotkey) 这个项目不光支持 hotkey 的发现,还支持 hotkey 的处理。
-
-
-
-**4、根据业务情况提前预估。**
-
-可以根据业务情况来预估一些 hotkey,比如参与秒杀活动的商品数据等。不过,我们无法预估所有 hotkey 的出现,比如突发的热点新闻事件等。
-
-**5、业务代码中记录分析。**
-
-在业务代码中添加相应的逻辑对 key 的访问情况进行记录分析。不过,这种方式会让业务代码的复杂性增加,一般也不会采用。
-
-**6、借助公有云的 Redis 分析服务。**
-
-如果你用的是公有云的 Redis 服务的话,可以看看其是否提供了 key 分析功能(一般都提供了)。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持 hotkey 实时分析、发现,文档地址:。
-
-
-
-#### 如何解决 hotkey?
-
-hotkey 的常见处理以及优化办法如下(这些方法可以配合起来使用):
-
-- **读写分离**:主节点处理写请求,从节点处理读请求。
-- **使用 Redis Cluster**:将热点数据分散存储在多个 Redis 节点上。
-- **二级缓存**:hotkey 采用二级缓存的方式进行处理,将 hotkey 存放一份到 JVM 本地内存中(可以用 Caffeine)。
-
-除了这些方法之外,如果你使用的公有云的 Redis 服务话,还可以留意其提供的开箱即用的解决方案。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持通过代理查询缓存功能(Proxy Query Cache)优化热点 Key 问题。
-
-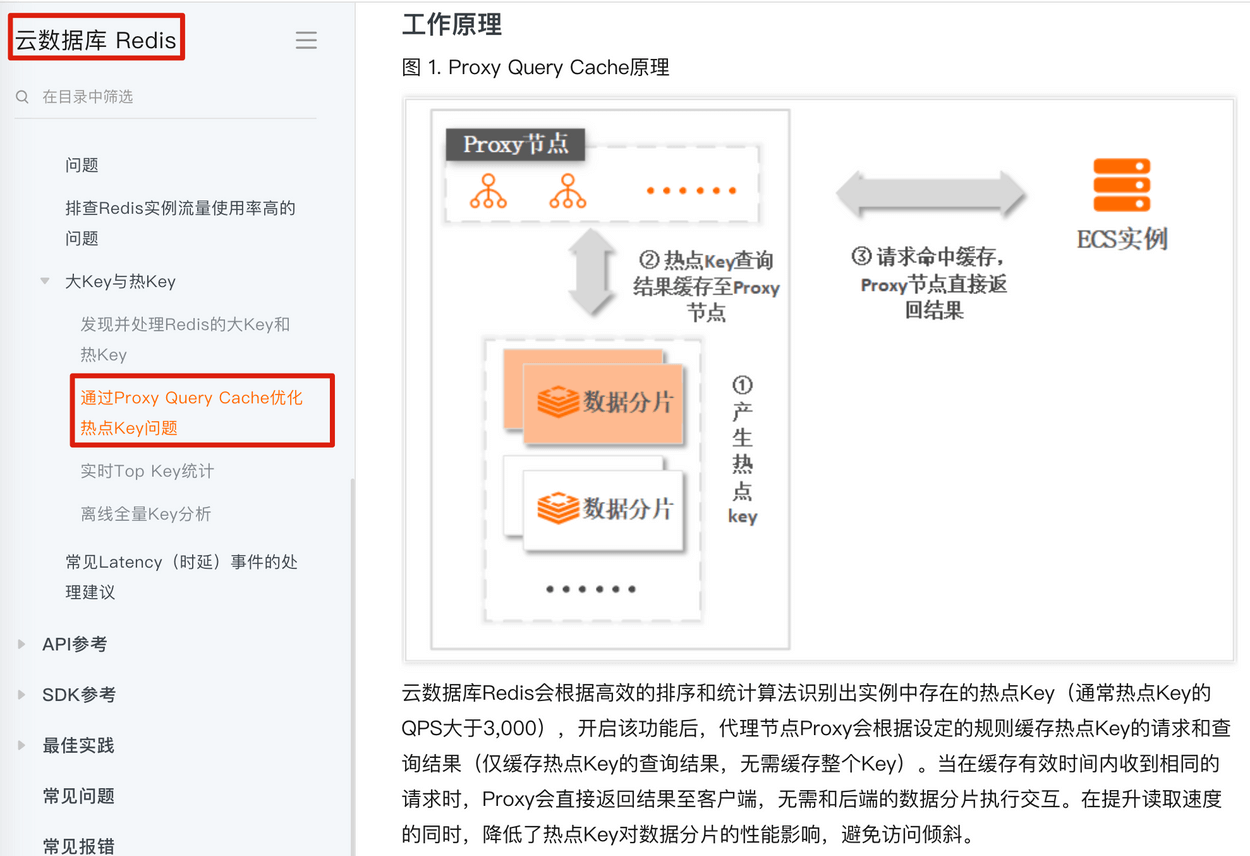
-
-### 慢查询命令
-
-#### 为什么会有慢查询命令?
-
-我们知道一个 Redis 命令的执行可以简化为以下 4 步:
-
-1. 发送命令;
-2. 命令排队;
-3. 命令执行;
-4. 返回结果。
-
-Redis 慢查询统计的是命令执行这一步骤的耗时,慢查询命令也就是那些命令执行时间较长的命令。
-
-Redis 为什么会有慢查询命令呢?
-
-Redis 中的大部分命令都是 O(1) 时间复杂度,但也有少部分 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令,例如:
-
-- `KEYS *`:会返回所有符合规则的 key。
-- `HGETALL`:会返回一个 Hash 中所有的键值对。
-- `LRANGE`:会返回 List 中指定范围内的元素。
-- `SMEMBERS`:返回 Set 中的所有元素。
-- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`:计算多个 Set 的交集/并集/差集。
-- ……
-
-由于这些命令时间复杂度是 O(n),有时候也会全表扫描,随着 n 的增大,执行耗时也会越长。不过, 这些命令并不是一定不能使用,但是需要明确 N 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
-
-除了这些 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令可能会导致慢查询之外,还有一些时间复杂度可能在 O(N) 以上的命令,例如:
-
-- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`:返回指定 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量,m 为返回的元素数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`:移除 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围/指定 score 范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量,m 被删除元素的数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- ……
-
-#### 如何找到慢查询命令?
-
-在 `redis.conf` 文件中,我们可以使用 `slowlog-log-slower-than` 参数设置耗时命令的阈值,并使用 `slowlog-max-len` 参数设置耗时命令的最大记录条数。
-
-当 Redis 服务器检测到执行时间超过 `slowlog-log-slower-than` 阈值的命令时,就会将该命令记录在慢查询日志(slow log)中,这点和 MySQL 记录慢查询语句类似。当慢查询日志超过设定的最大记录条数之后,Redis 会把最早的执行命令依次舍弃。
-
-⚠️注意:由于慢查询日志会占用一定内存空间,如果设置最大记录条数过大,可能会导致内存占用过高的问题。
-
-`slowlog-log-slower-than` 和 `slowlog-max-len` 的默认配置如下(可以自行修改):
-
-```properties
-# The following time is expressed in microseconds, so 1000000 is equivalent
-# to one second. Note that a negative number disables the slow log, while
-# a value of zero forces the logging of every command.
-slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
-
-# There is no limit to this length. Just be aware that it will consume memory.
-# You can reclaim memory used by the slow log with SLOWLOG RESET.
-slowlog-max-len 128
-```
-
-除了修改配置文件之外,你也可以直接通过 `CONFIG` 命令直接设置:
-
-```bash
-# 命令执行耗时超过 10000 微妙(即10毫秒)就会被记录
-CONFIG SET slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
-# 只保留最近 128 条耗时命令
-CONFIG SET slowlog-max-len 128
-```
-
-获取慢查询日志的内容很简单,直接使用 `SLOWLOG GET` 命令即可。
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG GET #慢日志查询
- 1) 1) (integer) 5
- 2) (integer) 1684326682
- 3) (integer) 12000
- 4) 1) "KEYS"
- 2) "*"
- 5) "172.17.0.1:61152"
- 6) ""
- // ...
-```
-
-慢查询日志中的每个条目都由以下六个值组成:
-
-1. 唯一渐进的日志标识符。
-2. 处理记录命令的 Unix 时间戳。
-3. 执行所需的时间量,以微秒为单位。
-4. 组成命令参数的数组。
-5. 客户端 IP 地址和端口。
-6. 客户端名称。
-
-`SLOWLOG GET` 命令默认返回最近 10 条的的慢查询命令,你也自己可以指定返回的慢查询命令的数量 `SLOWLOG GET N`。
-
-下面是其他比较常用的慢查询相关的命令:
-
-```bash
-# 返回慢查询命令的数量
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG LEN
-(integer) 128
-# 清空慢查询命令
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG RESET
-OK
-```
-
-### Redis 内存碎片
-
-**相关问题**:
-
-1. 什么是内存碎片?为什么会有 Redis 内存碎片?
-2. 如何清理 Redis 内存碎片?
-
-**参考答案**:[Redis 内存碎片详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.html)。
-
-## Redis 生产问题(重要)
-
-### 缓存穿透
-
-#### 什么是缓存穿透?
-
-缓存穿透说简单点就是大量请求的 key 是不合理的,**根本不存在于缓存中,也不存在于数据库中**。这就导致这些请求直接到了数据库上,根本没有经过缓存这一层,对数据库造成了巨大的压力,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-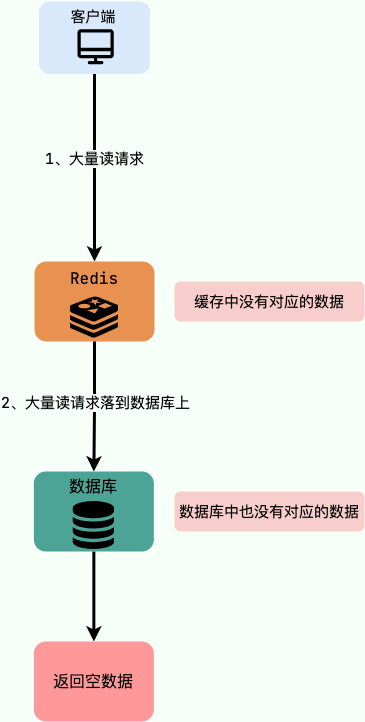
-
-举个例子:某个黑客故意制造一些非法的 key 发起大量请求,导致大量请求落到数据库,结果数据库上也没有查到对应的数据。也就是说这些请求最终都落到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-最基本的就是首先做好参数校验,一些不合法的参数请求直接抛出异常信息返回给客户端。比如查询的数据库 id 不能小于 0、传入的邮箱格式不对的时候直接返回错误消息给客户端等等。
-
-**1)缓存无效 key**
-
-如果缓存和数据库都查不到某个 key 的数据,就写一个到 Redis 中去并设置过期时间,具体命令如下:`SET key value EX 10086`。这种方式可以解决请求的 key 变化不频繁的情况,如果黑客恶意攻击,每次构建不同的请求 key,会导致 Redis 中缓存大量无效的 key。很明显,这种方案并不能从根本上解决此问题。如果非要用这种方式来解决穿透问题的话,尽量将无效的 key 的过期时间设置短一点,比如 1 分钟。
-
-另外,这里多说一嘴,一般情况下我们是这样设计 key 的:`表名:列名:主键名:主键值`。
-
-如果用 Java 代码展示的话,差不多是下面这样的:
-
-```java
-public Object getObjectInclNullById(Integer id) {
- // 从缓存中获取数据
- Object cacheValue = cache.get(id);
- // 缓存为空
- if (cacheValue == null) {
- // 从数据库中获取
- Object storageValue = storage.get(key);
- // 缓存空对象
- cache.set(key, storageValue);
- // 如果存储数据为空,需要设置一个过期时间(300秒)
- if (storageValue == null) {
- // 必须设置过期时间,否则有被攻击的风险
- cache.expire(key, 60 * 5);
- }
- return storageValue;
- }
- return cacheValue;
-}
-```
-
-**2)布隆过滤器**
-
-布隆过滤器是一个非常神奇的数据结构,通过它我们可以非常方便地判断一个给定数据是否存在于海量数据中。我们可以把它看作由二进制向量(或者说位数组)和一系列随机映射函数(哈希函数)两部分组成的数据结构。相比于我们平时常用的 List、Map、Set 等数据结构,它占用空间更少并且效率更高,但是缺点是其返回的结果是概率性的,而不是非常准确的。理论情况下添加到集合中的元素越多,误报的可能性就越大。并且,存放在布隆过滤器的数据不容易删除。
-
-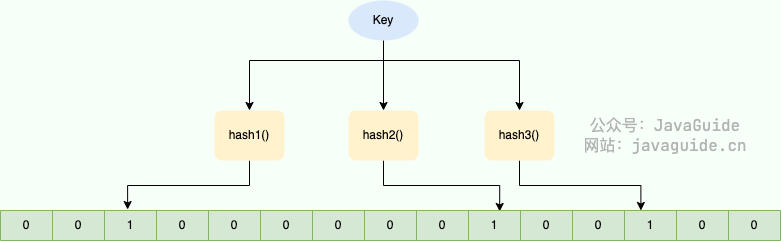
-
-Bloom Filter 会使用一个较大的 bit 数组来保存所有的数据,数组中的每个元素都只占用 1 bit ,并且每个元素只能是 0 或者 1(代表 false 或者 true),这也是 Bloom Filter 节省内存的核心所在。这样来算的话,申请一个 100w 个元素的位数组只占用 1000000Bit / 8 = 125000 Byte = 125000/1024 KB ≈ 122KB 的空间。
-
-
-
-具体是这样做的:把所有可能存在的请求的值都存放在布隆过滤器中,当用户请求过来,先判断用户发来的请求的值是否存在于布隆过滤器中。不存在的话,直接返回请求参数错误信息给客户端,存在的话才会走下面的流程。
-
-加入布隆过滤器之后的缓存处理流程图如下:
-
-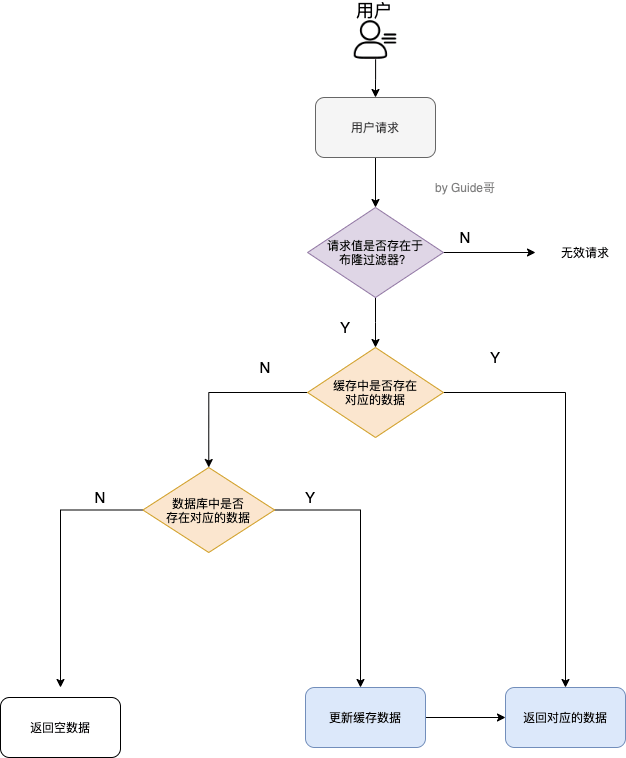
-
-更多关于布隆过滤器的详细介绍可以看看我的这篇原创:[不了解布隆过滤器?一文给你整的明明白白!](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/bloom-filter.html),强烈推荐。
-
-**3)接口限流**
-
-根据用户或者 IP 对接口进行限流,对于异常频繁的访问行为,还可以采取黑名单机制,例如将异常 IP 列入黑名单。
-
-后面提到的缓存击穿和雪崩都可以配合接口限流来解决,毕竟这些问题的关键都是有很多请求落到了数据库上造成数据库压力过大。
-
-限流的具体方案可以参考这篇文章:[服务限流详解](https://javaguide.cn/high-availability/limit-request.html)。
-
-### 缓存击穿
-
-#### 什么是缓存击穿?
-
-缓存击穿中,请求的 key 对应的是 **热点数据**,该数据 **存在于数据库中,但不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)**。这就可能会导致瞬时大量的请求直接打到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-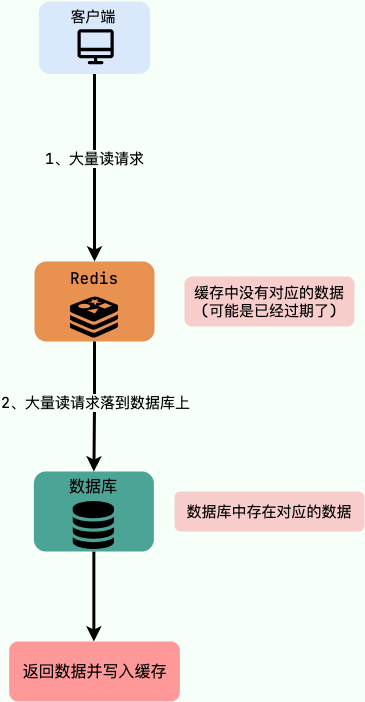
-
-举个例子:秒杀进行过程中,缓存中的某个秒杀商品的数据突然过期,这就导致瞬时大量对该商品的请求直接落到数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-1. **永不过期**(不推荐):设置热点数据永不过期或者过期时间比较长。
-2. **提前预热**(推荐):针对热点数据提前预热,将其存入缓存中并设置合理的过期时间比如秒杀场景下的数据在秒杀结束之前不过期。
-3. **加锁**(看情况):在缓存失效后,通过设置互斥锁确保只有一个请求去查询数据库并更新缓存。
-
-#### 缓存穿透和缓存击穿有什么区别?
-
-缓存穿透中,请求的 key 既不存在于缓存中,也不存在于数据库中。
-
-缓存击穿中,请求的 key 对应的是 **热点数据** ,该数据 **存在于数据库中,但不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)** 。
-
-### 缓存雪崩
-
-#### 什么是缓存雪崩?
-
-我发现缓存雪崩这名字起的有点意思,哈哈。
-
-实际上,缓存雪崩描述的就是这样一个简单的场景:**缓存在同一时间大面积的失效,导致大量的请求都直接落到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。** 这就好比雪崩一样,摧枯拉朽之势,数据库的压力可想而知,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-另外,缓存服务宕机也会导致缓存雪崩现象,导致所有的请求都落到了数据库上。
-
-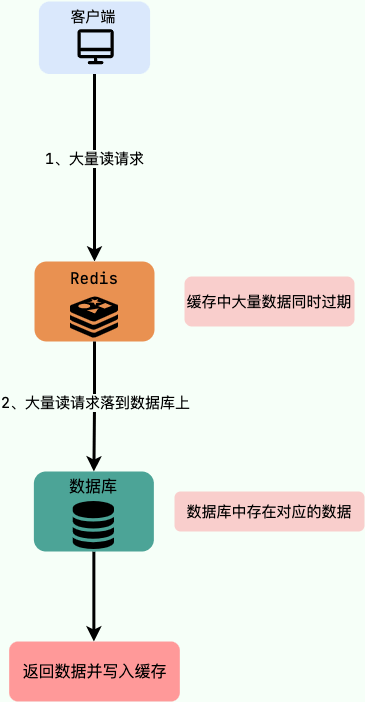
-
-举个例子:缓存中的大量数据在同一时间过期,这个时候突然有大量的请求需要访问这些过期的数据。这就导致大量的请求直接落到数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-**针对 Redis 服务不可用的情况**:
-
-1. **Redis 集群**:采用 Redis 集群,避免单机出现问题整个缓存服务都没办法使用。Redis Cluster 和 Redis Sentinel 是两种最常用的 Redis 集群实现方案,详细介绍可以参考:[Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html)。
-2. **多级缓存**:设置多级缓存,例如本地缓存+Redis 缓存的二级缓存组合,当 Redis 缓存出现问题时,还可以从本地缓存中获取到部分数据。
-
-**针对大量缓存同时失效的情况**:
-
-1. **设置随机失效时间**(可选):为缓存设置随机的失效时间,例如在固定过期时间的基础上加上一个随机值,这样可以避免大量缓存同时到期,从而减少缓存雪崩的风险。
-2. **提前预热**(推荐):针对热点数据提前预热,将其存入缓存中并设置合理的过期时间,比如秒杀场景下的数据在秒杀结束之前不过期。
-3. **持久缓存策略**(看情况):虽然一般不推荐设置缓存永不过期,但对于某些关键性和变化不频繁的数据,可以考虑这种策略。
-
-#### 缓存预热如何实现?
-
-常见的缓存预热方式有两种:
-
-1. 使用定时任务,比如 xxl-job,来定时触发缓存预热的逻辑,将数据库中的热点数据查询出来并存入缓存中。
-2. 使用消息队列,比如 Kafka,来异步地进行缓存预热,将数据库中的热点数据的主键或者 ID 发送到消息队列中,然后由缓存服务消费消息队列中的数据,根据主键或者 ID 查询数据库并更新缓存。
-
-#### 缓存雪崩和缓存击穿有什么区别?
-
-缓存雪崩和缓存击穿比较像,但缓存雪崩导致的原因是缓存中的大量或者所有数据失效,缓存击穿导致的原因主要是某个热点数据不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)。
-
-### 如何保证缓存和数据库数据的一致性?
-
-细说的话可以扯很多,但是我觉得其实没太大必要(小声 BB:很多解决方案我也没太弄明白)。我个人觉得引入缓存之后,如果为了短时间的不一致性问题,选择让系统设计变得更加复杂的话,完全没必要。
-
-下面单独对 **Cache Aside Pattern(旁路缓存模式)** 来聊聊。
-
-Cache Aside Pattern 中遇到写请求是这样的:更新数据库,然后直接删除缓存。
-
-如果更新数据库成功,而删除缓存这一步失败的情况的话,简单说有两个解决方案:
-
-1. **缓存失效时间变短**(不推荐,治标不治本):我们让缓存数据的过期时间变短,这样的话缓存就会从数据库中加载数据。另外,这种解决办法对于先操作缓存后操作数据库的场景不适用。
-2. **增加缓存更新重试机制**(常用):如果缓存服务当前不可用导致缓存删除失败的话,我们就隔一段时间进行重试,重试次数可以自己定。不过,这里更适合引入消息队列实现异步重试,将删除缓存重试的消息投递到消息队列,然后由专门的消费者来重试,直到成功。虽然说多引入了一个消息队列,但其整体带来的收益还是要更高一些。
-
-相关文章推荐:[缓存和数据库一致性问题,看这篇就够了 - 水滴与银弹](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIyOTYxNDI5OA==&mid=2247487312&idx=1&sn=fa19566f5729d6598155b5c676eee62d&chksm=e8beb8e5dfc931f3e35655da9da0b61c79f2843101c130cf38996446975014f958a6481aacf1&scene=178&cur_album_id=1699766580538032128#rd)。
-
-### 哪些情况可能会导致 Redis 阻塞?
-
-单独抽了一篇文章来总结可能会导致 Redis 阻塞的情况:[Redis 常见阻塞原因总结](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.html)。
-
-## Redis 集群
-
-**Redis Sentinel**:
-
-1. 什么是 Sentinel? 有什么用?
-2. Sentinel 如何检测节点是否下线?主观下线与客观下线的区别?
-3. Sentinel 是如何实现故障转移的?
-4. 为什么建议部署多个 sentinel 节点(哨兵集群)?
-5. Sentinel 如何选择出新的 master(选举机制)?
-6. 如何从 Sentinel 集群中选择出 Leader?
-7. Sentinel 可以防止脑裂吗?
-
-**Redis Cluster**:
-
-1. 为什么需要 Redis Cluster?解决了什么问题?有什么优势?
-2. Redis Cluster 是如何分片的?
-3. 为什么 Redis Cluster 的哈希槽是 16384 个?
-4. 如何确定给定 key 的应该分布到哪个哈希槽中?
-5. Redis Cluster 支持重新分配哈希槽吗?
-6. Redis Cluster 扩容缩容期间可以提供服务吗?
-7. Redis Cluster 中的节点是怎么进行通信的?
-
-**参考答案**:[Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html)。
-
-## Redis 使用规范
-
-实际使用 Redis 的过程中,我们尽量要准守一些常见的规范,比如:
-
-1. 使用连接池:避免频繁创建关闭客户端连接。
-2. 尽量不使用 O(n) 指令,使用 O(n) 命令时要关注 n 的数量:像 `KEYS *`、`HGETALL`、`LRANGE`、`SMEMBERS`、`SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF` 等 O(n) 命令并非不能使用,但是需要明确 n 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
-3. 使用批量操作减少网络传输:原生批量操作命令(比如 `MGET`、`MSET` 等等)、pipeline、Lua 脚本。
-4. 尽量不使用 Redis 事务:Redis 事务实现的功能比较鸡肋,可以使用 Lua 脚本代替。
-5. 禁止长时间开启 monitor:对性能影响比较大。
-6. 控制 key 的生命周期:避免 Redis 中存放了太多不经常被访问的数据。
-7. ……
-
-相关文章推荐:[阿里云 Redis 开发规范](https://developer.aliyun.com/article/531067)。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 开发与运维》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- Redis Transactions:
-- What is Redis Pipeline:
-- 一文详解 Redis 中 BigKey、HotKey 的发现与处理:
-- Bigkey 问题的解决思路与方式探索:
-- Redis 延迟问题全面排障指南:
-
-
+Redis transactions are different from what we usually understand as transactions in relational databases. We know that transactions have four major characteristics: **1. Atomicity**, **2. Isolation**, **3. Durability**,
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
index 1194f736374..e62a788c1c3 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
@@ -1,28 +1,27 @@
---
-title: Redis为什么用跳表实现有序集合
-category: 数据库
+title: Why Redis Uses Skip Lists to Implement Sorted Sets
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-## 前言
+## Introduction
-近几年针对 Redis 面试时会涉及常见数据结构的底层设计,其中就有这么一道比较有意思的面试题:“Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+树?”。
+In recent years, common data structure design questions have been frequently asked in Redis interviews. One interesting interview question is: "Why does Redis use skip lists for its sorted sets instead of balanced trees, red-black trees, or B+ trees?"
-本文就以这道大厂常问的面试题为切入点,带大家详细了解一下跳表这个数据结构。
+This article will use this commonly asked interview question as a starting point to provide a detailed understanding of the skip list data structure.
-本文整体脉络如下图所示,笔者会从有序集合的基本使用到跳表的源码分析和实现,让你会对 Redis 的有序集合底层实现的跳表有着更深刻的理解和掌握。
+The overall structure of this article is illustrated in the following diagram. I will guide you from the basic usage of sorted sets to the source code analysis and implementation of skip lists, giving you a deeper understanding and mastery of the skip list used in the underlying implementation of Redis's sorted sets.
-## 跳表在 Redis 中的运用
+## The Use of Skip Lists in Redis
-这里我们需要先了解一下 Redis 用到跳表的数据结构有序集合的使用,Redis 有个比较常用的数据结构叫**有序集合(sorted set,简称 zset)**,正如其名它是一个可以保证有序且元素唯一的集合,所以它经常用于排行榜等需要进行统计排列的场景。
+First, we need to understand the usage of the skip list data structure in Redis's sorted sets. Redis has a commonly used data structure called **sorted set (zset)**. As the name suggests, it is a collection that guarantees order and uniqueness of elements, making it frequently used in scenarios like leaderboards that require statistical ranking.
-这里我们通过命令行的形式演示一下排行榜的实现,可以看到笔者分别输入 3 名用户:**xiaoming**、**xiaohong**、**xiaowang**,它们的**score**分别是 60、80、60,最终按照成绩升级降序排列。
+Here, we will demonstrate the implementation of a leaderboard using command line. We can see that I entered three users: **xiaoming**, **xiaohong**, and **xiaowang**, with their **scores** being 60, 80, and 60, respectively, and they are finally ranked in descending order of their scores.
```bash
-
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 60 xiaoming
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 80 xiaohong
@@ -30,7 +29,7 @@ tag:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 60 xiaowang
(integer) 1
-# 返回有序集中指定区间内的成员,通过索引,分数从高到低
+# Return members in the specified range of the sorted set, indexed, with scores from high to low
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGE rankList 0 100 WITHSCORES
1) "xiaohong"
2) "80"
@@ -40,734 +39,42 @@ tag:
6) "60"
```
-此时我们通过 `object` 指令查看 zset 的数据结构,可以看到当前有序集合存储的还是**ziplist(压缩列表)**。
+At this point, we can check the data structure of the zset using the `object` command, and we can see that the current sorted set is still stored as a **ziplist**.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding rankList
"ziplist"
```
-因为设计者考虑到 Redis 数据存放于内存,为了节约宝贵的内存空间,在有序集合元素小于 64 字节且个数小于 128 的时候,会使用 ziplist,而这个阈值的默认值的设置就来自下面这两个配置项。
+The designer considered that Redis stores data in memory, and to save precious memory space, when the number of elements in the sorted set is less than 128 and each element is less than 64 bytes, it will use a ziplist. The default threshold for this setting comes from the following two configuration items.
```bash
zset-max-ziplist-value 64
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128
```
-一旦有序集合中的某个元素超出这两个其中的一个阈值它就会转为 **skiplist**(实际是 dict+skiplist,还会借用字典来提高获取指定元素的效率)。
+Once an element in the sorted set exceeds one of these two thresholds, it will switch to a **skiplist** (actually a dict + skiplist, which also uses a dictionary to improve the efficiency of retrieving specific elements).
-我们不妨在添加一个大于 64 字节的元素,可以看到有序集合的底层存储转为 skiplist。
+Let's add an element greater than 64 bytes and see that the underlying storage of the sorted set switches to a skiplist.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 90 yigemingzihuichaoguo64zijiedeyonghumingchengyongyuceshitiaobiaodeshijiyunyong
(integer) 1
-# 超过阈值,转为跳表
+# Exceeds the threshold, switches to skiplist
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding rankList
"skiplist"
```
-也就是说,ZSet 有两种不同的实现,分别是 ziplist 和 skiplist,具体使用哪种结构进行存储的规则如下:
-
-- 当有序集合对象同时满足以下两个条件时,使用 ziplist:
- 1. ZSet 保存的键值对数量少于 128 个;
- 2. 每个元素的长度小于 64 字节。
-- 如果不满足上述两个条件,那么使用 skiplist 。
-
-## 手写一个跳表
-
-为了更好的回答上述问题以及更好的理解和掌握跳表,这里可以通过手写一个简单的跳表的形式来帮助读者理解跳表这个数据结构。
-
-我们都知道有序链表在添加、查询、删除的平均时间复杂都都是 **O(n)** 即线性增长,所以一旦节点数量达到一定体量后其性能表现就会非常差劲。而跳表我们完全可以理解为在原始链表基础上,建立多级索引,通过多级索引检索定位将增删改查的时间复杂度变为 **O(log n)** 。
-
-可能这里说的有些抽象,我们举个例子,以下图跳表为例,其原始链表存储按序存储 1-10,有 2 级索引,每级索引的索引个数都是基于下层元素个数的一半。
-
-
-
-假如我们需要查询元素 6,其工作流程如下:
-
-1. 从 2 级索引开始,先来到节点 4。
-2. 查看 4 的后继节点,是 8 的 2 级索引,这个值大于 6,说明 2 级索引后续的索引都是大于 6 的,没有再往后搜寻的必要,我们索引向下查找。
-3. 来到 4 的 1 级索引,比对其后继节点为 6,查找结束。
-
-相较于原始有序链表需要 6 次,我们的跳表通过建立多级索引,我们只需两次就直接定位到了目标元素,其查寻的复杂度被直接优化为**O(log n)**。
-
-
-
-对应的添加也是一个道理,假如我们需要在这个有序集合中添加一个元素 7,那么我们就需要通过跳表找到**小于元素 7 的最大值**,也就是下图元素 6 的位置,将其插入到元素 6 的后面,让元素 6 的索引指向新插入的节点 7,其工作流程如下:
-
-1. 从 2 级索引开始定位到了元素 4 的索引。
-2. 查看索引 4 的后继索引为 8,索引向下推进。
-3. 来到 1 级索引,发现索引 4 后继索引为 6,小于插入元素 7,指针推进到索引 6 位置。
-4. 继续比较 6 的后继节点为索引 8,大于元素 7,索引继续向下。
-5. 最终我们来到 6 的原始节点,发现其后继节点为 7,指针没有继续向下的空间,自此我们可知元素 6 就是小于插入元素 7 的最大值,于是便将元素 7 插入。
-
-
-
-这里我们又面临一个问题,我们是否需要为元素 7 建立索引,索引多高合适?
-
-我们上文提到,理想情况是每一层索引是下一层元素个数的二分之一,假设我们的总共有 16 个元素,对应各级索引元素个数应该是:
-
-```bash
-1. 一级索引:16/2=8
-2. 二级索引:8/2 =4
-3. 三级索引:4/2=2
-```
-
-由此我们用数学归纳法可知:
-
-```bash
-1. 一级索引:16/2=16/2^1=8
-2. 二级索引:8/2 => 16/2^2 =4
-3. 三级索引:4/2=>16/2^3=2
-```
-
-假设元素个数为 n,那么对应 k 层索引的元素个数 r 计算公式为:
-
-```bash
-r=n/2^k
-```
-
-同理我们再来推断以下索引的最大高度,一般来说最高级索引的元素个数为 2,我们设元素总个数为 n,索引高度为 h,代入上述公式可得:
-
-```bash
-2= n/2^h
-=> 2*2^h=n
-=> 2^(h+1)=n
-=> h+1=log2^n
-=> h=log2^n -1
-```
-
-而 Redis 又是内存数据库,我们假设元素最大个数是**65536**,我们把**65536**代入上述公式可知最大高度为 16。所以我们建议添加一个元素后为其建立的索引高度不超过 16。
-
-因为我们要求尽可能保证每一个上级索引都是下级索引的一半,在实现高度生成算法时,我们可以这样设计:
-
-1. 跳表的高度计算从原始链表开始,即默认情况下插入的元素的高度为 1,代表没有索引,只有元素节点。
-2. 设计一个为插入元素生成节点索引高度 level 的方法。
-3. 进行一次随机运算,随机数值范围为 0-1 之间。
-4. 如果随机数大于 0.5 则为当前元素添加一级索引,自此我们保证生成一级索引的概率为 **50%** ,这也就保证了 1 级索引理想情况下只有一半的元素会生成索引。
-5. 同理后续每次随机算法得到的值大于 0.5 时,我们的索引高度就加 1,这样就可以保证节点生成的 2 级索引概率为 **25%** ,3 级索引为 **12.5%** ……
-
-我们回过头,上述插入 7 之后,我们通过随机算法得到 2,即要为其建立 1 级索引:
-
-
-
-最后我们再来说说删除,假设我们这里要删除元素 10,我们必须定位到当前跳表**各层**元素小于 10 的最大值,索引执行步骤为:
-
-1. 2 级索引 4 的后继节点为 8,指针推进。
-2. 索引 8 无后继节点,该层无要删除的元素,指针直接向下。
-3. 1 级索引 8 后继节点为 10,说明 1 级索引 8 在进行删除时需要将自己的指针和 1 级索引 10 断开联系,将 10 删除。
-4. 1 级索引完成定位后,指针向下,后继节点为 9,指针推进。
-5. 9 的后继节点为 10,同理需要让其指向 null,将 10 删除。
-
-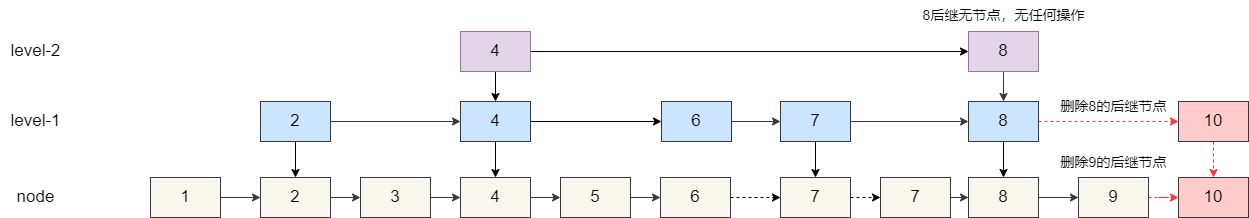
-
-### 模板定义
-
-有了整体的思路之后,我们可以开始实现一个跳表了,首先定义一下跳表中的节点**Node**,从上文的演示中可以看出每一个**Node**它都包含以下几个元素:
-
-1. 存储的**value**值。
-2. 后继节点的地址。
-3. 多级索引。
-
-为了更方便统一管理**Node**后继节点地址和多级索引指向的元素地址,笔者在**Node**中设置了一个**forwards**数组,用于记录原始链表节点的后继节点和多级索引的后继节点指向。
-
-以下图为例,我们**forwards**数组长度为 5,其中**索引 0**记录的是原始链表节点的后继节点地址,而其余自底向上表示从 1 级索引到 4 级索引的后继节点指向。
-
-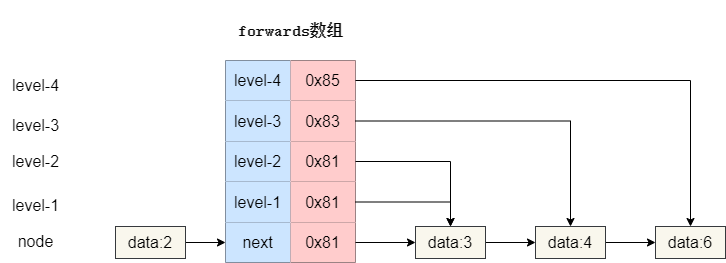
-
-于是我们的就有了这样一个代码定义,可以看出笔者对于数组的长度设置为固定的 16**(上文的推算最大高度建议是 16)**,默认**data**为-1,节点最大高度**maxLevel**初始化为 1,注意这个**maxLevel**的值代表原始链表加上索引的总高度。
-
-```java
-/**
- * 跳表索引最大高度为16
- */
-private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
-
-class Node {
- private int data = -1;
- private Node[] forwards = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
- private int maxLevel = 0;
-
-}
-```
-
-### 元素添加
-
-定义好节点之后,我们先实现以下元素的添加,添加元素时首先自然是设置**data**这一步我们直接根据将传入的**value**设置到**data**上即可。
-
-然后就是高度**maxLevel**的设置 ,我们在上文也已经给出了思路,默认高度为 1,即只有一个原始链表节点,通过随机算法每次大于 0.5 索引高度加 1,由此我们得出高度计算的算法`randomLevel()`:
-
-```java
-/**
- * 理论来讲,一级索引中元素个数应该占原始数据的 50%,二级索引中元素个数占 25%,三级索引12.5% ,一直到最顶层。
- * 因为这里每一层的晋升概率是 50%。对于每一个新插入的节点,都需要调用 randomLevel 生成一个合理的层数。
- * 该 randomLevel 方法会随机生成 1~MAX_LEVEL 之间的数,且 :
- * 50%的概率返回 1
- * 25%的概率返回 2
- * 12.5%的概率返回 3 ...
- * @return
- */
-private int randomLevel() {
- int level = 1;
- while (Math.random() > PROB && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
- ++level;
- }
- return level;
-}
-```
-
-然后再设置当前要插入的**Node**和**Node**索引的后继节点地址,这一步稍微复杂一点,我们假设当前节点的高度为 4,即 1 个节点加 3 个索引,所以我们创建一个长度为 4 的数组**maxOfMinArr** ,遍历各级索引节点中小于当前**value**的最大值。
-
-假设我们要插入的**value**为 5,我们的数组查找结果当前节点的前驱节点和 1 级索引、2 级索引的前驱节点都为 4,三级索引为空。
-
-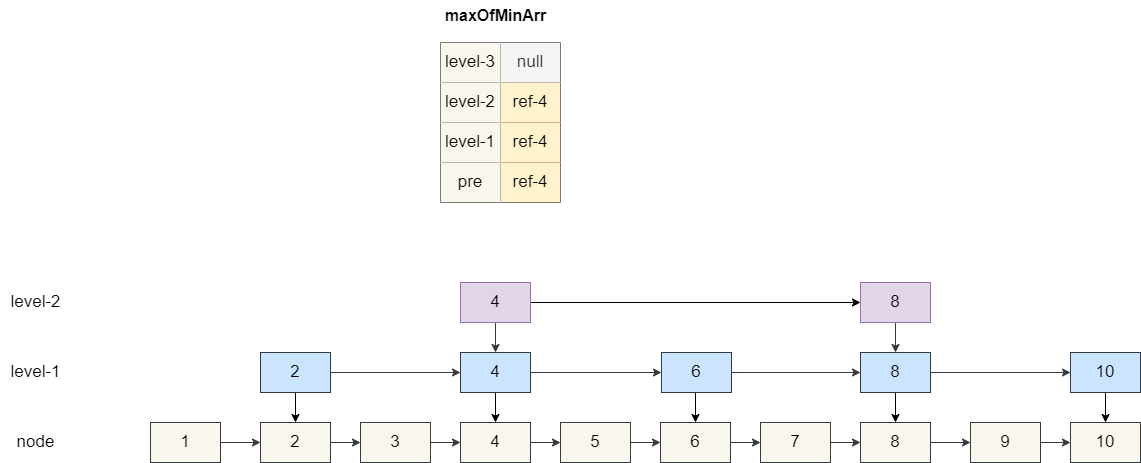
-
-然后我们基于这个数组**maxOfMinArr** 定位到各级的后继节点,让插入的元素 5 指向这些后继节点,而**maxOfMinArr**指向 5,结果如下图:
-
-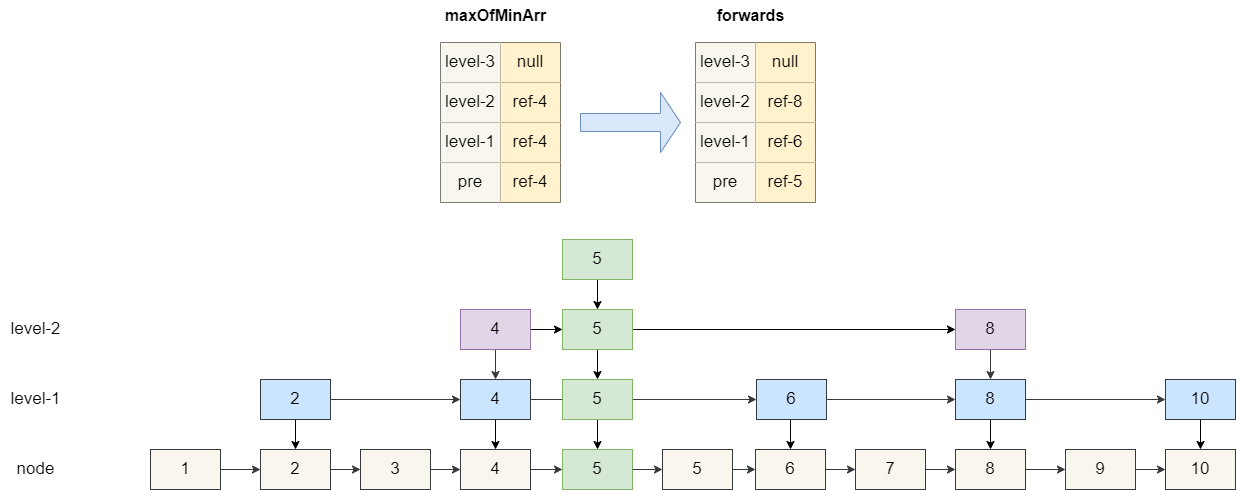
-
-转化成代码就是下面这个形式,是不是很简单呢?我们继续:
-
-```java
-/**
- * 默认情况下的高度为1,即只有自己一个节点
- */
-private int levelCount = 1;
-
-/**
- * 跳表最底层的节点,即头节点
- */
-private Node h = new Node();
-
-public void add(int value) {
-
- //随机生成高度
- int level = randomLevel();
-
- Node newNode = new Node();
- newNode.data = value;
- newNode.maxLevel = level;
-
- //创建一个node数组,用于记录小于当前value的最大值
- Node[] maxOfMinArr = new Node[level];
- //默认情况下指向头节点
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- maxOfMinArr[i] = h;
- }
-
- //基于上述结果拿到当前节点的后继节点
- Node p = h;
- for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- maxOfMinArr[i] = p;
- }
-
- //更新前驱节点的后继节点为当前节点newNode
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- newNode.forwards[i] = maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i];
- maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
- }
-
- //如果当前newNode高度大于跳表最高高度则更新levelCount
- if (levelCount < level) {
- levelCount = level;
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-### 元素查询
-
-查询逻辑比较简单,从跳表最高级的索引开始定位找到小于要查的 value 的最大值,以下图为例,我们希望查找到节点 8:
-
-1. 跳表的 3 级索引首先找找到 5 的索引,5 的 3 级索引 **forwards[3]** 指向空,索引直接向下。
-2. 来到 5 的 2 级索引,其后继 **forwards[2]** 指向 8,继续向下。
-3. 5 的 1 级索引 **forwards[1]** 指向索引 6,继续向前。
-4. 索引 6 的 **forwards[1]** 指向索引 8,继续向下。
-5. 我们在原始节点向前找到节点 7。
-6. 节点 7 后续就是节点 8,继续向前为节点 8,无法继续向下,结束搜寻。
-7. 判断 7 的前驱,等于 8,查找结束。
-
-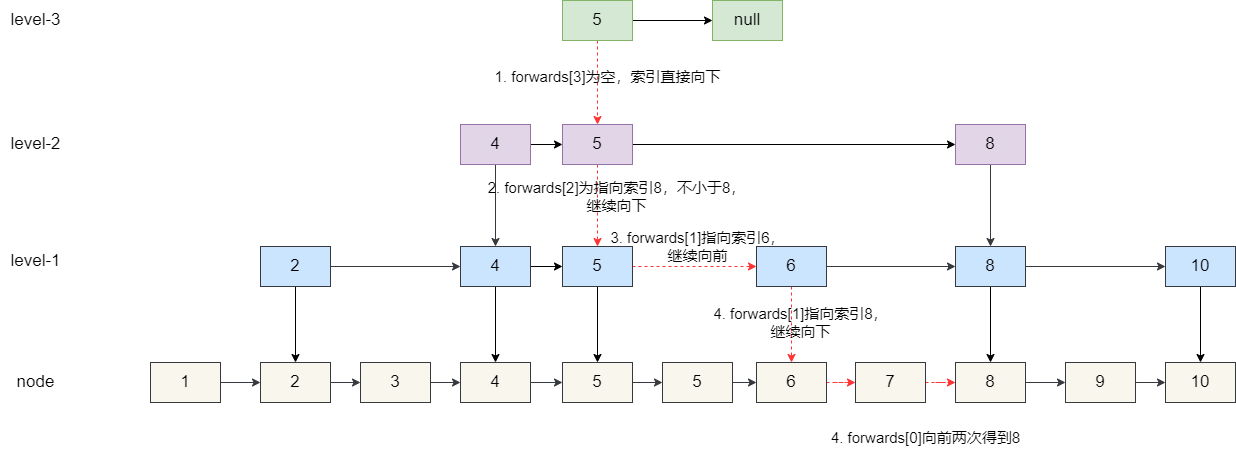
-
-所以我们的代码实现也很上述步骤差不多,从最高级索引开始向前查找,如果不为空且小于要查找的值,则继续向前搜寻,遇到不小于的节点则继续向下,如此往复,直到得到当前跳表中小于查找值的最大节点,查看其前驱是否等于要查找的值:
-
-```java
-public Node get(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到小于value的最大值
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- }
- //如果p的前驱节点等于value则直接返回
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- return p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- return null;
-}
-```
-
-### 元素删除
-
-最后是删除逻辑,需要查找各层级小于要删除节点的最大值,假设我们要删除 10:
-
-1. 3 级索引得到小于 10 的最大值为 5,继续向下。
-2. 2 级索引从索引 5 开始查找,发现小于 10 的最大值为 8,继续向下。
-3. 同理 1 级索引得到 8,继续向下。
-4. 原始节点找到 9。
-5. 从最高级索引开始,查看每个小于 10 的节点后继节点是否为 10,如果等于 10,则让这个节点指向 10 的后继节点,将节点 10 及其索引交由 GC 回收。
-
-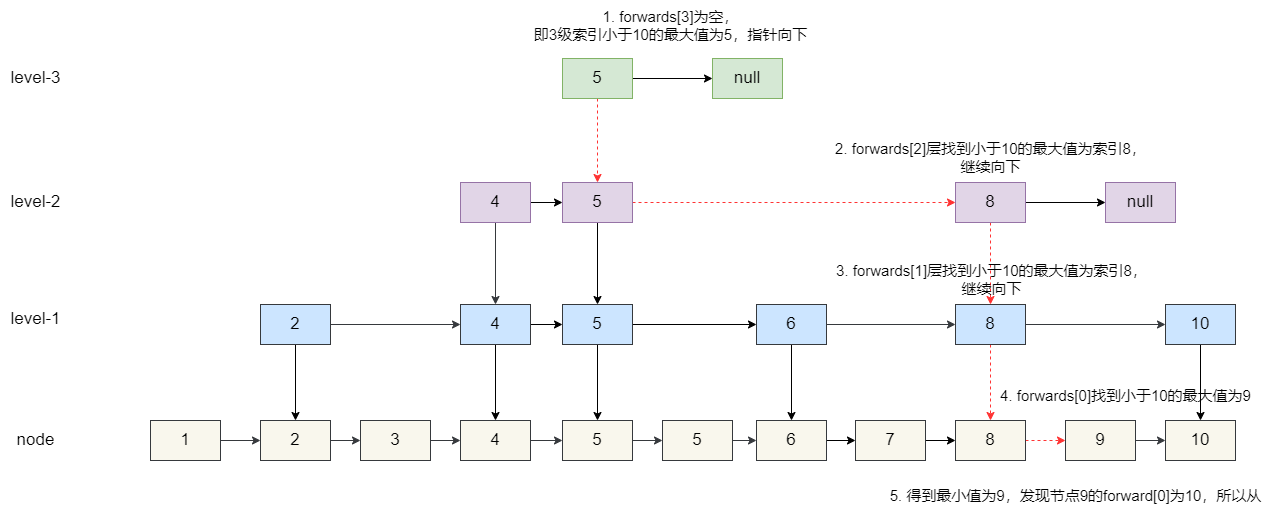
-
-```java
-/**
- * 删除
- *
- * @param value
- */
-public void delete(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到各级节点小于value的最大值
- Node[] updateArr = new Node[levelCount];
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- updateArr[i] = p;
- }
- //查看原始层节点前驱是否等于value,若等于则说明存在要删除的值
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- //从最高级索引开始查看其前驱是否等于value,若等于则将当前节点指向value节点的后继节点
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (updateArr[i].forwards[i] != null && updateArr[i].forwards[i].data == value) {
- updateArr[i].forwards[i] = updateArr[i].forwards[i].forwards[i];
- }
- }
- }
-
- //从最高级开始查看是否有一级索引为空,若为空则层级减1
- while (levelCount > 1 && h.forwards[levelCount - 1] == null) {
- levelCount--;
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-### 完整代码以及测试
-
-完整代码如下,读者可自行参阅:
-
-```java
-public class SkipList {
-
- /**
- * 跳表索引最大高度为16
- */
- private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
-
- /**
- * 每个节点添加一层索引高度的概率为二分之一
- */
- private static final float PROB = 0.5 f;
-
- /**
- * 默认情况下的高度为1,即只有自己一个节点
- */
- private int levelCount = 1;
-
- /**
- * 跳表最底层的节点,即头节点
- */
- private Node h = new Node();
-
- public SkipList() {}
-
- public class Node {
- private int data = -1;
- /**
- *
- */
- private Node[] forwards = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
- private int maxLevel = 0;
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Node{" +
- "data=" + data +
- ", maxLevel=" + maxLevel +
- '}';
- }
- }
-
- public void add(int value) {
-
- //随机生成高度
- int level = randomLevel();
-
- Node newNode = new Node();
- newNode.data = value;
- newNode.maxLevel = level;
-
- //创建一个node数组,用于记录小于当前value的最大值
- Node[] maxOfMinArr = new Node[level];
- //默认情况下指向头节点
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- maxOfMinArr[i] = h;
- }
-
- //基于上述结果拿到当前节点的后继节点
- Node p = h;
- for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- maxOfMinArr[i] = p;
- }
-
- //更新前驱节点的后继节点为当前节点newNode
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- newNode.forwards[i] = maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i];
- maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
- }
-
- //如果当前newNode高度大于跳表最高高度则更新levelCount
- if (levelCount < level) {
- levelCount = level;
- }
-
- }
-
- /**
- * 理论来讲,一级索引中元素个数应该占原始数据的 50%,二级索引中元素个数占 25%,三级索引12.5% ,一直到最顶层。
- * 因为这里每一层的晋升概率是 50%。对于每一个新插入的节点,都需要调用 randomLevel 生成一个合理的层数。
- * 该 randomLevel 方法会随机生成 1~MAX_LEVEL 之间的数,且 :
- * 50%的概率返回 1
- * 25%的概率返回 2
- * 12.5%的概率返回 3 ...
- * @return
- */
- private int randomLevel() {
- int level = 1;
- while (Math.random() > PROB && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
- ++level;
- }
- return level;
- }
-
- public Node get(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到小于value的最大值
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- }
- //如果p的前驱节点等于value则直接返回
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- return p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- return null;
- }
-
- /**
- * 删除
- *
- * @param value
- */
- public void delete(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到各级节点小于value的最大值
- Node[] updateArr = new Node[levelCount];
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- updateArr[i] = p;
- }
- //查看原始层节点前驱是否等于value,若等于则说明存在要删除的值
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- //从最高级索引开始查看其前驱是否等于value,若等于则将当前节点指向value节点的后继节点
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (updateArr[i].forwards[i] != null && updateArr[i].forwards[i].data == value) {
- updateArr[i].forwards[i] = updateArr[i].forwards[i].forwards[i];
- }
- }
- }
-
- //从最高级开始查看是否有一级索引为空,若为空则层级减1
- while (levelCount > 1 && h.forwards[levelCount - 1] == null) {
- levelCount--;
- }
-
- }
-
- public void printAll() {
- Node p = h;
- //基于最底层的非索引层进行遍历,只要后继节点不为空,则速速出当前节点,并移动到后继节点
- while (p.forwards[0] != null) {
- System.out.println(p.forwards[0]);
- p = p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-对应测试代码和输出结果如下:
-
-```java
-public static void main(String[] args) {
- SkipList skipList = new SkipList();
- for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
- skipList.add(i);
- }
-
- System.out.println("**********输出添加结果**********");
- skipList.printAll();
-
- SkipList.Node node = skipList.get(22);
- System.out.println("**********查询结果:" + node+" **********");
-
- skipList.delete(22);
- System.out.println("**********删除结果**********");
- skipList.printAll();
-
-
- }
-```
-
-输出结果:
-
-```bash
-**********输出添加结果**********
-Node{data=0, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=1, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=2, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=3, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=4, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=5, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=6, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=7, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=8, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=9, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=10, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=11, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=12, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=13, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=14, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=15, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=16, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=17, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=18, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=19, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=20, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=21, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=22, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=23, maxLevel=1}
-**********查询结果:Node{data=22, maxLevel=1} **********
-**********删除结果**********
-Node{data=0, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=1, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=2, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=3, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=4, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=5, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=6, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=7, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=8, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=9, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=10, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=11, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=12, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=13, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=14, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=15, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=16, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=17, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=18, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=19, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=20, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=21, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=23, maxLevel=1}
-```
-
-**Redis 跳表的特点**:
-
-1. 采用**双向链表**,不同于上面的示例,存在一个回退指针。主要用于简化操作,例如删除某个元素时,还需要找到该元素的前驱节点,使用回退指针会非常方便。
-2. `score` 值可以重复,如果 `score` 值一样,则按照 ele(节点存储的值,为 sds)字典排序
-3. Redis 跳跃表默认允许最大的层数是 32,被源码中 `ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL` 定义。
-
-## 和其余三种数据结构的比较
-
-最后,我们再来回答一下文章开头的那道面试题: “Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+树?”。
-
-### 平衡树 vs 跳表
-
-先来说说它和平衡树的比较,平衡树我们又会称之为 **AVL 树**,是一个严格的平衡二叉树,平衡条件必须满足(所有节点的左右子树高度差不超过 1,即平衡因子为范围为 `[-1,1]`)。平衡树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)** 。
-
-对于范围查询来说,它也可以通过中序遍历的方式达到和跳表一样的效果。但是它的每一次插入或者删除操作都需要保证整颗树左右节点的绝对平衡,只要不平衡就要通过旋转操作来保持平衡,这个过程是比较耗时的。
-
-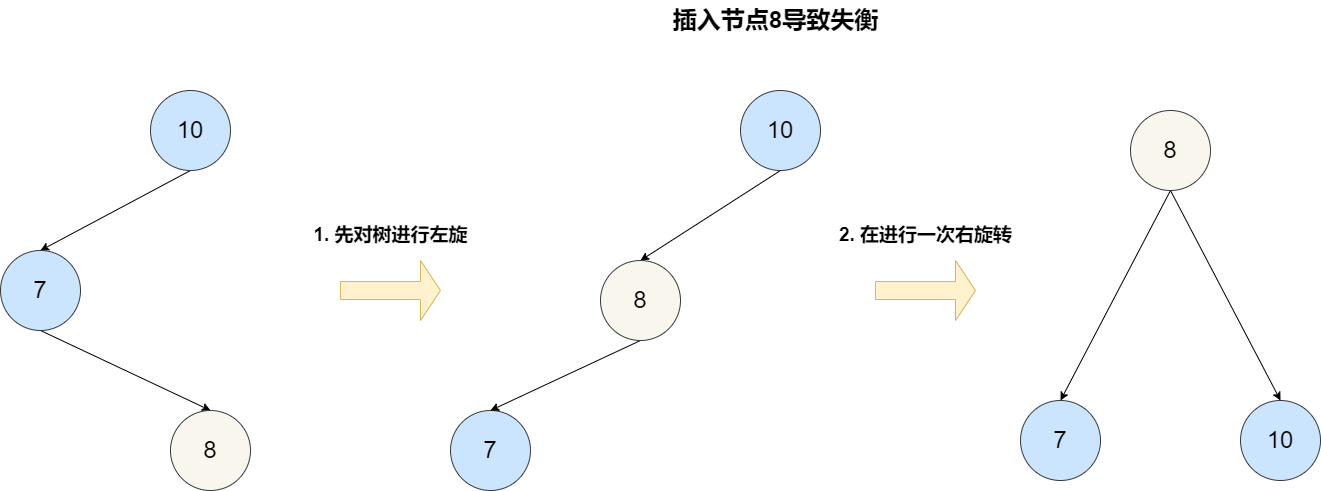
-
-跳表诞生的初衷就是为了克服平衡树的一些缺点,跳表的发明者在论文[《Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees》](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2018/papers/08-oltpindexes1/pugh-skiplists-cacm1990.pdf)中有详细提到:
-
-
-
-> Skip lists are a data structure that can be used in place of balanced trees. Skip lists use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing and as a result the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
->
-> 跳表是一种可以用来代替平衡树的数据结构。跳表使用概率平衡而不是严格强制的平衡,因此,跳表中的插入和删除算法比平衡树的等效算法简单得多,速度也快得多。
-
-笔者这里也贴出了 AVL 树插入操作的核心代码,可以看出每一次添加操作都需要进行一次递归定位插入位置,然后还需要根据回溯到根节点检查沿途的各层节点是否失衡,再通过旋转节点的方式进行调整。
-
-```java
-// 向二分搜索树中添加新的元素(key, value)
-public void add(K key, V value) {
- root = add(root, key, value);
-}
-
-// 向以node为根的二分搜索树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法
-// 返回插入新节点后二分搜索树的根
-private Node add(Node node, K key, V value) {
-
- if (node == null) {
- size++;
- return new Node(key, value);
- }
-
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
- node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
- else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
- node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
- else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
- node.value = value;
-
- node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right));
-
- int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node);
-
- // LL型需要右旋
- if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
- return rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //RR型失衡需要左旋
- if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
- return leftRotate(node);
- }
-
- //LR需要先左旋成LL型,然后再右旋
- if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) < 0) {
- node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
- return rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //RL
- if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) > 0) {
- node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
- return leftRotate(node);
- }
- return node;
-}
-```
-
-### 红黑树 vs 跳表
-
-红黑树(Red Black Tree)也是一种自平衡二叉查找树,它的查询性能略微逊色于 AVL 树,但插入和删除效率更高。红黑树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)** 。
-
-红黑树是一个**黑平衡树**,即从任意节点到另外一个叶子叶子节点,它所经过的黑节点是一样的。当对它进行插入操作时,需要通过旋转和染色(红黑变换)来保证黑平衡。不过,相较于 AVL 树为了维持平衡的开销要小一些。关于红黑树的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章:[红黑树](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/red-black-tree.html)。
-
-相比较于红黑树来说,跳表的实现也更简单一些。并且,按照区间来查找数据这个操作,红黑树的效率没有跳表高。
-
-
-
-对应红黑树添加的核心代码如下,读者可自行参阅理解:
-
-```java
-private Node < K, V > add(Node < K, V > node, K key, V val) {
-
- if (node == null) {
- size++;
- return new Node(key, val);
-
- }
-
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0) {
- node.left = add(node.left, key, val);
- } else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0) {
- node.right = add(node.right, key, val);
- } else {
- node.val = val;
- }
-
- //左节点不为红,右节点为红,左旋
- if (isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)) {
- node = leftRotate(node);
- }
-
- //左链右旋
- if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)) {
- node = rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //颜色翻转
- if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)) {
- flipColors(node);
- }
-
- return node;
-}
-```
-
-### B+树 vs 跳表
-
-想必使用 MySQL 的读者都知道 B+树这个数据结构,B+树是一种常用的数据结构,具有以下特点:
-
-1. **多叉树结构**:它是一棵多叉树,每个节点可以包含多个子节点,减小了树的高度,查询效率高。
-2. **存储效率高**:其中非叶子节点存储多个 key,叶子节点存储 value,使得每个节点更够存储更多的键,根据索引进行范围查询时查询效率更高。-
-3. **平衡性**:它是绝对的平衡,即树的各个分支高度相差不大,确保查询和插入时间复杂度为 **O(log n)** 。
-4. **顺序访问**:叶子节点间通过链表指针相连,范围查询表现出色。
-5. **数据均匀分布**:B+树插入时可能会导致数据重新分布,使得数据在整棵树分布更加均匀,保证范围查询和删除效率。
-
-
-
-所以,B+树更适合作为数据库和文件系统中常用的索引结构之一,它的核心思想是通过可能少的 IO 定位到尽可能多的索引来获得查询数据。对于 Redis 这种内存数据库来说,它对这些并不感冒,因为 Redis 作为内存数据库它不可能存储大量的数据,所以对于索引不需要通过 B+树这种方式进行维护,只需按照概率进行随机维护即可,节约内存。而且使用跳表实现 zset 时相较前者来说更简单一些,在进行插入时只需通过索引将数据插入到链表中合适的位置再随机维护一定高度的索引即可,也不需要像 B+树那样插入时发现失衡时还需要对节点分裂与合并。
-
-### Redis 作者给出的理由
-
-当然我们也可以通过 Redis 的作者自己给出的理由:
-
-> There are a few reasons:
-> 1、They are not very memory intensive. It's up to you basically. Changing parameters about the probability of a node to have a given number of levels will make then less memory intensive than btrees.
-> 2、A sorted set is often target of many ZRANGE or ZREVRANGE operations, that is, traversing the skip list as a linked list. With this operation the cache locality of skip lists is at least as good as with other kind of balanced trees.
-> 3、They are simpler to implement, debug, and so forth. For instance thanks to the skip list simplicity I received a patch (already in Redis master) with augmented skip lists implementing ZRANK in O(log(N)). It required little changes to the code.
-
-翻译过来的意思就是:
-
-> 有几个原因:
->
-> 1、它们不是很占用内存。这主要取决于你。改变节点拥有给定层数的概率的参数,会使它们比 B 树更节省内存。
->
-> 2、有序集合经常是许多 ZRANGE 或 ZREVRANGE 操作的目标,也就是说,以链表的方式遍历跳表。通过这种操作,跳表的缓存局部性至少和其他类型的平衡树一样好。
->
-> 3、它们更容易实现、调试等等。例如,由于跳表的简单性,我收到了一个补丁(已经在 Redis 主分支中),用增强的跳表实现了 O(log(N))的 ZRANK。它只需要对代码做很少的修改。
+In other words, ZSet has two different implementations: ziplist and skiplist. The specific rules for which structure to use for storage are as follows:
-## 小结
+- Use ziplist when the sorted set object meets both of the following conditions:
+ 1. The number of key-value pairs in ZSet is less than 128.
+ 1. The length of each element is less than 64 bytes.
+- If the above two conditions are not met, then use skiplist.
-本文通过大量篇幅介绍跳表的工作原理和实现,帮助读者更进一步的熟悉跳表这一数据结构的优劣,最后再结合各个数据结构操作的特点进行比对,从而帮助读者更好的理解这道面试题,建议读者实现理解跳表时,尽可能配合执笔模拟来了解跳表的增删改查详细过程。
+## Implementing a Skip List
-## 参考
+To better answer the above question and to understand and master skip lists, we can help readers understand this data structure by implementing a simple skip list.
-- 为啥 redis 使用跳表(skiplist)而不是使用 red-black?:
-- Skip List--跳表(全网最详细的跳表文章没有之一):
-- Redis 对象与底层数据结构详解:
-- Redis 有序集合(sorted set):
-- 红黑树和跳表比较:
-- 为什么 redis 的 zset 用跳跃表而不用 b+ tree?:
+We all know that the average time complexity for adding, querying, and deleting in a sorted linked list is **O(n)**, which grows linearly. Therefore, once the number of nodes reaches a certain size, its performance will be very poor. A skip list can be understood as building multiple levels of indexes on top of the original linked list, allowing for a time complexity of **O(log n)** for search, insert
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
index 4bf08f0fa0b..56510ad1b2c 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
@@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(1)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (1)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 必知必会](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=298)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Essentials](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=298)
-## 检索数据
+## Data Retrieval
-`SELECT` 用于从数据库中查询数据。
+`SELECT` is used to query data from the database.
-### 从 Customers 表中检索所有的 ID
+### Retrieve all IDs from the Customers table
-现有表 `Customers` 如下:
+The existing `Customers` table is as follows:
| cust_id |
| ------- |
@@ -22,18 +22,18 @@ tag:
| B |
| C |
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Customers` 表中检索所有的 `cust_id`。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve all `cust_id` from the `Customers` table.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_id
FROM Customers
```
-### 检索并列出已订购产品的清单
+### Retrieve and list the ordered product list
-表 `OrderItems` 含有非空的列 `prod_id` 代表商品 id,包含了所有已订购的商品(有些已被订购多次)。
+The `OrderItems` table contains a non-null column `prod_id` representing the product ID, which includes all ordered products (some may have been ordered multiple times).
| prod_id |
| ------- |
@@ -45,20 +45,20 @@ FROM Customers
| a6 |
| a7 |
-编写 SQL 语句,检索并列出所有已订购商品(`prod_id`)的去重后的清单。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve and list all distinct ordered products (`prod_id`).
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT DISTINCT prod_id
FROM OrderItems
```
-知识点:`DISTINCT` 用于返回列中的唯一不同值。
+Knowledge point: `DISTINCT` is used to return unique different values in a column.
-### 检索所有列
+### Retrieve all columns
-现在有 `Customers` 表(表中含有列 `cust_id` 代表客户 id,`cust_name` 代表客户姓名)
+Now there is a `Customers` table (which contains the column `cust_id` representing customer ID and `cust_name` representing customer name)
| cust_id | cust_name |
| ------- | --------- |
@@ -70,22 +70,22 @@ FROM OrderItems
| a6 | lee |
| a7 | hex |
-需要编写 SQL 语句,检索所有列。
+You need to write an SQL statement to retrieve all columns.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_id, cust_name
FROM Customers
```
-## 排序检索数据
+## Sorting Data Retrieval
-`ORDER BY` 用于对结果集按照一个列或者多个列进行排序。默认按照升序对记录进行排序,如果需要按照降序对记录进行排序,可以使用 `DESC` 关键字。
+`ORDER BY` is used to sort the result set by one or more columns. By default, records are sorted in ascending order; to sort records in descending order, you can use the `DESC` keyword.
-### 检索顾客名称并且排序
+### Retrieve customer names and sort
-有表 `Customers`,`cust_id` 代表客户 id,`cust_name` 代表客户姓名。
+There is a `Customers` table, where `cust_id` represents customer ID and `cust_name` represents customer name.
| cust_id | cust_name |
| ------- | --------- |
@@ -97,9 +97,9 @@ FROM Customers
| a6 | lee |
| a7 | hex |
-从 `Customers` 中检索所有的顾客名称(`cust_name`),并按从 Z 到 A 的顺序显示结果。
+Retrieve all customer names (`cust_name`) from `Customers` and display the results in descending order from Z to A.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_name
@@ -107,9 +107,9 @@ FROM Customers
ORDER BY cust_name DESC
```
-### 对顾客 ID 和日期排序
+### Sort by customer ID and date
-有 `Orders` 表:
+There is an `Orders` table:
| cust_id | order_num | order_date |
| ------- | --------- | ------------------- |
@@ -118,23 +118,23 @@ ORDER BY cust_name DESC
| bob | cccc | 2021-01-10 12:00:00 |
| dick | dddd | 2021-01-11 00:00:00 |
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Orders` 表中检索顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单号(`order_num`),并先按顾客 ID 对结果进行排序,再按订单日期倒序排列。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve customer ID (`cust_id`) and order number (`order_num`) from the `Orders` table, first sorting the results by customer ID, then sorting by order date in descending order.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
-# 根据列名排序
-# 注意:是 order_date 降序,而不是 order_num
+# Sort by column name
+# Note: order_date is in descending order, not order_num
SELECT cust_id, order_num
FROM Orders
-ORDER BY cust_id,order_date DESC
+ORDER BY cust_id, order_date DESC
```
-知识点:`order by` 对多列排序的时候,先排序的列放前面,后排序的列放后面。并且,不同的列可以有不同的排序规则。
+Knowledge point: When sorting multiple columns with `ORDER BY`, the first column to be sorted is placed first, and the subsequent columns follow. Different columns can have different sorting rules.
-### 按照数量和价格排序
+### Sort by quantity and price
-假设有一个 `OrderItems` 表:
+Assuming there is an `OrderItems` table:
| quantity | item_price |
| -------- | ---------- |
@@ -142,1687 +142,21 @@ ORDER BY cust_id,order_date DESC
| 10 | 1003 |
| 2 | 500 |
-编写 SQL 语句,显示 `OrderItems` 表中的数量(`quantity`)和价格(`item_price`),并按数量由多到少、价格由高到低排序。
+Write an SQL statement to display the quantity (`quantity`) and price (`item_price`) from the `OrderItems` table, sorted by quantity in descending order and price in descending order.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT quantity, item_price
FROM OrderItems
-ORDER BY quantity DESC,item_price DESC
+ORDER BY quantity DESC, item_price DESC
```
-### 检查 SQL 语句
+### Check SQL statement
-有 `Vendors` 表:
+There is a `Vendors` table:
| vend_name |
| --------- |
-| 海底捞 |
-| 小龙坎 |
-| 大龙燚 |
-
-下面的 SQL 语句有问题吗?尝试将它改正确,使之能够正确运行,并且返回结果根据`vend_name` 逆序排列。
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name,
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER vend_name DESC
-```
-
-改正后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vend_name DESC
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 逗号作用是用来隔开列与列之间的。
-- ORDER BY 是有 BY 的,需要撰写完整,且位置正确。
-
-## 过滤数据
-
-`WHERE` 可以过滤返回的数据。
-
-下面的运算符可以在 `WHERE` 子句中使用:
-
-| 运算符 | 描述 |
-| :------ | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
-| = | 等于 |
-| <> | 不等于。 **注释:** 在 SQL 的一些版本中,该操作符可被写成 != |
-| > | 大于 |
-| < | 小于 |
-| >= | 大于等于 |
-| <= | 小于等于 |
-| BETWEEN | 在某个范围内 |
-| LIKE | 搜索某种模式 |
-| IN | 指定针对某个列的多个可能值 |
-
-### 返回固定价格的产品
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | -------------- | ---------- |
-| a0018 | sockets | 9.49 |
-| a0019 | iphone13 | 600 |
-| b0018 | gucci t-shirts | 1000 |
-
-【问题】从 `Products` 表中检索产品 ID(`prod_id`)和产品名称(`prod_name`),只返回价格为 9.49 美元的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price = 9.49
-```
-
-### 返回更高价格的产品
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | -------------- | ---------- |
-| a0018 | sockets | 9.49 |
-| a0019 | iphone13 | 600 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts | 1000 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品 ID(`prod_id`)和产品名称(`prod_name`),只返回价格为 9 美元或更高的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 9
-```
-
-### 返回产品并且按照价格排序
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | --------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | egg | 3 |
-| a0019 | sockets | 4 |
-| b0019 | coffee | 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 `Products` 表中所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称(`prod_name`)和价格(`prod_price`),然后按价格对结果进行排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price BETWEEN 3 AND 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-
-# 或者
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 3 AND prod_price <= 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-```
-
-### 返回更多的产品
-
-`OrderItems` 表含有:订单号 `order_num`,`quantity`产品数量
-
-| order_num | quantity |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 200 |
-| a4 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 19 |
-| a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】从 `OrderItems` 表中检索出所有不同且不重复的订单号(`order_num`),其中每个订单都要包含 100 个或更多的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING SUM(quantity) >= 100
-```
-
-## 高级数据过滤
-
-`AND` 和 `OR` 运算符用于基于一个以上的条件对记录进行过滤,两者可以结合使用。`AND` 必须 2 个条件都成立,`OR`只要 2 个条件中的一个成立即可。
-
-### 检索供应商名称
-
-`Vendors` 表有字段供应商名称(`vend_name`)、供应商国家(`vend_country`)、供应商州(`vend_state`)
-
-| vend_name | vend_country | vend_state |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- |
-| apple | USA | CA |
-| vivo | CNA | shenzhen |
-| huawei | CNA | xian |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Vendors` 表中检索供应商名称(`vend_name`),仅返回加利福尼亚州的供应商(这需要按国家[USA]和州[CA]进行过滤,没准其他国家也存在一个 CA)
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
-```
-
-### 检索并列出已订购产品的清单
-
-`OrderItems` 表包含了所有已订购的产品(有些已被订购多次)。
-
-| prod_id | order_num | quantity |
-| ------- | --------- | -------- |
-| BR01 | a1 | 105 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 1100 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 200 |
-| BR03 | a4 | 1121 |
-| BR017 | a5 | 10 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 19 |
-| BR017 | a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,查找所有订购了数量至少 100 个的 `BR01`、`BR02` 或 `BR03` 的订单。你需要返回 `OrderItems` 表的订单号(`order_num`)、产品 ID(`prod_id`)和数量(`quantity`),并按产品 ID 和数量进行过滤。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id IN ('BR01', 'BR02', 'BR03') AND quantity >= 100
-```
-
-### 返回所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称和价格
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | --------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | egg | 3 |
-| a0019 | sockets | 4 |
-| b0019 | coffee | 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称(`prod_name`)和价格(`prod_price`),使用 AND 操作符,然后按价格对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 3 and prod_price <= 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-供应商表 `Vendors` 有字段供应商名称 `vend_name`、供应商国家 `vend_country`、供应商省份 `vend_state`
-
-| vend_name | vend_country | vend_state |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- |
-| apple | USA | CA |
-| vivo | CNA | shenzhen |
-| huawei | CNA | xian |
-
-【问题】修改正确下面 sql,使之正确返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vend_name
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA';
-```
-
-修改后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
-ORDER BY vend_name
-```
-
-`ORDER BY` 语句必须放在 `WHERE` 之后。
-
-## 用通配符进行过滤
-
-SQL 通配符必须与 `LIKE` 运算符一起使用
-
-在 SQL 中,可使用以下通配符:
-
-| 通配符 | 描述 |
-| :------------------------------- | :------------------------- |
-| `%` | 代表零个或多个字符 |
-| `_` | 仅替代一个字符 |
-| `[charlist]` | 字符列中的任何单一字符 |
-| `[^charlist]` 或者 `[!charlist]` | 不在字符列中的任何单一字符 |
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(一)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | -------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中包含 `toy` 一词的产品名称。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%'
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(二)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | -------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中未出现 `toy` 一词的产品,最后按”产品名称“对结果进行排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc NOT LIKE '%toy%'
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(三)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego carrots toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中同时出现 `toy` 和 `carrots` 的产品。有好几种方法可以执行此操作,但对于这个挑战题,请使用 `AND` 和两个 `LIKE` 比较。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%' AND prod_desc LIKE "%carrots%"
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(四)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy carrots |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 Products 表中检索产品名称(prod_name)和描述(prod_desc),仅返回在描述中以**先后顺序**同时出现 toy 和 carrots 的产品。提示:只需要用带有三个 `%` 符号的 `LIKE` 即可。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%carrots%'
-```
-
-## 创建计算字段
-
-### 别名
-
-别名的常见用法是在检索出的结果中重命名表的列字段(为了符合特定的报表要求或客户需求)。有表 `Vendors` 代表供应商信息,`vend_id` 供应商 id、`vend_name` 供应商名称、`vend_address` 供应商地址、`vend_city` 供应商城市。
-
-| vend_id | vend_name | vend_address | vend_city |
-| ------- | ------------- | ------------ | --------- |
-| a001 | tencent cloud | address1 | shenzhen |
-| a002 | huawei cloud | address2 | dongguan |
-| a003 | aliyun cloud | address3 | hangzhou |
-| a003 | netease cloud | address4 | guangzhou |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Vendors` 表中检索 `vend_id`、`vend_name`、`vend_address` 和 `vend_city`,将 `vend_name` 重命名为 `vname`,将 `vend_city` 重命名为 `vcity`,将 `vend_address` 重命名为 `vaddress`,按供应商名称对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_id, vend_name AS vname, vend_address AS vaddress, vend_city AS vcity
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vname
-# as 可以省略
-SELECT vend_id, vend_name vname, vend_address vaddress, vend_city vcity
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vname
-```
-
-### 打折
-
-我们的示例商店正在进行打折促销,所有产品均降价 10%。`Products` 表包含 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_price` 产品价格。
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中返回 `prod_id`、`prod_price` 和 `sale_price`。`sale_price` 是一个包含促销价格的计算字段。提示:可以乘以 0.9,得到原价的 90%(即 10%的折扣)。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_price, prod_price * 0.9 AS sale_price
-FROM Products
-```
-
-注意:`sale_price` 是对计算结果的命名,而不是原有的列名。
-
-## 使用函数处理数据
-
-### 顾客登录名
-
-我们的商店已经上线了,正在创建顾客账户。所有用户都需要登录名,默认登录名是其名称和所在城市的组合。
-
-给出 `Customers` 表 如下:
-
-| cust_id | cust_name | cust_contact | cust_city |
-| ------- | --------- | ------------ | --------- |
-| a1 | Andy Li | Andy Li | Oak Park |
-| a2 | Ben Liu | Ben Liu | Oak Park |
-| a3 | Tony Dai | Tony Dai | Oak Park |
-| a4 | Tom Chen | Tom Chen | Oak Park |
-| a5 | An Li | An Li | Oak Park |
-| a6 | Lee Chen | Lee Chen | Oak Park |
-| a7 | Hex Liu | Hex Liu | Oak Park |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回顾客 ID(`cust_id`)、顾客名称(`cust_name`)和登录名(`user_login`),其中登录名全部为大写字母,并由顾客联系人的前两个字符(`cust_contact`)和其所在城市的前三个字符(`cust_city`)组成。提示:需要使用函数、拼接和别名。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_id, cust_name, UPPER(CONCAT(SUBSTRING(cust_contact, 1, 2), SUBSTRING(cust_city, 1, 3))) AS user_login
-FROM Customers
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 截取函数`SUBSTRING()`:截取字符串,`substring(str ,n ,m)`(n 表示起始截取位置,m 表示要截取的字符个数)表示返回字符串 str 从第 n 个字符开始截取 m 个字符;
-- 拼接函数`CONCAT()`:将两个或多个字符串连接成一个字符串,select concat(A,B):连接字符串 A 和 B。
-
-- 大写函数 `UPPER()`:将指定字符串转换为大写。
-
-### 返回 2020 年 1 月的所有订单的订单号和订单日期
-
-`Orders` 订单表如下:
-
-| order_num | order_date |
-| --------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | 2020-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | 2020-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0003 | 2020-01-01 12:00:00 |
-| a0004 | 2020-02-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0005 | 2020-03-01 00:00:00 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 2020 年 1 月的所有订单的订单号(`order_num`)和订单日期(`order_date`),并按订单日期升序排序
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE month(order_date) = '01' AND YEAR(order_date) = '2020'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-也可以用通配符来做:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_date LIKE '2020-01%'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 日期格式:`YYYY-MM-DD`
-- 时间格式:`HH:MM:SS`
-
-日期和时间处理相关的常用函数:
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------------- | ------------------------------ |
-| `ADDDATE()` | 增加一个日期(天、周等) |
-| `ADDTIME()` | 增加一个时间(时、分等) |
-| `CURDATE()` | 返回当前日期 |
-| `CURTIME()` | 返回当前时间 |
-| `DATE()` | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
-| `DATEDIFF` | 计算两个日期之差 |
-| `DATE_FORMAT()` | 返回一个格式化的日期或时间串 |
-| `DAY()` | 返回一个日期的天数部分 |
-| `DAYOFWEEK()` | 对于一个日期,返回对应的星期几 |
-| `HOUR()` | 返回一个时间的小时部分 |
-| `MINUTE()` | 返回一个时间的分钟部分 |
-| `MONTH()` | 返回一个日期的月份部分 |
-| `NOW()` | 返回当前日期和时间 |
-| `SECOND()` | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
-| `TIME()` | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
-| `YEAR()` | 返回一个日期的年份部分 |
-
-## 汇总数据
-
-汇总数据相关的函数:
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| `AVG()` | 返回某列的平均值 |
-| `COUNT()` | 返回某列的行数 |
-| `MAX()` | 返回某列的最大值 |
-| `MIN()` | 返回某列的最小值 |
-| `SUM()` | 返回某列值之和 |
-
-### 确定已售出产品的总数
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表售出的产品,`quantity` 代表售出商品数量。
-
-| quantity |
-| -------- |
-| 10 |
-| 100 |
-| 1000 |
-| 10001 |
-| 2 |
-| 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,确定已售出产品的总数。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Sum(quantity) AS items_ordered
-FROM OrderItems
-```
-
-### 确定已售出产品项 BR01 的总数
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表售出的产品,`quantity` 代表售出商品数量,产品项为 `prod_id`。
-
-| quantity | prod_id |
-| -------- | ------- |
-| 10 | AR01 |
-| 100 | AR10 |
-| 1000 | BR01 |
-| 10001 | BR010 |
-
-【问题】修改创建的语句,确定已售出产品项(`prod_id`)为"BR01"的总数。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Sum(quantity) AS items_ordered
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 确定 Products 表中价格不超过 10 美元的最贵产品的价格
-
-`Products` 表如下,`prod_price` 代表商品的价格。
-
-| prod_price |
-| ---------- |
-| 9.49 |
-| 600 |
-| 1000 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,确定 `Products` 表中价格不超过 10 美元的最贵产品的价格(`prod_price`)。将计算所得的字段命名为 `max_price`。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Max(prod_price) AS max_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price <= 10
-```
-
-## 分组数据
-
-`GROUP BY`:
-
-- `GROUP BY` 子句将记录分组到汇总行中。
-- `GROUP BY` 为每个组返回一个记录。
-- `GROUP BY` 通常还涉及聚合`COUNT`,`MAX`,`SUM`,`AVG` 等。
-- `GROUP BY` 可以按一列或多列进行分组。
-- `GROUP BY` 按分组字段进行排序后,`ORDER BY` 可以以汇总字段来进行排序。
-
-`HAVING`:
-
-- `HAVING` 用于对汇总的 `GROUP BY` 结果进行过滤。
-- `HAVING` 必须要与 `GROUP BY` 连用。
-- `WHERE` 和 `HAVING` 可以在相同的查询中。
-
-`HAVING` vs `WHERE`:
-
-- `WHERE`:过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。
-- `HAVING`:过滤分组,必须要与 `GROUP BY` 连用,不能单独使用。
-
-### 返回每个订单号各有多少行数
-
-`OrderItems` 表包含每个订单的每个产品
-
-| order_num |
-| --------- |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a004 |
-| a007 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回每个订单号(`order_num`)各有多少行数(`order_lines`),并按 `order_lines` 对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, Count(order_num) AS order_lines
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-ORDER BY order_lines
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-1. `count(*)`,`count(列名)`都可以,区别在于,`count(列名)`是统计非 NULL 的行数;
-2. `order by` 最后执行,所以可以使用列别名;
-3. 分组聚合一定不要忘记加上 `group by` ,不然只会有一行结果。
-
-### 每个供应商成本最低的产品
-
-有 `Products` 表,含有字段 `prod_price` 代表产品价格,`vend_id` 代表供应商 id
-
-| vend_id | prod_price |
-| ------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | 100 |
-| a0019 | 0.1 |
-| b0019 | 1000 |
-| b0019 | 6980 |
-| b0019 | 20 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回名为 `cheapest_item` 的字段,该字段包含每个供应商成本最低的产品(使用 `Products` 表中的 `prod_price`),然后从最低成本到最高成本对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_id, Min(prod_price) AS cheapest_item
-FROM Products
-GROUP BY vend_id
-ORDER BY cheapest_item
-```
-
-### 返回订单数量总和不小于 100 的所有订单的订单号
-
-`OrderItems` 代表订单商品表,包括:订单号 `order_num` 和订单数量 `quantity`。
-
-| order_num | quantity |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 200 |
-| a4 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 19 |
-| a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】请编写 SQL 语句,返回订单数量总和不小于 100 的所有订单号,最后结果按照订单号升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 直接聚合
-SELECT order_num
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING Sum(quantity) >= 100
-ORDER BY order_num
-
-# 子查询
-SELECT a.order_num
-FROM (SELECT order_num, Sum(quantity) AS sum_num
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY order_num
- HAVING sum_num >= 100) a
-ORDER BY a.order_num
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- `where`:过滤过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。
-- `having`:过滤分组,与 `group by` 连用,不能单独使用。
-
-### 计算总和
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,包括字段:订单号 `order_num` 和 `item_price` 商品售出价格、`quantity` 商品数量。
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 10 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 1 | 200 |
-| a4 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 | 19 |
-| a7 | 7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,根据订单号聚合,返回订单总价不小于 1000 的所有订单号,最后的结果按订单号进行升序排序。
-
-提示:总价 = item_price 乘以 quantity
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, Sum(item_price * quantity) AS total_price
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING total_price >= 1000
-ORDER BY order_num
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-`OrderItems` 表含有 `order_num` 订单号
-
-| order_num |
-| --------- |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a004 |
-| a007 |
-
-【问题】将下面代码修改正确后执行
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, COUNT(*) AS items
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY items
-HAVING COUNT(*) >= 3
-ORDER BY items, order_num;
-```
-
-修改后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, COUNT(*) AS items
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING items >= 3
-ORDER BY items, order_num;
-```
-
-## 使用子查询
-
-子查询是嵌套在较大查询中的 SQL 查询,也称内部查询或内部选择,包含子查询的语句也称为外部查询或外部选择。简单来说,子查询就是指将一个 `SELECT` 查询(子查询)的结果作为另一个 SQL 语句(主查询)的数据来源或者判断条件。
-
-子查询可以嵌入 `SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 语句中,也可以和 `=`、`<`、`>`、`IN`、`BETWEEN`、`EXISTS` 等运算符一起使用。
-
-子查询常用在 `WHERE` 子句和 `FROM` 子句后边:
-
-- 当用于 `WHERE` 子句时,根据不同的运算符,子查询可以返回单行单列、多行单列、单行多列数据。子查询就是要返回能够作为 WHERE 子句查询条件的值。
-- 当用于 `FROM` 子句时,一般返回多行多列数据,相当于返回一张临时表,这样才符合 `FROM` 后面是表的规则。这种做法能够实现多表联合查询。
-
-> 注意:MySQL 数据库从 4.1 版本才开始支持子查询,早期版本是不支持的。
-
-用于 `WHERE` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM table1 [, table2 ]
-WHERE column_name operator
-(SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM table1 [, table2 ]
-[WHERE])
-```
-
-- 子查询需要放在括号`( )`内。
-- `operator` 表示用于 `WHERE` 子句的运算符,可以是比较运算符(如 `=`, `<`, `>`, `<>` 等)或逻辑运算符(如 `IN`, `NOT IN`, `EXISTS`, `NOT EXISTS` 等),具体根据需求来确定。
-
-用于 `FROM` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM (SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
- FROM table1 [, table2 ]
- [WHERE]) AS temp_table_name [, ...]
-[JOIN type JOIN table_name ON condition]
-WHERE condition;
-```
-
-- 用于 `FROM` 的子查询返回的结果相当于一张临时表,所以需要使用 AS 关键字为该临时表起一个名字。
-- 子查询需要放在括号 `( )` 内。
-- 可以指定多个临时表名,并使用 `JOIN` 语句连接这些表。
-
-### 返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表
-
-`OrderItems` 表示订单商品表,含有字段订单号:`order_num`、订单价格:`item_price`;`Orders` 表代表订单信息表,含有顾客 `id:cust_id` 和订单号:`order_num`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| order_num | item_price |
-| --------- | ---------- |
-| a1 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a4 | 2 |
-| a5 | 5 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a7 | 7 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | ------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a4 | cust2 |
-| a5 | cust5 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a7 | cust7 |
-
-【问题】使用子查询,返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表,结果无需排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_id
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN (SELECT DISTINCT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- where item_price >= 10)
-```
-
-### 确定哪些订单购买了 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品(一)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 `OrderItems` 中)购买了 `prod_id` 为 "BR01" 的产品,然后从 `Orders` 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单日期(`order_date`),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_id,order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN
- (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01' )
-ORDER BY order_date;
-
-# 写法 2: 连接表
-SELECT b.cust_id, b.order_date
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num AND a.prod_id = 'BR01'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-### 返回购买 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(一)
-
-你想知道订购 BR01 产品的日期,有表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`;`Customers` 表含有 `cust_email` 顾客邮件和 `cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息,`cust_id` 为顾客 id,`cust_email` 为顾客 email
-
-| cust_id | cust_email |
-| ------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | |
-| cust1 | |
-| cust2 | |
-
-【问题】返回购买 `prod_id` 为 `BR01` 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_email`),结果无需排序。
-
-提示:这涉及 `SELECT` 语句,最内层的从 `OrderItems` 表返回 `order_num`,中间的从 `Customers` 表返回 `cust_id`。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id
- FROM Orders
- WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01'))
-
-# 写法 2: 连接表(inner join)
-SELECT c.cust_email
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b,Customers c
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num AND b.cust_id = c.cust_id AND a.prod_id = 'BR01'
-
-# 写法 3:连接表(left join)
-SELECT c.cust_email
-FROM Orders a LEFT JOIN
- OrderItems b ON a.order_num = b.order_num LEFT JOIN
- Customers c ON a.cust_id = c.cust_id
-WHERE b.prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 返回每个顾客不同订单的总金额
-
-我们需要一个顾客 ID 列表,其中包含他们已订购的总金额。
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,`OrderItems` 表有订单号:`order_num` 和商品售出价格:`item_price`、商品数量:`quantity`。
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 10 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a0002 | 1 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 5 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 1 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 7 | 5 |
-
-`Orders` 表订单号:`order_num`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | ------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 |
-| a0002 | cust1 |
-| a0003 | cust1 |
-| a0013 | cust2 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,返回顾客 ID(`Orders` 表中的 `cust_id`),并使用子查询返回 `total_ordered` 以便返回每个顾客的订单总数,将结果按金额从大到小排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT o.cust_id, SUM(tb.total_ordered) AS `total_ordered`
-FROM (SELECT order_num, SUM(item_price * quantity) AS total_ordered
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY order_num) AS tb,
- Orders o
-WHERE tb.order_num = o.order_num
-GROUP BY o.cust_id
-ORDER BY total_ordered DESC;
-
-# 写法 2:连接表
-SELECT b.cust_id, Sum(a.quantity * a.item_price) AS total_ordered
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num
-GROUP BY cust_id
-ORDER BY total_ordered DESC
-```
-
-关于写法一详细介绍可以参考: [issue#2402:写法 1 存在的错误以及修改方法](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/2402)。
-
-### 从 Products 表中检索所有的产品名称以及对应的销售总数
-
-`Products` 表中检索所有的产品名称:`prod_name`、产品 id:`prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-
-`OrderItems` 代表订单商品表,订单产品:`prod_id`、售出数量:`quantity`
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 1100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索所有的产品名称(`prod_name`),以及名为 `quant_sold` 的计算列,其中包含所售产品的总数(在 `OrderItems` 表上使用子查询和 `SUM(quantity)` 检索)。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT p.prod_name, tb.quant_sold
-FROM (SELECT prod_id, Sum(quantity) AS quant_sold
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY prod_id) AS tb,
- Products p
-WHERE tb.prod_id = p.prod_id
-
-# 写法 2:连接表
-SELECT p.prod_name, Sum(o.quantity) AS quant_sold
-FROM Products p,
- OrderItems o
-WHERE p.prod_id = o.prod_id
-GROUP BY p.prod_name(这里不能用 p.prod_id,会报错)
-```
-
-## 连接表
-
-JOIN 是“连接”的意思,顾名思义,SQL JOIN 子句用于将两个或者多个表联合起来进行查询。
-
-连接表时需要在每个表中选择一个字段,并对这些字段的值进行比较,值相同的两条记录将合并为一条。**连接表的本质就是将不同表的记录合并起来,形成一张新表。当然,这张新表只是临时的,它仅存在于本次查询期间**。
-
-使用 `JOIN` 连接两个表的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT table1.column1, table2.column2...
-FROM table1
-JOIN table2
-ON table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2;
-```
-
-`table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2` 是连接条件,只有满足此条件的记录才会合并为一行。您可以使用多个运算符来连接表,例如 =、>、<、<>、<=、>=、!=、`between`、`like` 或者 `not`,但是最常见的是使用 =。
-
-当两个表中有同名的字段时,为了帮助数据库引擎区分是哪个表的字段,在书写同名字段名时需要加上表名。当然,如果书写的字段名在两个表中是唯一的,也可以不使用以上格式,只写字段名即可。
-
-另外,如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用 `USING`子句来代替 `ON`,举个例子:
-
-```sql
-# join....on
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-ON c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-
-# 如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用USING子句:JOIN....USING()
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-```
-
-**`ON` 和 `WHERE` 的区别**:
-
-- 连接表时,SQL 会根据连接条件生成一张新的临时表。`ON` 就是连接条件,它决定临时表的生成。
-- `WHERE` 是在临时表生成以后,再对临时表中的数据进行过滤,生成最终的结果集,这个时候已经没有 JOIN-ON 了。
-
-所以总结来说就是:**SQL 先根据 ON 生成一张临时表,然后再根据 WHERE 对临时表进行筛选**。
-
-SQL 允许在 `JOIN` 左边加上一些修饰性的关键词,从而形成不同类型的连接,如下表所示:
-
-| 连接类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| INNER JOIN 内连接 | (默认连接方式)只有当两个表都存在满足条件的记录时才会返回行。 |
-| LEFT JOIN / LEFT OUTER JOIN 左(外)连接 | 返回左表中的所有行,即使右表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| RIGHT JOIN / RIGHT OUTER JOIN 右(外)连接 | 返回右表中的所有行,即使左表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| FULL JOIN / FULL OUTER JOIN 全(外)连接 | 只要其中有一个表存在满足条件的记录,就返回行。 |
-| SELF JOIN | 将一个表连接到自身,就像该表是两个表一样。为了区分两个表,在 SQL 语句中需要至少重命名一个表。 |
-| CROSS JOIN | 交叉连接,从两个或者多个连接表中返回记录集的笛卡尔积。 |
-
-下图展示了 LEFT JOIN、RIGHT JOIN、INNER JOIN、OUTER JOIN 相关的 7 种用法。
-
-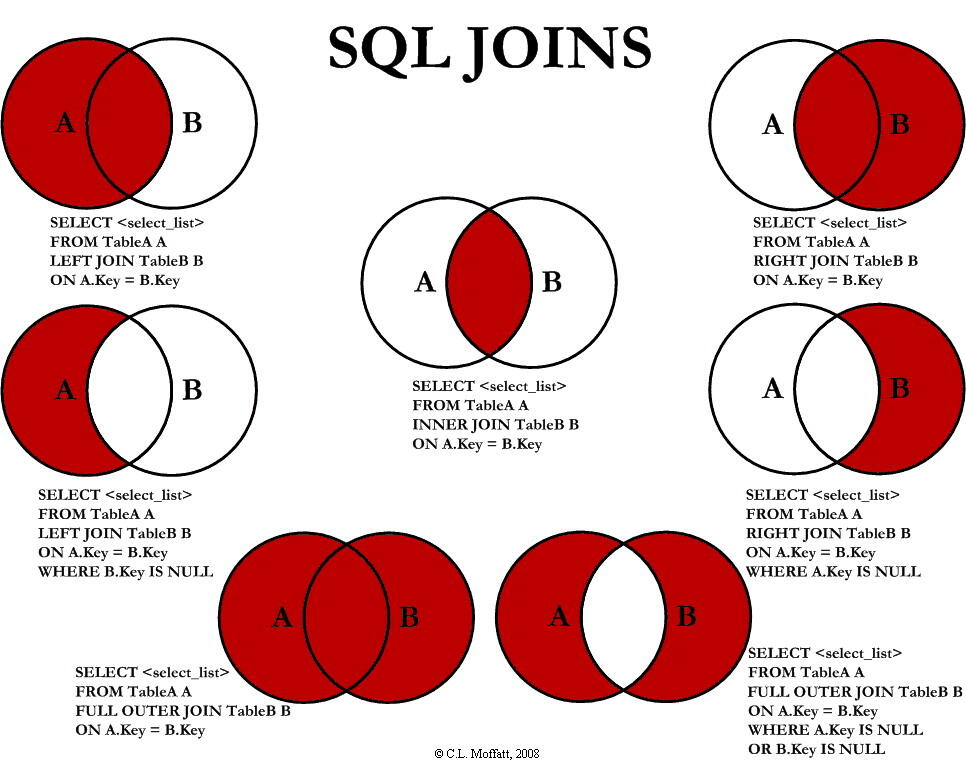
-
-如果不加任何修饰词,只写 `JOIN`,那么默认为 `INNER JOIN`
-
-对于 `INNER JOIN` 来说,还有一种隐式的写法,称为 “**隐式内连接**”,也就是没有 `INNER JOIN` 关键字,使用 `WHERE` 语句实现内连接的功能
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c,Orders o
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-
-# 显式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name;
-```
-
-### 返回顾客名称和相关订单号
-
-`Customers` 表有字段顾客名称 `cust_name`、顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 订单信息表,含有字段 `order_num` 订单号、`cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)和 `Orders` 表中的相关订单号(`order_num`),并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。你可以尝试用两个不同的写法,一个使用简单的等连接语法,另外一个使用 INNER JOIN。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c,Orders o
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num
-
-# 显式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num;
-```
-
-### 返回顾客名称和相关订单号以及每个订单的总价
-
-`Customers` 表有字段,顾客名称:`cust_name`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 订单信息表,含有字段,订单号:`order_num`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-`OrderItems` 表有字段,商品订单号:`order_num`、商品数量:`quantity`、商品价格:`item_price`
-
-| order_num | quantity | item_price |
-| --------- | -------- | ---------- |
-| a1 | 1000 | 10 |
-| a2 | 200 | 10 |
-| a3 | 10 | 15 |
-| a4 | 25 | 50 |
-| a5 | 15 | 25 |
-| a7 | 7 | 7 |
-
-【问题】除了返回顾客名称和订单号,返回 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)和 `Orders` 表中的相关订单号(`order_num`),添加第三列 `OrderTotal`,其中包含每个订单的总价,并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-# 简单的等连接语法
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num, SUM(quantity * item_price) AS OrderTotal
-FROM Customers c,Orders o,OrderItems oi
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id AND o.order_num = oi.order_num
-GROUP BY c.cust_name, o.order_num
-ORDER BY c.cust_name, o.order_num
-```
-
-注意,可能有小伙伴会这样写:
-
-```sql
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num, SUM(quantity * item_price) AS OrderTotal
-FROM Customers c,Orders o,OrderItems oi
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id AND o.order_num = oi.order_num
-GROUP BY c.cust_name
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num
-```
-
-这是错误的!只对 `cust_name` 进行聚类确实符合题意,但是不符合 `GROUP BY` 的语法。
-
-select 语句中,如果没有 `GROUP BY` 语句,那么 `cust_name`、`order_num` 会返回若干个值,而 `sum(quantity * item_price)` 只返回一个值,通过 `group by` `cust_name` 可以让 `cust_name` 和 `sum(quantity * item_price)` 一一对应起来,或者说**聚类**,所以同样的,也要对 `order_num` 进行聚类。
-
-> **一句话,select 中的字段要么都聚类,要么都不聚类**
-
-### 确定哪些订单购买了 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品(二)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 `OrderItems` 中)购买了 `prod_id` 为 "BR01" 的产品,然后从 `Orders` 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单日期(`order_date`),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
-
-提示:这一次使用连接和简单的等连接语法。
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01')
-ORDER BY order_date
-
-# 写法 2:连接表 inner join
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders o INNER JOIN
- (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01') tb ON o.order_num = tb.order_num
-ORDER BY order_date
-
-# 写法 3:写法 2 的简化版
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders
-INNER JOIN OrderItems USING(order_num)
-WHERE OrderItems.prod_id = 'BR01'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-### 返回购买 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(二)
-
-有表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`;`Customers` 表含有 `cust_email` 顾客邮件和 cust_id 顾客 id
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息,`cust_id` 为顾客 id,`cust_email` 为顾客 email
-
-| cust_id | cust_email |
-| ------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | |
-| cust1 | |
-| cust2 | |
-
-【问题】返回购买 `prod_id` 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_email`),结果无需排序。
-
-提示:涉及到 `SELECT` 语句,最内层的从 `OrderItems` 表返回 `order_num`,中间的从 `Customers` 表返回 `cust_id`,但是必须使用 INNER JOIN 语法。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_email
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders using(cust_id)
-INNER JOIN OrderItems using(order_num)
-WHERE OrderItems.prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(二)
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,确定最佳顾客的另一种方式是看他们花了多少钱,`OrderItems` 表有订单号 `order_num` 和 `item_price` 商品售出价格、`quantity` 商品数量
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 10 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 1 | 200 |
-| a4 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 | 19 |
-| a7 | 7 | 5 |
-
-`Orders` 表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号、`cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-顾客表 `Customers` 有字段 `cust_id` 客户 id、`cust_name` 客户姓名
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回订单总价不小于 1000 的客户名称和总额(`OrderItems` 表中的 `order_num`)。
-
-提示:需要计算总和(`item_price` 乘以 `quantity`)。按总额对结果进行排序,请使用 `INNER JOIN`语法。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, SUM(item_price * quantity) AS total_price
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders USING(cust_id)
-INNER JOIN OrderItems USING(order_num)
-GROUP BY cust_name
-HAVING total_price >= 1000
-ORDER BY total_price
-```
-
-## 创建高级连接
-
-### 检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(一)
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息含有顾客 id `cust_id` 和 顾客名称 `cust_name`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 表代表订单信息含有订单号 `order_num` 和顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-【问题】使用 INNER JOIN 编写 SQL 语句,检索每个顾客的名称(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_name`)和所有的订单号(`Orders` 表中的 `order_num`),最后根据顾客姓名 `cust_name` 升序返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, order_num
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY cust_name
-```
-
-### 检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(二)
-
-`Orders` 表代表订单信息含有订单号 `order_num` 和顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息含有顾客 id `cust_id` 和 顾客名称 `cust_name`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-| cust40 | ace |
-
-【问题】检索每个顾客的名称(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_name`)和所有的订单号(Orders 表中的 `order_num`),列出所有的顾客,即使他们没有下过订单。最后根据顾客姓名 `cust_name` 升序返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, order_num
-FROM Customers
-LEFT JOIN Orders
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY cust_name
-```
-
-### 返回产品名称和与之相关的订单号
-
-`Products` 表为产品信息表含有字段 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_name` 产品名称
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-| a0023 | soda |
-
-`OrderItems` 表为订单信息表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号和产品 id `prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | a105 |
-| a0002 | a1100 |
-| a0002 | a200 |
-| a0013 | a1121 |
-| a0003 | a10 |
-| a0003 | a19 |
-| a0003 | a5 |
-
-【问题】使用外连接(left join、 right join、full join)联结 `Products` 表和 `OrderItems` 表,返回产品名称(`prod_name`)和与之相关的订单号(`order_num`)的列表,并按照产品名称升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, order_num
-FROM Products
-LEFT JOIN OrderItems
-USING(prod_id)
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 返回产品名称和每一项产品的总订单数
-
-`Products` 表为产品信息表含有字段 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_name` 产品名称
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-| a0023 | soda |
-
-`OrderItems` 表为订单信息表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号和产品 id `prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | a105 |
-| a0002 | a1100 |
-| a0002 | a200 |
-| a0013 | a1121 |
-| a0003 | a10 |
-| a0003 | a19 |
-| a0003 | a5 |
-
-【问题】
-
-使用 OUTER JOIN 联结 `Products` 表和 `OrderItems` 表,返回产品名称(`prod_name`)和每一项产品的总订单数(不是订单号),并按产品名称升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, COUNT(order_num) AS orders
-FROM Products
-LEFT JOIN OrderItems
-USING(prod_id)
-GROUP BY prod_name
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 列出供应商及其可供产品的数量
-
-有 `Vendors` 表含有 `vend_id` (供应商 id)
-
-| vend_id |
-| ------- |
-| a0002 |
-| a0013 |
-| a0003 |
-| a0010 |
-
-有 `Products` 表含有 `vend_id`(供应商 id)和 prod_id(供应产品 id)
-
-| vend_id | prod_id |
-| ------- | -------------------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | prod_id_iphone |
-| a00113 | prod_id_tea |
-| a0003 | prod_id_vivo phone |
-| a0010 | prod_id_huawei phone |
-
-【问题】列出供应商(`Vendors` 表中的 `vend_id`)及其可供产品的数量,包括没有产品的供应商。你需要使用 OUTER JOIN 和 COUNT()聚合函数来计算 `Products` 表中每种产品的数量,最后根据 vend_id 升序排序。
-
-注意:`vend_id` 列会显示在多个表中,因此在每次引用它时都需要完全限定它。
-
-```sql
-SELECT v.vend_id, COUNT(prod_id) AS prod_id
-FROM Vendors v
-LEFT JOIN Products p
-USING(vend_id)
-GROUP BY v.vend_id
-ORDER BY v.vend_id
-```
-
-## 组合查询
-
-`UNION` 运算符将两个或更多查询的结果组合起来,并生成一个结果集,其中包含来自 `UNION` 中参与查询的提取行。
-
-`UNION` 基本规则:
-
-- 所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- 每个查询中涉及表的列的数据类型必须相同或兼容。
-- 通常返回的列名取自第一个查询。
-
-默认地,`UNION` 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 `UNION ALL`。
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
-UNION ALL
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;
-```
-
-`UNION` 结果集中的列名总是等于 `UNION` 中第一个 `SELECT` 语句中的列名。
-
-`JOIN` vs `UNION`:
-
-- `JOIN` 中连接表的列可能不同,但在 `UNION` 中,所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- `UNION` 将查询之后的行放在一起(垂直放置),但 `JOIN` 将查询之后的列放在一起(水平放置),即它构成一个笛卡尔积。
-
-### 将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来(一)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 包含订单产品信息,字段 `prod_id` 代表产品 id、`quantity` 代表产品数量
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-| BNBG | 10002 |
-
-【问题】将两个 `SELECT` 语句结合起来,以便从 `OrderItems` 表中检索产品 id(`prod_id`)和 `quantity`。其中,一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE quantity = 100
-UNION
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id LIKE 'BNBG%'
-```
-
-### 将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来(二)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 包含订单产品信息,字段 `prod_id` 代表产品 id、`quantity` 代表产品数量。
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-| BNBG | 10002 |
-
-【问题】将两个 `SELECT` 语句结合起来,以便从 `OrderItems` 表中检索产品 id(`prod_id`)和 `quantity`。其中,一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。 注意:**这次仅使用单个 SELECT 语句。**
-
-答案:
-
-要求只用一条 select 语句,那就用 `or` 不用 `union` 了。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE quantity = 100 OR prod_id LIKE 'BNBG%'
-```
-
-### 组合 Products 表中的产品名称和 Customers 表中的顾客名称
-
-`Products` 表含有字段 `prod_name` 代表产品名称
-
-| prod_name |
-| --------- |
-| flower |
-| rice |
-| ring |
-| umbrella |
-
-Customers 表代表顾客信息,cust_name 代表顾客名称
-
-| cust_name |
-| --------- |
-| andy |
-| ben |
-| tony |
-| tom |
-| an |
-| lee |
-| hex |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,组合 `Products` 表中的产品名称(`prod_name`)和 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)并返回,然后按产品名称对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-# UNION 结果集中的列名总是等于 UNION 中第一个 SELECT 语句中的列名。
-SELECT prod_name
-FROM Products
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name
-FROM Customers
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-表 `Customers` 含有字段 `cust_name` 顾客名、`cust_contact` 顾客联系方式、`cust_state` 顾客州、`cust_email` 顾客 `email`
-
-| cust_name | cust_contact | cust_state | cust_email |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | 8695192 | MI | |
-| cust1 | 8695193 | MI | |
-| cust2 | 8695194 | IL | |
-
-【问题】修正下面错误的 SQL
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'IL'ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-修正后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'IL'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-使用 `union` 组合查询时,只能使用一条 `order by` 字句,他必须位于最后一条 `select` 语句之后
-
-或者直接用 `or` 来做:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI' or cust_state = 'IL'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-
+| Haidilao |
+| Xia |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
index 2a4a3e496c6..2f88a9c173f 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
@@ -1,354 +1,354 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(2)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (2)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of the question: [Niuke Problem Boss - Advanced SQL Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-## 增删改操作
+## Insert, Delete, and Update Operations
-SQL 插入记录的方式汇总:
+Summary of SQL methods for inserting records:
-- **普通插入(全字段)** :`INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
-- **普通插入(限定字段)** :`INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
-- **多条一次性插入** :`INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...`
-- **从另一个表导入** :`INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]`
-- **带更新的插入** :`REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`(注意这种原理是检测到主键或唯一性索引键重复就删除原记录后重新插入)
+- **Normal Insert (All Fields)**: `INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
+- **Normal Insert (Specified Fields)**: `INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
+- **Insert Multiple Records at Once**: `INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...`
+- **Import from Another Table**: `INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]`
+- **Insert with Update**: `REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)` (Note that this method deletes the original record if a primary key or unique index key duplicate is detected, then reinserts it)
-### 插入记录(一)
+### Inserting Records (1)
-**描述**:牛客后台会记录每个用户的试卷作答记录到 `exam_record` 表,现在有两个用户的作答记录详情如下:
+**Description**: The Niuke backend records each user's exam record in the `exam_record` table. Two users' exam records are as follows:
-- 用户 1001 在 2021 年 9 月 1 日晚上 10 点 11 分 12 秒开始作答试卷 9001,并在 50 分钟后提交,得了 90 分;
-- 用户 1002 在 2021 年 9 月 4 日上午 7 点 1 分 2 秒开始作答试卷 9002,并在 10 分钟后退出了平台。
+- User 1001 started the exam 9001 at 10:11:12 PM on September 1, 2021, and submitted it after 50 minutes, scoring 90 points;
+- User 1002 started the exam 9002 at 7:01:02 AM on September 4, 2021, and left the platform after 10 minutes.
-试卷作答记录表`exam_record`中,表已建好,其结构如下,请用一条语句将这两条记录插入表中。
+The structure of the `exam_record` table is already established as follows; please use a single statement to insert these two records into the table.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-// 存在自增主键,无需手动赋值
+-- Auto-incrementing primary key, no manual assignment required
INSERT INTO exam_record (uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score) VALUES
(1001, 9001, '2021-09-01 22:11:12', '2021-09-01 23:01:12', 90),
(1002, 9002, '2021-09-04 07:01:02', NULL, NULL);
```
-### 插入记录(二)
+### Inserting Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表`exam_record`,结构如下表,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,由于数据越来越多,维护难度越来越大,需要对数据表内容做精简,历史数据做备份。
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing user exam records for many years. Due to the increasing amount of data, maintenance difficulty is getting higher, and the content of the data table needs to be simplified, with historical data backed up.
-表`exam_record`:
+Table `exam_record`:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-我们已经创建了一张新表`exam_record_before_2021`用来备份 2021 年之前的试题作答记录,结构和`exam_record`表一致,请将 2021 年之前的已完成了的试题作答纪录导入到该表。
+We have created a new table `exam_record_before_2021` to back up exam records before 2021, which has the same structure as the `exam_record` table. Please import the completed exam records before 2021 into this new table.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
INSERT INTO exam_record_before_2021 (uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score)
-SELECT uid,exam_id,start_time,submit_time,score
+SELECT uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score
FROM exam_record
WHERE YEAR(submit_time) < 2021;
```
-### 插入记录(三)
+### Inserting Records (3)
-**描述**:现在有一套 ID 为 9003 的高难度 SQL 试卷,时长为一个半小时,请你将 2021-01-01 00:00:00 作为发布时间插入到试题信息表`examination_info`,不管该 ID 试卷是否存在,都要插入成功,请尝试插入它。
+**Description**: There is a difficult SQL exam with ID 9003, which lasts for one and a half hours. Please insert the release time `2021-01-01 00:00:00` into the `examination_info` table, regardless of whether this ID exam exists or not.
-试题信息表`examination_info`:
+Table `examination_info`:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ------------ | ----------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ------------ |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| tag | varchar(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | 类别标签 |
-| difficulty | varchar(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | 难度 |
-| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 时长(分钟数) |
-| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 发布时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ------------ | ----------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ------------------ |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| tag | varchar(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | Category Tag |
+| difficulty | varchar(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | Difficulty |
+| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Duration (minutes) |
+| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Release Time |
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
REPLACE INTO examination_info VALUES
(NULL, 9003, "SQL", "hard", 90, "2021-01-01 00:00:00");
```
-### 更新记录(一)
+### Updating Records (1)
-**描述**:现在有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`, 表结构如下图所示:
+**Description**: There is an `examination_info` table. The table structure is as follows:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ------------ | -------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| tag | char(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | 类别标签 |
-| difficulty | char(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | 难度 |
-| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 时长 |
-| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 发布时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ------------ | -------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| tag | char(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | Category Tag |
+| difficulty | char(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | Difficulty |
+| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Duration |
+| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Release Time |
-请把**examination_info**表中`tag`为`PYTHON`的`tag`字段全部修改为`Python`。
+Please change all `tag` fields of `tag` equal to `PYTHON` in the `examination_info` table to `Python`.
-**思路**:这题有两种解题思路,最容易想到的是直接`update + where`来指定条件更新,第二种就是根据要修改的字段进行查找替换
+**Thought Process**: There are two ways to solve this problem. The most straightforward approach is to directly use `update + where` to specify the conditional update. The second method is to find and replace based on the field that needs to be modified.
-**答案一**:
+**Answer 1**:
```sql
UPDATE examination_info SET tag = 'Python' WHERE tag='PYTHON'
```
-**答案二**:
+**Answer 2**:
```sql
UPDATE examination_info
SET tag = REPLACE(tag,'PYTHON','Python')
-# REPLACE (目标字段,"查找内容","替换内容")
+# REPLACE (Target Field, "Search Content", "Replacement Content")
```
-### 更新记录(二)
+### Updating Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 exam_record,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:作答记录表 `exam_record`: **`submit_time`** 为 完成时间 (注意这句话)
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table, which contains years of user exam records. The table structure is as follows: The **`submit_time`** is the completion time (Note this statement).
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**题目要求**:请把 `exam_record` 表中 2021 年 9 月 1 日==之前==开始作答的==未完成==记录全部改为被动完成,即:将完成时间改为'2099-01-01 00:00:00',分数改为 0。
+**Requirement**: Please change all uncompleted records in the `exam_record` table that started before September 1, 2021, to be marked as completed. Specifically: Set the completion time to '2099-01-01 00:00:00' and the score to 0.
-**思路**:注意题干中的关键字(已经高亮) `" xxx 时间 "`之前这个条件, 那么这里马上就要想到要进行时间的比较 可以直接 `xxx_time < "2021-09-01 00:00:00",` 也可以采用`date()`函数来进行比较;第二个条件就是 `"未完成"`, 即完成时间为 NULL,也就是题目中的提交时间 ----- `submit_time 为 NULL`。
+**Thought Process**: Pay attention to the key phrases in the problem statement (highlighted) regarding "xxx time" before this condition. This suggests that we need to perform a time comparison using either `xxx_time < "2021-09-01 00:00:00"` or using the `date()` function for comparison. The second condition is "uncompleted", meaning the submission time is NULL; hence, `submit_time IS NULL`.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
UPDATE exam_record SET submit_time = '2099-01-01 00:00:00', score = 0 WHERE DATE(start_time) < "2021-09-01" AND submit_time IS null
```
-### 删除记录(一)
+### Deleting Records (1)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing many years of user records as follows:
-作答记录表`exam_record:` **`start_time`** 是试卷开始时间`submit_time` 是交卷,即结束时间。
+The exam record table `exam_record`: **`start_time`** is the start time and `submit_time` is the submission/end time.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中作答时间小于 5 分钟整且分数不及格(及格线为 60 分)的记录;
+**Requirement**: Delete records in the `exam_record` table where the exam duration is less than 5 minutes and the score is failing (the passing score is 60).
-**思路**:这一题虽然是练习删除,仔细看确是考察对时间函数的用法,这里提及的分钟数比较,常用的函数有 **`TIMEDIFF`**和**`TIMESTAMPDIFF`** ,两者用法稍有区别,后者更为灵活,这都是看个人习惯。
+**Thought Process**: While this question practices deletion, it exactly tests the usage of time functions. Two common functions for minute comparison are **`TIMEDIFF`** and **`TIMESTAMPDIFF`**, both with slightly different usages, with the latter being more flexible.
-1. `TIMEDIFF`:两个时间之间的差值
+1. `TIMEDIFF`: The time difference between two times
```sql
TIMEDIFF(time1, time2)
```
-两者参数都是必须的,都是一个时间或者日期时间表达式。如果指定的参数不合法或者是 NULL,那么函数将返回 NULL。
+Both parameters are required and must be a time or datetime expression. If either is invalid or NULL, the function returns NULL.
-对于这题而言,可以用在 minute 函数里面,因为 TIMEDIFF 计算出来的是时间的差值,在外面套一个 MINUTE 函数,计算出来的就是分钟数。
+For this problem, it can be applied within the minute function because the TIMEDIFF result gives the time difference, and wrapping this in a MINUTE function gives the minutes.
-2. `TIMESTAMPDIFF`:用于计算两个日期的时间差
+2. `TIMESTAMPDIFF`: Used to calculate the time difference between two dates
```sql
-TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit,datetime_expr1,datetime_expr2)
-# 参数说明
-#unit: 日期比较返回的时间差单位,常用可选值如下:
-SECOND:秒
-MINUTE:分钟
-HOUR:小时
-DAY:天
-WEEK:星期
-MONTH:月
-QUARTER:季度
-YEAR:年
-# TIMESTAMPDIFF函数返回datetime_expr2 - datetime_expr1的结果(人话: 后面的 - 前面的 即2-1),其中datetime_expr1和datetime_expr2可以是DATE或DATETIME类型值(人话:可以是“2023-01-01”, 也可以是“2023-01-01- 00:00:00”)
+TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit, datetime_expr1, datetime_expr2)
+# Parameter description
+# unit: Common optional values for the time difference returned:
+SECOND: seconds
+MINUTE: minutes
+HOUR: hours
+DAY: days
+WEEK: weeks
+MONTH: months
+QUARTER: quarters
+YEAR: years
+# The TIMESTAMPDIFF function returns the result of datetime_expr2 - datetime_expr1 (in simple terms: the latter - the former, i.e., 2-1), where datetime_expr1 and datetime_expr2 can be DATE or DATETIME type values.
```
-这题需要进行分钟的比较,那么就是 TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, 开始时间, 结束时间) < 5
+This question requires minute comparison, hence `TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5`.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE MINUTE (TIMEDIFF(submit_time , start_time)) < 5 AND score < 60
+DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE MINUTE (TIMEDIFF(submit_time, start_time)) < 5 AND score < 60
```
```sql
DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5 AND score < 60
```
-### 删除记录(二)
+### Deleting Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表`exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table that includes numerous user exam records, structured as follows:
-作答记录表`exam_record`:`start_time` 是试卷开始时间,`submit_time` 是交卷时间,即结束时间,如果未完成的话,则为空。
+Exam record table `exam_record`: `start_time` is the exam start time, and `submit_time` is the submission time. If incomplete, it is NULL.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 分数 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中未完成作答==或==作答时间小于 5 分钟整的记录中,开始作答时间最早的 3 条记录。
+**Requirement**: Delete the earliest 3 records among those that are either uncompleted or have an exam duration of less than 5 minutes.
-**思路**:这题比较简单,但是要注意题干中给出的信息,结束时间,如果未完成的话,则为空,这个其实就是一个条件
+**Thought Process**: This problem is relatively simple, but be sure to note the information given in the prompt. The end time, if incomplete, is NULL, which means this is one condition.
-还有一个条件就是小于 5 分钟,跟上题类似,但是这里是**或**,即两个条件满足一个就行;另外就是稍微考察到了排序和 limit 的用法。
+Another condition is being less than 5 minutes, similar to the previous question, but here it is **or**, so either condition suffices. Lastly, this tests sorting and the use of limit.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS null OR TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5
+DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS NULL OR TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5
ORDER BY start_time
LIMIT 3
-# 默认就是asc, desc是降序排列
+# The default is ascending, desc is descending order
```
-### 删除记录(三)
+### Deleting Records (3)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 exam_record,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing multi-year user exam records structured as follows:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 分数 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中所有记录,==并重置自增主键==
+**Requirement**: Delete all records in the `exam_record` table and reset the auto-incrementing primary key.
-**思路**:这题考察对三种删除语句的区别,注意高亮部分,要求重置主键;
+**Thought Process**: This question tests the differences between three delete statements. Note the highlighted part about resetting the primary key:
-- `DROP`: 清空表,删除表结构,不可逆
-- `TRUNCATE`: 格式化表,不删除表结构,不可逆
-- `DELETE`:删除数据,可逆
+- `DROP`: Deletes the table and its structure and is irreversible.
+- `TRUNCATE`: Clears the table but does not delete the structure. It is irreversible.
+- `DELETE`: Deletes data and is reversible.
-这里选用`TRUNCATE`的原因是:TRUNCATE 只能作用于表;`TRUNCATE`会清空表中的所有行,但表结构及其约束、索引等保持不变;`TRUNCATE`会重置表的自增值;使用`TRUNCATE`后会使表和索引所占用的空间会恢复到初始大小。
+In this case, `TRUNCATE` is chosen because it only affects the table; `TRUNCATE` clears all rows from the table but keeps the structure, constraints, indexes, etc.; `TRUNCATE` resets the auto-increment value; after using `TRUNCATE`, the space occupied by the table and indexes reverts to the initial size.
-这题也可以采用`DELETE`来做,但是在删除后,还需要手动`ALTER`表结构来设置主键初始值;
+This problem can also be approached with `DELETE`, but would require a manual `ALTER` after deleting to set the primary key initial value.
-同理也可以采用`DROP`来做,直接删除整张表,包括表结构,然后再新建表即可。
+Similarly, `DROP` could be used but involves deleting the entire table, including its structure and then recreating it.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-TRUNCATE exam_record;
+TRUNCATE exam_record;
```
-## 表与索引操作
+## Table and Index Operations
-### 创建一张新表
+### Creating a New Table
-**描述**:现有一张用户信息表,其中包含多年来在平台注册过的用户信息,随着牛客平台的不断壮大,用户量飞速增长,为了高效地为高活跃用户提供服务,现需要将部分用户拆分出一张新表。
+**Description**: There is a user information table that contains user information registered on the platform over the years. As the Niuke platform continues to grow, the user base is rapidly increasing. To efficiently serve high-activity users, there is a need to split some users into a new table.
-原来的用户信息表:
+Original user information table:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-作为数据分析师,请**创建一张优质用户信息表 user_info_vip**,表结构和用户信息表一致。
+As a data analyst, please **create a quality user information table named user_info_vip** with the same structure as the user information table.
-你应该返回的输出如下表格所示,请写出建表语句将表格中所有限制和说明记录到表里。
+The output you should return should match the table structure shown below. Please write the create table statement to include all constraints and comments.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-**思路**:如果这题给出了旧表的名称,可直接`create table 新表 as select * from 旧表;` 但是这题并没有给出旧表名称,所以需要自己创建,注意默认值和键的创建即可,比较简单。(注意:如果是在牛客网上面执行,请注意 comment 中要和题目中的 comment 保持一致,包括大小写,否则不通过,还有字符也要设置)
+**Thought Process**: If the old table name was provided, one could simply use `create table new_table as select * from old_table;` However, since the name is not given, it needs to be created manually, paying attention to defaults and key creation. This is relatively simple (Note: if executed on Niuke.com, ensure the comment matches the requirement, including case sensitivity, otherwise it will fail).
-答案:
+**Answer**:
```sql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_info_vip(
- id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT'自增ID',
- uid INT(11) UNIQUE NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
- nick_name VARCHAR(64) COMMENT'昵称',
- achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '成就值',
- `level` INT(11) COMMENT '用户等级',
- job VARCHAR(32) COMMENT '职业方向',
- register_time DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '注册时间'
-)CHARACTER SET UTF8
+ id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Auto-increment ID',
+ uid INT(11) UNIQUE NOT NULL COMMENT 'User ID',
+ nick_name VARCHAR(64) COMMENT 'Nickname',
+ achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 'Achievement Value',
+ `level` INT(11) COMMENT 'User Level',
+ job VARCHAR(32) COMMENT 'Career Direction',
+ register_time DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT 'Registration Time'
+) CHARACTER SET UTF8
```
-### 修改表
+### Modifying a Table
-**描述**: 现有一张用户信息表`user_info`,其中包含多年来在平台注册过的用户信息。
+**Description**: There is a user information table `user_info` which contains user information registered on the platform over the years.
-**用户信息表 `user_info`:**
+**User Information Table `user_info`:**
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-**要求:**请在用户信息表,字段 `level` 的后面增加一列最多可保存 15 个汉字的字段 `school`;并将表中 `job` 列名改为 `profession`,同时 `varchar` 字段长度变为 10;`achievement` 的默认值设置为 0。
+**Requirement**: Please add a new column `school` that can store a maximum of 15 Chinese characters after the `level` column in the user information table; rename the `job` column to `profession` while also changing the `varchar` field length to 10; set the default value of `achievement` to 0.
-**思路**:首先做这题之前,需要了解 ALTER 语句的基本用法:
+**Thought Process**: Before answering, one should understand the basic usage of the ALTER statement:
-- 添加一列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD COLUMN 列名 类型 【first | after 字段名】;`(first : 在某列之前添加,after 反之)
-- 修改列的类型或约束:`ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY COLUMN 列名 新类型 【新约束】;`
-- 修改列名:`ALTER TABLE 表名 change COLUMN 旧列名 新列名 类型;`
-- 删除列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 drop COLUMN 列名;`
-- 修改表名:`ALTER TABLE 表名 rename 【to】 新表名;`
-- 将某一列放到第一列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY COLUMN 列名 类型 first;`
+- Add a column: `ALTER TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN column_name type [first | after column_name];` (first: add before a certain column, after is the opposite)
+- Modify the column type or constraints: `ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name new_type [new_constraints];`
+- Rename the column: `ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE COLUMN old_column_name new_column_name type;`
+- Delete a column: `ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;`
+- Rename a table: `ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME [TO] new_table_name;`
+- Move a column to the first position: `ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name type FIRST;`
-`COLUMN` 关键字其实可以省略不写,这里基于规范还是罗列出来了。
+The `COLUMN` keyword can actually be omitted, but it is listed here for clarity in format.
-在修改时,如果有多个修改项,可以写到一起,但要注意格式
+When making modifications, if there are multiple changes, they can be combined, but formatting is essential.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
ALTER TABLE user_info
@@ -357,15 +357,15 @@ ALTER TABLE user_info
MODIFY achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0;
```
-### 删除表
+### Deleting a Table
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录。一般每年都会为 `exam_record` 表建立一张备份表 `exam_record_{YEAR},{YEAR}` 为对应年份。
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing numerous user exam records over the years. Every year, a backup table named `exam_record_{YEAR}` is created, where `{YEAR}` corresponds to the year.
-现在随着数据越来越多,存储告急,请你把很久前的(2011 到 2014 年)备份表都删掉(如果存在的话)。
+Now, due to increasing data, storage is running low, so please delete the old backup tables from 2011 to 2014 (if they exist).
-**思路**:这题很简单,直接删就行,如果嫌麻烦,可以将要删除的表用逗号隔开,写到一行;这里肯定会有小伙伴问:如果要删除很多张表呢?放心,如果要删除很多张表,可以写脚本来进行删除。
+**Thought Process**: This question is straightforward; just delete them. To avoid additional complexity, you can list the tables to be deleted separated by commas in one line; one might ask: What if there are many tables to delete? No worries, scripts can be written to delete multiple tables.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2011;
@@ -374,13 +374,13 @@ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2013;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2014;
```
-### 创建索引
+### Creating an Index
-**描述**:现有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`,其中包含各种类型试卷的信息。为了对表更方便快捷地查询,需要在 `examination_info` 表创建以下索引,
+**Description**: There is an `examination_info` table containing information on various types of exams. To facilitate quicker queries on this table, the following indexes need to be created in the `examination_info` table:
-规则如下:在 `duration` 列创建普通索引 `idx_duration`、在 `exam_id` 列创建唯一性索引 `uniq_idx_exam_id`、在 `tag` 列创建全文索引 `full_idx_tag`。
+The rules are as follows: create a normal index `idx_duration` on the `duration` column, create a unique index `uniq_idx_exam_id` on the `exam_id` column, and a full-text index `full_idx_tag` on the `tag` column.
-根据题意,将返回如下结果:
+Based on the question, the expected output is as follows:
| examination_info | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | | | | BTREE |
| ---------------- | --- | ---------------- | --- | -------- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | -------- |
@@ -388,32 +388,18 @@ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2014;
| examination_info | 1 | idx_duration | 1 | duration | A | 0 | | | | BTREE |
| examination_info | 1 | full_idx_tag | 1 | tag | | 0 | | | YES | FULLTEXT |
-备注:后台会通过 `SHOW INDEX FROM examination_info` 语句来对比输出结果
+Note: The backend will compare the output using `SHOW INDEX FROM examination_info`.
-**思路**:做这题首先需要了解常见的索引类型:
+**Thought Process**: Before answering, one needs to understand common index types:
-- B-Tree 索引:B-Tree(或称为平衡树)索引是最常见和默认的索引类型。它适用于各种查询条件,可以快速定位到符合条件的数据。B-Tree 索引适用于普通的查找操作,支持等值查询、范围查询和排序。
-- 唯一索引:唯一索引与普通的 B-Tree 索引类似,不同之处在于它要求被索引的列的值是唯一的。这意味着在插入或更新数据时,MySQL 会验证索引列的唯一性。
-- 主键索引:主键索引是一种特殊的唯一索引,它用于唯一标识表中的每一行数据。每个表只能有一个主键索引,它可以帮助提高数据的访问速度和数据完整性。
-- 全文索引:全文索引用于在文本数据中进行全文搜索。它支持在文本字段中进行关键字搜索,而不仅仅是简单的等值或范围查找。全文索引适用于需要进行全文搜索的应用场景。
+- B-Tree Index: The B-Tree (or balanced tree) index is the most common and default type. It's suitable for various query conditions and can quickly locate the data that meets the condition. It's typically used for ordinary queries supporting equality, range queries, and sorting.
+- Unique Index: Similar to the ordinary B-Tree index, but it requires the indexed column’s values to be unique, which means MySQL will check for uniqueness during insertion and updates.
+- Primary Key Index: This is a special type of unique index used to uniquely identify every row in a table. Each table can only have one primary key index, which helps enhance access speed and data integrity.
+- Full-Text Index: A full-text index is used for full-text searches within text data. It supports keyword searches in text fields, not just simple equality or range queries. It's suitable for applications needing full-text search.
-```sql
--- 示例:
--- 添加B-Tree索引:
- CREATE INDEX idx_name(索引名) ON 表名 (字段名); -- idx_name为索引名,以下都是
--- 创建唯一索引:
- CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_name ON 表名 (字段名);
--- 创建一个主键索引:
- ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD PRIMARY KEY (字段名);
--- 创建一个全文索引
- ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD FULLTEXT INDEX idx_name (字段名);
-
--- 通过以上示例,可以看出create 和 alter 都可以添加索引
-```
-
-有了以上的基础知识之后,该题答案也就浮出水面了。
+With this foundational knowledge, the answer to this question is now clear.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
ALTER TABLE examination_info
@@ -422,25 +408,25 @@ ALTER TABLE examination_info
ADD FULLTEXT INDEX full_idx_tag(tag);
```
-### 删除索引
+### Deleting an Index
-**描述**:请删除`examination_info`表上的唯一索引 uniq_idx_exam_id 和全文索引 full_idx_tag。
+**Description**: Please delete the unique index `uniq_idx_exam_id` and the full-text index `full_idx_tag` on the `examination_info` table.
-**思路**:该题考察删除索引的基本语法:
+**Thought Process**: This question tests the basic syntax for deleting an index:
```sql
--- 使用 DROP INDEX 删除索引
-DROP INDEX idx_name ON 表名;
+-- Using DROP INDEX to delete an index
+DROP INDEX idx_name ON table_name;
--- 使用 ALTER TABLE 删除索引
-ALTER TABLE employees DROP INDEX idx_email;
+-- Using ALTER TABLE to delete an index
+ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX idx_name;
```
-这里需要注意的是:在 MySQL 中,一次删除多个索引的操作是不支持的。每次删除索引时,只能指定一个索引名称进行删除。
+It is important to note that in MySQL, multiple indexes cannot be deleted in a single operation. Each operation can only specify one index name for deletion.
-而且 **DROP** 命令需要慎用!!!
+Additionally, **DROP** commands should be used with caution!
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
DROP INDEX uniq_idx_exam_id ON examination_info;
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
index f5acd8fc5c8..fe478879d90 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
@@ -1,31 +1,31 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(3)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (3)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+You can decide whether to skip difficult or challenging questions based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 聚合函数
+## Aggregate Functions
-### SQL 类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(较难)
+### Truncated Average Score of High-Difficulty SQL Papers (Difficult)
-**描述**: 牛客的运营同学想要查看大家在 SQL 类别中高难度试卷的得分情况。
+**Description**: The operations team at Niuke wants to see the score situation of users on high-difficulty SQL papers.
-请你帮她从`exam_record`数据表中计算所有用户完成 SQL 类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(去掉一个最大值和一个最小值后的平均值)。
+Please help her calculate the truncated average score (the average after removing one maximum and one minimum score) of all users who completed high-difficulty SQL papers from the `exam_record` data table.
-示例数据:`examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间)
+Sample data: `examination_info` (`exam_id` Paper ID, `tag` Paper Category, `difficulty` Paper Difficulty, `duration` Exam Duration, `release_time` Release Time)
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
+| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
+| --- | ------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | Algorithm | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-示例数据:`exam_record`(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分)
+Sample data: `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Paper ID, `start_time` Start Time, `submit_time` Submit Time, `score` Score)
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
@@ -40,1262 +40,16 @@ tag:
| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 50 |
| 10 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-根据输入你的查询结果如下:
+Based on your input, your query result is as follows:
| tag | difficulty | clip_avg_score |
| --- | ---------- | -------------- |
| SQL | hard | 81.7 |
-从`examination_info`表可知,试卷 9001 为高难度 SQL 试卷,该试卷被作答的得分有[80,81,84,90,50],去除最高分和最低分后为[80,81,84],平均分为 81.6666667,保留一位小数后为 81.7
+From the `examination_info` table, it can be seen that paper 9001 is a high-difficulty SQL paper, and the scores for this paper are [80, 81, 84, 90, 50]. After removing the highest and lowest scores, we have [80, 81, 84], and the average score is 81.6666667, which rounds to 81.7 when keeping one decimal place.
-**输入描述:**
+**Input Description:**
-输入数据中至少有 3 个有效分数
+The input data must contain at least 3 valid scores.
-**思路一:** 要找出高难度 sql 试卷,肯定需要联 examination_info 这张表,然后找出高难度的课程,由 examination_info 得知,高难度 sql 的 exam_id 为 9001,那么等下就以 exam_id = 9001 作为条件去查询;
-
-先找出 9001 号考试 `select * from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-然后,找出最高分 `select max(score) 最高分 from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-接着,找出最低分 `select min(score) 最低分 from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-在查询出来的分数结果集当中,去掉最高分和最低分,最直观能想到的就是 NOT IN 或者 用 NOT EXISTS 也行,这里以 NOT IN 来做
-
-首先将主体写出来`select tag, difficulty, round(avg(score), 1) clip_avg_score from examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record`
-
-**小 tips** : MYSQL 的 `ROUND()` 函数 ,`ROUND(X)`返回参数 X 最近似的整数 `ROUND(X,D)`返回 X ,其值保留到小数点后 D 位,第 D 位的保留方式为四舍五入。
-
-再将上面的 "碎片" 语句拼凑起来即可, 注意在 NOT IN 中两个子查询用 UNION ALL 来关联,用 union 把 max 和 min 的结果集中在一行当中,这样形成一列多行的效果。
-
-**答案一:**
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag, difficulty, ROUND(AVG(score), 1) clip_avg_score
- FROM examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record
- WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND record.exam_id = 9001
- AND record.score NOT IN(
- SELECT MAX(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id = 9001
- UNION ALL
- SELECT MIN(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id = 9001
- )
-```
-
-这是最直观,也是最容易想到的解法,但是还有待改进,这算是投机取巧过关,其实严格按照题目要求应该这么写:
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- difficulty,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 1) clip_avg_score
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND record.exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' )
- AND record.score NOT IN
- (SELECT MAX(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' )
- UNION ALL SELECT MIN(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' ) )
-```
-
-然而你会发现,重复的语句非常多,所以可以利用`WITH`来抽取公共部分
-
-**`WITH` 子句介绍**:
-
-`WITH` 子句,也称为公共表表达式(Common Table Expression,CTE),是在 SQL 查询中定义临时表的方式。它可以让我们在查询中创建一个临时命名的结果集,并且可以在同一查询中引用该结果集。
-
-基本用法:
-
-```sql
-WITH cte_name (column1, column2, ..., columnN) AS (
- -- 查询体
- SELECT ...
- FROM ...
- WHERE ...
-)
--- 主查询
-SELECT ...
-FROM cte_name
-WHERE ...
-```
-
-`WITH` 子句由以下几个部分组成:
-
-- `cte_name`: 给临时表起一个名称,可以在主查询中引用。
-- `(column1, column2, ..., columnN)`: 可选,指定临时表的列名。
-- `AS`: 必需,表示开始定义临时表。
-- `CTE 查询体`: 实际的查询语句,用于定义临时表中的数据。
-
-`WITH` 子句的主要用途之一是增强查询的可读性和可维护性,尤其在涉及多个嵌套子查询或需要重复使用相同的查询逻辑时。通过将这些逻辑放在一个命名的临时表中,我们可以更清晰地组织查询,并消除重复代码。
-
-此外,`WITH` 子句还可以在复杂的查询中实现递归查询。递归查询允许我们在单个查询中执行对同一表的多次迭代,逐步构建结果集。这在处理层次结构数据、组织结构和树状结构等场景中非常有用。
-
-**小细节**:MySQL 5.7 版本以及之前的版本不支持在 `WITH` 子句中直接使用别名。
-
-下面是改进后的答案:
-
-```sql
-WITH t1 AS
- (SELECT record.*,
- info.tag,
- info.difficulty
- FROM exam_record record
- INNER JOIN examination_info info ON record.exam_id = info.exam_id
- WHERE info.tag = "SQL"
- AND info.difficulty = "hard" )
-SELECT tag,
- difficulty,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 1)
-FROM t1
-WHERE score NOT IN
- (SELECT max(score)
- FROM t1
- UNION SELECT min(score)
- FROM t1)
-```
-
-**思路二:**
-
-- 筛选 SQL 高难度试卷:`where tag="SQL" and difficulty="hard"`
-- 计算截断平均值:`(和-最大值-最小值) / (总个数-2)`:
- - `(sum(score) - max(score) - min(score)) / (count(score) - 2)`
- - 有一个缺点就是,如果最大值和最小值有多个,这个方法就很难筛选出来, 但是题目中说了----->**`去掉一个最大值和一个最小值后的平均值`**, 所以这里可以用这个公式。
-
-**答案二:**
-
-```sql
-SELECT info.tag,
- info.difficulty,
- ROUND((SUM(record.score)- MIN(record.score)- MAX(record.score)) / (COUNT(record.score)- 2), 1) AS clip_avg_score
-FROM examination_info info,
- exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND info.tag = "SQL"
- AND info.difficulty = "hard";
-```
-
-### 统计作答次数
-
-有一个试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,请从中统计出总作答次数 `total_pv`、试卷已完成作答数 `complete_pv`、已完成的试卷数 `complete_exam_cnt`。
-
-示例数据 `exam_record` 表(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | 2021-05-02 10:30:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:31:01 | 84 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 50 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-示例输出:
-
-| total_pv | complete_pv | complete_exam_cnt |
-| -------- | ----------- | ----------------- |
-| 10 | 7 | 2 |
-
-解释:表示截止当前,有 10 次试卷作答记录,已完成的作答次数为 7 次(中途退出的为未完成状态,其交卷时间和份数为 NULL),已完成的试卷有 9001 和 9002 两份。
-
-**思路**: 这题一看到统计次数,肯定第一时间就要想到用`COUNT`这个函数来解决,问题是要统计不同的记录,该怎么来写?使用子查询就能解决这个题目(这题用 case when 也能写出来,解法类似,逻辑不同而已);首先在做这个题之前,让我们先来了解一下`COUNT`的基本用法;
-
-`COUNT()` 函数的基本语法如下所示:
-
-```sql
-COUNT(expression)
-```
-
-其中,`expression` 可以是列名、表达式、常量或通配符。下面是一些常见的用法示例:
-
-1. 计算表中所有行的数量:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-2. 计算特定列非空(不为 NULL)值的数量:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-3. 计算满足条件的行数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name WHERE condition;
-```
-
-4. 结合 `GROUP BY` 使用,计算分组后每个组的行数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name;
-```
-
-5. 计算不同列组合的唯一组合数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column_name1, column_name2) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-在使用 `COUNT()` 函数时,如果不指定任何参数或者使用 `COUNT(*)`,将会计算所有行的数量。而如果使用列名,则只会计算该列非空值的数量。
-
-另外,`COUNT()` 函数的结果是一个整数值。即使结果是零,也不会返回 NULL,这点需要谨记。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- count(*) total_pv,
- ( SELECT count(*) FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS NOT NULL ) complete_pv,
- ( SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT exam_id, score IS NOT NULL OR NULL ) FROM exam_record ) complete_exam_cnt
-FROM
- exam_record
-```
-
-这里着重说一下`COUNT( DISTINCT exam_id, score IS NOT NULL OR NULL )`这一句,判断 score 是否为 null ,如果是即为真,如果不是返回 null;注意这里如果不加 `or null` 在不是 null 的情况下只会返回 false 也就是返回 0;
-
-`COUNT`本身是不可以对多列求行数的,`distinct`的加入是的多列成为一个整体,可以求出现的行数了;`count distinct`在计算时只返回非 null 的行, 这个也要注意;
-
-另外通过本题 get 到了------>count 加条件常用句式`count( 列判断 or null)`
-
-### 得分不小于平均分的最低分
-
-**描述**: 请从试卷作答记录表中找到 SQL 试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分。
-
-示例数据 exam_record 表(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-`examination_info` 表(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间)
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-示例输出数据:
-
-| min_score_over_avg |
-| ------------------ |
-| 87 |
-
-**解释**:试卷 9001 和 9002 为 SQL 类别,作答这两份试卷的得分有[80,89,87,90],平均分为 86.5,不小于平均分的最小分数为 87
-
-**思路**:这类题目第一眼看确实很复杂, 因为不知道从哪入手,但是当我们仔细读题审题后,要学会抓住题干中的关键信息。以本题为例:`请从试卷作答记录表中找到SQL试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分。`你能一眼从中提取哪些有效信息来作为解题思路?
-
-第一条:找到==SQL==试卷得分
-
-第二条:该类试卷==平均得分==
-
-第三条:该类试卷的==用户最低得分==
-
-然后中间的 “桥梁” 就是==不小于==
-
-将条件拆分后,先逐步完成
-
-```sql
--- 找出tag为‘SQL’的得分 【80, 89,87,90】
--- 再算出这一组的平均得分
-select ROUND(AVG(score), 1) from examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record
- where info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- and tag= 'SQL'
-```
-
-然后再找出该类试卷的最低得分,接着将结果集`【80, 89,87,90】` 去和平均分数作比较,方可得出最终答案。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT MIN(score) AS min_score_over_avg
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND tag= 'SQL'
- AND score >=
- (SELECT ROUND(AVG(score), 1)
- FROM examination_info info
- INNER JOIN exam_record record
- WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND tag= 'SQL' )
-```
-
-其实这类题目给出的要求看似很 “绕”,但其实仔细梳理一遍,将大条件拆分成小条件,逐个拆分完以后,最后将所有条件拼凑起来。反正只要记住:**抓主干,理分支**,问题便迎刃而解。
-
-## 分组查询
-
-### 平均活跃天数和月活人数
-
-**描述**:用户在牛客试卷作答区作答记录存储在表 `exam_record` 中,内容如下:
-
-`exam_record` 表(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分)
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-07-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 19:01:01 | 2021-07-02 19:30:01 | 82 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-05 18:01:01 | 2021-07-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 13 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-09-02 12:11:01 | 2020-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请计算 2021 年每个月里试卷作答区用户平均月活跃天数 `avg_active_days` 和月度活跃人数 `mau`,上面数据的示例输出如下:
-
-| month | avg_active_days | mau |
-| ------ | --------------- | --- |
-| 202107 | 1.50 | 2 |
-| 202109 | 1.25 | 4 |
-
-**解释**:2021 年 7 月有 2 人活跃,共活跃了 3 天(1001 活跃 1 天,1002 活跃 2 天),平均活跃天数 1.5;2021 年 9 月有 4 人活跃,共活跃了 5 天,平均活跃天数 1.25,结果保留 2 位小数。
-
-注:此处活跃指有==交卷==行为。
-
-**思路**:读完题先注意高亮部分;一般求天数和月活跃人数马上就要想到相关的日期函数;这一题我们同样来进行拆分,把问题细化再解决;首先求活跃人数,肯定要用到`COUNT()`,那这里首先就有一个坑,不知道大家注意了没有?用户 1002 在 9 月份做了两种不同的试卷,所以这里要注意去重,不然在统计的时候,活跃人数是错的;第二个就是要知道日期的格式化,如上表,题目要求以`202107`这种日期格式展现,要用到`DATE_FORMAT`来进行格式化。
-
-基本用法:
-
-`DATE_FORMAT(date_value, format)`
-
-- `date_value` 参数是待格式化的日期或时间值。
-- `format` 参数是指定的日期或时间格式(这个和 Java 里面的日期格式一样)。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m') MONTH,
- round(count(DISTINCT UID, DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m%d')) / count(DISTINCT UID), 2) avg_active_days,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) mau
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE YEAR (submit_time) = 2021
-GROUP BY MONTH
-```
-
-这里多说一句, 使用`COUNT(DISTINCT uid, DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m%d'))` 可以统计在 `uid` 列和 `submit_time` 列按照年份、月份和日期进行格式化后的组合值的数量。
-
-### 月总刷题数和日均刷题数
-
-**描述**:现有一张题目练习记录表 `practice_record`,示例内容如下:
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请从中统计出 2021 年每个月里用户的月总刷题数 `month_q_cnt` 和日均刷题数 `avg_day_q_cnt`(按月份升序排序)以及该年的总体情况,示例数据输出如下:
-
-| submit_month | month_q_cnt | avg_day_q_cnt |
-| ------------ | ----------- | ------------- |
-| 202108 | 2 | 0.065 |
-| 202109 | 3 | 0.100 |
-| 2021 汇总 | 5 | 0.161 |
-
-**解释**:2021 年 8 月共有 2 次刷题记录,日均刷题数为 2/31=0.065(保留 3 位小数);2021 年 9 月共有 3 次刷题记录,日均刷题数为 3/30=0.100;2021 年共有 5 次刷题记录(年度汇总平均无实际意义,这里我们按照 31 天来算 5/31=0.161)
-
-> 牛客已经采用最新的 Mysql 版本,如果您运行结果出现错误:ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,意思是:对于 GROUP BY 聚合操作,如果在 SELECT 中的列,没有在 GROUP BY 中出现,那么这个 SQL 是不合法的,因为列不在 GROUP BY 从句中,也就是说查出来的列必须在 group by 后面出现否则就会报错,或者这个字段出现在聚合函数里面。
-
-**思路:**
-
-看到实例数据就要马上联想到相关的函数,比如`submit_month`就要用到`DATE_FORMAT`来格式化日期。然后查出每月的刷题数量。
-
-每月的刷题数量
-
-```sql
-SELECT MONTH ( submit_time ), COUNT( question_id )
-FROM
- practice_record
-GROUP BY
- MONTH (submit_time)
-```
-
-接着第三列这里要用到`DAY(LAST_DAY(date_value))`函数来查找给定日期的月份中的天数。
-
-示例代码如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY('2023-07-08')) AS days_in_month;
--- 输出:31
-
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY('2023-02-01')) AS days_in_month;
--- 输出:28 (闰年中的二月份)
-
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY(NOW())) AS days_in_current_month;
--- 输出:31 (当前月份的天数)
-```
-
-使用 `LAST_DAY()` 函数获取给定日期的当月最后一天,然后使用 `DAY()` 函数提取该日期的天数。这样就能获得指定月份的天数。
-
-需要注意的是,`LAST_DAY()` 函数返回的是日期值,而 `DAY()` 函数用于提取日期值中的天数部分。
-
-有了上述的分析之后,即可马上写出答案,这题复杂就复杂在处理日期上,其中的逻辑并不难。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m') submit_month,
- count(question_id) month_q_cnt,
- ROUND(COUNT(question_id) / DAY (LAST_DAY(submit_time)), 3) avg_day_q_cnt
-FROM practice_record
-WHERE DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y') = '2021'
-GROUP BY submit_month
-UNION ALL
-SELECT '2021汇总' AS submit_month,
- count(question_id) month_q_cnt,
- ROUND(COUNT(question_id) / 31, 3) avg_day_q_cnt
-FROM practice_record
-WHERE DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y') = '2021'
-ORDER BY submit_month
-```
-
-在实例数据输出中因为最后一行需要得出汇总数据,所以这里要 `UNION ALL`加到结果集中;别忘了最后要排序!
-
-### 未完成试卷数大于 1 的有效用户(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-07-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 19:01:01 | 2021-07-02 19:30:01 | 82 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-05 18:01:01 | 2021-07-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 13 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-09-02 12:11:01 | 2020-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-还有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-请统计 2021 年每个未完成试卷作答数大于 1 的有效用户的数据(有效用户指完成试卷作答数至少为 1 且未完成数小于 5),输出用户 ID、未完成试卷作答数、完成试卷作答数、作答过的试卷 tag 集合,按未完成试卷数量由多到少排序。示例数据的输出结果如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | complete_cnt | detail |
-| ---- | -------------- | ------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| 1002 | 2 | 4 | 2021-09-01:算法;2021-07-02:SQL;2021-09-02:SQL;2021-09-05:SQL;2021-07-05:SQL |
-
-**解释**:2021 年的作答记录中,除了 1004,其他用户均满足有效用户定义,但只有 1002 未完成试卷数大于 1,因此只输出 1002,detail 中是 1002 作答过的试卷{日期:tag}集合,日期和 tag 间用 **:** 连接,多元素间用 **;** 连接。
-
-**思路:**
-
-仔细读题后,分析出:首先要联表,因为后面要输出`tag`;
-
-筛选出 2021 年的数据
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM exam_record er
-LEFT JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR (er.start_time)= 2021
-```
-
-根据 uid 进行分组,然后对每个用户进行条件进行判断,题目中要求`完成试卷数至少为1,未完成试卷数要大于1,小于5`
-
-那么等会儿写 sql 的时候条件应该是:`未完成 > 1 and 已完成 >=1 and 未完成 < 5`
-
-因为最后要用到字符串的拼接,而且还要组合拼接,这个可以用`GROUP_CONCAT`函数,下面简单介绍一下该函数的用法:
-
-基本格式:
-
-```sql
-GROUP_CONCAT([DISTINCT] expr [ORDER BY {unsigned_integer | col_name | expr} [ASC | DESC] [, ...]] [SEPARATOR sep])
-```
-
-- `expr`:要连接的列或表达式。
-- `DISTINCT`:可选参数,用于去重。当指定了 `DISTINCT`,相同的值只会出现一次。
-- `ORDER BY`:可选参数,用于排序连接后的值。可以选择升序 (`ASC`) 或降序 (`DESC`) 排序。
-- `SEPARATOR sep`:可选参数,用于设置连接后的值的分隔符。(本题要用这个参数设置 ; 号 )
-
-`GROUP_CONCAT()` 函数常用于 `GROUP BY` 子句中,将一组行的值连接为一个字符串,并在结果集中以聚合的形式返回。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.uid,
- SUM(CASE
- WHEN a.submit_time IS NULL THEN 1
- END) AS incomplete_cnt,
- SUM(CASE
- WHEN a.submit_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1
- END) AS complete_cnt,
- GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT CONCAT(DATE_FORMAT(a.start_time, '%Y-%m-%d'), ':', b.tag)
- ORDER BY start_time SEPARATOR ";") AS detail
-FROM exam_record a
-LEFT JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR (a.start_time)= 2021
-GROUP BY a.uid
-HAVING incomplete_cnt > 1
-AND complete_cnt >= 1
-AND incomplete_cnt < 5
-ORDER BY incomplete_cnt DESC
-```
-
-- `SUM(CASE WHEN a.submit_time IS NULL THEN 1 END)` 统计了每个用户未完成的记录数量。
-- `SUM(CASE WHEN a.submit_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1 END)` 统计了每个用户已完成的记录数量。
-- `GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT CONCAT(DATE_FORMAT(a.start_time, '%Y-%m-%d'), ':', b.tag) ORDER BY a.start_time SEPARATOR ';')` 将每个用户的考试日期和标签以逗号分隔的形式连接成一个字符串,并按考试开始时间进行排序。
-
-## 嵌套子查询
-
-### 月均完成试卷数不小于 3 的用户爱作答的类别(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid`:用户 ID, `exam_id`:试卷 ID, `start_time`:开始作答时间, `submit_time`:交卷时间,没提交的话为 NULL, `score`:得分),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 13:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 13 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id`:试卷 ID, `tag`:试卷类别, `difficulty`:试卷难度, `duration`:考试时长, `release_time`:发布时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-请从表中统计出 “当月均完成试卷数”不小于 3 的用户们爱作答的类别及作答次数,按次数降序输出,示例输出如下:
-
-| tag | tag_cnt |
-| ---- | ------- |
-| C++ | 4 |
-| SQL | 2 |
-| 算法 | 1 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1002 和 1005 在 2021 年 09 月的完成试卷数目均为 3,其他用户均小于 3;然后用户 1002 和 1005 作答过的试卷 tag 分布结果按作答次数降序排序依次为 C++、SQL、算法。
-
-**思路**:这题考察联合子查询,重点在于`月均回答>=3`, 但是个人认为这里没有表述清楚,应该直接说查 9 月的就容易理解多了;这里不是每个月都要>=3 或者是所有答题次数/答题月份。不要理解错误了。
-
-先查询出哪些用户月均答题大于三次
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID
-FROM exam_record record
-GROUP BY UID,
- MONTH (start_time)
-HAVING count(submit_time) >= 3
-```
-
-有了这一步之后再进行深入,只要能理解上一步(我的意思是不被题目中的月均所困扰),然后再套一个子查询,查哪些用户包含其中,然后查出题目中所需的列即可。记得排序!!
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- count(start_time) AS tag_cnt
-FROM exam_record record
-INNER JOIN examination_info info ON record.exam_id = info.exam_id
-WHERE UID IN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM exam_record record
- GROUP BY UID,
- MONTH (start_time)
- HAVING count(submit_time) >= 3)
-GROUP BY tag
-ORDER BY tag_cnt DESC
-```
-
-### 试卷发布当天作答人数和平均分
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 1500 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1100 | 4 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-**释义**:用户 1001 昵称为牛客 1 号,成就值为 3100,用户等级是 7 级,职业方向为算法,注册时间 2020-01-01 10:00:00
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间) 示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分) 示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 70 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 12:01:01 | 2021-08-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-08-02 12:01:01 | 2021-08-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 11 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 13:01:01 | 2021-09-01 13:41:01 | 70 |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 16 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请计算每张 SQL 类别试卷发布后,当天 5 级以上的用户作答的人数 `uv` 和平均分 `avg_score`,按人数降序,相同人数的按平均分升序,示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | uv | avg_score |
-| ------- | --- | --------- |
-| 9001 | 3 | 81.3 |
-
-解释:只有一张 SQL 类别的试卷,试卷 ID 为 9001,发布当天(2021-09-01)有 1001、1002、1003、1005 作答过,但是 1003 是 5 级用户,其他 3 位为 5 级以上,他们三的得分有[70,80,85,90],平均分为 81.3(保留 1 位小数)。
-
-**思路**:这题看似很复杂,但是先逐步将“外边”条件拆分,然后合拢到一起,答案就出来,多表查询反正记住:由外向里,抽丝剥茧。
-
-先把三种表连起来,同时给定一些条件,比如题目中要求`等级> 5`的用户,那么可以先查出来
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT u_info.uid
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND u_info.LEVEL > 5
-```
-
-接着注意题目中要求:`每张sql类别试卷发布后,当天作答用户`,注意其中的==当天==,那我们马上就要想到要用到时间的比较。
-
-对试卷发布日期和开始考试日期进行比较:`DATE(e_info.release_time) = DATE(record.start_time)`;不用担心`submit_time` 为 null 的问题,后续在 where 中会给过滤掉。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT record.exam_id AS exam_id,
- COUNT(DISTINCT u_info.uid) AS uv,
- ROUND(SUM(record.score) / COUNT(u_info.uid), 1) AS avg_score
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND DATE (e_info.release_time) = DATE (record.start_time)
- AND submit_time IS NOT NULL
- AND tag = 'SQL'
- AND u_info.LEVEL > 5
-GROUP BY record.exam_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- avg_score ASC
-```
-
-注意最后的分组排序!先按人数排,若一致,按平均分排。
-
-### 作答试卷得分大于过 80 的人的用户等级分布
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 1500 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1100 | 4 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答信息表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 79 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 12:01:01 | 2021-08-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 11 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 13:01:01 | 2021-09-01 13:41:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 16 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-统计作答 SQL 类别的试卷得分大于过 80 的人的用户等级分布,按数量降序排序(保证数量都不同)。示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| level | level_cnt |
-| ----- | --------- |
-| 6 | 2 |
-| 5 | 1 |
-
-解释:9001 为 SQL 类试卷,作答该试卷大于 80 分的人有 1002、1003、1005 共 3 人,6 级两人,5 级一人。
-
-**思路:**这题和上一题都是一样的数据,只是查询条件改变了而已,上一题理解了,这题分分钟做出来。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT u_info.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- count(u_info.uid) AS level_cnt
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND record.score > 80
- AND submit_time IS NOT NULL
- AND tag = 'SQL'
-GROUP BY LEVEL
-ORDER BY level_cnt DESC
-```
-
-## 合并查询
-
-### 每个题目和每份试卷被作答的人数和次数
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-题目练习表 practice_record(uid 用户 ID, question_id 题目 ID, submit_time 提交时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请统计每个题目和每份试卷被作答的人数和次数,分别按照"试卷"和"题目"的 uv & pv 降序显示,示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tid | uv | pv |
-| ---- | --- | --- |
-| 9001 | 3 | 3 |
-| 9002 | 1 | 3 |
-| 8001 | 3 | 5 |
-| 8002 | 2 | 2 |
-
-**解释**:“试卷”有 3 人共练习 3 次试卷 9001,1 人作答 3 次 9002;“刷题”有 3 人刷 5 次 8001,有 2 人刷 2 次 8002
-
-**思路**:这题的难点和易错点在于`UNION`和`ORDER BY` 同时使用的问题
-
-有以下几种情况:使用`union`和多个`order by`不加括号,报错!
-
-`order by`在`union`连接的子句中不起作用;
-
-比如不加括号:
-
-```sql
-SELECT exam_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) AS uv,
- COUNT(UID) AS pv
-FROM exam_record
-GROUP BY exam_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- pv DESC
-UNION
-SELECT question_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) AS uv,
- COUNT(UID) AS pv
-FROM practice_record
-GROUP BY question_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- pv DESC
-```
-
-直接报语法错误,如果没有括号,只能有一个`order by`
-
-还有一种`order by`不起作用的情况,但是能在子句的子句中起作用,这里的解决方案就是在外面再套一层查询。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM
- (SELECT exam_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT exam_record.uid) uv,
- COUNT(*) pv
- FROM exam_record
- GROUP BY exam_id
- ORDER BY uv DESC, pv DESC) t1
-UNION
-SELECT *
-FROM
- (SELECT question_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT practice_record.uid) uv,
- COUNT(*) pv
- FROM practice_record
- GROUP BY question_id
- ORDER BY uv DESC, pv DESC) t2;
-```
-
-### 分别满足两个活动的人
-
-**描述**: 为了促进更多用户在牛客平台学习和刷题进步,我们会经常给一些既活跃又表现不错的用户发放福利。假使以前我们有两拨运营活动,分别给每次试卷得分都能到 85 分的人(activity1)、至少有一次用了一半时间就完成高难度试卷且分数大于 80 的人(activity2)发了福利券。
-
-现在,需要你一次性将这两个活动满足的人筛选出来,交给运营同学。请写出一个 SQL 实现:输出 2021 年里,所有每次试卷得分都能到 85 分的人以及至少有一次用了一半时间就完成高难度试卷且分数大于 80 的人的 id 和活动号,按用户 ID 排序输出。
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | **86** |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-
-示例数据输出结果:
-
-| uid | activity |
-| ---- | --------- |
-| 1001 | activity2 |
-| 1003 | activity1 |
-| 1004 | activity1 |
-| 1004 | activity2 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1001 最小分数 81 不满足活动 1,但 29 分 59 秒完成了 60 分钟长的试卷得分 81,满足活动 2;1003 最小分数 86 满足活动 1,完成时长都大于试卷时长的一半,不满足活动 2;用户 1004 刚好用了一半时间(30 分钟整)完成了试卷得分 85,满足活动 1 和活动 2。
-
-**思路**: 这一题需要涉及到时间的减法,需要用到 `TIMESTAMPDIFF()` 函数计算两个时间戳之间的分钟差值。
-
-下面我们来看一下基本用法
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, end_time)
-```
-
-`TIMESTAMPDIFF()` 函数的第一个参数是时间单位,这里我们选择 `MINUTE` 表示返回分钟差值。第二个参数是较早的时间戳,第三个参数是较晚的时间戳。函数会返回它们之间的分钟差值
-
-了解了这个函数的用法之后,我们再回过头来看`activity1`的要求,求分数大于 85 即可,那我们还是先把这个写出来,后续思路就会清晰很多
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT UID
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE score >= 85
- AND YEAR (start_time) = '2021'
-```
-
-根据条件 2,接着写出`在一半时间内完成高难度试卷且分数大于80的人`
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND (TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time)) < (info.duration / 2)
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND score >= 80
-```
-
-然后再把两者`UNION` 起来即可。(这里特别要注意括号问题和`order by`位置,具体用法在上一篇中已提及)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT UID UID,
- 'activity1' activity
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE UID not in
- (SELECT UID
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE score<85
- AND YEAR(submit_time) = 2021 )
-UNION
-SELECT DISTINCT UID UID,
- 'activity2' activity
-FROM exam_record e_r
-LEFT JOIN examination_info e_i ON e_r.exam_id = e_i.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR(submit_time) = 2021
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND TIMESTAMPDIFF(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) <= duration *30
- AND score>80
-ORDER BY UID
-```
-
-## 连接查询
-
-### 满足条件的用户的试卷完成数和题目练习数(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 user_info(uid 用户 ID,nick_name 昵称, achievement 成就值, level 等级, job 职业方向, register_time 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2300 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 2500 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 2000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 examination_info(exam_id 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, difficulty 试卷难度, duration 考试时长, release_time 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 86 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 80 |
-
-题目练习记录表 practice_record(uid 用户 ID, question_id 题目 ID, submit_time 提交时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 8 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:58:01 | 94 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 11 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请你找到高难度 SQL 试卷得分平均值大于 80 并且是 7 级的红名大佬,统计他们的 2021 年试卷总完成次数和题目总练习次数,只保留 2021 年有试卷完成记录的用户。结果按试卷完成数升序,按题目练习数降序。
-
-示例数据输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_cnt | question_cnt |
-| ---- | -------- | ------------ |
-| 1001 | 1 | 2 |
-| 1003 | 2 | 0 |
-
-解释:用户 1001、1003、1004、1006 满足高难度 SQL 试卷得分平均值大于 80,但只有 1001、1003 是 7 级红名大佬;1001 完成了 1 次试卷 1001,练习了 2 次题目;1003 完成了 2 次试卷 9001、9002,未练习题目(因此计数为 0)
-
-**思路:**
-
-先将条件进行初步筛选,比如先查出做过高难度 sql 试卷的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- record.uid
-FROM
- exam_record record
- INNER JOIN examination_info e_info ON record.exam_id = e_info.exam_id
- JOIN user_info u_info ON record.uid = u_info.uid
-WHERE
- e_info.tag = 'SQL'
- AND e_info.difficulty = 'hard'
-```
-
-然后根据题目要求,接着再往里叠条件即可;
-
-但是这里又要注意:
-
-第一:不能`YEAR(submit_time)= 2021`这个条件放到最后,要在`ON`条件里,因为左连接存在返回左表全部行,右表为 null 的情形,放在 `JOIN`条件的 `ON` 子句中的目的是为了确保在连接两个表时,只有满足年份条件的记录会进行连接。这样可以避免其他年份的记录被包含在结果中。即 1001 做过 2021 年的试卷,但没有练习过,如果把条件放到最后,就会排除掉这种情况。
-
-第二,必须是`COUNT(distinct er.exam_id) exam_cnt, COUNT(distinct pr.id) question_cnt,`要加 distinct,因为有左连接产生很多重复值。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT er.uid AS UID,
- count(DISTINCT er.exam_id) AS exam_cnt,
- count(DISTINCT pr.id) AS question_cnt
-FROM exam_record er
-LEFT JOIN practice_record pr ON er.uid = pr.uid
-AND YEAR (er.submit_time)= 2021
-AND YEAR (pr.submit_time)= 2021
-WHERE er.uid IN
- (SELECT er.uid
- FROM exam_record er
- LEFT JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
- LEFT JOIN user_info ui ON er.uid = ui.uid
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND LEVEL = 7
- GROUP BY er.uid
- HAVING avg(score) > 80)
-GROUP BY er.uid
-ORDER BY exam_cnt,
- question_cnt DESC
-```
-
-可能细心的小伙伴会发现,为什么明明将条件限制了`tag = 'SQL' AND difficulty = 'hard'`,但是用户 1003 仍然能查出两条考试记录,其中一条的考试`tag`为 `C++`; 这是由于`LEFT JOIN`的特性,即使没有与右表匹配的行,左表的所有记录仍然会被保留。
-
-### 每个 6/7 级用户活跃情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2300 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 2500 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 2600 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:59 | 84 |
-| 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 2020-09-01 13:01:01 | 2020-09-01 13:41:01 | 81 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-题目练习记录表 `practice_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `question_id` 题目 ID, `submit_time` 提交时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 1004 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1001 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1006 | 8002 | 2021-08-04 19:58:01 | 94 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2021-08-03 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2020-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请统计每个 6/7 级用户总活跃月份数、2021 年活跃天数、2021 年试卷作答活跃天数、2021 年答题活跃天数,按照总活跃月份数、2021 年活跃天数降序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | act_month_total | act_days_2021 | act_days_2021_exam |
-| ---- | --------------- | ------------- | ------------------ |
-| 1006 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
-| 1001 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
-| 1005 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
-
-**解释**:6/7 级用户共有 5 个,其中 1006 在 202109、202108、202008 共 3 个月活跃过,2021 年活跃的日期有 20210907、20210804、20210803、20210802 共 4 天,2021 年在试卷作答区 20210907 活跃 1 天,在题目练习区活跃了 3 天。
-
-**思路:**
-
-这题的关键在于`CASE WHEN THEN`的使用,不然要写很多的`left join` 因为会产生很多的结果集。
-
-`CASE WHEN THEN`语句是一种条件表达式,用于在 SQL 中根据条件执行不同的操作或返回不同的结果。
-
-语法结构如下:
-
-```sql
-CASE
- WHEN condition1 THEN result1
- WHEN condition2 THEN result2
- ...
- ELSE result
-END
-```
-
-在这个结构中,可以根据需要添加多个`WHEN`子句,每个`WHEN`子句后面跟着一个条件(condition)和一个结果(result)。条件可以是任何逻辑表达式,如果满足条件,将返回对应的结果。
-
-最后的`ELSE`子句是可选的,用于指定当所有前面的条件都不满足时的默认返回结果。如果没有提供`ELSE`子句,则默认返回`NULL`。
-
-例如:
-
-```sql
-SELECT score,
- CASE
- WHEN score >= 90 THEN '优秀'
- WHEN score >= 80 THEN '良好'
- WHEN score >= 60 THEN '及格'
- ELSE '不及格'
- END AS grade
-FROM student_scores;
-```
-
-在上述示例中,根据学生成绩(score)的不同范围,使用 CASE WHEN THEN 语句返回相应的等级(grade)。如果成绩大于等于 90,则返回"优秀";如果成绩大于等于 80,则返回"良好";如果成绩大于等于 60,则返回"及格";否则返回"不及格"。
-
-那了解到了上述的用法之后,回过头看看该题,要求列出不同的活跃天数。
-
-```sql
-count(distinct act_month) as act_month_total,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021'then act_day end) as act_days_2021,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021' and tag='exam' then act_day end) as act_days_2021_exam,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021' and tag='question'then act_day end) as act_days_2021_question
-```
-
-这里的 tag 是先给标记,方便对查询进行区分,将考试和答题分开。
-
-找出试卷作答区的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- exam_id AS ans_id,
- start_time AS act_time,
- date_format( start_time, '%Y%m' ) AS act_month,
- date_format( start_time, '%Y%m%d' ) AS act_day,
- 'exam' AS tag
- FROM
- exam_record
-```
-
-紧接着就是答题作答区的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- question_id AS ans_id,
- submit_time AS act_time,
- date_format( submit_time, '%Y%m' ) AS act_month,
- date_format( submit_time, '%Y%m%d' ) AS act_day,
- 'question' AS tag
- FROM
- practice_record
-```
-
-最后将两个结果进行`UNION` 最后别忘了将结果进行排序 (这题有点类似于分治法的思想)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT user_info.uid,
- count(DISTINCT act_month) AS act_month_total,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021'
- AND tag = 'exam' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021_exam,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021'
- AND tag = 'question' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021_question
-FROM
- (SELECT UID,
- exam_id AS ans_id,
- start_time AS act_time,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS act_month,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') AS act_day,
- 'exam' AS tag
- FROM exam_record
- UNION ALL SELECT UID,
- question_id AS ans_id,
- submit_time AS act_time,
- date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m') AS act_month,
- date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m%d') AS act_day,
- 'question' AS tag
- FROM practice_record) total
-RIGHT JOIN user_info ON total.uid = user_info.uid
-WHERE user_info.LEVEL IN (6,
- 7)
-GROUP BY user_info.uid
-ORDER BY act_month_total DESC,
- act_days_2021 DESC
-```
-
-
+**Approach 1:** To find high-difficulty SQL papers, you need to join the `examination_info` table and find the high-difficulty courses. From `examination_info`, we know that the exam_id for high-difficulty SQL is 900
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
index 84f1a2b3c8c..8d60b4e8ecc 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
@@ -1,55 +1,55 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(4)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (4)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of the questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+For more difficult questions, you can decide whether to skip them based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 专用窗口函数
+## Specialized Window Functions
-MySQL 8.0 版本引入了窗口函数的支持,下面是 MySQL 中常见的窗口函数及其用法:
+MySQL 8.0 introduced support for window functions. Below are common window functions in MySQL and their usage:
-1. `ROW_NUMBER()`: 为查询结果集中的每一行分配一个唯一的整数值。
+1. `ROW_NUMBER()`: Assigns a unique integer value to each row in the result set.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS row_num
FROM table;
```
-2. `RANK()`: 计算每一行在排序结果中的排名。
+2. `RANK()`: Calculates the rank of each row in the sorted result.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY col1 DESC) AS ranking
FROM table;
```
-3. `DENSE_RANK()`: 计算每一行在排序结果中的排名,保留相同的排名。
+3. `DENSE_RANK()`: Calculates the rank of each row in the sorted result, preserving the same rank for ties.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY col1 DESC) AS ranking
FROM table;
```
-4. `NTILE(n)`: 将结果分成 n 个基本均匀的桶,并为每个桶分配一个标识号。
+4. `NTILE(n)`: Divides the result into n evenly distributed buckets and assigns an identifier to each bucket.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS bucket
FROM table;
```
-5. `SUM()`, `AVG()`,`COUNT()`, `MIN()`, `MAX()`: 这些聚合函数也可以与窗口函数结合使用,计算窗口内指定列的汇总、平均值、计数、最小值和最大值。
+5. `SUM()`, `AVG()`, `COUNT()`, `MIN()`, `MAX()`: These aggregate functions can also be used with window functions to calculate the sum, average, count, minimum, and maximum of specified columns within the window.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, SUM(col1) OVER () AS sum_col
FROM table;
```
-6. `LEAD()` 和 `LAG()`: LEAD 函数用于获取当前行之后的某个偏移量的行的值,而 LAG 函数用于获取当前行之前的某个偏移量的行的值。
+6. `LEAD()` and `LAG()`: The LEAD function is used to get the value of a row at a specified offset after the current row, while the LAG function is used to get the value of a row at a specified offset before the current row.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, LEAD(col1, 1) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS next_col1,
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ SELECT col1, col2, LEAD(col1, 1) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS next_col1,
FROM table;
```
-7. `FIRST_VALUE()` 和 `LAST_VALUE()`: FIRST_VALUE 函数用于获取窗口内指定列的第一个值,LAST_VALUE 函数用于获取窗口内指定列的最后一个值。
+7. `FIRST_VALUE()` and `LAST_VALUE()`: The FIRST_VALUE function retrieves the first value of a specified column within the window, while the LAST_VALUE function retrieves the last value of a specified column within the window.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, FIRST_VALUE(col2) OVER (PARTITION BY col1 ORDER BY col2) AS first_val,
@@ -65,768 +65,24 @@ SELECT col1, col2, FIRST_VALUE(col2) OVER (PARTITION BY col1 ORDER BY col2) AS f
FROM table;
```
-窗口函数通常需要配合 OVER 子句一起使用,用于定义窗口的大小、排序规则和分组方式。
+Window functions typically need to be used in conjunction with the OVER clause to define the size of the window, sorting rules, and grouping methods.
-### 每类试卷得分前三名
+### Top Three Scores for Each Exam Type
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
+There is an exam information table `examination_info` (`exam_id` Exam ID, `tag` Exam Category, `difficulty` Exam Difficulty, `duration` Exam Duration, `release_time` Release Time):
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
+| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
+| --- | ------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
+| 3 | 9003 | Algorithm | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 86 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1005 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到每类试卷得分的前 3 名,如果两人最大分数相同,选择最小分数大者,如果还相同,选择 uid 大者。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tid | uid | ranking |
-| ---- | ---- | ------- |
-| SQL | 1003 | 1 |
-| SQL | 1004 | 2 |
-| SQL | 1002 | 3 |
-| 算法 | 1005 | 1 |
-| 算法 | 1006 | 2 |
-| 算法 | 1003 | 3 |
-
-**解释**:有作答得分记录的试卷 tag 有 SQL 和算法,SQL 试卷用户 1001、1002、1003、1004 有作答得分,最高得分分别为 81、81、89、85,最低得分分别为 78、81、86、40,因此先按最高得分排名再按最低得分排名取前三为 1003、1004、1002。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- UID,
- ranking
-FROM
- (SELECT b.tag AS tag,
- a.uid AS UID,
- ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY b.tag
- ORDER BY b.tag,
- max(a.score) DESC,
- min(a.score) DESC,
- a.uid DESC) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
- GROUP BY b.tag,
- a.uid) t
-WHERE ranking <= 3
-```
-
-### 第二快/慢用时之差大于试卷时长一半的试卷(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:51:01 | 78 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:59:01 | 86 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:02:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到第二快和第二慢用时之差大于试卷时长的一半的试卷信息,按试卷 ID 降序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | duration | release_time |
-| ------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 9001 | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-
-**解释**:试卷 9001 被作答用时有 50 分钟、58 分钟、30 分 1 秒、19 分钟、10 分钟,第二快和第二慢用时之差为 50 分钟-19 分钟=31 分钟,试卷时长为 60 分钟,因此满足大于试卷时长一半的条件,输出试卷 ID、时长、发布时间。
-
-**思路:**
-
-第一步,找到每张试卷完成时间的顺序排名和倒序排名 也就是表 a;
-
-第二步,与通过试卷信息表 b 建立内连接,并根据试卷 id 分组,利用`having`筛选排名为第二个数据,将秒转化为分钟并进行比较,最后再根据试卷 id 倒序排序就行
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.exam_id,
- b.duration,
- b.release_time
-FROM
- (SELECT exam_id,
- row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) DESC) rn1,
- row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) ASC) rn2,
- timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) timex
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE score IS NOT NULL ) a
-INNER JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
-GROUP BY a.exam_id
-HAVING (max(IF (rn1 = 2, a.timex, 0))- max(IF (rn2 = 2, a.timex, 0)))/ 60 > b.duration / 2
-ORDER BY a.exam_id DESC
-```
-
-### 连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗(较难)
-
-**描述**
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:02 | 84 |
-| 2 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:11:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | 2021-09-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 10:01:01 | 2021-09-05 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 10:31:01 | 2021-09-05 10:51:01 | 81 |
-
-请计算在 2021 年至少有两天作答过试卷的人中,计算该年连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗 `days_window`,那么根据该年的历史规律他在 `days_window` 天里平均会做多少套试卷,按最大时间窗和平均做答试卷套数倒序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | days_window | avg_exam_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------- | ------------ |
-| 1006 | 6 | 2.57 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1006 分别在 20210901、20210906、20210907 作答过 3 次试卷,连续两次作答最大时间窗为 6 天(1 号到 6 号),他 1 号到 7 号这 7 天里共做了 3 张试卷,平均每天 3/7=0.428571 张,那么 6 天里平均会做 0.428571\*6=2.57 张试卷(保留两位小数);用户 1005 在 20210905 做了两张试卷,但是只有一天的作答记录,过滤掉。
-
-**思路:**
-
-上面这个解释中提示要对作答记录去重,千万别被骗了,不要去重!去重就通不过测试用例。注意限制时间是 2021 年;
-
-而且要注意时间差要+1 天;还要注意==没交卷也算在内==!!!! (反正感觉这题描述不清,出的不是很好)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- max(datediff(next_time, start_time)) + 1 AS days_window,
- round(count(start_time)/(datediff(max(start_time), min(start_time))+ 1) * (max(datediff(next_time, start_time))+ 1), 2) AS avg_exam_cnt
-FROM
- (SELECT UID,
- start_time,
- lead(start_time, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY start_time) AS next_time
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE YEAR (start_time) = '2021' ) a
-GROUP BY UID
-HAVING count(DISTINCT date(start_time)) > 1
-ORDER BY days_window DESC,
- avg_exam_cnt DESC
-```
-
-### 近三个月未完成为 0 的用户完成情况
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid`:用户 ID, `exam_id`:试卷 ID, `start_time`:开始作答时间, `submit_time`:交卷时间,为空的话则代表未完成, `score`:得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | 2021-09-06 10:21:02 | 84 |
-| 2 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-08-02 12:11:01 | 2021-08-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-06-06 10:01:01 | 2021-06-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-05-06 10:01:01 | 2021-05-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-05-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 10:31:01 | 2021-09-05 10:51:01 | 81 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 09:01:01 | 2021-08-01 09:51:11 | 78 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 09:01:01 | 2021-07-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | 2021-07-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 10 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到每个人近三个有试卷作答记录的月份中没有试卷是未完成状态的用户的试卷作答完成数,按试卷完成数和用户 ID 降序排名。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_complete_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------------- |
-| 1006 | 3 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1006 近三个有作答试卷的月份为 202109、202108、202106,作答试卷数为 3,全部完成;用户 1001 近三个有作答试卷的月份为 202109、202108、202107,作答试卷数为 5,完成试卷数为 4,因为有未完成试卷,故过滤掉。
-
-**思路:**
-
-1. `找到每个人近三个有试卷作答记录的月份中没有试卷是未完成状态的用户的试卷作答完成数`首先看这句话,肯定要先根据人进行分组
-2. 最近三个月,可以采用连续重复排名,倒序排列,排名<=3
-3. 统计作答数
-4. 拼装剩余条件
-5. 排序
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- count(score) exam_complete_cnt
-FROM
- (SELECT *, DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) dr
- FROM exam_record) t1
-WHERE dr <= 3
-GROUP BY UID
-HAVING count(dr)= count(score)
-ORDER BY exam_complete_cnt DESC,
- UID DESC
-```
-
-### 未完成率较高的 50%用户近三个月答卷情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3200 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 18:01:01 | 2020-01-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 13 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | | |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | | |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | | |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | | |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 14 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | | |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | | |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 17 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-05-05 18:01:01 | | |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-05-06 12:01:01 | | |
-
-请统计 SQL 试卷上未完成率较高的 50%用户中,6 级和 7 级用户在有试卷作答记录的近三个月中,每个月的答卷数目和完成数目。按用户 ID、月份升序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | start_month | total_cnt | complete_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------- | --------- | ------------ |
-| 1002 | 202002 | 3 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 202003 | 2 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 202005 | 2 | 1 |
-
-解释:各个用户对 SQL 试卷的未完成数、作答总数、未完成率如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | total_cnt | incomplete_rate |
-| ---- | -------------- | --------- | --------------- |
-| 1001 | 3 | 7 | 0.4286 |
-| 1002 | 4 | 8 | 0.5000 |
-| 1003 | 1 | 1 | 1.0000 |
-
-1001、1002、1003 分别排在 1.0、0.5、0.0 的位置,因此较高的 50%用户(排位<=0.5)为 1002、1003;
-
-1003 不是 6 级或 7 级;
-
-有试卷作答记录的近三个月为 202005、202003、202002;
-
-这三个月里 1002 的作答题数分别为 3、2、2,完成数目分别为 1、1、1。
-
-**思路:**
-
-注意点:这题注意求的是所有的答题次数和完成次数,而 sql 类别的试卷是限制未完成率排名,6, 7 级用户限制的是做题记录。
-
-先求出未完成率的排名
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- count(submit_time IS NULL
- OR NULL)/ count(start_time) AS num,
- PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
- ORDER BY count(submit_time IS NULL
- OR NULL)/ count(start_time)) AS ranking
-FROM exam_record
-LEFT JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
-WHERE tag = 'SQL'
-GROUP BY UID
-```
-
-再求出最近三个月的练习记录
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS month_d,
- submit_time,
- exam_id,
- dense_rank() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) AS ranking
-FROM exam_record
-LEFT JOIN user_info USING (UID)
-WHERE LEVEL IN (6,7)
-```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT t1.uid,
- t1.month_d,
- count(*) AS total_cnt,
- count(t1.submit_time) AS complete_cnt
-FROM-- 先求出未完成率的排名
-
- (SELECT UID,
- count(submit_time IS NULL OR NULL)/ count(start_time) AS num,
- PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
- ORDER BY count(submit_time IS NULL OR NULL)/ count(start_time)) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record
- LEFT JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- GROUP BY UID) t
-INNER JOIN
- (-- 再求出近三个月的练习记录
- SELECT UID,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS month_d,
- submit_time,
- exam_id,
- dense_rank() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record
- LEFT JOIN user_info USING (UID)
- WHERE LEVEL IN (6,7) ) t1 USING (UID)
-WHERE t1.ranking <= 3 AND t.ranking >= 0.5 -- 使用限制找到符合条件的记录
-
-GROUP BY t1.uid,
- t1.month_d
-ORDER BY t1.uid,
- t1.month_d
-```
-
-### 试卷完成数同比 2020 年的增长率及排名变化(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
+There is an exam record table `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Exam ID, `start_time` Start Time, `submit_time` Submit Time, `score` Score):
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-08-02 10:01:01 | 2020-08-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-04-01 18:01:01 | 2020-04-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-04-01 09:01:01 | 2020-04-01 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-03-02 19:01:01 | 2021-03-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 12:01:01 | 2021-05-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | | |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 18 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | | |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-01-20 10:01:01 | 2021-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-04-02 19:01:01 | 2021-04-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 15 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-01-01 18:01:01 | 2021-01-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1004 | 9004 | 2020-05-02 12:01:01 | 2020-05-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 14 | 1002 | 9004 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-
-请计算 2021 年上半年各类试卷的做完次数相比 2020 年上半年同期的增长率(百分比格式,保留 1 位小数),以及做完次数排名变化,按增长率和 21 年排名降序输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tag | exam_cnt_20 | exam_cnt_21 | growth_rate | exam_cnt_rank_20 | exam_cnt_rank_21 | rank_delta |
-| --- | ----------- | ----------- | ----------- | ---------------- | ---------------- | ---------- |
-| SQL | 3 | 2 | -33.3% | 1 | 2 | 1 |
-
-解释:2020 年上半年有 3 个 tag 有作答完成的记录,分别是 C++、SQL、PYTHON,它们被做完的次数分别是 3、3、2,做完次数排名为 1、1(并列)、3;
-
-2021 年上半年有 2 个 tag 有作答完成的记录,分别是算法、SQL,它们被做完的次数分别是 3、2,做完次数排名为 1、2;具体如下:
-
-| tag | start_year | exam_cnt | exam_cnt_rank |
-| ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------- |
-| C++ | 2020 | 3 | 1 |
-| SQL | 2020 | 3 | 1 |
-| PYTHON | 2020 | 2 | 3 |
-| 算法 | 2021 | 3 | 1 |
-| SQL | 2021 | 2 | 2 |
-
-因此能输出同比结果的 tag 只有 SQL,从 2020 到 2021 年,做完次数 3=>2,减少 33.3%(保留 1 位小数);排名 1=>2,后退 1 名。
-
-**思路:**
-
-本题难点在于长整型的数据类型要求不能有负号产生,用 cast 函数转换数据类型为 signed。
-
-以及用到的`增长率计算公式:(exam_cnt_21-exam_cnt_20)/exam_cnt_20`
-
-做完次数排名变化(2021 年和 2020 年比排名升了或者降了多少)
-
-计算公式:`exam_cnt_rank_21 - exam_cnt_rank_20`
-
-在 MySQL 中,`CAST()` 函数用于将一个表达式的数据类型转换为另一个数据类型。它的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-CAST(expression AS data_type)
-
--- 将一个字符串转换成整数
-SELECT CAST('123' AS INT);
-```
-
-示例就不一一举例了,这个函数很简单
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- tag,
- exam_cnt_20,
- exam_cnt_21,
- concat(
- round(
- 100 * (exam_cnt_21 - exam_cnt_20) / exam_cnt_20,
- 1
- ),
- '%'
- ) AS growth_rate,
- exam_cnt_rank_20,
- exam_cnt_rank_21,
- cast(exam_cnt_rank_21 AS signed) - cast(exam_cnt_rank_20 AS signed) AS rank_delta
-FROM
- (
- #2020年、2021年上半年各类试卷的做完次数和做完次数排名
- SELECT
- tag,
- count(
- IF (
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') BETWEEN '20200101'
- AND '20200630',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) AS exam_cnt_20,
- count(
- IF (
- substring(start_time, 1, 10) BETWEEN '2021-01-01'
- AND '2021-06-30',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) AS exam_cnt_21,
- rank() over (
- ORDER BY
- count(
- IF (
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') BETWEEN '20200101'
- AND '20200630',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) DESC
- ) AS exam_cnt_rank_20,
- rank() over (
- ORDER BY
- count(
- IF (
- substring(start_time, 1, 10) BETWEEN '2021-01-01'
- AND '2021-06-30',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) DESC
- ) AS exam_cnt_rank_21
- FROM
- examination_info
- JOIN exam_record USING (exam_id)
- WHERE
- submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY
- tag
- ) main
-WHERE
- exam_cnt_21 * exam_cnt_20 <> 0
-ORDER BY
- growth_rate DESC,
- exam_cnt_rank_21 DESC
-```
-
-## 聚合窗口函数
-
-### 对试卷得分做 min-max 归一化
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 19:01:01 | 2020-01-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9004 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9005 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-在物理学及统计学数据计算时,有个概念叫 min-max 标准化,也被称为离差标准化,是对原始数据的线性变换,使结果值映射到[0 - 1]之间。
-
-转换函数为:
-
-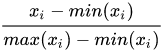
-
-请你将用户作答高难度试卷的得分在每份试卷作答记录内执行 min-max 归一化后缩放到[0,100]区间,并输出用户 ID、试卷 ID、归一化后分数平均值;最后按照试卷 ID 升序、归一化分数降序输出。(注:得分区间默认为[0,100],如果某个试卷作答记录中只有一个得分,那么无需使用公式,归一化并缩放后分数仍为原分数)。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | avg_new_score |
-| ---- | ------- | ------------- |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 98 |
-| 1003 | 9001 | 0 |
-| 1002 | 9002 | 88 |
-| 1003 | 9002 | 75 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 9002 | 0 |
-
-解释:高难度试卷有 9001、9002、9003;
-
-作答了 9001 的记录有 3 条,分数分别为 68、89、90,按给定公式归一化后分数为:0、95、100,而后两个得分都是用户 1001 作答的,因此用户 1001 对试卷 9001 的新得分为(95+100)/2≈98(只保留整数部分),用户 1003 对于试卷 9001 的新得分为 0。最后结果按照试卷 ID 升序、归一化分数降序输出。
-
-**思路:**
-
-注意点:
-
-1. 将高难度的试卷,按每类试卷的得分,利用 max/min (col) over()窗口函数求得各组内最大最小值,然后进行归一化公式计算,缩放区间为[0,100],即 min_max\*100
-2. 若某类试卷只有一个得分,则无需使用归一化公式,因只有一个分 max_score=min_score,score,公式后结果可能会变成 0。
-3. 最后结果按 uid、exam_id 分组求归一化后均值,score 为 NULL 的要过滤掉。
-
-最后就是仔细看上面公式 (说实话,这题看起来就很绕)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- exam_id,
- round(sum(min_max) / count(score), 0) AS avg_new_score
-FROM
- (
- SELECT
- *,
- IF (
- max_score = min_score,
- score,
- (score - min_score) / (max_score - min_score) * 100
- ) AS min_max
- FROM
- (
- SELECT
- uid,
- a.exam_id,
- score,
- max(score) over (PARTITION BY a.exam_id) AS max_score,
- min(score) over (PARTITION BY a.exam_id) AS min_score
- FROM
- exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN examination_info b USING (exam_id)
- WHERE
- difficulty = 'hard'
- ) t
- WHERE
- score IS NOT NULL
- ) t1
-GROUP BY
- uid,
- exam_id
-ORDER BY
- exam_id ASC,
- avg_new_score DESC;
-```
-
-### 每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数
-
-**描述:**
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-请输出每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数。
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | start_month | month_cnt | cum_exam_cnt |
-| ------- | ----------- | --------- | ------------ |
-| 9001 | 202001 | 2 | 2 |
-| 9001 | 202002 | 1 | 3 |
-| 9001 | 202003 | 3 | 6 |
-| 9001 | 202005 | 1 | 7 |
-| 9002 | 202001 | 1 | 1 |
-| 9002 | 202002 | 3 | 4 |
-| 9002 | 202003 | 1 | 5 |
-
-解释:试卷 9001 在 202001、202002、202003、202005 共 4 个月有被作答记录,每个月被作答数分别为 2、1、3、1,截止当月累积作答总数为 2、3、6、7。
-
-**思路:**
-
-这题就两个关键点:统计截止当月的作答总数、输出每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数
-
-这个是关键`**sum(count(*)) over(partition by exam_id order by date_format(start_time,'%Y%m'))**`
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT exam_id,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS start_month,
- count(*) AS month_cnt,
- sum(count(*)) OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m')) AS cum_exam_cnt
-FROM exam_record
-GROUP BY exam_id,
- start_month
-```
-
-### 每月及截止当月的答题情况(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-请输出自从有用户作答记录以来,每月的试卷作答记录中月活用户数、新增用户数、截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数。结果按月份升序输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| start_month | mau | month_add_uv | max_month_add_uv | cum_sum_uv |
-| ----------- | --- | ------------ | ---------------- | ---------- |
-| 202001 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
-| 202002 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
-| 202003 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
-| 202005 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
-
-| month | 1001 | 1002 | 1003 | 1004 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 202001 | 1 | 1 | | |
-| 202002 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-| 202003 | 1 | | 1 | 1 |
-| 202005 | | 1 | | |
-
-由上述矩阵可以看出,2020 年 1 月有 2 个用户活跃(mau=2),当月新增用户数为 2;
-
-2020 年 2 月有 4 个用户活跃,当月新增用户数为 2,最大单月新增用户数为 2,当前累积用户数为 4。
-
-**思路:**
-
-难点:
-
-1.如何求每月新增用户
-
-2.截至当月的答题情况
-
-大致流程:
-
-(1)统计每个人的首次登陆月份 `min()`
-
-(2)统计每月的月活和新增用户数:先得到每个人的首次登陆月份,再对首次登陆月份分组求和是该月份的新增人数
-
-(3)统计截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数 ,最终按照按月份升序输出
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
--- 截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数,按月份升序输出
-SELECT
- start_month,
- mau,
- month_add_uv,
- max( month_add_uv ) over ( ORDER BY start_month ),
- sum( month_add_uv ) over ( ORDER BY start_month )
-FROM
- (
- -- 统计每月的月活和新增用户数
- SELECT
- date_format( a.start_time, '%Y%m' ) AS start_month,
- count( DISTINCT a.uid ) AS mau,
- count( DISTINCT b.uid ) AS month_add_uv
- FROM
- exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN (
- -- 统计每个人的首次登陆月份
- SELECT uid, min( date_format( start_time, '%Y%m' )) AS first_month FROM exam_record GROUP BY uid ) b ON date_format( a.start_time, '%Y%m' ) = b.first_month
- GROUP BY
- start_month
- ) main
-ORDER BY
- start_month
-```
-
-
+| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
+| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
+| 3 | 1002 | 900 | | | |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
index c20af2cad39..7475e377940 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
@@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(5)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (5)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+Difficult or challenging questions can be skipped based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 空值处理
+## Handling Null Values
-### 统计有未完成状态的试卷的未完成数和未完成率
+### Count the number of unfinished exams and the unfinished rate for exams with an unfinished status
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),数据如下:
+There is an exam record table `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Exam ID, `start_time` Start time, `submit_time` Submission time, `score` Score), with the following data:
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
@@ -24,21 +24,21 @@ tag:
| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | 2021-05-02 10:30:01 | 81 |
| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-请统计有未完成状态的试卷的未完成数 incomplete_cnt 和未完成率 incomplete_rate。由示例数据结果输出如下:
+Please count the number of unfinished exams `incomplete_cnt` and the unfinished rate `incomplete_rate` for exams with an unfinished status. The output based on the example data is as follows:
| exam_id | incomplete_cnt | complete_rate |
| ------- | -------------- | ------------- |
| 9001 | 1 | 0.333 |
-解释:试卷 9001 有 3 次被作答的记录,其中两次完成,1 次未完成,因此未完成数为 1,未完成率为 0.333(保留 3 位小数)
+Explanation: Exam 9001 has 3 records, of which two are completed and one is unfinished, so the number of unfinished exams is 1, and the unfinished rate is 0.333 (retaining 3 decimal places).
-**思路**:
+**Thought Process**:
-这题只需要注意一个是有条件限制,一个是没条件限制的;要么分别查询条件,然后合并;要么直接在 select 里面进行条件判断。
+This question only requires attention to one condition with restrictions and one without; you can either query the conditions separately and then merge them, or directly perform conditional checks in the select statement.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
-写法 1:
+Method 1:
```sql
SELECT exam_id,
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ GROUP BY exam_id
HAVING incomplete_cnt <> 0
```
-写法 2:
+Method 2:
```sql
SELECT exam_id,
@@ -60,954 +60,22 @@ GROUP BY exam_id
HAVING incomplete_cnt <> 0
```
-两种写法都可以,只有中间的写法不一样,一个是对符合条件的才`COUNT`,一个是直接上`IF`,后者更为直观,最后这个`having`解释一下, 无论是 `complete_rate` 还是 `incomplete_cnt`,只要不为 0 即可,不为 0 就意味着有未完成的。
+Both methods are valid; only the middle part differs, one counts only those that meet the condition, while the other uses `IF` directly, which is more intuitive. Finally, this `HAVING` clause explains that as long as either `complete_rate` or `incomplete_cnt` is not 0, it means there are unfinished exams.
-### 0 级用户高难度试卷的平均用时和平均得分
+### Average time and average score for level 0 users on difficult exams
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间),数据如下:
+There is a user information table `user_info` (`uid` User ID, `nick_name` Nickname, `achievement` Achievement value, `level` Level, `job` Job direction, `register_time` Registration time), with the following data:
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 10 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
+| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | --------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 1001 | Niuke 1 | 10 | 0 | Algorithm | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 1002 | Niuke 2 | 2100 | 6 | Algorithm | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间),数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9004 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-
-请输出每个 0 级用户所有的高难度试卷考试平均用时和平均得分,未完成的默认试卷最大考试时长和 0 分处理。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | avg_score | avg_time_took |
-| ---- | --------- | ------------- |
-| 1001 | 33 | 36.7 |
-
-解释:0 级用户有 1001,高难度试卷有 9001,1001 作答 9001 的记录有 3 条,分别用时 20 分钟、未完成(试卷时长 60 分钟)、30 分钟(未满 31 分钟),分别得分为 80 分、未完成(0 分处理)、20 分。因此他的平均用时为 110/3=36.7(保留一位小数),平均得分为 33 分(取整)
-
-**思路**:这题用`IF`是判断的最方便的,因为涉及到 NULL 值的判断。当然 `case when`也可以,大同小异。这题的难点就在于空值的处理,其他的这些查询条件什么的,我相信难不倒大家。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- round(avg(new_socre)) AS avg_score,
- round(avg(time_diff), 1) AS avg_time_took
-FROM
- (SELECT er.uid,
- IF (er.submit_time IS NOT NULL, TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time), ef.duration) AS time_diff,
- IF (er.submit_time IS NOT NULL,er.score,0) AS new_socre
- FROM exam_record er
- LEFT JOIN user_info uf ON er.uid = uf.uid
- LEFT JOIN examination_info ef ON er.exam_id = ef.exam_id
- WHERE uf.LEVEL = 0 AND ef.difficulty = 'hard' ) t
-GROUP BY UID
-ORDER BY UID
-```
-
-## 高级条件语句
-
-### 筛选限定昵称成就值活跃日期的用户(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 1000 | 2 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 进击的 3 号 | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 3000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 13 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | 2021-09-06 12:21:01 | 80 |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 18 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-08-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-| 15 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-
-题目练习记录表 `practice_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `question_id` 题目 ID, `submit_time` 提交时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-09-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请找到昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾、成就值在 1200~2500 之间,且最近一次活跃(答题或作答试卷)在 2021 年 9 月的用户信息。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name | achievement |
-| ---- | --------- | ----------- |
-| 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 |
-
-**解释**:昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾且成就值在 1200~2500 之间的有 1002、1004;
-
-1002 最近一次试卷区活跃为 2021 年 9 月,最近一次题目区活跃为 2021 年 9 月;1004 最近一次试卷区活跃为 2021 年 8 月,题目区未活跃。
-
-因此最终满足条件的只有 1002。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先根据条件列出主要查询语句
-
-昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾: `nick_name LIKE "牛客%号"`
-
-成就值在 1200~2500 之间:`achievement BETWEEN 1200 AND 2500`
-
-第三个条件因为限定了为 9 月,所以直接写就行:`( date_format( record.submit_time, '%Y%m' )= 202109 OR date_format( pr.submit_time, '%Y%m' )= 202109 )`
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT u_info.uid,
- u_info.nick_name,
- u_info.achievement
-FROM user_info u_info
-LEFT JOIN exam_record record ON record.uid = u_info.uid
-LEFT JOIN practice_record pr ON u_info.uid = pr.uid
-WHERE u_info.nick_name LIKE "牛客%号"
- AND u_info.achievement BETWEEN 1200
- AND 2500
- AND (date_format(record.submit_time, '%Y%m')= 202109
- OR date_format(pr.submit_time, '%Y%m')= 202109)
-GROUP BY u_info.uid
-```
-
-### 筛选昵称规则和试卷规则的作答记录(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 1900 | 2 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
+There is an exam information table `examination_info` (`exam_id` Exam ID, `tag` Exam category, `difficulty` Exam difficulty, `duration` Exam duration, `release_time` Release time), with the following data:
| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
| --- | ------- | --- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | c# | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | 2021-09-06 12:21:01 | 80 |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 18 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 13 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-08-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-| 15 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-09-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-
-找到昵称以"牛客"+纯数字+"号"或者纯数字组成的用户对于字母 c 开头的试卷类别(如 C,C++,c#等)的已完成的试卷 ID 和平均得分,按用户 ID、平均分升序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | avg_score |
-| ---- | ------- | --------- |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 81 |
-| 1002 | 9002 | 85 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 84 |
-| 1006 | 9001 | 84 |
-
-解释:昵称满足条件的用户有 1002、1004、1005、1006;
-
-c 开头的试卷有 9001、9002;
-
-满足上述条件的作答记录中,1002 完成 9001 的得分有 81、80,平均分为 81(80.5 取整四舍五入得 81);
-
-1002 完成 9002 的得分有 90、82、83,平均分为 85;
-
-**思路**:
-
-还是老样子,既然给出了条件,就先把各个条件先写出来
-
-找到昵称以"牛客"+纯数字+"号"或者纯数字组成的用户: 我最开始是这么写的:`nick_name LIKE '牛客%号' OR nick_name REGEXP '^[0-9]+$'`,如果表中有个 “牛客 H 号” ,那也能通过。
-
-所以这里还得用正则: `nick_name LIKE '^牛客[0-9]+号'`
-
-对于字母 c 开头的试卷类别: `e_info.tag LIKE 'c%'` 或者 `tag regexp '^c|^C'` 第一个也能匹配到大写 C
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- exam_id,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 0) avg_score
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE UID IN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM user_info
- WHERE nick_name RLIKE "^牛客[0-9]+号 $"
- OR nick_name RLIKE "^[0-9]+$")
- AND exam_id IN
- (SELECT exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag RLIKE "^[cC]")
- AND score IS NOT NULL
-GROUP BY UID,exam_id
-ORDER BY UID,avg_score;
-```
-
-### 根据指定记录是否存在输出不同情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 进击的 3 号 | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-03 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 99 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 9 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请你筛选表中的数据,当有任意一个 0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2 时,输出每个 0 级用户的试卷未完成数和未完成率(保留 3 位小数);若不存在这样的用户,则输出所有有作答记录的用户的这两个指标。结果按未完成率升序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | incomplete_rate |
-| ---- | -------------- | --------------- |
-| 1004 | 0 | 0.000 |
-| 1003 | 1 | 0.500 |
-| 1001 | 4 | 0.667 |
-
-**解释**:0 级用户有 1001、1003、1004;他们作答试卷数和未完成数分别为:6:4、2:1、0:0;
-
-存在 1001 这个 0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2,因此输出这三个用户的未完成数和未完成率(1004 未作答过试卷,未完成率默认填 0,保留 3 位小数后是 0.000);
-
-结果按照未完成率升序排序。
-
-附:如果 1001 不满足『未完成试卷数大于 2』,则需要输出 1001、1002、1003 的这两个指标,因为试卷作答记录表里只有这三个用户的作答记录。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先把可能满足条件**“0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2”**的 SQL 写出来
-
-```sql
-SELECT ui.uid UID
-FROM user_info ui
-LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
-WHERE ui.uid IN
- (SELECT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 )
-GROUP BY ui.uid
-HAVING sum(IF(er.submit_time IS NULL, 1, 0)) > 2
-```
-
-然后再分别写出两种情况的 SQL 查询语句:
-
-情况 1. 查询存在条件要求的 0 级用户的试卷未完成率
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- tmp1.uid uid,
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 )) incomplete_cnt,
- round(
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 ))/ count( tmp1.uid ),
- 3
- ) incomplete_rate
-FROM
- (
- SELECT DISTINCT
- ui.uid
- FROM
- user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE
- er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0
- ) tmp1
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON tmp1.uid = er.uid
-GROUP BY
- tmp1.uid
-ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate
-```
-
-情况 2. 查询不存在条件要求时所有有作答记录的 yong 用户的试卷未完成率
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- ui.uid uid,
- sum( CASE WHEN er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1 ELSE 0 END ) incomplete_cnt,
- round(
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 ))/ count( ui.uid ),
- 3
- ) incomplete_rate
-FROM
- user_info ui
- JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
-GROUP BY
- ui.uid
-ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate
-```
-
-拼在一起,就是答案
-
-```sql
-WITH host_user AS
- (SELECT ui.uid UID
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE ui.uid IN
- (SELECT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 )
- GROUP BY ui.uid
- HAVING sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL, 1, 0))> 2),
- tt1 AS
- (SELECT tmp1.uid UID,
- sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0)) incomplete_cnt,
- round(sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0))/ count(tmp1.uid), 3) incomplete_rate
- FROM
- (SELECT DISTINCT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 ) tmp1
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON tmp1.uid = er.uid
- GROUP BY tmp1.uid
- ORDER BY incomplete_rate),
- tt2 AS
- (SELECT ui.uid UID,
- sum(CASE
- WHEN er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1
- ELSE 0
- END) incomplete_cnt,
- round(sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0))/ count(ui.uid), 3) incomplete_rate
- FROM user_info ui
- JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- GROUP BY ui.uid
- ORDER BY incomplete_rate)
- (SELECT tt1.*
- FROM tt1
- LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM host_user) t1 ON 1 = 1
- WHERE t1.uid IS NOT NULL )
-UNION ALL
- (SELECT tt2.*
- FROM tt2
- LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM host_user) t2 ON 1 = 1
- WHERE t2.uid IS NULL)
-```
-
-V2 版本(根据上面做出的改进,答案缩短了,逻辑更强):
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- ui.uid,
- SUM(
- IF
- ( start_time IS NOT NULL AND score IS NULL, 1, 0 )) AS incomplete_cnt,#3.试卷未完成数
- ROUND( AVG( IF ( start_time IS NOT NULL AND score IS NULL, 1, 0 )), 3 ) AS incomplete_rate #4.未完成率
-
-FROM
- user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record USING ( uid )
-WHERE
-CASE
-
- WHEN (#1.当有任意一个0级用户未完成试卷数大于2时
- SELECT
- MAX( lv0_incom_cnt )
- FROM
- (
- SELECT
- SUM(
- IF
- ( score IS NULL, 1, 0 )) AS lv0_incom_cnt
- FROM
- user_info
- JOIN exam_record USING ( uid )
- WHERE
- LEVEL = 0
- GROUP BY
- uid
- ) table1
- )> 2 THEN
- uid IN ( #1.1找出每个0级用户
- SELECT uid FROM user_info WHERE LEVEL = 0 ) ELSE uid IN ( #2.若不存在这样的用户,找出有作答记录的用户
- SELECT DISTINCT uid FROM exam_record )
- END
- GROUP BY
- ui.uid
- ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate #5.结果按未完成率升序排序
-```
-
-### 各用户等级的不同得分表现占比(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-03 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:41:01 | 76 |
-
-为了得到用户试卷作答的定性表现,我们将试卷得分按分界点[90,75,60]分为优良中差四个得分等级(分界点划分到左区间),请统计不同用户等级的人在完成过的试卷中各得分等级占比(结果保留 3 位小数),未完成过试卷的用户无需输出,结果按用户等级降序、占比降序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| level | score_grade | ratio |
-| ----- | ----------- | ----- |
-| 3 | 良 | 0.667 |
-| 3 | 优 | 0.333 |
-| 0 | 良 | 0.500 |
-| 0 | 中 | 0.167 |
-| 0 | 优 | 0.167 |
-| 0 | 差 | 0.167 |
-
-解释:完成过试卷的用户有 1001、1002;完成了的试卷对应的用户等级和分数等级如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | score | level | score_grade |
-| ---- | ------- | ----- | ----- | ----------- |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 80 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 75 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 60 | 0 | 中 |
-| 1001 | 9003 | 90 | 0 | 优 |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 20 | 0 | 差 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 89 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 99 | 3 | 优 |
-| 1002 | 9003 | 82 | 3 | 良 |
-| 1002 | 9003 | 76 | 3 | 良 |
-
-因此 0 级用户(只有 1001)的各分数等级比例为:优 1/6,良 1/6,中 1/6,差 3/6;3 级用户(只有 1002)各分数等级比例为:优 1/3,良 2/3。结果保留 3 位小数。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先把 **“将试卷得分按分界点[90,75,60]分为优良中差四个得分等级”**这个条件写出来,这里可以用到`case when`
-
-```sql
-CASE
- WHEN a.score >= 90 THEN
- '优'
- WHEN a.score < 90 AND a.score >= 75 THEN
- '良'
- WHEN a.score < 75 AND a.score >= 60 THEN
- '中' ELSE '差'
-END
-```
-
-这题的关键点就在于这,其他剩下的就是条件拼接了
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.LEVEL,
- a.score_grade,
- ROUND(a.cur_count / b.total_num, 3) AS ratio
-FROM
- (SELECT b.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- (CASE
- WHEN a.score >= 90 THEN '优'
- WHEN a.score < 90
- AND a.score >= 75 THEN '良'
- WHEN a.score < 75
- AND a.score >= 60 THEN '中'
- ELSE '差'
- END) AS score_grade,
- count(1) AS cur_count
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN user_info b ON a.uid = b.uid
- WHERE a.submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY b.LEVEL,
- score_grade) a
-LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT b.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- count(b.LEVEL) AS total_num
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN user_info b ON a.uid = b.uid
- WHERE a.submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY b.LEVEL) b ON a.LEVEL = b.LEVEL
-ORDER BY a.LEVEL DESC,
- ratio DESC
-```
-
-## 限量查询
-
-### 注册时间最早的三个人
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 4000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-11-01 10:00:00 |
-
-请从中找到注册时间最早的 3 个人。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name | register_time |
-| ---- | ------------ | ------------------- |
-| 1001 | 牛客 1 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-| 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-
-解释:按注册时间排序后选取前三名,输出其用户 ID、昵称、注册时间。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT uid, nick_name, register_time
- FROM user_info
- ORDER BY register_time
- LIMIT 3
-```
-
-### 注册当天就完成了试卷的名单第三页(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 4000 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 7 | 1007 | 牛客 7 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 8 | 1008 | 牛客 8 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 9 | 1009 | 牛客 9 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 10 | 1010 | 牛客 10 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 11 | 1011 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 examination_info(exam_id 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, difficulty 试卷难度, duration 考试时长, release_time 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 19:01:01 | 2020-01-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1008 | 9003 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1008 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 11 | 1009 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 12 | 1010 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | 2020-01-02 12:41:01 | 76 |
-| 13 | 1011 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-
-
-找到求职方向为算法工程师,且注册当天就完成了算法类试卷的人,按参加过的所有考试最高得分排名。排名榜很长,我们将采用分页展示,每页 3 条,现在需要你取出第 3 页(页码从 1 开始)的人的信息。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | level | register_time | max_score |
-| ---- | ----- | ------------------- | --------- |
-| 1010 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 76 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 75 |
-| 1004 | 0 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 | 60 |
-
-解释:除了 1011 其他用户的求职方向都为算法工程师;算法类试卷有 9001 和 9002,11 个用户注册当天都完成了算法类试卷;计算他们的所有考试最大分时,只有 1002 和 1008 完成了两次考试,其他人只完成了一场考试,1002 两场考试最高分为 81,1008 最高分为 99。
-
-按最高分排名如下:
-
-| uid | level | register_time | max_score |
-| ---- | ----- | ------------------- | --------- |
-| 1008 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 99 |
-| 1005 | 7 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 90 |
-| 1007 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 89 |
-| 1002 | 3 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 83 |
-| 1009 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 82 |
-| 1001 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 80 |
-| 1010 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 76 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 75 |
-| 1004 | 0 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 | 60 |
-| 1006 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 20 |
-
-每页 3 条,第三页也就是第 7~9 条,返回 1010、1003、1004 的行记录即可。
-
-**思路**:
-
-1. 每页三条,即需要取出第三页的人的信息,要用到`limit`
-
-2. 统计求职方向为算法工程师且注册当天就完成了算法类试卷的人的**信息和每次记录的得分**,先求满足条件的用户,后用 left join 做连接查找信息和每次记录的得分
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT t1.uid,
- LEVEL,
- register_time,
- max(score) AS max_score
-FROM exam_record t
-JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
-JOIN user_info t1 ON t.uid = t1.uid
-AND date(t.submit_time) = date(t1.register_time)
-WHERE job = '算法'
- AND tag = '算法'
-GROUP BY t1.uid,
- LEVEL,
- register_time
-ORDER BY max_score DESC
-LIMIT 6,3
-```
-
-## 文本转换函数
-
-### 修复串列了的记录
-
-**描述**:现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | -------------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | 算法,medium,80 | | 0 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-录题同学有一次手误将部分记录的试题类别 tag、难度、时长同时录入到了 tag 字段,请帮忙找出这些录错了的记录,并拆分后按正确的列类型输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration |
-| ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- |
-| 9004 | 算法 | medium | 80 |
-
-**思路**:
-
-先来学习下本题要用到的函数
-
-`SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数用于提取字符串中指定分隔符的部分。它接受三个参数:原始字符串、分隔符和指定要返回的部分的数量。
-
-以下是 `SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数的语法:
-
-```sql
-SUBSTRING_INDEX(str, delimiter, count)
-```
-
-- `str`:要进行分割的原始字符串。
-- `delimiter`:用作分割的字符串或字符。
-- `count`:指定要返回的部分的数量。
- - 如果 `count` 大于 0,则返回从左边开始的前 `count` 个部分(以分隔符为界)。
- - 如果 `count` 小于 0,则返回从右边开始的前 `count` 个部分(以分隔符为界),即从右侧向左计数。
-
-下面是一些示例,演示了 `SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数的使用:
-
-1. 提取字符串中的第一个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', 1);
- -- 输出结果:'apple'
- ```
-
-2. 提取字符串中的最后一个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', -1);
- -- 输出结果:'cherry'
- ```
-
-3. 提取字符串中的前两个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', 2);
- -- 输出结果:'apple,banana'
- ```
-
-4. 提取字符串中的最后两个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', -2);
- -- 输出结果:'banana,cherry'
- ```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- exam_id,
- substring_index( tag, ',', 1 ) tag,
- substring_index( substring_index( tag, ',', 2 ), ',',- 1 ) difficulty,
- substring_index( tag, ',',- 1 ) duration
-FROM
- examination_info
-WHERE
- difficulty = ''
-```
-
-### 对过长的昵称截取处理
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ---------------------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5678901234 号 | 4000 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 67890123456789 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-
-有的用户的昵称特别长,在一些展示场景会导致样式混乱,因此需要将特别长的昵称转换一下再输出,请输出字符数大于 10 的用户信息,对于字符数大于 13 的用户输出前 10 个字符然后加上三个点号:『...』。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name |
-| ---- | ------------------ |
-| 1005 | 牛客 5678901234 号 |
-| 1006 | 牛客 67890123... |
-
-解释:字符数大于 10 的用户有 1005 和 1006,长度分别为 13、17;因此需要对 1006 的昵称截断输出。
-
-**思路**:
-
-这题涉及到字符的计算,要计算字符串的字符数(即字符串的长度),可以使用 `LENGTH` 函数或 `CHAR_LENGTH` 函数。这两个函数的区别在于对待多字节字符的方式。
-
-1. `LENGTH` 函数:它返回给定字符串的字节数。对于包含多字节字符的字符串,每个字符都会被当作一个字节来计算。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-SELECT LENGTH('你好'); -- 输出结果:6,因为 '你好' 中的每个汉字每个占3个字节
-```
-
-1. `CHAR_LENGTH` 函数:它返回给定字符串的字符数。对于包含多字节字符的字符串,每个字符会被当作一个字符来计算。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-SELECT CHAR_LENGTH('你好'); -- 输出结果:2,因为 '你好' 中有两个字符,即两个汉字
-```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
-CASE
-
- WHEN CHAR_LENGTH( nick_name ) > 13 THEN
- CONCAT( SUBSTR( nick_name, 1, 10 ), '...' ) ELSE nick_name
- END AS nick_name
-FROM
- user_info
-WHERE
- CHAR_LENGTH( nick_name ) > 10
-GROUP BY
- uid;
-```
-
-### 大小写混乱时的筛选统计(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | sql | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 9005 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 9006 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 7 | 9007 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 8 | 9008 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 9 | 9009 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 10 | 9010 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答信息表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1007 | 9003 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1008 | 9004 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1008 | 9001 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 11 | 1009 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1010 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1010 | 9001 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-试卷的类别 tag 可能出现大小写混乱的情况,请先筛选出试卷作答数小于 3 的类别 tag,统计将其转换为大写后对应的原本试卷作答数。
-
-如果转换后 tag 并没有发生变化,不输出该条结果。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tag | answer_cnt |
-| --- | ---------- |
-| C++ | 6 |
-
-解释:被作答过的试卷有 9001、9002、9003、9004,他们的 tag 和被作答次数如下:
-
-| exam_id | tag | answer_cnt |
-| ------- | ---- | ---------- |
-| 9001 | 算法 | 4 |
-| 9002 | C++ | 6 |
-| 9003 | c++ | 2 |
-| 9004 | sql | 2 |
-
-作答次数小于 3 的 tag 有 c++和 sql,而转为大写后只有 C++本来就有作答数,于是输出 c++转化大写后的作答次数为 6。
-
-**思路**:
-
-首先,这题有点混乱,9004 根据示例数据查出来只有 1 次,这里显示有 2 次。
-
-先看一下大小写转换函数:
-
-1.`UPPER(s)`或`UCASE(s)`函数可以将字符串 s 中的字母字符全部转换成大写字母;
-
-2.`LOWER(s)`或者`LCASE(s)`函数可以将字符串 s 中的字母字符全部转换成小写字母。
-
-难点在于相同表做连接要查询不同的值
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-WITH a AS
- (SELECT tag,
- COUNT(start_time) AS answer_cnt
- FROM exam_record er
- JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
- GROUP BY tag)
-SELECT a.tag,
- b.answer_cnt
-FROM a
-INNER JOIN a AS b ON UPPER(a.tag)= b.tag #a小写 b大写
-AND a.tag != b.tag
-WHERE a.answer_cnt < 3;
-```
-
-
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-01-01 |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
index cff0b931495..c11eadd7bd9 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
@@ -1,1212 +1,100 @@
---
-title: SQL语法基础知识总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Basic SQL Syntax
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 本文整理完善自下面这两份资料:
+> This article is organized and improved based on the following two resources:
>
-> - [SQL 语法速成手册](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903790571700231)
-> - [MySQL 超全教程](https://www.begtut.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html)
+> - [SQL Syntax Quick Reference](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903790571700231)
+> - [Comprehensive MySQL Tutorial](https://www.begtut.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html)
-## 基本概念
+## Basic Concepts
-### 数据库术语
+### Database Terminology
-- `数据库(database)` - 保存有组织的数据的容器(通常是一个文件或一组文件)。
-- `数据表(table)` - 某种特定类型数据的结构化清单。
-- `模式(schema)` - 关于数据库和表的布局及特性的信息。模式定义了数据在表中如何存储,包含存储什么样的数据,数据如何分解,各部分信息如何命名等信息。数据库和表都有模式。
-- `列(column)` - 表中的一个字段。所有表都是由一个或多个列组成的。
-- `行(row)` - 表中的一个记录。
-- `主键(primary key)` - 一列(或一组列),其值能够唯一标识表中每一行。
+- `Database` - A container for storing organized data (usually a file or a set of files).
+- `Table` - A structured list of a specific type of data.
+- `Schema` - Information about the layout and characteristics of the database and tables. The schema defines how data is stored in tables, what types of data are stored, how data is decomposed, and how parts of the information are named. Both databases and tables have schemas.
+- `Column` - A field in a table. All tables consist of one or more columns.
+- `Row` - A record in a table.
+- `Primary Key` - A column (or a set of columns) whose values uniquely identify each row in the table.
-### SQL 语法
+### SQL Syntax
-SQL(Structured Query Language),标准 SQL 由 ANSI 标准委员会管理,从而称为 ANSI SQL。各个 DBMS 都有自己的实现,如 PL/SQL、Transact-SQL 等。
+SQL (Structured Query Language) is managed by the ANSI standards committee, hence it is referred to as ANSI SQL. Each DBMS has its own implementation, such as PL/SQL, Transact-SQL, etc.
-#### SQL 语法结构
+#### SQL Syntax Structure
-SQL 语法结构包括:
+The SQL syntax structure includes:
-- **`子句`** - 是语句和查询的组成成分。(在某些情况下,这些都是可选的。)
-- **`表达式`** - 可以产生任何标量值,或由列和行的数据库表
-- **`谓词`** - 给需要评估的 SQL 三值逻辑(3VL)(true/false/unknown)或布尔真值指定条件,并限制语句和查询的效果,或改变程序流程。
-- **`查询`** - 基于特定条件检索数据。这是 SQL 的一个重要组成部分。
-- **`语句`** - 可以持久地影响纲要和数据,也可以控制数据库事务、程序流程、连接、会话或诊断。
+- **`Clause`** - Components of statements and queries. (In some cases, these are optional.)
+- **`Expression`** - Can produce any scalar value or be derived from columns and rows of a database table.
+- **`Predicate`** - Specifies conditions for evaluating SQL three-valued logic (3VL) (true/false/unknown) or Boolean truth values, and limits the effects of statements and queries or alters program flow.
+- **`Query`** - Retrieves data based on specific conditions. This is an important component of SQL.
+- **`Statement`** - Can permanently affect schemas and data, and can also control database transactions, program flow, connections, sessions, or diagnostics.
-#### SQL 语法要点
+#### Key Points of SQL Syntax
-- **SQL 语句不区分大小写**,但是数据库表名、列名和值是否区分,依赖于具体的 DBMS 以及配置。例如:`SELECT` 与 `select`、`Select` 是相同的。
-- **多条 SQL 语句必须以分号(`;`)分隔**。
-- 处理 SQL 语句时,**所有空格都被忽略**。
+- **SQL statements are case-insensitive**, but whether database table names, column names, and values are case-sensitive depends on the specific DBMS and configuration. For example, `SELECT`, `select`, and `Select` are the same.
+- **Multiple SQL statements must be separated by a semicolon (`;`).**
+- When processing SQL statements, **all whitespace is ignored**.
-SQL 语句可以写成一行,也可以分写为多行。
+SQL statements can be written in a single line or split into multiple lines.
```sql
--- 一行 SQL 语句
+-- Single line SQL statement
UPDATE user SET username='robot', password='robot' WHERE username = 'root';
--- 多行 SQL 语句
+-- Multi-line SQL statement
UPDATE user
SET username='robot', password='robot'
WHERE username = 'root';
```
-SQL 支持三种注释:
+SQL supports three types of comments:
```sql
-## 注释1
--- 注释2
-/* 注释3 */
+## Comment 1
+-- Comment 2
+/* Comment 3 */
```
-### SQL 分类
+### SQL Classification
-#### 数据定义语言(DDL)
+#### Data Definition Language (DDL)
-数据定义语言(Data Definition Language,DDL)是 SQL 语言集中负责数据结构定义与数据库对象定义的语言。
+Data Definition Language (DDL) is the part of SQL responsible for defining data structures and database objects.
-DDL 的主要功能是**定义数据库对象**。
+The main function of DDL is to **define database objects**.
-DDL 的核心指令是 `CREATE`、`ALTER`、`DROP`。
+The core commands of DDL are `CREATE`, `ALTER`, `DROP`.
-#### 数据操纵语言(DML)
+#### Data Manipulation Language (DML)
-数据操纵语言(Data Manipulation Language, DML)是用于数据库操作,对数据库其中的对象和数据运行访问工作的编程语句。
+Data Manipulation Language (DML) is used for database operations, executing access operations on database objects and data.
-DML 的主要功能是 **访问数据**,因此其语法都是以**读写数据库**为主。
+The main function of DML is to **access data**, so its syntax is primarily focused on **reading and writing databases**.
-DML 的核心指令是 `INSERT`、`UPDATE`、`DELETE`、`SELECT`。这四个指令合称 CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete),即增删改查。
+The core commands of DML are `INSERT`, `UPDATE`, `DELETE`, `SELECT`. These four commands are collectively referred to as CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
-#### 事务控制语言(TCL)
+#### Transaction Control Language (TCL)
-事务控制语言 (Transaction Control Language, TCL) 用于**管理数据库中的事务**。这些用于管理由 DML 语句所做的更改。它还允许将语句分组为逻辑事务。
+Transaction Control Language (TCL) is used to **manage transactions in the database**. These manage changes made by DML statements. It also allows grouping statements into logical transactions.
-TCL 的核心指令是 `COMMIT`、`ROLLBACK`。
+The core commands of TCL are `COMMIT`, `ROLLBACK`.
-#### 数据控制语言(DCL)
+#### Data Control Language (DCL)
-数据控制语言 (Data Control Language, DCL) 是一种可对数据访问权进行控制的指令,它可以控制特定用户账户对数据表、查看表、预存程序、用户自定义函数等数据库对象的控制权。
+Data Control Language (DCL) is a set of commands that control data access rights, allowing control over specific user accounts regarding database objects such as tables, views, stored procedures, and user-defined functions.
-DCL 的核心指令是 `GRANT`、`REVOKE`。
+The core commands of DCL are `GRANT`, `REVOKE`.
-DCL 以**控制用户的访问权限**为主,因此其指令作法并不复杂,可利用 DCL 控制的权限有:`CONNECT`、`SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE`、`DELETE`、`EXECUTE`、`USAGE`、`REFERENCES`。
+DCL primarily focuses on **controlling user access rights**, so its commands are not complex. The permissions that can be controlled by DCL include: `CONNECT`, `SELECT`, `INSERT`, `UPDATE`, `DELETE`, `EXECUTE`, `USAGE`, `REFERENCES`.
-根据不同的 DBMS 以及不同的安全性实体,其支持的权限控制也有所不同。
-
-**我们先来介绍 DML 语句用法。 DML 的主要功能是读写数据库实现增删改查。**
-
-## 增删改查
-
-增删改查,又称为 CRUD,数据库基本操作中的基本操作。
-
-### 插入数据
-
-`INSERT INTO` 语句用于向表中插入新记录。
-
-**插入完整的行**
-
-```sql
-# 插入一行
-INSERT INTO user
-VALUES (10, 'root', 'root', 'xxxx@163.com');
-# 插入多行
-INSERT INTO user
-VALUES (10, 'root', 'root', 'xxxx@163.com'), (12, 'user1', 'user1', 'xxxx@163.com'), (18, 'user2', 'user2', 'xxxx@163.com');
-```
-
-**插入行的一部分**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO user(username, password, email)
-VALUES ('admin', 'admin', 'xxxx@163.com');
-```
-
-**插入查询出来的数据**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO user(username)
-SELECT name
-FROM account;
-```
-
-### 更新数据
-
-`UPDATE` 语句用于更新表中的记录。
-
-```sql
-UPDATE user
-SET username='robot', password='robot'
-WHERE username = 'root';
-```
-
-### 删除数据
-
-- `DELETE` 语句用于删除表中的记录。
-- `TRUNCATE TABLE` 可以清空表,也就是删除所有行。说明:`TRUNCATE` 语句不属于 DML 语法而是 DDL 语法。
-
-**删除表中的指定数据**
-
-```sql
-DELETE FROM user
-WHERE username = 'robot';
-```
-
-**清空表中的数据**
-
-```sql
-TRUNCATE TABLE user;
-```
-
-### 查询数据
-
-`SELECT` 语句用于从数据库中查询数据。
-
-`DISTINCT` 用于返回唯一不同的值。它作用于所有列,也就是说所有列的值都相同才算相同。
-
-`LIMIT` 限制返回的行数。可以有两个参数,第一个参数为起始行,从 0 开始;第二个参数为返回的总行数。
-
-- `ASC`:升序(默认)
-- `DESC`:降序
-
-**查询单列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询多列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询所有列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询不同的值**
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT
-vend_id FROM products;
-```
-
-**限制查询结果**
-
-```sql
--- 返回前 5 行
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 5;
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 0, 5;
--- 返回第 3 ~ 5 行
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 2, 3;
-```
-
-## 排序
-
-`order by` 用于对结果集按照一个列或者多个列进行排序。默认按照升序对记录进行排序,如果需要按照降序对记录进行排序,可以使用 `desc` 关键字。
-
-`order by` 对多列排序的时候,先排序的列放前面,后排序的列放后面。并且,不同的列可以有不同的排序规则。
-
-```sql
-SELECT * FROM products
-ORDER BY prod_price DESC, prod_name ASC;
-```
-
-## 分组
-
-**`group by`**:
-
-- `group by` 子句将记录分组到汇总行中。
-- `group by` 为每个组返回一个记录。
-- `group by` 通常还涉及聚合`count`,`max`,`sum`,`avg` 等。
-- `group by` 可以按一列或多列进行分组。
-- `group by` 按分组字段进行排序后,`order by` 可以以汇总字段来进行排序。
-
-**分组**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(cust_address) AS addr_num
-FROM Customers GROUP BY cust_name;
-```
-
-**分组后排序**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(cust_address) AS addr_num
-FROM Customers GROUP BY cust_name
-ORDER BY cust_name DESC;
-```
-
-**`having`**:
-
-- `having` 用于对汇总的 `group by` 结果进行过滤。
-- `having` 一般都是和 `group by` 连用。
-- `where` 和 `having` 可以在相同的查询中。
-
-**使用 WHERE 和 HAVING 过滤数据**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(*) AS NumberOfOrders
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_email IS NOT NULL
-GROUP BY cust_name
-HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
-```
-
-**`having` vs `where`**:
-
-- `where`:过滤过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。`where` 在`group by` 前。
-- `having`:过滤分组,一般都是和 `group by` 连用,不能单独使用。`having` 在 `group by` 之后。
-
-## 子查询
-
-子查询是嵌套在较大查询中的 SQL 查询,也称内部查询或内部选择,包含子查询的语句也称为外部查询或外部选择。简单来说,子查询就是指将一个 `select` 查询(子查询)的结果作为另一个 SQL 语句(主查询)的数据来源或者判断条件。
-
-子查询可以嵌入 `SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 语句中,也可以和 `=`、`<`、`>`、`IN`、`BETWEEN`、`EXISTS` 等运算符一起使用。
-
-子查询常用在 `WHERE` 子句和 `FROM` 子句后边:
-
-- 当用于 `WHERE` 子句时,根据不同的运算符,子查询可以返回单行单列、多行单列、单行多列数据。子查询就是要返回能够作为 `WHERE` 子句查询条件的值。
-- 当用于 `FROM` 子句时,一般返回多行多列数据,相当于返回一张临时表,这样才符合 `FROM` 后面是表的规则。这种做法能够实现多表联合查询。
-
-> 注意:MYSQL 数据库从 4.1 版本才开始支持子查询,早期版本是不支持的。
-
-用于 `WHERE` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select column_name [, column_name ]
-from table1 [, table2 ]
-where column_name operator
- (select column_name [, column_name ]
- from table1 [, table2 ]
- [where])
-```
-
-- 子查询需要放在括号`( )`内。
-- `operator` 表示用于 where 子句的运算符。
-
-用于 `FROM` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select column_name [, column_name ]
-from (select column_name [, column_name ]
- from table1 [, table2 ]
- [where]) as temp_table_name
-where condition
-```
-
-用于 `FROM` 的子查询返回的结果相当于一张临时表,所以需要使用 AS 关键字为该临时表起一个名字。
-
-**子查询的子查询**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact
-FROM customers
-WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id
- FROM orders
- WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM orderitems
- WHERE prod_id = 'RGAN01'));
-```
-
-内部查询首先在其父查询之前执行,以便可以将内部查询的结果传递给外部查询。执行过程可以参考下图:
-
-
-
-### WHERE
-
-- `WHERE` 子句用于过滤记录,即缩小访问数据的范围。
-- `WHERE` 后跟一个返回 `true` 或 `false` 的条件。
-- `WHERE` 可以与 `SELECT`,`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 一起使用。
-- 可以在 `WHERE` 子句中使用的操作符。
-
-| 运算符 | 描述 |
-| ------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
-| = | 等于 |
-| <> | 不等于。注释:在 SQL 的一些版本中,该操作符可被写成 != |
-| > | 大于 |
-| < | 小于 |
-| >= | 大于等于 |
-| <= | 小于等于 |
-| BETWEEN | 在某个范围内 |
-| LIKE | 搜索某种模式 |
-| IN | 指定针对某个列的多个可能值 |
-
-**`SELECT` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-SELECT * FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-**`UPDATE` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-UPDATE Customers
-SET cust_name = 'Jack Jones'
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-**`DELETE` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-DELETE FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-### IN 和 BETWEEN
-
-- `IN` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是在指定的几个特定值中任选一个值。
-- `BETWEEN` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是选取介于某个范围内的值。
-
-**IN 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id IN ('DLL01', 'BRS01');
-```
-
-**BETWEEN 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_price BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
-```
-
-### AND、OR、NOT
-
-- `AND`、`OR`、`NOT` 是用于对过滤条件的逻辑处理指令。
-- `AND` 优先级高于 `OR`,为了明确处理顺序,可以使用 `()`。
-- `AND` 操作符表示左右条件都要满足。
-- `OR` 操作符表示左右条件满足任意一个即可。
-- `NOT` 操作符用于否定一个条件。
-
-**AND 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01' AND prod_price <= 4;
-```
-
-**OR 示例**
-
-```ini
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01' OR vend_id = 'BRS01';
-```
-
-**NOT 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_price NOT BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
-```
-
-### LIKE
-
-- `LIKE` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是确定字符串是否匹配模式。
-- 只有字段是文本值时才使用 `LIKE`。
-- `LIKE` 支持两个通配符匹配选项:`%` 和 `_`。
-- 不要滥用通配符,通配符位于开头处匹配会非常慢。
-- `%` 表示任何字符出现任意次数。
-- `_` 表示任何字符出现一次。
-
-**% 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_name LIKE '%bean bag%';
-```
-
-**\_ 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_name LIKE '__ inch teddy bear';
-```
-
-## 连接
-
-JOIN 是“连接”的意思,顾名思义,SQL JOIN 子句用于将两个或者多个表联合起来进行查询。
-
-连接表时需要在每个表中选择一个字段,并对这些字段的值进行比较,值相同的两条记录将合并为一条。**连接表的本质就是将不同表的记录合并起来,形成一张新表。当然,这张新表只是临时的,它仅存在于本次查询期间**。
-
-使用 `JOIN` 连接两个表的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select table1.column1, table2.column2...
-from table1
-join table2
-on table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2;
-```
-
-`table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2` 是连接条件,只有满足此条件的记录才会合并为一行。您可以使用多个运算符来连接表,例如 =、>、<、<>、<=、>=、!=、`between`、`like` 或者 `not`,但是最常见的是使用 =。
-
-当两个表中有同名的字段时,为了帮助数据库引擎区分是哪个表的字段,在书写同名字段名时需要加上表名。当然,如果书写的字段名在两个表中是唯一的,也可以不使用以上格式,只写字段名即可。
-
-另外,如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用 `USING`子句来代替 `ON`,举个例子:
-
-```sql
-# join....on
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c
-inner join Orders o
-on c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-order by c.cust_name;
-
-# 如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用USING子句:join....using()
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c
-inner join Orders o
-using(cust_id)
-order by c.cust_name;
-```
-
-**`ON` 和 `WHERE` 的区别**:
-
-- 连接表时,SQL 会根据连接条件生成一张新的临时表。`ON` 就是连接条件,它决定临时表的生成。
-- `WHERE` 是在临时表生成以后,再对临时表中的数据进行过滤,生成最终的结果集,这个时候已经没有 JOIN-ON 了。
-
-所以总结来说就是:**SQL 先根据 ON 生成一张临时表,然后再根据 WHERE 对临时表进行筛选**。
-
-SQL 允许在 `JOIN` 左边加上一些修饰性的关键词,从而形成不同类型的连接,如下表所示:
-
-| 连接类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| INNER JOIN 内连接 | (默认连接方式)只有当两个表都存在满足条件的记录时才会返回行。 |
-| LEFT JOIN / LEFT OUTER JOIN 左(外)连接 | 返回左表中的所有行,即使右表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| RIGHT JOIN / RIGHT OUTER JOIN 右(外)连接 | 返回右表中的所有行,即使左表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| FULL JOIN / FULL OUTER JOIN 全(外)连接 | 只要其中有一个表存在满足条件的记录,就返回行。 |
-| SELF JOIN | 将一个表连接到自身,就像该表是两个表一样。为了区分两个表,在 SQL 语句中需要至少重命名一个表。 |
-| CROSS JOIN | 交叉连接,从两个或者多个连接表中返回记录集的笛卡尔积。 |
-
-下图展示了 LEFT JOIN、RIGHT JOIN、INNER JOIN、OUTER JOIN 相关的 7 种用法。
-
-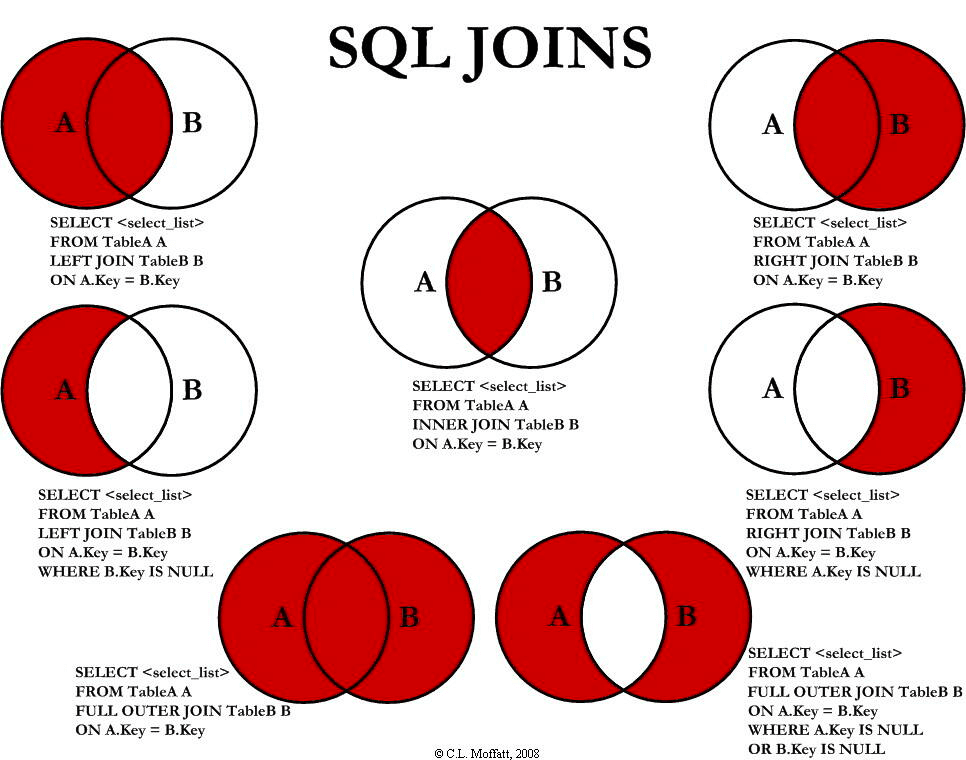
-
-如果不加任何修饰词,只写 `JOIN`,那么默认为 `INNER JOIN`
-
-对于 `INNER JOIN` 来说,还有一种隐式的写法,称为 “**隐式内连接**”,也就是没有 `INNER JOIN` 关键字,使用 `WHERE` 语句实现内连接的功能
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c, Orders o
-where c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-order by c.cust_name;
-
-# 显式内连接
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c inner join Orders o
-using(cust_id)
-order by c.cust_name;
-```
-
-## 组合
-
-`UNION` 运算符将两个或更多查询的结果组合起来,并生成一个结果集,其中包含来自 `UNION` 中参与查询的提取行。
-
-`UNION` 基本规则:
-
-- 所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- 每个查询中涉及表的列的数据类型必须相同或兼容。
-- 通常返回的列名取自第一个查询。
-
-默认地,`UNION` 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 `UNION ALL`。
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
-UNION ALL
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;
-```
-
-`UNION` 结果集中的列名总是等于 `UNION` 中第一个 `SELECT` 语句中的列名。
-
-`JOIN` vs `UNION`:
-
-- `JOIN` 中连接表的列可能不同,但在 `UNION` 中,所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- `UNION` 将查询之后的行放在一起(垂直放置),但 `JOIN` 将查询之后的列放在一起(水平放置),即它构成一个笛卡尔积。
-
-## 函数
-
-不同数据库的函数往往各不相同,因此不可移植。本节主要以 MySQL 的函数为例。
-
-### 文本处理
-
-| 函数 | 说明 |
-| -------------------- | ---------------------- |
-| `LEFT()`、`RIGHT()` | 左边或者右边的字符 |
-| `LOWER()`、`UPPER()` | 转换为小写或者大写 |
-| `LTRIM()`、`RTRIM()` | 去除左边或者右边的空格 |
-| `LENGTH()` | 长度,以字节为单位 |
-| `SOUNDEX()` | 转换为语音值 |
-
-其中, **`SOUNDEX()`** 可以将一个字符串转换为描述其语音表示的字母数字模式。
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM mytable
-WHERE SOUNDEX(col1) = SOUNDEX('apple')
-```
-
-### 日期和时间处理
-
-- 日期格式:`YYYY-MM-DD`
-- 时间格式:`HH:MM:SS`
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------------- | ------------------------------ |
-| `AddDate()` | 增加一个日期(天、周等) |
-| `AddTime()` | 增加一个时间(时、分等) |
-| `CurDate()` | 返回当前日期 |
-| `CurTime()` | 返回当前时间 |
-| `Date()` | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
-| `DateDiff()` | 计算两个日期之差 |
-| `Date_Add()` | 高度灵活的日期运算函数 |
-| `Date_Format()` | 返回一个格式化的日期或时间串 |
-| `Day()` | 返回一个日期的天数部分 |
-| `DayOfWeek()` | 对于一个日期,返回对应的星期几 |
-| `Hour()` | 返回一个时间的小时部分 |
-| `Minute()` | 返回一个时间的分钟部分 |
-| `Month()` | 返回一个日期的月份部分 |
-| `Now()` | 返回当前日期和时间 |
-| `Second()` | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
-| `Time()` | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
-| `Year()` | 返回一个日期的年份部分 |
-
-### 数值处理
-
-| 函数 | 说明 |
-| ------ | ------ |
-| SIN() | 正弦 |
-| COS() | 余弦 |
-| TAN() | 正切 |
-| ABS() | 绝对值 |
-| SQRT() | 平方根 |
-| MOD() | 余数 |
-| EXP() | 指数 |
-| PI() | 圆周率 |
-| RAND() | 随机数 |
-
-### 汇总
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| `AVG()` | 返回某列的平均值 |
-| `COUNT()` | 返回某列的行数 |
-| `MAX()` | 返回某列的最大值 |
-| `MIN()` | 返回某列的最小值 |
-| `SUM()` | 返回某列值之和 |
-
-`AVG()` 会忽略 NULL 行。
-
-使用 `DISTINCT` 可以让汇总函数值汇总不同的值。
-
-```sql
-SELECT AVG(DISTINCT col1) AS avg_col
-FROM mytable
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 DDL 语句用法。DDL 的主要功能是定义数据库对象(如:数据库、数据表、视图、索引等)**
-
-## 数据定义
-
-### 数据库(DATABASE)
-
-#### 创建数据库
-
-```sql
-CREATE DATABASE test;
-```
-
-#### 删除数据库
-
-```sql
-DROP DATABASE test;
-```
-
-#### 选择数据库
-
-```sql
-USE test;
-```
-
-### 数据表(TABLE)
-
-#### 创建数据表
-
-**普通创建**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE user (
- id int(10) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT 'Id',
- username varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '用户名',
- password varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '密码',
- email varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '邮箱'
-) COMMENT='用户表';
-```
-
-**根据已有的表创建新表**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE vip_user AS
-SELECT * FROM user;
-```
-
-#### 删除数据表
-
-```sql
-DROP TABLE user;
-```
-
-#### 修改数据表
-
-**添加列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-ADD age int(3);
-```
-
-**删除列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP COLUMN age;
-```
-
-**修改列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE `user`
-MODIFY COLUMN age tinyint;
-```
-
-**添加主键**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-ADD PRIMARY KEY (id);
-```
-
-**删除主键**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP PRIMARY KEY;
-```
-
-### 视图(VIEW)
-
-定义:
-
-- 视图是基于 SQL 语句的结果集的可视化的表。
-- 视图是虚拟的表,本身不包含数据,也就不能对其进行索引操作。对视图的操作和对普通表的操作一样。
-
-作用:
-
-- 简化复杂的 SQL 操作,比如复杂的联结;
-- 只使用实际表的一部分数据;
-- 通过只给用户访问视图的权限,保证数据的安全性;
-- 更改数据格式和表示。
-
-
-
-#### 创建视图
-
-```sql
-CREATE VIEW top_10_user_view AS
-SELECT id, username
-FROM user
-WHERE id < 10;
-```
-
-#### 删除视图
-
-```sql
-DROP VIEW top_10_user_view;
-```
-
-### 索引(INDEX)
-
-**索引是一种用于快速查询和检索数据的数据结构,其本质可以看成是一种排序好的数据结构。**
-
-索引的作用就相当于书的目录。打个比方: 我们在查字典的时候,如果没有目录,那我们就只能一页一页的去找我们需要查的那个字,速度很慢。如果有目录了,我们只需要先去目录里查找字的位置,然后直接翻到那一页就行了。
-
-**优点**:
-
-- 使用索引可以大大加快 数据的检索速度(大大减少检索的数据量), 这也是创建索引的最主要的原因。
-- 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。
-
-**缺点**:
-
-- 创建索引和维护索引需要耗费许多时间。当对表中的数据进行增删改的时候,如果数据有索引,那么索引也需要动态的修改,会降低 SQL 执行效率。
-- 索引需要使用物理文件存储,也会耗费一定空间。
-
-但是,**使用索引一定能提高查询性能吗?**
-
-大多数情况下,索引查询都是比全表扫描要快的。但是如果数据库的数据量不大,那么使用索引也不一定能够带来很大提升。
-
-关于索引的详细介绍,请看我写的 [MySQL 索引详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/mysql/mysql-index.html) 这篇文章。
-
-#### 创建索引
-
-```sql
-CREATE INDEX user_index
-ON user (id);
-```
-
-#### 添加索引
-
-```sql
-ALTER table user ADD INDEX user_index(id)
-```
-
-#### 创建唯一索引
-
-```sql
-CREATE UNIQUE INDEX user_index
-ON user (id);
-```
-
-#### 删除索引
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP INDEX user_index;
-```
-
-### 约束
-
-SQL 约束用于规定表中的数据规则。
-
-如果存在违反约束的数据行为,行为会被约束终止。
-
-约束可以在创建表时规定(通过 CREATE TABLE 语句),或者在表创建之后规定(通过 ALTER TABLE 语句)。
-
-约束类型:
-
-- `NOT NULL` - 指示某列不能存储 NULL 值。
-- `UNIQUE` - 保证某列的每行必须有唯一的值。
-- `PRIMARY KEY` - NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合。确保某列(或两个列多个列的结合)有唯一标识,有助于更容易更快速地找到表中的一个特定的记录。
-- `FOREIGN KEY` - 保证一个表中的数据匹配另一个表中的值的参照完整性。
-- `CHECK` - 保证列中的值符合指定的条件。
-- `DEFAULT` - 规定没有给列赋值时的默认值。
-
-创建表时使用约束条件:
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE Users (
- Id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增Id',
- Username VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '用户名',
- Password VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '密码',
- Email VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '邮箱地址',
- Enabled TINYINT(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '是否有效',
- PRIMARY KEY (Id)
-) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='用户表';
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 TCL 语句用法。TCL 的主要功能是管理数据库中的事务。**
-
-## 事务处理
-
-不能回退 `SELECT` 语句,回退 `SELECT` 语句也没意义;也不能回退 `CREATE` 和 `DROP` 语句。
-
-**MySQL 默认是隐式提交**,每执行一条语句就把这条语句当成一个事务然后进行提交。当出现 `START TRANSACTION` 语句时,会关闭隐式提交;当 `COMMIT` 或 `ROLLBACK` 语句执行后,事务会自动关闭,重新恢复隐式提交。
-
-通过 `set autocommit=0` 可以取消自动提交,直到 `set autocommit=1` 才会提交;`autocommit` 标记是针对每个连接而不是针对服务器的。
-
-指令:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` - 指令用于标记事务的起始点。
-- `SAVEPOINT` - 指令用于创建保留点。
-- `ROLLBACK TO` - 指令用于回滚到指定的保留点;如果没有设置保留点,则回退到 `START TRANSACTION` 语句处。
-- `COMMIT` - 提交事务。
-
-```sql
--- 开始事务
-START TRANSACTION;
-
--- 插入操作 A
-INSERT INTO `user`
-VALUES (1, 'root1', 'root1', 'xxxx@163.com');
-
--- 创建保留点 updateA
-SAVEPOINT updateA;
-
--- 插入操作 B
-INSERT INTO `user`
-VALUES (2, 'root2', 'root2', 'xxxx@163.com');
-
--- 回滚到保留点 updateA
-ROLLBACK TO updateA;
-
--- 提交事务,只有操作 A 生效
-COMMIT;
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 DCL 语句用法。DCL 的主要功能是控制用户的访问权限。**
-
-## 权限控制
-
-要授予用户帐户权限,可以用`GRANT`命令。要撤销用户的权限,可以用`REVOKE`命令。这里以 MySQL 为例,介绍权限控制实际应用。
-
-`GRANT`授予权限语法:
-
-```sql
-GRANT privilege,[privilege],.. ON privilege_level
-TO user [IDENTIFIED BY password]
-[REQUIRE tsl_option]
-[WITH [GRANT_OPTION | resource_option]];
-```
-
-简单解释一下:
-
-1. 在`GRANT`关键字后指定一个或多个权限。如果授予用户多个权限,则每个权限由逗号分隔。
-2. `ON privilege_level` 确定权限应用级别。MySQL 支持 global(`*.*`),database(`database.*`),table(`database.table`)和列级别。如果使用列权限级别,则必须在每个权限之后指定一个或逗号分隔列的列表。
-3. `user` 是要授予权限的用户。如果用户已存在,则`GRANT`语句将修改其权限。否则,`GRANT`语句将创建一个新用户。可选子句`IDENTIFIED BY`允许您为用户设置新的密码。
-4. `REQUIRE tsl_option`指定用户是否必须通过 SSL,X059 等安全连接连接到数据库服务器。
-5. 可选 `WITH GRANT OPTION` 子句允许您授予其他用户或从其他用户中删除您拥有的权限。此外,您可以使用`WITH`子句分配 MySQL 数据库服务器的资源,例如,设置用户每小时可以使用的连接数或语句数。这在 MySQL 共享托管等共享环境中非常有用。
-
-`REVOKE` 撤销权限语法:
-
-```sql
-REVOKE privilege_type [(column_list)]
- [, priv_type [(column_list)]]...
-ON [object_type] privilege_level
-FROM user [, user]...
-```
-
-简单解释一下:
-
-1. 在 `REVOKE` 关键字后面指定要从用户撤消的权限列表。您需要用逗号分隔权限。
-2. 指定在 `ON` 子句中撤销特权的特权级别。
-3. 指定要撤消 `FROM` 子句中的权限的用户帐户。
-
-`GRANT` 和 `REVOKE` 可在几个层次上控制访问权限:
-
-- 整个服务器,使用 `GRANT ALL` 和 `REVOKE ALL`;
-- 整个数据库,使用 `ON database.*`;
-- 特定的表,使用 `ON database.table`;
-- 特定的列;
-- 特定的存储过程。
-
-新创建的账户没有任何权限。账户用 `username@host` 的形式定义,`username@%` 使用的是默认主机名。MySQL 的账户信息保存在 mysql 这个数据库中。
-
-```sql
-USE mysql;
-SELECT user FROM user;
-```
-
-下表说明了可用于`GRANT`和`REVOKE`语句的所有允许权限:
-
-| **特权** | **说明** | **级别** | | | | | |
-| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------- | ------ | -------- | -------- | --- | --- |
-| **全局** | 数据库 | **表** | **列** | **程序** | **代理** | | |
-| ALL [PRIVILEGES] | 授予除 GRANT OPTION 之外的指定访问级别的所有权限 | | | | | | |
-| ALTER | 允许用户使用 ALTER TABLE 语句 | X | X | X | | | |
-| ALTER ROUTINE | 允许用户更改或删除存储的例程 | X | X | | | X | |
-| CREATE | 允许用户创建数据库和表 | X | X | X | | | |
-| CREATE ROUTINE | 允许用户创建存储的例程 | X | X | | | | |
-| CREATE TABLESPACE | 允许用户创建,更改或删除表空间和日志文件组 | X | | | | | |
-| CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES | 允许用户使用 CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE 创建临时表 | X | X | | | | |
-| CREATE USER | 允许用户使用 CREATE USER,DROP USER,RENAME USER 和 REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES 语句。 | X | | | | | |
-| CREATE VIEW | 允许用户创建或修改视图。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| DELETE | 允许用户使用 DELETE | X | X | X | | | |
-| DROP | 允许用户删除数据库,表和视图 | X | X | X | | | |
-| EVENT | 启用事件计划程序的事件使用。 | X | X | | | | |
-| EXECUTE | 允许用户执行存储的例程 | X | X | X | | | |
-| FILE | 允许用户读取数据库目录中的任何文件。 | X | | | | | |
-| GRANT OPTION | 允许用户拥有授予或撤消其他帐户权限的权限。 | X | X | X | | X | X |
-| INDEX | 允许用户创建或删除索引。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| INSERT | 允许用户使用 INSERT 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| LOCK TABLES | 允许用户对具有 SELECT 权限的表使用 LOCK TABLES | X | X | | | | |
-| PROCESS | 允许用户使用 SHOW PROCESSLIST 语句查看所有进程。 | X | | | | | |
-| PROXY | 启用用户代理。 | | | | | | |
-| REFERENCES | 允许用户创建外键 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| RELOAD | 允许用户使用 FLUSH 操作 | X | | | | | |
-| REPLICATION CLIENT | 允许用户查询以查看主服务器或从属服务器的位置 | X | | | | | |
-| REPLICATION SLAVE | 允许用户使用复制从属从主服务器读取二进制日志事件。 | X | | | | | |
-| SELECT | 允许用户使用 SELECT 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| SHOW DATABASES | 允许用户显示所有数据库 | X | | | | | |
-| SHOW VIEW | 允许用户使用 SHOW CREATE VIEW 语句 | X | X | X | | | |
-| SHUTDOWN | 允许用户使用 mysqladmin shutdown 命令 | X | | | | | |
-| SUPER | 允许用户使用其他管理操作,例如 CHANGE MASTER TO,KILL,PURGE BINARY LOGS,SET GLOBAL 和 mysqladmin 命令 | X | | | | | |
-| TRIGGER | 允许用户使用 TRIGGER 操作。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| UPDATE | 允许用户使用 UPDATE 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| USAGE | 相当于“没有特权” | | | | | | |
-
-### 创建账户
-
-```sql
-CREATE USER myuser IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
-```
-
-### 修改账户名
-
-```sql
-UPDATE user SET user='newuser' WHERE user='myuser';
-FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
-```
-
-### 删除账户
-
-```sql
-DROP USER myuser;
-```
-
-### 查看权限
-
-```sql
-SHOW GRANTS FOR myuser;
-```
-
-### 授予权限
-
-```sql
-GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON *.* TO myuser;
-```
-
-### 删除权限
-
-```sql
-REVOKE SELECT, INSERT ON *.* FROM myuser;
-```
-
-### 更改密码
-
-```sql
-SET PASSWORD FOR myuser = 'mypass';
-```
-
-## 存储过程
-
-存储过程可以看成是对一系列 SQL 操作的批处理。存储过程可以由触发器,其他存储过程以及 Java, Python,PHP 等应用程序调用。
-
-
-
-使用存储过程的好处:
-
-- 代码封装,保证了一定的安全性;
-- 代码复用;
-- 由于是预先编译,因此具有很高的性能。
-
-创建存储过程:
-
-- 命令行中创建存储过程需要自定义分隔符,因为命令行是以 `;` 为结束符,而存储过程中也包含了分号,因此会错误把这部分分号当成是结束符,造成语法错误。
-- 包含 `in`、`out` 和 `inout` 三种参数。
-- 给变量赋值都需要用 `select into` 语句。
-- 每次只能给一个变量赋值,不支持集合的操作。
-
-需要注意的是:**阿里巴巴《Java 开发手册》强制禁止使用存储过程。因为存储过程难以调试和扩展,更没有移植性。**
-
-
-
-至于到底要不要在项目中使用,还是要看项目实际需求,权衡好利弊即可!
-
-### 创建存储过程
-
-```sql
-DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `proc_adder`;
-DELIMITER ;;
-CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `proc_adder`(IN a int, IN b int, OUT sum int)
-BEGIN
- DECLARE c int;
- if a is null then set a = 0;
- end if;
-
- if b is null then set b = 0;
- end if;
-
- set sum = a + b;
-END
-;;
-DELIMITER ;
-```
-
-### 使用存储过程
-
-```less
-set @b=5;
-call proc_adder(2,@b,@s);
-select @s as sum;
-```
-
-## 游标
-
-游标(cursor)是一个存储在 DBMS 服务器上的数据库查询,它不是一条 `SELECT` 语句,而是被该语句检索出来的结果集。
-
-在存储过程中使用游标可以对一个结果集进行移动遍历。
-
-游标主要用于交互式应用,其中用户需要滚动屏幕上的数据,并对数据进行浏览或做出更改。
-
-使用游标的几个明确步骤:
-
-- 在使用游标前,必须声明(定义)它。这个过程实际上没有检索数据, 它只是定义要使用的 `SELECT` 语句和游标选项。
-
-- 一旦声明,就必须打开游标以供使用。这个过程用前面定义的 SELECT 语句把数据实际检索出来。
-
-- 对于填有数据的游标,根据需要取出(检索)各行。
-
-- 在结束游标使用时,必须关闭游标,可能的话,释放游标(有赖于具
-
- 体的 DBMS)。
-
-```sql
-DELIMITER $
-CREATE PROCEDURE getTotal()
-BEGIN
- DECLARE total INT;
- -- 创建接收游标数据的变量
- DECLARE sid INT;
- DECLARE sname VARCHAR(10);
- -- 创建总数变量
- DECLARE sage INT;
- -- 创建结束标志变量
- DECLARE done INT DEFAULT false;
- -- 创建游标
- DECLARE cur CURSOR FOR SELECT id,name,age from cursor_table where age>30;
- -- 指定游标循环结束时的返回值
- DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = true;
- SET total = 0;
- OPEN cur;
- FETCH cur INTO sid, sname, sage;
- WHILE(NOT done)
- DO
- SET total = total + 1;
- FETCH cur INTO sid, sname, sage;
- END WHILE;
-
- CLOSE cur;
- SELECT total;
-END $
-DELIMITER ;
-
--- 调用存储过程
-call getTotal();
-```
-
-## 触发器
-
-触发器是一种与表操作有关的数据库对象,当触发器所在表上出现指定事件时,将调用该对象,即表的操作事件触发表上的触发器的执行。
-
-我们可以使用触发器来进行审计跟踪,把修改记录到另外一张表中。
-
-使用触发器的优点:
-
-- SQL 触发器提供了另一种检查数据完整性的方法。
-- SQL 触发器可以捕获数据库层中业务逻辑中的错误。
-- SQL 触发器提供了另一种运行计划任务的方法。通过使用 SQL 触发器,您不必等待运行计划任务,因为在对表中的数据进行更改之前或之后会自动调用触发器。
-- SQL 触发器对于审计表中数据的更改非常有用。
-
-使用触发器的缺点:
-
-- SQL 触发器只能提供扩展验证,并且不能替换所有验证。必须在应用程序层中完成一些简单的验证。例如,您可以使用 JavaScript 在客户端验证用户的输入,或者使用服务器端脚本语言(如 JSP,PHP,ASP.NET,Perl)在服务器端验证用户的输入。
-- 从客户端应用程序调用和执行 SQL 触发器是不可见的,因此很难弄清楚数据库层中发生了什么。
-- SQL 触发器可能会增加数据库服务器的开销。
-
-MySQL 不允许在触发器中使用 CALL 语句 ,也就是不能调用存储过程。
-
-> 注意:在 MySQL 中,分号 `;` 是语句结束的标识符,遇到分号表示该段语句已经结束,MySQL 可以开始执行了。因此,解释器遇到触发器执行动作中的分号后就开始执行,然后会报错,因为没有找到和 BEGIN 匹配的 END。
->
-> 这时就会用到 `DELIMITER` 命令(DELIMITER 是定界符,分隔符的意思)。它是一条命令,不需要语句结束标识,语法为:`DELIMITER new_delimiter`。`new_delimiter` 可以设为 1 个或多个长度的符号,默认的是分号 `;`,我们可以把它修改为其他符号,如 `$` - `DELIMITER $` 。在这之后的语句,以分号结束,解释器不会有什么反应,只有遇到了 `$`,才认为是语句结束。注意,使用完之后,我们还应该记得把它给修改回来。
-
-在 MySQL 5.7.2 版之前,可以为每个表定义最多六个触发器。
-
-- `BEFORE INSERT` - 在将数据插入表格之前激活。
-- `AFTER INSERT` - 将数据插入表格后激活。
-- `BEFORE UPDATE` - 在更新表中的数据之前激活。
-- `AFTER UPDATE` - 更新表中的数据后激活。
-- `BEFORE DELETE` - 在从表中删除数据之前激活。
-- `AFTER DELETE` - 从表中删除数据后激活。
-
-但是,从 MySQL 版本 5.7.2+开始,可以为同一触发事件和操作时间定义多个触发器。
-
-**`NEW` 和 `OLD`**:
-
-- MySQL 中定义了 `NEW` 和 `OLD` 关键字,用来表示触发器的所在表中,触发了触发器的那一行数据。
-- 在 `INSERT` 型触发器中,`NEW` 用来表示将要(`BEFORE`)或已经(`AFTER`)插入的新数据;
-- 在 `UPDATE` 型触发器中,`OLD` 用来表示将要或已经被修改的原数据,`NEW` 用来表示将要或已经修改为的新数据;
-- 在 `DELETE` 型触发器中,`OLD` 用来表示将要或已经被删除的原数据;
-- 使用方法:`NEW.columnName` (columnName 为相应数据表某一列名)
-
-### 创建触发器
-
-> 提示:为了理解触发器的要点,有必要先了解一下创建触发器的指令。
-
-`CREATE TRIGGER` 指令用于创建触发器。
-
-语法:
-
-```sql
-CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
-trigger_time
-trigger_event
-ON table_name
-FOR EACH ROW
-BEGIN
- trigger_statements
-END;
-```
-
-说明:
-
-- `trigger_name`:触发器名
-- `trigger_time` : 触发器的触发时机。取值为 `BEFORE` 或 `AFTER`。
-- `trigger_event` : 触发器的监听事件。取值为 `INSERT`、`UPDATE` 或 `DELETE`。
-- `table_name` : 触发器的监听目标。指定在哪张表上建立触发器。
-- `FOR EACH ROW`: 行级监视,Mysql 固定写法,其他 DBMS 不同。
-- `trigger_statements`: 触发器执行动作。是一条或多条 SQL 语句的列表,列表内的每条语句都必须用分号 `;` 来结尾。
-
-当触发器的触发条件满足时,将会执行 `BEGIN` 和 `END` 之间的触发器执行动作。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-DELIMITER $
-CREATE TRIGGER `trigger_insert_user`
-AFTER INSERT ON `user`
-FOR EACH ROW
-BEGIN
- INSERT INTO `user_history`(user_id, operate_type, operate_time)
- VALUES (NEW.id, 'add a user', now());
-END $
-DELIMITER ;
-```
-
-### 查看触发器
-
-```sql
-SHOW TRIGGERS;
-```
-
-### 删除触发器
-
-```sql
-DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trigger_insert_user;
-```
-
-## 文章推荐
-
-- [后端程序员必备:SQL 高性能优化指南!35+条优化建议立马 GET!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/I-ZT3zGTNBZ6egS7T09jyQ)
-- [后端程序员必备:书写高质量 SQL 的 30 条建议](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247486461&idx=1&sn=60a22279196d084cc398936fe3b37772&chksm=cea24436f9d5cd20a4fa0e907590f3e700d7378b3f608d7b33bb52cfb96f503b7ccb65a1deed&token=1987003517&lang=zh_CN#rd)
-
-
+The supported permission controls may vary depending on different DBMS and security entities.
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md b/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
index e9b9f27e6dd..4ab33311d2c 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
@@ -1,63 +1,63 @@
---
-title: API网关基础知识总结
-category: 分布式
+title: API Gateway Basic Knowledge Summary
+category: Distributed
---
-## 什么是网关?
+## What is a Gateway?
-微服务背景下,一个系统被拆分为多个服务,但是像安全认证,流量控制,日志,监控等功能是每个服务都需要的,没有网关的话,我们就需要在每个服务中单独实现,这使得我们做了很多重复的事情并且没有一个全局的视图来统一管理这些功能。
+In the context of microservices, a system is split into multiple services, but features such as security authentication, traffic control, logging, and monitoring are required by each service. Without a gateway, we would need to implement these features individually in each service, leading to a lot of duplication and lacking a global view to manage these functions uniformly.
-
+
-一般情况下,网关可以为我们提供请求转发、安全认证(身份/权限认证)、流量控制、负载均衡、降级熔断、日志、监控、参数校验、协议转换等功能。
+Generally, a gateway can provide us with features such as request forwarding, security authentication (identity/authorization authentication), traffic control, load balancing, circuit breaking, logging, monitoring, parameter validation, and protocol conversion.
-上面介绍了这么多功能,实际上,网关主要做了两件事情:**请求转发** + **请求过滤**。
+Despite all these features, the gateway mainly does two things: **request forwarding** + **request filtering**.
-由于引入网关之后,会多一步网络转发,因此性能会有一点影响(几乎可以忽略不计,尤其是内网访问的情况下)。 另外,我们需要保障网关服务的高可用,避免单点风险。
+Since introducing a gateway adds a step of network forwarding, performance may be slightly affected (virtually negligible, especially in the case of internal network access). Additionally, we need to ensure high availability of the gateway service to avoid single points of failure.
-如下图所示,网关服务外层通过 Nginx(其他负载均衡设备/软件也行) 进⾏负载转发以达到⾼可⽤。Nginx 在部署的时候,尽量也要考虑高可用,避免单点风险。
+As shown in the figure below, the outer layer of the gateway service uses Nginx (other load balancing devices/software can also be used) for load forwarding to achieve high availability. When deploying Nginx, considerations for high availability should be made to avoid single points of risk.
-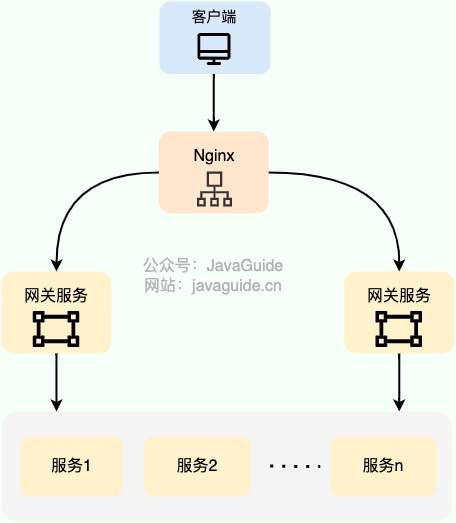
+
-## 网关能提供哪些功能?
+## What Functions Can a Gateway Provide?
-绝大部分网关可以提供下面这些功能(有一些功能需要借助其他框架或者中间件):
+Most gateways can provide the following functions (some functions may require the assistance of other frameworks or middleware):
-- **请求转发**:将请求转发到目标微服务。
-- **负载均衡**:根据各个微服务实例的负载情况或者具体的负载均衡策略配置对请求实现动态的负载均衡。
-- **安全认证**:对用户请求进行身份验证并仅允许可信客户端访问 API,并且还能够使用类似 RBAC 等方式来授权。
-- **参数校验**:支持参数映射与校验逻辑。
-- **日志记录**:记录所有请求的行为日志供后续使用。
-- **监控告警**:从业务指标、机器指标、JVM 指标等方面进行监控并提供配套的告警机制。
-- **流量控制**:对请求的流量进行控制,也就是限制某一时刻内的请求数。
-- **熔断降级**:实时监控请求的统计信息,达到配置的失败阈值后,自动熔断,返回默认值。
-- **响应缓存**:当用户请求获取的是一些静态的或更新不频繁的数据时,一段时间内多次请求获取到的数据很可能是一样的。对于这种情况可以将响应缓存起来。这样用户请求可以直接在网关层得到响应数据,无需再去访问业务服务,减轻业务服务的负担。
-- **响应聚合**:某些情况下用户请求要获取的响应内容可能会来自于多个业务服务。网关作为业务服务的调用方,可以把多个服务的响应整合起来,再一并返回给用户。
-- **灰度发布**:将请求动态分流到不同的服务版本(最基本的一种灰度发布)。
-- **异常处理**:对于业务服务返回的异常响应,可以在网关层在返回给用户之前做转换处理。这样可以把一些业务侧返回的异常细节隐藏,转换成用户友好的错误提示返回。
-- **API 文档:** 如果计划将 API 暴露给组织以外的开发人员,那么必须考虑使用 API 文档,例如 Swagger 或 OpenAPI。
-- **协议转换**:通过协议转换整合后台基于 REST、AMQP、Dubbo 等不同风格和实现技术的微服务,面向 Web Mobile、开放平台等特定客户端提供统一服务。
-- **证书管理**:将 SSL 证书部署到 API 网关,由一个统一的入口管理接口,降低了证书更换时的复杂度。
+- **Request Forwarding**: Forward requests to the target microservice.
+- **Load Balancing**: Implement dynamic load balancing based on the load of each microservice instance or specific load balancing strategy configurations.
+- **Security Authentication**: Verify user requests and only allow trusted clients to access the API, and authorization can be done using methods like RBAC.
+- **Parameter Validation**: Support parameter mapping and validation logic.
+- **Logging**: Record the behavior logs of all requests for future use.
+- **Monitoring and Alerts**: Monitor from operational metrics, machine metrics, JVM metrics, etc., and provide a corresponding alert mechanism.
+- **Traffic Control**: Control the traffic of requests, limiting the number of requests at a certain time.
+- **Circuit Breaking**: Monitor request statistics in real-time, and when the configured failure threshold is reached, automatically break the circuit and return default values.
+- **Response Caching**: When user requests are for some static or infrequently updated data, multiple requests for data within a certain time period may yield the same result. In such cases, responses can be cached. This way, user requests can directly receive response data at the gateway layer without going through the business service, reducing the load on the business service.
+- **Response Aggregation**: In some cases, the response content that user requests may come from multiple business services. The gateway, as the caller of the business services, can aggregate the responses from multiple services and return them to the user together.
+- **Gray Release**: Dynamically divert requests to different service versions (a basic form of gray release).
+- **Exception Handling**: For exception responses returned by business services, the gateway layer can transform them before returning them to the user. This can obscure some details of the exceptions returned from the business side, converting them into user-friendly error messages.
+- **API Documentation**: If planning to expose APIs to developers outside the organization, it's necessary to consider using API documentation tools like Swagger or OpenAPI.
+- **Protocol Conversion**: Through protocol conversion, integrate backend microservices based on REST, AMQP, Dubbo, etc., providing unified services for specific clients like Web Mobile and open platforms.
+- **Certificate Management**: Deploy SSL certificates to the API gateway, managing interfaces through a unified entry point, reducing the complexity during certificate replacement.
-下图来源于[百亿规模 API 网关服务 Shepherd 的设计与实现 - 美团技术团队 - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iITqdIiHi3XGKq6u6FRVdg)这篇文章。
+The following diagram is sourced from [Design and Implementation of the Billion-scale API Gateway Service Shepherd - Meituan Technical Team - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iITqdIiHi3XGKq6u6FRVdg).
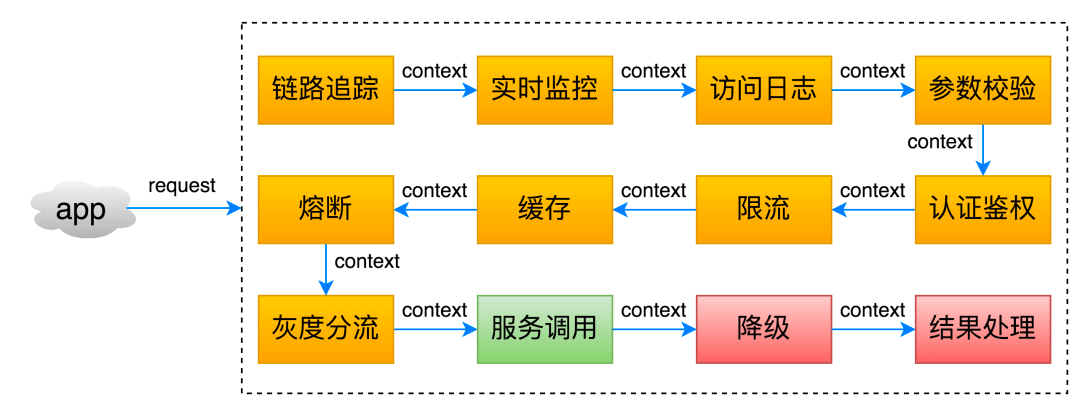
-## 有哪些常见的网关系统?
+## What Common Gateway Systems Are There?
### Netflix Zuul
-Zuul 是 Netflix 开发的一款提供动态路由、监控、弹性、安全的网关服务,基于 Java 技术栈开发,可以和 Eureka、Ribbon、Hystrix 等组件配合使用。
+Zuul is a gateway service developed by Netflix that provides dynamic routing, monitoring, elasticity, and security, developed on the Java technology stack and can be used with components like Eureka, Ribbon, and Hystrix.
-Zuul 核心架构如下:
+The core architecture of Zuul is as follows:
-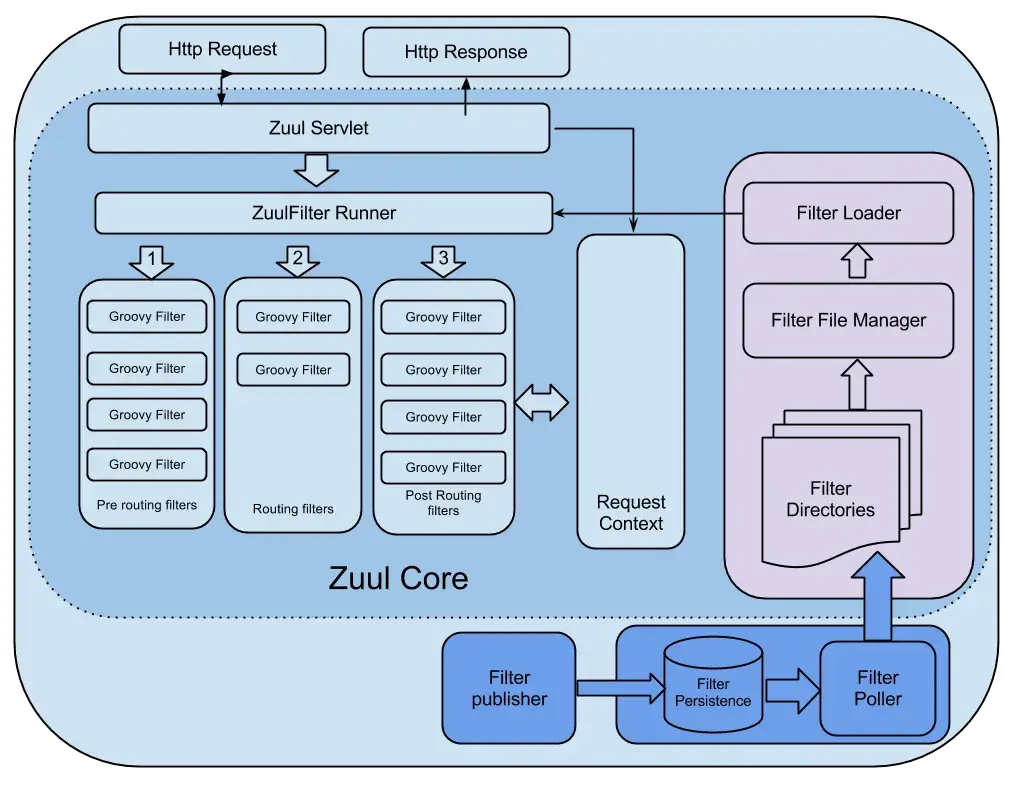
+
-Zuul 主要通过过滤器(类似于 AOP)来过滤请求,从而实现网关必备的各种功能。
+Zuul mainly uses filters (similar to AOP) to filter requests, thereby implementing various necessary functions of a gateway.
-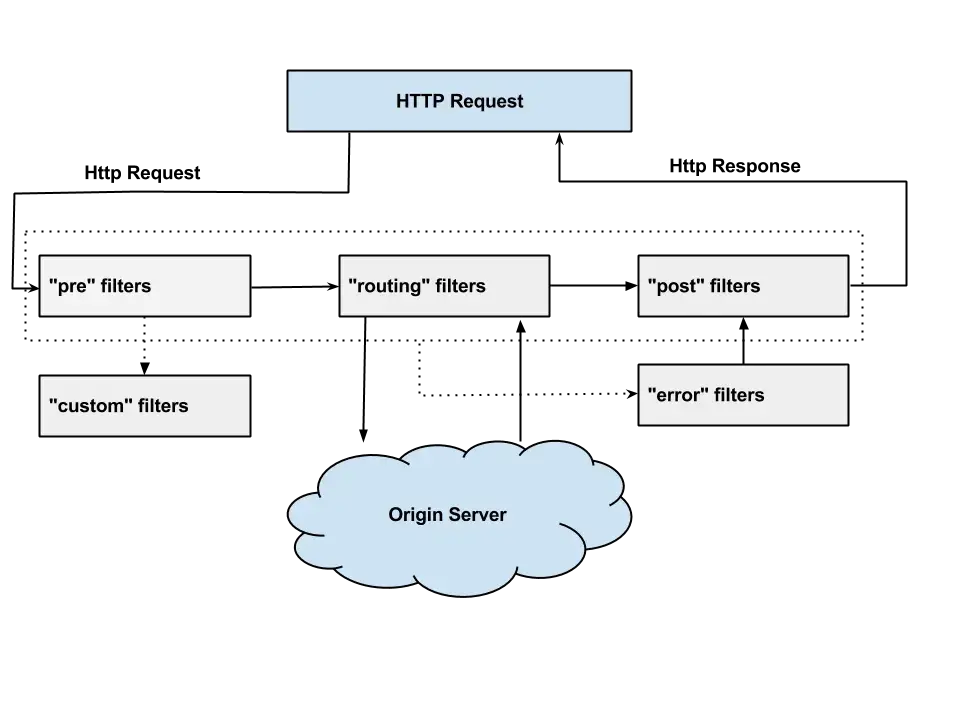
+
-我们可以自定义过滤器来处理请求,并且,Zuul 生态本身就有很多现成的过滤器供我们使用。就比如限流可以直接用国外朋友写的 [spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit](https://github.com/marcosbarbero/spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit) (这里只是举例说明,一般是配合 hystrix 来做限流):
+We can customize filters to handle requests, and the Zuul ecosystem already has many ready-made filters for us to use. For instance, rate limiting can directly use a repository written by overseas friends called [spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit](https://github.com/marcosbarbero/spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit) (this is just an example; generally, it is used in conjunction with Hystrix for rate limiting):
```xml
@@ -71,60 +71,60 @@ Zuul 主要通过过滤器(类似于 AOP)来过滤请求,从而实现网
```
-[Zuul 1.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/announcing-zuul-edge-service-in-the-cloud-ab3af5be08ee) 基于同步 IO,性能较差。[Zuul 2.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/open-sourcing-zuul-2-82ea476cb2b3) 基于 Netty 实现了异步 IO,性能得到了大幅改进。
+[Zuul 1.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/announcing-zuul-edge-service-in-the-cloud-ab3af5be08ee) is based on synchronous I/O, which performs poorly. [Zuul 2.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/open-sourcing-zuul-2-82ea476cb2b3) implements asynchronous I/O based on Netty, significantly improving performance.
-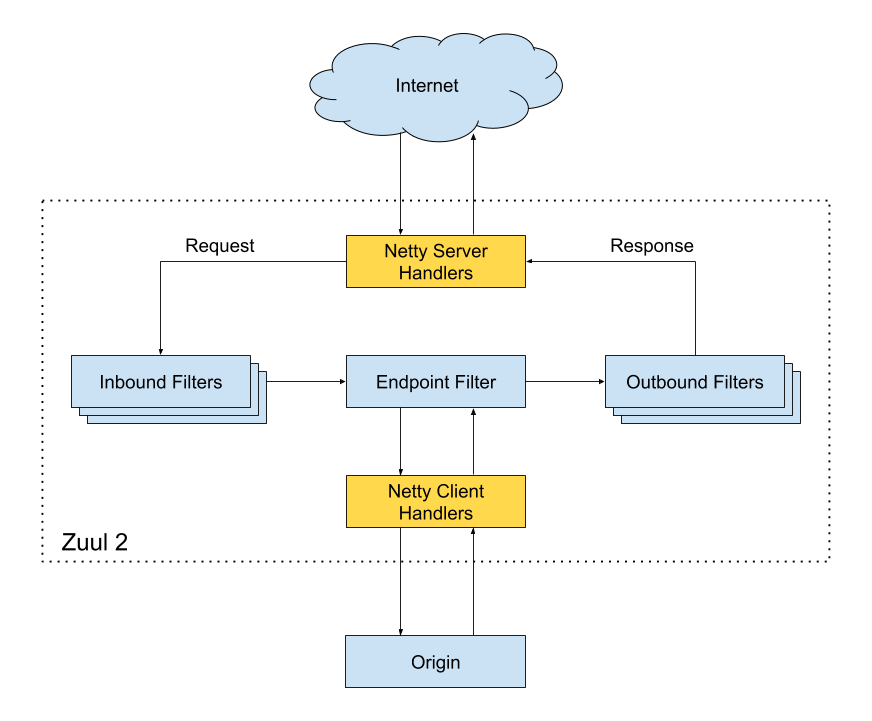
+
-- GitHub 地址:
-- 官方 Wiki:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Wiki:
### Spring Cloud Gateway
-SpringCloud Gateway 属于 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,其诞生的目标是为了替代老牌网关 **Zuul**。准确点来说,应该是 Zuul 1.x。SpringCloud Gateway 起步要比 Zuul 2.x 更早。
+Spring Cloud Gateway is a gateway in the Spring Cloud ecosystem born to replace the legacy gateway **Zuul**. More precisely, it should be Zuul 1.x. Spring Cloud Gateway started earlier than Zuul 2.x.
-为了提升网关的性能,SpringCloud Gateway 基于 Spring WebFlux 。Spring WebFlux 使用 Reactor 库来实现响应式编程模型,底层基于 Netty 实现同步非阻塞的 I/O。
+To enhance gateway performance, Spring Cloud Gateway is built on Spring WebFlux. Spring WebFlux uses the Reactor library to implement a reactive programming model, based on Netty for synchronous, non-blocking I/O.
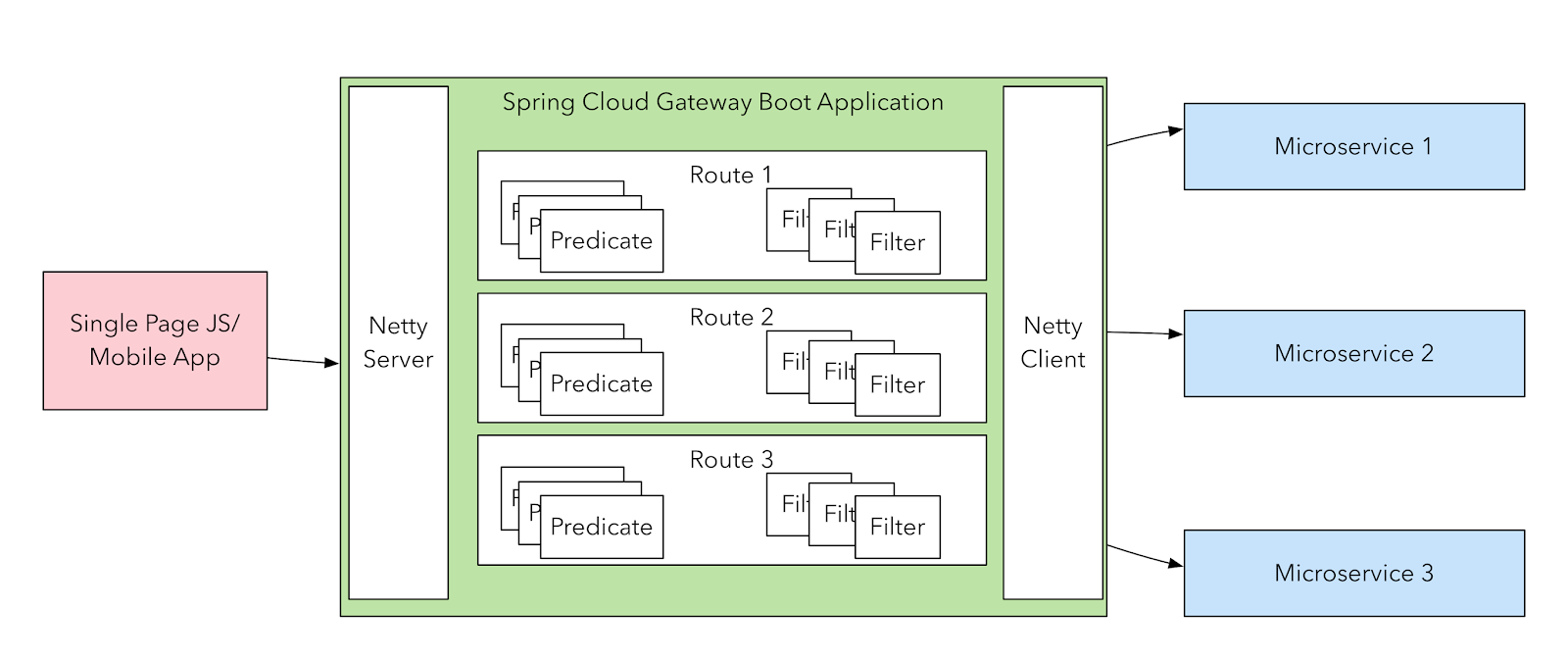
-Spring Cloud Gateway 不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,限流。
+Spring Cloud Gateway provides not only a unified routing method but also offers basic gateway functionalities based on a filter chain, such as security, monitoring/metrics, and rate limiting.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 和 Zuul 2.x 的差别不大,也是通过过滤器来处理请求。不过,目前更加推荐使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 而非 Zuul,Spring Cloud 生态对其支持更加友好。
+There aren't many differences between Spring Cloud Gateway and Zuul 2.x, both use filters to process requests. However, Spring Cloud Gateway is currently more recommended over Zuul, as the Spring Cloud ecosystem supports it more favorably.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### OpenResty
-根据官方介绍:
+According to the official introduction:
-> OpenResty 是一个基于 Nginx 与 Lua 的高性能 Web 平台,其内部集成了大量精良的 Lua 库、第三方模块以及大多数的依赖项。用于方便地搭建能够处理超高并发、扩展性极高的动态 Web 应用、Web 服务和动态网关。
+> OpenResty is a high-performance web platform based on Nginx and Lua, which integrates numerous high-quality Lua libraries, third-party modules, and most dependencies. It is used to conveniently build dynamic web applications, web services, and dynamic gateways that can handle ultra-high concurrency with high scalability.
-
+
-OpenResty 基于 Nginx,主要还是看中了其优秀的高并发能力。不过,由于 Nginx 采用 C 语言开发,二次开发门槛较高。如果想在 Nginx 上实现一些自定义的逻辑或功能,就需要编写 C 语言的模块,并重新编译 Nginx。
+OpenResty is based on Nginx, primarily due to its excellent high concurrency capability. However, because Nginx is developed in C language, the barrier to secondary development is relatively high. If you want to implement some custom logic or functionality on Nginx, it requires writing C language modules and recompiling Nginx.
-为了解决这个问题,OpenResty 通过实现 `ngx_lua` 和 `stream_lua` 等 Nginx 模块,把 Lua/LuaJIT 完美地整合进了 Nginx,从而让我们能够在 Nginx 内部里嵌入 Lua 脚本,使得可以通过简单的 Lua 语言来扩展网关的功能,比如实现自定义的路由规则、过滤器、缓存策略等。
+To solve this problem, OpenResty integrates Lua/LuaJIT perfectly into Nginx by implementing `ngx_lua` and `stream_lua` modules, allowing us to embed Lua scripts inside Nginx. This makes it possible to extend the gateway's functionality using simple Lua language, such as implementing custom routing rules, filters, caching strategies, etc.
-> Lua 是一种非常快速的动态脚本语言,它的运行速度接近于 C 语言。LuaJIT 是 Lua 的一个即时编译器,它可以显著提高 Lua 代码的执行效率。LuaJIT 将一些常用的 Lua 函数和工具库预编译并缓存,这样在下次调用时就可以直接使用缓存的字节码,从而大大加快了执行速度。
+> Lua is a very fast dynamic scripting language, with running speeds close to those of C language. LuaJIT is a just-in-time compiler for Lua that can significantly improve the execution efficiency of Lua code. LuaJIT precompiles and caches commonly used Lua functions and tool libraries, so they can be directly reused in the next call, greatly speeding up execution.
-关于 OpenResty 的入门以及网关安全实战推荐阅读这篇文章:[每个后端都应该了解的 OpenResty 入门以及网关安全实战](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3HglZs06W95vF3tSa3KrXw)。
+For an introduction to OpenResty and practical gateway security, it is recommended to read this article: [OpenResty Introduction and Gateway Security Practices Every Backend Should Know](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3HglZs06W95vF3tSa3KrXw).
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### Kong
-Kong 是一款基于 [OpenResty](https://github.com/openresty/) (Nginx + Lua)的高性能、云原生、可扩展、生态丰富的网关系统,主要由 3 个组件组成:
+Kong is a high-performance, cloud-native, scalable, and rich ecosystem gateway system based on [OpenResty](https://github.com/openresty/) (Nginx + Lua), mainly consisting of three components:
-- Kong Server:基于 Nginx 的服务器,用来接收 API 请求。
-- Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL:用来存储操作数据。
-- Kong Dashboard:官方推荐 UI 管理工具,当然,也可以使用 RESTful 方式 管理 Admin api。
+- Kong Server: A server based on Nginx, used to receive API requests.
+- Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL: Used to store operational data.
+- Kong Dashboard: Officially recommended UI management tool. Alternatively, RESTful methods can be used to manage the Admin API.
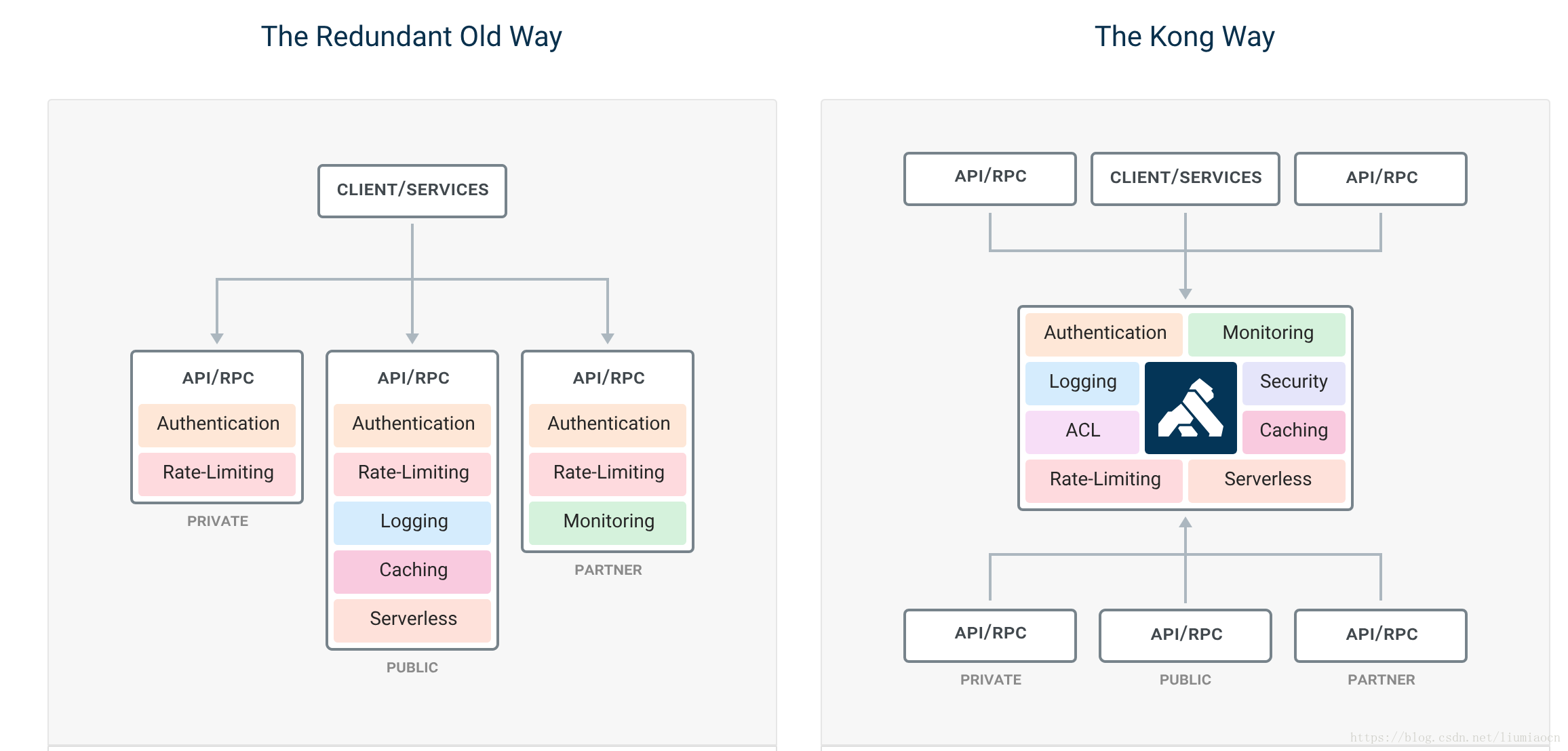
-由于默认使用 Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL 存储数据,Kong 的整个架构比较臃肿,并且会带来高可用的问题。
+Due to the default use of Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL for data storage, Kong's entire architecture can be somewhat bulky and may introduce high availability issues.
-Kong 提供了插件机制来扩展其功能,插件在 API 请求响应循环的生命周期中被执行。比如在服务上启用 Zipkin 插件:
+Kong offers a plugin mechanism to extend its functionality, executed during the API request-response lifecycle. For example, to enable the Zipkin plugin on a service:
```shell
$ curl -X POST http://kong:8001/services/{service}/plugins \
@@ -133,79 +133,79 @@ $ curl -X POST http://kong:8001/services/{service}/plugins \
--data "config.sample_ratio=0.001"
```
-Kong 本身就是一个 Lua 应用程序,并且是在 Openresty 的基础之上做了一层封装的应用。归根结底就是利用 Lua 嵌入 Nginx 的方式,赋予了 Nginx 可编程的能力,这样以插件的形式在 Nginx 这一层能够做到无限想象的事情。例如限流、安全访问策略、路由、负载均衡等等。编写一个 Kong 插件,就是按照 Kong 插件编写规范,写一个自己自定义的 Lua 脚本,然后加载到 Kong 中,最后引用即可。
+Kong itself is a Lua application, but it is also an encapsulated application built on top of OpenResty. Ultimately, it empowers Nginx with programmable capabilities using the embedded Lua approach, enabling endless possibilities through plugins for things like rate limiting, security access policies, routing, load balancing, and so on. Writing a Kong plugin involves creating a custom Lua script following the Kong plugin development standards and loading it into Kong.
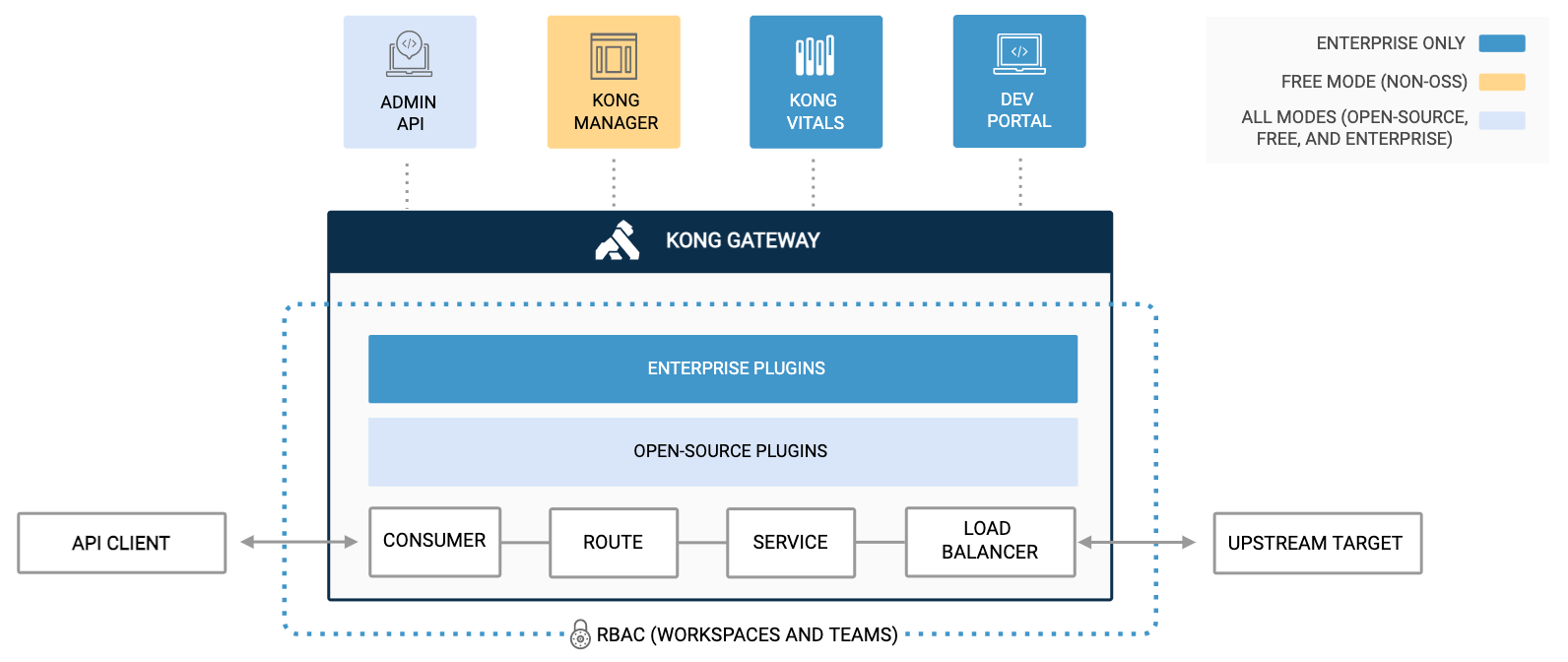
-除了 Lua,Kong 还可以基于 Go 、JavaScript、Python 等语言开发插件,得益于对应的 PDK(插件开发工具包)。
+In addition to Lua, Kong can also develop plugins based on Go, JavaScript, Python, and other languages, thanks to the corresponding PDK (Plugin Development Kit).
-关于 Kong 插件的详细介绍,推荐阅读官方文档:,写的比较详细。
+For a detailed introduction to Kong plugins, it is recommended to read the official documentation: , which is quite comprehensive.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### APISIX
-APISIX 是一款基于 OpenResty 和 etcd 的高性能、云原生、可扩展的网关系统。
+APISIX is a high-performance, cloud-native, scalable gateway system based on OpenResty and etcd.
-> etcd 是使用 Go 语言开发的一个开源的、高可用的分布式 key-value 存储系统,使用 Raft 协议做分布式共识。
+> etcd is an open-source, high-availability distributed key-value store system developed using Go, utilizing the Raft protocol for distributed consensus.
-与传统 API 网关相比,APISIX 具有动态路由和插件热加载,特别适合微服务系统下的 API 管理。并且,APISIX 与 SkyWalking(分布式链路追踪系统)、Zipkin(分布式链路追踪系统)、Prometheus(监控系统) 等 DevOps 生态工具对接都十分方便。
+Compared to traditional API gateways, APISIX has dynamic routing and hot plugin loading, making it especially suitable for API management in microservice systems. Additionally, APISIX integrates easily with various DevOps tools such as SkyWalking (distributed tracing system), Zipkin (distributed tracing system), and Prometheus (monitoring system).
-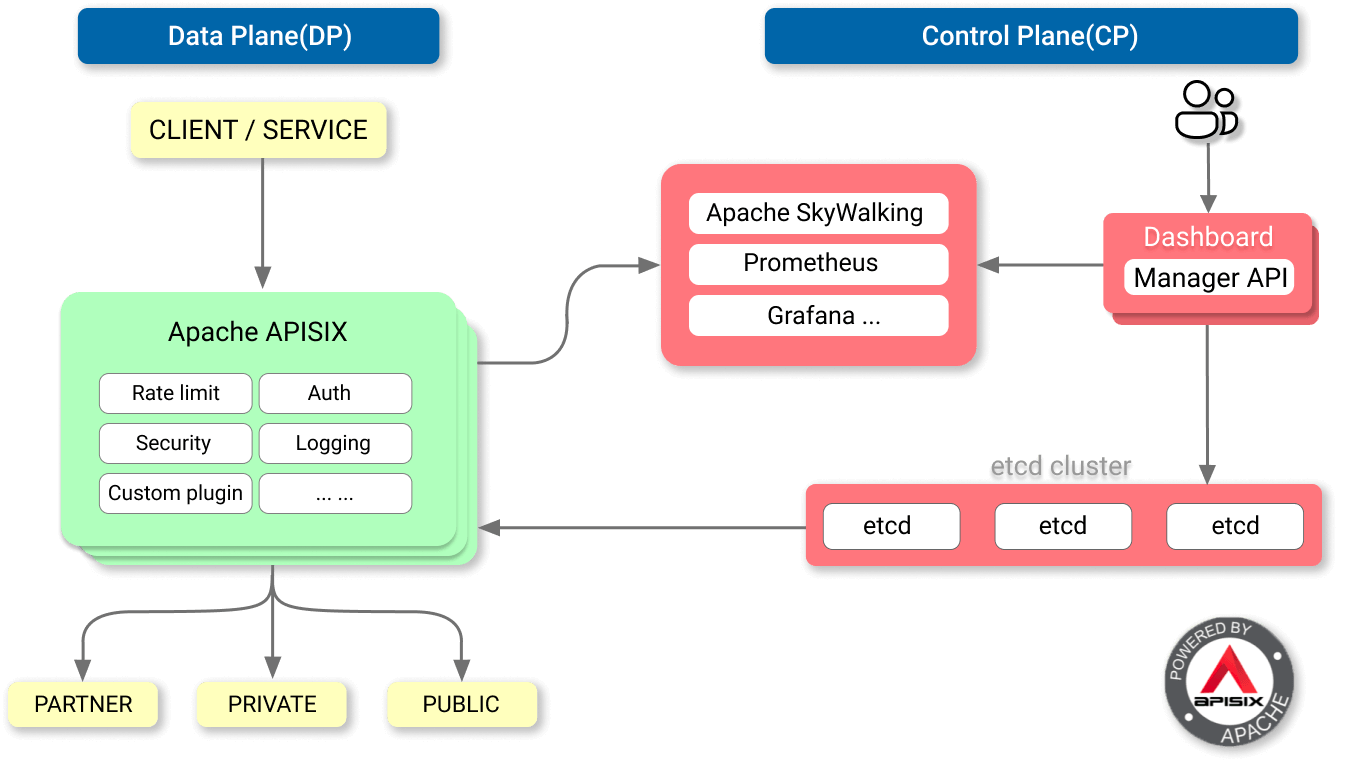
+
-作为 Nginx 和 Kong 的替代项目,APISIX 目前已经是 Apache 顶级开源项目,并且是最快毕业的国产开源项目。国内目前已经有很多知名企业(比如金山、有赞、爱奇艺、腾讯、贝壳)使用 APISIX 处理核心的业务流量。
+As an alternative project to Nginx and Kong, APISIX is currently an Apache top-level open-source project and is the fastest domestic open-source project to graduate. Many well-known domestic enterprises (such as Kingsoft, Youzan, iQIYI, Tencent, and Beike) are using APISIX to handle core business traffic.
-根据官网介绍:“APISIX 已经生产可用,功能、性能、架构全面优于 Kong”。
+According to the official site: "APISIX is already production-ready and has comprehensive features, performance, and architecture surpassing Kong."
-APISIX 同样支持定制化的插件开发。开发者除了能够使用 Lua 语言开发插件,还能通过下面两种方式开发来避开 Lua 语言的学习成本:
+APISIX also supports customizable plugin development. Developers can create plugins using Lua, and they can also do so in the following two ways to avoid the learning cost of Lua:
-- 通过 Plugin Runner 来支持更多的主流编程语言(比如 Java、Python、Go 等等)。通过这样的方式,可以让后端工程师通过本地 RPC 通信,使用熟悉的编程语言开发 APISIX 的插件。这样做的好处是减少了开发成本,提高了开发效率,但是在性能上会有一些损失。
-- 使用 Wasm(WebAssembly) 开发插件。Wasm 被嵌入到了 APISIX 中,用户可以使用 Wasm 去编译成 Wasm 的字节码在 APISIX 中运行。
+- Use Plugin Runner to support more mainstream programming languages (such as Java, Python, Go, etc.). This allows backend engineers to develop APISIX plugins using familiar programming languages via local RPC communication. This approach reduces development costs and improves efficiency, although there will be some performance losses.
+- Use Wasm (WebAssembly) to develop plugins. Wasm is embedded in APISIX, allowing users to compile their code into Wasm bytecode to run in APISIX.
-> Wasm 是基于堆栈的虚拟机的二进制指令格式,一种低级汇编语言,旨在非常接近已编译的机器代码,并且非常接近本机性能。Wasm 最初是为浏览器构建的,但是随着技术的成熟,在服务器端看到了越来越多的用例。
+> Wasm is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine, a low-level assembly language designed to be very close to compiled machine code and very close to native performance. Originally built for browsers, as the technology matured, more use cases for server-side applications have emerged.

-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
-相关阅读:
+Related articles:
-- [为什么说 Apache APISIX 是最好的 API 网关?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j8ggPGEHFu3x5ekJZyeZnA)
-- [有了 NGINX 和 Kong,为什么还需要 Apache APISIX](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog/why-we-need-Apache-APISIX)
-- [APISIX 技术博客](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog)
-- [APISIX 用户案例](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/usercases)(推荐)
+- [Why Apache APISIX is the Best API Gateway?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j8ggPGEHFu3x5ekJZyeZnA)
+- [With NGINX and Kong, Why Do We Still Need Apache APISIX](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog/why-we-need-Apache-APISIX)
+- [APISIX Technical Blog](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog)
+- [APISIX User Cases](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/usercases) (Recommended)
### Shenyu
-Shenyu 是一款基于 WebFlux 的可扩展、高性能、响应式网关,Apache 顶级开源项目。
+Shenyu is an extensible, high-performance, and reactive gateway based on WebFlux, and is an Apache top-level open-source project.
-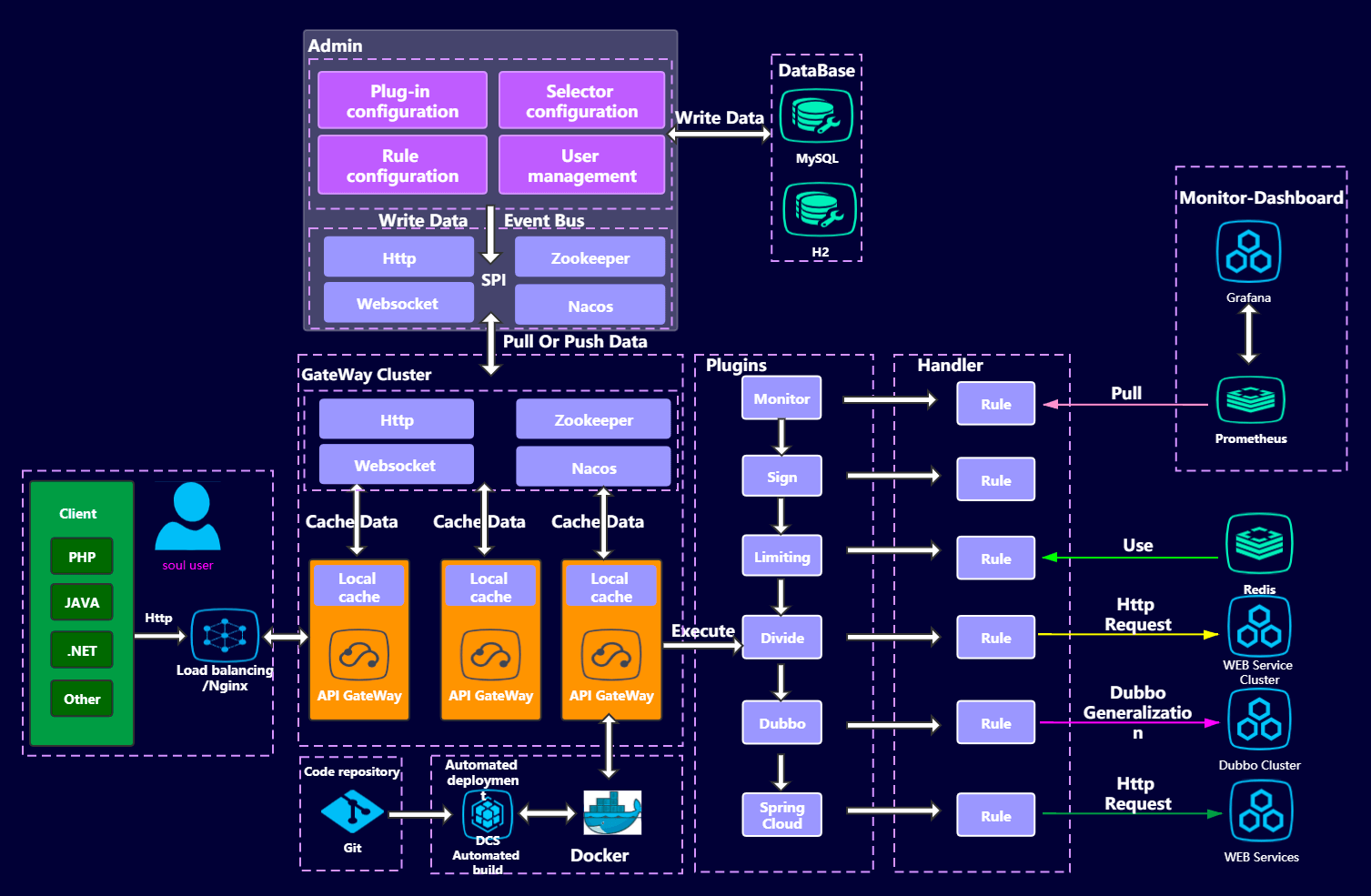
+
-Shenyu 通过插件扩展功能,插件是 ShenYu 的灵魂,并且插件也是可扩展和热插拔的。不同的插件实现不同的功能。Shenyu 自带了诸如限流、熔断、转发、重写、重定向、和路由监控等插件。
+Shenyu extends its functionality through plugins, which are the soul of Shenyu, and the plugins are also extensible and hot-swappable. Different plugins implement different features. Shenyu comes with built-in plugins for rate limiting, circuit breaking, forwarding, rewriting, redirection, and routing monitoring.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
-## 如何选择?
+## How to Choose?
-上面介绍的几个常见的网关系统,最常用的是 Spring Cloud Gateway、Kong、APISIX 这三个。
+Among the common gateway systems introduced above, the three most commonly used are Spring Cloud Gateway, Kong, and APISIX.
-对于公司业务以 Java 为主要开发语言的情况下,Spring Cloud Gateway 通常是个不错的选择,其优点有:简单易用、成熟稳定、与 Spring Cloud 生态系统兼容、Spring 社区成熟等等。不过,Spring Cloud Gateway 也有一些局限性和不足之处, 一般还需要结合其他网关一起使用比如 OpenResty。并且,其性能相比较于 Kong 和 APISIX,还是差一些。如果对性能要求比较高的话,Spring Cloud Gateway 不是一个好的选择。
+For companies where Java is the primary development language, Spring Cloud Gateway is typically a good choice, with advantages such as: simplicity, maturity and stability, compatibility with the Spring Cloud ecosystem, and a mature Spring community, etc. However, Spring Cloud Gateway also has some limitations and shortcomings, generally requiring it to be used in conjunction with other gateways like OpenResty. Moreover, its performance is still somewhat inferior compared to Kong and APISIX. If performance is a significant concern, Spring Cloud Gateway is not a good choice.
-Kong 和 APISIX 功能更丰富,性能更强大,技术架构更贴合云原生。Kong 是开源 API 网关的鼻祖,生态丰富,用户群体庞大。APISIX 属于后来者,更优秀一些,根据 APISIX 官网介绍:“APISIX 已经生产可用,功能、性能、架构全面优于 Kong”。下面简单对比一下二者:
+Kong and APISIX offer more robust functionality, with stronger performance and a technology architecture more aligned with cloud-native principles. Kong is the pioneer of open-source API gateways, with a rich ecosystem and a large user base. APISIX, as a later entrant, is even better; according to its official site: "APISIX is already production-ready, with functionality, performance, and architecture comprehensively superior to Kong." Below is a brief comparison between the two:
-- APISIX 基于 etcd 来做配置中心,不存在单点问题,云原生友好;而 Kong 基于 Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL ,存在单点风险,需要额外的基础设施保障做高可用。
-- APISIX 支持热更新,并且实现了毫秒级别的热更新响应;而 Kong 不支持热更新。
-- APISIX 的性能要优于 Kong 。
-- APISIX 支持的插件更多,功能更丰富。
+- APISIX uses etcd as a configuration center, avoiding single point issues and is cloud-native friendly; whereas Kong relies on Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL, which has single point risks and requires additional infrastructure for high availability.
+- APISIX supports hot updates and achieves milliseconds-level hot update response; while Kong does not support hot updates.
+- APISIX exhibits superior performance compared to Kong.
+- APISIX supports a greater number of plugins, with richer functionalities.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Kong 插件开发教程[通俗易懂]:
-- API 网关 Kong 实战:
-- Spring Cloud Gateway 原理介绍和应用:
-- 微服务为什么要用到 API 网关?:
+- Kong Plugin Development Tutorial \[Easy to Understand\]:
+- API Gateway Kong Practical Application:
+- Introduction to Spring Cloud Gateway Principles and Applications:
+- Why Do Microservices Need an API Gateway?:
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
index 2e00aec70a3..1759140bcd6 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
---
-title: 分布式配置中心常见问题总结(付费)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Issues in Distributed Configuration Centers (Paid)
+category: Distributed
---
-**分布式配置中心** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了《Java 面试指北》中。
+The interview questions related to **Distributed Configuration Centers** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to see the detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled into the "Java Interview Guide."

diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
index 5b737f34593..8d545e4cfb9 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
@@ -1,173 +1,62 @@
---
-title: 分布式ID设计指南
-category: 分布式
+title: Distributed ID Design Guide
+category: Distributed
---
::: tip
-看到百度 Geek 说的一篇结合具体场景聊分布式 ID 设计的文章,感觉挺不错的。于是,我将这篇文章的部分内容整理到了这里。原文传送门:[分布式 ID 生成服务的技术原理和项目实战](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bFDLb6U6EgI-DvCdLTq_QA) 。
+I came across an article by Baidu Geek discussing the design of distributed IDs in specific scenarios, and I found it quite insightful. Therefore, I have organized some of the content from this article here. You can find the original article here: [Technical Principles and Project Practice of Distributed ID Generation Service](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bFDLb6U6EgI-DvCdLTq_QA).
:::
-网上绝大多数的分布式 ID 生成服务,一般着重于技术原理剖析,很少见到根据具体的业务场景去选型 ID 生成服务的文章。
+Most distributed ID generation services available online generally focus on technical principles and rarely discuss how to choose ID generation services based on specific business scenarios.
-本文结合一些使用场景,进一步探讨业务场景中对 ID 有哪些具体的要求。
+This article explores the specific requirements for IDs in various business scenarios.
-## 场景一:订单系统
+## Scenario 1: Order System
-我们在商场买东西一码付二维码,下单生成的订单号,使用到的优惠券码,联合商品兑换券码,这些是在网上购物经常使用到的单号,那么为什么有些单号那么长,有些只有几位数?有些单号一看就知道年月日的信息,有些却看不出任何意义?下面展开分析下订单系统中不同场景的 id 服务的具体实现。
+When we shop in a mall, we often use a QR code for payment, and the order number generated upon placing an order, along with the coupon codes and product exchange codes, are frequently used identifiers in online shopping. So why are some order numbers so long while others are only a few digits? Some order numbers clearly indicate the date, while others seem meaningless. Below, we analyze the specific implementations of ID services in different scenarios within the order system.
-### 1、一码付
+### 1. One-Code Payment
-我们常见的一码付,指的是一个二维码可以使用支付宝或者微信进行扫码支付。
+The common one-code payment refers to a QR code that can be scanned using Alipay or WeChat for payment.
-二维码的本质是一个字符串。聚合码的本质就是一个链接地址。用户使用支付宝微信直接扫一个码付钱,不用担心拿支付宝扫了微信的收款码或者用微信扫了支付宝的收款码,这极大减少了用户扫码支付的时间。
+The essence of a QR code is a string. The aggregation code is essentially a link. Users can directly scan a code with Alipay or WeChat to make payments without worrying about scanning the wrong payment code, which greatly reduces the time taken for users to complete the payment.
-实现原理是当客户用 APP 扫码后,网站后台就会判断客户的扫码环境。(微信、支付宝、QQ 钱包、京东支付、云闪付等)。
+The implementation principle is that when a customer scans the code with the app, the website backend determines the customer's scanning environment (WeChat, Alipay, QQ Wallet, JD Pay, UnionPay, etc.).
-判断扫码环境的原理就是根据打开链接浏览器的 HTTP header。任何浏览器打开 http 链接时,请求的 header 都会有 User-Agent(UA、用户代理)信息。
+The principle for determining the scanning environment is based on the HTTP header of the browser that opens the link. Any browser that opens an HTTP link will have a User-Agent (UA) information in the request header.
-UA 是一个特殊字符串头,服务器依次可以识别出客户使用的操作系统及版本、CPU 类型、浏览器及版本、浏览器渲染引擎、浏览器语言、浏览器插件等很多信息。
+The UA is a special string header that allows the server to identify the customer's operating system and version, CPU type, browser and version, browser rendering engine, browser language, browser plugins, and much more.
-各渠道对应支付产品的名称不一样,一定要仔细看各支付产品的 API 介绍。
+The names of payment products vary across different channels, so it is essential to carefully review the API documentation for each payment product.
-1. 微信支付:JSAPI 支付支付
-2. 支付宝:手机网站支付
-3. QQ 钱包:公众号支付
+1. WeChat Pay: JSAPI Payment
+1. Alipay: Mobile Website Payment
+1. QQ Wallet: Public Account Payment
-其本质均为在 APP 内置浏览器中实现 HTML5 支付。
+Essentially, they all implement HTML5 payment within the app's built-in browser.
-
+
-文库的研发同学在这个思路上,做了优化迭代。动态生成一码付的二维码预先绑定用户所选的商品信息和价格,根据用户所选的商品动态更新。这样不仅支持一码多平台调起支付,而且不用用户选择商品输入金额,即可完成订单支付的功能,很丝滑。用户在真正扫码后,服务端才通过前端获取用户 UID,结合二维码绑定的商品信息,真正的生成订单,发送支付信息到第三方(qq、微信、支付宝),第三方生成支付订单推给用户设备,从而调起支付。
+The development team at the library has optimized this approach. They dynamically generate a one-code payment QR code that is pre-bound to the product information and price selected by the user, updating dynamically based on the user's selection. This not only supports multi-platform payment initiation but also allows users to complete order payments without selecting products or entering amounts, providing a smooth experience. Only after the user scans the code does the server obtain the user's UID from the frontend, combine it with the product information bound to the QR code, truly generate the order, and send the payment information to third parties (QQ, WeChat, Alipay), which then generate the payment order and push it to the user's device to initiate payment.
-区别于固定的一码付,在文库的应用中,使用到了动态二维码,二维码本质是一个短网址,ID 服务提供短网址的唯一标志参数。唯一的短网址映射的 ID 绑定了商品的订单信息,技术和业务的深度结合,缩短了支付流程,提升用户的支付体验。
+Unlike fixed one-code payments, the library's application uses dynamic QR codes, where the QR code is essentially a short URL, and the ID service provides a unique identifier for the short URL. The unique short URL maps to the ID bound to the product's order information, deeply integrating technology and business, shortening the payment process, and enhancing the user's payment experience.
-### 2、订单号
+### 2. Order Number
-订单号在实际的业务过程中作为一个订单的唯一标识码存在,一般实现以下业务场景:
+In actual business processes, the order number serves as a unique identifier for an order and generally fulfills the following business scenarios:
-1. 用户订单遇到问题,需要找客服进行协助;
-2. 对订单进行操作,如线下收款,订单核销;
-3. 下单,改单,成单,退单,售后等系统内部的订单流程处理和跟进。
+1. Users encounter issues with their orders and need to contact customer service for assistance.
+1. Operations on the order, such as offline payments and order verification.
+1. Internal order processing and follow-up for placing, modifying, completing, canceling, and after-sales orders.
-很多时候搜索订单相关信息的时候都是以订单 ID 作为唯一标识符,这是由于订单号的生成规则的唯一性决定的。从技术角度看,除了 ID 服务必要的特性之外,在订单号的设计上需要体现几个特性:
+Often, when searching for order-related information, the order ID is used as a unique identifier, which is determined by the uniqueness of the order number generation rules. From a technical perspective, in addition to the necessary characteristics of the ID service, the design of the order number needs to reflect several features:
-**(1)信息安全**
+**(1) Information Security**
-编号不能透露公司的运营情况,比如日销、公司流水号等信息,以及商业信息和用户手机号,身份证等隐私信息。并且不能有明显的整体规律(可以有局部规律),任意修改一个字符就能查询到另一个订单信息,这也是不允许的。
+The numbering should not reveal the company's operational status, such as daily sales, company serial numbers, or any commercial information and user privacy information like phone numbers and ID numbers. Additionally, there should not be any obvious overall patterns (local patterns are acceptable), and modifying a single character should not allow access to another order's information.
-类比于我们高考时候的考生编号的生成规则,一定不能是连号的,否则只需要根据顺序往下查询就能搜索到别的考生的成绩,这是绝对不可允许。
+This is akin to the generation rules for student numbers during our college entrance examination, which must not be sequential; otherwise, one could easily search for another student's scores based on the order.
-**(2)部分可读**
-
-位数要便于操作,因此要求订单号的位数适中,且局部有规律。这样可以方便在订单异常,或者退货时客服查询。
-
-过长的订单号或易读性差的订单号会导致客服输入困难且易错率较高,影响用户体验的售后体验。因此在实际的业务场景中,订单号的设计通常都会适当携带一些允许公开的对使用场景有帮助的信息,如时间,星期,类型等等,这个主要根据所涉及的编号对应的使用场景来。
-
-而且像时间、星期这些自增长的属于作为订单号的设计的一部分元素,有助于解决业务累积而导致的订单号重复的问题。
-
-**(3)查询效率**
-
-常见的电商平台订单号大多是纯数字组成,兼具可读性的同时,int 类型相对 varchar 类型的查询效率更高,对在线业务更加友好。
-
-### 3、优惠券和兑换券
-
-优惠券、兑换券是运营推广最常用的促销工具之一,合理使用它们,可以让买家得到实惠,商家提升商品销量。常见场景有:
-
-1. 在文库购买【文库 VIP+QQ 音乐年卡】联合商品,支付成功后会得到 QQ 音乐年卡的兑换码,可以去 QQ 音乐 App 兑换音乐会员年卡;
-2. 疫情期间,部分地方政府发放的消费券;
-3. 瓶装饮料经常会出现输入优惠编码兑换奖品。
-
-
-
-从技术角度看,有些场景适合 ID 即时生成,比如电商平台购物领取的优惠券,只需要在用户领取时分配优惠券信息即可。有些线上线下结合的场景,比如疫情优惠券,瓶盖开奖,京东卡,超市卡这种,则需要预先生成,预先生成的券码具备以下特性:
-
-1.预先生成,在活动正式开始前提供出来进行活动预热;
-
-2.优惠券体量大,以万为单位,通常在 10 万级别以上;
-
-3.不可破解、仿制券码;
-
-4.支持用后核销;
-
-5.优惠券、兑换券属于广撒网的策略,所以利用率低,也就不适合使用数据库进行存储 **(占空间,有效的数据又少)**。
-
-设计思路上,需要设计一种有效的兑换码生成策略,支持预先生成,支持校验,内容简洁,生成的兑换码都具有唯一性,那么这种策略就是一种特殊的编解码策略,按照约定的编解码规则支撑上述需求。
-
-既然是一种编解码规则,那么需要约定编码空间(也就是用户看到的组成兑换码的字符),编码空间由字符 a-z,A-Z,数字 0-9 组成,为了增强兑换码的可识别度,剔除大写字母 O 以及 I,可用字符如下所示,共 60 个字符:
-
-abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXZY0123456789
-
-之前说过,兑换码要求尽可能简洁,那么设计时就需要考虑兑换码的字符数,假设上限为 12 位,而字符空间有 60 位,那么可以表示的空间范围为 60^12=130606940160000000000000(也就是可以 12 位的兑换码可以生成天量,应该够运营同学挥霍了),转换成 2 进制:
-
-1001000100000000101110011001101101110011000000000000000000000(61 位)
-
-**兑换码组成成分分析**
-
-兑换码可以预先生成,并且不需要额外的存储空间保存这些信息,每一个优惠方案都有独立的一组兑换码(指运营同学组织的每一场运营活动都有不同的兑换码,不能混合使用, 例如双 11 兑换码不能使用在双 12 活动上),每个兑换码有自己的编号,防止重复,为了保证兑换码的有效性,对兑换码的数据需要进行校验,当前兑换码的数据组成如下所示:
-
-优惠方案 ID + 兑换码序列号 i + 校验码
-
-**编码方案**
-
-1. 兑换码序列号 i,代表当前兑换码是当前活动中第 i 个兑换码,兑换码序列号的空间范围决定了优惠活动可以发行的兑换码数目,当前采用 30 位 bit 位表示,可表示范围:1073741824(10 亿个券码)。
-2. 优惠方案 ID, 代表当前优惠方案的 ID 号,优惠方案的空间范围决定了可以组织的优惠活动次数,当前采用 15 位表示,可以表示范围:32768(考虑到运营活动的频率,以及 ID 的初始值 10000,15 位足够,365 天每天有运营活动,可以使用 54 年)。
-3. 校验码,校验兑换码是否有效,主要为了快捷的校验兑换码信息的是否正确,其次可以起到填充数据的目的,增强数据的散列性,使用 13 位表示校验位,其中分为两部分,前 6 位和后 7 位。
-
-深耕业务还会有区分通用券和单独券的情况,分别具备以下特点,技术实现需要因地制宜地思考。
-
-1. 通用券:多个玩家都可以输入兑换,然后有总量限制,期限限制。
-2. 单独券:运营同学可以在后台设置兑换码的奖励物品、期限、个数,然后由后台生成兑换码的列表,兑换之后核销。
-
-## 场景二:Tracing
-
-### 1、日志跟踪
-
-在分布式服务架构下,一个 Web 请求从网关流入,有可能会调用多个服务对请求进行处理,拿到最终结果。这个过程中每个服务之间的通信又是单独的网络请求,无论请求经过的哪个服务出了故障或者处理过慢都会对前端造成影响。
-
-处理一个 Web 请求要调用的多个服务,为了能更方便的查询哪个环节的服务出现了问题,现在常用的解决方案是为整个系统引入分布式链路跟踪。
-
-
-
-在分布式链路跟踪中有两个重要的概念:跟踪(trace)和 跨度( span)。trace 是请求在分布式系统中的整个链路视图,span 则代表整个链路中不同服务内部的视图,span 组合在一起就是整个 trace 的视图。
-
-在整个请求的调用链中,请求会一直携带 traceid 往下游服务传递,每个服务内部也会生成自己的 spanid 用于生成自己的内部调用视图,并和 traceid 一起传递给下游服务。
-
-### 2、TraceId 生成规则
-
-这种场景下,生成的 ID 除了要求唯一之外,还要求生成的效率高、吞吐量大。traceid 需要具备接入层的服务器实例自主生成的能力,如果每个 trace 中的 ID 都需要请求公共的 ID 服务生成,纯纯的浪费网络带宽资源。且会阻塞用户请求向下游传递,响应耗时上升,增加了没必要的风险。所以需要服务器实例最好可以自行计算 tracid,spanid,避免依赖外部服务。
-
-产生规则:服务器 IP + ID 产生的时间 + 自增序列 + 当前进程号 ,比如:
-
-0ad1348f1403169275002100356696
-
-前 8 位 0ad1348f 即产生 TraceId 的机器的 IP,这是一个十六进制的数字,每两位代表 IP 中的一段,我们把这个数字,按每两位转成 10 进制即可得到常见的 IP 地址表示方式 10.209.52.143,您也可以根据这个规律来查找到请求经过的第一个服务器。
-
-后面的 13 位 1403169275002 是产生 TraceId 的时间。之后的 4 位 1003 是一个自增的序列,从 1000 涨到 9000,到达 9000 后回到 1000 再开始往上涨。最后的 5 位 56696 是当前的进程 ID,为了防止单机多进程出现 TraceId 冲突的情况,所以在 TraceId 末尾添加了当前的进程 ID。
-
-### 3、SpanId 生成规则
-
-span 是层的意思,比如在第一个实例算是第一层, 请求代理或者分流到下一个实例处理,就是第二层,以此类推。通过层,SpanId 代表本次调用在整个调用链路树中的位置。
-
-假设一个 服务器实例 A 接收了一次用户请求,代表是整个调用的根节点,那么 A 层处理这次请求产生的非服务调用日志记录 spanid 的值都是 0,A 层需要通过 RPC 依次调用 B、C、D 三个服务器实例,那么在 A 的日志中,SpanId 分别是 0.1,0.2 和 0.3,在 B、C、D 中,SpanId 也分别是 0.1,0.2 和 0.3;如果 C 系统在处理请求的时候又调用了 E,F 两个服务器实例,那么 C 系统中对应的 spanid 是 0.2.1 和 0.2.2,E、F 两个系统对应的日志也是 0.2.1 和 0.2.2。
-
-根据上面的描述可以知道,如果把一次调用中所有的 SpanId 收集起来,可以组成一棵完整的链路树。
-
-**spanid 的生成本质:在跨层传递透传的同时,控制大小版本号的自增来实现的。**
-
-## 场景三:短网址
-
-短网址主要功能包括网址缩短与还原两大功能。相对于长网址,短网址可以更方便地在电子邮件,社交网络,微博和手机上传播,例如原来很长的网址通过短网址服务即可生成相应的短网址,避免折行或超出字符限制。
-
-
-
-常用的 ID 生成服务比如:MySQL ID 自增、 Redis 键自增、号段模式,生成的 ID 都是一串数字。短网址服务把客户的长网址转换成短网址,
-
-实际是在 dwz.cn 域名后面拼接新产生的数字类型 ID,直接用数字 ID,网址长度也有些长,服务可以通过数字 ID 转更高进制的方式压缩长度。这种算法在短网址的技术实现上越来越多了起来,它可以进一步压缩网址长度。转进制的压缩算法在生活中有广泛的应用场景,举例:
-
-- 客户的长网址:
-- ID 映射的短网址: (演示使用,可能无法正确打开)
-- 转进制后的短网址: (演示使用,可能无法正确打开)
-
-
+\*\*(2) Partial
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
index 9920f8f7753..e23a8336dbf 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
@@ -1,65 +1,65 @@
---
-title: 分布式ID介绍&实现方案总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Introduction to Distributed ID & Summary of Implementation Solutions
+category: Distributed
---
-## 分布式 ID 介绍
+## Introduction to Distributed ID
-### 什么是 ID?
+### What is an ID?
-日常开发中,我们需要对系统中的各种数据使用 ID 唯一表示,比如用户 ID 对应且仅对应一个人,商品 ID 对应且仅对应一件商品,订单 ID 对应且仅对应一个订单。
+In daily development, we need to uniquely represent various data in the system using IDs. For example, a user ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one person, a product ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one product, and an order ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one order.
-我们现实生活中也有各种 ID,比如身份证 ID 对应且仅对应一个人、地址 ID 对应且仅对应一个地址。
+In real life, we also have various IDs, such as an ID card ID that corresponds to and only corresponds to one person, and an address ID that corresponds to and only corresponds to one address.
-简单来说,**ID 就是数据的唯一标识**。
+In simple terms, **an ID is a unique identifier for data**.
-### 什么是分布式 ID?
+### What is a Distributed ID?
-分布式 ID 是分布式系统下的 ID。分布式 ID 不存在与现实生活中,属于计算机系统中的一个概念。
+A distributed ID is an ID used in a distributed system. Distributed IDs do not exist in real life; they are a concept within computer systems.
-我简单举一个分库分表的例子。
+Let me give a simple example of sharding.
-我司的一个项目,使用的是单机 MySQL 。但是,没想到的是,项目上线一个月之后,随着使用人数越来越多,整个系统的数据量将越来越大。单机 MySQL 已经没办法支撑了,需要进行分库分表(推荐 Sharding-JDBC)。
+In one of our projects, we used a standalone MySQL database. However, unexpectedly, after the project went live for a month, as the number of users increased, the data volume of the entire system grew larger. The standalone MySQL could no longer support it, and we needed to implement sharding (recommended Sharding-JDBC).
-在分库之后, 数据遍布在不同服务器上的数据库,数据库的自增主键已经没办法满足生成的主键唯一了。**我们如何为不同的数据节点生成全局唯一主键呢?**
+After sharding, the data is distributed across databases on different servers, and the auto-incrementing primary key of the database can no longer guarantee the uniqueness of the generated primary key. **How do we generate a globally unique primary key for different data nodes?**
-这个时候就需要生成**分布式 ID**了。
+At this point, we need to generate **distributed IDs**.
-### 分布式 ID 需要满足哪些要求?
+### What Requirements Must Distributed IDs Meet?
-分布式 ID 作为分布式系统中必不可少的一环,很多地方都要用到分布式 ID。
+As an essential part of a distributed system, distributed IDs are needed in many places.
-一个最基本的分布式 ID 需要满足下面这些要求:
+A basic distributed ID must meet the following requirements:
-- **全局唯一**:ID 的全局唯一性肯定是首先要满足的!
-- **高性能**:分布式 ID 的生成速度要快,对本地资源消耗要小。
-- **高可用**:生成分布式 ID 的服务要保证可用性无限接近于 100%。
-- **方便易用**:拿来即用,使用方便,快速接入!
+- **Globally Unique**: The global uniqueness of the ID must be guaranteed!
+- **High Performance**: The generation speed of distributed IDs must be fast, with minimal local resource consumption.
+- **High Availability**: The service generating distributed IDs must ensure availability close to 100%.
+- **Convenient and Easy to Use**: It should be ready to use, easy to implement, and quickly integrated!
-除了这些之外,一个比较好的分布式 ID 还应保证:
+In addition to these, a good distributed ID should also ensure:
-- **安全**:ID 中不包含敏感信息。
-- **有序递增**:如果要把 ID 存放在数据库的话,ID 的有序性可以提升数据库写入速度。并且,很多时候 ,我们还很有可能会直接通过 ID 来进行排序。
-- **有具体的业务含义**:生成的 ID 如果能有具体的业务含义,可以让定位问题以及开发更透明化(通过 ID 就能确定是哪个业务)。
-- **独立部署**:也就是分布式系统单独有一个发号器服务,专门用来生成分布式 ID。这样就生成 ID 的服务可以和业务相关的服务解耦。不过,这样同样带来了网络调用消耗增加的问题。总的来说,如果需要用到分布式 ID 的场景比较多的话,独立部署的发号器服务还是很有必要的。
+- **Security**: The ID should not contain sensitive information.
+- **Ordered Increment**: If IDs are to be stored in a database, the order of IDs can improve database write speed. Moreover, many times, we may directly sort by ID.
+- **Specific Business Meaning**: If the generated ID has specific business meaning, it can make problem identification and development more transparent (the ID can indicate which business it belongs to).
+- **Independent Deployment**: This means that the distributed system has a separate ID generator service specifically for generating distributed IDs. This decouples the ID generation service from business-related services. However, this also increases the overhead of network calls. Overall, if there are many scenarios requiring distributed IDs, an independently deployed ID generator service is still very necessary.
-## 分布式 ID 常见解决方案
+## Common Solutions for Distributed IDs
-### 数据库
+### Database
-#### 数据库主键自增
+#### Auto-Incrementing Database Primary Key
-这种方式就比较简单直白了,就是通过关系型数据库的自增主键产生来唯一的 ID。
+This method is quite straightforward; it generates a unique ID through the auto-incrementing primary key of a relational database.
-
+
-以 MySQL 举例,我们通过下面的方式即可。
+Taking MySQL as an example, we can do it as follows.
-**1.创建一个数据库表。**
+**1. Create a database table.**
```sql
CREATE TABLE `sequence_id` (
@@ -70,9 +70,9 @@ CREATE TABLE `sequence_id` (
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
```
-`stub` 字段无意义,只是为了占位,便于我们插入或者修改数据。并且,给 `stub` 字段创建了唯一索引,保证其唯一性。
+The `stub` field is meaningless; it is just a placeholder to facilitate data insertion or modification. Additionally, a unique index is created for the `stub` field to ensure its uniqueness.
-**2.通过 `replace into` 来插入数据。**
+**2. Insert data using `replace into`.**
```java
BEGIN;
@@ -81,315 +81,11 @@ SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
COMMIT;
```
-插入数据这里,我们没有使用 `insert into` 而是使用 `replace into` 来插入数据,具体步骤是这样的:
+In this data insertion, we use `replace into` instead of `insert into`. The specific steps are as follows:
-- 第一步:尝试把数据插入到表中。
+- Step 1: Attempt to insert data into the table.
+- Step 2: If a duplicate data error occurs due to the primary key or unique index field, delete the conflicting row containing the duplicate key value from the table, and then attempt to insert the data again.
-- 第二步:如果主键或唯一索引字段出现重复数据错误而插入失败时,先从表中删除含有重复关键字值的冲突行,然后再次尝试把数据插入到表中。
+The advantages and disadvantages of this method are also quite clear:
-这种方式的优缺点也比较明显:
-
-- **优点**:实现起来比较简单、ID 有序递增、存储消耗空间小
-- **缺点**:支持的并发量不大、存在数据库单点问题(可以使用数据库集群解决,不过增加了复杂度)、ID 没有具体业务含义、安全问题(比如根据订单 ID 的递增规律就能推算出每天的订单量,商业机密啊! )、每次获取 ID 都要访问一次数据库(增加了对数据库的压力,获取速度也慢)
-
-#### 数据库号段模式
-
-数据库主键自增这种模式,每次获取 ID 都要访问一次数据库,ID 需求比较大的时候,肯定是不行的。
-
-如果我们可以批量获取,然后存在在内存里面,需要用到的时候,直接从内存里面拿就舒服了!这也就是我们说的 **基于数据库的号段模式来生成分布式 ID。**
-
-数据库的号段模式也是目前比较主流的一种分布式 ID 生成方式。像滴滴开源的[Tinyid](https://github.com/didi/tinyid/wiki/tinyid原理介绍) 就是基于这种方式来做的。不过,TinyId 使用了双号段缓存、增加多 db 支持等方式来进一步优化。
-
-以 MySQL 举例,我们通过下面的方式即可。
-
-**1. 创建一个数据库表。**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE `sequence_id_generator` (
- `id` int(10) NOT NULL,
- `current_max_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '当前最大id',
- `step` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '号段的长度',
- `version` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '版本号',
- `biz_type` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '业务类型',
- PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
-) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-```
-
-`current_max_id` 字段和`step`字段主要用于获取批量 ID,获取的批量 id 为:`current_max_id ~ current_max_id+step`。
-
-
-
-`version` 字段主要用于解决并发问题(乐观锁),`biz_type` 主要用于表示业务类型。
-
-**2. 先插入一行数据。**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO `sequence_id_generator` (`id`, `current_max_id`, `step`, `version`, `biz_type`)
-VALUES
- (1, 0, 100, 0, 101);
-```
-
-**3. 通过 SELECT 获取指定业务下的批量唯一 ID**
-
-```sql
-SELECT `current_max_id`, `step`,`version` FROM `sequence_id_generator` where `biz_type` = 101
-```
-
-结果:
-
-```plain
-id current_max_id step version biz_type
-1 0 100 0 101
-```
-
-**4. 不够用的话,更新之后重新 SELECT 即可。**
-
-```sql
-UPDATE sequence_id_generator SET current_max_id = 0+100, version=version+1 WHERE version = 0 AND `biz_type` = 101
-SELECT `current_max_id`, `step`,`version` FROM `sequence_id_generator` where `biz_type` = 101
-```
-
-结果:
-
-```plain
-id current_max_id step version biz_type
-1 100 100 1 101
-```
-
-相比于数据库主键自增的方式,**数据库的号段模式对于数据库的访问次数更少,数据库压力更小。**
-
-另外,为了避免单点问题,你可以从使用主从模式来提高可用性。
-
-**数据库号段模式的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:ID 有序递增、存储消耗空间小
-- **缺点**:存在数据库单点问题(可以使用数据库集群解决,不过增加了复杂度)、ID 没有具体业务含义、安全问题(比如根据订单 ID 的递增规律就能推算出每天的订单量,商业机密啊! )
-
-#### NoSQL
-
-
-
-一般情况下,NoSQL 方案使用 Redis 多一些。我们通过 Redis 的 `incr` 命令即可实现对 id 原子顺序递增。
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> set sequence_id_biz_type 1
-OK
-127.0.0.1:6379> incr sequence_id_biz_type
-(integer) 2
-127.0.0.1:6379> get sequence_id_biz_type
-"2"
-```
-
-为了提高可用性和并发,我们可以使用 Redis Cluster。Redis Cluster 是 Redis 官方提供的 Redis 集群解决方案(3.0+版本)。
-
-除了 Redis Cluster 之外,你也可以使用开源的 Redis 集群方案[Codis](https://github.com/CodisLabs/codis) (大规模集群比如上百个节点的时候比较推荐)。
-
-除了高可用和并发之外,我们知道 Redis 基于内存,我们需要持久化数据,避免重启机器或者机器故障后数据丢失。Redis 支持两种不同的持久化方式:**快照(snapshotting,RDB)**、**只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)**。 并且,Redis 4.0 开始支持 **RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化**(默认关闭,可以通过配置项 `aof-use-rdb-preamble` 开启)。
-
-关于 Redis 持久化,我这里就不过多介绍。不了解这部分内容的小伙伴,可以看看 [Redis 持久化机制详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-persistence.html)这篇文章。
-
-**Redis 方案的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:性能不错并且生成的 ID 是有序递增的
-- **缺点**:和数据库主键自增方案的缺点类似
-
-除了 Redis 之外,MongoDB ObjectId 经常也会被拿来当做分布式 ID 的解决方案。
-
-
-
-MongoDB ObjectId 一共需要 12 个字节存储:
-
-- 0~3:时间戳
-- 3~6:代表机器 ID
-- 7~8:机器进程 ID
-- 9~11:自增值
-
-**MongoDB 方案的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:性能不错并且生成的 ID 是有序递增的
-- **缺点**:需要解决重复 ID 问题(当机器时间不对的情况下,可能导致会产生重复 ID)、有安全性问题(ID 生成有规律性)
-
-### 算法
-
-#### UUID
-
-UUID 是 Universally Unique Identifier(通用唯一标识符) 的缩写。UUID 包含 32 个 16 进制数字(8-4-4-4-12)。
-
-JDK 就提供了现成的生成 UUID 的方法,一行代码就行了。
-
-```java
-//输出示例:cb4a9ede-fa5e-4585-b9bb-d60bce986eaa
-UUID.randomUUID()
-```
-
-[RFC 4122](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4122) 中关于 UUID 的示例是这样的:
-
-
-
-我们这里重点关注一下这个 Version(版本),不同的版本对应的 UUID 的生成规则是不同的。
-
-8 种不同的 Version(版本)值分别对应的含义(参考[维基百科对于 UUID 的介绍](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/通用唯一识别码)):
-
-- **版本 1 (基于时间和节点 ID)** : 基于时间戳(通常是当前时间)和节点 ID(通常为设备的 MAC 地址)生成。当包含 MAC 地址时,可以保证全球唯一性,但也因此存在隐私泄露的风险。
-- **版本 2 (基于标识符、时间和节点 ID)** : 与版本 1 类似,也基于时间和节点 ID,但额外包含了本地标识符(例如用户 ID 或组 ID)。
-- **版本 3 (基于命名空间和名称的 MD5 哈希)**:使用 MD5 哈希算法,将命名空间标识符(一个 UUID)和名称字符串组合计算得到。相同的命名空间和名称总是生成相同的 UUID(**确定性生成**)。
-- **版本 4 (基于随机数)**:几乎完全基于随机数生成,通常使用伪随机数生成器(PRNG)或加密安全随机数生成器(CSPRNG)来生成。 虽然理论上存在碰撞的可能性,但理论上碰撞概率极低(2^122 的可能性),可以认为在实际应用中是唯一的。
-- **版本 5 (基于命名空间和名称的 SHA-1 哈希)**:类似于版本 3,但使用 SHA-1 哈希算法。
-- **版本 6 (基于时间戳、计数器和节点 ID)**:改进了版本 1,将时间戳放在最高有效位(Most Significant Bit,MSB),使得 UUID 可以直接按时间排序。
-- **版本 7 (基于时间戳和随机数据)**:基于 Unix 时间戳和随机数据生成。 由于时间戳位于最高有效位,因此支持按时间排序。并且,不依赖 MAC 地址或节点 ID,避免了隐私问题。
-- **版本 8 (自定义)**:允许用户根据自己的需求定义 UUID 的生成方式。其结构和内容由用户决定,提供更大的灵活性。
-
-下面是 Version 1 版本下生成的 UUID 的示例:
-
-
-
-JDK 中通过 `UUID` 的 `randomUUID()` 方法生成的 UUID 的版本默认为 4。
-
-```java
-UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
-int version = uuid.version();// 4
-```
-
-另外,Variant(变体)也有 4 种不同的值,这种值分别对应不同的含义。这里就不介绍了,貌似平时也不怎么需要关注。
-
-需要用到的时候,去看看维基百科对于 UUID 的 Variant(变体) 相关的介绍即可。
-
-从上面的介绍中可以看出,UUID 可以保证唯一性,因为其生成规则包括 MAC 地址、时间戳、名字空间(Namespace)、随机或伪随机数、时序等元素,计算机基于这些规则生成的 UUID 是肯定不会重复的。
-
-虽然,UUID 可以做到全局唯一性,但是,我们一般很少会使用它。
-
-比如使用 UUID 作为 MySQL 数据库主键的时候就非常不合适:
-
-- 数据库主键要尽量越短越好,而 UUID 的消耗的存储空间比较大(32 个字符串,128 位)。
-- UUID 是无顺序的,InnoDB 引擎下,数据库主键的无序性会严重影响数据库性能。
-
-最后,我们再简单分析一下 **UUID 的优缺点** (面试的时候可能会被问到的哦!) :
-
-- **优点**:生成速度通常比较快、简单易用
-- **缺点**:存储消耗空间大(32 个字符串,128 位)、 不安全(基于 MAC 地址生成 UUID 的算法会造成 MAC 地址泄露)、无序(非自增)、没有具体业务含义、需要解决重复 ID 问题(当机器时间不对的情况下,可能导致会产生重复 ID)
-
-#### Snowflake(雪花算法)
-
-Snowflake 是 Twitter 开源的分布式 ID 生成算法。Snowflake 由 64 bit 的二进制数字组成,这 64bit 的二进制被分成了几部分,每一部分存储的数据都有特定的含义:
-
-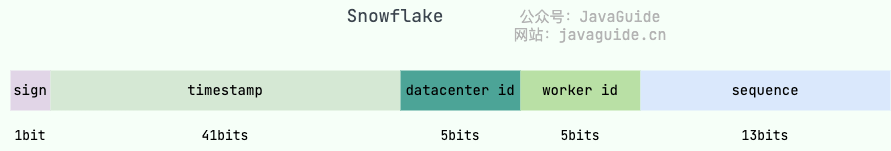
-
-- **sign(1bit)**:符号位(标识正负),始终为 0,代表生成的 ID 为正数。
-- **timestamp (41 bits)**:一共 41 位,用来表示时间戳,单位是毫秒,可以支撑 2 ^41 毫秒(约 69 年)
-- **datacenter id + worker id (10 bits)**:一般来说,前 5 位表示机房 ID,后 5 位表示机器 ID(实际项目中可以根据实际情况调整)。这样就可以区分不同集群/机房的节点。
-- **sequence (12 bits)**:一共 12 位,用来表示序列号。 序列号为自增值,代表单台机器每毫秒能够产生的最大 ID 数(2^12 = 4096),也就是说单台机器每毫秒最多可以生成 4096 个 唯一 ID。
-
-在实际项目中,我们一般也会对 Snowflake 算法进行改造,最常见的就是在 Snowflake 算法生成的 ID 中加入业务类型信息。
-
-我们再来看看 Snowflake 算法的优缺点:
-
-- **优点**:生成速度比较快、生成的 ID 有序递增、比较灵活(可以对 Snowflake 算法进行简单的改造比如加入业务 ID)
-- **缺点**:需要解决重复 ID 问题(ID 生成依赖时间,在获取时间的时候,可能会出现时间回拨的问题,也就是服务器上的时间突然倒退到之前的时间,进而导致会产生重复 ID)、依赖机器 ID 对分布式环境不友好(当需要自动启停或增减机器时,固定的机器 ID 可能不够灵活)。
-
-如果你想要使用 Snowflake 算法的话,一般不需要你自己再造轮子。有很多基于 Snowflake 算法的开源实现比如美团 的 Leaf、百度的 UidGenerator(后面会提到),并且这些开源实现对原有的 Snowflake 算法进行了优化,性能更优秀,还解决了 Snowflake 算法的时间回拨问题和依赖机器 ID 的问题。
-
-并且,Seata 还提出了“改良版雪花算法”,针对原版雪花算法进行了一定的优化改良,解决了时间回拨问题,大幅提高的 QPS。具体介绍和改进原理,可以参考下面这两篇文章:
-
-- [Seata 基于改良版雪花算法的分布式 UUID 生成器分析](https://seata.io/zh-cn/blog/seata-analysis-UUID-generator.html)
-- [在开源项目中看到一个改良版的雪花算法,现在它是你的了。](https://www.cnblogs.com/thisiswhy/p/17611163.html)
-
-### 开源框架
-
-#### UidGenerator(百度)
-
-[UidGenerator](https://github.com/baidu/uid-generator) 是百度开源的一款基于 Snowflake(雪花算法)的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-不过,UidGenerator 对 Snowflake(雪花算法)进行了改进,生成的唯一 ID 组成如下:
-
-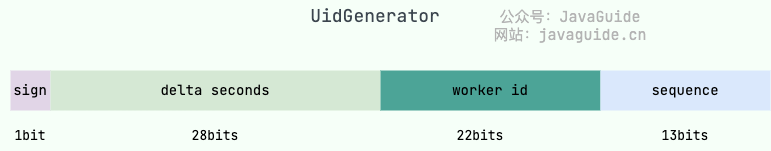
-
-- **sign(1bit)**:符号位(标识正负),始终为 0,代表生成的 ID 为正数。
-- **delta seconds (28 bits)**:当前时间,相对于时间基点"2016-05-20"的增量值,单位:秒,最多可支持约 8.7 年
-- **worker id (22 bits)**:机器 id,最多可支持约 420w 次机器启动。内置实现为在启动时由数据库分配,默认分配策略为用后即弃,后续可提供复用策略。
-- **sequence (13 bits)**:每秒下的并发序列,13 bits 可支持每秒 8192 个并发。
-
-可以看出,和原始 Snowflake(雪花算法)生成的唯一 ID 的组成不太一样。并且,上面这些参数我们都可以自定义。
-
-UidGenerator 官方文档中的介绍如下:
-
-
-
-自 18 年后,UidGenerator 就基本没有再维护了,我这里也不过多介绍。想要进一步了解的朋友,可以看看 [UidGenerator 的官方介绍](https://github.com/baidu/uid-generator/blob/master/README.zh_cn.md)。
-
-#### Leaf(美团)
-
-[Leaf](https://github.com/Meituan-Dianping/Leaf) 是美团开源的一个分布式 ID 解决方案 。这个项目的名字 Leaf(树叶) 起源于德国哲学家、数学家莱布尼茨的一句话:“There are no two identical leaves in the world”(世界上没有两片相同的树叶) 。这名字起得真心挺不错的,有点文艺青年那味了!
-
-Leaf 提供了 **号段模式** 和 **Snowflake(雪花算法)** 这两种模式来生成分布式 ID。并且,它支持双号段,还解决了雪花 ID 系统时钟回拨问题。不过,时钟问题的解决需要弱依赖于 Zookeeper(使用 Zookeeper 作为注册中心,通过在特定路径下读取和创建子节点来管理 workId) 。
-
-Leaf 的诞生主要是为了解决美团各个业务线生成分布式 ID 的方法多种多样以及不可靠的问题。
-
-Leaf 对原有的号段模式进行改进,比如它这里增加了双号段避免获取 DB 在获取号段的时候阻塞请求获取 ID 的线程。简单来说,就是我一个号段还没用完之前,我自己就主动提前去获取下一个号段(图片来自于美团官方文章:[《Leaf——美团点评分布式 ID 生成系统》](https://tech.meituan.com/2017/04/21/mt-leaf.html))。
-
-
-
-根据项目 README 介绍,在 4C8G VM 基础上,通过公司 RPC 方式调用,QPS 压测结果近 5w/s,TP999 1ms。
-
-#### Tinyid(滴滴)
-
-[Tinyid](https://github.com/didi/tinyid) 是滴滴开源的一款基于数据库号段模式的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-数据库号段模式的原理我们在上面已经介绍过了。**Tinyid 有哪些亮点呢?**
-
-为了搞清楚这个问题,我们先来看看基于数据库号段模式的简单架构方案。(图片来自于 Tinyid 的官方 wiki:[《Tinyid 原理介绍》](https://github.com/didi/tinyid/wiki/tinyid%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D))
-
-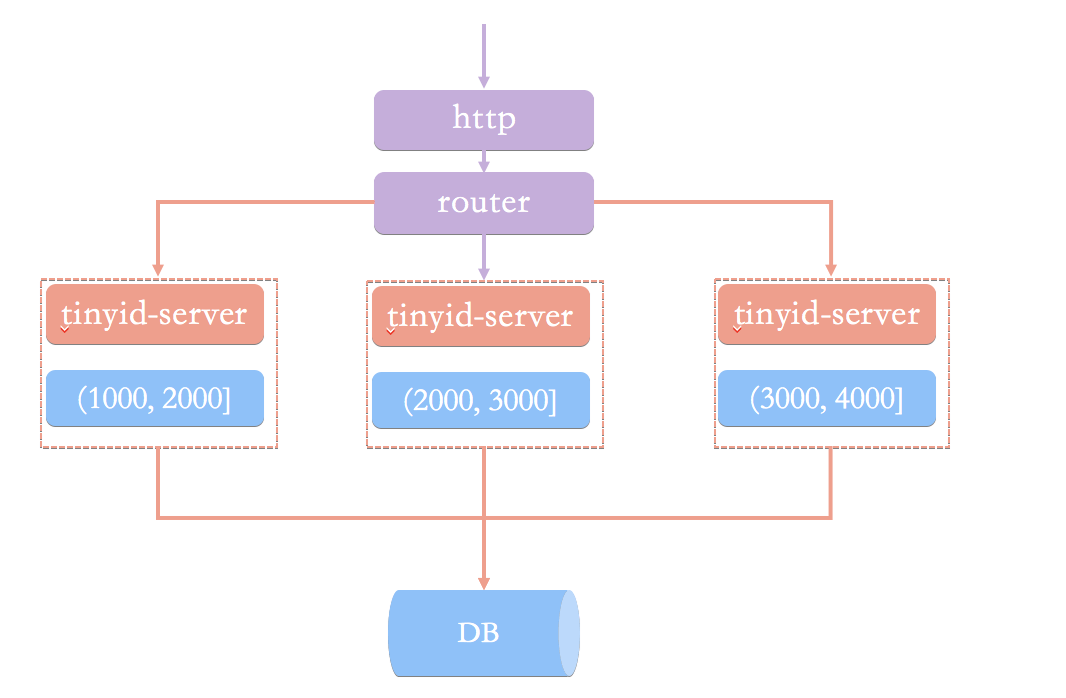
-
-在这种架构模式下,我们通过 HTTP 请求向发号器服务申请唯一 ID。负载均衡 router 会把我们的请求送往其中的一台 tinyid-server。
-
-这种方案有什么问题呢?在我看来(Tinyid 官方 wiki 也有介绍到),主要由下面这 2 个问题:
-
-- 获取新号段的情况下,程序获取唯一 ID 的速度比较慢。
-- 需要保证 DB 高可用,这个是比较麻烦且耗费资源的。
-
-除此之外,HTTP 调用也存在网络开销。
-
-Tinyid 的原理比较简单,其架构如下图所示:
-
-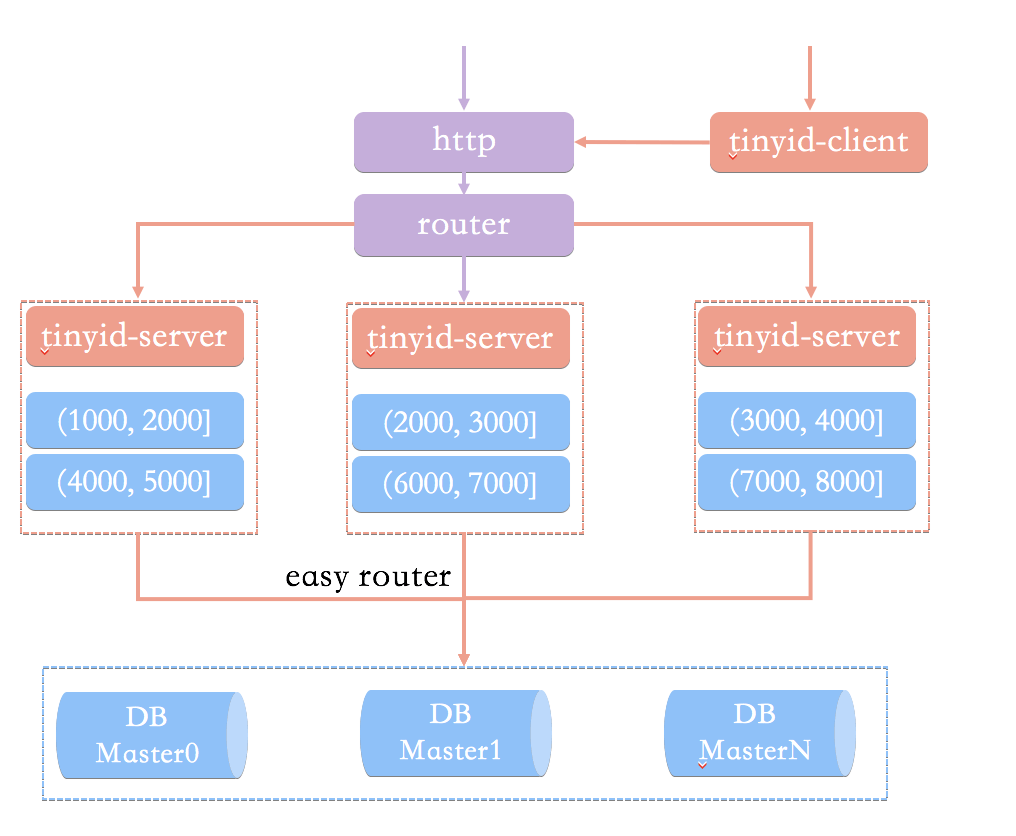
-
-相比于基于数据库号段模式的简单架构方案,Tinyid 方案主要做了下面这些优化:
-
-- **双号段缓存**:为了避免在获取新号段的情况下,程序获取唯一 ID 的速度比较慢。 Tinyid 中的号段在用到一定程度的时候,就会去异步加载下一个号段,保证内存中始终有可用号段。
-- **增加多 db 支持**:支持多个 DB,并且,每个 DB 都能生成唯一 ID,提高了可用性。
-- **增加 tinyid-client**:纯本地操作,无 HTTP 请求消耗,性能和可用性都有很大提升。
-
-Tinyid 的优缺点这里就不分析了,结合数据库号段模式的优缺点和 Tinyid 的原理就能知道。
-
-#### IdGenerator(个人)
-
-和 UidGenerator、Leaf 一样,[IdGenerator](https://github.com/yitter/IdGenerator) 也是一款基于 Snowflake(雪花算法)的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-IdGenerator 有如下特点:
-
-- 生成的唯一 ID 更短;
-- 兼容所有雪花算法(号段模式或经典模式,大厂或小厂);
-- 原生支持 C#/Java/Go/C/Rust/Python/Node.js/PHP(C 扩展)/SQL/ 等语言,并提供多线程安全调用动态库(FFI);
-- 解决了时间回拨问题,支持手工插入新 ID(当业务需要在历史时间生成新 ID 时,用本算法的预留位能生成 5000 个每秒);
-- 不依赖外部存储系统;
-- 默认配置下,ID 可用 71000 年不重复。
-
-IdGenerator 生成的唯一 ID 组成如下:
-
-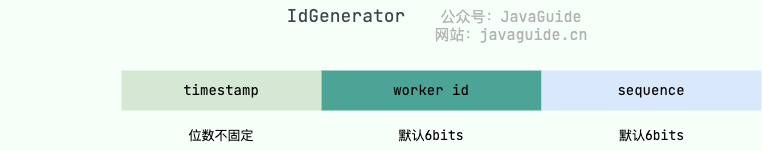
-
-- **timestamp (位数不固定)**:时间差,是生成 ID 时的系统时间减去 BaseTime(基础时间,也称基点时间、原点时间、纪元时间,默认值为 2020 年) 的总时间差(毫秒单位)。初始为 5bits,随着运行时间而增加。如果觉得默认值太老,你可以重新设置,不过要注意,这个值以后最好不变。
-- **worker id (默认 6 bits)**:机器 id,机器码,最重要参数,是区分不同机器或不同应用的唯一 ID,最大值由 `WorkerIdBitLength`(默认 6)限定。如果一台服务器部署多个独立服务,需要为每个服务指定不同的 WorkerId。
-- **sequence (默认 6 bits)**:序列数,是每毫秒下的序列数,由参数中的 `SeqBitLength`(默认 6)限定。增加 `SeqBitLength` 会让性能更高,但生成的 ID 也会更长。
-
-Java 语言使用示例:。
-
-## 总结
-
-通过这篇文章,我基本上已经把最常见的分布式 ID 生成方案都总结了一波。
-
-除了上面介绍的方式之外,像 ZooKeeper 这类中间件也可以帮助我们生成唯一 ID。**没有银弹,一定要结合实际项目来选择最适合自己的方案。**
-
-不过,本文主要介绍的是分布式 ID 的理论知识。在实际的面试中,面试官可能会结合具体的业务场景来考察你对分布式 ID 的设计,你可以参考这篇文章:[分布式 ID 设计指南](./distributed-id-design)(对于实际工作中分布式 ID 的设计也非常有帮助)。
-
-
+- **Advantages**: Simple to implement, IDs are ordered and incrementing,
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
index cb4504c4a7a..fbb695d1020 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
@@ -1,19 +1,19 @@
---
-title: 分布式锁常见实现方案总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Distributed Lock Implementation Solutions
+category: Distributed
---
-通常情况下,我们一般会选择基于 Redis 或者 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁,Redis 用的要更多一点,我这里也先以 Redis 为例介绍分布式锁的实现。
+In general, we usually choose to implement distributed locks based on Redis or ZooKeeper, with Redis being the more commonly used option. Here, I will introduce the implementation of distributed locks using Redis as an example.
-## 基于 Redis 实现分布式锁
+## Implementing Distributed Locks Based on Redis
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现一个最简易的分布式锁?
+### How to Implement a Simple Distributed Lock Using Redis?
-不论是本地锁还是分布式锁,核心都在于“互斥”。
+Whether it's a local lock or a distributed lock, the core concept is "mutual exclusion."
-在 Redis 中, `SETNX` 命令是可以帮助我们实现互斥。`SETNX` 即 **SET** if **N**ot e**X**ists (对应 Java 中的 `setIfAbsent` 方法),如果 key 不存在的话,才会设置 key 的值。如果 key 已经存在, `SETNX` 啥也不做。
+In Redis, the `SETNX` command helps us achieve mutual exclusion. `SETNX` stands for **SET** if **N**ot e**X**ists (corresponding to the `setIfAbsent` method in Java). It sets the key's value only if the key does not exist. If the key already exists, `SETNX` does nothing.
```bash
> SETNX lockKey uniqueValue
@@ -22,19 +22,19 @@ category: 分布式
(integer) 0
```
-释放锁的话,直接通过 `DEL` 命令删除对应的 key 即可。
+To release the lock, simply delete the corresponding key using the `DEL` command.
```bash
> DEL lockKey
(integer) 1
```
-为了防止误删到其他的锁,这里我们建议使用 Lua 脚本通过 key 对应的 value(唯一值)来判断。
+To prevent accidentally deleting other locks, it is recommended to use a Lua script to check the value (unique value) corresponding to the key.
-选用 Lua 脚本是为了保证解锁操作的原子性。因为 Redis 在执行 Lua 脚本时,可以以原子性的方式执行,从而保证了锁释放操作的原子性。
+Using a Lua script ensures the atomicity of the unlock operation. When Redis executes a Lua script, it does so atomically, thus guaranteeing the atomicity of the lock release operation.
```lua
-// 释放锁时,先比较锁对应的 value 值是否相等,避免锁的误释放
+// When releasing the lock, first compare the value of the lock to avoid accidental release
if redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then
return redis.call("del",KEYS[1])
else
@@ -42,340 +42,40 @@ else
end
```
-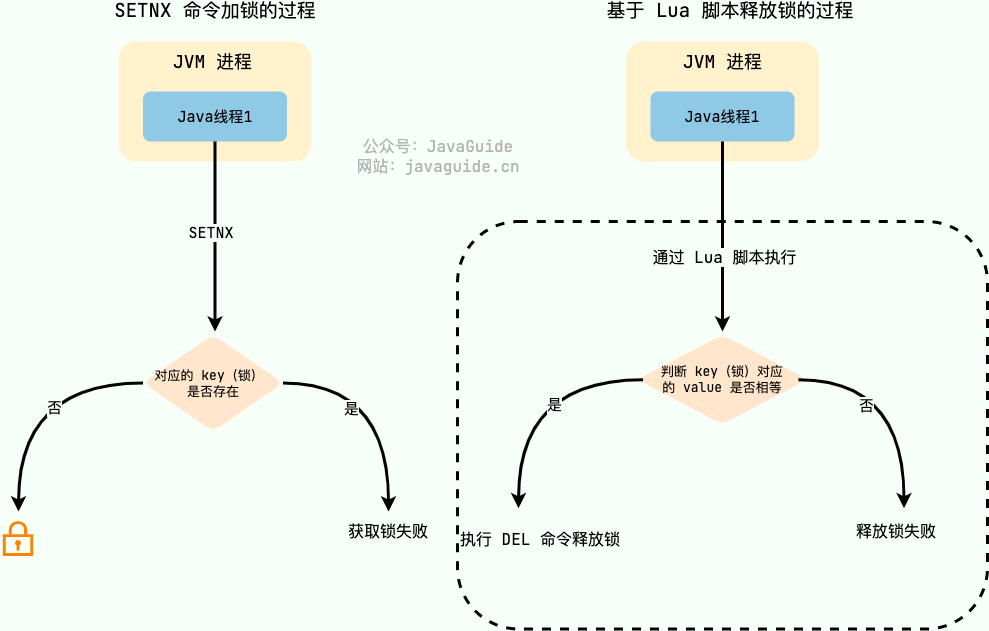
+
-这是一种最简易的 Redis 分布式锁实现,实现方式比较简单,性能也很高效。不过,这种方式实现分布式锁存在一些问题。就比如应用程序遇到一些问题比如释放锁的逻辑突然挂掉,可能会导致锁无法被释放,进而造成共享资源无法再被其他线程/进程访问。
+This is a simple implementation of a Redis distributed lock, which is straightforward and efficient. However, this method has some issues. For example, if the application encounters a problem and the logic for releasing the lock suddenly crashes, it may lead to the lock not being released, causing shared resources to be inaccessible to other threads/processes.
-### 为什么要给锁设置一个过期时间?
+### Why Set an Expiration Time for the Lock?
-为了避免锁无法被释放,我们可以想到的一个解决办法就是:**给这个 key(也就是锁) 设置一个过期时间** 。
+To avoid the lock being unreleased, one solution is to **set an expiration time for this key (the lock)**.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> SET lockKey uniqueValue EX 3 NX
OK
```
-- **lockKey**:加锁的锁名;
-- **uniqueValue**:能够唯一标识锁的随机字符串;
-- **NX**:只有当 lockKey 对应的 key 值不存在的时候才能 SET 成功;
-- **EX**:过期时间设置(秒为单位)EX 3 标示这个锁有一个 3 秒的自动过期时间。与 EX 对应的是 PX(毫秒为单位),这两个都是过期时间设置。
+- **lockKey**: The name of the lock;
+- **uniqueValue**: A random string that uniquely identifies the lock;
+- **NX**: The SET operation will only succeed if the key corresponding to lockKey does not exist;
+- **EX**: Sets the expiration time (in seconds). EX 3 indicates that this lock has an automatic expiration time of 3 seconds. The counterpart to EX is PX (in milliseconds), and both are used for setting expiration times.
-**一定要保证设置指定 key 的值和过期时间是一个原子操作!!!** 不然的话,依然可能会出现锁无法被释放的问题。
+**It is crucial to ensure that setting the specified key's value and expiration time is an atomic operation!!!** Otherwise, the issue of the lock not being released may still occur.
-这样确实可以解决问题,不过,这种解决办法同样存在漏洞:**如果操作共享资源的时间大于过期时间,就会出现锁提前过期的问题,进而导致分布式锁直接失效。如果锁的超时时间设置过长,又会影响到性能。**
+This indeed solves the problem, but this solution also has vulnerabilities: **If the time taken to operate on the shared resource exceeds the expiration time, the lock may expire prematurely, leading to the distributed lock becoming invalid. If the timeout is set too long, it may affect performance.**
-你或许在想:**如果操作共享资源的操作还未完成,锁过期时间能够自己续期就好了!**
+You might be wondering: **If the operation on the shared resource is not yet complete, it would be great if the lock's expiration time could be renewed automatically!**
-### 如何实现锁的优雅续期?
+### How to Implement Elegant Lock Renewal?
-对于 Java 开发的小伙伴来说,已经有了现成的解决方案:**[Redisson](https://github.com/redisson/redisson)** 。其他语言的解决方案,可以在 Redis 官方文档中找到,地址: 。
+For Java developers, there is already a ready-made solution: **[Redisson](https://github.com/redisson/redisson)**. Solutions for other languages can be found in the official Redis documentation at: .

-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,不仅仅包括多种分布式锁的实现。并且,Redisson 还支持 Redis 单机、Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster 等多种部署架构。
+Redisson is an open-source Redis client for Java that provides many out-of-the-box features, including various implementations of distributed locks. Additionally, Redisson supports multiple deployment architectures such as Redis standalone, Redis Sentinel, and Redis Cluster.
-Redisson 中的分布式锁自带自动续期机制,使用起来非常简单,原理也比较简单,其提供了一个专门用来监控和续期锁的 **Watch Dog( 看门狗)**,如果操作共享资源的线程还未执行完成的话,Watch Dog 会不断地延长锁的过期时间,进而保证锁不会因为超时而被释放。
+The distributed lock in Redisson comes with an automatic renewal mechanism, making it very easy to use. The principle is quite simple: it provides a dedicated **Watch Dog** to monitor and renew the lock. If the thread operating on the shared resource has not completed its execution, the Watch Dog will continuously extend the lock's expiration time, ensuring that the lock is not released due to timeout.
-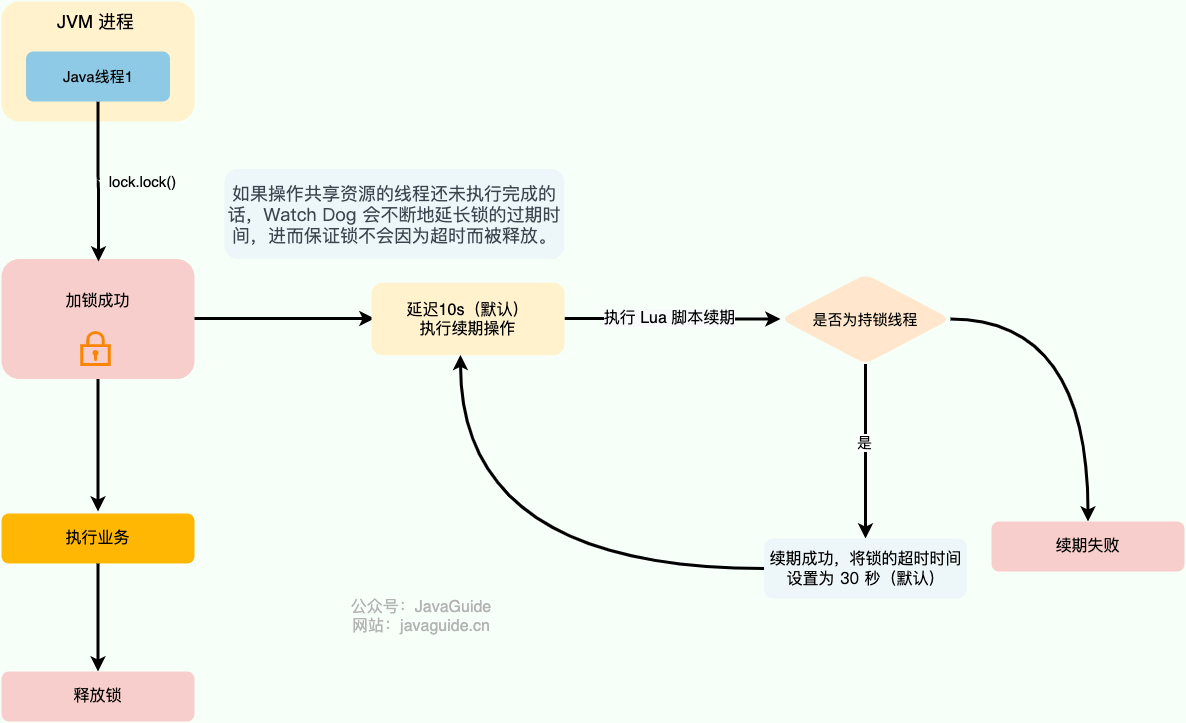
+
-看门狗名字的由来于 `getLockWatchdogTimeout()` 方法,这个方法返回的是看门狗给锁续期的过期时间,默认为 30 秒([redisson-3.17.6](https://github.com/redisson/redisson/releases/tag/redisson-3.17.6))。
-
-```java
-//默认 30秒,支持修改
-private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;
-
-public Config setLockWatchdogTimeout(long lockWatchdogTimeout) {
- this.lockWatchdogTimeout = lockWatchdogTimeout;
- return this;
-}
-public long getLockWatchdogTimeout() {
- return lockWatchdogTimeout;
-}
-```
-
-`renewExpiration()` 方法包含了看门狗的主要逻辑:
-
-```java
-private void renewExpiration() {
- //......
- Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
- @Override
- public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
- //......
- // 异步续期,基于 Lua 脚本
- CompletionStage future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
- future.whenComplete((res, e) -> {
- if (e != null) {
- // 无法续期
- log.error("Can't update lock " + getRawName() + " expiration", e);
- EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
- return;
- }
-
- if (res) {
- // 递归调用实现续期
- renewExpiration();
- } else {
- // 取消续期
- cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
- }
- });
- }
- // 延迟 internalLockLeaseTime/3(默认 10s,也就是 30/3) 再调用
- }, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
-
- ee.setTimeout(task);
- }
-```
-
-默认情况下,每过 10 秒,看门狗就会执行续期操作,将锁的超时时间设置为 30 秒。看门狗续期前也会先判断是否需要执行续期操作,需要才会执行续期,否则取消续期操作。
-
-Watch Dog 通过调用 `renewExpirationAsync()` 方法实现锁的异步续期:
-
-```java
-protected CompletionStage renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
- return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
- // 判断是否为持锁线程,如果是就执行续期操作,就锁的过期时间设置为 30s(默认)
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return 1; " +
- "end; " +
- "return 0;",
- Collections.singletonList(getRawName()),
- internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
-}
-```
-
-可以看出, `renewExpirationAsync` 方法其实是调用 Lua 脚本实现的续期,这样做主要是为了保证续期操作的原子性。
-
-我这里以 Redisson 的分布式可重入锁 `RLock` 为例来说明如何使用 Redisson 实现分布式锁:
-
-```java
-// 1.获取指定的分布式锁对象
-RLock lock = redisson.getLock("lock");
-// 2.拿锁且不设置锁超时时间,具备 Watch Dog 自动续期机制
-lock.lock();
-// 3.执行业务
-...
-// 4.释放锁
-lock.unlock();
-```
-
-只有未指定锁超时时间,才会使用到 Watch Dog 自动续期机制。
-
-```java
-// 手动给锁设置过期时间,不具备 Watch Dog 自动续期机制
-lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
-```
-
-如果使用 Redis 来实现分布式锁的话,还是比较推荐直接基于 Redisson 来做的。
-
-### 如何实现可重入锁?
-
-所谓可重入锁指的是在一个线程中可以多次获取同一把锁,比如一个线程在执行一个带锁的方法,该方法中又调用了另一个需要相同锁的方法,则该线程可以直接执行调用的方法即可重入 ,而无需重新获得锁。像 Java 中的 `synchronized` 和 `ReentrantLock` 都属于可重入锁。
-
-**不可重入的分布式锁基本可以满足绝大部分业务场景了,一些特殊的场景可能会需要使用可重入的分布式锁。**
-
-可重入分布式锁的实现核心思路是线程在获取锁的时候判断是否为自己的锁,如果是的话,就不用再重新获取了。为此,我们可以为每个锁关联一个可重入计数器和一个占有它的线程。当可重入计数器大于 0 时,则锁被占有,需要判断占有该锁的线程和请求获取锁的线程是否为同一个。
-
-实际项目中,我们不需要自己手动实现,推荐使用我们上面提到的 **Redisson** ,其内置了多种类型的锁比如可重入锁(Reentrant Lock)、自旋锁(Spin Lock)、公平锁(Fair Lock)、多重锁(MultiLock)、 红锁(RedLock)、 读写锁(ReadWriteLock)。
-
-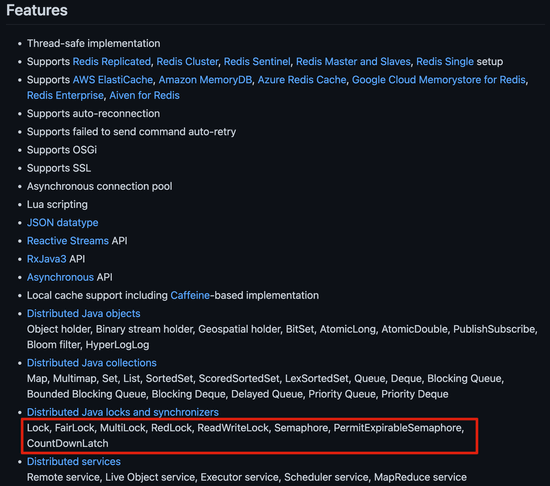
-
-### Redis 如何解决集群情况下分布式锁的可靠性?
-
-为了避免单点故障,生产环境下的 Redis 服务通常是集群化部署的。
-
-Redis 集群下,上面介绍到的分布式锁的实现会存在一些问题。由于 Redis 集群数据同步到各个节点时是异步的,如果在 Redis 主节点获取到锁后,在没有同步到其他节点时,Redis 主节点宕机了,此时新的 Redis 主节点依然可以获取锁,所以多个应用服务就可以同时获取到锁。
-
-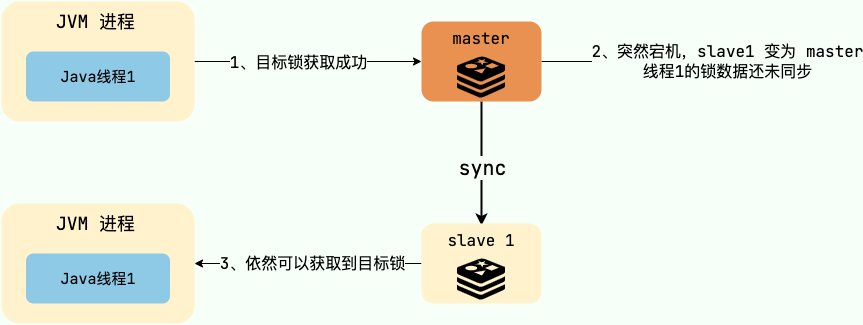
-
-针对这个问题,Redis 之父 antirez 设计了 [Redlock 算法](https://redis.io/topics/distlock) 来解决。
-
-
-
-Redlock 算法的思想是让客户端向 Redis 集群中的多个独立的 Redis 实例依次请求申请加锁,如果客户端能够和半数以上的实例成功地完成加锁操作,那么我们就认为,客户端成功地获得分布式锁,否则加锁失败。
-
-即使部分 Redis 节点出现问题,只要保证 Redis 集群中有半数以上的 Redis 节点可用,分布式锁服务就是正常的。
-
-Redlock 是直接操作 Redis 节点的,并不是通过 Redis 集群操作的,这样才可以避免 Redis 集群主从切换导致的锁丢失问题。
-
-Redlock 实现比较复杂,性能比较差,发生时钟变迁的情况下还存在安全性隐患。《数据密集型应用系统设计》一书的作者 Martin Kleppmann 曾经专门发文([How to do distributed locking - Martin Kleppmann - 2016](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2016/02/08/how-to-do-distributed-locking.html))怼过 Redlock,他认为这是一个很差的分布式锁实现。感兴趣的朋友可以看看[Redis 锁从面试连环炮聊到神仙打架](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3NjU3NTkwMQ==&mid=2247505097&idx=1&sn=5c03cb769c4458350f4d4a321ad51f5a&source=41#wechat_redirect)这篇文章,有详细介绍到 antirez 和 Martin Kleppmann 关于 Redlock 的激烈辩论。
-
-实际项目中不建议使用 Redlock 算法,成本和收益不成正比,可以考虑基于 Redis 主从复制+哨兵模式实现分布式锁。
-
-## 基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁
-
-ZooKeeper 相比于 Redis 实现分布式锁,除了提供相对更高的可靠性之外,在功能层面还有一个非常有用的特性:**Watch 机制**。这个机制可以用来实现公平的分布式锁。不过,使用 ZooKeeper 实现的分布式锁在性能方面相对较差,因此如果对性能要求比较高的话,ZooKeeper 可能就不太适合了。
-
-### 如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁?
-
-ZooKeeper 分布式锁是基于 **临时顺序节点** 和 **Watcher(事件监听器)** 实现的。
-
-获取锁:
-
-1. 首先我们要有一个持久节点`/locks`,客户端获取锁就是在`locks`下创建临时顺序节点。
-2. 假设客户端 1 创建了`/locks/lock1`节点,创建成功之后,会判断 `lock1`是否是 `/locks` 下最小的子节点。
-3. 如果 `lock1`是最小的子节点,则获取锁成功。否则,获取锁失败。
-4. 如果获取锁失败,则说明有其他的客户端已经成功获取锁。客户端 1 并不会不停地循环去尝试加锁,而是在前一个节点比如`/locks/lock0`上注册一个事件监听器。这个监听器的作用是当前一个节点释放锁之后通知客户端 1(避免无效自旋),这样客户端 1 就加锁成功了。
-
-释放锁:
-
-1. 成功获取锁的客户端在执行完业务流程之后,会将对应的子节点删除。
-2. 成功获取锁的客户端在出现故障之后,对应的子节点由于是临时顺序节点,也会被自动删除,避免了锁无法被释放。
-3. 我们前面说的事件监听器其实监听的就是这个子节点删除事件,子节点删除就意味着锁被释放。
-
-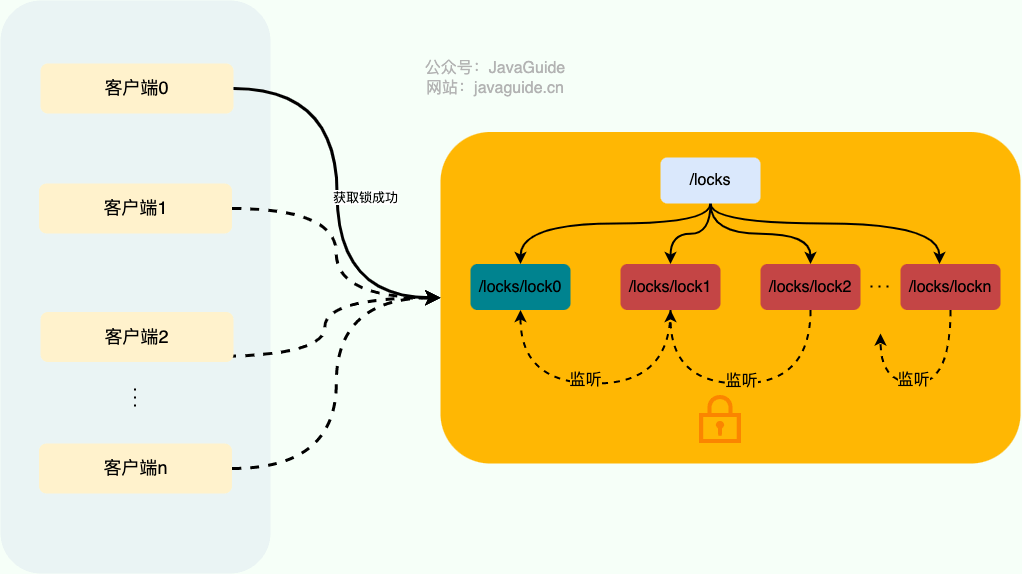
-
-实际项目中,推荐使用 Curator 来实现 ZooKeeper 分布式锁。Curator 是 Netflix 公司开源的一套 ZooKeeper Java 客户端框架,相比于 ZooKeeper 自带的客户端 zookeeper 来说,Curator 的封装更加完善,各种 API 都可以比较方便地使用。
-
-`Curator`主要实现了下面四种锁:
-
-- `InterProcessMutex`:分布式可重入排它锁
-- `InterProcessSemaphoreMutex`:分布式不可重入排它锁
-- `InterProcessReadWriteLock`:分布式读写锁
-- `InterProcessMultiLock`:将多个锁作为单个实体管理的容器,获取锁的时候获取所有锁,释放锁也会释放所有锁资源(忽略释放失败的锁)。
-
-```java
-CuratorFramework client = ZKUtils.getClient();
-client.start();
-// 分布式可重入排它锁
-InterProcessLock lock1 = new InterProcessMutex(client, lockPath1);
-// 分布式不可重入排它锁
-InterProcessLock lock2 = new InterProcessSemaphoreMutex(client, lockPath2);
-// 将多个锁作为一个整体
-InterProcessMultiLock lock = new InterProcessMultiLock(Arrays.asList(lock1, lock2));
-
-if (!lock.acquire(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("不能获取多锁");
-}
-System.out.println("已获取多锁");
-System.out.println("是否有第一个锁: " + lock1.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-System.out.println("是否有第二个锁: " + lock2.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-try {
- // 资源操作
- resource.use();
-} finally {
- System.out.println("释放多个锁");
- lock.release();
-}
-System.out.println("是否有第一个锁: " + lock1.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-System.out.println("是否有第二个锁: " + lock2.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-client.close();
-```
-
-### 为什么要用临时顺序节点?
-
-每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。
-
-我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
-
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。并且,**临时节点只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性。
-
-可以看出,临时节点相比持久节点,最主要的是对会话失效的情况处理不一样,临时节点会话消失则对应的节点消失。这样的话,如果客户端发生异常导致没来得及释放锁也没关系,会话失效节点自动被删除,不会发生死锁的问题。
-
-使用 Redis 实现分布式锁的时候,我们是通过过期时间来避免锁无法被释放导致死锁问题的,而 ZooKeeper 直接利用临时节点的特性即可。
-
-假设不使用顺序节点的话,所有尝试获取锁的客户端都会对持有锁的子节点加监听器。当该锁被释放之后,势必会造成所有尝试获取锁的客户端来争夺锁,这样对性能不友好。使用顺序节点之后,只需要监听前一个节点就好了,对性能更友好。
-
-### 为什么要设置对前一个节点的监听?
-
-> Watcher(事件监听器),是 ZooKeeper 中的一个很重要的特性。ZooKeeper 允许用户在指定节点上注册一些 Watcher,并且在一些特定事件触发的时候,ZooKeeper 服务端会将事件通知到感兴趣的客户端上去,该机制是 ZooKeeper 实现分布式协调服务的重要特性。
-
-同一时间段内,可能会有很多客户端同时获取锁,但只有一个可以获取成功。如果获取锁失败,则说明有其他的客户端已经成功获取锁。获取锁失败的客户端并不会不停地循环去尝试加锁,而是在前一个节点注册一个事件监听器。
-
-这个事件监听器的作用是:**当前一个节点对应的客户端释放锁之后(也就是前一个节点被删除之后,监听的是删除事件),通知获取锁失败的客户端(唤醒等待的线程,Java 中的 `wait/notifyAll` ),让它尝试去获取锁,然后就成功获取锁了。**
-
-### 如何实现可重入锁?
-
-这里以 Curator 的 `InterProcessMutex` 对可重入锁的实现来介绍(源码地址:[InterProcessMutex.java](https://github.com/apache/curator/blob/master/curator-recipes/src/main/java/org/apache/curator/framework/recipes/locks/InterProcessMutex.java))。
-
-当我们调用 `InterProcessMutex#acquire`方法获取锁的时候,会调用`InterProcessMutex#internalLock`方法。
-
-```java
-// 获取可重入互斥锁,直到获取成功为止
-@Override
-public void acquire() throws Exception {
- if (!internalLock(-1, null)) {
- throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);
- }
-}
-```
-
-`internalLock` 方法会先获取当前请求锁的线程,然后从 `threadData`( `ConcurrentMap` 类型)中获取当前线程对应的 `lockData` 。 `lockData` 包含锁的信息和加锁的次数,是实现可重入锁的关键。
-
-第一次获取锁的时候,`lockData`为 `null`。获取锁成功之后,会将当前线程和对应的 `lockData` 放到 `threadData` 中
-
-```java
-private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
- // 获取当前请求锁的线程
- Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
- // 拿对应的 lockData
- LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
- // 第一次获取锁的话,lockData 为 null
- if (lockData != null) {
- // 当前线程获取过一次锁之后
- // 因为当前线程的锁存在, lockCount 自增后返回,实现锁重入.
- lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
- return true;
- }
- // 尝试获取锁
- String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
- if (lockPath != null) {
- LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
- // 获取锁成功之后,将当前线程和对应的 lockData 放到 threadData 中
- threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
- return true;
- }
-
- return false;
-}
-```
-
-`LockData`是 `InterProcessMutex`中的一个静态内部类。
-
-```java
-private final ConcurrentMap threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
-
-private static class LockData
-{
- // 当前持有锁的线程
- final Thread owningThread;
- // 锁对应的子节点
- final String lockPath;
- // 加锁的次数
- final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
-
- private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath)
- {
- this.owningThread = owningThread;
- this.lockPath = lockPath;
- }
-}
-```
-
-如果已经获取过一次锁,后面再来获取锁的话,直接就会在 `if (lockData != null)` 这里被拦下了,然后就会执行`lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();` 将加锁次数加 1。
-
-整个可重入锁的实现逻辑非常简单,直接在客户端判断当前线程有没有获取锁,有的话直接将加锁次数加 1 就可以了。
-
-## 总结
-
-在这篇文章中,我介绍了实现分布式锁的两种常见方式:**Redis** 和 **ZooKeeper**。至于具体选择 Redis 还是 ZooKeeper 来实现分布式锁,还是要根据业务的具体需求来决定。
-
-- 如果对性能要求比较高的话,建议使用 Redis 实现分布式锁。推荐优先选择 **Redisson** 提供的现成分布式锁,而不是自己实现。实际项目中不建议使用 Redlock 算法,成本和收益不成正比,可以考虑基于 Redis 主从复制+哨兵模式实现分布式锁。
-- 如果对可靠性要求比较高,建议使用 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁,推荐基于 **Curator** 框架来实现。不过,现在很多项目都不会用到 ZooKeeper,如果单纯是因为分布式锁而引入 ZooKeeper 的话,那是不太可取的,不建议这样做,为了一个小小的功能增加了系统的复杂度。
-
-需要注意的是,无论选择哪种方式实现分布式锁,包括 Redis、ZooKeeper 或 Etcd(本文没介绍,但也经常用来实现分布式锁),都无法保证 100% 的安全性,特别是在遇到进程垃圾回收(GC)、网络延迟等异常情况下。
-
-为了进一步提高系统的可靠性,建议引入一个兜底机制。例如,可以通过 **版本号(Fencing Token)机制** 来避免并发冲突。
-
-最后,再分享几篇我觉得写的还不错的文章:
-
-- [分布式锁实现原理与最佳实践 - 阿里云开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JzCHpIOiFVmBoAko58ZuGw)
-- [聊聊分布式锁 - 字节跳动技术团队](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-N4x6EkxwAYDGdJhwvmZLw)
-- [Redis、ZooKeeper、Etcd,谁有最好用的分布式锁? - 腾讯云开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yZC6VJGxt1ANZkn0SljZBg)
-
-
+The name "Watch Dog" comes from the \`getLockWatchdog
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
index ba53f443d03..9d6403b1f0e 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
@@ -1,84 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 分布式锁介绍
-category: 分布式
+title: Introduction to Distributed Locks
+category: Distributed
---
-网上有很多分布式锁相关的文章,写了一个相对简洁易懂的版本,针对面试和工作应该够用了。
+There are many articles online about distributed locks, and I have written a relatively concise and easy-to-understand version that should be sufficient for interviews and work.
-这篇文章我们先介绍一下分布式锁的基本概念。
+In this article, we will first introduce the basic concepts of distributed locks.
-## 为什么需要分布式锁?
+## Why Do We Need Distributed Locks?
-在多线程环境中,如果多个线程同时访问共享资源(例如商品库存、外卖订单),会发生数据竞争,可能会导致出现脏数据或者系统问题,威胁到程序的正常运行。
+In a multithreaded environment, if multiple threads access shared resources (such as product inventory or food delivery orders) simultaneously, data contention can occur, potentially leading to dirty data or system issues, threatening the normal operation of the program.
-举个例子,假设现在有 100 个用户参与某个限时秒杀活动,每位用户限购 1 件商品,且商品的数量只有 3 个。如果不对共享资源进行互斥访问,就可能出现以下情况:
+For example, suppose there are 100 users participating in a limited-time flash sale, with each user allowed to purchase 1 item, and there are only 3 items available. If mutual exclusion is not applied to the shared resource, the following situation may occur:
-- 线程 1、2、3 等多个线程同时进入抢购方法,每一个线程对应一个用户。
-- 线程 1 查询用户已经抢购的数量,发现当前用户尚未抢购且商品库存还有 1 个,因此认为可以继续执行抢购流程。
-- 线程 2 也执行查询用户已经抢购的数量,发现当前用户尚未抢购且商品库存还有 1 个,因此认为可以继续执行抢购流程。
-- 线程 1 继续执行,将库存数量减少 1 个,然后返回成功。
-- 线程 2 继续执行,将库存数量减少 1 个,然后返回成功。
-- 此时就发生了超卖问题,导致商品被多卖了一份。
+- Threads 1, 2, 3, etc., enter the purchase method simultaneously, with each thread corresponding to a user.
+- Thread 1 queries the number of items the user has already purchased, finds that the current user has not yet purchased and that there is still 1 item in stock, and thus believes it can continue the purchase process.
+- Thread 2 also executes the query for the number of items the user has already purchased, finds that the current user has not yet purchased and that there is still 1 item in stock, and thus believes it can continue the purchase process.
+- Thread 1 continues to execute, reducing the stock quantity by 1, and then returns success.
+- Thread 2 continues to execute, reducing the stock quantity by 1, and then returns success.
+- At this point, an overselling issue occurs, resulting in the product being sold more than once.
-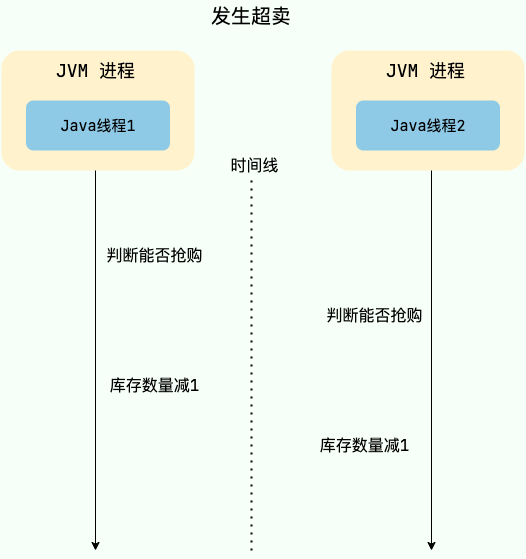
+
-为了保证共享资源被安全地访问,我们需要使用互斥操作对共享资源进行保护,即同一时刻只允许一个线程访问共享资源,其他线程需要等待当前线程释放后才能访问。这样可以避免数据竞争和脏数据问题,保证程序的正确性和稳定性。
+To ensure that shared resources are accessed safely, we need to use mutual exclusion operations to protect shared resources, allowing only one thread to access the shared resource at any given time, while other threads must wait until the current thread releases it. This can avoid data contention and dirty data issues, ensuring the correctness and stability of the program.
-**如何才能实现共享资源的互斥访问呢?** 锁是一个比较通用的解决方案,更准确点来说是悲观锁。
+**How can we achieve mutual access to shared resources?** Locks are a relatively general solution, more specifically, pessimistic locks.
-悲观锁总是假设最坏的情况,认为共享资源每次被访问的时候就会出现问题(比如共享数据被修改),所以每次在获取资源操作的时候都会上锁,这样其他线程想拿到这个资源就会阻塞直到锁被上一个持有者释放。也就是说,**共享资源每次只给一个线程使用,其它线程阻塞,用完后再把资源转让给其它线程**。
+Pessimistic locks always assume the worst-case scenario, believing that issues will arise every time shared resources are accessed (for example, shared data being modified). Therefore, every time a resource operation is performed, a lock is acquired, causing other threads that want to access this resource to block until the lock is released by the previous holder. In other words, **the shared resource is used by only one thread at a time, while other threads are blocked, and after use, the resource is transferred to other threads**.
-对于单机多线程来说,在 Java 中,我们通常使用 `ReentrantLock` 类、`synchronized` 关键字这类 JDK 自带的 **本地锁** 来控制一个 JVM 进程内的多个线程对本地共享资源的访问。
+For single-machine multithreading, in Java, we typically use the `ReentrantLock` class or the `synchronized` keyword, which are built-in **local locks** provided by the JDK, to control access to local shared resources by multiple threads within a single JVM process.
-下面是我对本地锁画的一张示意图。
+Here is a diagram I created to illustrate local locks.
-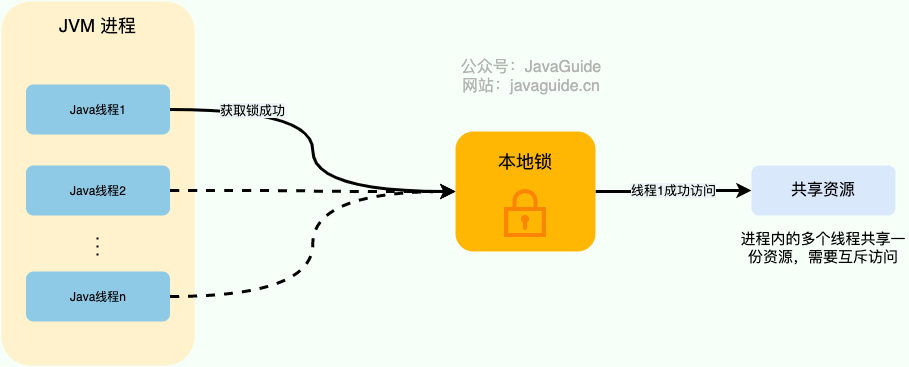
+
-从图中可以看出,这些线程访问共享资源是互斥的,同一时刻只有一个线程可以获取到本地锁访问共享资源。
+From the diagram, it can be seen that these threads access shared resources mutually exclusively, with only one thread able to acquire the local lock to access the shared resource at any given time.
-分布式系统下,不同的服务/客户端通常运行在独立的 JVM 进程上。如果多个 JVM 进程共享同一份资源的话,使用本地锁就没办法实现资源的互斥访问了。于是,**分布式锁** 就诞生了。
+In a distributed system, different services/clients typically run in separate JVM processes. If multiple JVM processes share the same resource, local locks cannot achieve mutual access to the resource. Thus, **distributed locks** were born.
-举个例子:系统的订单服务一共部署了 3 份,都对外提供服务。用户下订单之前需要检查库存,为了防止超卖,这里需要加锁以实现对检查库存操作的同步访问。由于订单服务位于不同的 JVM 进程中,本地锁在这种情况下就没办法正常工作了。我们需要用到分布式锁,这样的话,即使多个线程不在同一个 JVM 进程中也能获取到同一把锁,进而实现共享资源的互斥访问。
+For example: The order service of the system is deployed in 3 instances, all providing services externally. Before a user places an order, they need to check the inventory. To prevent overselling, a lock is needed to synchronize access to the inventory check operation. Since the order service is located in different JVM processes, local locks cannot function properly in this case. We need to use distributed locks, which allow multiple threads, even if they are not in the same JVM process, to acquire the same lock, thereby achieving mutual access to shared resources.
-下面是我对分布式锁画的一张示意图。
+Here is a diagram I created to illustrate distributed locks.
-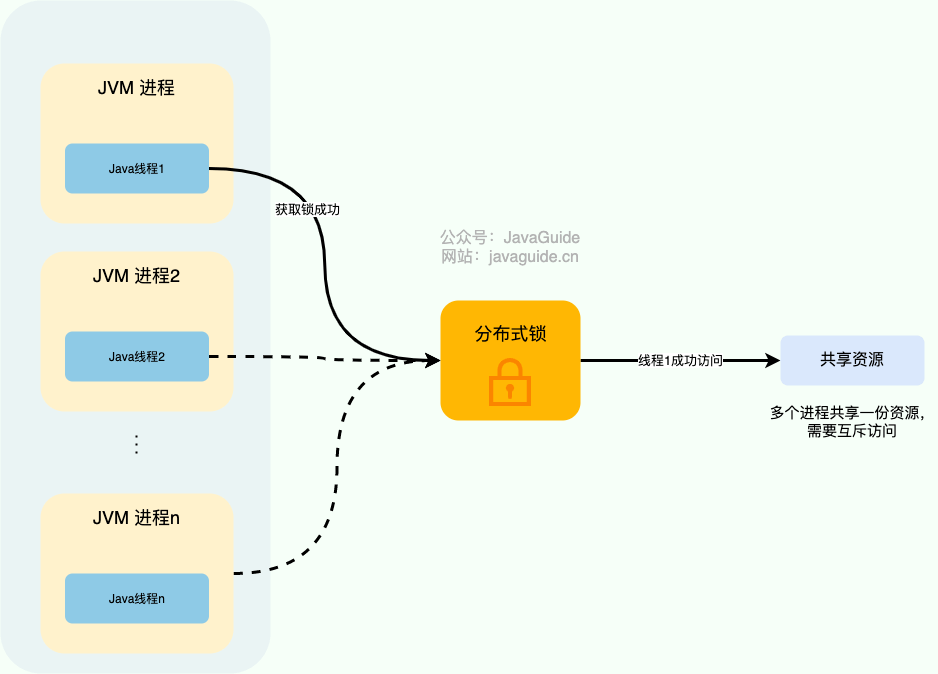
+
-从图中可以看出,这些独立的进程中的线程访问共享资源是互斥的,同一时刻只有一个线程可以获取到分布式锁访问共享资源。
+From the diagram, it can be seen that threads in these independent processes access shared resources mutually exclusively, with only one thread able to acquire the distributed lock to access the shared resource at any given time.
-## 分布式锁应该具备哪些条件?
+## What Conditions Should a Distributed Lock Meet?
-一个最基本的分布式锁需要满足:
+A basic distributed lock needs to satisfy the following:
-- **互斥**:任意一个时刻,锁只能被一个线程持有。
-- **高可用**:锁服务是高可用的,当一个锁服务出现问题,能够自动切换到另外一个锁服务。并且,即使客户端的释放锁的代码逻辑出现问题,锁最终一定还是会被释放,不会影响其他线程对共享资源的访问。这一般是通过超时机制实现的。
-- **可重入**:一个节点获取了锁之后,还可以再次获取锁。
-
-除了上面这三个基本条件之外,一个好的分布式锁还需要满足下面这些条件:
-
-- **高性能**:获取和释放锁的操作应该快速完成,并且不应该对整个系统的性能造成过大影响。
-- **非阻塞**:如果获取不到锁,不能无限期等待,避免对系统正常运行造成影响。
-
-## 分布式锁的常见实现方式有哪些?
-
-常见分布式锁实现方案如下:
-
-- 基于关系型数据库比如 MySQL 实现分布式锁。
-- 基于分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁。
-- 基于分布式键值存储系统比如 Redis 、Etcd 实现分布式锁。
-
-关系型数据库的方式一般是通过唯一索引或者排他锁实现。不过,一般不会使用这种方式,问题太多比如性能太差、不具备锁失效机制。
-
-基于 ZooKeeper 或者 Redis 实现分布式锁这两种实现方式要用的更多一些,我专门写了一篇文章来详细介绍这两种方案:[分布式锁常见实现方案总结](./distributed-lock-implementations.md)。
-
-## 总结
-
-这篇文章我们主要介绍了:
-
-- 分布式锁的用途:分布式系统下,不同的服务/客户端通常运行在独立的 JVM 进程上。如果多个 JVM 进程共享同一份资源的话,使用本地锁就没办法实现资源的互斥访问了。
-- 分布式锁的应该具备的条件:互斥、高可用、可重入、高性能、非阻塞。
-- 分布式锁的常见实现方式:关系型数据库比如 MySQL、分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper、分布式键值存储系统比如 Redis 、Etcd 。
-
-
+- **Mutual Exclusion**: At any given time, the lock can only be held by one thread.
+- **High Availability**: The lock service is highly available. When one
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
index af6f3de5a21..e9065b67c9f 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
@@ -1,76 +1,76 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper 实战
-category: 分布式
+title: ZooKeeper Practical Guide
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-这篇文章简单给演示一下 ZooKeeper 常见命令的使用以及 ZooKeeper Java 客户端 Curator 的基本使用。介绍到的内容都是最基本的操作,能满足日常工作的基本需要。
+This article will briefly demonstrate the use of common ZooKeeper commands and the basic usage of the ZooKeeper Java client, Curator. The topics covered are the most basic operations and can meet the basic needs of daily work.
-如果文章有任何需要改善和完善的地方,欢迎在评论区指出,共同进步!
+If there are any areas in the article that need improvement or enhancement, feel free to point them out in the comments section for our mutual progress!
-## ZooKeeper 安装
+## ZooKeeper Installation
-### 使用 Docker 安装 zookeeper
+### Installing ZooKeeper Using Docker
-**a.使用 Docker 下载 ZooKeeper**
+**a. Download ZooKeeper using Docker**
```shell
docker pull zookeeper:3.5.8
```
-**b.运行 ZooKeeper**
+**b. Run ZooKeeper**
```shell
docker run -d --name zookeeper -p 2181:2181 zookeeper:3.5.8
```
-### 连接 ZooKeeper 服务
+### Connecting to the ZooKeeper Service
-**a.进入 ZooKeeper 容器中**
+**a. Enter the ZooKeeper container**
-先使用 `docker ps` 查看 ZooKeeper 的 ContainerID,然后使用 `docker exec -it ContainerID /bin/bash` 命令进入容器中。
+First, use `docker ps` to check the ContainerID of ZooKeeper, and then use the command `docker exec -it ContainerID /bin/bash` to enter the container.
-**b.先进入 bin 目录,然后通过 `./zkCli.sh -server 127.0.0.1:2181`命令连接 ZooKeeper 服务**
+**b. Navigate to the bin directory and connect to the ZooKeeper service using the command `./zkCli.sh -server 127.0.0.1:2181`**
```bash
root@eaf70fc620cb:/apache-zookeeper-3.5.8-bin# cd bin
```
-如果你看到控制台成功打印出如下信息的话,说明你已经成功连接 ZooKeeper 服务。
+If you see the following message successfully printed in the console, it indicates that you have successfully connected to the ZooKeeper service.
-
+
-## ZooKeeper 常用命令演示
+## Common ZooKeeper Commands Demonstration
-### 查看常用命令(help 命令)
+### View Common Commands (help Command)
-通过 `help` 命令查看 ZooKeeper 常用命令
+Use the `help` command to view common ZooKeeper commands.
-### 创建节点(create 命令)
+### Create Node (create Command)
-通过 `create` 命令在根目录创建了 node1 节点,与它关联的字符串是"node1"
+Use the `create` command to create the node1 in the root directory, with the associated string "node1".
```shell
-[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 34] create /node1 “node1”
+[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 34] create /node1 "node1"
```
-通过 `create` 命令在根目录创建了 node1 节点,与它关联的内容是数字 123
+Use the `create` command to create the node1.1 under node1, with the associated content as the number 123.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 1] create /node1/node1.1 123
Created /node1/node1.1
```
-### 更新节点数据内容(set 命令)
+### Update Node Data Content (set Command)
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 11] set /node1 "set node1"
```
-### 获取节点的数据(get 命令)
+### Retrieve Node Data (get Command)
-`get` 命令可以获取指定节点的数据内容和节点的状态,可以看出我们通过 `set` 命令已经将节点数据内容改为 "set node1"。
+The `get` command can retrieve the data content and status of the specified node, showing that we have already changed the node data to "set node1" using the `set` command.
```shell
[zk: zookeeper(CONNECTED) 12] get -s /node1
@@ -86,30 +86,29 @@ aclVersion = 0
ephemeralOwner = 0x0
dataLength = 9
numChildren = 1
-
```
-### 查看某个目录下的子节点(ls 命令)
+### View Subnodes of a Directory (ls Command)
-通过 `ls` 命令查看根目录下的节点
+Use the `ls` command to view the nodes in the root directory.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 37] ls /
[dubbo, ZooKeeper, node1]
```
-通过 `ls` 命令查看 node1 目录下的节点
+Use the `ls` command to view the nodes under the node1 directory.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 5] ls /node1
[node1.1]
```
-ZooKeeper 中的 ls 命令和 linux 命令中的 ls 类似, 这个命令将列出绝对路径 path 下的所有子节点信息(列出 1 级,并不递归)
+The `ls` command in ZooKeeper is similar to the `ls` command in Linux; this command will list all subnode information under the absolute path (only listing 1 level, not recursively).
-### 查看节点状态(stat 命令)
+### View Node Status (stat Command)
-通过 `stat` 命令查看节点状态
+Use the `stat` command to view the node status.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 10] stat /node1
@@ -126,14 +125,14 @@ dataLength = 11
numChildren = 1
```
-上面显示的一些信息比如 cversion、aclVersion、numChildren 等等,我在上面 “[ZooKeeper 相关概念总结(入门)](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.html)” 这篇文章中已经介绍到。
+The information displayed above, such as cversion, aclVersion, numChildren, etc., has been introduced in my previous article “[Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Beginner)](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.html)”.
-### 查看节点信息和状态(ls2 命令)
+### View Node Information and Status (ls2 Command)
-`ls2` 命令更像是 `ls` 命令和 `stat` 命令的结合。 `ls2` 命令返回的信息包括 2 部分:
+The `ls2` command is more like a combination of the `ls` and `stat` commands. The information returned by the `ls2` command includes 2 parts:
-1. 子节点列表
-2. 当前节点的 stat 信息。
+1. List of subnodes
+1. The current node's stat information.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 7] ls2 /node1
@@ -149,28 +148,27 @@ aclVersion = 0
ephemeralOwner = 0x0
dataLength = 11
numChildren = 1
-
```
-### 删除节点(delete 命令)
+### Delete Node (delete Command)
-这个命令很简单,但是需要注意的一点是如果你要删除某一个节点,那么这个节点必须无子节点才行。
+This command is straightforward, but it is crucial to note that if you want to delete a node, that node must have no children.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 3] delete /node1/node1.1
```
-在后面我会介绍到 Java 客户端 API 的使用以及开源 ZooKeeper 客户端 ZkClient 和 Curator 的使用。
+Later, I will introduce the use of the Java client API and the open-source ZooKeeper clients ZkClient and Curator.
-## ZooKeeper Java 客户端 Curator 简单使用
+## Simple Usage of ZooKeeper Java Client Curator
-Curator 是 Netflix 公司开源的一套 ZooKeeper Java 客户端框架,相比于 Zookeeper 自带的客户端 zookeeper 来说,Curator 的封装更加完善,各种 API 都可以比较方便地使用。
+Curator is an open-source ZooKeeper Java client framework developed by Netflix. Compared to the built-in ZooKeeper client, Curator's encapsulation is more comprehensive, allowing various APIs to be used more conveniently.

-下面我们就来简单地演示一下 Curator 的使用吧!
+Now, let's briefly demonstrate the usage of Curator!
-Curator4.0+版本对 ZooKeeper 3.5.x 支持比较好。开始之前,请先将下面的依赖添加进你的项目。
+Curator version 4.0+ has good support for ZooKeeper 3.5.x. Before starting, please add the following dependencies to your project.
```xml
@@ -185,9 +183,9 @@ Curator4.0+版本对 ZooKeeper 3.5.x 支持比较好。开始之前,请先将
```
-### 连接 ZooKeeper 客户端
+### Connecting to ZooKeeper Client
-通过 `CuratorFrameworkFactory` 创建 `CuratorFramework` 对象,然后再调用 `CuratorFramework` 对象的 `start()` 方法即可!
+Create a `CuratorFramework` object through `CuratorFrameworkFactory`, and then call the `start()` method on the `CuratorFramework` object!
```java
private static final int BASE_SLEEP_TIME = 1000;
@@ -203,92 +201,92 @@ CuratorFramework zkClient = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
zkClient.start();
```
-对于一些基本参数的说明:
+Here are explanations of some basic parameters:
-- `baseSleepTimeMs`:重试之间等待的初始时间
-- `maxRetries`:最大重试次数
-- `connectString`:要连接的服务器列表
-- `retryPolicy`:重试策略
+- `baseSleepTimeMs`: The initial time to wait between retries
+- `maxRetries`: The maximum number of retries
+- `connectString`: The list of servers to connect to
+- `retryPolicy`: The retry policy
-### 数据节点的增删改查
+### CRUD Operations on Data Nodes
-#### 创建节点
+#### Create Node
-我们在 [ZooKeeper 常见概念解读](./zookeeper-intro.md) 中介绍到,我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
+As we discussed in [Common Concepts of ZooKeeper](./zookeeper-intro.md), we generally categorize znodes into 4 major types:
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。并且,临时节点 **只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性。
+- **Persistent (PERSISTENT) Nodes**: Once created, they always exist even if the ZooKeeper cluster crashes, until deleted.
+- **Ephemeral (EPHEMERAL) Nodes**: The lifecycle of ephemeral nodes is bound to the **client session**; **the session disappears, and the node disappears**. Moreover, ephemeral nodes **can only be leaf nodes**, and cannot have child nodes.
+- **Persistent Sequential (PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL) Nodes**: In addition to having the characteristics of persistent nodes, the names of child nodes also have order. For example, `/node1/app0000000001`, `/node1/app0000000002`.
+- **Ephemeral Sequential (EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL) Nodes**: In addition to having the characteristics of ephemeral nodes, the names of child nodes also have order.
-你在使用的 ZooKeeper 的时候,会发现 `CreateMode` 类中实际有 7 种 znode 类型 ,但是用的最多的还是上面介绍的 4 种。
+When using ZooKeeper, you will find that the `CreateMode` class has a total of 7 types of znodes, but the most commonly used are the 4 types mentioned above.
-**a.创建持久化节点**
+**a. Create Persistent Node**
-你可以通过下面两种方式创建持久化的节点。
+You can create persistent nodes in the following two ways.
```java
-//注意:下面的代码会报错,下文说了具体原因
+// Note: The following code will cause an error; the specific reason will be explained later
zkClient.create().forPath("/node1/00001");
zkClient.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/node1/00002");
```
-但是,你运行上面的代码会报错,这是因为的父节点`node1`还未创建。
+However, running the above code will raise an error because the parent node `node1` has not been created yet.
-你可以先创建父节点 `node1` ,然后再执行上面的代码就不会报错了。
+You can first create the parent node `node1`, and then the above code will not cause an error.
```java
zkClient.create().forPath("/node1");
```
-更推荐的方式是通过下面这行代码, **`creatingParentsIfNeeded()` 可以保证父节点不存在的时候自动创建父节点,这是非常有用的。**
+A more recommended way is to use the following line of code. **`creatingParentsIfNeeded()` ensures that if the parent node does not exist, it will be created automatically, which is very useful.**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**b.创建临时节点**
+**b. Create Ephemeral Node**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**c.创建节点并指定数据内容**
+**c. Create Node and Specify Data Content**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001","java".getBytes());
-zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");//获取节点的数据内容,获取到的是 byte数组
+zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");// Retrieve the data content of the node; the result is a byte array
```
-**d.检测节点是否创建成功**
+**d. Check if the Node Was Created Successfully**
```java
-zkClient.checkExists().forPath("/node1/00001");//不为null的话,说明节点创建成功
+zkClient.checkExists().forPath("/node1/00001");// If not null, it indicates that the node was created successfully
```
-#### 删除节点
+#### Delete Node
-**a.删除一个子节点**
+**a. Delete a Child Node**
```java
zkClient.delete().forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**b.删除一个节点以及其下的所有子节点**
+**b. Delete a Node and All Its Children**
```java
zkClient.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/node1");
```
-#### 获取/更新节点数据内容
+#### Retrieve/Update Node Data Content
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001","java".getBytes());
-zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");//获取节点的数据内容
-zkClient.setData().forPath("/node1/00001","c++".getBytes());//更新节点数据内容
+zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");// Retrieve the data content of the node
+zkClient.setData().forPath("/node1/00001","c++".getBytes());// Update the data content of the node
```
-#### 获取某个节点的所有子节点路径
+#### Retrieve All Child Node Paths of a Specific Node
```java
List childrenPaths = zkClient.getChildren().forPath("/node1");
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
index 955c5d2813a..11bebd0d158 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
@@ -1,316 +1,52 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper相关概念总结(入门)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Introduction)
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-相信大家对 ZooKeeper 应该不算陌生。但是你真的了解 ZooKeeper 到底有啥用不?如果别人/面试官让你给他讲讲对于 ZooKeeper 的认识,你能回答到什么地步呢?
+I believe everyone is somewhat familiar with ZooKeeper. But do you really understand what ZooKeeper is used for? If someone, like an interviewer, asks you to explain your understanding of ZooKeeper, how far could you go in your answer?
-拿我自己来说吧!我本人在大学曾经使用 Dubbo 来做分布式项目的时候,使用了 ZooKeeper 作为注册中心。为了保证分布式系统能够同步访问某个资源,我还使用 ZooKeeper 做过分布式锁。另外,我在学习 Kafka 的时候,知道 Kafka 很多功能的实现依赖了 ZooKeeper。
+Let me share my own experience! During my university days, I used Dubbo for a distributed project and employed ZooKeeper as the registration center. To ensure that the distributed system could synchronously access a certain resource, I also used ZooKeeper for distributed locking. Additionally, while learning Kafka, I realized that many of Kafka's functionalities depend on ZooKeeper.
-前几天,总结项目经验的时候,我突然问自己 ZooKeeper 到底是个什么东西?想了半天,脑海中只是简单的能浮现出几句话:
+A few days ago, while summarizing project experiences, I suddenly asked myself, what exactly is ZooKeeper? After thinking for a long time, I could only recall a few simple statements:
-1. ZooKeeper 可以被用作注册中心、分布式锁;
-2. ZooKeeper 是 Hadoop 生态系统的一员;
-3. 构建 ZooKeeper 集群的时候,使用的服务器最好是奇数台。
+1. ZooKeeper can be used as a registration center and for distributed locks;
+1. ZooKeeper is a part of the Hadoop ecosystem;
+1. When building a ZooKeeper cluster, it is best to use an odd number of servers.
-由此可见,我对于 ZooKeeper 的理解仅仅是停留在了表面。
+From this, it is clear that my understanding of ZooKeeper was merely superficial.
-所以,通过本文,希望带大家稍微详细的了解一下 ZooKeeper 。如果没有学过 ZooKeeper ,那么本文将会是你进入 ZooKeeper 大门的垫脚砖。如果你已经接触过 ZooKeeper ,那么本文将带你回顾一下 ZooKeeper 的一些基础概念。
+Therefore, through this article, I hope to provide a more detailed understanding of ZooKeeper. If you have never learned about ZooKeeper, this article will serve as a stepping stone for you to enter the world of ZooKeeper. If you have already been exposed to ZooKeeper, this article will help you review some basic concepts.
-另外,本文不光会涉及到 ZooKeeper 的一些概念,后面的文章会介绍到 ZooKeeper 常见命令的使用以及使用 Apache Curator 作为 ZooKeeper 的客户端。
+Moreover, this article will not only cover some concepts of ZooKeeper; subsequent articles will introduce common commands for ZooKeeper and the use of Apache Curator as a client for ZooKeeper.
-_如果文章有任何需要改善和完善的地方,欢迎在评论区指出,共同进步!_
+_If there are any areas in the article that need improvement or enhancement, please feel free to point them out in the comments section for our mutual progress!_
-## ZooKeeper 介绍
+## Introduction to ZooKeeper
-### ZooKeeper 由来
+### Origin of ZooKeeper
-正式介绍 ZooKeeper 之前,我们先来看看 ZooKeeper 的由来,还挺有意思的。
+Before formally introducing ZooKeeper, let's take a look at its origin, which is quite interesting.
-下面这段内容摘自《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper》第四章第一节,推荐大家阅读一下:
+The following excerpt is from Chapter 4, Section 1 of "From Paxos to ZooKeeper," and I recommend everyone read it:
-> ZooKeeper 最早起源于雅虎研究院的一个研究小组。在当时,研究人员发现,在雅虎内部很多大型系统基本都需要依赖一个类似的系统来进行分布式协调,但是这些系统往往都存在分布式单点问题。所以,雅虎的开发人员就试图开发一个通用的无单点问题的分布式协调框架,以便让开发人员将精力集中在处理业务逻辑上。
+> ZooKeeper originated from a research group at Yahoo! Research. At that time, researchers found that many large systems within Yahoo! relied on a similar system for distributed coordination, but these systems often had distributed single point issues. Therefore, Yahoo! developers attempted to create a general-purpose distributed coordination framework without single points of failure, allowing developers to focus on business logic.
>
-> 关于“ZooKeeper”这个项目的名字,其实也有一段趣闻。在立项初期,考虑到之前内部很多项目都是使用动物的名字来命名的(例如著名的 Pig 项目),雅虎的工程师希望给这个项目也取一个动物的名字。时任研究院的首席科学家 RaghuRamakrishnan 开玩笑地说:“在这样下去,我们这儿就变成动物园了!”此话一出,大家纷纷表示就叫动物园管理员吧一一一因为各个以动物命名的分布式组件放在一起,雅虎的整个分布式系统看上去就像一个大型的动物园了,而 ZooKeeper 正好要用来进行分布式环境的协调一一于是,ZooKeeper 的名字也就由此诞生了。
+> Regarding the name "ZooKeeper," there is also an interesting story. In the early stages of the project, considering that many previous internal projects were named after animals (such as the famous Pig project), Yahoo! engineers wanted to give this project an animal name as well. The then chief scientist of the research institute, Raghu Ramakrishnan, jokingly said, "At this rate, we will turn into a zoo!" Once this was said, everyone agreed to call it ZooKeeper—because various distributed components named after animals together made Yahoo!'s entire distributed system look like a large zoo, and ZooKeeper was just meant for coordinating in a distributed environment—thus, the name ZooKeeper was born.
-### ZooKeeper 概览
+### Overview of ZooKeeper
-ZooKeeper 是一个开源的**分布式协调服务**,它的设计目标是将那些复杂且容易出错的分布式一致性服务封装起来,构成一个高效可靠的原语集,并以一系列简单易用的接口提供给用户使用。
+ZooKeeper is an open-source **distributed coordination service** designed to encapsulate complex and error-prone distributed consistency services into a set of efficient and reliable primitives, providing users with a series of simple and easy-to-use interfaces.
-> **原语:** 操作系统或计算机网络用语范畴。是由若干条指令组成的,用于完成一定功能的一个过程。具有不可分割性,即原语的执行必须是连续的,在执行过程中不允许被中断。
+> **Primitive:** A term used in operating systems or computer networks. It is a process composed of several instructions used to accomplish a certain function. It has indivisibility, meaning that the execution of a primitive must be continuous and cannot be interrupted during execution.
-ZooKeeper 为我们提供了高可用、高性能、稳定的分布式数据一致性解决方案,通常被用于实现诸如数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master 选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。这些功能的实现主要依赖于 ZooKeeper 提供的 **数据存储+事件监听** 功能(后文会详细介绍到) 。
+ZooKeeper provides us with a high-availability, high-performance, and stable distributed data consistency solution, commonly used to implement functionalities such as data publishing/subscription, load balancing, naming services, distributed coordination/notification, cluster management, master election, distributed locks, and distributed queues. The implementation of these functionalities mainly relies on the **data storage + event listening** capabilities provided by ZooKeeper (which will be detailed later).
-ZooKeeper 将数据保存在内存中,性能是不错的。 在“读”多于“写”的应用程序中尤其地高性能,因为“写”会导致所有的服务器间同步状态。(“读”多于“写”是协调服务的典型场景)。
+ZooKeeper stores data in memory, resulting in good performance, especially in applications where "reads" outnumber "writes," as "writes" cause synchronization of states among all servers. (The scenario of "reads" outnumbering "writes" is typical for coordination services).
-另外,很多顶级的开源项目都用到了 ZooKeeper,比如:
+Additionally, many top open-source projects utilize ZooKeeper, such as:
-- **Kafka** : ZooKeeper 主要为 Kafka 提供 Broker 和 Topic 的注册以及多个 Partition 的负载均衡等功能。不过,在 Kafka 2.8 之后,引入了基于 Raft 协议的 KRaft 模式,不再依赖 Zookeeper,大大简化了 Kafka 的架构。
-- **Hbase** : ZooKeeper 为 Hbase 提供确保整个集群只有一个 Master 以及保存和提供 regionserver 状态信息(是否在线)等功能。
-- **Hadoop** : ZooKeeper 为 Namenode 提供高可用支持。
-
-### ZooKeeper 特点
-
-- **顺序一致性:** 从同一客户端发起的事务请求,最终将会严格地按照顺序被应用到 ZooKeeper 中去。
-- **原子性:** 所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有机器上的应用情况是一致的,也就是说,要么整个集群中所有的机器都成功应用了某一个事务,要么都没有应用。
-- **单一系统映像:** 无论客户端连到哪一个 ZooKeeper 服务器上,其看到的服务端数据模型都是一致的。
-- **可靠性:** 一旦一次更改请求被应用,更改的结果就会被持久化,直到被下一次更改覆盖。
-- **实时性:** 一旦数据发生变更,其他节点会实时感知到。每个客户端的系统视图都是最新的。
-- **集群部署**:3~5 台(最好奇数台)机器就可以组成一个集群,每台机器都在内存保存了 ZooKeeper 的全部数据,机器之间互相通信同步数据,客户端连接任何一台机器都可以。
-- **高可用:**如果某台机器宕机,会保证数据不丢失。集群中挂掉不超过一半的机器,都能保证集群可用。比如 3 台机器可以挂 1 台,5 台机器可以挂 2 台。
-
-### ZooKeeper 应用场景
-
-ZooKeeper 概览中,我们介绍到使用其通常被用于实现诸如数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master 选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。
-
-下面选 3 个典型的应用场景来专门说说:
-
-1. **命名服务**:可以通过 ZooKeeper 的顺序节点生成全局唯一 ID。
-2. **数据发布/订阅**:通过 **Watcher 机制** 可以很方便地实现数据发布/订阅。当你将数据发布到 ZooKeeper 被监听的节点上,其他机器可通过监听 ZooKeeper 上节点的变化来实现配置的动态更新。
-3. **分布式锁**:通过创建唯一节点获得分布式锁,当获得锁的一方执行完相关代码或者是挂掉之后就释放锁。分布式锁的实现也需要用到 **Watcher 机制** ,我在 [分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock.html) 这篇文章中有详细介绍到如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁。
-
-实际上,这些功能的实现基本都得益于 ZooKeeper 可以保存数据的功能,但是 ZooKeeper 不适合保存大量数据,这一点需要注意。
-
-## ZooKeeper 重要概念
-
-_破音:拿出小本本,下面的内容非常重要哦!_
-
-### Data model(数据模型)
-
-ZooKeeper 数据模型采用层次化的多叉树形结构,每个节点上都可以存储数据,这些数据可以是数字、字符串或者是二进制序列。并且。每个节点还可以拥有 N 个子节点,最上层是根节点以“/”来代表。每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。并且,每个 znode 都有一个唯一的路径标识。
-
-强调一句:**ZooKeeper 主要是用来协调服务的,而不是用来存储业务数据的,所以不要放比较大的数据在 znode 上,ZooKeeper 给出的每个节点的数据大小上限是 1M 。**
-
-从下图可以更直观地看出:ZooKeeper 节点路径标识方式和 Unix 文件系统路径非常相似,都是由一系列使用斜杠"/"进行分割的路径表示,开发人员可以向这个节点中写入数据,也可以在节点下面创建子节点。这些操作我们后面都会介绍到。
-
-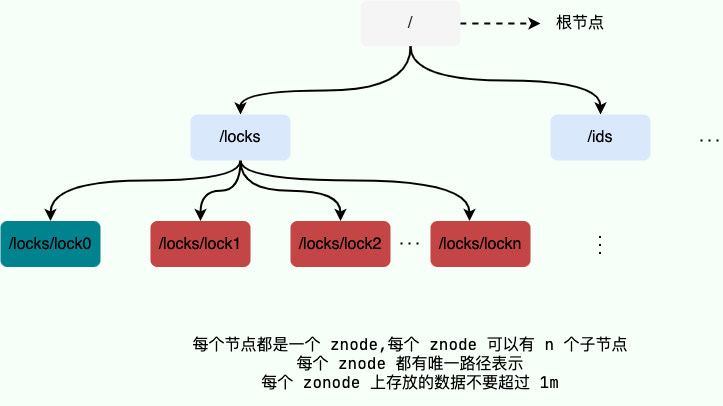
-
-### znode(数据节点)
-
-介绍了 ZooKeeper 树形数据模型之后,我们知道每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。你要存放的数据就放在上面,是你使用 ZooKeeper 过程中经常需要接触到的一个概念。
-
-我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
-
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失**。并且,**临时节点只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性
-
-每个 znode 由 2 部分组成:
-
-- **stat**:状态信息
-- **data**:节点存放的数据的具体内容
-
-如下所示,我通过 get 命令来获取 根目录下的 dubbo 节点的内容。(get 命令在下面会介绍到)。
-
-```shell
-[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 6] get /dubbo
-# 该数据节点关联的数据内容为空
-null
-# 下面是该数据节点的一些状态信息,其实就是 Stat 对象的格式化输出
-cZxid = 0x2
-ctime = Tue Nov 27 11:05:34 CST 2018
-mZxid = 0x2
-mtime = Tue Nov 27 11:05:34 CST 2018
-pZxid = 0x3
-cversion = 1
-dataVersion = 0
-aclVersion = 0
-ephemeralOwner = 0x0
-dataLength = 0
-numChildren = 1
-```
-
-Stat 类中包含了一个数据节点的所有状态信息的字段,包括事务 ID(cZxid)、节点创建时间(ctime) 和子节点个数(numChildren) 等等。
-
-下面我们来看一下每个 znode 状态信息究竟代表的是什么吧!(下面的内容来源于《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper 分布式一致性原理与实践》,因为 Guide 确实也不是特别清楚,要学会参考资料的嘛! ):
-
-| znode 状态信息 | 解释 |
-| -------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| cZxid | create ZXID,即该数据节点被创建时的事务 id |
-| ctime | create time,即该节点的创建时间 |
-| mZxid | modified ZXID,即该节点最终一次更新时的事务 id |
-| mtime | modified time,即该节点最后一次的更新时间 |
-| pZxid | 该节点的子节点列表最后一次修改时的事务 id,只有子节点列表变更才会更新 pZxid,子节点内容变更不会更新 |
-| cversion | 子节点版本号,当前节点的子节点每次变化时值增加 1 |
-| dataVersion | 数据节点内容版本号,节点创建时为 0,每更新一次节点内容(不管内容有无变化)该版本号的值增加 1 |
-| aclVersion | 节点的 ACL 版本号,表示该节点 ACL 信息变更次数 |
-| ephemeralOwner | 创建该临时节点的会话的 sessionId;如果当前节点为持久节点,则 ephemeralOwner=0 |
-| dataLength | 数据节点内容长度 |
-| numChildren | 当前节点的子节点个数 |
-
-### 版本(version)
-
-在前面我们已经提到,对应于每个 znode,ZooKeeper 都会为其维护一个叫作 **Stat** 的数据结构,Stat 中记录了这个 znode 的三个相关的版本:
-
-- **dataVersion**:当前 znode 节点的版本号
-- **cversion**:当前 znode 子节点的版本
-- **aclVersion**:当前 znode 的 ACL 的版本。
-
-### ACL(权限控制)
-
-ZooKeeper 采用 ACL(AccessControlLists)策略来进行权限控制,类似于 UNIX 文件系统的权限控制。
-
-对于 znode 操作的权限,ZooKeeper 提供了以下 5 种:
-
-- **CREATE** : 能创建子节点
-- **READ**:能获取节点数据和列出其子节点
-- **WRITE** : 能设置/更新节点数据
-- **DELETE** : 能删除子节点
-- **ADMIN** : 能设置节点 ACL 的权限
-
-其中尤其需要注意的是,**CREATE** 和 **DELETE** 这两种权限都是针对 **子节点** 的权限控制。
-
-对于身份认证,提供了以下几种方式:
-
-- **world**:默认方式,所有用户都可无条件访问。
-- **auth** :不使用任何 id,代表任何已认证的用户。
-- **digest** :用户名:密码认证方式:_username:password_ 。
-- **ip** : 对指定 ip 进行限制。
-
-### Watcher(事件监听器)
-
-Watcher(事件监听器),是 ZooKeeper 中的一个很重要的特性。ZooKeeper 允许用户在指定节点上注册一些 Watcher,并且在一些特定事件触发的时候,ZooKeeper 服务端会将事件通知到感兴趣的客户端上去,该机制是 ZooKeeper 实现分布式协调服务的重要特性。
-
-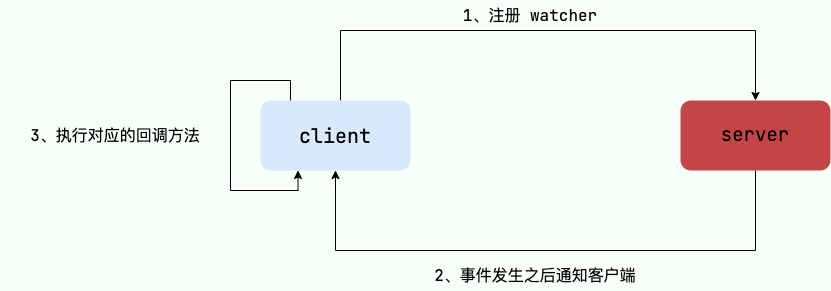
-
-_破音:非常有用的一个特性,都拿出小本本记好了,后面用到 ZooKeeper 基本离不开 Watcher(事件监听器)机制。_
-
-### 会话(Session)
-
-Session 可以看作是 ZooKeeper 服务器与客户端的之间的一个 TCP 长连接,通过这个连接,客户端能够通过心跳检测与服务器保持有效的会话,也能够向 ZooKeeper 服务器发送请求并接受响应,同时还能够通过该连接接收来自服务器的 Watcher 事件通知。
-
-Session 有一个属性叫做:`sessionTimeout` ,`sessionTimeout` 代表会话的超时时间。当由于服务器压力太大、网络故障或是客户端主动断开连接等各种原因导致客户端连接断开时,只要在`sessionTimeout`规定的时间内能够重新连接上集群中任意一台服务器,那么之前创建的会话仍然有效。
-
-另外,在为客户端创建会话之前,服务端首先会为每个客户端都分配一个 `sessionID`。由于 `sessionID`是 ZooKeeper 会话的一个重要标识,许多与会话相关的运行机制都是基于这个 `sessionID` 的,因此,无论是哪台服务器为客户端分配的 `sessionID`,都务必保证全局唯一。
-
-## ZooKeeper 集群
-
-为了保证高可用,最好是以集群形态来部署 ZooKeeper,这样只要集群中大部分机器是可用的(能够容忍一定的机器故障),那么 ZooKeeper 本身仍然是可用的。通常 3 台服务器就可以构成一个 ZooKeeper 集群了。ZooKeeper 官方提供的架构图就是一个 ZooKeeper 集群整体对外提供服务。
-
-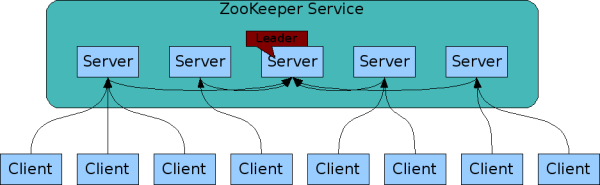
-
-上图中每一个 Server 代表一个安装 ZooKeeper 服务的服务器。组成 ZooKeeper 服务的服务器都会在内存中维护当前的服务器状态,并且每台服务器之间都互相保持着通信。集群间通过 ZAB 协议(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)来保持数据的一致性。
-
-**最典型集群模式:Master/Slave 模式(主备模式)**。在这种模式中,通常 Master 服务器作为主服务器提供写服务,其他的 Slave 服务器从服务器通过异步复制的方式获取 Master 服务器最新的数据提供读服务。
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群角色
-
-但是,在 ZooKeeper 中没有选择传统的 Master/Slave 概念,而是引入了 Leader、Follower 和 Observer 三种角色。如下图所示
-
-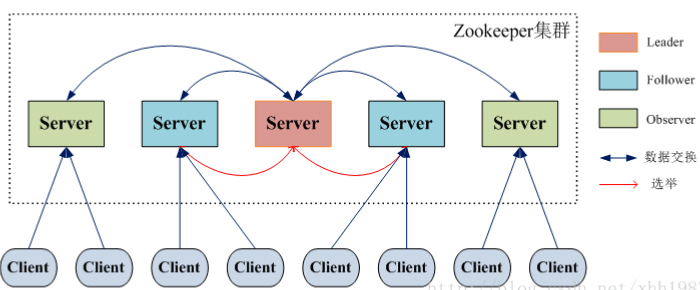
-
-ZooKeeper 集群中的所有机器通过一个 **Leader 选举过程** 来选定一台称为 “**Leader**” 的机器,Leader 既可以为客户端提供写服务又能提供读服务。除了 Leader 外,**Follower** 和 **Observer** 都只能提供读服务。Follower 和 Observer 唯一的区别在于 Observer 机器不参与 Leader 的选举过程,也不参与写操作的“过半写成功”策略,因此 Observer 机器可以在不影响写性能的情况下提升集群的读性能。
-
-| 角色 | 说明 |
-| -------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| Leader | 为客户端提供读和写的服务,负责投票的发起和决议,更新系统状态。 |
-| Follower | 为客户端提供读服务,如果是写服务则转发给 Leader。参与选举过程中的投票。 |
-| Observer | 为客户端提供读服务,如果是写服务则转发给 Leader。不参与选举过程中的投票,也不参与“过半写成功”策略。在不影响写性能的情况下提升集群的读性能。此角色于 ZooKeeper3.3 系列新增的角色。 |
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群 Leader 选举过程
-
-当 Leader 服务器出现网络中断、崩溃退出与重启等异常情况时,就会进入 Leader 选举过程,这个过程会选举产生新的 Leader 服务器。
-
-这个过程大致是这样的:
-
-1. **Leader election(选举阶段)**:节点在一开始都处于选举阶段,只要有一个节点得到超半数节点的票数,它就可以当选准 leader。
-2. **Discovery(发现阶段)**:在这个阶段,followers 跟准 leader 进行通信,同步 followers 最近接收的事务提议。
-3. **Synchronization(同步阶段)**:同步阶段主要是利用 leader 前一阶段获得的最新提议历史,同步集群中所有的副本。同步完成之后准 leader 才会成为真正的 leader。
-4. **Broadcast(广播阶段)**:到了这个阶段,ZooKeeper 集群才能正式对外提供事务服务,并且 leader 可以进行消息广播。同时如果有新的节点加入,还需要对新节点进行同步。
-
-ZooKeeper 集群中的服务器状态有下面几种:
-
-- **LOOKING**:寻找 Leader。
-- **LEADING**:Leader 状态,对应的节点为 Leader。
-- **FOLLOWING**:Follower 状态,对应的节点为 Follower。
-- **OBSERVING**:Observer 状态,对应节点为 Observer,该节点不参与 Leader 选举。
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群为啥最好奇数台?
-
-ZooKeeper 集群在宕掉几个 ZooKeeper 服务器之后,如果剩下的 ZooKeeper 服务器个数大于宕掉的个数的话整个 ZooKeeper 才依然可用。假如我们的集群中有 n 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,那么也就是剩下的服务数必须大于 n/2。先说一下结论,2n 和 2n-1 的容忍度是一样的,都是 n-1,大家可以先自己仔细想一想,这应该是一个很简单的数学问题了。
-
-比如假如我们有 3 台,那么最大允许宕掉 1 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,如果我们有 4 台的的时候也同样只允许宕掉 1 台。
-假如我们有 5 台,那么最大允许宕掉 2 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,如果我们有 6 台的的时候也同样只允许宕掉 2 台。
-
-综上,何必增加那一个不必要的 ZooKeeper 呢?
-
-### ZooKeeper 选举的过半机制防止脑裂
-
-**何为集群脑裂?**
-
-对于一个集群,通常多台机器会部署在不同机房,来提高这个集群的可用性。保证可用性的同时,会发生一种机房间网络线路故障,导致机房间网络不通,而集群被割裂成几个小集群。这时候子集群各自选主导致“脑裂”的情况。
-
-举例说明:比如现在有一个由 6 台服务器所组成的一个集群,部署在了 2 个机房,每个机房 3 台。正常情况下只有 1 个 leader,但是当两个机房中间网络断开的时候,每个机房的 3 台服务器都会认为另一个机房的 3 台服务器下线,而选出自己的 leader 并对外提供服务。若没有过半机制,当网络恢复的时候会发现有 2 个 leader。仿佛是 1 个大脑(leader)分散成了 2 个大脑,这就发生了脑裂现象。脑裂期间 2 个大脑都可能对外提供了服务,这将会带来数据一致性等问题。
-
-**过半机制是如何防止脑裂现象产生的?**
-
-ZooKeeper 的过半机制导致不可能产生 2 个 leader,因为少于等于一半是不可能产生 leader 的,这就使得不论机房的机器如何分配都不可能发生脑裂。
-
-## ZAB 协议和 Paxos 算法
-
-Paxos 算法应该可以说是 ZooKeeper 的灵魂了。但是,ZooKeeper 并没有完全采用 Paxos 算法 ,而是使用 ZAB 协议作为其保证数据一致性的核心算法。另外,在 ZooKeeper 的官方文档中也指出,ZAB 协议并不像 Paxos 算法那样,是一种通用的分布式一致性算法,它是一种特别为 Zookeeper 设计的崩溃可恢复的原子消息广播算法。
-
-### ZAB 协议介绍
-
-ZAB(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast,原子广播) 协议是为分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper 专门设计的一种支持崩溃恢复的原子广播协议。 在 ZooKeeper 中,主要依赖 ZAB 协议来实现分布式数据一致性,基于该协议,ZooKeeper 实现了一种主备模式的系统架构来保持集群中各个副本之间的数据一致性。
-
-### ZAB 协议两种基本的模式:崩溃恢复和消息广播
-
-ZAB 协议包括两种基本的模式,分别是
-
-- **崩溃恢复**:当整个服务框架在启动过程中,或是当 Leader 服务器出现网络中断、崩溃退出与重启等异常情况时,ZAB 协议就会进入恢复模式并选举产生新的 Leader 服务器。当选举产生了新的 Leader 服务器,同时集群中已经有过半的机器与该 Leader 服务器完成了状态同步之后,ZAB 协议就会退出恢复模式。其中,**所谓的状态同步是指数据同步,用来保证集群中存在过半的机器能够和 Leader 服务器的数据状态保持一致**。
-- **消息广播**:**当集群中已经有过半的 Follower 服务器完成了和 Leader 服务器的状态同步,那么整个服务框架就可以进入消息广播模式了。** 当一台同样遵守 ZAB 协议的服务器启动后加入到集群中时,如果此时集群中已经存在一个 Leader 服务器在负责进行消息广播,那么新加入的服务器就会自觉地进入数据恢复模式:找到 Leader 所在的服务器,并与其进行数据同步,然后一起参与到消息广播流程中去。
-
-### ZAB 协议&Paxos 算法文章推荐
-
-关于 **ZAB 协议&Paxos 算法** 需要讲和理解的东西太多了,具体可以看下面这几篇文章:
-
-- [Paxos 算法详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.html)
-- [ZooKeeper 与 Zab 协议 · Analyze](https://wingsxdu.com/posts/database/zookeeper/)
-- [Raft 算法详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.html)
-
-## ZooKeeper VS ETCD
-
-[ETCD](https://etcd.io/) 是一种强一致性的分布式键值存储,它提供了一种可靠的方式来存储需要由分布式系统或机器集群访问的数据。ETCD 内部采用 [Raft 算法](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.html)作为一致性算法,基于 Go 语言实现。
-
-与 ZooKeeper 类似,ETCD 也可用于数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、分布式锁等场景。那二者如何选择呢?
-
-得物技术的[浅析如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现高可用架构](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pBI3rjv5NdS1124Z7HQ-JA)这篇文章给出了如下的对比表格(我进一步做了优化),可以作为参考:
-
-| | ZooKeeper | ETCD |
-| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
-| **语言** | Java | Go |
-| **协议** | TCP | Grpc |
-| **接口调用** | 必须要使用自己的 client 进行调用 | 可通过 HTTP 传输,即可通过 CURL 等命令实现调用 |
-| **一致性算法** | Zab 协议 | Raft 算法 |
-| **Watcher 机制** | 较局限,一次性触发器 | 一次 Watch 可以监听所有的事件 |
-| **数据模型** | 基于目录的层次模式 | 参考了 zk 的数据模型,是个扁平的 kv 模型 |
-| **存储** | kv 存储,使用的是 ConcurrentHashMap,内存存储,一般不建议存储较多数据 | kv 存储,使用 bbolt 存储引擎,可以处理几个 GB 的数据。 |
-| **MVCC** | 不支持 | 支持,通过两个 B+ Tree 进行版本控制 |
-| **全局 Session** | 存在缺陷 | 实现更灵活,避免了安全性问题 |
-| **权限校验** | ACL | RBAC |
-| **事务能力** | 提供了简易的事务能力 | 只提供了版本号的检查能力 |
-| **部署维护** | 复杂 | 简单 |
-
-ZooKeeper 在存储性能、全局 Session、Watcher 机制等方面存在一定局限性,越来越多的开源项目在替换 ZooKeeper 为 Raft 实现或其它分布式协调服务,例如:[Kafka Needs No Keeper - Removing ZooKeeper Dependency (confluent.io)](https://www.confluent.io/blog/removing-zookeeper-dependency-in-kafka/)、[Moving Toward a ZooKeeper-Less Apache Pulsar (streamnative.io)](https://streamnative.io/blog/moving-toward-zookeeper-less-apache-pulsar)。
-
-ETCD 相对来说更优秀一些,提供了更稳定的高负载读写能力,对 ZooKeeper 暴露的许多问题进行了改进优化。并且,ETCD 基本能够覆盖 ZooKeeper 的所有应用场景,实现对其的替代。
-
-## 总结
-
-1. ZooKeeper 本身就是一个分布式程序(只要半数以上节点存活,ZooKeeper 就能正常服务)。
-2. 为了保证高可用,最好是以集群形态来部署 ZooKeeper,这样只要集群中大部分机器是可用的(能够容忍一定的机器故障),那么 ZooKeeper 本身仍然是可用的。
-3. ZooKeeper 将数据保存在内存中,这也就保证了 高吞吐量和低延迟(但是内存限制了能够存储的容量不太大,此限制也是保持 znode 中存储的数据量较小的进一步原因)。
-4. ZooKeeper 是高性能的。 在“读”多于“写”的应用程序中尤其地明显,因为“写”会导致所有的服务器间同步状态。(“读”多于“写”是协调服务的典型场景。)
-5. ZooKeeper 有临时节点的概念。 当创建临时节点的客户端会话一直保持活动,瞬时节点就一直存在。而当会话终结时,瞬时节点被删除。持久节点是指一旦这个 znode 被创建了,除非主动进行 znode 的移除操作,否则这个 znode 将一直保存在 ZooKeeper 上。
-6. ZooKeeper 底层其实只提供了两个功能:① 管理(存储、读取)用户程序提交的数据;② 为用户程序提供数据节点监听服务。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper 分布式一致性原理与实践》
-- 谈谈 ZooKeeper 的局限性:
-
-
+- **Kafka**: ZooKeeper primarily provides registration for Brokers and Topics, as well as load balancing for multiple Partitions. However, after Kafka 2.8, it introduced the KRaft mode based on the Raft protocol, eliminating the dependency on ZooKeeper and greatly simplifying Kafka's architecture.
+- **HBase**: ZooKeeper ensures that there is only one Master in the entire HBase cluster and provides and saves the status information of region servers (whether they are online).
+- **Hadoop**: ZooKeeper provides high availability support for the Namen
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
index 856378a0cd5..ad6193591ea 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
@@ -1,386 +1,44 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper相关概念总结(进阶)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Advanced)
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-> [FrancisQ](https://juejin.im/user/5c33853851882525ea106810) 投稿。
+> [FrancisQ](https://juejin.im/user/5c33853851882525ea106810) Contribution.
-## 什么是 ZooKeeper
+## What is ZooKeeper
-`ZooKeeper` 由 `Yahoo` 开发,后来捐赠给了 `Apache` ,现已成为 `Apache` 顶级项目。`ZooKeeper` 是一个开源的分布式应用程序协调服务器,其为分布式系统提供一致性服务。其一致性是通过基于 `Paxos` 算法的 `ZAB` 协议完成的。其主要功能包括:配置维护、分布式同步、集群管理等。
+`ZooKeeper` was developed by `Yahoo` and later donated to `Apache`, and it has now become an Apache top-level project. `ZooKeeper` is an open-source distributed application coordination server that provides consistency services for distributed systems. Its consistency is achieved through the `ZAB` protocol based on the `Paxos` algorithm. Its main functions include configuration maintenance, distributed synchronization, cluster management, and more.
-简单来说, `ZooKeeper` 是一个 **分布式协调服务框架** 。分布式?协调服务?这啥玩意?🤔🤔
+In simple terms, `ZooKeeper` is a **distributed coordination service framework**. Distributed? Coordination service? What is that? 🤔🤔
-其实解释到分布式这个概念的时候,我发现有些同学并不是能把 **分布式和集群** 这两个概念很好的理解透。前段时间有同学和我探讨起分布式的东西,他说分布式不就是加机器吗?一台机器不够用再加一台抗压呗。当然加机器这种说法也无可厚非,你一个分布式系统必定涉及到多个机器,但是你别忘了,计算机学科中还有一个相似的概念—— `Cluster` ,集群不也是加机器吗?但是 集群 和 分布式 其实就是两个完全不同的概念。
+When explaining the concept of distribution, I found that some students do not fully understand the difference between **distributed systems and clusters**. Recently, a student discussed distributed systems with me, saying that isn't distributed just about adding machines? If one machine is not enough, just add another to handle the load. Of course, saying "add machines" is not entirely wrong; a distributed system must involve multiple machines. However, don't forget that there is a similar concept in computer science—`Cluster`. Isn't a cluster also about adding machines? But clusters and distributed systems are actually two completely different concepts.
-比如,我现在有一个秒杀服务,并发量太大单机系统承受不住,那我加几台服务器也 **一样** 提供秒杀服务,这个时候就是 **`Cluster` 集群** 。
+For example, I now have a flash sale service, and the concurrency is too high for a single machine to handle. If I add a few servers, I can still provide the flash sale service; this is a **`Cluster`**.
-但是,我现在换一种方式,我将一个秒杀服务 **拆分成多个子服务** ,比如创建订单服务,增加积分服务,扣优惠券服务等等,**然后我将这些子服务都部署在不同的服务器上** ,这个时候就是 **`Distributed` 分布式** 。
+However, if I take a different approach and **split a flash sale service into multiple sub-services**, such as creating an order service, a points service, a coupon deduction service, etc., **and then deploy these sub-services on different servers**, this is a **`Distributed`** system.

-而我为什么反驳同学所说的分布式就是加机器呢?因为我认为加机器更加适用于构建集群,因为它真是只有加机器。而对于分布式来说,你首先需要将业务进行拆分,然后再加机器(不仅仅是加机器那么简单),同时你还要去解决分布式带来的一系列问题。
+Why do I refute the student's claim that distributed means just adding machines? Because I believe that adding machines is more applicable to building a cluster, as it truly only involves adding machines. In contrast, for a distributed system, you first need to split the business, and then add machines (it's not just as simple as adding machines). At the same time, you also need to solve a series of problems brought by distribution.

-比如各个分布式组件如何协调起来,如何减少各个系统之间的耦合度,分布式事务的处理,如何去配置整个分布式系统等等。`ZooKeeper` 主要就是解决这些问题的。
+For example, how various distributed components coordinate, how to reduce coupling between systems, handling distributed transactions, how to configure the entire distributed system, etc. `ZooKeeper` mainly addresses these issues.
-## 一致性问题
+## Consistency Issues
-设计一个分布式系统必定会遇到一个问题—— **因为分区容忍性(partition tolerance)的存在,就必定要求我们需要在系统可用性(availability)和数据一致性(consistency)中做出权衡** 。这就是著名的 `CAP` 定理。
+Designing a distributed system will inevitably encounter a problem—**due to the existence of partition tolerance, we must make trade-offs between system availability and data consistency**. This is the famous `CAP` theorem.
-理解起来其实很简单,比如说把一个班级作为整个系统,而学生是系统中的一个个独立的子系统。这个时候班里的小红小明偷偷谈恋爱被班里的大嘴巴小花发现了,小花欣喜若狂告诉了周围的人,然后小红小明谈恋爱的消息在班级里传播起来了。当在消息的传播(散布)过程中,你抓到一个同学问他们的情况,如果回答你不知道,那么说明整个班级系统出现了数据不一致的问题(因为小花已经知道这个消息了)。而如果他直接不回答你,因为整个班级有消息在进行传播(为了保证一致性,需要所有人都知道才可提供服务),这个时候就出现了系统的可用性问题。
+Understanding it is actually quite simple. For example, consider a class as the entire system, and the students are independent subsystems within the system. At this point, if Xiaohong and Xiaoming in the class are secretly dating and are discovered by the gossiping Xiaohua, who excitedly tells those around her, the news of Xiaohong and Xiaoming's relationship spreads throughout the class. If you catch a student during the spread of the news and ask them about it, if they respond with "I don't know," it indicates that the entire class system has a data inconsistency issue (because Xiaohua already knows this news). If they simply do not answer you, it means that the entire class is in the process of spreading the news (to ensure consistency, everyone must know before services can be provided), and at this point, a system availability issue arises.

-而上述前者就是 `Eureka` 的处理方式,它保证了 AP(可用性),后者就是我们今天所要讲的 `ZooKeeper` 的处理方式,它保证了 CP(数据一致性)。
+The former is the handling method of `Eureka`, which guarantees AP (availability), while the latter is the handling method of `ZooKeeper`, which guarantees CP (data consistency).
-## 一致性协议和算法
+## Consistency Protocols and Algorithms
-而为了解决数据一致性问题,在科学家和程序员的不断探索中,就出现了很多的一致性协议和算法。比如 2PC(两阶段提交),3PC(三阶段提交),Paxos 算法等等。
-
-这时候请你思考一个问题,同学之间如果采用传纸条的方式去传播消息,那么就会出现一个问题——我咋知道我的小纸条有没有传到我想要传递的那个人手中呢?万一被哪个小家伙给劫持篡改了呢,对吧?
-
-
-
-这个时候就引申出一个概念—— **拜占庭将军问题** 。它意指 **在不可靠信道上试图通过消息传递的方式达到一致性是不可能的**, 所以所有的一致性算法的 **必要前提** 就是安全可靠的消息通道。
-
-而为什么要去解决数据一致性的问题?你想想,如果一个秒杀系统将服务拆分成了下订单和加积分服务,这两个服务部署在不同的机器上了,万一在消息的传播过程中积分系统宕机了,总不能你这边下了订单却没加积分吧?你总得保证两边的数据需要一致吧?
-
-### 2PC(两阶段提交)
-
-两阶段提交是一种保证分布式系统数据一致性的协议,现在很多数据库都是采用的两阶段提交协议来完成 **分布式事务** 的处理。
-
-在介绍 2PC 之前,我们先来想想分布式事务到底有什么问题呢?
-
-还拿秒杀系统的下订单和加积分两个系统来举例吧(我想你们可能都吐了 🤮🤮🤮),我们此时下完订单会发个消息给积分系统告诉它下面该增加积分了。如果我们仅仅是发送一个消息也不收回复,那么我们的订单系统怎么能知道积分系统的收到消息的情况呢?如果我们增加一个收回复的过程,那么当积分系统收到消息后返回给订单系统一个 `Response` ,但在中间出现了网络波动,那个回复消息没有发送成功,订单系统是不是以为积分系统消息接收失败了?它是不是会回滚事务?但此时积分系统是成功收到消息的,它就会去处理消息然后给用户增加积分,这个时候就会出现积分加了但是订单没下成功。
-
-所以我们所需要解决的是在分布式系统中,整个调用链中,我们所有服务的数据处理要么都成功要么都失败,即所有服务的 **原子性问题** 。
-
-在两阶段提交中,主要涉及到两个角色,分别是协调者和参与者。
-
-第一阶段:当要执行一个分布式事务的时候,事务发起者首先向协调者发起事务请求,然后协调者会给所有参与者发送 `prepare` 请求(其中包括事务内容)告诉参与者你们需要执行事务了,如果能执行我发的事务内容那么就先执行但不提交,执行后请给我回复。然后参与者收到 `prepare` 消息后,他们会开始执行事务(但不提交),并将 `Undo` 和 `Redo` 信息记入事务日志中,之后参与者就向协调者反馈是否准备好了。
-
-第二阶段:第二阶段主要是协调者根据参与者反馈的情况来决定接下来是否可以进行事务的提交操作,即提交事务或者回滚事务。
-
-比如这个时候 **所有的参与者** 都返回了准备好了的消息,这个时候就进行事务的提交,协调者此时会给所有的参与者发送 **`Commit` 请求** ,当参与者收到 `Commit` 请求的时候会执行前面执行的事务的 **提交操作** ,提交完毕之后将给协调者发送提交成功的响应。
-
-而如果在第一阶段并不是所有参与者都返回了准备好了的消息,那么此时协调者将会给所有参与者发送 **回滚事务的 `rollback` 请求**,参与者收到之后将会 **回滚它在第一阶段所做的事务处理** ,然后再将处理情况返回给协调者,最终协调者收到响应后便给事务发起者返回处理失败的结果。
-
-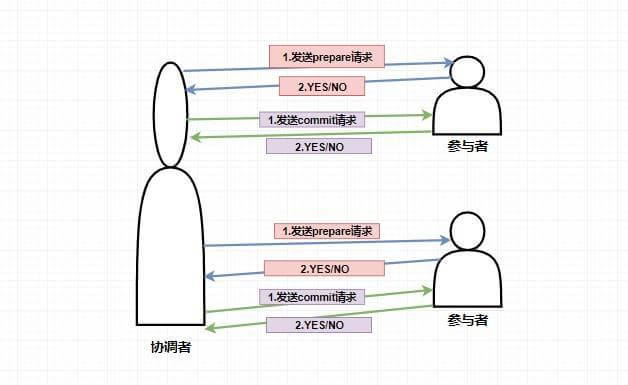
-
-个人觉得 2PC 实现得还是比较鸡肋的,因为事实上它只解决了各个事务的原子性问题,随之也带来了很多的问题。
-
-
-
-- **单点故障问题**,如果协调者挂了那么整个系统都处于不可用的状态了。
-- **阻塞问题**,即当协调者发送 `prepare` 请求,参与者收到之后如果能处理那么它将会进行事务的处理但并不提交,这个时候会一直占用着资源不释放,如果此时协调者挂了,那么这些资源都不会再释放了,这会极大影响性能。
-- **数据不一致问题**,比如当第二阶段,协调者只发送了一部分的 `commit` 请求就挂了,那么也就意味着,收到消息的参与者会进行事务的提交,而后面没收到的则不会进行事务提交,那么这时候就会产生数据不一致性问题。
-
-### 3PC(三阶段提交)
-
-因为 2PC 存在的一系列问题,比如单点,容错机制缺陷等等,从而产生了 **3PC(三阶段提交)** 。那么这三阶段又分别是什么呢?
-
-> 千万不要吧 PC 理解成个人电脑了,其实他们是 phase-commit 的缩写,即阶段提交。
-
-1. **CanCommit 阶段**:协调者向所有参与者发送 `CanCommit` 请求,参与者收到请求后会根据自身情况查看是否能执行事务,如果可以则返回 YES 响应并进入预备状态,否则返回 NO 。
-2. **PreCommit 阶段**:协调者根据参与者返回的响应来决定是否可以进行下面的 `PreCommit` 操作。如果上面参与者返回的都是 YES,那么协调者将向所有参与者发送 `PreCommit` 预提交请求,**参与者收到预提交请求后,会进行事务的执行操作,并将 `Undo` 和 `Redo` 信息写入事务日志中** ,最后如果参与者顺利执行了事务则给协调者返回成功的响应。如果在第一阶段协调者收到了 **任何一个 NO** 的信息,或者 **在一定时间内** 并没有收到全部的参与者的响应,那么就会中断事务,它会向所有参与者发送中断请求(abort),参与者收到中断请求之后会立即中断事务,或者在一定时间内没有收到协调者的请求,它也会中断事务。
-3. **DoCommit 阶段**:这个阶段其实和 `2PC` 的第二阶段差不多,如果协调者收到了所有参与者在 `PreCommit` 阶段的 YES 响应,那么协调者将会给所有参与者发送 `DoCommit` 请求,**参与者收到 `DoCommit` 请求后则会进行事务的提交工作**,完成后则会给协调者返回响应,协调者收到所有参与者返回的事务提交成功的响应之后则完成事务。若协调者在 `PreCommit` 阶段 **收到了任何一个 NO 或者在一定时间内没有收到所有参与者的响应** ,那么就会进行中断请求的发送,参与者收到中断请求后则会 **通过上面记录的回滚日志** 来进行事务的回滚操作,并向协调者反馈回滚状况,协调者收到参与者返回的消息后,中断事务。
-
-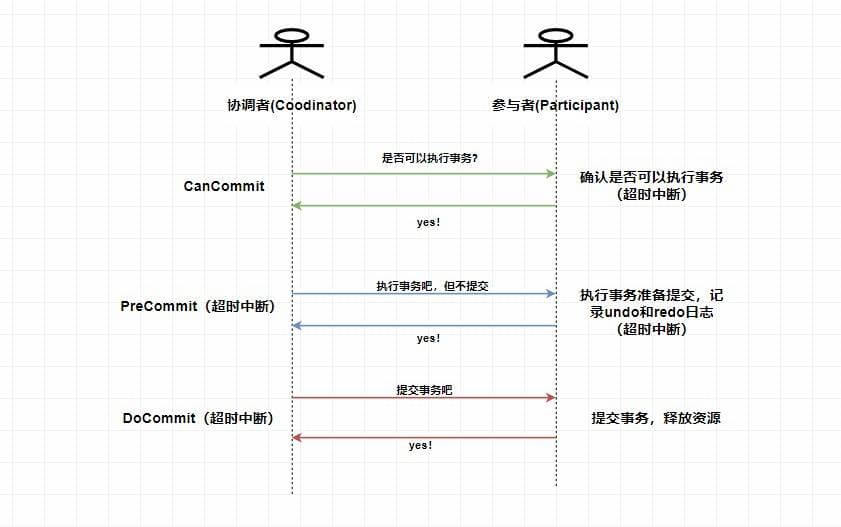
-
-> 这里是 `3PC` 在成功的环境下的流程图,你可以看到 `3PC` 在很多地方进行了超时中断的处理,比如协调者在指定时间内未收到全部的确认消息则进行事务中断的处理,这样能 **减少同步阻塞的时间** 。还有需要注意的是,**`3PC` 在 `DoCommit` 阶段参与者如未收到协调者发送的提交事务的请求,它会在一定时间内进行事务的提交**。为什么这么做呢?是因为这个时候我们肯定**保证了在第一阶段所有的协调者全部返回了可以执行事务的响应**,这个时候我们有理由**相信其他系统都能进行事务的执行和提交**,所以**不管**协调者有没有发消息给参与者,进入第三阶段参与者都会进行事务的提交操作。
-
-总之,`3PC` 通过一系列的超时机制很好的缓解了阻塞问题,但是最重要的一致性并没有得到根本的解决,比如在 `DoCommit` 阶段,当一个参与者收到了请求之后其他参与者和协调者挂了或者出现了网络分区,这个时候收到消息的参与者都会进行事务提交,这就会出现数据不一致性问题。
-
-所以,要解决一致性问题还需要靠 `Paxos` 算法 ⭐️ ⭐️ ⭐️ 。
-
-### `Paxos` 算法
-
-`Paxos` 算法是基于**消息传递且具有高度容错特性的一致性算法**,是目前公认的解决分布式一致性问题最有效的算法之一,**其解决的问题就是在分布式系统中如何就某个值(决议)达成一致** 。
-
-在 `Paxos` 中主要有三个角色,分别为 `Proposer提案者`、`Acceptor表决者`、`Learner学习者`。`Paxos` 算法和 `2PC` 一样,也有两个阶段,分别为 `Prepare` 和 `accept` 阶段。
-
-#### prepare 阶段
-
-- `Proposer提案者`:负责提出 `proposal`,每个提案者在提出提案时都会首先获取到一个 **具有全局唯一性的、递增的提案编号 N**,即在整个集群中是唯一的编号 N,然后将该编号赋予其要提出的提案,在**第一阶段是只将提案编号发送给所有的表决者**。
-- `Acceptor表决者`:每个表决者在 `accept` 某提案后,会将该提案编号 N 记录在本地,这样每个表决者中保存的已经被 accept 的提案中会存在一个**编号最大的提案**,其编号假设为 `maxN`。每个表决者仅会 `accept` 编号大于自己本地 `maxN` 的提案,在批准提案时表决者会将以前接受过的最大编号的提案作为响应反馈给 `Proposer` 。
-
-> 下面是 `prepare` 阶段的流程图,你可以对照着参考一下。
-
-
-
-#### accept 阶段
-
-当一个提案被 `Proposer` 提出后,如果 `Proposer` 收到了超过半数的 `Acceptor` 的批准(`Proposer` 本身同意),那么此时 `Proposer` 会给所有的 `Acceptor` 发送真正的提案(你可以理解为第一阶段为试探),这个时候 `Proposer` 就会发送提案的内容和提案编号。
-
-表决者收到提案请求后会再次比较本身已经批准过的最大提案编号和该提案编号,如果该提案编号 **大于等于** 已经批准过的最大提案编号,那么就 `accept` 该提案(此时执行提案内容但不提交),随后将情况返回给 `Proposer` 。如果不满足则不回应或者返回 NO 。
-
-
-
-当 `Proposer` 收到超过半数的 `accept` ,那么它这个时候会向所有的 `acceptor` 发送提案的提交请求。需要注意的是,因为上述仅仅是超过半数的 `acceptor` 批准执行了该提案内容,其他没有批准的并没有执行该提案内容,所以这个时候需要**向未批准的 `acceptor` 发送提案内容和提案编号并让它无条件执行和提交**,而对于前面已经批准过该提案的 `acceptor` 来说 **仅仅需要发送该提案的编号** ,让 `acceptor` 执行提交就行了。
-
-
-
-而如果 `Proposer` 如果没有收到超过半数的 `accept` 那么它将会将 **递增** 该 `Proposal` 的编号,然后 **重新进入 `Prepare` 阶段** 。
-
-> 对于 `Learner` 来说如何去学习 `Acceptor` 批准的提案内容,这有很多方式,读者可以自己去了解一下,这里不做过多解释。
-
-#### paxos 算法的死循环问题
-
-其实就有点类似于两个人吵架,小明说我是对的,小红说我才是对的,两个人据理力争的谁也不让谁 🤬🤬。
-
-比如说,此时提案者 P1 提出一个方案 M1,完成了 `Prepare` 阶段的工作,这个时候 `acceptor` 则批准了 M1,但是此时提案者 P2 同时也提出了一个方案 M2,它也完成了 `Prepare` 阶段的工作。然后 P1 的方案已经不能在第二阶段被批准了(因为 `acceptor` 已经批准了比 M1 更大的 M2),所以 P1 自增方案变为 M3 重新进入 `Prepare` 阶段,然后 `acceptor` ,又批准了新的 M3 方案,它又不能批准 M2 了,这个时候 M2 又自增进入 `Prepare` 阶段。。。
-
-就这样无休无止的永远提案下去,这就是 `paxos` 算法的死循环问题。
-
-
-
-那么如何解决呢?很简单,人多了容易吵架,我现在 **就允许一个能提案** 就行了。
-
-## 引出 ZAB
-
-### Zookeeper 架构
-
-作为一个优秀高效且可靠的分布式协调框架,`ZooKeeper` 在解决分布式数据一致性问题时并没有直接使用 `Paxos` ,而是专门定制了一致性协议叫做 `ZAB(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)` 原子广播协议,该协议能够很好地支持 **崩溃恢复** 。
-
-
-
-### ZAB 中的三个角色
-
-和介绍 `Paxos` 一样,在介绍 `ZAB` 协议之前,我们首先来了解一下在 `ZAB` 中三个主要的角色,`Leader 领导者`、`Follower跟随者`、`Observer观察者` 。
-
-- `Leader`:集群中 **唯一的写请求处理者** ,能够发起投票(投票也是为了进行写请求)。
-- `Follower`:能够接收客户端的请求,如果是读请求则可以自己处理,**如果是写请求则要转发给 `Leader`** 。在选举过程中会参与投票,**有选举权和被选举权** 。
-- `Observer`:就是没有选举权和被选举权的 `Follower` 。
-
-在 `ZAB` 协议中对 `zkServer`(即上面我们说的三个角色的总称) 还有两种模式的定义,分别是 **消息广播** 和 **崩溃恢复** 。
-
-### 消息广播模式
-
-说白了就是 `ZAB` 协议是如何处理写请求的,上面我们不是说只有 `Leader` 能处理写请求嘛?那么我们的 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 是不是也需要 **同步更新数据** 呢?总不能数据只在 `Leader` 中更新了,其他角色都没有得到更新吧?
-
-不就是 **在整个集群中保持数据的一致性** 嘛?如果是你,你会怎么做呢?
-
-废话,第一步肯定需要 `Leader` 将写请求 **广播** 出去呀,让 `Leader` 问问 `Followers` 是否同意更新,如果超过半数以上的同意那么就进行 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 的更新(和 `Paxos` 一样)。当然这么说有点虚,画张图理解一下。
-
-
-
-嗯。。。看起来很简单,貌似懂了 🤥🤥🤥。这两个 `Queue` 哪冒出来的?答案是 **`ZAB` 需要让 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 保证顺序性** 。何为顺序性,比如我现在有一个写请求 A,此时 `Leader` 将请求 A 广播出去,因为只需要半数同意就行,所以可能这个时候有一个 `Follower` F1 因为网络原因没有收到,而 `Leader` 又广播了一个请求 B,因为网络原因,F1 竟然先收到了请求 B 然后才收到了请求 A,这个时候请求处理的顺序不同就会导致数据的不同,从而 **产生数据不一致问题** 。
-
-所以在 `Leader` 这端,它为每个其他的 `zkServer` 准备了一个 **队列** ,采用先进先出的方式发送消息。由于协议是 **通过 `TCP`** 来进行网络通信的,保证了消息的发送顺序性,接受顺序性也得到了保证。
-
-除此之外,在 `ZAB` 中还定义了一个 **全局单调递增的事务 ID `ZXID`** ,它是一个 64 位 long 型,其中高 32 位表示 `epoch` 年代,低 32 位表示事务 id。`epoch` 是会根据 `Leader` 的变化而变化的,当一个 `Leader` 挂了,新的 `Leader` 上位的时候,年代(`epoch`)就变了。而低 32 位可以简单理解为递增的事务 id。
-
-定义这个的原因也是为了顺序性,每个 `proposal` 在 `Leader` 中生成后需要 **通过其 `ZXID` 来进行排序** ,才能得到处理。
-
-### 崩溃恢复模式
-
-说到崩溃恢复我们首先要提到 `ZAB` 中的 `Leader` 选举算法,当系统出现崩溃影响最大应该是 `Leader` 的崩溃,因为我们只有一个 `Leader` ,所以当 `Leader` 出现问题的时候我们势必需要重新选举 `Leader` 。
-
-`Leader` 选举可以分为两个不同的阶段,第一个是我们提到的 `Leader` 宕机需要重新选举,第二则是当 `Zookeeper` 启动时需要进行系统的 `Leader` 初始化选举。下面我先来介绍一下 `ZAB` 是如何进行初始化选举的。
-
-假设我们集群中有 3 台机器,那也就意味着我们需要两台以上同意(超过半数)。比如这个时候我们启动了 `server1` ,它会首先 **投票给自己** ,投票内容为服务器的 `myid` 和 `ZXID` ,因为初始化所以 `ZXID` 都为 0,此时 `server1` 发出的投票为 (1,0)。但此时 `server1` 的投票仅为 1,所以不能作为 `Leader` ,此时还在选举阶段所以整个集群处于 **`Looking` 状态**。
-
-接着 `server2` 启动了,它首先也会将投票选给自己(2,0),并将投票信息广播出去(`server1`也会,只是它那时没有其他的服务器了),`server1` 在收到 `server2` 的投票信息后会将投票信息与自己的作比较。**首先它会比较 `ZXID` ,`ZXID` 大的优先为 `Leader`,如果相同则比较 `myid`,`myid` 大的优先作为 `Leader`**。所以此时`server1` 发现 `server2` 更适合做 `Leader`,它就会将自己的投票信息更改为(2,0)然后再广播出去,之后`server2` 收到之后发现和自己的一样无需做更改,并且自己的 **投票已经超过半数** ,则 **确定 `server2` 为 `Leader`**,`server1` 也会将自己服务器设置为 `Following` 变为 `Follower`。整个服务器就从 `Looking` 变为了正常状态。
-
-当 `server3` 启动发现集群没有处于 `Looking` 状态时,它会直接以 `Follower` 的身份加入集群。
-
-还是前面三个 `server` 的例子,如果在整个集群运行的过程中 `server2` 挂了,那么整个集群会如何重新选举 `Leader` 呢?其实和初始化选举差不多。
-
-首先毫无疑问的是剩下的两个 `Follower` 会将自己的状态 **从 `Following` 变为 `Looking` 状态** ,然后每个 `server` 会向初始化投票一样首先给自己投票(这不过这里的 `zxid` 可能不是 0 了,这里为了方便随便取个数字)。
-
-假设 `server1` 给自己投票为(1,99),然后广播给其他 `server`,`server3` 首先也会给自己投票(3,95),然后也广播给其他 `server`。`server1` 和 `server3` 此时会收到彼此的投票信息,和一开始选举一样,他们也会比较自己的投票和收到的投票(`zxid` 大的优先,如果相同那么就 `myid` 大的优先)。这个时候 `server1` 收到了 `server3` 的投票发现没自己的合适故不变,`server3` 收到 `server1` 的投票结果后发现比自己的合适于是更改投票为(1,99)然后广播出去,最后 `server1` 收到了发现自己的投票已经超过半数就把自己设为 `Leader`,`server3` 也随之变为 `Follower`。
-
-> 请注意 `ZooKeeper` 为什么要设置奇数个结点?比如这里我们是三个,挂了一个我们还能正常工作,挂了两个我们就不能正常工作了(已经没有超过半数的节点数了,所以无法进行投票等操作了)。而假设我们现在有四个,挂了一个也能工作,**但是挂了两个也不能正常工作了**,这是和三个一样的,而三个比四个还少一个,带来的效益是一样的,所以 `Zookeeper` 推荐奇数个 `server` 。
-
-那么说完了 `ZAB` 中的 `Leader` 选举方式之后我们再来了解一下 **崩溃恢复** 是什么玩意?
-
-其实主要就是 **当集群中有机器挂了,我们整个集群如何保证数据一致性?**
-
-如果只是 `Follower` 挂了,而且挂的没超过半数的时候,因为我们一开始讲了在 `Leader` 中会维护队列,所以不用担心后面的数据没接收到导致数据不一致性。
-
-如果 `Leader` 挂了那就麻烦了,我们肯定需要先暂停服务变为 `Looking` 状态然后进行 `Leader` 的重新选举(上面我讲过了),但这个就要分为两种情况了,分别是 **确保已经被 Leader 提交的提案最终能够被所有的 Follower 提交** 和 **跳过那些已经被丢弃的提案** 。
-
-确保已经被 Leader 提交的提案最终能够被所有的 Follower 提交是什么意思呢?
-
-假设 `Leader (server2)` 发送 `commit` 请求(忘了请看上面的消息广播模式),他发送给了 `server3`,然后要发给 `server1` 的时候突然挂了。这个时候重新选举的时候我们如果把 `server1` 作为 `Leader` 的话,那么肯定会产生数据不一致性,因为 `server3` 肯定会提交刚刚 `server2` 发送的 `commit` 请求的提案,而 `server1` 根本没收到所以会丢弃。
-
-
-
-那怎么解决呢?
-
-聪明的同学肯定会质疑,**这个时候 `server1` 已经不可能成为 `Leader` 了,因为 `server1` 和 `server3` 进行投票选举的时候会比较 `ZXID` ,而此时 `server3` 的 `ZXID` 肯定比 `server1` 的大了**。(不理解可以看前面的选举算法)
-
-那么跳过那些已经被丢弃的提案又是什么意思呢?
-
-假设 `Leader (server2)` 此时同意了提案 N1,自身提交了这个事务并且要发送给所有 `Follower` 要 `commit` 的请求,却在这个时候挂了,此时肯定要重新进行 `Leader` 的选举,比如说此时选 `server1` 为 `Leader` (这无所谓)。但是过了一会,这个 **挂掉的 `Leader` 又重新恢复了** ,此时它肯定会作为 `Follower` 的身份进入集群中,需要注意的是刚刚 `server2` 已经同意提交了提案 N1,但其他 `server` 并没有收到它的 `commit` 信息,所以其他 `server` 不可能再提交这个提案 N1 了,这样就会出现数据不一致性问题了,所以 **该提案 N1 最终需要被抛弃掉** 。
-
-
-
-## Zookeeper 的几个理论知识
-
-了解了 `ZAB` 协议还不够,它仅仅是 `Zookeeper` 内部实现的一种方式,而我们如何通过 `Zookeeper` 去做一些典型的应用场景呢?比如说集群管理,分布式锁,`Master` 选举等等。
-
-这就涉及到如何使用 `Zookeeper` 了,但在使用之前我们还需要掌握几个概念。比如 `Zookeeper` 的 **数据模型**、**会话机制**、**ACL**、**Watcher 机制** 等等。
-
-### 数据模型
-
-`zookeeper` 数据存储结构与标准的 `Unix` 文件系统非常相似,都是在根节点下挂很多子节点(树型)。但是 `zookeeper` 中没有文件系统中目录与文件的概念,而是 **使用了 `znode` 作为数据节点** 。`znode` 是 `zookeeper` 中的最小数据单元,每个 `znode` 上都可以保存数据,同时还可以挂载子节点,形成一个树形化命名空间。
-
-
-
-每个 `znode` 都有自己所属的 **节点类型** 和 **节点状态**。
-
-其中节点类型可以分为 **持久节点**、**持久顺序节点**、**临时节点** 和 **临时顺序节点**。
-
-- 持久节点:一旦创建就一直存在,直到将其删除。
-- 持久顺序节点:一个父节点可以为其子节点 **维护一个创建的先后顺序** ,这个顺序体现在 **节点名称** 上,是节点名称后自动添加一个由 10 位数字组成的数字串,从 0 开始计数。
-- 临时节点:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。临时节点 **只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- 临时顺序节点:父节点可以创建一个维持了顺序的临时节点(和前面的持久顺序性节点一样)。
-
-节点状态中包含了很多节点的属性比如 `czxid`、`mzxid` 等等,在 `zookeeper` 中是使用 `Stat` 这个类来维护的。下面我列举一些属性解释。
-
-- `czxid`:`Created ZXID`,该数据节点被 **创建** 时的事务 ID。
-- `mzxid`:`Modified ZXID`,节点 **最后一次被更新时** 的事务 ID。
-- `ctime`:`Created Time`,该节点被创建的时间。
-- `mtime`:`Modified Time`,该节点最后一次被修改的时间。
-- `version`:节点的版本号。
-- `cversion`:**子节点** 的版本号。
-- `aversion`:节点的 `ACL` 版本号。
-- `ephemeralOwner`:创建该节点的会话的 `sessionID` ,如果该节点为持久节点,该值为 0。
-- `dataLength`:节点数据内容的长度。
-- `numChildre`:该节点的子节点个数,如果为临时节点为 0。
-- `pzxid`:该节点子节点列表最后一次被修改时的事务 ID,注意是子节点的 **列表** ,不是内容。
-
-### 会话
-
-我想这个对于后端开发的朋友肯定不陌生,不就是 `session` 吗?只不过 `zk` 客户端和服务端是通过 **`TCP` 长连接** 维持的会话机制,其实对于会话来说你可以理解为 **保持连接状态** 。
-
-在 `zookeeper` 中,会话还有对应的事件,比如 `CONNECTION_LOSS 连接丢失事件`、`SESSION_MOVED 会话转移事件`、`SESSION_EXPIRED 会话超时失效事件` 。
-
-### ACL
-
-`ACL` 为 `Access Control Lists` ,它是一种权限控制。在 `zookeeper` 中定义了 5 种权限,它们分别为:
-
-- `CREATE`:创建子节点的权限。
-- `READ`:获取节点数据和子节点列表的权限。
-- `WRITE`:更新节点数据的权限。
-- `DELETE`:删除子节点的权限。
-- `ADMIN`:设置节点 ACL 的权限。
-
-### Watcher 机制
-
-`Watcher` 为事件监听器,是 `zk` 非常重要的一个特性,很多功能都依赖于它,它有点类似于订阅的方式,即客户端向服务端 **注册** 指定的 `watcher` ,当服务端符合了 `watcher` 的某些事件或要求则会 **向客户端发送事件通知** ,客户端收到通知后找到自己定义的 `Watcher` 然后 **执行相应的回调方法** 。
-
-
-
-## Zookeeper 的几个典型应用场景
-
-前面说了这么多的理论知识,你可能听得一头雾水,这些玩意有啥用?能干啥事?别急,听我慢慢道来。
-
-
-
-### 选主
-
-还记得上面我们的所说的临时节点吗?因为 `Zookeeper` 的强一致性,能够很好地在保证 **在高并发的情况下保证节点创建的全局唯一性** (即无法重复创建同样的节点)。
-
-利用这个特性,我们可以 **让多个客户端创建一个指定的节点** ,创建成功的就是 `master`。
-
-但是,如果这个 `master` 挂了怎么办???
-
-你想想为什么我们要创建临时节点?还记得临时节点的生命周期吗?`master` 挂了是不是代表会话断了?会话断了是不是意味着这个节点没了?还记得 `watcher` 吗?我们是不是可以 **让其他不是 `master` 的节点监听节点的状态** ,比如说我们监听这个临时节点的父节点,如果子节点个数变了就代表 `master` 挂了,这个时候我们 **触发回调函数进行重新选举** ,或者我们直接监听节点的状态,我们可以通过节点是否已经失去连接来判断 `master` 是否挂了等等。
-
-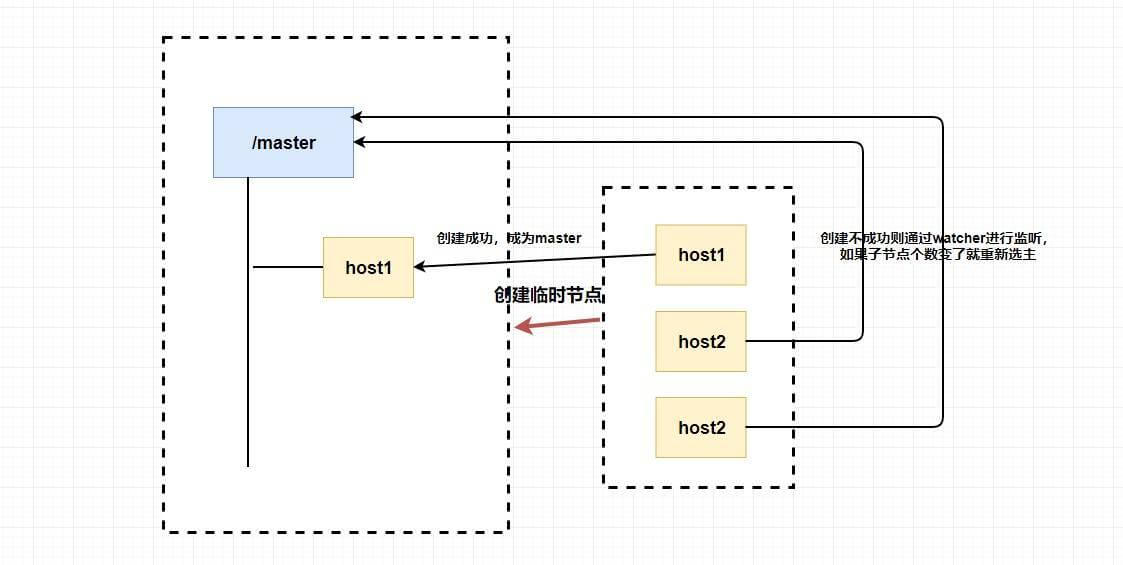
-
-总的来说,我们可以完全 **利用 临时节点、节点状态 和 `watcher` 来实现选主的功能**,临时节点主要用来选举,节点状态和`watcher` 可以用来判断 `master` 的活性和进行重新选举。
-
-### 数据发布/订阅
-
-还记得 Zookeeper 的 `Watcher` 机制吗? Zookeeper 通过这种推拉相结合的方式实现客户端与服务端的交互:客户端向服务端注册节点,一旦相应节点的数据变更,服务端就会向“监听”该节点的客户端发送 `Watcher` 事件通知,客户端接收到通知后需要 **主动** 到服务端获取最新的数据。基于这种方式,Zookeeper 实现了 **数据发布/订阅** 功能。
-
-一个典型的应用场景为 **全局配置信息的集中管理**。 客户端在启动时会主动到 Zookeeper 服务端获取配置信息,同时 **在指定节点注册一个** `Watcher` **监听**。当配置信息发生变更,服务端通知所有订阅的客户端重新获取配置信息,实现配置信息的实时更新。
-
-上面所提到的全局配置信息通常包括机器列表信息、运行时的开关配置、数据库配置信息等。需要注意的是,这类全局配置信息通常具备以下特性:
-
-- 数据量较小
-- 数据内容在运行时动态变化
-- 集群中机器共享一致配置
-
-### 负载均衡
-
-可以通过 Zookeeper 的 **临时节点** 实现负载均衡。回顾一下临时节点的特性:当创建节点的客户端与服务端之间断开连接,即客户端会话(session)消失时,对应节点也会自动消失。因此,我们可以使用临时节点来维护 Server 的地址列表,从而保证请求不会被分配到已停机的服务上。
-
-具体地,我们需要在集群的每一个 Server 中都使用 Zookeeper 客户端连接 Zookeeper 服务端,同时用 Server **自身的地址信息**在服务端指定目录下创建临时节点。当客户端请求调用集群服务时,首先通过 Zookeeper 获取该目录下的节点列表 (即所有可用的 Server),随后根据不同的负载均衡策略将请求转发到某一具体的 Server。
-
-### 分布式锁
-
-分布式锁的实现方式有很多种,比如 `Redis`、数据库、`zookeeper` 等。个人认为 `zookeeper` 在实现分布式锁这方面是非常非常简单的。
-
-上面我们已经提到过了 **zk 在高并发的情况下保证节点创建的全局唯一性**,这玩意一看就知道能干啥了。实现互斥锁呗,又因为能在分布式的情况下,所以能实现分布式锁呗。
-
-如何实现呢?这玩意其实跟选主基本一样,我们也可以利用临时节点的创建来实现。
-
-首先肯定是如何获取锁,因为创建节点的唯一性,我们可以让多个客户端同时创建一个临时节点,**创建成功的就说明获取到了锁** 。然后没有获取到锁的客户端也像上面选主的非主节点创建一个 `watcher` 进行节点状态的监听,如果这个互斥锁被释放了(可能获取锁的客户端宕机了,或者那个客户端主动释放了锁)可以调用回调函数重新获得锁。
-
-> `zk` 中不需要向 `redis` 那样考虑锁得不到释放的问题了,因为当客户端挂了,节点也挂了,锁也释放了。是不是很简单?
-
-那能不能使用 `zookeeper` 同时实现 **共享锁和独占锁** 呢?答案是可以的,不过稍微有点复杂而已。
-
-还记得 **有序的节点** 吗?
-
-这个时候我规定所有创建节点必须有序,当你是读请求(要获取共享锁)的话,如果 **没有比自己更小的节点,或比自己小的节点都是读请求** ,则可以获取到读锁,然后就可以开始读了。**若比自己小的节点中有写请求** ,则当前客户端无法获取到读锁,只能等待前面的写请求完成。
-
-如果你是写请求(获取独占锁),若 **没有比自己更小的节点** ,则表示当前客户端可以直接获取到写锁,对数据进行修改。若发现 **有比自己更小的节点,无论是读操作还是写操作,当前客户端都无法获取到写锁** ,等待所有前面的操作完成。
-
-这就很好地同时实现了共享锁和独占锁,当然还有优化的地方,比如当一个锁得到释放它会通知所有等待的客户端从而造成 **羊群效应** 。此时你可以通过让等待的节点只监听他们前面的节点。
-
-具体怎么做呢?其实也很简单,你可以让 **读请求监听比自己小的最后一个写请求节点,写请求只监听比自己小的最后一个节点** ,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自己去研究一下。
-
-### 命名服务
-
-如何给一个对象设置 ID,大家可能都会想到 `UUID`,但是 `UUID` 最大的问题就在于它太长了。。。(太长不一定是好事,嘿嘿嘿)。那么在条件允许的情况下,我们能不能使用 `zookeeper` 来实现呢?
-
-我们之前提到过 `zookeeper` 是通过 **树形结构** 来存储数据节点的,那也就是说,对于每个节点的 **全路径**,它必定是唯一的,我们可以使用节点的全路径作为命名方式了。而且更重要的是,路径是我们可以自己定义的,这对于我们对有些有语意的对象的 ID 设置可以更加便于理解。
-
-### 集群管理和注册中心
-
-看到这里是不是觉得 `zookeeper` 实在是太强大了,它怎么能这么能干!
-
-别急,它能干的事情还很多呢。可能我们会有这样的需求,我们需要了解整个集群中有多少机器在工作,我们想对集群中的每台机器的运行时状态进行数据采集,对集群中机器进行上下线操作等等。
-
-而 `zookeeper` 天然支持的 `watcher` 和 临时节点能很好的实现这些需求。我们可以为每条机器创建临时节点,并监控其父节点,如果子节点列表有变动(我们可能创建删除了临时节点),那么我们可以使用在其父节点绑定的 `watcher` 进行状态监控和回调。
-
-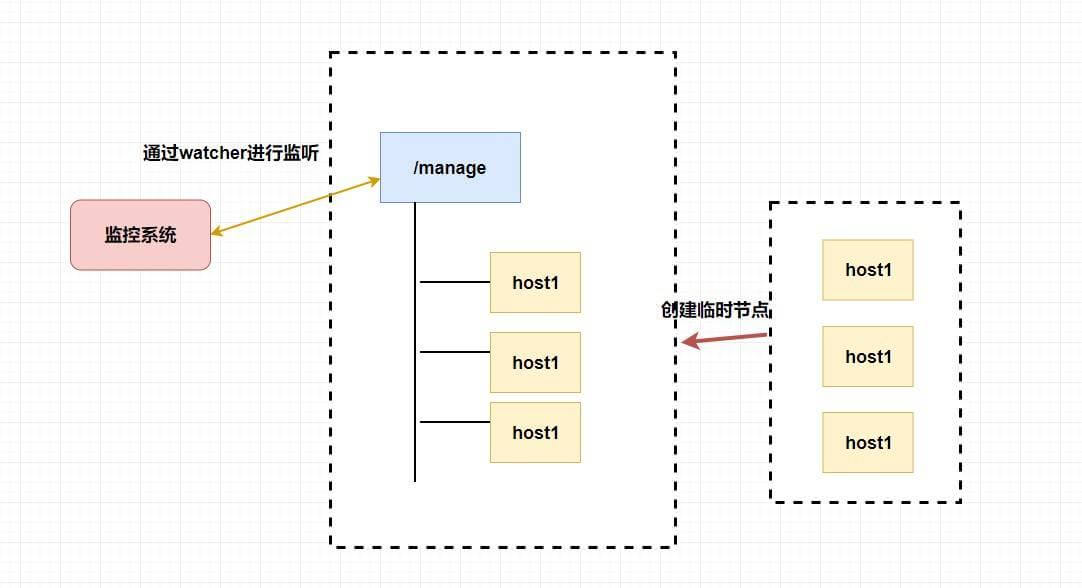
-
-至于注册中心也很简单,我们同样也是让 **服务提供者** 在 `zookeeper` 中创建一个临时节点并且将自己的 `ip、port、调用方式` 写入节点,当 **服务消费者** 需要进行调用的时候会 **通过注册中心找到相应的服务的地址列表(IP 端口什么的)** ,并缓存到本地(方便以后调用),当消费者调用服务时,不会再去请求注册中心,而是直接通过负载均衡算法从地址列表中取一个服务提供者的服务器调用服务。
-
-当服务提供者的某台服务器宕机或下线时,相应的地址会从服务提供者地址列表中移除。同时,注册中心会将新的服务地址列表发送给服务消费者的机器并缓存在消费者本机(当然你可以让消费者进行节点监听,我记得 `Eureka` 会先试错,然后再更新)。
-
-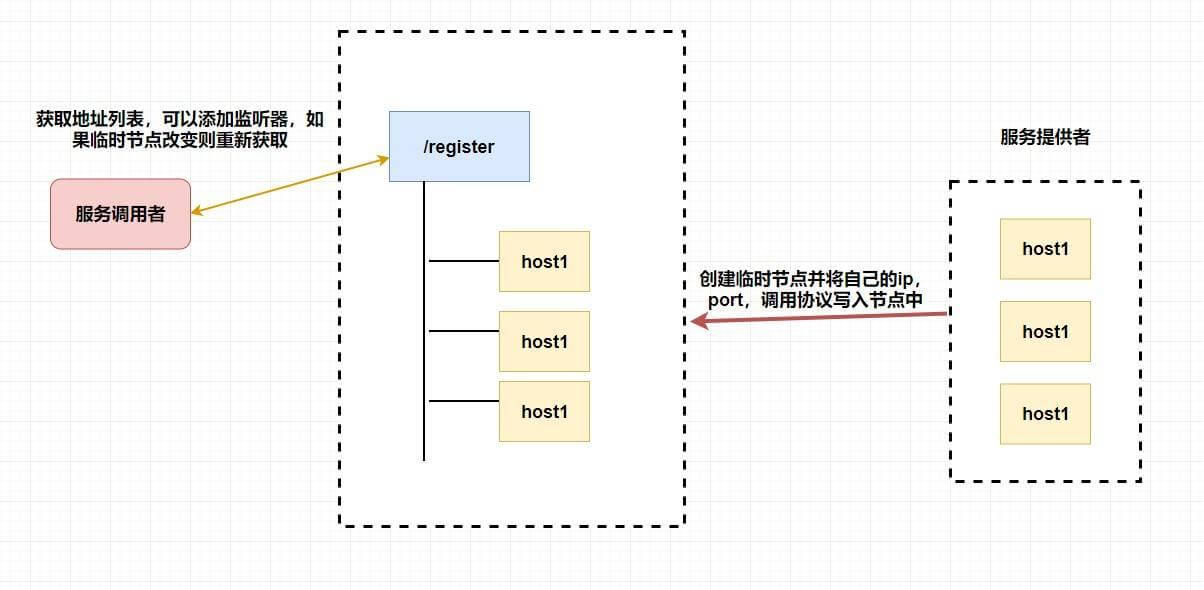
-
-## 总结
-
-看到这里的同学实在是太有耐心了 👍👍👍 不知道大家是否还记得我讲了什么 😒。
-
-
-
-这篇文章中我带大家入门了 `zookeeper` 这个强大的分布式协调框架。现在我们来简单梳理一下整篇文章的内容。
-
-- 分布式与集群的区别
-
-- `2PC`、`3PC` 以及 `paxos` 算法这些一致性框架的原理和实现。
-
-- `zookeeper` 专门的一致性算法 `ZAB` 原子广播协议的内容(`Leader` 选举、崩溃恢复、消息广播)。
-
-- `zookeeper` 中的一些基本概念,比如 `ACL`,数据节点,会话,`watcher`机制等等。
-
-- `zookeeper` 的典型应用场景,比如选主,注册中心等等。
-
- 如果忘了可以回去看看再次理解一下,如果有疑问和建议欢迎提出 🤝🤝🤝。
-
-
+To solve the data consistency problem, many consistency protocols
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
index fa4c83c743c..decdd90f1fe 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
---
-title: 分布式事务常见解决方案总结(付费)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Solutions for Distributed Transactions (Paid)
+category: Distributed
---
-**分布式事务** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了《Java 面试指北》中。
+**Distributed Transactions** interview questions are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to view detailed information and joining methods) and have been organized into the "Java Interview Guide."

diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
index 36a2fa54d4a..eeb5fbb9193 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
@@ -1,161 +1,161 @@
---
-title: CAP & BASE理论详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Explanation of CAP & BASE Theories
+category: Distributed Systems
tag:
- - 分布式理论
+ - Distributed Theory
---
-经历过技术面试的小伙伴想必对 CAP & BASE 这个两个理论已经再熟悉不过了!
+Those who have experienced technical interviews are likely very familiar with the CAP & BASE theories!
-我当年参加面试的时候,不夸张地说,只要问到分布式相关的内容,面试官几乎是必定会问这两个分布式相关的理论。一是因为这两个分布式基础理论是学习分布式知识的必备前置基础,二是因为很多面试官自己比较熟悉这两个理论(方便提问)。
+When I participated in interviews back then, I can say without exaggeration that as soon as distributed-related topics came up, interviewers almost invariably asked about these two distributed theories. This is partly because these two foundational theories are essential prerequisites for learning about distributed systems, and partly because many interviewers themselves are familiar with these theories (making it easier to ask questions).
-我们非常有必要将这两个理论搞懂,并且能够用自己的理解给别人讲出来。
+It is very necessary for us to understand these two theories and be able to explain them to others in our own words.
-## CAP 理论
+## CAP Theory
-[CAP 理论/定理](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86)起源于 2000 年,由加州大学伯克利分校的 Eric Brewer 教授在分布式计算原理研讨会(PODC)上提出,因此 CAP 定理又被称作 **布鲁尔定理(Brewer’s theorem)**
+[CAP Theorem](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86) originated in 2000, proposed by Professor Eric Brewer from the University of California, Berkeley at the Principles of Distributed Computing (PODC) symposium. Therefore, the CAP theorem is also known as **Brewer's theorem**.
-2 年后,麻省理工学院的 Seth Gilbert 和 Nancy Lynch 发表了布鲁尔猜想的证明,CAP 理论正式成为分布式领域的定理。
+Two years later, Seth Gilbert and Nancy Lynch from MIT published a proof of Brewer's conjecture, and the CAP theory officially became a theorem in the distributed field.
-### 简介
+### Introduction
-**CAP** 也就是 **Consistency(一致性)**、**Availability(可用性)**、**Partition Tolerance(分区容错性)** 这三个单词首字母组合。
+**CAP** is a combination of the first letters of **Consistency**, **Availability**, and **Partition Tolerance**.
-CAP 理论的提出者布鲁尔在提出 CAP 猜想的时候,并没有详细定义 **Consistency**、**Availability**、**Partition Tolerance** 三个单词的明确定义。
+When Brewer proposed the CAP conjecture, he did not provide a detailed definition of **Consistency**, **Availability**, and **Partition Tolerance**.
-因此,对于 CAP 的民间解读有很多,一般比较被大家推荐的是下面 👇 这种版本的解读。
+As a result, there are many informal interpretations of CAP, with the most commonly recommended interpretation being the one below 👇.
-在理论计算机科学中,CAP 定理(CAP theorem)指出对于一个分布式系统来说,当设计读写操作时,只能同时满足以下三点中的两个:
+In theoretical computer science, the CAP theorem states that for a distributed system, when designing read and write operations, it can only simultaneously satisfy two of the following three points:
-- **一致性(Consistency)** : 所有节点访问同一份最新的数据副本
-- **可用性(Availability)**: 非故障的节点在合理的时间内返回合理的响应(不是错误或者超时的响应)。
-- **分区容错性(Partition Tolerance)** : 分布式系统出现网络分区的时候,仍然能够对外提供服务。
+- **Consistency**: All nodes access the same up-to-date data copy.
+- **Availability**: Non-faulty nodes return reasonable responses (not errors or timeouts) within a reasonable time.
+- **Partition Tolerance**: The system continues to provide services despite network partitions.
-**什么是网络分区?**
+**What is a network partition?**
-分布式系统中,多个节点之间的网络本来是连通的,但是因为某些故障(比如部分节点网络出了问题)某些节点之间不连通了,整个网络就分成了几块区域,这就叫 **网络分区**。
+In a distributed system, multiple nodes are originally connected, but due to some faults (like issues with part of the node's network), some nodes become unreachable, and the entire network splits into several regions. This is called a **network partition**.
-### 不是所谓的“3 选 2”
+### Not a "choose 2 of 3"
-大部分人解释这一定律时,常常简单的表述为:“一致性、可用性、分区容忍性三者你只能同时达到其中两个,不可能同时达到”。实际上这是一个非常具有误导性质的说法,而且在 CAP 理论诞生 12 年之后,CAP 之父也在 2012 年重写了之前的论文。
+Most people simplistically explain this theorem by saying: "You can only achieve two of consistency, availability, and partition tolerance at the same time, and cannot achieve all three." This is actually a very misleading statement, and twelve years after the CAP theory was born, its father also rewrote his earlier paper in 2012.
-> **当发生网络分区的时候,如果我们要继续服务,那么强一致性和可用性只能 2 选 1。也就是说当网络分区之后 P 是前提,决定了 P 之后才有 C 和 A 的选择。也就是说分区容错性(Partition tolerance)我们是必须要实现的。**
+> **When a network partition occurs, if we are to continue providing services, then strong consistency and availability can only be chosen between 2 out of 1. In other words, when a network partition happens, P is the prerequisite, determining the choice of C or A thereafter. This means partition tolerance (P) is something we must implement.**
>
-> 简而言之就是:CAP 理论中分区容错性 P 是一定要满足的,在此基础上,只能满足可用性 A 或者一致性 C。
+> In short: In the CAP theory, partition tolerance P must be satisfied, and on this basis, we can only satisfy either availability A or consistency C.
-因此,**分布式系统理论上不可能选择 CA 架构,只能选择 CP 或者 AP 架构。** 比如 ZooKeeper、HBase 就是 CP 架构,Cassandra、Eureka 就是 AP 架构,Nacos 不仅支持 CP 架构也支持 AP 架构。
+Therefore, **theoretically, a distributed system cannot choose a CA architecture but can only choose a CP or AP architecture.** For example, ZooKeeper and HBase are CP architectures, while Cassandra and Eureka are AP architectures. Nacos supports both CP and AP architectures.
-**为啥不可能选择 CA 架构呢?** 举个例子:若系统出现“分区”,系统中的某个节点在进行写操作。为了保证 C, 必须要禁止其他节点的读写操作,这就和 A 发生冲突了。如果为了保证 A,其他节点的读写操作正常的话,那就和 C 发生冲突了。
+**Why is it impossible to choose a CA architecture?** For example: If a "partition" occurs in the system and a certain node is performing a write operation. To ensure C, we must prohibit other nodes’ read and write operations, which conflicts with A. Conversely, if we ensure A and allow other nodes to perform read and write operations, that would conflict with C.
-**选择 CP 还是 AP 的关键在于当前的业务场景,没有定论,比如对于需要确保强一致性的场景如银行一般会选择保证 CP 。**
+**The choice between CP and AP depends on the current business scenario, with no conclusive answer. For scenarios requiring strong consistency, such as banking, CP is generally chosen.**
-另外,需要补充说明的一点是:**如果网络分区正常的话(系统在绝大部分时候所处的状态),也就说不需要保证 P 的时候,C 和 A 能够同时保证。**
+Additionally, it should be noted that: **If the network partition is functioning normally (which is the state the system is in most of the time), that is, when P does not need to be ensured, C and A can be guaranteed simultaneously.**
-### CAP 实际应用案例
+### Practical Application of CAP
-我这里以注册中心来探讨一下 CAP 的实际应用。考虑到很多小伙伴不知道注册中心是干嘛的,这里简单以 Dubbo 为例说一说。
+I will explore the practical application of CAP using a registration center. Considering many may not know what a registration center is for, I will briefly explain it using Dubbo as an example.
-下图是 Dubbo 的架构图。**注册中心 Registry 在其中扮演了什么角色呢?提供了什么服务呢?**
+The following diagram is the architecture of Dubbo. **What role does the registration center play? What services does it provide?**
-注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互,注册中心不转发请求,压力较小。
+The registration center is responsible for the registration and discovery of service addresses, analogous to a directory service. Service providers and consumers only interact with the registration center upon starting, and the registration center does not forward requests, resulting in low pressure.
-常见的可以作为注册中心的组件有:ZooKeeper、Eureka、Nacos...。
+Common components that can serve as registration centers include: ZooKeeper, Eureka, Nacos...
-1. **ZooKeeper 保证的是 CP。** 任何时刻对 ZooKeeper 的读请求都能得到一致性的结果,但是, ZooKeeper 不保证每次请求的可用性比如在 Leader 选举过程中或者半数以上的机器不可用的时候服务就是不可用的。
-2. **Eureka 保证的则是 AP。** Eureka 在设计的时候就是优先保证 A (可用性)。在 Eureka 中不存在什么 Leader 节点,每个节点都是一样的、平等的。因此 Eureka 不会像 ZooKeeper 那样出现选举过程中或者半数以上的机器不可用的时候服务就是不可用的情况。 Eureka 保证即使大部分节点挂掉也不会影响正常提供服务,只要有一个节点是可用的就行了。只不过这个节点上的数据可能并不是最新的。
-3. **Nacos 不仅支持 CP 也支持 AP。**
+1. **ZooKeeper guarantees CP.** Any read request to ZooKeeper will provide a consistent result; however, ZooKeeper does not guarantee availability during events like Leader election or when more than half of the machines are unavailable—services would then be unavailable.
+1. **Eureka guarantees AP.** Eureka was designed with priority on A (availability). There is no Leader node in Eureka; each node is the same and equal. Thus, unlike ZooKeeper, Eureka does not face unavailability during election processes or when more than half of the machines are unavailable. Eureka ensures that as long as one node is available, normal services can continue, even if that node's data may not be the latest.
+1. **Nacos supports both CP and AP.**
-**🐛 修正(参见:[issue#1906](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1906))**:
+**🐛 Correction (see: [issue#1906](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1906))**:
-ZooKeeper 通过可线性化(Linearizable)写入、全局 FIFO 顺序访问等机制来保障数据一致性。多节点部署的情况下, ZooKeeper 集群处于 Quorum 模式。Quorum 模式下的 ZooKeeper 集群, 是一组 ZooKeeper 服务器节点组成的集合,其中大多数节点必须同意任何变更才能被视为有效。
+ZooKeeper ensures data consistency through linearizable writes, global FIFO access, and other mechanisms. In a multi-node deployment, the ZooKeeper cluster operates in Quorum mode. In this mode, a group of ZooKeeper server nodes is formed, where the majority must agree to any changes for them to be considered valid.
-由于 Quorum 模式下的读请求不会触发各个 ZooKeeper 节点之间的数据同步,因此在某些情况下还是可能会存在读取到旧数据的情况,导致不同的客户端视图上看到的结果不同,这可能是由于网络延迟、丢包、重传等原因造成的。ZooKeeper 为了解决这个问题,提供了 Watcher 机制和版本号机制来帮助客户端检测数据的变化和版本号的变更,以保证数据的一致性。
+Due to the nature of Quorum mode, read requests do not trigger data synchronization between different ZooKeeper nodes, resulting in situations where outdated data may still be read, leading to inconsistent views on different clients due to reasons like network latency, packet loss, or retransmission. To address this, ZooKeeper provides a Watcher mechanism and versioning to help clients detect changes in data and version changes to ensure data consistency.
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-在进行分布式系统设计和开发时,我们不应该仅仅局限在 CAP 问题上,还要关注系统的扩展性、可用性等等
+In designing and developing distributed systems, we should not be limited to the CAP issue but also focus on aspects such as system scalability and availability.
-在系统发生“分区”的情况下,CAP 理论只能满足 CP 或者 AP。要注意的是,这里的前提是系统发生了“分区”
+In the event of a network "partition", the CAP theorem can only satisfy CP or AP. It is important to note that this assumes a "partition" has occurred.
-如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,节点间的网络连接通信正常的话,也就不存在 P 了。这个时候,我们就可以同时保证 C 和 A 了。
+If there is no "partition" in the system and the network communication among nodes is normal, P no longer exists. At that point, we can simultaneously ensure C and A.
-总结:**如果系统发生“分区”,我们要考虑选择 CP 还是 AP。如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,我们要思考如何保证 CA 。**
+In summary: **If a partition occurs in the system, we must consider whether to choose CP or AP. If there is no partition, we should think about how to ensure CA.**
-### 推荐阅读
+### Recommended Reading
-1. [CAP 定理简化](https://medium.com/@ravindraprasad/cap-theorem-simplified-28499a67eab4) (英文,有趣的案例)
-2. [神一样的 CAP 理论被应用在何方](https://juejin.im/post/6844903936718012430) (中文,列举了很多实际的例子)
-3. [请停止呼叫数据库 CP 或 AP](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2015/05/11/please-stop-calling-databases-cp-or-ap.html) (英文,带给你不一样的思考)
+1. [Simplifying the CAP Theorem](https://medium.com/@ravindraprasad/cap-theorem-simplified-28499a67eab4) (English, with interesting examples)
+1. [Where is the Amazing CAP Theory Applied](https://juejin.im/post/6844903936718012430) (Chinese, listing many practical examples)
+1. [Please Stop Calling Databases CP or AP](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2015/05/11/please-stop-calling-databases-cp-or-ap.html) (English, offering a different perspective)
-## BASE 理论
+## BASE Theory
-[BASE 理论](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1394127.1394128)起源于 2008 年, 由 eBay 的架构师 Dan Pritchett 在 ACM 上发表。
+[BASE Theory](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1394127.1394128) originated in 2008 and was published by eBay architect Dan Pritchett in ACM.
-### 简介
+### Introduction
-**BASE** 是 **Basically Available(基本可用)**、**Soft-state(软状态)** 和 **Eventually Consistent(最终一致性)** 三个短语的缩写。BASE 理论是对 CAP 中一致性 C 和可用性 A 权衡的结果,其来源于对大规模互联网系统分布式实践的总结,是基于 CAP 定理逐步演化而来的,它大大降低了我们对系统的要求。
+**BASE** is an acronym for **Basically Available**, **Soft-state**, and **Eventually Consistent**. The BASE theory is the result of the trade-offs between consistency (C) and availability (A) in CAP, arising from a summary of distributed practices in large-scale Internet systems. It has gradually evolved from the CAP theorem, significantly relaxing our requirements of the system.
-### BASE 理论的核心思想
+### Core Idea of BASE Theory
-即使无法做到强一致性,但每个应用都可以根据自身业务特点,采用适当的方式来使系统达到最终一致性。
+Even if strong consistency cannot be achieved, every application can adopt appropriate methods to achieve eventual consistency according to its business characteristics.
-> 也就是牺牲数据的一致性来满足系统的高可用性,系统中一部分数据不可用或者不一致时,仍需要保持系统整体“主要可用”。
+> This means sacrificing data consistency to ensure high system availability, wherein part of the system's data may be unavailable or inconsistent, yet the system overall still remains "mostly available".
-**BASE 理论本质上是对 CAP 的延伸和补充,更具体地说,是对 CAP 中 AP 方案的一个补充。**
+**The BASE theory is essentially an extension and supplement to CAP, specifically, it supplements the AP solution in CAP.**
-**为什么这样说呢?**
+**Why do I say this?**
-CAP 理论这节我们也说过了:
+As mentioned in the section on the CAP theory:
-> 如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,节点间的网络连接通信正常的话,也就不存在 P 了。这个时候,我们就可以同时保证 C 和 A 了。因此,**如果系统发生“分区”,我们要考虑选择 CP 还是 AP。如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,我们要思考如何保证 CA 。**
+> If the system has not undergone a "partition," and the network connections between nodes are functioning normally, then P does not exist. At that point, we can guarantee both C and A. Thus, **if a partition occurs in the system, we must consider choosing between CP or AP. If there is no "partition," we should think about how to ensure CA.**
-因此,AP 方案只是在系统发生分区的时候放弃一致性,而不是永远放弃一致性。在分区故障恢复后,系统应该达到最终一致性。这一点其实就是 BASE 理论延伸的地方。
+Therefore, the AP solution only sacrifices consistency during system partitions but does not permanently relinquish consistency. After recovering from partition faults, the system should achieve eventual consistency. This is, in fact, the essence of the extension provided by the BASE theory.
-### BASE 理论三要素
+### Three Elements of BASE Theory
-
+
-#### 基本可用
+#### Basically Available
-基本可用是指分布式系统在出现不可预知故障的时候,允许损失部分可用性。但是,这绝不等价于系统不可用。
+Basically available means that when unexpected failures occur in a distributed system, it allows some loss of availability. However, this does not equate to the system being unavailable.
-**什么叫允许损失部分可用性呢?**
+**What does it mean to allow loss of availability?**
-- **响应时间上的损失**: 正常情况下,处理用户请求需要 0.5s 返回结果,但是由于系统出现故障,处理用户请求的时间变为 3 s。
-- **系统功能上的损失**:正常情况下,用户可以使用系统的全部功能,但是由于系统访问量突然剧增,系统的部分非核心功能无法使用。
+- **Loss in response time**: Normally, it takes 0.5s to handle a user request, but due to system failures, the response time extends to 3s.
+- **Loss in system functionality**: Normally, users can access all features of the system, but due to a sudden surge in traffic, some non-core functionalities may become unavailable.
-#### 软状态
+#### Soft State
-软状态指允许系统中的数据存在中间状态(**CAP 理论中的数据不一致**),并认为该中间状态的存在不会影响系统的整体可用性,即允许系统在不同节点的数据副本之间进行数据同步的过程存在延时。
+Soft state refers to allowing data in the system to exist in intermediate states (**data inconsistency as described in the CAP theory**) while recognizing that the existence of this intermediate state will not affect the overall availability of the system. This means allowing delays in the synchronization process of data replicas between different nodes.
-#### 最终一致性
+#### Eventually Consistent
-最终一致性强调的是系统中所有的数据副本,在经过一段时间的同步后,最终能够达到一个一致的状态。因此,最终一致性的本质是需要系统保证最终数据能够达到一致,而不需要实时保证系统数据的强一致性。
+Eventually consistent emphasizes that all data replicas in the system can achieve a consistent state after a period of synchronization. Therefore, the essence of eventual consistency is that the system needs to ensure that the final data can achieve consistency, rather than requiring real-time strong consistency of the data.
-> 分布式一致性的 3 种级别:
+> The three levels of distributed consistency:
>
-> 1. **强一致性**:系统写入了什么,读出来的就是什么。
-> 2. **弱一致性**:不一定可以读取到最新写入的值,也不保证多少时间之后读取到的数据是最新的,只是会尽量保证某个时刻达到数据一致的状态。
-> 3. **最终一致性**:弱一致性的升级版,系统会保证在一定时间内达到数据一致的状态。
+> 1. **Strong consistency**: What is written in the system is exactly what is read.
+> 1. **Weak consistency**: It is not certain that the most recently written value can be read, nor is there a guarantee that the data read after a certain time will be the latest; it only aims to achieve data consistency at a given moment.
+> 1. **Eventual consistency**: This is an upgraded version of weak consistency, wherein the system guarantees that data will achieve consistency within a certain period.
>
-> **业界比较推崇是最终一致性级别,但是某些对数据一致要求十分严格的场景比如银行转账还是要保证强一致性。**
+> **The industry tends to commend the eventual consistency level, but in certain scenarios where data consistency is critically required, such as banking transactions, strong consistency must still be guaranteed.**
-那实现最终一致性的具体方式是什么呢? [《分布式协议与算法实战》](http://gk.link/a/10rZM) 中是这样介绍:
+What are the specific ways to achieve eventual consistency? In [《Distributed Protocols and Algorithms in Practice》](http://gk.link/a/10rZM), it is introduced as follows:
-> - **读时修复** : 在读取数据时,检测数据的不一致,进行修复。比如 Cassandra 的 Read Repair 实现,具体来说,在向 Cassandra 系统查询数据的时候,如果检测到不同节点的副本数据不一致,系统就自动修复数据。
-> - **写时修复** : 在写入数据,检测数据的不一致时,进行修复。比如 Cassandra 的 Hinted Handoff 实现。具体来说,Cassandra 集群的节点之间远程写数据的时候,如果写失败 就将数据缓存下来,然后定时重传,修复数据的不一致性。
-> - **异步修复** : 这个是最常用的方式,通过定时对账检测副本数据的一致性,并修复。
+> - **Read Repair**: During data reads, inconsistencies are detected and repaired. For example, Cassandra's Read Repair implementation automatically fixes data when inconsistencies are found among the replicas during a read query.
+> - **Write Repair**: During data writes, inconsistencies are detected and repaired. For example, Cassandra's Hinted Handoff implementation caches data that fails to write remotely between cluster nodes and retransmits it periodically to fix the inconsistencies.
+> - **Asynchronous Repair**: This is the most commonly used method, conducted through regular reconciliation checks to verify the consistency of replica data and repair it.
-比较推荐 **写时修复**,这种方式对性能消耗比较低。
+**Write Repair** is highly recommended as this method is less demanding on performance.
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-**ACID 是数据库事务完整性的理论,CAP 是分布式系统设计理论,BASE 是 CAP 理论中 AP 方案的延伸。**
+**ACID is a theory of transaction integrity in databases, CAP is a theory of distributed system design, and BASE is an extension of the AP solution in CAP theory.**
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
index 5590401a9b6..c6db7b9630f 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
@@ -1,145 +1,62 @@
---
-title: Gossip 协议详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Gossip Protocol
+category: Distributed
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithms
---
-## 背景
+## Background
-在分布式系统中,不同的节点进行数据/信息共享是一个基本的需求。
+In distributed systems, data/information sharing among different nodes is a fundamental requirement.
-一种比较简单粗暴的方法就是 **集中式发散消息**,简单来说就是一个主节点同时共享最新信息给其他所有节点,比较适合中心化系统。这种方法的缺陷也很明显,节点多的时候不光同步消息的效率低,还太依赖与中心节点,存在单点风险问题。
+A relatively simple and straightforward method is **centralized message dissemination**, which essentially involves a primary node sharing the latest information with all other nodes simultaneously, making it more suitable for centralized systems. The drawbacks of this method are also quite evident; when there are many nodes, not only is the efficiency of message synchronization low, but it also heavily relies on the central node, posing a single point of failure risk.
-于是,**分散式发散消息** 的 **Gossip 协议** 就诞生了。
+Thus, the **Gossip Protocol** for **decentralized message dissemination** was born.
-## Gossip 协议介绍
+## Introduction to the Gossip Protocol
-Gossip 直译过来就是闲话、流言蜚语的意思。流言蜚语有什么特点呢?容易被传播且传播速度还快,你传我我传他,然后大家都知道了。
+Gossip literally translates to idle talk or rumors. What are the characteristics of rumors? They are easily spread and propagate quickly; you tell me, I tell him, and then everyone knows.

-**Gossip 协议** 也叫 Epidemic 协议(流行病协议)或者 Epidemic propagation 算法(疫情传播算法),别名很多。不过,这些名字的特点都具有 **随机传播特性** (联想一下病毒传播、癌细胞扩散等生活中常见的情景),这也正是 Gossip 协议最主要的特点。
+The **Gossip Protocol** is also known as the Epidemic Protocol or Epidemic Propagation Algorithm, and it has many aliases. However, the common feature of these names is the **random propagation characteristic** (think of scenarios like virus transmission or cancer cell spread in everyday life), which is also the main feature of the Gossip Protocol.
-Gossip 协议最早是在 ACM 上的一篇 1987 年发表的论文 [《Epidemic Algorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance》](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/41840.41841)中被提出的。根据论文标题,我们大概就能知道 Gossip 协议当时提出的主要应用是在分布式数据库系统中各个副本节点同步数据。
+The Gossip Protocol was first proposed in a paper published in 1987 in ACM titled [“Epidemic Algorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance”](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/41840.41841). From the title of the paper, we can infer that the main application of the Gossip Protocol at that time was to synchronize data among various replica nodes in distributed database systems.
-正如 Gossip 协议其名一样,这是一种随机且带有传染性的方式将信息传播到整个网络中,并在一定时间内,使得系统内的所有节点数据一致。
+As the name suggests, the Gossip Protocol is a random and contagious way to disseminate information throughout the network, ensuring that all nodes in the system achieve data consistency within a certain time frame.
-在 Gossip 协议下,没有所谓的中心节点,每个节点周期性地随机找一个节点互相同步彼此的信息,理论上来说,各个节点的状态最终会保持一致。
+Under the Gossip Protocol, there is no so-called central node; each node periodically and randomly selects another node to synchronize information with each other. Theoretically, the states of all nodes will eventually remain consistent.
-下面我们来对 Gossip 协议的定义做一个总结:**Gossip 协议是一种允许在分布式系统中共享状态的去中心化通信协议,通过这种通信协议,我们可以将信息传播给网络或集群中的所有成员。**
+To summarize the definition of the Gossip Protocol: **The Gossip Protocol is a decentralized communication protocol that allows state sharing in distributed systems, enabling us to disseminate information to all members in a network or cluster.**
-## Gossip 协议应用
+## Applications of the Gossip Protocol
-NoSQL 数据库 Redis 和 Apache Cassandra、服务网格解决方案 Consul 等知名项目都用到了 Gossip 协议,学习 Gossip 协议有助于我们搞清很多技术的底层原理。
+Notable projects such as the NoSQL databases Redis and Apache Cassandra, as well as service mesh solutions like Consul, utilize the Gossip Protocol. Learning about the Gossip Protocol helps us understand the underlying principles of many technologies.
-我们这里以 Redis Cluster 为例说明 Gossip 协议的实际应用。
+Here, we will illustrate the practical application of the Gossip Protocol using Redis Cluster as an example.
-我们经常使用的分布式缓存 Redis 的官方集群解决方案(3.0 版本引入) Redis Cluster 就是基于 Gossip 协议来实现集群中各个节点数据的最终一致性。
+The official clustering solution for the distributed cache Redis (introduced in version 3.0), Redis Cluster, is based on the Gossip Protocol to achieve eventual consistency of data among various nodes in the cluster.
-
+
-Redis Cluster 是一个典型的分布式系统,分布式系统中的各个节点需要互相通信。既然要相互通信就要遵循一致的通信协议,Redis Cluster 中的各个节点基于 **Gossip 协议** 来进行通信共享信息,每个 Redis 节点都维护了一份集群的状态信息。
+Redis Cluster is a typical distributed system where various nodes need to communicate with each other. Since communication is required, a consistent communication protocol must be followed. The nodes in Redis Cluster communicate and share information based on the **Gossip Protocol**, with each Redis node maintaining a copy of the cluster's state information.
-Redis Cluster 的节点之间会相互发送多种 Gossip 消息:
+Nodes in Redis Cluster send various Gossip messages to each other:
-- **MEET**:在 Redis Cluster 中的某个 Redis 节点上执行 `CLUSTER MEET ip port` 命令,可以向指定的 Redis 节点发送一条 MEET 信息,用于将其添加进 Redis Cluster 成为新的 Redis 节点。
-- **PING/PONG**:Redis Cluster 中的节点都会定时地向其他节点发送 PING 消息,来交换各个节点状态信息,检查各个节点状态,包括在线状态、疑似下线状态 PFAIL 和已下线状态 FAIL。
-- **FAIL**:Redis Cluster 中的节点 A 发现 B 节点 PFAIL ,并且在下线报告的有效期限内集群中半数以上的节点将 B 节点标记为 PFAIL,节点 A 就会向集群广播一条 FAIL 消息,通知其他节点将故障节点 B 标记为 FAIL 。
+- **MEET**: Executing the `CLUSTER MEET ip port` command on a Redis node in Redis Cluster sends a MEET message to a specified Redis node, adding it as a new Redis node in the cluster.
+- **PING/PONG**: Nodes in Redis Cluster periodically send PING messages to other nodes to exchange status information, checking the status of each node, including online status, suspected offline status (PFAIL), and offline status (FAIL).
+- **FAIL**: If node A in Redis Cluster detects that node B is PFAIL, and more than half of the nodes in the cluster mark B as PFAIL within the validity period of the offline report, node A will broadcast a FAIL message to the cluster, notifying other nodes to mark the faulty node B as FAIL.
- ……
-下图就是主从架构的 Redis Cluster 的示意图,图中的虚线代表的就是各个节点之间使用 Gossip 进行通信 ,实线表示主从复制。
+The diagram below illustrates the master-slave architecture of Redis Cluster, where the dashed lines represent communication between nodes using Gossip, and the solid lines indicate master-slave replication.

-有了 Redis Cluster 之后,不需要专门部署 Sentinel 集群服务了。Redis Cluster 相当于是内置了 Sentinel 机制,Redis Cluster 内部的各个 Redis 节点通过 Gossip 协议共享集群内信息。
+With Redis Cluster, there is no need to deploy a separate Sentinel cluster service. Redis Cluster effectively has a built-in Sentinel mechanism, with the various Redis nodes internally sharing cluster information through the Gossip Protocol.
-关于 Redis Cluster 的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章 [Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html) 。
+For a detailed introduction to Redis Cluster, you can refer to this article [Detailed Explanation of Redis Cluster (Paid)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html).
-## Gossip 协议消息传播模式
+## Gossip Protocol Message Propagation Modes
-Gossip 设计了两种可能的消息传播模式:**反熵(Anti-Entropy)** 和 **传谣(Rumor-Mongering)**。
-
-### 反熵(Anti-entropy)
-
-根据维基百科:
-
-> 熵的概念最早起源于[物理学](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/物理学),用于度量一个热力学系统的混乱程度。熵最好理解为不确定性的量度而不是确定性的量度,因为越随机的信源的熵越大。
-
-在这里,你可以把反熵中的熵理解为节点之间数据的混乱程度/差异性,反熵就是指消除不同节点中数据的差异,提升节点间数据的相似度,从而降低熵值。
-
-具体是如何反熵的呢?集群中的节点,每隔段时间就随机选择某个其他节点,然后通过互相交换自己的所有数据来消除两者之间的差异,实现数据的最终一致性。
-
-在实现反熵的时候,主要有推、拉和推拉三种方式:
-
-- 推方式,就是将自己的所有副本数据,推给对方,修复对方副本中的熵。
-- 拉方式,就是拉取对方的所有副本数据,修复自己副本中的熵。
-- 推拉就是同时修复自己副本和对方副本中的熵。
-
-伪代码如下:
-
-
-
-在我们实际应用场景中,一般不会采用随机的节点进行反熵,而是可以设计成一个闭环。这样的话,我们能够在一个确定的时间范围内实现各个节点数据的最终一致性,而不是基于随机的概率。像 InfluxDB 就是这样来实现反熵的。
-
-
-
-1. 节点 A 推送数据给节点 B,节点 B 获取到节点 A 中的最新数据。
-2. 节点 B 推送数据给 C,节点 C 获取到节点 A,B 中的最新数据。
-3. 节点 C 推送数据给 A,节点 A 获取到节点 B,C 中的最新数据。
-4. 节点 A 再推送数据给 B 形成闭环,这样节点 B 就获取到节点 C 中的最新数据。
-
-虽然反熵很简单实用,但是,节点过多或者节点动态变化的话,反熵就不太适用了。这个时候,我们想要实现最终一致性就要靠 **谣言传播(Rumor mongering)** 。
-
-### 谣言传播(Rumor mongering)
-
-谣言传播指的是分布式系统中的一个节点一旦有了新数据之后,就会变为活跃节点,活跃节点会周期性地联系其他节点向其发送新数据,直到所有的节点都存储了该新数据。
-
-如下图所示(下图来自于[INTRODUCTION TO GOSSIP](https://managementfromscratch.wordpress.com/2016/04/01/introduction-to-gossip/) 这篇文章):
-
-
-
-伪代码如下:
-
-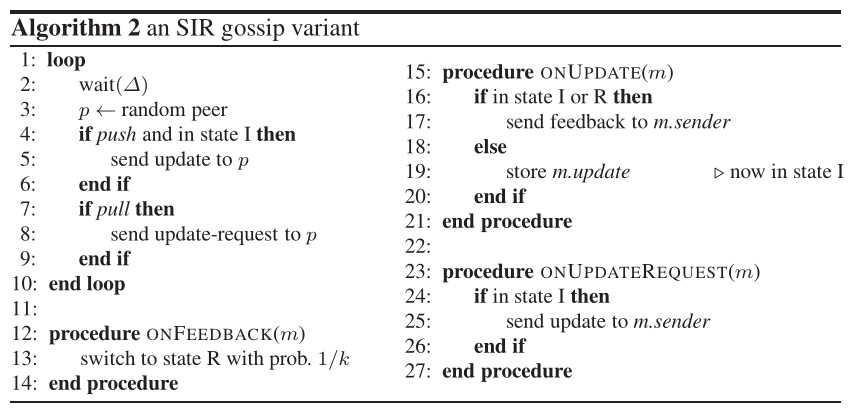
-
-谣言传播比较适合节点数量比较多的情况,不过,这种模式下要尽量避免传播的信息包不能太大,避免网络消耗太大。
-
-### 总结
-
-- 反熵(Anti-Entropy)会传播节点的所有数据,而谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)只会传播节点新增的数据。
-- 我们一般会给反熵设计一个闭环。
-- 谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)比较适合节点数量比较多或者节点动态变化的场景。
-
-## Gossip 协议优势和缺陷
-
-**优势:**
-
-1、相比于其他分布式协议/算法来说,Gossip 协议理解起来非常简单。
-
-2、能够容忍网络上节点的随意地增加或者减少,宕机或者重启,因为 Gossip 协议下这些节点都是平等的,去中心化的。新增加或者重启的节点在理想情况下最终是一定会和其他节点的状态达到一致。
-
-3、速度相对较快。节点数量比较多的情况下,扩散速度比一个主节点向其他节点传播信息要更快(多播)。
-
-**缺陷** :
-
-1、消息需要通过多个传播的轮次才能传播到整个网络中,因此,必然会出现各节点状态不一致的情况。毕竟,Gossip 协议强调的是最终一致,至于达到各个节点的状态一致需要多长时间,谁也无从得知。
-
-2、由于拜占庭将军问题,不允许存在恶意节点。
-
-3、可能会出现消息冗余的问题。由于消息传播的随机性,同一个节点可能会重复收到相同的消息。
-
-## 总结
-
-- Gossip 协议是一种允许在分布式系统中共享状态的通信协议,通过这种通信协议,我们可以将信息传播给网络或集群中的所有成员。
-- Gossip 协议被 Redis、Apache Cassandra、Consul 等项目应用。
-- 谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)比较适合节点数量比较多或者节点动态变化的场景。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 一万字详解 Redis Cluster Gossip 协议:
-- 《分布式协议与算法实战》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-
-
+Gossip has designed two possible message propagation modes: \*\*Anti-Entropy
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
index c820209f4a8..d1e5d437f71 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
@@ -1,83 +1,83 @@
---
-title: Paxos 算法详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Paxos Algorithm
+category: Distributed
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithms
---
-## 背景
+## Background
-Paxos 算法是 Leslie Lamport([莱斯利·兰伯特](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/莱斯利·兰伯特))在 **1990** 年提出了一种分布式系统 **共识** 算法。这也是第一个被证明完备的共识算法(前提是不存在拜占庭将军问题,也就是没有恶意节点)。
+The Paxos algorithm is a consensus algorithm for distributed systems proposed by Leslie Lamport in **1990**. It is also the first consensus algorithm to be proven to be complete (under the assumption that the Byzantine Generals problem does not exist, meaning there are no malicious nodes).
-为了介绍 Paxos 算法,兰伯特专门写了一篇幽默风趣的论文。在这篇论文中,他虚拟了一个叫做 Paxos 的希腊城邦来更形象化地介绍 Paxos 算法。
+To introduce the Paxos algorithm, Lamport wrote a humorous and witty paper. In this paper, he created a fictional Greek city-state called Paxos to more vividly illustrate the Paxos algorithm.
-不过,审稿人并不认可这篇论文的幽默。于是,他们就给兰伯特说:“如果你想要成功发表这篇论文的话,必须删除所有 Paxos 相关的故事背景”。兰伯特一听就不开心了:“我凭什么修改啊,你们这些审稿人就是缺乏幽默细胞,发不了就不发了呗!”。
+However, the reviewers did not appreciate the humor in the paper. They told Lamport, "If you want to successfully publish this paper, you must remove all the background stories related to Paxos." Lamport was not pleased and replied, "Why should I make changes? You reviewers are simply lacking a sense of humor. If you can't publish it, then do not publish it!"
-于是乎,提出 Paxos 算法的那篇论文在当时并没有被成功发表。
+As a result, the paper proposing the Paxos algorithm was not successfully published at that time.
-直到 1998 年,系统研究中心 (Systems Research Center,SRC)的两个技术研究员需要找一些合适的分布式算法来服务他们正在构建的分布式系统,Paxos 算法刚好可以解决他们的部分需求。因此,兰伯特就把论文发给了他们。在看了论文之后,这俩大佬觉得论文还是挺不错的。于是,兰伯特在 **1998** 年重新发表论文 [《The Part-Time Parliament》](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/lamport-paxos.pdf)。
+It wasn't until **1998** that two technical researchers from the Systems Research Center (SRC) needed to find suitable distributed algorithms for the distributed system they were building, and the Paxos algorithm happened to fulfill some of their requirements. Lamport then sent the paper to them. After reviewing the paper, these two researchers found it to be quite impressive. Thus, Lamport republished his paper titled [“The Part-Time Parliament”](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/lamport-paxos.pdf) in **1998**.
-论文发表之后,各路学者直呼看不懂,言语中还略显调侃之意。这谁忍得了,在 **2001** 年的时候,兰伯特专门又写了一篇 [《Paxos Made Simple》](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/paxos-simple.pdf) 的论文来简化对 Paxos 的介绍,主要讲述两阶段共识协议部分,顺便还不忘嘲讽一下这群学者。
+After the paper was published, scholars around the world exclaimed that it was hard to understand, with a hint of mocking tone in their words. Who could stand that? In **2001**, Lamport specifically wrote another paper [“Paxos Made Simple”](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/paxos-simple.pdf) to simplify the introduction of Paxos, mainly discussing the two-phase consensus protocol, while also taking a dig at those scholars.
-《Paxos Made Simple》这篇论文就 14 页,相比于 《The Part-Time Parliament》的 33 页精简了不少。最关键的是这篇论文的摘要就一句话:
+The paper "Paxos Made Simple" is only 14 pages long, considerably shorter than the 33 pages of "The Part-Time Parliament." The key point is that the abstract of this paper is just one sentence:

> The Paxos algorithm, when presented in plain English, is very simple.
-翻译过来的意思大概就是:当我用无修饰的英文来描述时,Paxos 算法真心简单!
+This roughly translates to: "When I describe it in straightforward English, the Paxos algorithm is genuinely simple!"
-有没有感觉到来自兰伯特大佬满满地嘲讽的味道?
+Do you sense the strong flavor of sarcasm from Lamport?
-## 介绍
+## Introduction
-Paxos 算法是第一个被证明完备的分布式系统共识算法。共识算法的作用是让分布式系统中的多个节点之间对某个提案(Proposal)达成一致的看法。提案的含义在分布式系统中十分宽泛,像哪一个节点是 Leader 节点、多个事件发生的顺序等等都可以是一个提案。
+The Paxos algorithm is the first proven comprehensive consensus algorithm for distributed systems. The role of a consensus algorithm is to reach a unanimous opinion among multiple nodes in a distributed system about a certain proposal (Proposal). The meaning of a proposal in a distributed system is quite broad, encompassing which node is the Leader, the order of multiple events, etc.
-兰伯特当时提出的 Paxos 算法主要包含 2 个部分:
+The Paxos algorithm proposed by Lamport actually comprises 2 parts:
-- **Basic Paxos 算法**:描述的是多节点之间如何就某个值(提案 Value)达成共识。
-- **Multi-Paxos 思想**:描述的是执行多个 Basic Paxos 实例,就一系列值达成共识。Multi-Paxos 说白了就是执行多次 Basic Paxos ,核心还是 Basic Paxos 。
+- **Basic Paxos Algorithm**: This describes how multiple nodes can reach a consensus on a certain value (proposed Value).
+- **Multi-Paxos Concept**: This describes executing multiple Basic Paxos instances to achieve consensus on a series of values. Multi-Paxos, simply put, entails executing Basic Paxos multiple times, with the core still being Basic Paxos.
-由于 Paxos 算法在国际上被公认的非常难以理解和实现,因此不断有人尝试简化这一算法。到了 2013 年才诞生了一个比 Paxos 算法更易理解和实现的共识算法—[Raft 算法](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/theorem&algorithm&protocol/raft-algorithm.html) 。更具体点来说,Raft 是 Multi-Paxos 的一个变种,其简化了 Multi-Paxos 的思想,变得更容易被理解以及工程实现。
+Due to the international consensus that the Paxos algorithm is particularly difficult to understand and implement, continuous attempts have been made to simplify this algorithm. It wasn't until 2013 that a consensus algorithm more understandable and implementable than Paxos—the [Raft algorithm](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/theorem&algorithm&protocol/raft-algorithm.html)—was born. More specifically, Raft is a variant of Multi-Paxos that simplifies the ideas behind Multi-Paxos, making it easier to understand and engineer.
-针对没有恶意节点的情况,除了 Raft 算法之外,当前最常用的一些共识算法比如 **ZAB 协议**、 **Fast Paxos** 算法都是基于 Paxos 算法改进的。
+For scenarios without malicious nodes, some commonly used consensus algorithms, like the **ZAB protocol**, **Fast Paxos**, are all improvements based on the Paxos algorithm.
-针对存在恶意节点的情况,一般使用的是 **工作量证明(POW,Proof-of-Work)**、 **权益证明(PoS,Proof-of-Stake )** 等共识算法。这类共识算法最典型的应用就是区块链,就比如说前段时间以太坊官方宣布其共识机制正在从工作量证明(PoW)转变为权益证明(PoS)。
+In cases with malicious nodes, consensus algorithms like **Proof-of-Work (PoW)** and **Proof-of-Stake (PoS)** are generally used. A typical application of such consensus algorithms is in blockchain technology. For example, recently, Ethereum's official announcement indicated that its consensus mechanism is transitioning from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
-区块链系统使用的共识算法需要解决的核心问题是 **拜占庭将军问题** ,这和我们日常接触到的 ZooKeeper、Etcd、Consul 等分布式中间件不太一样。
+The core problem that consensus algorithms used in blockchain systems need to solve is the **Byzantine Generals problem**, which is quite different from the distributed middleware we encounter in daily life, such as ZooKeeper, Etcd, and Consul.
-下面我们来对 Paxos 算法的定义做一个总结:
+Now, let's summarize the definition of the Paxos algorithm:
-- Paxos 算法是兰伯特在 **1990** 年提出了一种分布式系统共识算法。
-- 兰伯特当时提出的 Paxos 算法主要包含 2 个部分: Basic Paxos 算法和 Multi-Paxos 思想。
-- Raft 算法、ZAB 协议、 Fast Paxos 算法都是基于 Paxos 算法改进而来。
+- The Paxos algorithm is a consensus algorithm for distributed systems proposed by Lamport in **1990**.
+- The Paxos algorithm proposed by Lamport primarily consists of 2 parts: the Basic Paxos algorithm and the Multi-Paxos concept.
+- The Raft algorithm, ZAB protocol, and Fast Paxos algorithm are all derived from improvements over the Paxos algorithm.
-## Basic Paxos 算法
+## Basic Paxos Algorithm
-Basic Paxos 中存在 3 个重要的角色:
+The Basic Paxos algorithm involves 3 important roles:
-1. **提议者(Proposer)**:也可以叫做协调者(coordinator),提议者负责接受客户端的请求并发起提案。提案信息通常包括提案编号 (Proposal ID) 和提议的值 (Value)。
-2. **接受者(Acceptor)**:也可以叫做投票员(voter),负责对提议者的提案进行投票,同时需要记住自己的投票历史;
-3. **学习者(Learner)**:如果有超过半数接受者就某个提议达成了共识,那么学习者就需要接受这个提议,并就该提议作出运算,然后将运算结果返回给客户端。
+1. **Proposer**: Also known as the Coordinator, the proposer is responsible for accepting client requests and initiating proposals. Proposal information typically includes a proposal number (Proposal ID) and the proposed value (Value).
+1. **Acceptor**: Also referred to as a voter, the acceptor is responsible for voting on proposals from the proposer and must remember its voting history.
+1. **Learner**: If more than half of the acceptors reach a consensus on a certain proposal, the learner must accept that proposal, perform computations based on it, and then return the computation results to the client.
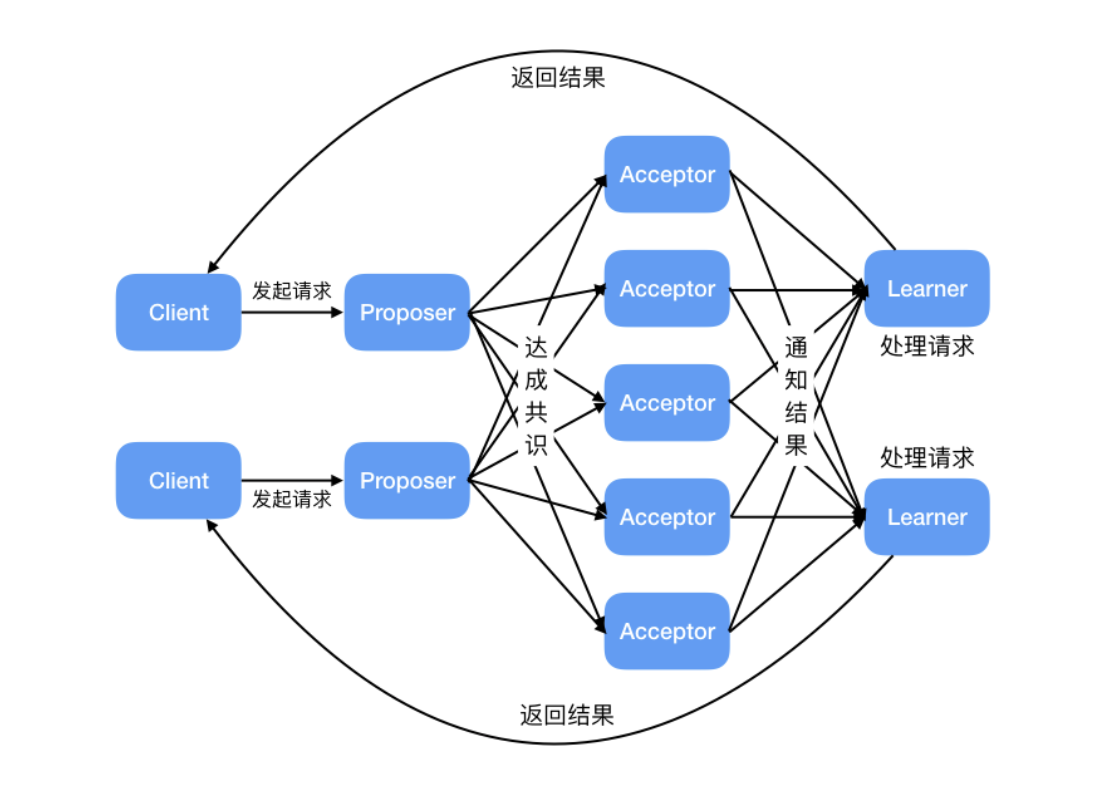
-为了减少实现该算法所需的节点数,一个节点可以身兼多个角色。并且,一个提案被选定需要被半数以上的 Acceptor 接受。这样的话,Basic Paxos 算法还具备容错性,在少于一半的节点出现故障时,集群仍能正常工作。
+To reduce the number of nodes required to implement this algorithm, a single node can take on multiple roles. Additionally, a proposal must be accepted by more than half of the acceptors to be chosen. This way, the Basic Paxos algorithm also possesses fault tolerance, allowing the cluster to operate normally even when less than half of the nodes fail.
-## Multi Paxos 思想
+## Multi-Paxos Concept
-Basic Paxos 算法的仅能就单个值达成共识,为了能够对一系列的值达成共识,我们需要用到 Multi Paxos 思想。
+The Basic Paxos algorithm can only reach consensus on a single value. To achieve consensus on a series of values, we need to employ the Multi-Paxos concept.
-⚠️**注意**:Multi-Paxos 只是一种思想,这种思想的核心就是通过多个 Basic Paxos 实例就一系列值达成共识。也就是说,Basic Paxos 是 Multi-Paxos 思想的核心,Multi-Paxos 就是多执行几次 Basic Paxos。
+⚠️**Note**: Multi-Paxos is merely a concept; the core of this concept is to reach consensus on a series of values through multiple Basic Paxos instances. In other words, Basic Paxos is at the heart of the Multi-Paxos concept, while Multi-Paxos simply entails executing Basic Paxos several times.
-由于兰伯特提到的 Multi-Paxos 思想缺少代码实现的必要细节(比如怎么选举领导者),所以在理解和实现上比较困难。
+Since the Multi-Paxos concept mentioned by Lamport lacks the essential details for code implementation (such as how to elect a leader), it can be somewhat challenging to understand and implement.
-不过,也不需要担心,我们并不需要自己实现基于 Multi-Paxos 思想的共识算法,业界已经有了比较出名的实现。像 Raft 算法就是 Multi-Paxos 的一个变种,其简化了 Multi-Paxos 的思想,变得更容易被理解以及工程实现,实际项目中可以优先考虑 Raft 算法。
+However, there's no need to worry; we do not need to implement a consensus algorithm based on the Multi-Paxos concept ourselves. The industry has already produced some notable implementations. For instance, the Raft algorithm is a variant of Multi-Paxos that simplifies its ideas, making it easier to understand and implement. In actual projects, Raft should be prioritized.
-## 参考
+## References
-
-- 分布式系统中的一致性与共识算法:
+- Consistency and Consensus Algorithms in Distributed Systems:
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
index 18d2c2eb0cb..aad8a9af1cf 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
@@ -1,167 +1,166 @@
---
-title: Raft 算法详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Raft Algorithm
+category: Distributed Systems
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithm
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [Xieqijun](https://github.com/jun0315) 共同完成。
+> This article is jointly completed by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [Xieqijun](https://github.com/jun0315).
-## 1 背景
+## 1 Background
-当今的数据中心和应用程序在高度动态的环境中运行,为了应对高度动态的环境,它们通过额外的服务器进行横向扩展,并且根据需求进行扩展和收缩。同时,服务器和网络故障也很常见。
+Today’s data centers and applications operate in highly dynamic environments. To cope with such environments, they horizontally scale with additional servers and adjust resources based on demand. At the same time, server and network failures are quite common.
-因此,系统必须在正常操作期间处理服务器的上下线。它们必须对变故做出反应并在几秒钟内自动适应;对客户来说的话,明显的中断通常是不可接受的。
+Therefore, systems must handle server ups and downs during normal operations. They must react to incidents and adapt automatically within seconds; significant interruptions are usually unacceptable for customers.
-幸运的是,分布式共识可以帮助应对这些挑战。
+Fortunately, distributed consensus can help address these challenges.
-### 1.1 拜占庭将军
+### 1.1 Byzantine Generals
-在介绍共识算法之前,先介绍一个简化版拜占庭将军的例子来帮助理解共识算法。
+Before introducing consensus algorithms, let's first present a simplified example of Byzantine generals to help understand the consensus algorithm.
-> 假设多位拜占庭将军中没有叛军,信使的信息可靠但有可能被暗杀的情况下,将军们如何达成是否要进攻的一致性决定?
+> Suppose there are multiple Byzantine generals with no traitors, and the messenger's information is reliable but may get assassinated. How can the generals reach a consensus on whether to attack?
-解决方案大致可以理解成:先在所有的将军中选出一个大将军,用来做出所有的决定。
+The solution can be roughly understood as: first, select a general to be the Grand General among all the generals, who will make all the decisions.
-举例如下:假如现在一共有 3 个将军 A,B 和 C,每个将军都有一个随机时间的倒计时器,倒计时一结束,这个将军就把自己当成大将军候选人,然后派信使传递选举投票的信息给将军 B 和 C,如果将军 B 和 C 还没有把自己当作候选人(自己的倒计时还没有结束),并且没有把选举票投给其他人,它们就会把票投给将军 A,信使回到将军 A 时,将军 A 知道自己收到了足够的票数,成为大将军。在有了大将军之后,是否需要进攻就由大将军 A 决定,然后再去派信使通知另外两个将军,自己已经成为了大将军。如果一段时间还没收到将军 B 和 C 的回复(信使可能会被暗杀),那就再重派一个信使,直到收到回复。
+For example, suppose there are 3 generals A, B, and C. Each general has a countdown timer that runs for a random time. Once the timer reaches zero, that general declares themselves a candidate for Grand General and sends messages to generals B and C with details of the election vote. If generals B and C have not declared themselves candidates (their countdowners have not expired) and have not voted for anyone else, they will vote for general A. When messenger returns to general A, they will know they have received enough votes to become the Grand General. With the Grand General in place, whether to attack will be determined by Grand General A, who will then inform the other two generals about it. If there is still no response from generals B and C after a period of time (the messenger may have been assassinated), a new messenger will be dispatched until a response is received.
-### 1.2 共识算法
+### 1.2 Consensus Algorithm
-共识是可容错系统中的一个基本问题:即使面对故障,服务器也可以在共享状态上达成一致。
+Consensus is a fundamental problem in fault-tolerant systems: even in the presence of failures, servers must agree on a shared state.
-共识算法允许一组节点像一个整体一样一起工作,即使其中的一些节点出现故障也能够继续工作下去,其正确性主要是源于复制状态机的性质:一组`Server`的状态机计算相同状态的副本,即使有一部分的`Server`宕机了它们仍然能够继续运行。
+Consensus algorithms allow a group of nodes to work together as a whole, ensuring that the system can continue to function even if some nodes fail. Its correctness primarily stems from the properties of replicated state machines: a set of `Servers` computes replicas of the same state machine, which can continue to operate even if part of the `Servers` goes down.
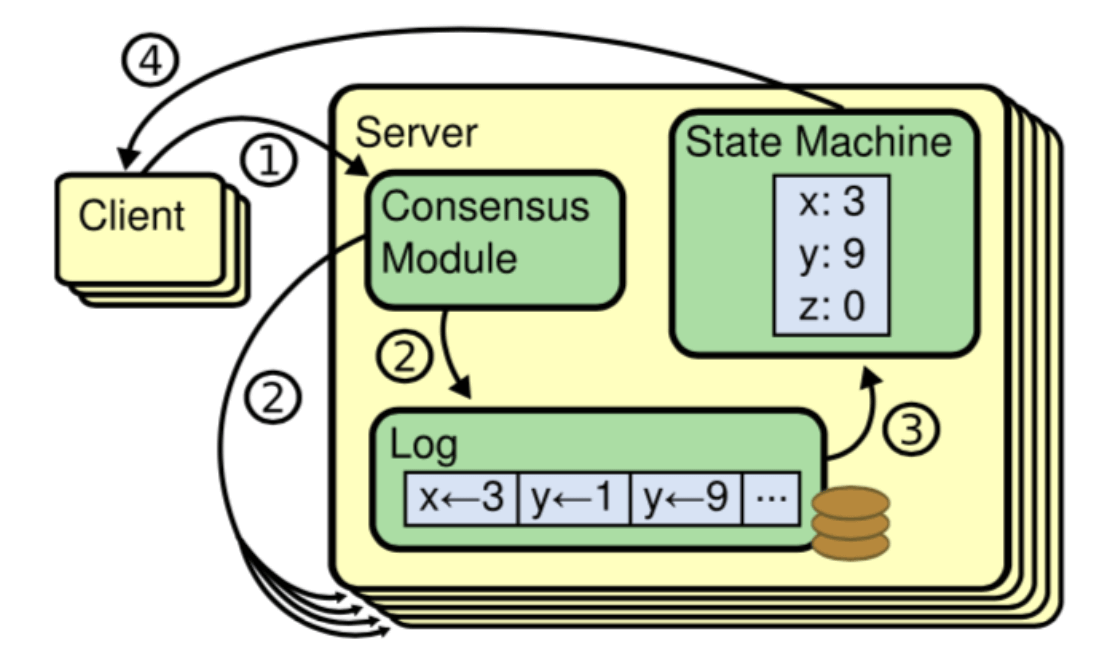
-`图-1 复制状态机架构`
+`Figure 1: Replicated State Machine Architecture`
-一般通过使用复制日志来实现复制状态机。每个`Server`存储着一份包括命令序列的日志文件,状态机会按顺序执行这些命令。因为每个日志包含相同的命令,并且顺序也相同,所以每个状态机处理相同的命令序列。由于状态机是确定性的,所以处理相同的状态,得到相同的输出。
+Typically, replicated state machines are implemented using replicated logs. Each `Server` stores a log file that includes a sequence of commands; state machines execute these commands in order. Since each log contains the same commands executed in the same order, every state machine processes the same command sequence. As the state machine is deterministic, it produces the same output when processing the same state.
-因此共识算法的工作就是保持复制日志的一致性。服务器上的共识模块从客户端接收命令并将它们添加到日志中。它与其他服务器上的共识模块通信,以确保即使某些服务器发生故障。每个日志最终包含相同顺序的请求。一旦命令被正确地复制,它们就被称为已提交。每个服务器的状态机按照日志顺序处理已提交的命令,并将输出返回给客户端,因此,这些服务器形成了一个单一的、高度可靠的状态机。
+Thus, the job of the consensus algorithm is to maintain the consistency of the replicated logs. The consensus module on each server receives commands from clients and adds them to the log. It communicates with the consensus modules on other servers to ensure that all logs contain requests in the same order, even if some servers fail. Once commands are correctly replicated, they are said to be committed. The state machine of each server processes committed commands in log order and returns the output to the client; hence, these servers form a single, highly reliable state machine.
-适用于实际系统的共识算法通常具有以下特性:
+Consensus algorithms suitable for real systems typically have the following characteristics:
-- 安全。确保在非拜占庭条件(也就是上文中提到的简易版拜占庭)下的安全性,包括网络延迟、分区、包丢失、复制和重新排序。
-- 高可用。只要大多数服务器都是可操作的,并且可以相互通信,也可以与客户端进行通信,那么这些服务器就可以看作完全功能可用的。因此,一个典型的由五台服务器组成的集群可以容忍任何两台服务器端故障。假设服务器因停止而发生故障;它们稍后可能会从稳定存储上的状态中恢复并重新加入集群。
-- 一致性不依赖时序。错误的时钟和极端的消息延迟,在最坏的情况下也只会造成可用性问题,而不会产生一致性问题。
+- Safety. Ensures safety under non-Byzantine conditions (i.e., the simplified version of Byzantine mentioned above), including network delays, partitions, packet losses, and message reordering.
+- High availability. As long as a majority of servers are operational and can communicate with each other and with clients, these servers can be considered fully functional. Thus, a typical cluster of five servers can tolerate the failure of any two servers. If servers fail due to stoppage, they can later recover from stable storage and rejoin the cluster.
+- Consistency does not depend on timing. Erroneous clocks and extreme message delays will only cause availability issues in the worst case and will not result in consistency problems.
+- As long as the majority of servers respond in the cluster, commands can be completed without being affected by a few slow servers.
-- 在集群中大多数服务器响应,命令就可以完成,不会被少数运行缓慢的服务器来影响整体系统性能。
+## 2 Basics
-## 2 基础
+### 2.1 Node Types
-### 2.1 节点类型
+A Raft cluster consists of several servers. Taking a typical cluster of 5 servers as an example, at any given time, each server will be in one of the following three states:
-一个 Raft 集群包括若干服务器,以典型的 5 服务器集群举例。在任意的时间,每个服务器一定会处于以下三个状态中的一个:
+- `Leader`: Responsible for initiating heartbeats, responding to clients, creating logs, and synchronizing logs.
+- `Candidate`: A temporary role during the leader election process, transformed from Follower, initiating votes to participate in the election.
+- `Follower`: Accepts heartbeats and log synchronization data from the Leader, voting for the Candidate.
-- `Leader`:负责发起心跳,响应客户端,创建日志,同步日志。
-- `Candidate`:Leader 选举过程中的临时角色,由 Follower 转化而来,发起投票参与竞选。
-- `Follower`:接受 Leader 的心跳和日志同步数据,投票给 Candidate。
-
-在正常的情况下,只有一个服务器是 Leader,剩下的服务器是 Follower。Follower 是被动的,它们不会发送任何请求,只是响应来自 Leader 和 Candidate 的请求。
+Under normal conditions, only one server is the Leader, while the remaining servers are Followers. Followers are passive; they do not send requests but only respond to requests from the Leader and Candidates.
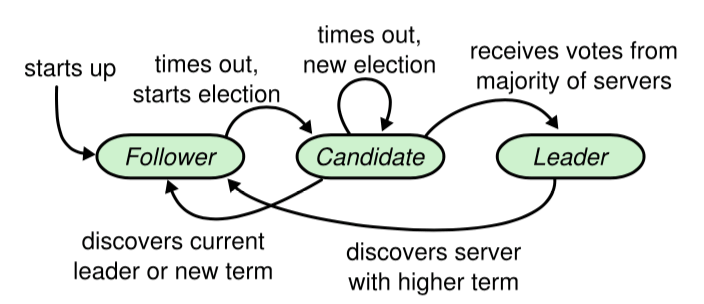
-`图-2:服务器的状态`
+`Figure 2: Server States`
-### 2.2 任期
+### 2.2 Terms
-`图-3:任期`
+`Figure 3: Terms`
-如图 3 所示,raft 算法将时间划分为任意长度的任期(term),任期用连续的数字表示,看作当前 term 号。每一个任期的开始都是一次选举,在选举开始时,一个或多个 Candidate 会尝试成为 Leader。如果一个 Candidate 赢得了选举,它就会在该任期内担任 Leader。如果没有选出 Leader,将会开启另一个任期,并立刻开始下一次选举。raft 算法保证在给定的一个任期最少要有一个 Leader。
+As shown in Figure 3, the Raft algorithm divides time into terms of arbitrary length, represented by consecutive numbers considered the current term number. The beginning of each term is an election; at the start of an election, one or more Candidates will attempt to become the Leader. If a Candidate wins the election, they will serve as the Leader for that term. If no Leader is elected, a new term will be initiated, and the next election will begin immediately. The Raft algorithm guarantees that there is at least one Leader in a given term.
-每个节点都会存储当前的 term 号,当服务器之间进行通信时会交换当前的 term 号;如果有服务器发现自己的 term 号比其他人小,那么他会更新到较大的 term 值。如果一个 Candidate 或者 Leader 发现自己的 term 过期了,他会立即退回成 Follower。如果一台服务器收到的请求的 term 号是过期的,那么它会拒绝此次请求。
+Each node stores the current term number, and during communication between servers, they exchange their current term numbers. If a server finds its term number is smaller than others, it will update to the larger term value. If a Candidate or Leader finds its term has expired, it will revert to Follower immediately. If a server receives a request with an expired term number, it will reject the request.
-### 2.3 日志
+### 2.3 Logs
-- `entry`:每一个事件成为 entry,只有 Leader 可以创建 entry。entry 的内容为``其中 cmd 是可以应用到状态机的操作。
-- `log`:由 entry 构成的数组,每一个 entry 都有一个表明自己在 log 中的 index。只有 Leader 才可以改变其他节点的 log。entry 总是先被 Leader 添加到自己的 log 数组中,然后再发起共识请求,获得同意后才会被 Leader 提交给状态机。Follower 只能从 Leader 获取新日志和当前的 commitIndex,然后把对应的 entry 应用到自己的状态机中。
+- `entry`: Each event becomes an entry, and only the Leader can create entries. The content of an entry is `` where cmd is an operation that can be applied to the state machine.
+- `log`: An array composed of entries, where each entry has an index indicating its position in the log. Only the Leader can change the logs of other nodes. Entries are always first added to the Leader's log array, and only after initiating a consensus request and obtaining agreement can they be committed to the state machine. Followers can only obtain new logs and the current commitIndex from the Leader and then apply the corresponding entries to their state machines.
-## 3 领导人选举
+## 3 Leader Election
-raft 使用心跳机制来触发 Leader 的选举。
+Raft uses a heartbeat mechanism to trigger Leader elections.
-如果一台服务器能够收到来自 Leader 或者 Candidate 的有效信息,那么它会一直保持为 Follower 状态,并且刷新自己的 electionElapsed,重新计时。
+If a server receives valid information from a Leader or Candidate, it will remain in the Follower state and refresh its electionElapsed timer.
-Leader 会向所有的 Follower 周期性发送心跳来保证自己的 Leader 地位。如果一个 Follower 在一个周期内没有收到心跳信息,就叫做选举超时,然后它就会认为此时没有可用的 Leader,并且开始进行一次选举以选出一个新的 Leader。
+The Leader periodically sends heartbeats to all Followers to ensure its leadership status. If a Follower does not receive heartbeat information within a cycle, it triggers an election timeout and assumes there is currently no available Leader, initiating an election to elect a new Leader.
-为了开始新的选举,Follower 会自增自己的 term 号并且转换状态为 Candidate。然后他会向所有节点发起 RequestVoteRPC 请求, Candidate 的状态会持续到以下情况发生:
+To start a new election, the Follower increments its term number and changes its state to Candidate. It will then send a RequestVoteRPC to all nodes, and the Candidate's state will persist until one of the following occurs:
-- 赢得选举
-- 其他节点赢得选举
-- 一轮选举结束,无人胜出
+- Wins the election
+- Other nodes win the election
+- One round of the election ends with no winner
-赢得选举的条件是:一个 Candidate 在一个任期内收到了来自集群内的多数选票`(N/2+1)`,就可以成为 Leader。
+The condition for winning the election is: a Candidate must receive votes from a majority of the cluster `(N/2+1)` in one term to become the Leader.
-在 Candidate 等待选票的时候,它可能收到其他节点声明自己是 Leader 的心跳,此时有两种情况:
+While waiting for votes, a Candidate may receive heartbeat messages from other nodes claiming to be the Leader, resulting in two situations:
-- 该 Leader 的 term 号大于等于自己的 term 号,说明对方已经成为 Leader,则自己回退为 Follower。
-- 该 Leader 的 term 号小于自己的 term 号,那么会拒绝该请求并让该节点更新 term。
+- The term number of that Leader is greater than or equal to its own; indicating that the other has become the Leader, it will revert to Follower.
+- The term number of that Leader is less than its own. In this case, the request is rejected, prompting that node to update its term.
-由于可能同一时刻出现多个 Candidate,导致没有 Candidate 获得大多数选票,如果没有其他手段来重新分配选票的话,那么可能会无限重复下去。
+As multiple Candidates may appear simultaneously without any means to redistribute votes, it could lead to an infinite loop of elections.
-raft 使用了随机的选举超时时间来避免上述情况。每一个 Candidate 在发起选举后,都会随机化一个新的选举超时时间,这种机制使得各个服务器能够分散开来,在大多数情况下只有一个服务器会率先超时;它会在其他服务器超时之前赢得选举。
+Raft uses a random election timeout to avoid the above situation. Each Candidate randomizes a new election timeout after initiating an election, allowing servers to spread apart; in most cases, only one server will timeout first, winning the election before others do.
-## 4 日志复制
+## 4 Log Replication
-一旦选出了 Leader,它就开始接受客户端的请求。每一个客户端的请求都包含一条需要被复制状态机(`Replicated State Machine`)执行的命令。
+Once a Leader is elected, it starts receiving client requests. Each client's request includes a command that needs to be executed by the replicated state machine (`Replicated State Machine`).
-Leader 收到客户端请求后,会生成一个 entry,包含``,再将这个 entry 添加到自己的日志末尾后,向所有的节点广播该 entry,要求其他服务器复制这条 entry。
+After the Leader receives the client request, it generates an entry containing ``, adds this entry to its log's end, and broadcasts it to all nodes, asking the other servers to replicate the entry.
-如果 Follower 接受该 entry,则会将 entry 添加到自己的日志后面,同时返回给 Leader 同意。
+If a Follower accepts the entry, it will append the entry to its log and return a consent response to the Leader.
-如果 Leader 收到了多数的成功响应,Leader 会将这个 entry 应用到自己的状态机中,之后可以称这个 entry 是 committed 的,并且向客户端返回执行结果。
+If the Leader receives a majority of successful responses, it will apply this entry to its state machine, and this entry can then be termed as committed, eventually returning the execution result to the client.
-raft 保证以下两个性质:
+Raft guarantees the following two properties:
-- 在两个日志里,有两个 entry 拥有相同的 index 和 term,那么它们一定有相同的 cmd
-- 在两个日志里,有两个 entry 拥有相同的 index 和 term,那么它们前面的 entry 也一定相同
+- Among two logs, if two entries have the same index and term, their cmds must also be the same.
+- Among two logs, if two entries have the same index and term, their preceding entries must also be the same.
-通过“仅有 Leader 可以生成 entry”来保证第一个性质,第二个性质需要一致性检查来进行保证。
+The first property is guaranteed by "only the Leader can generate entries," while the second property requires consistency checks to ensure.
-一般情况下,Leader 和 Follower 的日志保持一致,然后,Leader 的崩溃会导致日志不一样,这样一致性检查会产生失败。Leader 通过强制 Follower 复制自己的日志来处理日志的不一致。这就意味着,在 Follower 上的冲突日志会被领导者的日志覆盖。
+Generally, the logs of Leaders and Followers remain consistent; however, a Leader's crash may result in inconsistent logs, causing consistency checks to fail. The Leader handles log inconsistency by forcing Followers to replicate its logs, meaning any conflicting logs on Followers will be overwritten by the Leader's logs.
-为了使得 Follower 的日志和自己的日志一致,Leader 需要找到 Follower 与它日志一致的地方,然后删除 Follower 在该位置之后的日志,接着把这之后的日志发送给 Follower。
+To ensure Followers' logs align with its own, the Leader must find the point of consistency in the Follower's log and delete any log entries after that point, then send the missing logs from that position onward to the Follower.
-`Leader` 给每一个`Follower` 维护了一个 `nextIndex`,它表示 `Leader` 将要发送给该追随者的下一条日志条目的索引。当一个 `Leader` 开始掌权时,它会将 `nextIndex` 初始化为它的最新的日志条目索引数+1。如果一个 `Follower` 的日志和 `Leader` 的不一致,`AppendEntries` 一致性检查会在下一次 `AppendEntries RPC` 时返回失败。在失败之后,`Leader` 会将 `nextIndex` 递减然后重试 `AppendEntries RPC`。最终 `nextIndex` 会达到一个 `Leader` 和 `Follower` 日志一致的地方。这时,`AppendEntries` 会返回成功,`Follower` 中冲突的日志条目都被移除了,并且添加所缺少的上了 `Leader` 的日志条目。一旦 `AppendEntries` 返回成功,`Follower` 和 `Leader` 的日志就一致了,这样的状态会保持到该任期结束。
+The `Leader` maintains a `nextIndex` for each `Follower`, representing the index of the next log entry that the `Leader` will send to that Follower. When a `Leader` begins authority, it initializes `nextIndex` to the number of its latest log entry index + 1. If a `Follower`'s log is inconsistent with the `Leader`'s, the consistency check in `AppendEntries` will return a failure in the next `AppendEntries RPC`. After a failure, the `Leader` decrements `nextIndex` and retries `AppendEntries RPC`. Eventually, `nextIndex` reaches a point of consistency between the `Leader` and `Follower` logs. At that point, `AppendEntries` succeeds, and any conflicting log entries on the `Follower` are removed, with the missing log entries appended from the `Leader`. Once `AppendEntries` succeeds, the logs of `Follower` and `Leader` are consistent, maintaining this state until the end of the term.
-## 5 安全性
+## 5 Safety
-### 5.1 选举限制
+### 5.1 Election Constraints
-Leader 需要保证自己存储全部已经提交的日志条目。这样才可以使日志条目只有一个流向:从 Leader 流向 Follower,Leader 永远不会覆盖已经存在的日志条目。
+The Leader must ensure it stores all committed log entries. This assures that log entries have only one direction: from Leader to Follower; the Leader will never overwrite already existing log entries.
-每个 Candidate 发送 RequestVoteRPC 时,都会带上最后一个 entry 的信息。所有节点收到投票信息时,会对该 entry 进行比较,如果发现自己的更新,则拒绝投票给该 Candidate。
+Every Candidate sends a RequestVoteRPC with information on the last entry. When all nodes receive the voting information, they compare this entry against their own updates; if they find their logs more up-to-date, they refuse to vote for that Candidate.
-判断日志新旧的方式:如果两个日志的 term 不同,term 大的更新;如果 term 相同,更长的 index 更新。
+The way to determine the recency of logs: if the terms of the two logs differ, the log with the larger term updates; if the terms are the same, the longer index updates.
-### 5.2 节点崩溃
+### 5.2 Node Crashes
-如果 Leader 崩溃,集群中的节点在 electionTimeout 时间内没有收到 Leader 的心跳信息就会触发新一轮的选主,在选主期间整个集群对外是不可用的。
+If the Leader crashes, nodes in the cluster that do not receive heartbeat information from the Leader within the electionTimeout period will trigger a new round of leader election, during which the entire cluster becomes unavailable to outside requests.
-如果 Follower 和 Candidate 崩溃,处理方式会简单很多。之后发送给它的 RequestVoteRPC 和 AppendEntriesRPC 会失败。由于 raft 的所有请求都是幂等的,所以失败的话会无限的重试。如果崩溃恢复后,就可以收到新的请求,然后选择追加或者拒绝 entry。
+If Followers or Candidates crash, the process is much simpler. Subsequent RequestVoteRPCs and AppendEntriesRPCs sent to them will fail. Since all Raft requests are idempotent, failures will result in infinite retries. After recovery from a crash, they can receive new requests, choosing to append or reject entries.
-### 5.3 时间与可用性
+### 5.3 Time and Availability
-raft 的要求之一就是安全性不依赖于时间:系统不能仅仅因为一些事件发生的比预想的快一些或者慢一些就产生错误。为了保证上述要求,最好能满足以下的时间条件:
+One of Raft's requirements is that safety does not depend on time: the system cannot generate errors simply because some events occur faster or slower than expected. To ensure the above requirement, it is best to satisfy the following time conditions:
`broadcastTime << electionTimeout << MTBF`
-- `broadcastTime`:向其他节点并发发送消息的平均响应时间;
-- `electionTimeout`:选举超时时间;
-- `MTBF(mean time between failures)`:单台机器的平均健康时间;
+- `broadcastTime`: The average response time for concurrently sending messages to other nodes.
+- `electionTimeout`: The timeout for elections.
+- `MTBF(mean time between failures)`: The average healthy uptime of a single machine.
-`broadcastTime`应该比`electionTimeout`小一个数量级,为的是使`Leader`能够持续发送心跳信息(heartbeat)来阻止`Follower`开始选举;
+`broadcastTime` should be an order of magnitude smaller than `electionTimeout` to allow the `Leader` to continually send heartbeat messages to prevent `Follower` from initiating elections.
-`electionTimeout`也要比`MTBF`小几个数量级,为的是使得系统稳定运行。当`Leader`崩溃时,大约会在整个`electionTimeout`的时间内不可用;我们希望这种情况仅占全部时间的很小一部分。
+`electionTimeout` should also be several orders smaller than `MTBF` to keep the system running stably. When `Leader` crashes, the system will be unavailable for approximately the entire duration of `electionTimeout`; we wish for this situation to occupy only a small part of the total time.
-由于`broadcastTime`和`MTBF`是由系统决定的属性,因此需要决定`electionTimeout`的时间。
+Since `broadcastTime` and `MTBF` are system-determined properties, it is necessary to set the duration of `electionTimeout`.
-一般来说,broadcastTime 一般为 `0.5~20ms`,electionTimeout 可以设置为 `10~500ms`,MTBF 一般为一两个月。
+In general, `broadcastTime` is usually between `0.5-20ms`, while `electionTimeout` can be set to `10-500ms`, and `MTBF` is typically one to two months.
-## 6 参考
+## 6 References
-
-
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
index 3eaee38b50c..703d0f1f7d0 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
@@ -1,461 +1,71 @@
---
-title: Dubbo常见问题总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Dubbo Issues
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
::: tip
-- Dubbo3 已经发布,这篇文章是基于 Dubbo2 写的。Dubbo3 基于 Dubbo2 演进而来,在保持原有核心功能特性的同时, Dubbo3 在易用性、超大规模微服务实践、云原生基础设施适配、安全设计等几大方向上进行了全面升级。
-- 本文中的很多链接已经失效,主要原因是因为 Dubbo 官方文档进行了修改导致 URL 失效。
+- Dubbo3 has been released, and this article is based on Dubbo2. Dubbo3 is evolved from Dubbo2, maintaining the original core functional characteristics while undergoing comprehensive upgrades in usability, large-scale microservice practices, cloud-native infrastructure adaptation, and security design.
+- Many links in this article are outdated, mainly due to changes in the official Dubbo documentation that have caused URL failures.
:::
-这篇文章是我根据官方文档以及自己平时的使用情况,对 Dubbo 所做的一个总结。欢迎补充!
+This article is a summary of Dubbo based on the official documentation and my own usage experience. Contributions are welcome!
-## Dubbo 基础
+## Dubbo Basics
-### 什么是 Dubbo?
+### What is Dubbo?
-
+
-[Apache Dubbo](https://github.com/apache/dubbo) |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源 WEB 和 RPC 框架。
+[Apache Dubbo](https://github.com/apache/dubbo) |ˈdʌbəʊ| is a high-performance, lightweight open-source WEB and RPC framework.
-根据 [Dubbo 官方文档](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/)的介绍,Dubbo 提供了六大核心能力
+According to the [official Dubbo documentation](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/), Dubbo provides six core capabilities:
-1. 面向接口代理的高性能 RPC 调用。
-2. 智能容错和负载均衡。
-3. 服务自动注册和发现。
-4. 高度可扩展能力。
-5. 运行期流量调度。
-6. 可视化的服务治理与运维。
+1. High-performance RPC calls oriented to interface proxies.
+1. Intelligent fault tolerance and load balancing.
+1. Automatic service registration and discovery.
+1. Highly extensible capabilities.
+1. Runtime traffic scheduling.
+1. Visual service governance and operation.
-
+
-简单来说就是:**Dubbo 不光可以帮助我们调用远程服务,还提供了一些其他开箱即用的功能比如智能负载均衡。**
+In simple terms: **Dubbo not only helps us call remote services but also provides other out-of-the-box features like intelligent load balancing.**
-Dubbo 目前已经有接近 34.4 k 的 Star 。
+Dubbo currently has nearly 34.4k stars.
-在 **2020 年度 OSC 中国开源项目** 评选活动中,Dubbo 位列开发框架和基础组件类项目的第 7 名。相比几年前来说,热度和排名有所下降。
+In the **2020 OSC China Open Source Project** selection event, Dubbo ranked 7th among development frameworks and basic component projects. Compared to a few years ago, its popularity and ranking have declined.

-Dubbo 是由阿里开源,后来加入了 Apache 。正是由于 Dubbo 的出现,才使得越来越多的公司开始使用以及接受分布式架构。
+Dubbo was open-sourced by Alibaba and later joined Apache. It is the emergence of Dubbo that has led to more and more companies beginning to use and accept distributed architectures.
-### 为什么要用 Dubbo?
+### Why Use Dubbo?
-随着互联网的发展,网站的规模越来越大,用户数量越来越多。单一应用架构、垂直应用架构无法满足我们的需求,这个时候分布式服务架构就诞生了。
+With the development of the internet, websites are becoming larger, and the number of users is increasing. Single application architectures and vertical application architectures can no longer meet our needs, which is when distributed service architectures were born.
-分布式服务架构下,系统被拆分成不同的服务比如短信服务、安全服务,每个服务独立提供系统的某个核心服务。
+In a distributed service architecture, the system is split into different services, such as SMS service and security service, with each service independently providing a core service of the system.
-我们可以使用 Java RMI(Java Remote Method Invocation)、Hessian 这种支持远程调用的框架来简单地暴露和引用远程服务。但是!当服务越来越多之后,服务调用关系越来越复杂。当应用访问压力越来越大后,负载均衡以及服务监控的需求也迫在眉睫。我们可以用 F5 这类硬件来做负载均衡,但这样增加了成本,并且存在单点故障的风险。
+We can use frameworks that support remote calls, such as Java RMI (Java Remote Method Invocation) and Hessian, to simply expose and reference remote services. However! As the number of services increases, the relationships between service calls become increasingly complex. When application access pressure increases, the need for load balancing and service monitoring becomes urgent. We can use hardware like F5 for load balancing, but this increases costs and poses a risk of single points of failure.
-不过,Dubbo 的出现让上述问题得到了解决。**Dubbo 帮助我们解决了什么问题呢?**
+However, the emergence of Dubbo has solved the above problems. **What problems does Dubbo help us solve?**
-1. **负载均衡**:同一个服务部署在不同的机器时该调用哪一台机器上的服务。
-2. **服务调用链路生成**:随着系统的发展,服务越来越多,服务间依赖关系变得错踪复杂,甚至分不清哪个应用要在哪个应用之前启动,架构师都不能完整的描述应用的架构关系。Dubbo 可以为我们解决服务之间互相是如何调用的。
-3. **服务访问压力以及时长统计、资源调度和治理**:基于访问压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。
-4. ……
+1. **Load Balancing**: When the same service is deployed on different machines, which machine's service should be called?
+1. **Service Call Chain Generation**: As the system evolves, the number of services increases, and the dependencies between services become complex, making it difficult to determine which application should start before which. Even architects cannot fully describe the architectural relationships of applications. Dubbo can help us understand how services call each other.
+1. **Service Access Pressure and Duration Statistics, Resource Scheduling, and Governance**: Real-time management of cluster capacity based on access pressure to improve cluster utilization.
+1. ……
-
+
-另外,Dubbo 除了能够应用在分布式系统中,也可以应用在现在比较火的微服务系统中。不过,由于 Spring Cloud 在微服务中应用更加广泛,所以,我觉得一般我们提 Dubbo 的话,大部分是分布式系统的情况。
+Additionally, Dubbo can be applied not only in distributed systems but also in the currently popular microservice systems. However, since Spring Cloud is more widely used in microservices, I believe that when we mention Dubbo, it is mostly in the context of distributed systems.
-**我们刚刚提到了分布式这个概念,下面再给大家介绍一下什么是分布式?为什么要分布式?**
+**We just mentioned the concept of distribution, so let’s introduce what distribution is and why it is necessary.**
-## 分布式基础
+## Basics of Distribution
-### 什么是分布式?
+### What is Distribution?
-分布式或者说 SOA 分布式重要的就是面向服务,说简单的分布式就是我们把整个系统拆分成不同的服务然后将这些服务放在不同的服务器上减轻单体服务的压力提高并发量和性能。比如电商系统可以简单地拆分成订单系统、商品系统、登录系统等等,拆分之后的每个服务可以部署在不同的机器上,如果某一个服务的访问量比较大的话也可以将这个服务同时部署在多台机器上。
-
-
-
-### 为什么要分布式?
-
-从开发角度来讲单体应用的代码都集中在一起,而分布式系统的代码根据业务被拆分。所以,每个团队可以负责一个服务的开发,这样提升了开发效率。另外,代码根据业务拆分之后更加便于维护和扩展。
-
-另外,我觉得将系统拆分成分布式之后不光便于系统扩展和维护,更能提高整个系统的性能。你想一想嘛?把整个系统拆分成不同的服务/系统,然后每个服务/系统 单独部署在一台服务器上,是不是很大程度上提高了系统性能呢?
-
-## Dubbo 架构
-
-### Dubbo 架构中的核心角色有哪些?
-
-[官方文档中的框架设计章节](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/design/) 已经介绍的非常详细了,我这里把一些比较重要的点再提一下。
-
-
-
-上述节点简单介绍以及他们之间的关系:
-
-- **Container:** 服务运行容器,负责加载、运行服务提供者。必须。
-- **Provider:** 暴露服务的服务提供方,会向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。必须。
-- **Consumer:** 调用远程服务的服务消费方,会向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。必须。
-- **Registry:** 服务注册与发现的注册中心。注册中心会返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者。非必须。
-- **Monitor:** 统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的监控中心。服务消费者和提供者会定时发送统计数据到监控中心。 非必须。
-
-### Dubbo 中的 Invoker 概念了解么?
-
-`Invoker` 是 Dubbo 领域模型中非常重要的一个概念,你如果阅读过 Dubbo 源码的话,你会无数次看到这玩意。就比如下面我要说的负载均衡这块的源码中就有大量 `Invoker` 的身影。
-
-简单来说,`Invoker` 就是 Dubbo 对远程调用的抽象。
-
-
-
-按照 Dubbo 官方的话来说,`Invoker` 分为
-
-- 服务提供 `Invoker`
-- 服务消费 `Invoker`
-
-假如我们需要调用一个远程方法,我们需要动态代理来屏蔽远程调用的细节吧!我们屏蔽掉的这些细节就依赖对应的 `Invoker` 实现, `Invoker` 实现了真正的远程服务调用。
-
-### Dubbo 的工作原理了解么?
-
-下图是 Dubbo 的整体设计,从下至上分为十层,各层均为单向依赖。
-
-> 左边淡蓝背景的为服务消费方使用的接口,右边淡绿色背景的为服务提供方使用的接口,位于中轴线上的为双方都用到的接口。
-
-
-
-- **config 配置层**:Dubbo 相关的配置。支持代码配置,同时也支持基于 Spring 来做配置,以 `ServiceConfig`, `ReferenceConfig` 为中心
-- **proxy 服务代理层**:调用远程方法像调用本地的方法一样简单的一个关键,真实调用过程依赖代理类,以 `ServiceProxy` 为中心。
-- **registry 注册中心层**:封装服务地址的注册与发现。
-- **cluster 路由层**:封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以 `Invoker` 为中心。
-- **monitor 监控层**:RPC 调用次数和调用时间监控,以 `Statistics` 为中心。
-- **protocol 远程调用层**:封装 RPC 调用,以 `Invocation`, `Result` 为中心。
-- **exchange 信息交换层**:封装请求响应模式,同步转异步,以 `Request`, `Response` 为中心。
-- **transport 网络传输层**:抽象 mina 和 netty 为统一接口,以 `Message` 为中心。
-- **serialize 数据序列化层**:对需要在网络传输的数据进行序列化。
-
-### Dubbo 的 SPI 机制了解么? 如何扩展 Dubbo 中的默认实现?
-
-SPI(Service Provider Interface) 机制被大量用在开源项目中,它可以帮助我们动态寻找服务/功能(比如负载均衡策略)的实现。
-
-SPI 的具体原理是这样的:我们将接口的实现类放在配置文件中,我们在程序运行过程中读取配置文件,通过反射加载实现类。这样,我们可以在运行的时候,动态替换接口的实现类。和 IoC 的解耦思想是类似的。
-
-Java 本身就提供了 SPI 机制的实现。不过,Dubbo 没有直接用,而是对 Java 原生的 SPI 机制进行了增强,以便更好满足自己的需求。
-
-**那我们如何扩展 Dubbo 中的默认实现呢?**
-
-比如说我们想要实现自己的负载均衡策略,我们创建对应的实现类 `XxxLoadBalance` 实现 `LoadBalance` 接口或者 `AbstractLoadBalance` 类。
-
-```java
-package com.xxx;
-
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
-
-public class XxxLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
- public Invoker select(List> invokers, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
- // ...
- }
-}
-```
-
-我们将这个实现类的路径写入到`resources` 目录下的 `META-INF/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance`文件中即可。
-
-```java
-src
- |-main
- |-java
- |-com
- |-xxx
- |-XxxLoadBalance.java (实现LoadBalance接口)
- |-resources
- |-META-INF
- |-dubbo
- |-org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance (纯文本文件,内容为:xxx=com.xxx.XxxLoadBalance)
-```
-
-`org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance`
-
-```plain
-xxx=com.xxx.XxxLoadBalance
-```
-
-其他还有很多可供扩展的选择,你可以在[官方文档](https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/overview/home/)中找到。
-
-### Dubbo 的微内核架构了解吗?
-
-Dubbo 采用 微内核(Microkernel) + 插件(Plugin) 模式,简单来说就是微内核架构。微内核只负责组装插件。
-
-**何为微内核架构呢?** 《软件架构模式》 这本书是这样介绍的:
-
-> 微内核架构模式(有时被称为插件架构模式)是实现基于产品应用程序的一种自然模式。基于产品的应用程序是已经打包好并且拥有不同版本,可作为第三方插件下载的。然后,很多公司也在开发、发布自己内部商业应用像有版本号、说明及可加载插件式的应用软件(这也是这种模式的特征)。微内核系统可让用户添加额外的应用如插件,到核心应用,继而提供了可扩展性和功能分离的用法。
-
-微内核架构包含两类组件:**核心系统(core system)** 和 **插件模块(plug-in modules)**。
-
-
-
-核心系统提供系统所需核心能力,插件模块可以扩展系统的功能。因此, 基于微内核架构的系统,非常易于扩展功能。
-
-我们常见的一些 IDE,都可以看作是基于微内核架构设计的。绝大多数 IDE 比如 IDEA、VSCode 都提供了插件来丰富自己的功能。
-
-正是因为 Dubbo 基于微内核架构,才使得我们可以随心所欲替换 Dubbo 的功能点。比如你觉得 Dubbo 的序列化模块实现的不满足自己要求,没关系啊!你自己实现一个序列化模块就好了啊!
-
-通常情况下,微核心都会采用 Factory、IoC、OSGi 等方式管理插件生命周期。Dubbo 不想依赖 Spring 等 IoC 容器,也不想自己造一个小的 IoC 容器(过度设计),因此采用了一种最简单的 Factory 方式管理插件:**JDK 标准的 SPI 扩展机制** (`java.util.ServiceLoader`)。
-
-### 关于 Dubbo 架构的一些自测小问题
-
-#### 注册中心的作用了解么?
-
-注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互。
-
-#### 服务提供者宕机后,注册中心会做什么?
-
-注册中心会立即推送事件通知消费者。
-
-#### 监控中心的作用呢?
-
-监控中心负责统计各服务调用次数,调用时间等。
-
-#### 注册中心和监控中心都宕机的话,服务都会挂掉吗?
-
-不会。两者都宕机也不影响已运行的提供者和消费者,消费者在本地缓存了提供者列表。注册中心和监控中心都是可选的,服务消费者可以直连服务提供者。
-
-## Dubbo 的负载均衡策略
-
-### 什么是负载均衡?
-
-先来看一下稍微官方点的解释。下面这段话摘自维基百科对负载均衡的定义:
-
-> 负载均衡改善了跨多个计算资源(例如计算机,计算机集群,网络链接,中央处理单元或磁盘驱动)的工作负载分布。负载平衡旨在优化资源使用,最大化吞吐量,最小化响应时间,并避免任何单个资源的过载。使用具有负载平衡而不是单个组件的多个组件可以通过冗余提高可靠性和可用性。负载平衡通常涉及专用软件或硬件。
-
-**上面讲的大家可能不太好理解,再用通俗的话给大家说一下。**
-
-我们的系统中的某个服务的访问量特别大,我们将这个服务部署在了多台服务器上,当客户端发起请求的时候,多台服务器都可以处理这个请求。那么,如何正确选择处理该请求的服务器就很关键。假如,你就要一台服务器来处理该服务的请求,那该服务部署在多台服务器的意义就不复存在了。负载均衡就是为了避免单个服务器响应同一请求,容易造成服务器宕机、崩溃等问题,我们从负载均衡的这四个字就能明显感受到它的意义。
-
-### Dubbo 提供的负载均衡策略有哪些?
-
-在集群负载均衡时,Dubbo 提供了多种均衡策略,默认为 `random` 随机调用。我们还可以自行扩展负载均衡策略(参考 Dubbo SPI 机制)。
-
-在 Dubbo 中,所有负载均衡实现类均继承自 `AbstractLoadBalance`,该类实现了 `LoadBalance` 接口,并封装了一些公共的逻辑。
-
-```java
-public abstract class AbstractLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
-
- static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) {
- }
-
- @Override
- public Invoker select(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
- }
-
- protected abstract Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation);
-
-
- int getWeight(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) {
-
- }
-}
-```
-
-`AbstractLoadBalance` 的实现类有下面这些:
-
-
-
-官方文档对负载均衡这部分的介绍非常详细,推荐小伙伴们看看,地址:[https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#m-zhdocsv27devsourceloadbalance](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#m-zhdocsv27devsourceloadbalance) 。
-
-#### RandomLoadBalance
-
-根据权重随机选择(对加权随机算法的实现)。这是 Dubbo 默认采用的一种负载均衡策略。
-
-`RandomLoadBalance` 具体的实现原理非常简单,假如有两个提供相同服务的服务器 S1,S2,S1 的权重为 7,S2 的权重为 3。
-
-我们把这些权重值分布在坐标区间会得到:S1->[0, 7) ,S2->[7, 10)。我们生成[0, 10) 之间的随机数,随机数落到对应的区间,我们就选择对应的服务器来处理请求。
-
-
-
-`RandomLoadBalance` 的源码非常简单,简单花几分钟时间看一下。
-
-> 以下源码来自 Dubbo master 分支上的最新的版本 2.7.9。
-
-```java
-public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
-
- public static final String NAME = "random";
-
- @Override
- protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
-
- int length = invokers.size();
- boolean sameWeight = true;
- int[] weights = new int[length];
- int totalWeight = 0;
- // 下面这个for循环的主要作用就是计算所有该服务的提供者的权重之和 totalWeight(),
- // 除此之外,还会检测每个服务提供者的权重是否相同
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
- totalWeight += weight;
- weights[i] = totalWeight;
- if (sameWeight && totalWeight != weight * (i + 1)) {
- sameWeight = false;
- }
- }
- if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
- // 随机生成一个 [0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字
- int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
- // 判断会落在哪个服务提供者的区间
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- if (offset < weights[i]) {
- return invokers.get(i);
- }
- }
-
- return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
- }
-
-}
-
-```
-
-#### LeastActiveLoadBalance
-
-`LeastActiveLoadBalance` 直译过来就是**最小活跃数负载均衡**。
-
-这个名字起得有点不直观,不仔细看官方对活跃数的定义,你压根不知道这玩意是干嘛的。
-
-我这么说吧!初始状态下所有服务提供者的活跃数均为 0(每个服务提供者的中特定方法都对应一个活跃数,我在后面的源码中会提到),每收到一个请求后,对应的服务提供者的活跃数 +1,当这个请求处理完之后,活跃数 -1。
-
-因此,**Dubbo 就认为谁的活跃数越少,谁的处理速度就越快,性能也越好,这样的话,我就优先把请求给活跃数少的服务提供者处理。**
-
-**如果有多个服务提供者的活跃数相等怎么办?**
-
-很简单,那就再走一遍 `RandomLoadBalance` 。
-
-```java
-public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
-
- public static final String NAME = "leastactive";
-
- @Override
- protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
- int length = invokers.size();
- int leastActive = -1;
- int leastCount = 0;
- int[] leastIndexes = new int[length];
- int[] weights = new int[length];
- int totalWeight = 0;
- int firstWeight = 0;
- boolean sameWeight = true;
- // 这个 for 循环的主要作用是遍历 invokers 列表,找出活跃数最小的 Invoker
- // 如果有多个 Invoker 具有相同的最小活跃数,还会记录下这些 Invoker 在 invokers 集合中的下标,并累加它们的权重,比较它们的权重值是否相等
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- Invoker invoker = invokers.get(i);
- // 获取 invoker 对应的活跃(active)数
- int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
- int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
- weights[i] = afterWarmup;
- if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) {
- leastActive = active;
- leastCount = 1;
- leastIndexes[0] = i;
- totalWeight = afterWarmup;
- firstWeight = afterWarmup;
- sameWeight = true;
- } else if (active == leastActive) {
- leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i;
- totalWeight += afterWarmup;
- if (sameWeight && afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
- sameWeight = false;
- }
- }
- }
- // 如果只有一个 Invoker 具有最小的活跃数,此时直接返回该 Invoker 即可
- if (leastCount == 1) {
- return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]);
- }
- // 如果有多个 Invoker 具有相同的最小活跃数,但它们之间的权重不同
- // 这里的处理方式就和 RandomLoadBalance 一致了
- if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
- int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
- for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
- int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i];
- offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex];
- if (offsetWeight < 0) {
- return invokers.get(leastIndex);
- }
- }
- }
- return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]);
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-活跃数是通过 `RpcStatus` 中的一个 `ConcurrentMap` 保存的,根据 URL 以及服务提供者被调用的方法的名称,我们便可以获取到对应的活跃数。也就是说服务提供者中的每一个方法的活跃数都是互相独立的。
-
-```java
-public class RpcStatus {
-
- private static final ConcurrentMap> METHOD_STATISTICS =
- new ConcurrentHashMap>();
-
- public static RpcStatus getStatus(URL url, String methodName) {
- String uri = url.toIdentityString();
- ConcurrentMap map = METHOD_STATISTICS.computeIfAbsent(uri, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
- return map.computeIfAbsent(methodName, k -> new RpcStatus());
- }
- public int getActive() {
- return active.get();
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-#### ConsistentHashLoadBalance
-
-`ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 小伙伴们应该也不会陌生,在分库分表、各种集群中就经常使用这个负载均衡策略。
-
-`ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 即**一致性 Hash 负载均衡策略**。 `ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 中没有权重的概念,具体是哪个服务提供者处理请求是由你的请求的参数决定的,也就是说相同参数的请求总是发到同一个服务提供者。
-
-
-
-另外,Dubbo 为了避免数据倾斜问题(节点不够分散,大量请求落到同一节点),还引入了虚拟节点的概念。通过虚拟节点可以让节点更加分散,有效均衡各个节点的请求量。
-
-
-
-官方有详细的源码分析:[https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#23-consistenthashloadbalance](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#23-consistenthashloadbalance) 。这里还有一个相关的 [PR#5440](https://github.com/apache/dubbo/pull/5440) 来修复老版本中 ConsistentHashLoadBalance 存在的一些 Bug。感兴趣的小伙伴,可以多花点时间研究一下。我这里不多分析了,这个作业留给你们!
-
-#### RoundRobinLoadBalance
-
-加权轮询负载均衡。
-
-轮询就是把请求依次分配给每个服务提供者。加权轮询就是在轮询的基础上,让更多的请求落到权重更大的服务提供者上。比如假如有两个提供相同服务的服务器 S1,S2,S1 的权重为 7,S2 的权重为 3。
-
-如果我们有 10 次请求,那么 7 次会被 S1 处理,3 次被 S2 处理。
-
-但是,如果是 `RandomLoadBalance` 的话,很可能存在 10 次请求有 9 次都被 S1 处理的情况(概率性问题)。
-
-Dubbo 中的 `RoundRobinLoadBalance` 的代码实现被修改重建了好几次,Dubbo-2.6.5 版本的 `RoundRobinLoadBalance` 为平滑加权轮询算法。
-
-## Dubbo 序列化协议
-
-### Dubbo 支持哪些序列化方式呢?
-
-
-
-Dubbo 支持多种序列化方式:JDK 自带的序列化、hessian2、JSON、Kryo、FST、Protostuff,ProtoBuf 等等。
-
-Dubbo 默认使用的序列化方式是 hessian2。
-
-### 谈谈你对这些序列化协议了解?
-
-一般我们不会直接使用 JDK 自带的序列化方式。主要原因有两个:
-
-1. **不支持跨语言调用** : 如果调用的是其他语言开发的服务的时候就不支持了。
-2. **性能差**:相比于其他序列化框架性能更低,主要原因是序列化之后的字节数组体积较大,导致传输成本加大。
-
-JSON 序列化由于性能问题,我们一般也不会考虑使用。
-
-像 Protostuff,ProtoBuf、hessian2 这些都是跨语言的序列化方式,如果有跨语言需求的话可以考虑使用。
-
-Kryo 和 FST 这两种序列化方式是 Dubbo 后来才引入的,性能非常好。不过,这两者都是专门针对 Java 语言的。Dubbo 官网的一篇文章中提到说推荐使用 Kryo 作为生产环境的序列化方式。
-
-Dubbo 官方文档中还有一个关于这些[序列化协议的性能对比图](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/serialization/#m-zhdocsv27userserialization)可供参考。
-
-
-
-
+Distribution, or SOA, is fundamentally service-oriented. In simple terms, distribution means splitting the entire system into different services and placing these services on different servers to reduce the pressure on monolithic services and
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
index 35301d0bceb..ed51c28908d 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
@@ -1,196 +1,196 @@
---
-title: 有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?
-category: 分布式
+title: With HTTP Protocol, Why is RPC Still Needed?
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
-> 本文来自[小白 debug](https://juejin.cn/user/4001878057422087)投稿,原文: 。
+> This article is contributed by [Xiao Bai debug](https://juejin.cn/user/4001878057422087), original text: .
-我想起了我刚工作的时候,第一次接触 RPC 协议,当时就很懵,我 HTTP 协议用的好好的,为什么还要用 RPC 协议?
+I remember when I first started working and encountered RPC protocol for the first time. I was confused; I was using HTTP protocol just fine, so why do we need RPC protocol?
-于是就到网上去搜。
+So, I searched online.
-不少解释显得非常官方,我相信大家在各种平台上也都看到过,解释了又好像没解释,都在**用一个我们不认识的概念去解释另外一个我们不认识的概念**,懂的人不需要看,不懂的人看了还是不懂。
+Many explanations seemed very official. I'm sure everyone has seen them on various platforms, explaining but seemingly not explaining; they all used **one concept we don't understand to explain another concept we don't understand**. Those who understood didn't need to read it, and those who didn't understand remained confused.
-这种看了,又好像没看的感觉,云里雾里的很难受,**我懂**。
+That feeling of having read but not having grasped it is quite uncomfortable, **I understand**.
-为了避免大家有强烈的**审丑疲劳**,今天我们来尝试重新换个方式讲一讲。
+To avoid eliciting strong **aesthetic fatigue**, let's try to explain this in a different way today.
-## 从 TCP 聊起
+## Let's Start with TCP
-作为一个程序员,假设我们需要在 A 电脑的进程发一段数据到 B 电脑的进程,我们一般会在代码里使用 socket 进行编程。
+As a programmer, suppose we need to send some data from a process on computer A to a process on computer B, we typically use sockets in our code for programming.
-这时候,我们可选项一般也就**TCP 和 UDP 二选一。TCP 可靠,UDP 不可靠。** 除非是马总这种神级程序员(早期 QQ 大量使用 UDP),否则,只要稍微对可靠性有些要求,普通人一般无脑选 TCP 就对了。
+At this point, our options generally come down to **TCP or UDP**. TCP is reliable, while UDP is not. Unless someone like Ma Huateng, a legendary programmer (who heavily used UDP in early QQ), opts for UDP, most ordinary people tend to choose TCP without thinking if there's any requirement for reliability.
-类似下面这样。
+It looks something like this.
```ini
fd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
```
-其中`SOCK_STREAM`,是指使用**字节流**传输数据,说白了就是**TCP 协议**。
+Where `SOCK_STREAM` indicates the use of **byte stream** to transmit data, which simply means **TCP protocol**.
-在定义了 socket 之后,我们就可以愉快的对这个 socket 进行操作,比如用`bind()`绑定 IP 端口,用`connect()`发起建连。
+After defining the socket, we can happily perform operations on it, such as using `bind()` to bind the IP port and `connect()` to initiate a connection.
-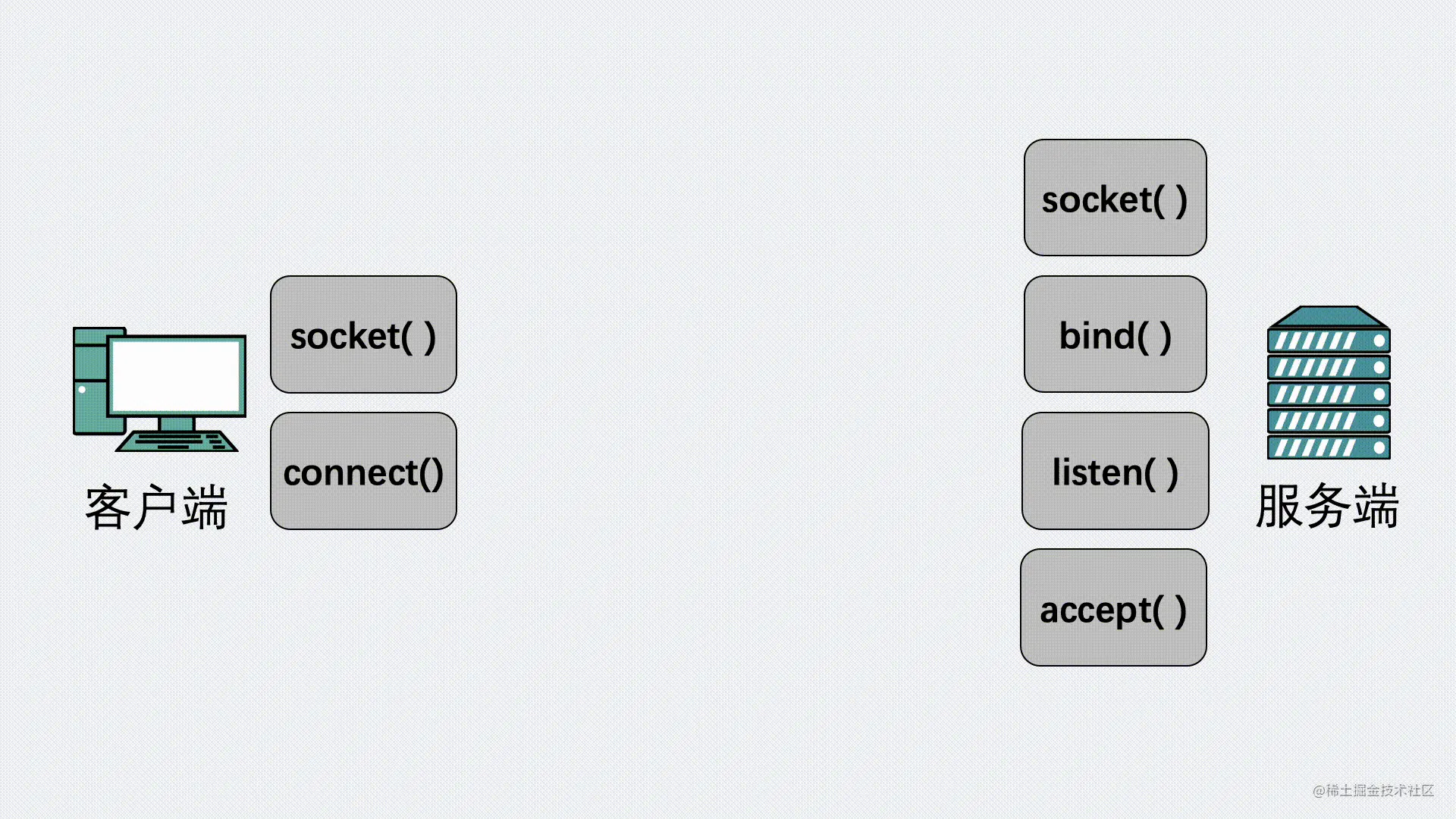
+
-在连接建立之后,我们就可以使用`send()`发送数据,`recv()`接收数据。
+Once the connection is established, we can use `send()` to send data and `recv()` to receive data.
-光这样一个纯裸的 TCP 连接,就可以做到收发数据了,那是不是就够了?
+A pure naked TCP connection can achieve data transmission; isn't that enough?
-不行,这么用会有问题。
+No, there are problems with using it this way.
-## 使用纯裸 TCP 会有什么问题
+## What are the Problems with Using Pure Naked TCP?
-八股文常背,TCP 是有三个特点,**面向连接**、**可靠**、基于**字节流**。
+It's often repeated that TCP has three characteristics: **connection-oriented**, **reliable**, and based on **byte stream**.
-
+
-这三个特点真的概括的 **非常精辟** ,这个八股文我们没白背。
+These three characteristics are indeed **very concise**; we didn’t memorize them for nothing.
-每个特点展开都能聊一篇文章,而今天我们需要关注的是 **基于字节流** 这一点。
+Each characteristic can be discussed in its own article, but today we need to focus on **byte stream**.
-字节流可以理解为一个双向的通道里流淌的二进制数据,也就是 **01 串** 。纯裸 TCP 收发的这些 01 串之间是 **没有任何边界** 的,你根本不知道到哪个地方才算一条完整消息。
+A byte stream can be understood as flowing binary data in a bidirectional channel, which is essentially a string of **01**. The 01 strings transmitted by pure naked TCP have **no boundaries** between them; you have no idea where a complete message starts and ends.
-
+
-正因为这个没有任何边界的特点,所以当我们选择使用 TCP 发送 **"夏洛"和"特烦恼"** 的时候,接收端收到的就是 **"夏洛特烦恼"** ,这时候接收端没发区分你是想要表达 **"夏洛"+"特烦恼"** 还是 **"夏洛特"+"烦恼"** 。
+Because of this lack of boundaries, when we choose to send **"Xia Luo" and "Te Fan Nao"** over TCP, the receiving end gets **"Xia Luo Te Fan Nao."** At this point, the receiver cannot distinguish whether you meant to express **"Xia Luo" + "Te Fan Nao"** or **"Xia Luo Te" + "Fan Nao."**
-
+
-这就是所谓的 **粘包问题**,之前也写过一篇专门的[文章](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0-YBxU1cSbDdzcZEZjmQYA)聊过这个问题。
+This is known as the **sticky packet problem**, and I have previously written a dedicated [article](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0-YBxU1cSbDdzcZEZjmQYA) discussing this issue.
-说这个的目的是为了告诉大家,纯裸 TCP 是不能直接拿来用的,你需要在这个基础上加入一些 **自定义的规则** ,用于区分 **消息边界** 。
+The point of mentioning this is to let everyone know that pure naked TCP cannot be used directly; you need to add some **custom rules** to distinguish **message boundaries.**
-于是我们会把每条要发送的数据都包装一下,比如加入 **消息头** ,消息头里写清楚一个完整的包长度是多少,根据这个长度可以继续接收数据,截取出来后它们就是我们真正要传输的 **消息体** 。
+So, we typically wrap each piece of data to be sent, such as adding a **message header** that clearly states the length of a complete packet. Based on this length, we can continue receiving data and extract it, which forms our actual **message body**.
-
+
-而这里头提到的 **消息头** ,还可以放各种东西,比如消息体是否被压缩过和消息体格式之类的,只要上下游都约定好了,互相都认就可以了,这就是所谓的 **协议。**
+The mentioned **message header** can also contain various pieces of information, such as whether the message body is compressed and the format of the message body. As long as both ends agree on the protocol, it's fine.
-每个使用 TCP 的项目都可能会定义一套类似这样的协议解析标准,他们可能 **有区别,但原理都类似**。
+Every project using TCP may define a set of parsing standards similar to this; they may **differ but the principles are similar.**
-**于是基于 TCP,就衍生了非常多的协议,比如 HTTP 和 RPC。**
+**Thus, many protocols have emerged based on TCP, such as HTTP and RPC.**
-## HTTP 和 RPC
+## HTTP and RPC
-### RPC 其实是一种调用方式
+### RPC is Essentially a Calling Method
-我们回过头来看网络的分层图。
+Let’s turn back to the network layering diagram.
-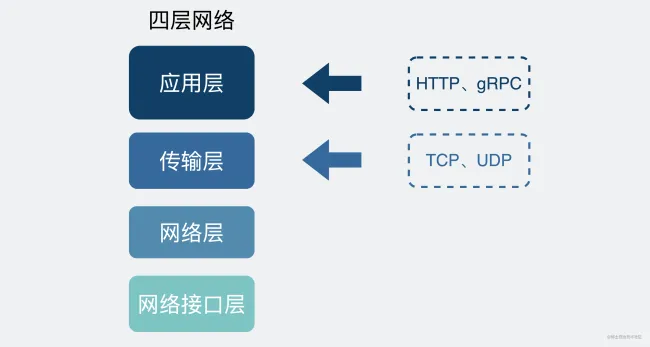
+
-**TCP 是传输层的协议** ,而基于 TCP 造出来的 HTTP 和各类 RPC 协议,它们都只是定义了不同消息格式的 **应用层协议** 而已。
+**TCP is a transport layer protocol**, while HTTP and various RPC protocols built on TCP are merely **application layer protocols** that define different message formats.
-**HTTP**(**H**yper **T**ext **T**ransfer **P**rotocol)协议又叫做 **超文本传输协议** 。我们用的比较多,平时上网在浏览器上敲个网址就能访问网页,这里用到的就是 HTTP 协议。
+**HTTP** (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) is commonly known as the **hypertext transfer protocol**. We use it quite often; when browsing the internet, we can access a webpage by typing a URL in the browser, which utilizes the HTTP protocol.
-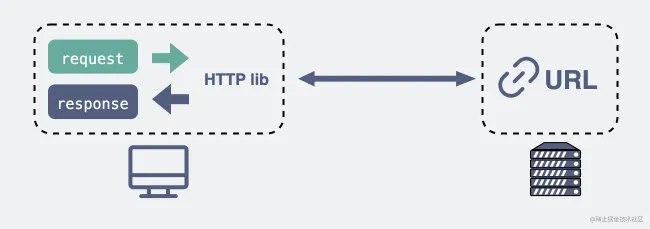
+
-而 **RPC**(**R**emote **P**rocedure **C**all)又叫做 **远程过程调用**,它本身并不是一个具体的协议,而是一种 **调用方式** 。
+On the other hand, **RPC** (Remote Procedure Call) is also known as **remote procedure invocation**. It is not a specific protocol; it represents a **calling method**.
-举个例子,我们平时调用一个 **本地方法** 就像下面这样。
+For example, when we usually call a **local method**, it looks something like this.
```ini
- res = localFunc(req)
+res = localFunc(req)
```
-如果现在这不是个本地方法,而是个**远端服务器**暴露出来的一个方法`remoteFunc`,如果我们还能像调用本地方法那样去调用它,这样就可以**屏蔽掉一些网络细节**,用起来更方便,岂不美哉?
+If now this isn't a local method, but a method `remoteFunc` exposed by a **remote server**, and we can still call it just like a local method, it can **mask some network details**, making it more convenient, wouldn't that be great?
```ini
res = remoteFunc(req)
```
-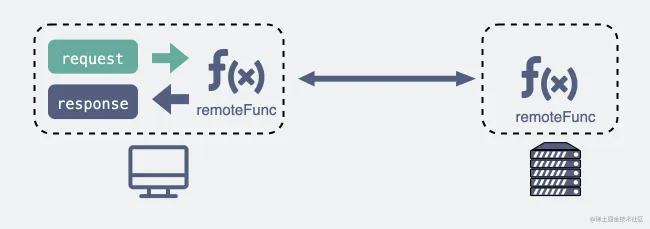
+
-基于这个思路,大佬们造出了非常多款式的 RPC 协议,比如比较有名的`gRPC`,`thrift`。
+Based on this idea, many different types of RPC protocols have been created, such as the well-known `gRPC` and `thrift`.
-值得注意的是,虽然大部分 RPC 协议底层使用 TCP,但实际上 **它们不一定非得使用 TCP,改用 UDP 或者 HTTP,其实也可以做到类似的功能。**
+It's important to note that although most RPC protocols use TCP underneath, in reality, **they don't have to use TCP; they could also use UDP or HTTP, achieving similar functionalities.**
-到这里,我们回到文章标题的问题。
+Now, let's return to the question posed in the article title.
-### 那既然有 RPC 了,为什么还要有 HTTP 呢?
+### If RPC Exists, Why is HTTP Still Needed?
-其实,TCP 是 **70 年** 代出来的协议,而 HTTP 是 **90 年代** 才开始流行的。而直接使用裸 TCP 会有问题,可想而知,这中间这么多年有多少自定义的协议,而这里面就有 **80 年代** 出来的`RPC`。
+In fact, TCP was a protocol developed in the **1970s**, while HTTP didn't begin to gain popularity until the **1990s**. Given that directly using naked TCP has its problems, it’s easy to see how many custom protocols have emerged over the years; and RPC was developed in the **1980s**.
-所以我们该问的不是 **既然有 HTTP 协议为什么要有 RPC** ,而是 **为什么有 RPC 还要有 HTTP 协议?**
+Therefore, we should not ask **why RPC exists alongside HTTP** but rather **why does HTTP still exist alongside RPC?**
-现在电脑上装的各种联网软件,比如 xx 管家,xx 卫士,它们都作为客户端(Client) 需要跟服务端(Server) 建立连接收发消息,此时都会用到应用层协议,在这种 Client/Server (C/S) 架构下,它们可以使用自家造的 RPC 协议,因为它只管连自己公司的服务器就 ok 了。
+Various networked applications installed on computers, such as xx Manager and xx Guardian, act as clients requiring connection to servers to send and receive messages; they utilize application layer protocols. In this Client/Server (C/S) architecture, they can use their own RPC protocols since they only need to connect to their company’s server.
-但有个软件不同,浏览器(Browser) ,不管是 Chrome 还是 IE,它们不仅要能访问自家公司的**服务器(Server)** ,还需要访问其他公司的网站服务器,因此它们需要有个统一的标准,不然大家没法交流。于是,HTTP 就是那个时代用于统一 **Browser/Server (B/S)** 的协议。
+However, one type of software is different: browsers (Browser). Whether it’s Chrome or IE, they need not only to access their own company’s **server** but also to reach websites hosted by other companies; therefore, they need a unified standard, otherwise, communication would be impossible. Consequently, HTTP serves as that standard for unifying **Browser/Server (B/S)** communication.
-也就是说在多年以前,**HTTP 主要用于 B/S 架构,而 RPC 更多用于 C/S 架构。但现在其实已经没分那么清了,B/S 和 C/S 在慢慢融合。** 很多软件同时支持多端,比如某度云盘,既要支持**网页版**,还要支持**手机端和 PC 端**,如果通信协议都用 HTTP 的话,那服务器只用同一套就够了。而 RPC 就开始退居幕后,一般用于公司内部集群里,各个微服务之间的通讯。
+In other words, many years ago, **HTTP was primarily used for B/S architecture, while RPC was more for C/S architecture. However, such distinctions have blurred over time; B/S and C/S are gradually merging.** Many applications now support multiple platforms, such as a certain cloud storage service needing both **web** and **mobile/PC** support. If communication protocols only used HTTP, the server would only need to deal with one set of protocols. Consequently, RPC has begun to take a backseat and is generally used for communication between various microservices within company internal clusters.
-那这么说的话,**都用 HTTP 得了,还用什么 RPC?**
+So that raises the question: **Why not just use HTTP; why use RPC at all?**
-仿佛又回到了文章开头的样子,那这就要从它们之间的区别开始说起。
+It feels like we're back at the beginning of the article, so we’ll need to discuss the differences between them.
-### HTTP 和 RPC 有什么区别
+### What Are the Differences Between HTTP and RPC?
-我们来看看 RPC 和 HTTP 区别比较明显的几个点。
+Let's look at a few points that clearly distinguish RPC from HTTP.
-#### 服务发现
+#### Service Discovery
-首先要向某个服务器发起请求,你得先建立连接,而建立连接的前提是,你得知道 **IP 地址和端口** 。这个找到服务对应的 IP 端口的过程,其实就是 **服务发现**。
+To initiate a request to a server, you must first establish a connection, and the prerequisite for establishing that connection is knowing the **IP address and port**. The process of finding the service's corresponding IP and port is known as **service discovery**.
-在 **HTTP** 中,你知道服务的域名,就可以通过 **DNS 服务** 去解析得到它背后的 IP 地址,默认 **80 端口**。
+In **HTTP**, if you know the domain name of the service, you can resolve the IP address behind it through **DNS services**, typically on the **default port 80**.
-而 **RPC** 的话,就有些区别,一般会有专门的中间服务去保存服务名和 IP 信息,比如 **Consul、Etcd、Nacos、ZooKeeper,甚至是 Redis**。想要访问某个服务,就去这些中间服务去获得 IP 和端口信息。由于 DNS 也是服务发现的一种,所以也有基于 DNS 去做服务发现的组件,比如 **CoreDNS**。
+In the case of **RPC**, there are some differences. Typically, there will be dedicated intermediary services responsible for storing service names and IP information, such as **Consul, Etcd, Nacos, ZooKeeper, or even Redis**. To access a certain service, you'd query these intermediary services to obtain the IP and port information. Since DNS also functions as a form of service discovery, there exist components that achieve service discovery based on DNS, such as **CoreDNS**.
-可以看出服务发现这一块,两者是有些区别,但不太能分高低。
+It's evident that the service discovery aspect does show some differences between the two, but they are not significantly superior or inferior to one another.
-#### 底层连接形式
+#### Underlying Connection Method
-以主流的 **HTTP1.1** 协议为例,其默认在建立底层 TCP 连接之后会一直保持这个连接(**keep alive**),之后的请求和响应都会复用这条连接。
+Taking the mainstream **HTTP/1.1** protocol as an example, its default behavior is to maintain a TCP connection once established (the **keep-alive** feature), allowing subsequent requests and responses to reuse this connection.
-而 **RPC** 协议,也跟 HTTP 类似,也是通过建立 TCP 长链接进行数据交互,但不同的地方在于,RPC 协议一般还会再建个 **连接池**,在请求量大的时候,建立多条连接放在池内,要发数据的时候就从池里取一条连接出来,用完放回去,下次再复用,可以说非常环保。
+On the other hand, **RPC protocols** also establish TCP long connections for data interactions, but unlike HTTP, RPC protocols typically create a **connection pool**. During times of high request volume, multiple connections are established and kept in the pool; when data needs to be sent, a connection is retrieved from the pool, used, and then returned for future reuse, which is quite efficient.
-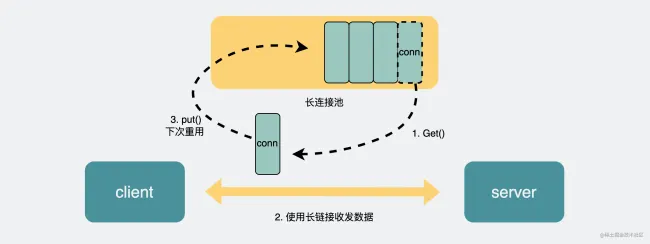
+
-由于连接池有利于提升网络请求性能,所以不少编程语言的网络库里都会给 HTTP 加个连接池,比如 Go 就是这么干的。
+Connection pools help improve network request performance, which is why many programming languages' network libraries introduce a connection pool for HTTP, as seen in Go.
-可以看出这一块两者也没太大区别,所以也不是关键。
+From this perspective, there isn’t a significant distinction in practices between them, so it’s not a key difference either.
-#### 传输的内容
+#### Content Being Transmitted
-基于 TCP 传输的消息,说到底,无非都是 **消息头 Header 和消息体 Body。**
+Messages transmitted using TCP ultimately consist of **header and body**.
-**Header** 是用于标记一些特殊信息,其中最重要的是 **消息体长度**。
+**Header** is used to denote certain special information, with the most important aspect being the **length of the message body**.
-**Body** 则是放我们真正需要传输的内容,而这些内容只能是二进制 01 串,毕竟计算机只认识这玩意。所以 TCP 传字符串和数字都问题不大,因为字符串可以转成编码再变成 01 串,而数字本身也能直接转为二进制。但结构体呢,我们得想个办法将它也转为二进制 01 串,这样的方案现在也有很多现成的,比如 **JSON,Protocol Buffers (Protobuf)** 。
+**Body** contains the actual content we need to transmit, which must be represented in binary as 01 strings since computers only recognize this format. Thus, TCP can handle strings and numbers without issue, because strings can be encoded as 01 strings, and numbers can be directly converted into binary. For structures, however, we need a method to convert them into binary 01 strings, and there are many existing solutions for this, such as **JSON** and **Protocol Buffers (Protobuf)**.
-这个将结构体转为二进制数组的过程就叫 **序列化** ,反过来将二进制数组复原成结构体的过程叫 **反序列化**。
+The process of converting a structure into a binary array is called **serialization**, while reverting a binary array back into a structure is called **deserialization**.
-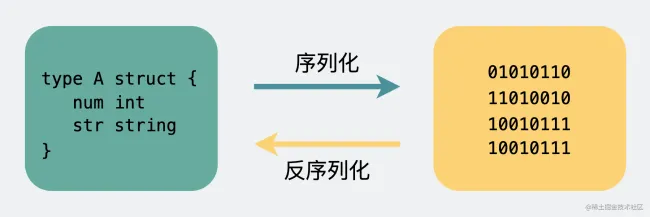
+
-对于主流的 HTTP1.1,虽然它现在叫超文本协议,支持音频视频,但 HTTP 设计 初是用于做网页文本展示的,所以它传的内容以字符串为主。Header 和 Body 都是如此。在 Body 这块,它使用 **JSON** 来 **序列化** 结构体数据。
+For mainstream HTTP/1.1, although it is referred to as a hypertext protocol—supporting audio and video—HTTP was originally designed primarily for displaying web text, so the content it transmits is predominantly string-based. Both the header and body follow this pattern. In the body section, it employs **JSON** to **serialize** structured data.
-我们可以随便截个图直观看下。
+We can capture a snapshot for a more intuitive view.
-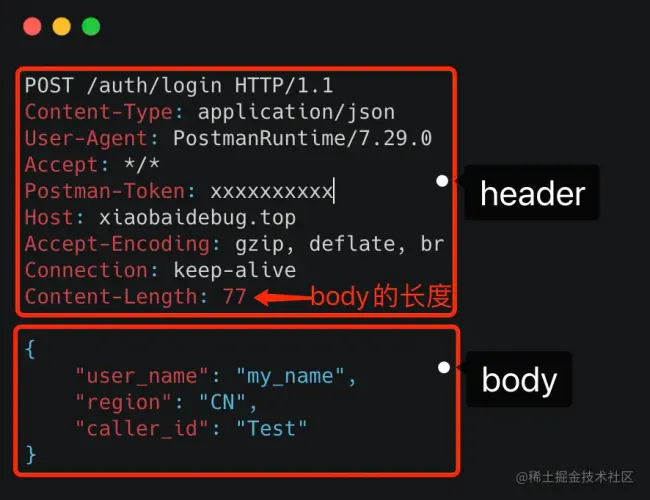
+
-可以看到这里面的内容非常多的冗余,显得非常啰嗦。最明显的,像 Header 里的那些信息,其实如果我们约定好头部的第几位是 `Content-Type`,就不需要每次都真的把 `Content-Type` 这个字段都传过来,类似的情况其实在 Body 的 JSON 结构里也特别明显。
+The content here exhibits significant redundancy and appears verbose. Most noticeably, information in the header (like `Content-Type`) could be effectively conveyed by agreeing on a specific bit's position in the header instead of transmitting the `Content-Type` field literally each time. Similar situations can also be observed in the body's JSON structure.
-而 RPC,因为它定制化程度更高,可以采用体积更小的 Protobuf 或其他序列化协议去保存结构体数据,同时也不需要像 HTTP 那样考虑各种浏览器行为,比如 302 重定向跳转啥的。**因此性能也会更好一些,这也是在公司内部微服务中抛弃 HTTP,选择使用 RPC 的最主要原因。**
+In contrast, RPC, due to its higher level of customization, can utilize smaller serialization formats like Protobuf to retain structured data, without needing to accommodate various browser behaviors (like 302 redirection). **Thus, its performance can be better, which is a major reason for opting for RPC instead of HTTP in internal microservice communications.**
-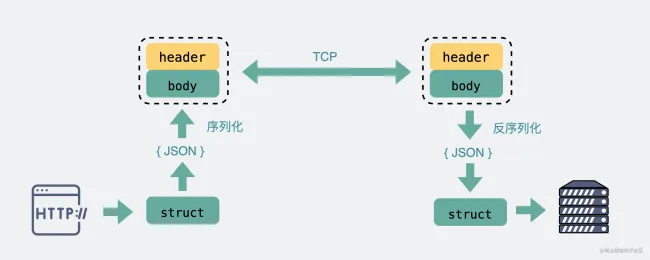
+
-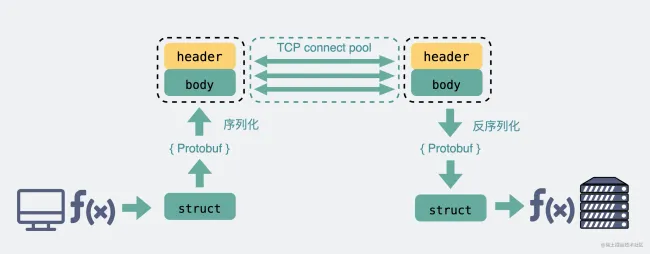
+
-当然上面说的 HTTP,其实 **特指的是现在主流使用的 HTTP1.1**,`HTTP2`在前者的基础上做了很多改进,所以 **性能可能比很多 RPC 协议还要好**,甚至连`gRPC`底层都直接用的`HTTP2`。
+It’s worth noting that the HTTP referred to here specifically denotes the currently mainstream HTTP/1.1. `HTTP/2` has made many improvements on top of this, so **its performance may exceed many RPC protocols**, with `gRPC` directly utilizing `HTTP/2` at its core.
-那么问题又来了。
+This prompts yet another question.
-### 为什么既然有了 HTTP2,还要有 RPC 协议?
+### Why, Since We've Emerged with HTTP/2, Do We Still Need RPC Protocols?
-这个是由于 HTTP2 是 2015 年出来的。那时候很多公司内部的 RPC 协议都已经跑了好些年了,基于历史原因,一般也没必要去换了。
+The reason is that HTTP/2 was introduced in 2015, by which time many internal RPC protocols had already been running for several years; thus, due to historical reasons, there typically wasn’t a pressing need to shift to alternatives.
-## 总结
+## Conclusion
-- 纯裸 TCP 是能收发数据,但它是个无边界的数据流,上层需要定义消息格式用于定义 **消息边界** 。于是就有了各种协议,HTTP 和各类 RPC 协议就是在 TCP 之上定义的应用层协议。
-- **RPC 本质上不算是协议,而是一种调用方式**,而像 gRPC 和 Thrift 这样的具体实现,才是协议,它们是实现了 RPC 调用的协议。目的是希望程序员能像调用本地方法那样去调用远端的服务方法。同时 RPC 有很多种实现方式,**不一定非得基于 TCP 协议**。
-- 从发展历史来说,**HTTP 主要用于 B/S 架构,而 RPC 更多用于 C/S 架构。但现在其实已经没分那么清了,B/S 和 C/S 在慢慢融合。** 很多软件同时支持多端,所以对外一般用 HTTP 协议,而内部集群的微服务之间则采用 RPC 协议进行通讯。
-- RPC 其实比 HTTP 出现的要早,且比目前主流的 HTTP1.1 性能要更好,所以大部分公司内部都还在使用 RPC。
-- **HTTP2.0** 在 **HTTP1.1** 的基础上做了优化,性能可能比很多 RPC 协议都要好,但由于是这几年才出来的,所以也不太可能取代掉 RPC。
+- Pure naked TCP can send and receive data, but it is a borderless data stream, requiring the upper layers to define a message format to establish **message boundaries**. Thus, various application layer protocols, including HTTP and various RPC protocols, are defined on top of TCP.
+- **RPC is not essentially a protocol but a method of invocation**, while implementations like gRPC and Thrift are the protocols that realize RPC calls. The goal is to allow programmers to invoke remote service methods like local methods. Moreover, there are various ways to implement RPC, **and it does not have to be based on the TCP protocol**.
+- From a historical development perspective, **HTTP was primarily used for B/S architecture, while RPC was more oriented towards C/S architecture. However, now the distinction has become less clear as B/S and C/S are gradually merging.** Many applications support multiple platforms, making HTTP generally suitable for external communications, while RPC protocols are used for communication within internal clusters.
+- RPC actually predates HTTP and tends to perform better than the currently mainstream HTTP/1.1, which is why most companies still utilize RPC internally.
+- **HTTP/2** has been optimized upon **HTTP/1.1**, potentially outperforming many RPC protocols; however, it was introduced only in recent years, making it more challenging to replace RPC quickly.
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
index d2c5fb5e9c7..8d5e2801222 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
@@ -1,141 +1,138 @@
---
-title: RPC基础知识总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Basic RPC Knowledge
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
-这篇文章会简单介绍一下 RPC 相关的基础概念。
+This article will briefly introduce the basic concepts related to RPC.
-## RPC 是什么?
+## What is RPC?
-**RPC(Remote Procedure Call)** 即远程过程调用,通过名字我们就能看出 RPC 关注的是远程调用而非本地调用。
+**RPC (Remote Procedure Call)** refers to remote procedure calls, and from its name, we can see that RPC focuses on remote calls rather than local calls.
-**为什么要 RPC ?** 因为,两个不同的服务器上的服务提供的方法不在一个内存空间,所以,需要通过网络编程才能传递方法调用所需要的参数。并且,方法调用的结果也需要通过网络编程来接收。但是,如果我们自己手动网络编程来实现这个调用过程的话工作量是非常大的,因为,我们需要考虑底层传输方式(TCP 还是 UDP)、序列化方式等等方面。
+**Why use RPC?** Because the methods provided by services on two different servers do not share the same memory space, it is necessary to use network programming to pass the parameters required for the method call. Furthermore, the results of the method call also need to be received through network programming. However, if we were to manually implement this calling process through network programming, the workload would be extensive, as we need to consider various factors such as the underlying transmission method (TCP or UDP), serialization methods, and more.
-**RPC 能帮助我们做什么呢?** 简单来说,通过 RPC 可以帮助我们调用远程计算机上某个服务的方法,这个过程就像调用本地方法一样简单。并且!我们不需要了解底层网络编程的具体细节。
+**What can RPC help us with?** Simply put, RPC allows us to call a method from a service on a remote computer as easily as calling a local method. Moreover, we do not need to understand the specific details of underlying network programming.
-举个例子:两个不同的服务 A、B 部署在两台不同的机器上,服务 A 如果想要调用服务 B 中的某个方法的话就可以通过 RPC 来做。
+For example, if service A, deployed on one machine, wants to call a method from service B, deployed on another machine, it can do so via RPC.
-一言蔽之:**RPC 的出现就是为了让你调用远程方法像调用本地方法一样简单。**
+In short: **The purpose of RPC is to make calling remote methods as simple as calling local methods.**
-## RPC 的原理是什么?
+## What is the principle of RPC?
-为了能够帮助小伙伴们理解 RPC 原理,我们可以将整个 RPC 的 核心功能看作是下面 👇 5 个部分实现的:
+To help understand the principle of RPC, we can view the entire core functionality of RPC as being implemented in the following five parts:
-1. **客户端(服务消费端)**:调用远程方法的一端。
-1. **客户端 Stub(桩)**:这其实就是一代理类。代理类主要做的事情很简单,就是把你调用方法、类、方法参数等信息传递到服务端。
-1. **网络传输**:网络传输就是你要把你调用的方法的信息比如说参数啊这些东西传输到服务端,然后服务端执行完之后再把返回结果通过网络传输给你传输回来。网络传输的实现方式有很多种比如最基本的 Socket 或者性能以及封装更加优秀的 Netty(推荐)。
-1. **服务端 Stub(桩)**:这个桩就不是代理类了。我觉得理解为桩实际不太好,大家注意一下就好。这里的服务端 Stub 实际指的就是接收到客户端执行方法的请求后,去执行对应的方法然后返回结果给客户端的类。
-1. **服务端(服务提供端)**:提供远程方法的一端。
+1. **Client (Service Consumer)**: The end that calls the remote method.
+1. **Client Stub**: This is essentially a proxy class. Its main responsibility is to pass information about the method call, class, and method parameters to the server.
+1. **Network Transmission**: This involves sending the information regarding the method call, such as parameters, to the server. After the server completes execution, it sends the return result back to you via network transmission. There are many ways to implement network transmission; for example, the basic Socket or the more efficient and encapsulated Netty (recommended).
+1. **Server Stub**: This stub is not a proxy class. It's important to note here that the server stub refers to the class that receives the method execution request from the client, executes the corresponding method, and then returns the result to the client.
+1. **Server (Service Provider)**: The end that provides the remote method.
-具体原理图如下,后面我会串起来将整个 RPC 的过程给大家说一下。
+The detailed principle diagram is as follows, and later I will explain the entire RPC process to everyone.
-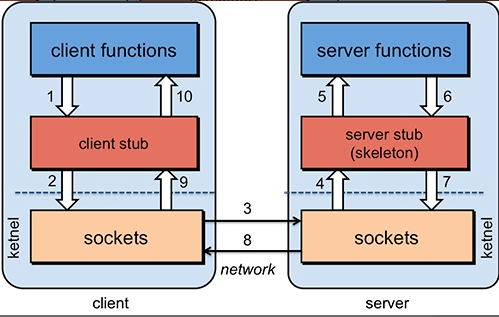
+
-1. 服务消费端(client)以本地调用的方式调用远程服务;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub) 接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体(序列化):`RpcRequest`;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub) 找到远程服务的地址,并将消息发送到服务提供端;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)收到消息将消息反序列化为 Java 对象: `RpcRequest`;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)根据`RpcRequest`中的类、方法、方法参数等信息调用本地的方法;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)得到方法执行结果并将组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体:`RpcResponse`(序列化)发送至消费方;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub)接收到消息并将消息反序列化为 Java 对象:`RpcResponse` ,这样也就得到了最终结果。over!
+1. The service consumer (client) calls the remote service as if it were a local call;
+1. The client stub receives the call and is responsible for assembling the method, parameters, etc., into a message body for network transmission (serialization): `RpcRequest`;
+1. The client stub finds the address of the remote service and sends the message to the service provider;
+1. The server stub receives the message and deserializes it into a Java object: `RpcRequest`;
+1. The server stub invokes the local method based on the class, method, and method parameters in the `RpcRequest`;
+1. The server stub obtains the execution result and assembles it into a message body for network transmission: `RpcResponse` (serialization) to send back to the consumer;
+1. The client stub receives the message and deserializes it into a Java object: `RpcResponse`, thus obtaining the final result. Over!
-相信小伙伴们看完上面的讲解之后,已经了解了 RPC 的原理。
+I believe that after reading the explanation above, everyone understands the principle of RPC.
-虽然篇幅不多,但是基本把 RPC 框架的核心原理讲清楚了!另外,对于上面的技术细节,我会在后面的章节介绍到。
+Although the content is not extensive, it effectively clarifies the core principles of RPC frameworks! Additionally, I will introduce the technical details mentioned above in subsequent sections.
-**最后,对于 RPC 的原理,希望小伙伴不单单要理解,还要能够自己画出来并且能够给别人讲出来。因为,在面试中这个问题在面试官问到 RPC 相关内容的时候基本都会碰到。**
+**Finally, when it comes to the principles of RPC, I hope everyone not only understands but can also reproduce it and explain it to others. This is a common question you will encounter in interviews when the interviewer asks about RPC-related content.**
-## 有哪些常见的 RPC 框架?
+## What are some common RPC frameworks?
-我们这里说的 RPC 框架指的是可以让客户端直接调用服务端方法,就像调用本地方法一样简单的框架,比如我下面介绍的 Dubbo、Motan、gRPC 这些。 如果需要和 HTTP 协议打交道,解析和封装 HTTP 请求和响应。这类框架并不能算是“RPC 框架”,比如 Feign。
+The RPC frameworks we refer to here are those that allow clients to directly call server methods as easily as calling local methods, such as Dubbo, Motan, and gRPC that I will introduce below. If you need to interact with the HTTP protocol, parse, and encapsulate HTTP requests and responses, those frameworks cannot be classified as "RPC frameworks," such as Feign.
### Dubbo

-Apache Dubbo 是一款微服务框架,为大规模微服务实践提供高性能 RPC 通信、流量治理、可观测性等解决方案,
-涵盖 Java、Golang 等多种语言 SDK 实现。
+Apache Dubbo is a microservice framework that provides high-performance RPC communication, traffic governance, observability, and other solutions for large-scale microservices practices, covering various language SDK implementations including Java and Golang.
-Dubbo 提供了从服务定义、服务发现、服务通信到流量管控等几乎所有的服务治理能力,支持 Triple 协议(基于 HTTP/2 之上定义的下一代 RPC 通信协议)、应用级服务发现、Dubbo Mesh (Dubbo3 赋予了很多云原生友好的新特性)等特性。
+Dubbo offers almost all service governance capabilities, from service definition, service discovery, service communication to traffic control, supporting the Triple protocol (the next generation RPC communication protocol defined over HTTP/2), application-level service discovery, and Dubbo Mesh (Dubbo3 has introduced many cloud-native friendly new features).

-Dubbo 是由阿里开源,后来加入了 Apache 。正是由于 Dubbo 的出现,才使得越来越多的公司开始使用以及接受分布式架构。
+Dubbo was open-sourced by Alibaba and later joined Apache. It is due to the emergence of Dubbo that more and more companies have begun to adopt and accept distributed architectures.
-Dubbo 算的是比较优秀的国产开源项目了,它的源码也是非常值得学习和阅读的!
+Dubbo is considered one of the more excellent domestic open-source projects, and its source code is worthy of study and reading!
-- GitHub:[https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo](https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo "https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo")
-- 官网:
+- GitHub: [https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo](https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo "https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo")
+- Official Website:
### Motan
-Motan 是新浪微博开源的一款 RPC 框架,据说在新浪微博正支撑着千亿次调用。不过笔者倒是很少看到有公司使用,而且网上的资料也比较少。
+Motan is an RPC framework open-sourced by Sina Weibo, reportedly supporting billions of calls at Sina Weibo. However, the author has rarely seen any companies using it, and there are also relatively few resources available online.
-很多人喜欢拿 Motan 和 Dubbo 作比较,毕竟都是国内大公司开源的。笔者在查阅了很多资料,以及简单查看了其源码之后发现:**Motan 更像是一个精简版的 Dubbo,可能是借鉴了 Dubbo 的思想,Motan 的设计更加精简,功能更加纯粹。**
+Many people like to compare Motan with Dubbo, as both are open-sourced by large domestic companies. After reviewing many materials and briefly checking the source code, I found that **Motan is more like a simplified version of Dubbo. It may have borrowed ideas from Dubbo, but its design is simpler and its functionality more refined.**
-不过,我不推荐你在实际项目中使用 Motan。如果你要是公司实际使用的话,还是推荐 Dubbo ,其社区活跃度以及生态都要好很多。
+However, I do not recommend using Motan in actual projects. If your company intends to use it, I still recommend Dubbo, as its community activity and ecosystem are much better.
-- 从 Motan 看 RPC 框架设计:[http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/](http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/ "http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/")
-- Motan 中文文档:[https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview](https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview "https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview")
+- Looking at RPC framework design from Motan: [http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/](http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/ "http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/")
+- Motan Chinese Documentation: [https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview](https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview "https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview")
### gRPC
-gRPC 是 Google 开源的一个高性能、通用的开源 RPC 框架。其由主要面向移动应用开发并基于 HTTP/2 协议标准而设计(支持双向流、消息头压缩等功能,更加节省带宽),基于 ProtoBuf 序列化协议开发,并且支持众多开发语言。
+gRPC is a high-performance, open-source RPC framework developed by Google. It is primarily designed for mobile application development and is based on the HTTP/2 protocol standard (supporting bidirectional streaming, message header compression, etc., which saves bandwidth), and is developed based on the ProtoBuf serialization protocol, supporting many programming languages.
-**何谓 ProtoBuf?** [ProtoBuf( Protocol Buffer)](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) 是一种更加灵活、高效的数据格式,可用于通讯协议、数据存储等领域,基本支持所有主流编程语言且与平台无关。不过,通过 ProtoBuf 定义接口和数据类型还挺繁琐的,这是一个小问题。
+**What is ProtoBuf?** [ProtoBuf (Protocol Buffer)](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) is a more flexible and efficient data format that can be used in communication protocols, data storage, and other fields. It supports almost all mainstream programming languages and is platform-independent. However, defining interfaces and data types using ProtoBuf can be a bit cumbersome; that's a minor drawback.
-不得不说,gRPC 的通信层的设计还是非常优秀的,[Dubbo-go 3.0](https://dubbogo.github.io/) 的通信层改进主要借鉴了 gRPC。
+It must be said that the design of gRPC's communication layer is exceptionally well done, and the communication layer improvement of [Dubbo-go 3.0](https://dubbogo.github.io/) has heavily borrowed from gRPC.
-不过,gRPC 的设计导致其几乎没有服务治理能力。如果你想要解决这个问题的话,就需要依赖其他组件比如腾讯的 PolarisMesh(北极星)了。
+However, gRPC's design leads to almost no service governance capabilities. If you want to solve this problem, you will need to rely on other components, such as Tencent's PolarisMesh (North Star).
-- GitHub:[https://github.com/grpc/grpc](https://github.com/grpc/grpc "https://github.com/grpc/grpc")
-- 官网:[https://grpc.io/](https://grpc.io/ "https://grpc.io/")
+- GitHub: [https://github.com/grpc/grpc](https://github.com/grpc/grpc "https://github.com/grpc/grpc")
+- Official Website: [https://grpc.io/](https://grpc.io/ "https://grpc.io/")
### Thrift
-Apache Thrift 是 Facebook 开源的跨语言的 RPC 通信框架,目前已经捐献给 Apache 基金会管理,由于其跨语言特性和出色的性能,在很多互联网公司得到应用,有能力的公司甚至会基于 thrift 研发一套分布式服务框架,增加诸如服务注册、服务发现等功能。
+Apache Thrift is a cross-language RPC communication framework open-sourced by Facebook and is now managed by the Apache Foundation. Due to its cross-language features and excellent performance, it is applied in many internet companies. Capable companies may even develop a distributed service framework based on Thrift, adding features such as service registration and service discovery.
-`Thrift`支持多种不同的**编程语言**,包括`C++`、`Java`、`Python`、`PHP`、`Ruby`等(相比于 gRPC 支持的语言更多 )。
+`Thrift` supports various **programming languages**, including `C++`, `Java`, `Python`, `PHP`, `Ruby`, etc., and it supports more languages compared to gRPC.
-- 官网:[https://thrift.apache.org/](https://thrift.apache.org/ "https://thrift.apache.org/")
-- Thrift 简单介绍:[https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9")
+- Official Website: [https://thrift.apache.org/](https://thrift.apache.org/ "https://thrift.apache.org/")
+- Simple Introduction to Thrift: [https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9")
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-gRPC 和 Thrift 虽然支持跨语言的 RPC 调用,但是它们只提供了最基本的 RPC 框架功能,缺乏一系列配套的服务化组件和服务治理功能的支撑。
+Although gRPC and Thrift support cross-language RPC calls, they only provide the most basic RPC framework functionalities, lacking a series of supporting services and governance features.
-Dubbo 不论是从功能完善程度、生态系统还是社区活跃度来说都是最优秀的。而且,Dubbo 在国内有很多成功的案例比如当当网、滴滴等等,是一款经得起生产考验的成熟稳定的 RPC 框架。最重要的是你还能找到非常多的 Dubbo 参考资料,学习成本相对也较低。
+Dubbo is the most outstanding framework in terms of functionality completeness, ecosystem, and community activity. Moreover, there are many successful domestic cases of Dubbo, such as Dangdang, Didi, and others; it is a mature and stable RPC framework that has withstood practical tests. Most importantly, you can find a wealth of reference materials on Dubbo, making the learning curve relatively low.
-下图展示了 Dubbo 的生态系统。
+The following diagram shows Dubbo's ecosystem.

-Dubbo 也是 Spring Cloud Alibaba 里面的一个组件。
+Dubbo is also a component of Spring Cloud Alibaba.

-但是,Dubbo 和 Motan 主要是给 Java 语言使用。虽然,Dubbo 和 Motan 目前也能兼容部分语言,但是不太推荐。如果需要跨多种语言调用的话,可以考虑使用 gRPC。
+However, both Dubbo and Motan are mainly used for the Java language. Although they can currently also support some other languages, it's not highly recommended. If you need to call across multiple languages, consider using gRPC.
-综上,如果是 Java 后端技术栈,并且你在纠结选择哪一种 RPC 框架的话,我推荐你考虑一下 Dubbo。
+In summary, if you are in a Java backend tech stack and are conflicted about which RPC framework to choose, I recommend considering Dubbo.
-## 如何设计并实现一个 RPC 框架?
+## How to design and implement an RPC framework?
-**《手写 RPC 框架》** 是我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)的一个内部小册,我写了 12 篇文章来讲解如何从零开始基于 Netty+Kyro+Zookeeper 实现一个简易的 RPC 框架。
+**"Writing an RPC Framework"** is an internal booklet of my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html), where I wrote 12 articles explaining how to start from scratch and implement a simple RPC framework based on Netty+Kyro+Zookeeper.
-麻雀虽小五脏俱全,项目代码注释详细,结构清晰,并且集成了 Check Style 规范代码结构,非常适合阅读和学习。
+Although the project is compact, it covers all essential aspects, with detailed comments in the code, a clear structure, and integrated Check Style norms for code structure, making it very suitable for reading and learning.
-**内容概览**:
+**Content Overview**:
-## 既然有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?
+## Since there is an HTTP protocol, why is there still a need for RPC?
-关于这个问题的详细答案,请看这篇文章:[有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?](http&rpc.md) 。
-
-
+For a detailed answer to this question, please refer to this article: [Since there is an HTTP protocol, why is there still a need for RPC?](http&rpc.md).
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md b/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
index 1e6e86845af..e9f0103c590 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
@@ -1,138 +1,138 @@
---
-title: Spring Cloud Gateway常见问题总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Issues with Spring Cloud Gateway
+category: Distributed
---
-> 本文重构完善自[6000 字 | 16 图 | 深入理解 Spring Cloud Gateway 的原理 - 悟空聊架构](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/XjFYsP1IUqNzWqXZdJn-Aw)这篇文章。
+> This article is a refined version of [6000 words | 16 images | In-depth Understanding of the Principles of Spring Cloud Gateway - Wukong Talks Architecture](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/XjFYsP1IUqNzWqXZdJn-Aw).
-## 什么是 Spring Cloud Gateway?
+## What is Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 属于 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,其诞生的目标是为了替代老牌网关 **Zuul**。准确点来说,应该是 Zuul 1.x。Spring Cloud Gateway 起步要比 Zuul 2.x 更早。
+Spring Cloud Gateway is a gateway in the Spring Cloud ecosystem, designed to replace the legacy gateway **Zuul**. More precisely, it aims to replace Zuul 1.x, as Spring Cloud Gateway was developed earlier than Zuul 2.x.
-为了提升网关的性能,Spring Cloud Gateway 基于 Spring WebFlux 。Spring WebFlux 使用 Reactor 库来实现响应式编程模型,底层基于 Netty 实现同步非阻塞的 I/O。
+To enhance gateway performance, Spring Cloud Gateway is built on Spring WebFlux. Spring WebFlux utilizes the Reactor library to implement a reactive programming model, and is based on Netty for synchronous non-blocking I/O at the core.

-Spring Cloud Gateway 不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,限流。
+Spring Cloud Gateway not only provides a unified routing method but also offers basic gateway functions based on a chain of filters, such as security, monitoring/metrics, and rate limiting.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 和 Zuul 2.x 的差别不大,也是通过过滤器来处理请求。不过,目前更加推荐使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 而非 Zuul,Spring Cloud 生态对其支持更加友好。
+The differences between Spring Cloud Gateway and Zuul 2.x are minimal, as both handle requests through filters. However, Spring Cloud Gateway is currently more recommended than Zuul, as the Spring Cloud ecosystem offers better support for it.
-- GitHub 地址:
-- 官网:
+- GitHub address:
+- Official website:
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程?
+## What is the workflow of Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程如下图所示:
+The workflow of Spring Cloud Gateway is illustrated in the following diagram:
-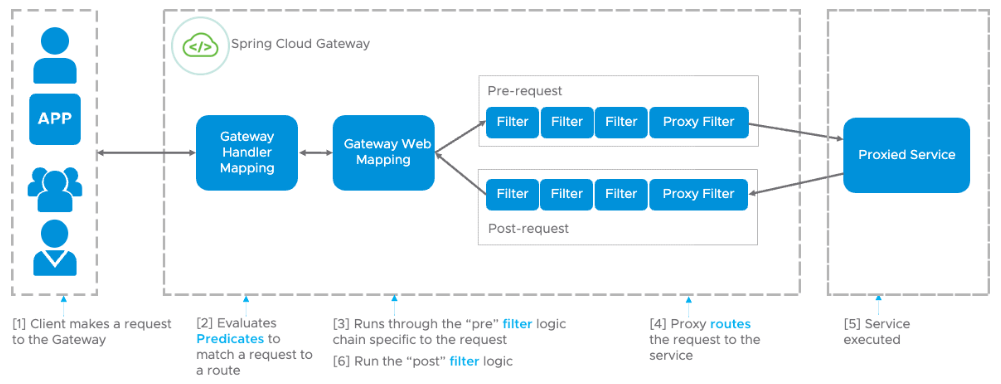
+
-这是 Spring 官方博客中的一张图,原文地址:。
+This is an image from the official Spring blog, original text address: .
-具体的流程分析:
+Specific process analysis:
-1. **路由判断**:客户端的请求到达网关后,先经过 Gateway Handler Mapping 处理,这里面会做断言(Predicate)判断,看下符合哪个路由规则,这个路由映射后端的某个服务。
-2. **请求过滤**:然后请求到达 Gateway Web Handler,这里面有很多过滤器,组成过滤器链(Filter Chain),这些过滤器可以对请求进行拦截和修改,比如添加请求头、参数校验等等,有点像净化污水。然后将请求转发到实际的后端服务。这些过滤器逻辑上可以称作 Pre-Filters,Pre 可以理解为“在...之前”。
-3. **服务处理**:后端服务会对请求进行处理。
-4. **响应过滤**:后端处理完结果后,返回给 Gateway 的过滤器再次做处理,逻辑上可以称作 Post-Filters,Post 可以理解为“在...之后”。
-5. **响应返回**:响应经过过滤处理后,返回给客户端。
+1. **Route Determination**: Once the client's request reaches the gateway, it first passes through the Gateway Handler Mapping, where predicate assertions are evaluated to see which route rule applies. This route maps to a certain backend service.
+1. **Request Filtering**: The request then reaches the Gateway Web Handler, which has many filters that form a filter chain. These filters can intercept and modify requests, such as adding request headers, validating parameters, etc., akin to purifying wastewater. The request is then forwarded to the actual backend service. These filters are logically termed Pre-Filters, where Pre can be understood as "before...".
+1. **Service Processing**: The backend service processes the request.
+1. **Response Filtering**: After the backend has finished processing and returned the result, it is processed again by the Gateway's filters, logically termed Post-Filters, where Post can be understood as "after...".
+1. **Response Return**: After filtering, the response is returned to the client.
-总结:客户端的请求先通过匹配规则找到合适的路由,就能映射到具体的服务。然后请求经过过滤器处理后转发给具体的服务,服务处理后,再次经过过滤器处理,最后返回给客户端。
+In summary: the client's request first finds the appropriate route by matching rules, mapping it to a specific service. After passing through filter processing, the request is forwarded to the specific service, which is processed, filtered again, and ultimately returned to the client.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的断言是什么?
+## What are predicates in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-断言(Predicate)这个词听起来极其深奥,它是一种编程术语,我们生活中根本就不会用它。说白了它就是对一个表达式进行 if 判断,结果为真或假,如果为真则做这件事,否则做那件事。
+The term predicate might sound complex; it is a programming term that we do not commonly use in our daily life. Simply put, it refers to performing an if-judgment on an expression, yielding a true or false result. If true, an action is taken; if false, another action is executed.
-在 Gateway 中,如果客户端发送的请求满足了断言的条件,则映射到指定的路由器,就能转发到指定的服务上进行处理。
+In the Gateway, if the client's request meets the predicate's conditions, it maps to the specified router, enabling forwarding to the designated service for processing.
-断言配置的示例如下,配置了两个路由规则,有一个 predicates 断言配置,当请求 url 中包含 `api/thirdparty`,就匹配到了第一个路由 `route_thirdparty`。
+An example of predicate configuration is shown below, which configures two routing rules, with a predicates assertion that matches when the request URL contains `api/thirdparty`, corresponding to the first route `route_thirdparty`.
-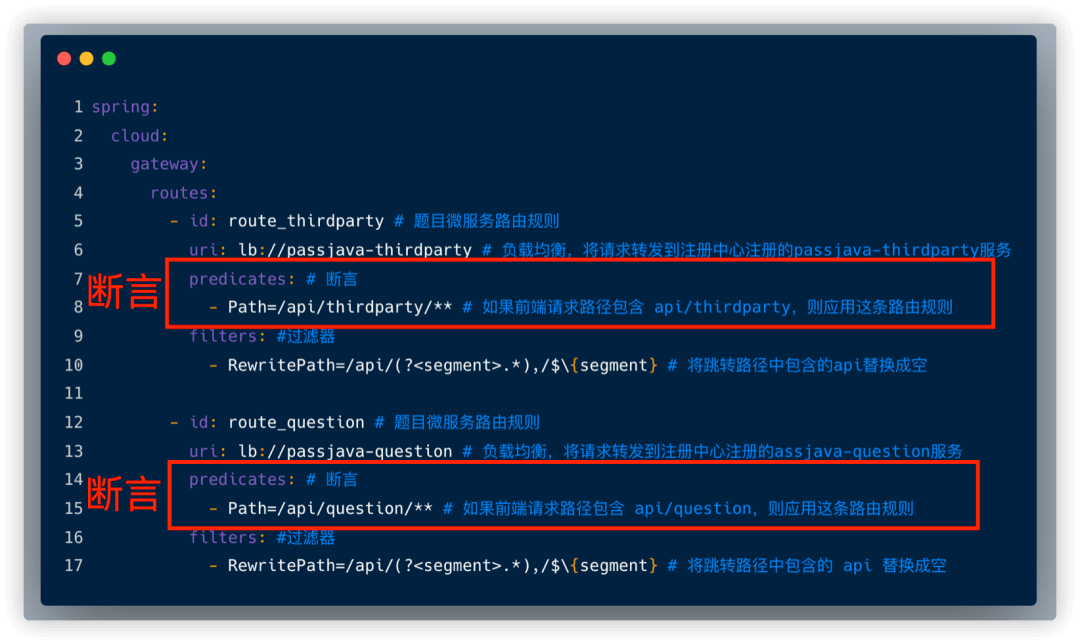
+
-常见的路由断言规则如下图所示:
+Common routing predicate rules are shown in the following diagram:
-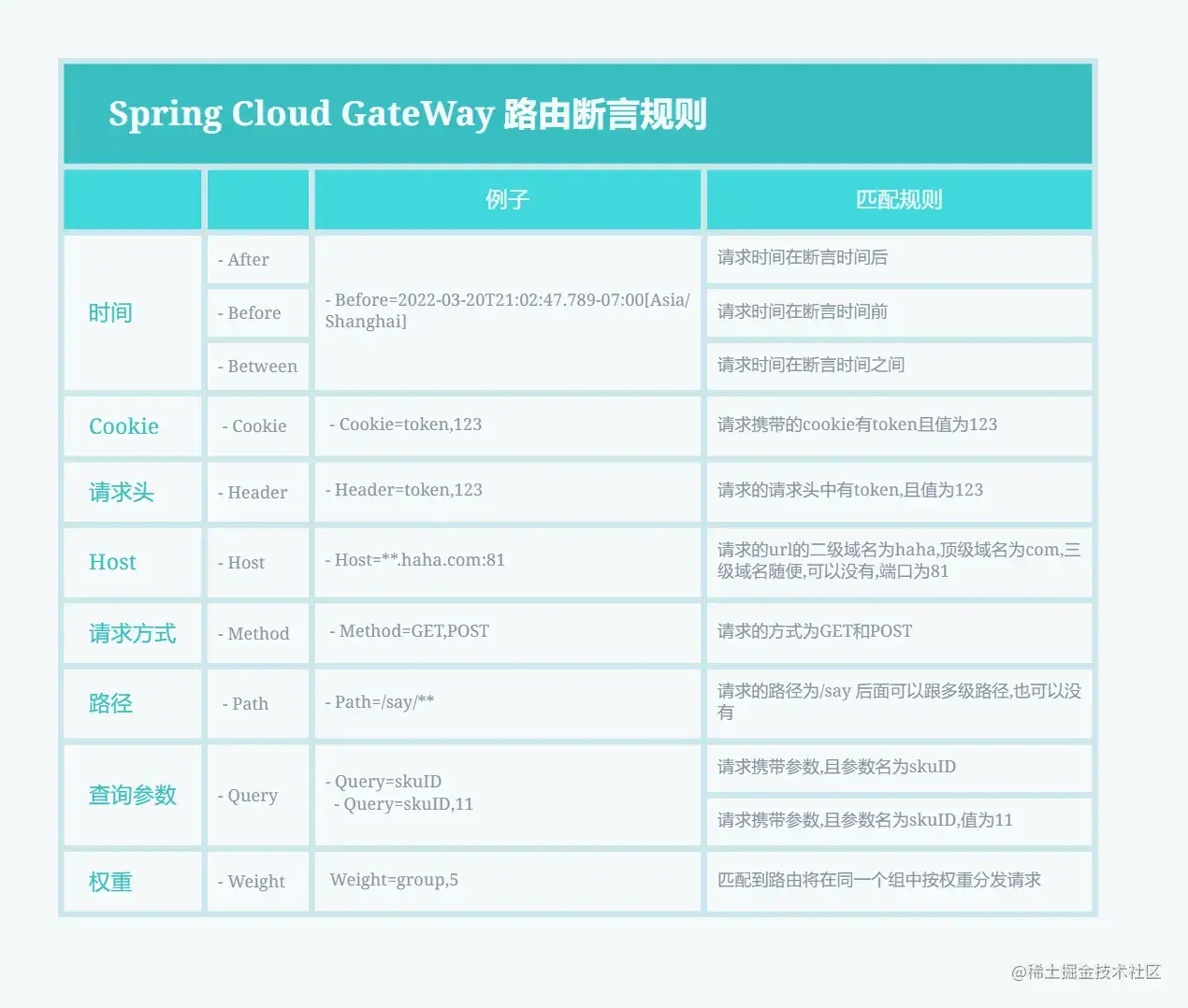
+
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的路由和断言是什么关系?
+## What is the relationship between routes and predicates in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Route 路由和 Predicate 断言的对应关系如下::
+The correspondence between Route and Predicate is as follows:
-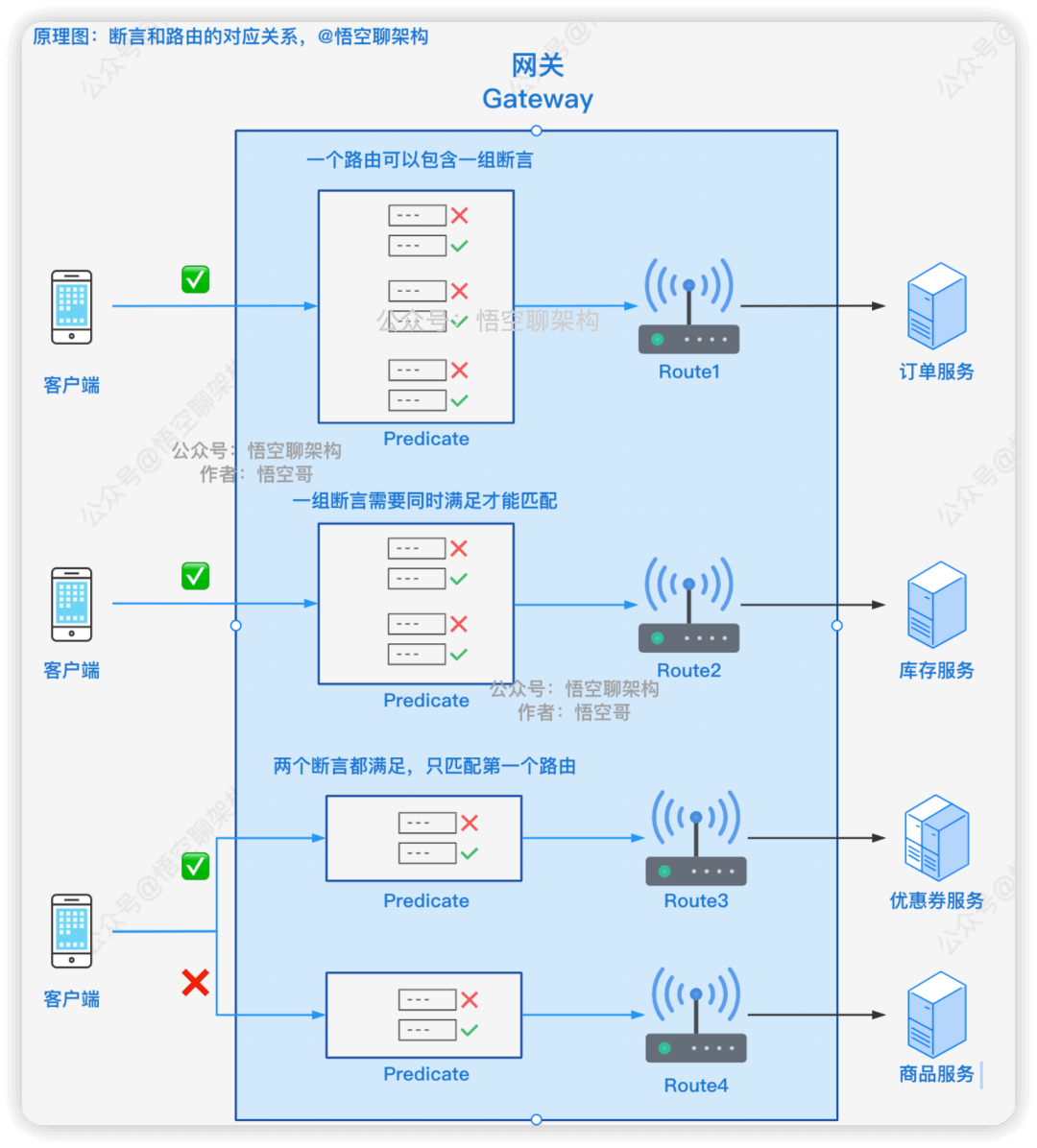
+
-- **一对多**:一个路由规则可以包含多个断言。如上图中路由 Route1 配置了三个断言 Predicate。
-- **同时满足**:如果一个路由规则中有多个断言,则需要同时满足才能匹配。如上图中路由 Route2 配置了两个断言,客户端发送的请求必须同时满足这两个断言,才能匹配路由 Route2。
-- **第一个匹配成功**:如果一个请求可以匹配多个路由,则映射第一个匹配成功的路由。如上图所示,客户端发送的请求满足 Route3 和 Route4 的断言,但是 Route3 的配置在配置文件中靠前,所以只会匹配 Route3。
+- **One-to-Many**: One routing rule can contain multiple predicates. As shown in the image, Route1 is configured with three predicates.
+- **Simultaneous Satisfaction**: If a routing rule has multiple predicates, all must be satisfied for a match. In the image, for Route2, the client's request must satisfy both predicates to match Route2.
+- **First Match Success**: If a request can match multiple routes, the first successfully matching route is chosen. In the image, the client's request satisfies both Route3 and Route4's predicates, but since Route3's configuration appears earlier in the configuration file, it will only match Route3.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 如何实现动态路由?
+## How does Spring Cloud Gateway achieve dynamic routing?
-在使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 的时候,官方文档提供的方案总是基于配置文件或代码配置的方式。
+When using Spring Cloud Gateway, official documentation often provides solutions based on configuration files or code configurations.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 作为微服务的入口,需要尽量避免重启,而现在配置更改需要重启服务不能满足实际生产过程中的动态刷新、实时变更的业务需求,所以我们需要在 Spring Cloud Gateway 运行时动态配置网关。
+As the entry point for microservices, Spring Cloud Gateway should aim to avoid restarts. However, current configuration changes require server restarts, which cannot meet the dynamic refresh and real-time change demands in actual production. Thus, we need to dynamically configure the gateway during its runtime.
-实现动态路由的方式有很多种,其中一种推荐的方式是基于 Nacos 注册中心来做。 Spring Cloud Gateway 可以从注册中心获取服务的元数据(例如服务名称、路径等),然后根据这些信息自动生成路由规则。这样,当你添加、移除或更新服务实例时,网关会自动感知并相应地调整路由规则,无需手动维护路由配置。
+There are many ways to achieve dynamic routing, and one recommended method is based on the Nacos registry. Spring Cloud Gateway can retrieve service metadata (such as service name, path, etc.) from the registry and automatically generate routing rules based on this information. Thus, when you add, remove, or update service instances, the gateway will automatically perceive these changes and adjust the routing rules accordingly, eliminating the need for manual maintenance of routing configurations.
-其实这些复杂的步骤并不需要我们手动实现,通过 Nacos Server 和 Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config 即可实现配置的动态变更,官方文档地址: 。
+In fact, these complex steps do not require manual implementation since dynamic configuration changes can be achieved through Nacos Server and Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config. For the official documentation, visit: .
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的过滤器有哪些?
+## What are the filters in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-过滤器 Filter 按照请求和响应可以分为两种:
+Filters can be categorized into two types based on requests and responses:
-- **Pre 类型**:在请求被转发到微服务之前,对请求进行拦截和修改,例如参数校验、权限校验、流量监控、日志输出以及协议转换等操作。
-- **Post 类型**:微服务处理完请求后,返回响应给网关,网关可以再次进行处理,例如修改响应内容或响应头、日志输出、流量监控等。
+- **Pre Type**: Intercepts and modifies requests before they are forwarded to microservices, including parameter validation, permission checks, traffic monitoring, logging, and protocol conversion.
+- **Post Type**: After the microservice processes the request and returns a response to the gateway, the gateway can perform further processing, such as modifying the response content or headers, logging, and traffic monitoring.
-另外一种分类是按照过滤器 Filter 作用的范围进行划分:
+Another classification divides filters based on their scope of action:
-- **GatewayFilter**:局部过滤器,应用在单个路由或一组路由上的过滤器。标红色表示比较常用的过滤器。
-- **GlobalFilter**:全局过滤器,应用在所有路由上的过滤器。
+- **GatewayFilter**: Local filters applied to a single route or a group of routes. The red-colored ones are commonly used filters.
+- **GlobalFilter**: Global filters applied across all routes.
-### 局部过滤器
+### Local Filters
-常见的局部过滤器如下图所示:
+Common local filters are illustrated in the following diagram:
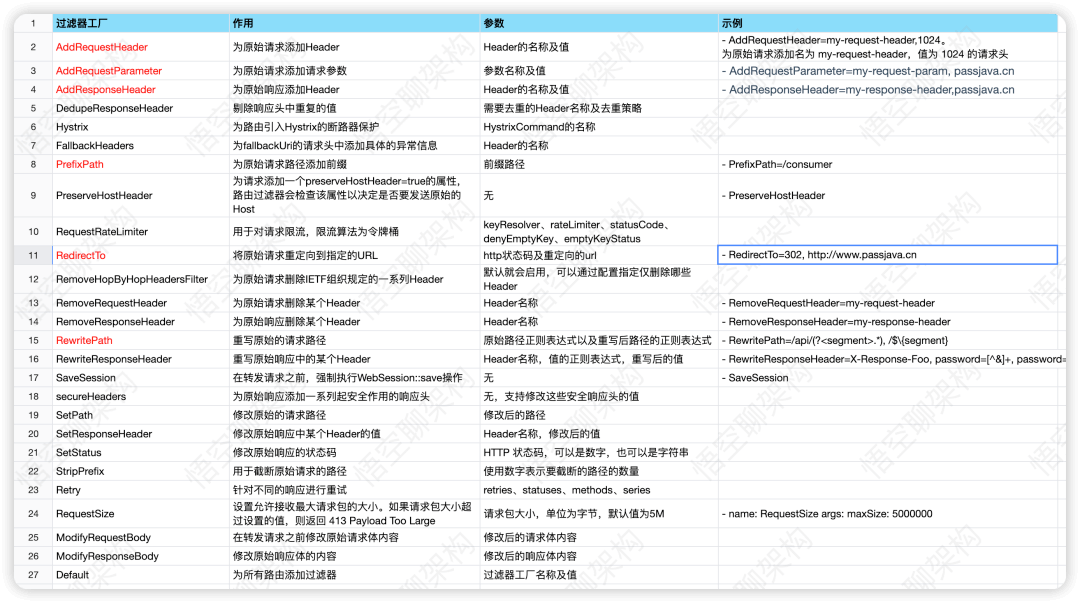
-具体怎么用呢?这里有个示例,如果 URL 匹配成功,则去掉 URL 中的 “api”。
+How is it used? Here’s an example: if the URL matches successfully, it removes "api" from the URL.
```yaml
-filters: #过滤器
- - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # 将跳转路径中包含的 “api” 替换成空
+filters: # Filters
+ - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # Replace "api" in the redirection path with empty
```
-当然我们也可以自定义过滤器,本篇不做展开。
+Of course, we can also define custom filters, but this article does not elaborate on that.
-### 全局过滤器
+### Global Filters
-常见的全局过滤器如下图所示:
+Common global filters are illustrated in the following diagram:

-全局过滤器最常见的用法是进行负载均衡。配置如下所示:
+The most common use of global filters is for load balancing. The configuration is as follows:
```yaml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- - id: route_member # 第三方微服务路由规则
- uri: lb://passjava-member # 负载均衡,将请求转发到注册中心注册的 passjava-member 服务
- predicates: # 断言
- - Path=/api/member/** # 如果前端请求路径包含 api/member,则应用这条路由规则
- filters: #过滤器
- - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # 将跳转路径中包含的api替换成空
+ - id: route_member # Third-party microservice routing rule
+ uri: lb://passjava-member # Load balancing, forward requests to the registered passjava-member service in the registry
+ predicates: # Predicates
+ - Path=/api/member/** # If the frontend request path includes api/member, this routing rule applies
+ filters: # Filters
+ - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # Replace "api" in the redirection path with empty
```
-这里有个关键字 `lb`,用到了全局过滤器 `LoadBalancerClientFilter`,当匹配到这个路由后,会将请求转发到 passjava-member 服务,且支持负载均衡转发,也就是先将 passjava-member 解析成实际的微服务的 host 和 port,然后再转发给实际的微服务。
+Here we have a keyword `lb`, which utilizes the global filter `LoadBalancerClientFilter`. When this route matches, the request will be forwarded to the passjava-member service, supporting load-balanced forwarding, meaning it first resolves passjava-member to the actual microservice's host and port before forwarding it to the actual microservice.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 支持限流吗?
+## Does Spring Cloud Gateway support rate limiting?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 自带了限流过滤器,对应的接口是 `RateLimiter`,`RateLimiter` 接口只有一个实现类 `RedisRateLimiter` (基于 Redis + Lua 实现的限流),提供的限流功能比较简易且不易使用。
+Spring Cloud Gateway comes with a built-in rate limiting filter, corresponding to the interface `RateLimiter`. The `RateLimiter` interface has only one implementation class `RedisRateLimiter` (a rate limiter based on Redis + Lua), providing relatively simple and not very user-friendly rate limiting functionality.
-从 Sentinel 1.6.0 版本开始,Sentinel 引入了 Spring Cloud Gateway 的适配模块,可以提供两种资源维度的限流:route 维度和自定义 API 维度。也就是说,Spring Cloud Gateway 可以结合 Sentinel 实现更强大的网关流量控制。
+Starting from Sentinel version 1.6.0, Sentinel introduced an adaptation module for Spring Cloud Gateway that provides two dimensions for rate limiting: route dimension and custom API dimension. This means Spring Cloud Gateway can combine with Sentinel to achieve more powerful gateway traffic control.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 如何自定义全局异常处理?
+## How do we customize global exception handling in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-在 SpringBoot 项目中,我们捕获全局异常只需要在项目中配置 `@RestControllerAdvice`和 `@ExceptionHandler`就可以了。不过,这种方式在 Spring Cloud Gateway 下不适用。
+In SpringBoot projects, we can capture global exceptions by simply configuring `@RestControllerAdvice` and `@ExceptionHandler`. However, this method is not applicable under Spring Cloud Gateway.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 提供了多种全局处理的方式,比较常用的一种是实现`ErrorWebExceptionHandler`并重写其中的`handle`方法。
+Spring Cloud Gateway provides various global handling methods, with a commonly used one being to implement `ErrorWebExceptionHandler` and override its `handle` method.
```java
@Order(-1)
@@ -148,10 +148,10 @@ public class GlobalErrorWebExceptionHandler implements ErrorWebExceptionHandler
}
```
-## 参考
+## References
-- Spring Cloud Gateway 官方文档:
-- Creating a custom Spring Cloud Gateway Filter:
-- 全局异常处理:
+- Official Spring Cloud Gateway documentation:
+- Creating a custom Spring Cloud Gateway Filter:
+- Global exception handling:
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md b/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
index 59725fa0521..34607fc1964 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
-title: 降级&熔断详解(付费)
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Downgrading & Circuit Breaking (Paid)
+category: High Availability
icon: circuit
---
-**降级&熔断** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html)中。
+The interview questions related to **Downgrading & Circuit Breaking** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to view detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled in [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html).

diff --git a/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md b/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
index f461f93e99b..44f49e5dc56 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
@@ -1,71 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 高可用系统设计指南
-category: 高可用
+title: High Availability System Design Guide
+category: High Availability
icon: design
---
-## 什么是高可用?可用性的判断标准是啥?
+## What is High Availability? What are the criteria for determining availability?
-高可用描述的是一个系统在大部分时间都是可用的,可以为我们提供服务的。高可用代表系统即使在发生硬件故障或者系统升级的时候,服务仍然是可用的。
+High availability describes a system that is available most of the time and can provide services to us. High availability means that the system remains available even during hardware failures or system upgrades.
-一般情况下,我们使用多少个 9 来评判一个系统的可用性,比如 99.9999% 就是代表该系统在所有的运行时间中只有 0.0001% 的时间是不可用的,这样的系统就是非常非常高可用的了!当然,也会有系统如果可用性不太好的话,可能连 9 都上不了。
+Generally, we use the number of nines to evaluate a system's availability. For example, 99.9999% means that the system is unavailable only 0.0001% of the time during all operational hours, making it extremely high availability! Of course, there are systems with poor availability that may not even reach a single nine.
-除此之外,系统的可用性还可以用某功能的失败次数与总的请求次数之比来衡量,比如对网站请求 1000 次,其中有 10 次请求失败,那么可用性就是 99%。
+In addition, the availability of a system can also be measured by the ratio of the number of failures of a certain function to the total number of requests. For example, if a website receives 1000 requests and 10 of them fail, the availability would be 99%.
-## 哪些情况会导致系统不可用?
+## What situations can lead to system unavailability?
-1. 黑客攻击;
-2. 硬件故障,比如服务器坏掉。
-3. 并发量/用户请求量激增导致整个服务宕掉或者部分服务不可用。
-4. 代码中的坏味道导致内存泄漏或者其他问题导致程序挂掉。
-5. 网站架构某个重要的角色比如 Nginx 或者数据库突然不可用。
-6. 自然灾害或者人为破坏。
-7. ……
+1. Hacker attacks;
+1. Hardware failures, such as server breakdowns.
+1. A surge in concurrent users/request volume causing the entire service to crash or parts of the service to become unavailable.
+1. Code smells leading to memory leaks or other issues causing the program to crash.
+1. An important component of the website architecture, such as Nginx or the database, suddenly becomes unavailable.
+1. Natural disasters or human destruction.
+1. ……
-## 有哪些提高系统可用性的方法?
+## What methods are there to improve system availability?
-### 注重代码质量,测试严格把关
+### Focus on Code Quality, Strict Testing
-我觉得这个是最最最重要的,代码质量有问题比如比较常见的内存泄漏、循环依赖都是对系统可用性极大的损害。大家都喜欢谈限流、降级、熔断,但是我觉得从代码质量这个源头把关是首先要做好的一件很重要的事情。如何提高代码质量?比较实际可用的就是 CodeReview,不要在乎每天多花的那 1 个小时左右的时间,作用可大着呢!
+I believe this is the most important aspect. Issues with code quality, such as common memory leaks and circular dependencies, can greatly harm system availability. Everyone likes to talk about rate limiting, degradation, and circuit breaking, but I think ensuring code quality from the source is a crucial first step. How can we improve code quality? A practical approach is Code Review; don't worry about spending an extra hour each day, as the benefits can be significant!
-另外,安利几个对提高代码质量有实际效果的神器:
+Additionally, here are a few tools that can effectively improve code quality:
- [Sonarqube](https://www.sonarqube.org/);
-- Alibaba 开源的 Java 诊断工具 [Arthas](https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/);
-- [阿里巴巴 Java 代码规范](https://github.com/alibaba/p3c)(Alibaba Java Code Guidelines);
-- IDEA 自带的代码分析等工具。
+- Alibaba's open-source Java diagnostic tool [Arthas](https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/);
+- [Alibaba Java Code Guidelines](https://github.com/alibaba/p3c);
+- Built-in code analysis tools in IDEA.
-### 使用集群,减少单点故障
+### Use Clusters to Reduce Single Points of Failure
-先拿常用的 Redis 举个例子!我们如何保证我们的 Redis 缓存高可用呢?答案就是使用集群,避免单点故障。当我们使用一个 Redis 实例作为缓存的时候,这个 Redis 实例挂了之后,整个缓存服务可能就挂了。使用了集群之后,即使一台 Redis 实例挂了,不到一秒就会有另外一台 Redis 实例顶上。
+Let's take the commonly used Redis as an example! How can we ensure our Redis cache is highly available? The answer is to use a cluster to avoid single points of failure. When we use a single Redis instance as a cache, if that instance goes down, the entire cache service may fail. With a cluster, even if one Redis instance fails, another instance will take over in less than a second.
-### 限流
+### Rate Limiting
-流量控制(flow control),其原理是监控应用流量的 QPS 或并发线程数等指标,当达到指定的阈值时对流量进行控制,以避免被瞬时的流量高峰冲垮,从而保障应用的高可用性。——来自 [alibaba-Sentinel](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel "Sentinel") 的 wiki。
+Flow control involves monitoring application traffic metrics such as QPS or concurrent thread counts. When a specified threshold is reached, traffic is controlled to avoid being overwhelmed by sudden traffic spikes, thereby ensuring high application availability. — From the [alibaba-Sentinel](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel "Sentinel") wiki.
-### 超时和重试机制设置
+### Timeout and Retry Mechanism Settings
-一旦用户请求超过某个时间的得不到响应,就抛出异常。这个是非常重要的,很多线上系统故障都是因为没有进行超时设置或者超时设置的方式不对导致的。我们在读取第三方服务的时候,尤其适合设置超时和重试机制。一般我们使用一些 RPC 框架的时候,这些框架都自带的超时重试的配置。如果不进行超时设置可能会导致请求响应速度慢,甚至导致请求堆积进而让系统无法再处理请求。重试的次数一般设为 3 次,再多次的重试没有好处,反而会加重服务器压力(部分场景使用失败重试机制会不太适合)。
+If a user request does not receive a response within a certain time, an exception should be thrown. This is very important; many online system failures occur due to the lack of timeout settings or incorrect timeout configurations. When reading from third-party services, it is especially suitable to set timeout and retry mechanisms. Generally, when using some RPC frameworks, these frameworks come with built-in timeout and retry configurations. Not setting a timeout can lead to slow response times and even request accumulation, making the system unable to process requests. The retry count is usually set to 3 times; retrying more than that is not beneficial and may increase server pressure (in some scenarios, using a failure retry mechanism may not be suitable).
-### 熔断机制
+### Circuit Breaker Mechanism
-超时和重试机制设置之外,熔断机制也是很重要的。 熔断机制说的是系统自动收集所依赖服务的资源使用情况和性能指标,当所依赖的服务恶化或者调用失败次数达到某个阈值的时候就迅速失败,让当前系统立即切换依赖其他备用服务。 比较常用的流量控制和熔断降级框架是 Netflix 的 Hystrix 和 alibaba 的 Sentinel。
+In addition to timeout and retry mechanism settings, the circuit breaker mechanism is also very important. The circuit breaker mechanism automatically collects resource usage and performance metrics of the dependent services. When the performance of the dependent service deteriorates or the number of failed calls reaches a certain threshold, it quickly fails, allowing the current system to switch to other backup services immediately. Commonly used flow control and circuit breaker frameworks include Netflix's Hystrix and Alibaba's Sentinel.
-### 异步调用
+### Asynchronous Calls
-异步调用的话我们不需要关心最后的结果,这样我们就可以用户请求完成之后就立即返回结果,具体处理我们可以后续再做,秒杀场景用这个还是蛮多的。但是,使用异步之后我们可能需要 **适当修改业务流程进行配合**,比如**用户在提交订单之后,不能立即返回用户订单提交成功,需要在消息队列的订单消费者进程真正处理完该订单之后,甚至出库后,再通过电子邮件或短信通知用户订单成功**。除了可以在程序中实现异步之外,我们常常还使用消息队列,消息队列可以通过异步处理提高系统性能(削峰、减少响应所需时间)并且可以降低系统耦合性。
-
-### 使用缓存
-
-如果我们的系统属于并发量比较高的话,如果我们单纯使用数据库的话,当大量请求直接落到数据库可能数据库就会直接挂掉。使用缓存缓存热点数据,因为缓存存储在内存中,所以速度相当地快!
-
-### 其他
-
-- **核心应用和服务优先使用更好的硬件**
-- **监控系统资源使用情况增加报警设置。**
-- **注意备份,必要时候回滚。**
-- **灰度发布:** 将服务器集群分成若干部分,每天只发布一部分机器,观察运行稳定没有故障,第二天继续发布一部分机器,持续几天才把整个集群全部发布完毕,期间如果发现问题,只需要回滚已发布的一部分服务器即可
-- **定期检查/更换硬件:** 如果不是购买的云服务的话,定期还是需要对硬件进行一波检查的,对于一些需要更换或者升级的硬件,要及时更换或者升级。
-- ……
-
-
+With asynchronous calls, we do not need to worry about the final result, allowing us to return results immediately after the user request is completed. The specific processing can be done later, which is quite common in flash sale scenarios. However, after using asynchronous calls, we may need to **appropriately modify the business process to accommodate** this, such as **not immediately returning a success message to the user after submitting an order. Instead, we should notify the user of the order success via email or SMS only after the order has been processed by the message queue's order consumer process, or even after it has been shipped**. In addition to implementing
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md b/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
index 41384457ccb..8d122a9b38f 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
-title: 接口幂等方案总结(付费)
-category: 高可用
+title: Summary of Idempotency Solutions for APIs (Paid)
+category: High Availability
icon: security-fill
---
-**接口幂等** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html)中。
+**Idempotency of APIs** related interview questions are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link for detailed introduction and joining methods), and have been compiled in [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html).

diff --git a/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md b/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
index 22db662eedf..c45eafd8b55 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
@@ -1,298 +1,63 @@
---
-title: 服务限流详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Rate Limiting
+category: High Availability
icon: limit_rate
---
-针对软件系统来说,限流就是对请求的速率进行限制,避免瞬时的大量请求击垮软件系统。毕竟,软件系统的处理能力是有限的。如果说超过了其处理能力的范围,软件系统可能直接就挂掉了。
+For software systems, rate limiting refers to the restriction of request rates to prevent a sudden influx of requests from overwhelming the system. After all, the processing capacity of a software system is limited. If the number of requests exceeds its processing capacity, the software system may crash.
-限流可能会导致用户的请求无法被正确处理或者无法立即被处理,不过,这往往也是权衡了软件系统的稳定性之后得到的最优解。
+Rate limiting may result in user requests not being processed correctly or not being processed immediately; however, this is often the optimal solution after weighing the stability of the software system.
-现实生活中,处处都有限流的实际应用,就比如排队买票是为了避免大量用户涌入购票而导致售票员无法处理。
+In real life, there are many practical applications of rate limiting. For example, queuing to buy tickets is intended to prevent a large number of users from flooding in and overwhelming the ticket seller.
-## 常见限流算法有哪些?
+## What are the Common Rate Limiting Algorithms?
-简单介绍 4 种非常好理解并且容易实现的限流算法!
+Here’s a brief introduction to four very understandable and easy-to-implement rate limiting algorithms!
-> 图片来源于 InfoQ 的一篇文章[《分布式服务限流实战,已经为你排好坑了》](https://www.infoq.cn/article/Qg2tX8fyw5Vt-f3HH673)。
+> Image source: An article from InfoQ [“Practical Distributed Service Rate Limiting, Already Prepared for You”](https://www.infoq.cn/article/Qg2tX8fyw5Vt-f3HH673).
-### 固定窗口计数器算法
+### Fixed Window Counter Algorithm
-固定窗口其实就是时间窗口,其原理是将时间划分为固定大小的窗口,在每个窗口内限制请求的数量或速率,即固定窗口计数器算法规定了系统单位时间处理的请求数量。
+A fixed window is essentially a time window. Its principle is to divide time into fixed-size windows, limiting the number of requests or the rate within each window. The fixed window counter algorithm specifies the number of requests the system can handle in a unit of time.
-假如我们规定系统中某个接口 1 分钟只能被访问 33 次的话,使用固定窗口计数器算法的实现思路如下:
+For example, if we specify that a certain interface in the system can only be accessed 33 times in one minute, the implementation idea of the fixed window counter algorithm is as follows:
-- 将时间划分固定大小窗口,这里是 1 分钟一个窗口。
-- 给定一个变量 `counter` 来记录当前接口处理的请求数量,初始值为 0(代表接口当前 1 分钟内还未处理请求)。
-- 1 分钟之内每处理一个请求之后就将 `counter+1` ,当 `counter=33` 之后(也就是说在这 1 分钟内接口已经被访问 33 次的话),后续的请求就会被全部拒绝。
-- 等到 1 分钟结束后,将 `counter` 重置 0,重新开始计数。
+- Divide time into fixed-size windows, here it is one window per minute.
+- Set a variable `counter` to record the number of requests processed by the current interface, with an initial value of 0 (indicating that no requests have been processed in the current minute).
+- For each request processed within one minute, increment `counter` by 1. Once `counter=33` (meaning the interface has been accessed 33 times in this minute), all subsequent requests will be rejected.
+- At the end of one minute, reset `counter` to 0 and start counting again.
-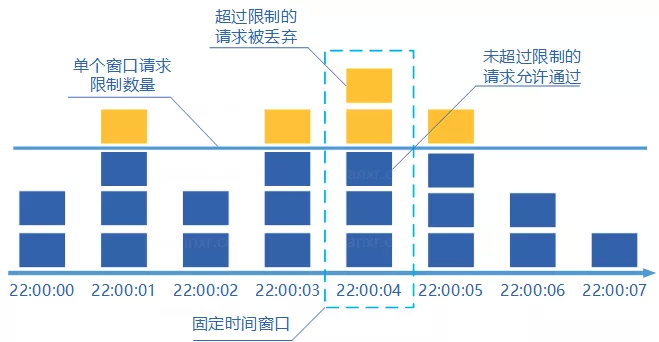
+
-优点:实现简单,易于理解。
+Advantages: Simple to implement and easy to understand.
-缺点:
+Disadvantages:
-- 限流不够平滑。例如,我们限制某个接口每分钟只能访问 30 次,假设前 30 秒就有 30 个请求到达的话,那后续 30 秒将无法处理请求,这是不可取的,用户体验极差!
-- 无法保证限流速率,因而无法应对突然激增的流量。例如,我们限制某个接口 1 分钟只能访问 1000 次,该接口的 QPS 为 500,前 55s 这个接口 1 个请求没有接收,后 1s 突然接收了 1000 个请求。然后,在当前场景下,这 1000 个请求在 1s 内是没办法被处理的,系统直接就被瞬时的大量请求给击垮了。
+- Rate limiting is not smooth enough. For example, if we limit a certain interface to only 30 accesses per minute, and 30 requests arrive in the first 30 seconds, then no requests can be processed in the following 30 seconds, which is undesirable and results in a poor user experience!
+- It cannot guarantee the rate limiting speed, thus unable to cope with sudden surges in traffic. For instance, if we limit a certain interface to only 1000 accesses per minute, and the QPS of that interface is 500, if no requests are received in the first 55 seconds, but suddenly 1000 requests arrive in the last second, these 1000 requests cannot be processed in that second, and the system will be overwhelmed by the sudden influx of requests.
-### 滑动窗口计数器算法
+### Sliding Window Counter Algorithm
-**滑动窗口计数器算法** 算的上是固定窗口计数器算法的升级版,限流的颗粒度更小。
+**The sliding window counter algorithm** can be considered an upgraded version of the fixed window counter algorithm, with finer granularity for rate limiting.
-滑动窗口计数器算法相比于固定窗口计数器算法的优化在于:**它把时间以一定比例分片** 。
+The optimization of the sliding window counter algorithm compared to the fixed window counter algorithm is that **it divides time into segments at a certain ratio**.
-例如我们的接口限流每分钟处理 60 个请求,我们可以把 1 分钟分为 60 个窗口。每隔 1 秒移动一次,每个窗口一秒只能处理不大于 `60(请求数)/60(窗口数)` 的请求, 如果当前窗口的请求计数总和超过了限制的数量的话就不再处理其他请求。
+For example, if our interface limits processing to 60 requests per minute, we can divide one minute into 60 windows. Each window can only handle no more than `60(requests)/60(window)` requests per second. If the total request count in the current window exceeds the limit, no further requests will be processed.
-很显然, **当滑动窗口的格子划分的越多,滑动窗口的滚动就越平滑,限流的统计就会越精确。**
+Clearly, **the more segments the sliding window is divided into, the smoother the sliding window's movement will be, and the more accurate the rate limiting statistics will be.**
-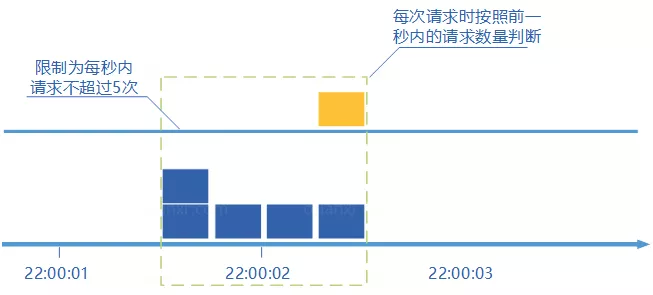
+
-优点:
+Advantages:
-- 相比于固定窗口算法,滑动窗口计数器算法可以应对突然激增的流量。
-- 相比于固定窗口算法,滑动窗口计数器算法的颗粒度更小,可以提供更精确的限流控制。
+- Compared to the fixed window algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm can handle sudden surges in traffic.
+- Compared to the fixed window algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm has finer granularity, allowing for more precise rate limiting control.
-缺点:
+Disadvantages:
-- 与固定窗口计数器算法类似,滑动窗口计数器算法依然存在限流不够平滑的问题。
-- 相比较于固定窗口计数器算法,滑动窗口计数器算法实现和理解起来更复杂一些。
+- Similar to the fixed window counter algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm still suffers from the issue of insufficiently smooth rate limiting.
+- Compared to the fixed window counter algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm is more complex to implement and understand.
-### 漏桶算法
+### Leaky Bucket Algorithm
-我们可以把发请求的动作比作成注水到桶中,我们处理请求的过程可以比喻为漏桶漏水。我们往桶中以任意速率流入水,以一定速率流出水。当水超过桶流量则丢弃,因为桶容量是不变的,保证了整体的速率。
-
-如果想要实现这个算法的话也很简单,准备一个队列用来保存请求,然后我们定期从队列中拿请求来执行就好了(和消息队列削峰/限流的思想是一样的)。
-
-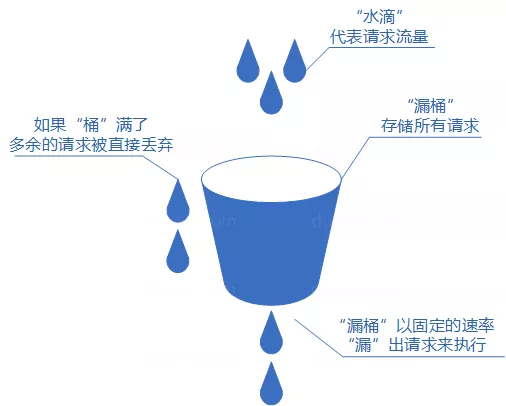
-
-优点:
-
-- 实现简单,易于理解。
-- 可以控制限流速率,避免网络拥塞和系统过载。
-
-缺点:
-
-- 无法应对突然激增的流量,因为只能以固定的速率处理请求,对系统资源利用不够友好。
-- 桶流入水(发请求)的速率如果一直大于桶流出水(处理请求)的速率的话,那么桶会一直是满的,一部分新的请求会被丢弃,导致服务质量下降。
-
-实际业务场景中,基本不会使用漏桶算法。
-
-### 令牌桶算法
-
-令牌桶算法也比较简单。和漏桶算法算法一样,我们的主角还是桶(这限流算法和桶过不去啊)。不过现在桶里装的是令牌了,请求在被处理之前需要拿到一个令牌,请求处理完毕之后将这个令牌丢弃(删除)。我们根据限流大小,按照一定的速率往桶里添加令牌。如果桶装满了,就不能继续往里面继续添加令牌了。
-
-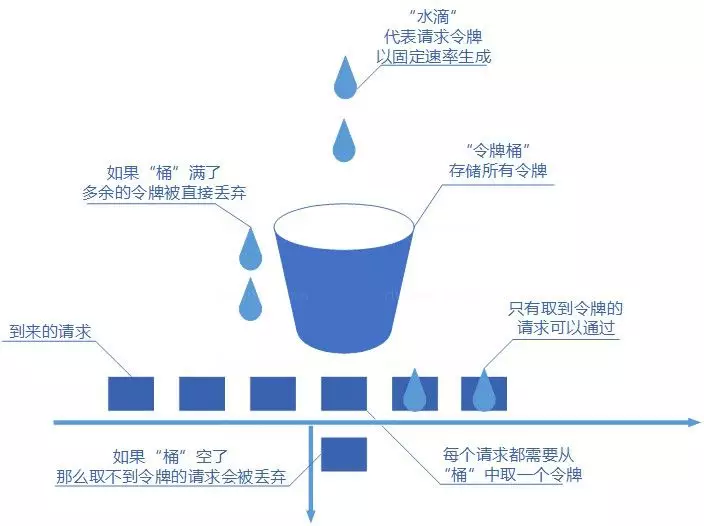
-
-优点:
-
-- 可以限制平均速率和应对突然激增的流量。
-- 可以动态调整生成令牌的速率。
-
-缺点:
-
-- 如果令牌产生速率和桶的容量设置不合理,可能会出现问题比如大量的请求被丢弃、系统过载。
-- 相比于其他限流算法,实现和理解起来更复杂一些。
-
-## 针对什么来进行限流?
-
-实际项目中,还需要确定限流对象,也就是针对什么来进行限流。常见的限流对象如下:
-
-- IP :针对 IP 进行限流,适用面较广,简单粗暴。
-- 业务 ID:挑选唯一的业务 ID 以实现更针对性地限流。例如,基于用户 ID 进行限流。
-- 个性化:根据用户的属性或行为,进行不同的限流策略。例如, VIP 用户不限流,而普通用户限流。根据系统的运行指标(如 QPS、并发调用数、系统负载等),动态调整限流策略。例如,当系统负载较高的时候,控制每秒通过的请求减少。
-
-针对 IP 进行限流是目前比较常用的一个方案。不过,实际应用中需要注意用户真实 IP 地址的正确获取。常用的真实 IP 获取方法有 X-Forwarded-For 和 TCP Options 字段承载真实源 IP 信息。虽然 X-Forwarded-For 字段可能会被伪造,但因为其实现简单方便,很多项目还是直接用的这种方法。
-
-除了我上面介绍到的限流对象之外,还有一些其他较为复杂的限流对象策略,比如阿里的 Sentinel 还支持 [基于调用关系的限流](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/流量控制#基于调用关系的流量控制)(包括基于调用方限流、基于调用链入口限流、关联流量限流等)以及更细维度的 [热点参数限流](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/热点参数限流)(实时的统计热点参数并针对热点参数的资源调用进行流量控制)。
-
-另外,一个项目可以根据具体的业务需求选择多种不同的限流对象搭配使用。
-
-## 单机限流怎么做?
-
-单机限流针对的是单体架构应用。
-
-单机限流可以直接使用 Google Guava 自带的限流工具类 `RateLimiter` 。 `RateLimiter` 基于令牌桶算法,可以应对突发流量。
-
-> Guava 地址:
-
-除了最基本的令牌桶算法(平滑突发限流)实现之外,Guava 的`RateLimiter`还提供了 **平滑预热限流** 的算法实现。
-
-平滑突发限流就是按照指定的速率放令牌到桶里,而平滑预热限流会有一段预热时间,预热时间之内,速率会逐渐提升到配置的速率。
-
-我们下面通过两个简单的小例子来详细了解吧!
-
-我们直接在项目中引入 Guava 相关的依赖即可使用。
-
-```xml
-
- com.google.guava
- guava
- 31.0.1-jre
-
-```
-
-下面是一个简单的 Guava 平滑突发限流的 Demo。
-
-```java
-import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
-
-/**
- * 微信搜 JavaGuide 回复"面试突击"即可免费领取个人原创的 Java 面试手册
- *
- * @author Guide哥
- * @date 2021/10/08 19:12
- **/
-public class RateLimiterDemo {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 1s 放 5 个令牌到桶里也就是 0.2s 放 1个令牌到桶里
- RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5);
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- double sleepingTime = rateLimiter.acquire(1);
- System.out.printf("get 1 tokens: %ss%n", sleepingTime);
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-输出:
-
-```bash
-get 1 tokens: 0.0s
-get 1 tokens: 0.188413s
-get 1 tokens: 0.197811s
-get 1 tokens: 0.198316s
-get 1 tokens: 0.19864s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199363s
-get 1 tokens: 0.193997s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199623s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199357s
-get 1 tokens: 0.195676s
-```
-
-下面是一个简单的 Guava 平滑预热限流的 Demo。
-
-```java
-import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
-import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
-/**
- * 微信搜 JavaGuide 回复"面试突击"即可免费领取个人原创的 Java 面试手册
- *
- * @author Guide哥
- * @date 2021/10/08 19:12
- **/
-public class RateLimiterDemo {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 1s 放 5 个令牌到桶里也就是 0.2s 放 1个令牌到桶里
- // 预热时间为3s,也就说刚开始的 3s 内发牌速率会逐渐提升到 0.2s 放 1 个令牌到桶里
- RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
- double sleepingTime = rateLimiter.acquire(1);
- System.out.printf("get 1 tokens: %sds%n", sleepingTime);
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-输出:
-
-```bash
-get 1 tokens: 0.0s
-get 1 tokens: 0.561919s
-get 1 tokens: 0.516931s
-get 1 tokens: 0.463798s
-get 1 tokens: 0.41286s
-get 1 tokens: 0.356172s
-get 1 tokens: 0.300489s
-get 1 tokens: 0.252545s
-get 1 tokens: 0.203996s
-get 1 tokens: 0.198359s
-```
-
-另外,**Bucket4j** 是一个非常不错的基于令牌/漏桶算法的限流库。
-
-> Bucket4j 地址:
-
-相对于,Guava 的限流工具类来说,Bucket4j 提供的限流功能更加全面。不仅支持单机限流和分布式限流,还可以集成监控,搭配 Prometheus 和 Grafana 使用。
-
-不过,毕竟 Guava 也只是一个功能全面的工具类库,其提供的开箱即用的限流功能在很多单机场景下还是比较实用的。
-
-Spring Cloud Gateway 中自带的单机限流的早期版本就是基于 Bucket4j 实现的。后来,替换成了 **Resilience4j**。
-
-Resilience4j 是一个轻量级的容错组件,其灵感来自于 Hystrix。自[Netflix 宣布不再积极开发 Hystrix](https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/commit/a7df971cbaddd8c5e976b3cc5f14013fe6ad00e6) 之后,Spring 官方和 Netflix 都更推荐使用 Resilience4j 来做限流熔断。
-
-> Resilience4j 地址:
-
-一般情况下,为了保证系统的高可用,项目的限流和熔断都是要一起做的。
-
-Resilience4j 不仅提供限流,还提供了熔断、负载保护、自动重试等保障系统高可用开箱即用的功能。并且,Resilience4j 的生态也更好,很多网关都使用 Resilience4j 来做限流熔断的。
-
-因此,在绝大部分场景下 Resilience4j 或许会是更好的选择。如果是一些比较简单的限流场景的话,Guava 或者 Bucket4j 也是不错的选择。
-
-## 分布式限流怎么做?
-
-分布式限流针对的分布式/微服务应用架构应用,在这种架构下,单机限流就不适用了,因为会存在多种服务,并且一种服务也可能会被部署多份。
-
-分布式限流常见的方案:
-
-- **借助中间件限流**:可以借助 Sentinel 或者使用 Redis 来自己实现对应的限流逻辑。
-- **网关层限流**:比较常用的一种方案,直接在网关层把限流给安排上了。不过,通常网关层限流通常也需要借助到中间件/框架。就比如 Spring Cloud Gateway 的分布式限流实现`RedisRateLimiter`就是基于 Redis+Lua 来实现的,再比如 Spring Cloud Gateway 还可以整合 Sentinel 来做限流。
-
-如果你要基于 Redis 来手动实现限流逻辑的话,建议配合 Lua 脚本来做。
-
-**为什么建议 Redis+Lua 的方式?** 主要有两点原因:
-
-- **减少了网络开销**:我们可以利用 Lua 脚本来批量执行多条 Redis 命令,这些 Redis 命令会被提交到 Redis 服务器一次性执行完成,大幅减小了网络开销。
-- **原子性**:一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰。
-
-我这里就不放具体的限流脚本代码了,网上也有很多现成的优秀的限流脚本供你参考,就比如 Apache 网关项目 ShenYu 的 RateLimiter 限流插件就基于 Redis + Lua 实现了令牌桶算法/并发令牌桶算法、漏桶算法、滑动窗口算法。
-
-> ShenYu 地址:
-
-
-
-另外,如果不想自己写 Lua 脚本的话,也可以直接利用 Redisson 中的 `RRateLimiter` 来实现分布式限流,其底层实现就是基于 Lua 代码+令牌桶算法。
-
-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,比如 Java 中常用的数据结构实现、分布式锁、延迟队列等等。并且,Redisson 还支持 Redis 单机、Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster 等多种部署架构。
-
-`RRateLimiter` 的使用方式非常简单。我们首先需要获取一个`RRateLimiter`对象,直接通过 Redisson 客户端获取即可。然后,设置限流规则就好。
-
-```java
-// 创建一个 Redisson 客户端实例
-RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create();
-// 获取一个名为 "javaguide.limiter" 的限流器对象
-RRateLimiter rateLimiter = redissonClient.getRateLimiter("javaguide.limiter");
-// 尝试设置限流器的速率为每小时 100 次
-// RateType 有两种,OVERALL是全局限流,ER_CLIENT是单Client限流(可以认为就是单机限流)
-rateLimiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 100, 1, RateIntervalUnit.HOURS);
-```
-
-接下来我们调用`acquire()`方法或`tryAcquire()`方法即可获取许可。
-
-```java
-// 获取一个许可,如果超过限流器的速率则会等待
-// acquire()是同步方法,对应的异步方法:acquireAsync()
-rateLimiter.acquire(1);
-// 尝试在 5 秒内获取一个许可,如果成功则返回 true,否则返回 false
-// tryAcquire()是同步方法,对应的异步方法:tryAcquireAsync()
-boolean res = rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
-```
-
-## 总结
-
-这篇文章主要介绍了常见的限流算法、限流对象的选择以及单机限流和分布式限流分别应该怎么做。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 服务治理之轻量级熔断框架 Resilience4j:
-- 超详细的 Guava RateLimiter 限流原理解析:
-- 实战 Spring Cloud Gateway 之限流篇 👍:
-- 详解 Redisson 分布式限流的实现原理:
-- 一文详解 Java 限流接口实现 - 阿里云开发者:
-- 分布式限流方案的探索与实践 - 腾讯云开发者:
-
-
+We can compare the action of sending requests to pouring water into a bucket, while the process of handling requests can be likened to water leaking from the bucket. We can pour water into the bucket at any rate, and it leaks out at a certain rate. If the water exceeds the bucket's capacity, it will
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md b/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
index 47201441d7e..0cb09454396 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
@@ -1,178 +1,178 @@
---
-title: 性能测试入门
-category: 高可用
+title: Introduction to Performance Testing
+category: High Availability
icon: et-performance
---
-性能测试一般情况下都是由测试这个职位去做的,那还需要我们开发学这个干嘛呢?了解性能测试的指标、分类以及工具等知识有助于我们更好地去写出性能更好的程序,另外作为开发这个角色,如果你会性能测试的话,相信也会为你的履历加分不少。
+Performance testing is generally conducted by testers, so why should developers learn about it? Understanding performance testing metrics, classifications, and tools helps us write better-performing programs. Furthermore, if you as a developer possess performance testing skills, it will undoubtedly enhance your resume.
-这篇文章是我会结合自己的实际经历以及在测试这里取的经所得,除此之外,我还借鉴了一些优秀书籍,希望对你有帮助。
+This article combines my personal experiences and insights from testing, along with references to some excellent books, hoping to be of help to you.
-## 不同角色看网站性能
+## Perspectives on Website Performance from Different Roles
-### 用户
+### Users
-当用户打开一个网站的时候,最关注的是什么?当然是网站响应速度的快慢。比如我们点击了淘宝的主页,淘宝需要多久将首页的内容呈现在我的面前,我点击了提交订单按钮需要多久返回结果等等。
+When a user opens a website, what do they pay the most attention to? Certainly, it is the website's response speed. For instance, when we click on the homepage of Taobao, how long does it take for Taobao to display the content? How long does it take to return a result after clicking the "submit order" button, etc.
-所以,用户在体验我们系统的时候往往根据你的响应速度的快慢来评判你的网站的性能。
+Therefore, when users experience our system, they often judge the performance of your website based on its response speed.
-### 开发人员
+### Developers
-用户与开发人员都关注速度,这个速度实际上就是我们的系统**处理用户请求的速度**。
+Both users and developers focus on speed, which truly refers to our system's **processing speed of user requests**.
-开发人员一般情况下很难直观的去评判自己网站的性能,我们往往会根据网站当前的架构以及基础设施情况给一个大概的值,比如:
+Developers generally find it challenging to intuitively assess the performance of their website. We often provide an approximate value based on the current architecture and infrastructure of the website, for instance:
-1. 项目架构是分布式的吗?
-2. 用到了缓存和消息队列没有?
-3. 高并发的业务有没有特殊处理?
-4. 数据库设计是否合理?
-5. 系统用到的算法是否还需要优化?
-6. 系统是否存在内存泄露的问题?
-7. 项目使用的 Redis 缓存多大?服务器性能如何?用的是机械硬盘还是固态硬盘?
-8. ……
+1. Is the project architecture distributed?
+1. Are caching and messaging queues utilized?
+1. Are there any special handling for high-concurrency business?
+1. Is the database design reasonable?
+1. Do the algorithms used in the system need optimization?
+1. Does the system have memory leak issues?
+1. How large is the Redis cache used in the project? What is the server performance like? Is it using a mechanical hard disk or a solid-state drive?
+1. ……
-### 测试人员
+### Testers
-测试人员一般会根据性能测试工具来测试,然后一般会做出一个表格。这个表格可能会涵盖下面这些重要的内容:
+Testers typically conduct tests according to performance testing tools and usually create a table. This table might cover important contents like:
-1. 响应时间;
-2. 请求成功率;
-3. 吞吐量;
-4. ……
+1. Response time;
+1. Request success rate;
+1. Throughput;
+1. ……
-### 运维人员
+### Operations Personnel
-运维人员会倾向于根据基础设施和资源的利用率来判断网站的性能,比如我们的服务器资源使用是否合理、数据库资源是否存在滥用的情况、当然,这是传统的运维人员,现在 Devops 火起来后,单纯干运维的很少了。我们这里暂且还保留有这个角色。
+Operations personnel tend to evaluate the website's performance based on infrastructure and resource utilization rates. For instance, they might analyze whether resource usage on our servers is reasonable or whether there is abuse of database resources. Of course, this is the traditional role of operations personnel. With the rise of DevOps, pure operations roles are less common now, although we still acknowledge this role for the time being.
-## 性能测试需要注意的点
+## Key Points to Note in Performance Testing
-几乎没有文章在讲性能测试的时候提到这个问题,大家都会讲如何去性能测试,有哪些性能测试指标这些东西。
+Few articles address this issue when discussing performance testing. Most articles focus on how to conduct performance tests and what performance testing metrics exist.
-### 了解系统的业务场景
+### Understanding the Business Context of the System
-**性能测试之前更需要你了解当前的系统的业务场景。** 对系统业务了解的不够深刻,我们很容易犯测试方向偏执的错误,从而导致我们忽略了对系统某些更需要性能测试的地方进行测试。比如我们的系统可以为用户提供发送邮件的功能,用户配置成功邮箱后只需输入相应的邮箱之后就能发送,系统每天大概能处理上万次发邮件的请求。很多人看到这个可能就直接开始使用相关工具测试邮箱发送接口,但是,发送邮件这个场景可能不是当前系统的性能瓶颈,这么多人用我们的系统发邮件, 还可能有很多人一起发邮件,单单这个场景就这么人用,那用户管理可能才是性能瓶颈吧!
+**Before performance testing, it is crucial to comprehend the business context of the current system.** If our understanding of the system's business is not deep enough, we easily make biased testing direction mistakes, leading us to overlook certain areas of the system that need performance testing. For example, if our system provides users with the ability to send emails, after setting up a successful email address, users can simply input the corresponding email to send, and the system can handle thousands of email-sending requests daily. Many would immediately begin using relevant tools to test the email-sending interface, but sending emails may not currently be the performance bottleneck of the system. With so many users sending emails, there might be many others sending emails simultaneously, so user management could be the actual performance bottleneck!
-### 历史数据非常有用
+### Historical Data is Very Useful
-当前系统所留下的历史数据非常重要,一般情况下,我们可以通过相应的些历史数据初步判定这个系统哪些接口调用的比较多、哪些服务承受的压力最大,这样的话,我们就可以针对这些地方进行更细致的性能测试与分析。
+The historical data left by the current system is very important. Generally, we can use relevant historical data to initially determine which interfaces are being called frequently and which services are under the most pressure. This allows us to conduct more detailed performance testing and analysis targeted at these areas.
-另外,这些地方也就像这个系统的一个短板一样,优化好了这些地方会为我们的系统带来质的提升。
+Moreover, these areas are like weak points in the system; optimizing them can result in a significant qualitative improvement for our system.
-## 常见性能指标
+## Common Performance Metrics
-### 响应时间
+### Response Time
-**响应时间 RT(Response-time)就是用户发出请求到用户收到系统处理结果所需要的时间。**
+**Response Time RT (Response-time) is the time taken from when a user issues a request to when the user receives the system's processed result.**
-RT 是一个非常重要且直观的指标,RT 数值大小直接反应了系统处理用户请求速度的快慢。
+RT is a very important and intuitive metric. The size of the RT value directly reflects how quickly the system processes user requests.
-### 并发数
+### Concurrent Users
-**并发数可以简单理解为系统能够同时供多少人访问使用也就是说系统同时能处理的请求数量。**
+**Concurrent users can be simply understood as the number of people the system can support to access and use simultaneously, meaning the number of requests the system can handle at the same time.**
-并发数反应了系统的负载能力。
+The number of concurrent users reflects the system's load capacity.
-### QPS 和 TPS
+### QPS and TPS
-- **QPS(Query Per Second)** :服务器每秒可以执行的查询次数;
-- **TPS(Transaction Per Second)** :服务器每秒处理的事务数(这里的一个事务可以理解为客户发出请求到收到服务器的过程);
+- **QPS (Queries Per Second)**: The number of queries the server can execute per second;
+- **TPS (Transactions Per Second)**: The number of transactions processed by the server per second (a transaction can be understood as the process from when a customer issues a request to when they receive a response from the server).
-书中是这样描述 QPS 和 TPS 的区别的。
+The book describes the difference between QPS and TPS as follows:
-> QPS vs TPS:QPS 基本类似于 TPS,但是不同的是,对于一个页面的一次访问,形成一个 TPS;但一次页面请求,可能产生多次对服务器的请求,服务器对这些请求,就可计入“QPS”之中。如,访问一个页面会请求服务器 2 次,一次访问,产生一个“T”,产生 2 个“Q”。
+> QPS vs TPS: QPS is quite similar to TPS, but the difference lies in that one access to a page counts as one TPS; however, a single page request may generate multiple requests to the server, which can be counted as "QPS." For example, if accessing a page generates 2 requests to the server, one access would result in one "T" and two "Q".
-### 吞吐量
+### Throughput
-**吞吐量指的是系统单位时间内系统处理的请求数量。**
+**Throughput refers to the number of requests processed by the system within a unit of time.**
-一个系统的吞吐量与请求对系统的资源消耗等紧密关联。请求对系统资源消耗越多,系统吞吐能力越低,反之则越高。
+The throughput of a system is closely related to the resource consumption of requests. The more resources a request consumes from the system, the lower the system's throughput capability, and vice versa.
-TPS、QPS 都是吞吐量的常用量化指标。
+TPS and QPS are commonly used quantitative metrics for throughput.
-- **QPS(TPS)** = 并发数/平均响应时间(RT)
-- **并发数** = QPS \* 平均响应时间(RT)
+- **QPS (TPS)** = Concurrent Users / Average Response Time (RT)
+- **Concurrent Users** = QPS * Average Response Time (RT)
-## 系统活跃度指标
+## System Activity Indicators
-### PV(Page View)
+### PV (Page View)
-访问量, 即页面浏览量或点击量,衡量网站用户访问的网页数量;在一定统计周期内用户每打开或刷新一个页面就记录 1 次,多次打开或刷新同一页面则浏览量累计。UV 从网页打开的数量/刷新的次数的角度来统计的。
+Page Views refer to website traffic or click counts, measuring the number of pages visited by users; each time a user opens or refreshes a page within a specific statistical period, it records one instance; multiple openings or refreshes of the same page accumulate the view count. UV is counted from the perspective of the number of pages opened/refreshed.
-### UV(Unique Visitor)
+### UV (Unique Visitor)
-独立访客,统计 1 天内访问某站点的用户数。1 天内相同访客多次访问网站,只计算为 1 个独立访客。UV 是从用户个体的角度来统计的。
+Unique Visitors refer to the count of users visiting a site within one day. If the same visitor accesses the site multiple times in one day, they are only counted as one unique visitor. UV is counted from the perspective of individual users.
-### DAU(Daily Active User)
+### DAU (Daily Active Users)
-日活跃用户数量。
+The number of daily active users.
-### MAU(monthly active users)
+### MAU (Monthly Active Users)
-月活跃用户人数。
+The number of monthly active users.
-举例:某网站 DAU 为 1200w, 用户日均使用时长 1 小时,RT 为 0.5s,求并发量和 QPS。
+For example, if a website has a DAU of 12 million, with an average usage time of 1 hour per day, and an RT of 0.5s, we can calculate the concurrent user load and QPS.
-平均并发量 = DAU(1200w)\* 日均使用时长(1 小时,3600 秒) /一天的秒数(86400)=1200w/24 = 50w
+Average concurrent users = DAU (12 million) * Average usage time (1 hour, 3600 seconds) / Seconds in a day (86400) = 12 million / 24 = 500,000
-真实并发量(考虑到某些时间段使用人数比较少) = DAU(1200w)\* 日均使用时长(1 小时,3600 秒) /一天的秒数-访问量比较小的时间段假设为 8 小时(57600)=1200w/16 = 75w
+Real concurrent users (considering lower usage during certain periods) = DAU (12 million) * Average usage time (1 hour, 3600 seconds) / Seconds in a day - assume 8 hours (57600) for low access time = 12 million / 16 = 750,000
-峰值并发量 = 平均并发量 \* 6 = 300w
+Peak concurrent users = Average concurrent users * 6 = 3 million
-QPS = 真实并发量/RT = 75W/0.5=150w/s
+QPS = Real concurrent users / RT = 750,000 / 0.5 = 1.5 million/s
-## 性能测试分类
+## Classification of Performance Testing
-### 性能测试
+### Performance Testing
-性能测试方法是通过测试工具模拟用户请求系统,目的主要是为了测试系统的性能是否满足要求。通俗地说,这种方法就是要在特定的运行条件下验证系统的能力状态。
+Performance testing methods simulate user requests to the system using testing tools, primarily to verify whether the system's performance meets the requirements. Simply put, this method aims to validate the system's capacity under specific operating conditions.
-性能测试是你在对系统性能已经有了解的前提之后进行的,并且有明确的性能指标。
+Performance testing is carried out after you have some understanding of system performance, with clear performance metrics.
-### 负载测试
+### Load Testing
-对被测试的系统继续加大请求压力,直到服务器的某个资源已经达到饱和了,比如系统的缓存已经不够用了或者系统的响应时间已经不满足要求了。
+Continuously increasing request pressure on the tested system until some resource on the server reaches saturation, such as when system caching is insufficient or the response time is no longer acceptable.
-负载测试说白点就是测试系统的上限。
+In simpler terms, load testing tests the limits of the system.
-### 压力测试
+### Stress Testing
-不去管系统资源的使用情况,对系统继续加大请求压力,直到服务器崩溃无法再继续提供服务。
+Pressuring the system with requests regardless of resource utilization until the server crashes and can no longer provide services.
-### 稳定性测试
+### Stability Testing
-模拟真实场景,给系统一定压力,看看业务是否能稳定运行。
+Simulating real scenarios by applying a certain amount of pressure on the system to see if the business can operate stably.
-## 常用性能测试工具
+## Commonly Used Performance Testing Tools
-### 后端常用
+### Common Backend Tools
-既然系统设计涉及到系统性能方面的问题,那在面试的时候,面试官就很可能会问:**你是如何进行性能测试的?**
+Since system design involves performance-related issues, interviewers are likely to ask, **How do you conduct performance testing?**
-推荐 4 个比较常用的性能测试工具:
+Here are four commonly used performance testing tools:
-1. **Jmeter** :Apache JMeter 是 JAVA 开发的性能测试工具。
-2. **LoadRunner**:一款商业的性能测试工具。
-3. **Galtling** :一款基于 Scala 开发的高性能服务器性能测试工具。
-4. **ab** :全称为 Apache Bench 。Apache 旗下的一款测试工具,非常实用。
+1. **JMeter**: Apache JMeter is a performance testing tool developed in Java.
+1. **LoadRunner**: A commercial performance testing tool.
+1. **Gatling**: A high-performance server performance testing tool developed in Scala.
+1. **ab**: Full name is Apache Bench. It is a testing tool under the Apache umbrella and is very practical.
-没记错的话,除了 **LoadRunner** 其他几款性能测试工具都是开源免费的。
+If I remember correctly, all the performance testing tools mentioned, except for **LoadRunner**, are open-source and free.
-### 前端常用
+### Common Frontend Tools
-1. **Fiddler**:抓包工具,它可以修改请求的数据,甚至可以修改服务器返回的数据,功能非常强大,是 Web 调试的利器。
-2. **HttpWatch**: 可用于录制 HTTP 请求信息的工具。
+1. **Fiddler**: A packet capturing tool that can modify request data, and even server response data, with powerful features; it's an essential tool for web debugging.
+1. **HttpWatch**: A tool for recording HTTP request information.
-## 常见的性能优化策略
+## Common Performance Optimization Strategies
-性能优化之前我们需要对请求经历的各个环节进行分析,排查出可能出现性能瓶颈的地方,定位问题。
+Before performance optimization, we need to analyze each stage of the requests to identify potential performance bottlenecks and locate issues.
-下面是一些性能优化时,我经常拿来自问的一些问题:
+Here are some questions I often ask myself during performance optimization:
-1. 系统是否需要缓存?
-2. 系统架构本身是不是就有问题?
-3. 系统是否存在死锁的地方?
-4. 系统是否存在内存泄漏?(Java 的自动回收内存虽然很方便,但是,有时候代码写的不好真的会造成内存泄漏)
-5. 数据库索引使用是否合理?
-6. ……
+1. Does the system require caching?
+1. Does the system architecture itself have problems?
+1. Are there deadlock situations in the system?
+1. Does the system have memory leaks? (While Java’s automatic memory recovery is very convenient, poorly written code can sometimes lead to memory leaks.)
+1. Is the database indexing reasonable?
+1. ……
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md b/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
index 9d14d726675..1f40115ee83 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
@@ -1,47 +1,45 @@
---
-title: 冗余设计详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redundant Design
+category: High Availability
icon: cluster
---
-冗余设计是保证系统和数据高可用的最常的手段。
+Redundant design is the most common means to ensure high availability of systems and data.
-对于服务来说,冗余的思想就是相同的服务部署多份,如果正在使用的服务突然挂掉的话,系统可以很快切换到备份服务上,大大减少系统的不可用时间,提高系统的可用性。
+For services, the idea of redundancy is to deploy multiple instances of the same service. If the currently used service suddenly fails, the system can quickly switch to a backup service, significantly reducing downtime and improving system availability.
-对于数据来说,冗余的思想就是相同的数据备份多份,这样就可以很简单地提高数据的安全性。
+For data, the idea of redundancy is to have multiple backups of the same data, which can easily enhance data security.
-实际上,日常生活中就有非常多的冗余思想的应用。
+In fact, there are many applications of redundancy in daily life.
-拿我自己来说,我对于重要文件的保存方法就是冗余思想的应用。我日常所使用的重要文件都会同步一份在 GitHub 以及个人云盘上,这样就可以保证即使电脑硬盘损坏,我也可以通过 GitHub 或者个人云盘找回自己的重要文件。
+For example, my method of saving important files is an application of redundancy. I synchronize important files I use daily to both GitHub and my personal cloud storage, ensuring that even if my computer's hard drive fails, I can retrieve my important files from GitHub or my personal cloud.
-高可用集群(High Availability Cluster,简称 HA Cluster)、同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活和异地多活是冗余思想在高可用系统设计中最典型的应用。
+High Availability Cluster (HA Cluster), local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, and remote active-active are the most typical applications of redundancy in high availability system design.
-- **高可用集群** : 同一份服务部署两份或者多份,当正在使用的服务突然挂掉的话,可以切换到另外一台服务,从而保证服务的高可用。
-- **同城灾备**:一整个集群可以部署在同一个机房,而同城灾备中相同服务部署在同一个城市的不同机房中。并且,备用服务不处理请求。这样可以避免机房出现意外情况比如停电、火灾。
-- **异地灾备**:类似于同城灾备,不同的是,相同服务部署在异地(通常距离较远,甚至是在不同的城市或者国家)的不同机房中
-- **同城多活**:类似于同城灾备,但备用服务可以处理请求,这样可以充分利用系统资源,提高系统的并发。
-- **异地多活** : 将服务部署在异地的不同机房中,并且,它们可以同时对外提供服务。
+- **High Availability Cluster**: The same service is deployed in two or more instances. If the currently used service suddenly fails, it can switch to another service, ensuring high availability.
+- **Local Disaster Recovery**: An entire cluster can be deployed in the same data center, while in local disaster recovery, the same service is deployed in different data centers within the same city. Additionally, the backup service does not handle requests. This helps avoid unexpected situations in the data center, such as power outages or fires.
+- **Remote Disaster Recovery**: Similar to local disaster recovery, but the same service is deployed in different data centers in remote locations (usually far apart, even in different cities or countries).
+- **Local Active-Active**: Similar to local disaster recovery, but the backup service can handle requests, allowing for better utilization of system resources and increased concurrency.
+- **Remote Active-Active**: Services are deployed in different data centers in remote locations, and they can provide services simultaneously.
-高可用集群单纯是服务的冗余,并没有强调地域。同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活和异地多活实现了地域上的冗余。
+High Availability Clusters focus solely on service redundancy without emphasizing geographic location. Local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, and remote active-active achieve geographic redundancy.
-同城和异地的主要区别在于机房之间的距离。异地通常距离较远,甚至是在不同的城市或者国家。
+The main difference between local and remote is the distance between data centers. Remote locations are usually farther apart, even in different cities or countries.
-和传统的灾备设计相比,同城多活和异地多活最明显的改变在于“多活”,即所有站点都是同时在对外提供服务的。异地多活是为了应对突发状况比如火灾、地震等自然或者人为灾害。
+Compared to traditional disaster recovery design, the most significant change in local active-active and remote active-active is the "active-active" aspect, meaning all sites are simultaneously providing services. Remote active-active is designed to respond to emergencies such as fires, earthquakes, or other natural or man-made disasters.
-光做好冗余还不够,必须要配合上 **故障转移** 才可以! 所谓故障转移,简单来说就是实现不可用服务快速且自动地切换到可用服务,整个过程不需要人为干涉。
+Simply having redundancy is not enough; it must be paired with **failover**! Failover, in simple terms, is the ability to quickly and automatically switch from an unavailable service to an available one without human intervention.
-举个例子:哨兵模式的 Redis 集群中,如果 Sentinel(哨兵) 检测到 master 节点出现故障的话, 它就会帮助我们实现故障转移,自动将某一台 slave 升级为 master,确保整个 Redis 系统的可用性。整个过程完全自动,不需要人工介入。我在[《Java 面试指北》](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7)的「技术面试题篇」中的数据库部分详细介绍了 Redis 集群相关的知识点&面试题,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
+For example, in a Redis cluster using Sentinel mode, if the Sentinel detects a failure in the master node, it will help us achieve failover by automatically promoting one of the slaves to master, ensuring the availability of the entire Redis system. The entire process is fully automated and requires no manual intervention. I have detailed the relevant knowledge and interview questions about Redis clusters in the database section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7), which interested readers can check out.
-再举个例子:Nginx 可以结合 Keepalived 来实现高可用。如果 Nginx 主服务器宕机的话,Keepalived 可以自动进行故障转移,备用 Nginx 主服务器升级为主服务。并且,这个切换对外是透明的,因为使用的虚拟 IP,虚拟 IP 不会改变。我在[《Java 面试指北》](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7)的「技术面试题篇」中的「服务器」部分详细介绍了 Nginx 相关的知识点&面试题,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
+Another example: Nginx can be combined with Keepalived to achieve high availability. If the primary Nginx server goes down, Keepalived can automatically perform failover, promoting the backup Nginx server to primary. Moreover, this switch is transparent to external users because a virtual IP is used, which does not change. I have detailed the relevant knowledge and interview questions about Nginx in the "Servers" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7), which interested readers can check out.
-异地多活架构实施起来非常难,需要考虑的因素非常多。本人不才,实际项目中并没有实践过异地多活架构,我对其了解还停留在书本知识。
+Implementing a remote active-active architecture is very challenging, with many factors to consider. I have not personally practiced remote active-active architecture in actual projects, and my understanding remains at the theoretical level.
-如果你想要深入学习异地多活相关的知识,我这里推荐几篇我觉得还不错的文章:
+If you want to delve deeper into knowledge related to remote active-active, I recommend a few articles that I find quite good:
-- [搞懂异地多活,看这篇就够了- 水滴与银弹 - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/T6mMDdtTfBuIiEowCpqu6Q)
-- [四步构建异地多活](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hMD-IS__4JE5_nQhYPYSTg)
-- [《从零开始学架构》— 28 | 业务高可用的保障:异地多活架构](http://gk.link/a/10pKZ)
+- [Understanding Remote Active-Active, This Article is Enough - Water Droplets and Silver Bullets - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/T6mMDdtTfBuIiEowCpqu6Q)
+- [Building Remote Active-Active in Four Steps](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hMD-IS__4JE5_nQhYPYSTg)
+- [“Learning Architecture from Scratch” — 28 | Ensuring Business High Availability: Remote Active-Active Architecture](http://gk.link/a/10pKZ)
-不过,这些文章大多也都是在介绍概念知识。目前,网上还缺少真正介绍具体要如何去实践落地异地多活架构的资料。
-
-
+However, most of these articles mainly introduce conceptual knowledge. Currently, there is
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md b/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
index 3c7ba1ac9cd..8b5f3a4a161 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
@@ -1,86 +1,58 @@
---
-title: 超时&重试详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Timeout & Retry Explained
+category: High Availability
icon: retry
---
-由于网络问题、系统或者服务内部的 Bug、服务器宕机、操作系统崩溃等问题的不确定性,我们的系统或者服务永远不可能保证时刻都是可用的状态。
+Due to uncertainties such as network issues, internal bugs in systems or services, server crashes, and operating system failures, our systems or services can never guarantee constant availability.
-为了最大限度的减小系统或者服务出现故障之后带来的影响,我们需要用到的 **超时(Timeout)** 和 **重试(Retry)** 机制。
+To minimize the impact of failures in systems or services, we need to utilize **Timeout** and **Retry** mechanisms.
-想要把超时和重试机制讲清楚其实很简单,因为它俩本身就不是什么高深的概念。
+Explaining the timeout and retry mechanisms is actually quite simple, as they are not complex concepts.
-虽然超时和重试机制的思想很简单,但是它俩是真的非常实用。你平时接触到的绝大部分涉及到远程调用的系统或者服务都会应用超时和重试机制。尤其是对于微服务系统来说,正确设置超时和重试非常重要。单体服务通常只涉及数据库、缓存、第三方 API、中间件等的网络调用,而微服务系统内部各个服务之间还存在着网络调用。
+Although the ideas behind timeout and retry mechanisms are straightforward, they are indeed very practical. Most systems or services you encounter that involve remote calls will apply timeout and retry mechanisms. This is especially important for microservices systems, where correctly setting timeouts and retries is crucial. Monolithic services typically only involve network calls to databases, caches, third-party APIs, and middleware, while microservices systems also involve network calls between various services.
-## 超时机制
+## Timeout Mechanism
-### 什么是超时机制?
+### What is the Timeout Mechanism?
-超时机制说的是当一个请求超过指定的时间(比如 1s)还没有被处理的话,这个请求就会直接被取消并抛出指定的异常或者错误(比如 `504 Gateway Timeout`)。
+The timeout mechanism refers to the cancellation of a request if it exceeds a specified time (e.g., 1 second) without being processed, resulting in a specified exception or error being thrown (e.g., `504 Gateway Timeout`).
-我们平时接触到的超时可以简单分为下面 2 种:
+Timeouts can generally be categorized into the following two types:
-- **连接超时(ConnectTimeout)**:客户端与服务端建立连接的最长等待时间。
-- **读取超时(ReadTimeout)**:客户端和服务端已经建立连接,客户端等待服务端处理完请求的最长时间。实际项目中,我们关注比较多的还是读取超时。
+- **Connect Timeout**: The maximum wait time for the client to establish a connection with the server.
+- **Read Timeout**: The maximum time the client waits for the server to complete processing the request after a connection has been established. In practical projects, we often focus more on read timeouts.
-一些连接池客户端框架中可能还会有获取连接超时和空闲连接清理超时。
+Some connection pool client frameworks may also have connection acquisition timeouts and idle connection cleanup timeouts.
-如果没有设置超时的话,就可能会导致服务端连接数爆炸和大量请求堆积的问题。
+If timeouts are not set, it can lead to an explosion of server connections and a backlog of requests.
-这些堆积的连接和请求会消耗系统资源,影响新收到的请求的处理。严重的情况下,甚至会拖垮整个系统或者服务。
+These accumulated connections and requests consume system resources, affecting the processing of new incoming requests. In severe cases, it can even bring down the entire system or service.
-我之前在实际项目就遇到过类似的问题,整个网站无法正常处理请求,服务器负载直接快被拉满。后面发现原因是项目超时设置错误加上客户端请求处理异常,导致服务端连接数直接接近 40w+,这么多堆积的连接直接把系统干趴了。
+I encountered a similar issue in a previous project where the entire website could not process requests normally, and the server load was nearly maxed out. The cause was found to be incorrect timeout settings combined with exceptions in client request handling, leading to server connections approaching 400,000+. Such a backlog of connections directly caused the system to crash.
-### 超时时间应该如何设置?
+### How Should Timeout Values Be Set?
-超时到底设置多长时间是一个难题!超时值设置太高或者太低都有风险。如果设置太高的话,会降低超时机制的有效性,比如你设置超时为 10s 的话,那设置超时就没啥意义了,系统依然可能会出现大量慢请求堆积的问题。如果设置太低的话,就可能会导致在系统或者服务在某些处理请求速度变慢的情况下(比如请求突然增多),大量请求重试(超时通常会结合重试)继续加重系统或者服务的压力,进而导致整个系统或者服务被拖垮的问题。
+Determining the appropriate timeout duration is a challenge! Setting the timeout value too high or too low both carry risks. If set too high, it reduces the effectiveness of the timeout mechanism; for example, if you set the timeout to 10 seconds, then the timeout becomes meaningless, and the system may still experience a backlog of slow requests. If set too low, it may lead to a situation where, under certain conditions (e.g., a sudden increase in requests), a large number of requests are retried (timeouts are usually combined with retries), further increasing the pressure on the system or service, potentially leading to a complete system failure.
-通常情况下,我们建议读取超时设置为 **1500ms** ,这是一个比较普适的值。如果你的系统或者服务对于延迟比较敏感的话,那读取超时值可以适当在 **1500ms** 的基础上进行缩短。反之,读取超时值也可以在 **1500ms** 的基础上进行加长,不过,尽量还是不要超过 **1500ms** 。连接超时可以适当设置长一些,建议在 **1000ms ~ 5000ms** 之内。
+In general, we recommend setting the read timeout to **1500ms**, which is a relatively universal value. If your system or service is sensitive to latency, the read timeout can be shortened from the **1500ms** baseline. Conversely, it can also be extended, but it is best not to exceed **1500ms**. The connect timeout can be set a bit longer, ideally within **1000ms to 5000ms**.
-没有银弹!超时值具体该设置多大,还是要根据实际项目的需求和情况慢慢调整优化得到。
+There is no silver bullet! The specific timeout value should be adjusted and optimized based on the actual project requirements and conditions.
-更上一层,参考[美团的 Java 线程池参数动态配置](https://tech.meituan.com/2020/04/02/java-pooling-pratice-in-meituan.html)思想,我们也可以将超时弄成可配置化的参数而不是固定的,比较简单的一种办法就是将超时的值放在配置中心中。这样的话,我们就可以根据系统或者服务的状态动态调整超时值了。
+Furthermore, referring to [Meituan's dynamic configuration of Java thread pool parameters](https://tech.meituan.com/2020/04/02/java-pooling-pratice-in-meituan.html), we can also make timeouts configurable parameters rather than fixed values. A simple approach is to place the timeout values in a configuration center. This way, we can dynamically adjust the timeout values based on the state of the system or service.
-## 重试机制
+## Retry Mechanism
-### 什么是重试机制?
+### What is the Retry Mechanism?
-重试机制一般配合超时机制一起使用,指的是多次发送相同的请求来避免瞬态故障和偶然性故障。
+The retry mechanism is generally used in conjunction with the timeout mechanism, referring to the repeated sending of the same request to avoid transient and occasional failures.
-瞬态故障可以简单理解为某一瞬间系统偶然出现的故障,并不会持久。偶然性故障可以理解为哪些在某些情况下偶尔出现的故障,频率通常较低。
+Transient failures can be simply understood as faults that occur momentarily in the system and are not persistent. Occasional failures can be understood as faults that occur infrequently under certain conditions.
-重试的核心思想是通过消耗服务器的资源来尽可能获得请求更大概率被成功处理。由于瞬态故障和偶然性故障是很少发生的,因此,重试对于服务器的资源消耗几乎是可以被忽略的。
+The core idea of retrying is to consume server resources to maximize the probability of successfully processing a request. Since transient and occasional failures are rare, the resource consumption from retries is almost negligible.
-### 常见的重试策略有哪些?
+### What Are Common Retry Strategies?
-常见的重试策略有两种:
+There are two common retry strategies:
-1. **固定间隔时间重试**:每次重试之间都使用相同的时间间隔,比如每隔 1.5 秒进行一次重试。这种重试策略的优点是实现起来比较简单,不需要考虑重试次数和时间的关系,也不需要维护额外的状态信息。但是这种重试策略的缺点是可能会导致重试过于频繁或过于稀疏,从而影响系统的性能和效率。如果重试间隔太短,可能会对目标系统造成过大的压力,导致雪崩效应;如果重试间隔太长,可能会导致用户等待时间过长,影响用户体验。
-2. **梯度间隔重试**:根据重试次数的增加去延长下次重试时间,比如第一次重试间隔为 1 秒,第二次为 2 秒,第三次为 4 秒,以此类推。这种重试策略的优点是能够有效提高重试成功的几率(随着重试次数增加,但是重试依然不成功,说明目标系统恢复时间比较长,因此可以根据重试次数延长下次重试时间),也能通过柔性化的重试避免对下游系统造成更大压力。但是这种重试策略的缺点是实现起来比较复杂,需要考虑重试次数和时间的关系,以及设置合理的上限和下限值。另外,这种重试策略也可能会导致用户等待时间过长,影响用户体验。
-
-这两种适合的场景各不相同。固定间隔时间重试适用于目标系统恢复时间比较稳定和可预测的场景,比如网络波动或服务重启。梯度间隔重试适用于目标系统恢复时间比较长或不可预测的场景,比如网络故障和服务故障。
-
-### 重试的次数如何设置?
-
-重试的次数不宜过多,否则依然会对系统负载造成比较大的压力。
-
-重试的次数通常建议设为 3 次。大部分情况下,我们还是更建议使用梯度间隔重试策略,比如说我们要重试 3 次的话,第 1 次请求失败后,等待 1 秒再进行重试,第 2 次请求失败后,等待 2 秒再进行重试,第 3 次请求失败后,等待 3 秒再进行重试。
-
-### 什么是重试幂等?
-
-超时和重试机制在实际项目中使用的话,需要注意保证同一个请求没有被多次执行。
-
-什么情况下会出现一个请求被多次执行呢?客户端等待服务端完成请求完成超时但此时服务端已经执行了请求,只是由于短暂的网络波动导致响应在发送给客户端的过程中延迟了。
-
-举个例子:用户支付购买某个课程,结果用户支付的请求由于重试的问题导致用户购买同一门课程支付了两次。对于这种情况,我们在执行用户购买课程的请求的时候需要判断一下用户是否已经购买过。这样的话,就不会因为重试的问题导致重复购买了。
-
-### Java 中如何实现重试?
-
-如果要手动编写代码实现重试逻辑的话,可以通过循环(例如 while 或 for 循环)或者递归实现。不过,一般不建议自己动手实现,有很多第三方开源库提供了更完善的重试机制实现,例如 Spring Retry、Resilience4j、Guava Retrying。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 微服务之间调用超时的设置治理:
-- 超时、重试和抖动回退:
-
-
+1. **Fixed Interval Retry**: Each retry uses the same time interval, such as retrying every 1.5 seconds. The advantage of this strategy is its simplicity; there is no need to consider the relationship between retry count and time, nor maintain additional state information. However, the downside is that it may lead to retries being too frequent or too sparse, affecting system performance and efficiency. If the retry interval is too short, it may put excessive pressure on the target system, leading to
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/cdn.md b/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
index f4ca0eab5f2..417a6a70b4f 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
@@ -1,135 +1,135 @@
---
-title: CDN工作原理详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of How CDN Works
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: CDN,内容分发网络
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: CDN, Content Delivery Network
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.
---
-## 什么是 CDN ?
+## What is CDN?
-**CDN** 全称是 Content Delivery Network/Content Distribution Network,翻译过的意思是 **内容分发网络** 。
+**CDN** stands for Content Delivery Network, which translates to **Content Distribution Network**.
-我们可以将内容分发网络拆开来看:
+We can break down the concept of a content distribution network:
-- 内容:指的是静态资源比如图片、视频、文档、JS、CSS、HTML。
-- 分发网络:指的是将这些静态资源分发到位于多个不同的地理位置机房中的服务器上,这样,就可以实现静态资源的就近访问比如北京的用户直接访问北京机房的数据。
+- Content: Refers to static resources such as images, videos, documents, JS, CSS, and HTML.
+- Distribution Network: Refers to distributing these static resources to servers located in different geographic locations, allowing for nearby access to static resources, such as a user in Beijing directly accessing data from the Beijing data center.
-所以,简单来说,**CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。**
+So, simply put, **CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.**
-类似于京东建立的庞大的仓储运输体系,京东物流在全国拥有非常多的仓库,仓储网络几乎覆盖全国所有区县。这样的话,用户下单的第一时间,商品就从距离用户最近的仓库,直接发往对应的配送站,再由京东小哥送到你家。
+Similar to the massive warehousing and transportation system established by JD.com, JD logistics has many warehouses across the country, with a storage network covering almost all districts and counties in the country. This way, when a user places an order, the product is sent directly from the nearest warehouse to the corresponding distribution station, and then delivered to your home by JD couriers.
-
+
-你可以将 CDN 看作是服务上一层的特殊缓存服务,分布在全国各地,主要用来处理静态资源的请求。
+You can think of CDN as a special caching service on top of the server, distributed across the country, primarily used to handle requests for static resources.
-
+
-我们经常拿全站加速和内容分发网络做对比,不要把两者搞混了!全站加速(不同云服务商叫法不同,腾讯云叫 ECDN、阿里云叫 DCDN)既可以加速静态资源又可以加速动态资源,内容分发网络(CDN)主要针对的是 **静态资源** 。
+We often compare full-site acceleration with content delivery networks; do not confuse the two! Full-site acceleration (known as ECDN by Tencent Cloud and DCDN by Alibaba Cloud) can accelerate both static and dynamic resources, whereas content delivery network (CDN) mainly targets **static resources**.
-
+
-绝大部分公司都会在项目开发中使用 CDN 服务,但很少会有自建 CDN 服务的公司。基于成本、稳定性和易用性考虑,建议直接选择专业的云厂商(比如阿里云、腾讯云、华为云、青云)或者 CDN 厂商(比如网宿、蓝汛)提供的开箱即用的 CDN 服务。
+Most companies will use CDN services in their project development, but very few will build their own CDN services. Considering cost, stability, and usability, it is advisable to choose ready-to-use CDN services offered by professional cloud vendors (such as Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, QingCloud) or CDN providers (such as Wangsu, Blue boolean).
-很多朋友可能要问了:**既然是就近访问,为什么不直接将服务部署在多个不同的地方呢?**
+Many friends may ask: **Since it's about nearby access, why not deploy services directly in multiple different places?**
-- 成本太高,需要部署多份相同的服务。
-- 静态资源通常占用空间比较大且经常会被访问到,如果直接使用服务器或者缓存来处理静态资源请求的话,对系统资源消耗非常大,可能会影响到系统其他服务的正常运行。
+- The cost is too high, as multiple identical services need to be deployed.
+- Static resources usually take up a lot of space and are frequently accessed. If we use servers or caches to handle static resource requests directly, it consumes a lot of system resources, potentially affecting the normal operation of other system services.
-同一个服务在在多个不同的地方部署多份(比如同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活、异地多活)是为了实现系统的高可用而不是就近访问。
+Deploying the same service in multiple different locations (such as local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, remote active-active) is for achieving high availability of the system, not for nearby access.
-## CDN 工作原理是什么?
+## What is the Working Principle of CDN?
-搞懂下面 3 个问题也就搞懂了 CDN 的工作原理:
+Understanding the following three questions will help you grasp the working principle of CDN:
-1. 静态资源是如何被缓存到 CDN 节点中的?
-2. 如何找到最合适的 CDN 节点?
-3. 如何防止静态资源被盗用?
+1. How are static resources cached to CDN nodes?
+1. How to find the most suitable CDN node?
+1. How to prevent static resources from being misused?
-### 静态资源是如何被缓存到 CDN 节点中的?
+### How are static resources cached to CDN nodes?
-你可以通过 **预热** 的方式将源站的资源同步到 CDN 的节点中。这样的话,用户首次请求资源可以直接从 CDN 节点中取,无需回源。这样可以降低源站压力,提升用户体验。
+You can synchronize the origin server's resources to the CDN nodes through **warming**. This way, users requesting resources for the first time can directly retrieve them from the CDN node without needing to go back to the origin, reducing the pressure on the origin server and improving user experience.
-如果不预热的话,你访问的资源可能不在 CDN 节点中,这个时候 CDN 节点将请求源站获取资源,这个过程是大家经常说的 **回源**。
+If resources are not warmed, the requested resources may not be present at the CDN node. In this case, the CDN node will fetch the resources from the origin server, which is often referred to as **back to source**.
-> - 回源:当 CDN 节点上没有用户请求的资源或该资源的缓存已经过期时,CDN 节点需要从原始服务器获取最新的资源内容,这个过程就是回源。当用户请求发生回源的话,会导致该请求的响应速度比未使用 CDN 还慢,因为相比于未使用 CDN 还多了一层 CDN 的调用流程。
-> - 预热:预热是指在 CDN 上提前将内容缓存到 CDN 节点上。这样当用户在请求这些资源时,能够快速地从最近的 CDN 节点获取到而不需要回源,进而减少了对源站的访问压力,提高了访问速度。
+> - Back to Source: When the CDN node does not have the requested resource or the resource's cache has expired, the CDN node needs to retrieve the latest resource content from the original server. This process is known as back to source. When a user request undergoes back to source, it results in a response speed slower than without using CDN, as it adds an extra layer of CDN call process.
+> - Warming: Warming refers to caching content in advance at the CDN nodes. This allows users to quickly retrieve resources from the nearest CDN node without going back to the origin, thereby reducing the access pressure on the origin server and improving access speed.
-
+
-如果资源有更新的话,你也可以对其 **刷新** ,删除 CDN 节点上缓存的旧资源,并强制 CDN 节点回源站获取最新资源。
+If there are updates to resources, you can also **refresh** them by deleting the old cached resources on the CDN node and forcing the CDN node to go back to the origin server to fetch the latest resources.
-几乎所有云厂商提供的 CDN 服务都具备缓存的刷新和预热功能(下图是阿里云 CDN 服务提供的相应功能):
+Almost all cloud providers' CDN services offer cache refresh and warming functions (the following image shows the corresponding functions provided by Alibaba Cloud CDN):
-
+
-**命中率** 和 **回源率** 是衡量 CDN 服务质量两个重要指标。命中率越高越好,回源率越低越好。
+**Hit Rate** and **Back to Source Rate** are two important indicators for measuring the quality of CDN services. The higher the hit rate, the better, and the lower the back to source rate, the better.
-### 如何找到最合适的 CDN 节点?
+### How to find the most suitable CDN node?
-GSLB (Global Server Load Balance,全局负载均衡)是 CDN 的大脑,负责多个 CDN 节点之间相互协作,最常用的是基于 DNS 的 GSLB。
+GSLB (Global Server Load Balance) is the brain of the CDN, responsible for the cooperation among multiple CDN nodes. The most commonly used is DNS-based GSLB.
-CDN 会通过 GSLB 找到最合适的 CDN 节点,更具体点来说是下面这样的:
+CDN uses GSLB to find the most suitable CDN node, specifically as follows:
-1. 浏览器向 DNS 服务器发送域名请求;
-2. DNS 服务器向根据 CNAME( Canonical Name ) 别名记录向 GSLB 发送请求;
-3. GSLB 返回性能最好(通常距离请求地址最近)的 CDN 节点(边缘服务器,真正缓存内容的地方)的地址给浏览器;
-4. 浏览器直接访问指定的 CDN 节点。
+1. The browser sends a domain name request to the DNS server;
+1. The DNS server sends a request to GSLB based on the CNAME (Canonical Name) alias record;
+1. GSLB returns the address of the best-performing (usually the nearest to the request address) CDN node (edge server, the actual caching location) to the browser;
+1. The browser directly accesses the specified CDN node.
-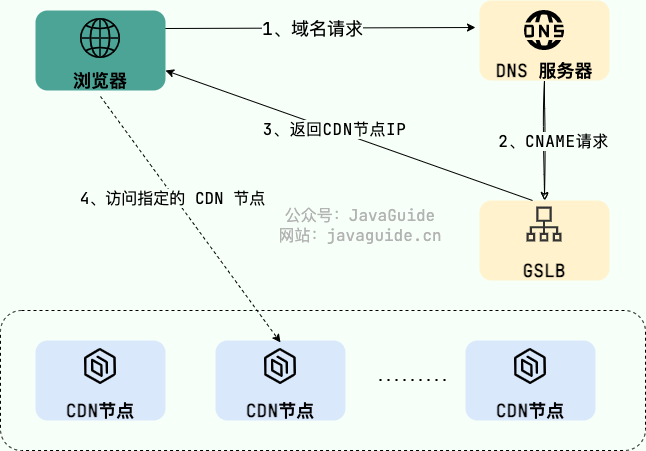
+
-为了方便理解,上图其实做了一点简化。GSLB 内部可以看作是 CDN 专用 DNS 服务器和负载均衡系统组合。CDN 专用 DNS 服务器会返回负载均衡系统 IP 地址给浏览器,浏览器使用 IP 地址请求负载均衡系统进而找到对应的 CDN 节点。
+To facilitate understanding, the above diagram simplifies certain aspects. Internally, GSLB can be viewed as a combination of a CDN-specific DNS server and a load-balancing system. The CDN-specific DNS server returns the IP address of the load-balancing system to the browser, which then uses this IP address to request the load-balancing system to find the corresponding CDN node.
-**GSLB 是如何选择出最合适的 CDN 节点呢?** GSLB 会根据请求的 IP 地址、CDN 节点状态(比如负载情况、性能、响应时间、带宽)等指标来综合判断具体返回哪一个 CDN 节点的地址。
+**How does GSLB choose the most suitable CDN node?** GSLB comprehensively judges which CDN node’s address to return based on metrics such as the request's IP address, the status of the CDN node (such as load status, performance, response time, bandwidth), etc.
-### 如何防止资源被盗刷?
+### How to prevent misuse of resources?
-如果我们的资源被其他用户或者网站非法盗刷的话,将会是一笔不小的开支。
+If our resources are illegally accessed or scraped by other users or websites, it could result in significant expenses.
-解决这个问题最常用最简单的办法设置 **Referer 防盗链**,具体来说就是根据 HTTP 请求的头信息里面的 Referer 字段对请求进行限制。我们可以通过 Referer 字段获取到当前请求页面的来源页面的网站地址,这样我们就能确定请求是否来自合法的网站。
+The most common and straightforward solution to this problem is to set up **Referer anti-hotlinking**. Specifically, this limits requests based on the Referer field in the HTTP request headers. By utilizing the Referer field, we can determine the originating website address of the current request and ascertain whether it comes from a legitimate website.
-CDN 服务提供商几乎都提供了这种比较基础的防盗链机制。
+Almost all CDN service providers offer this basic anti-hotlinking mechanism.
-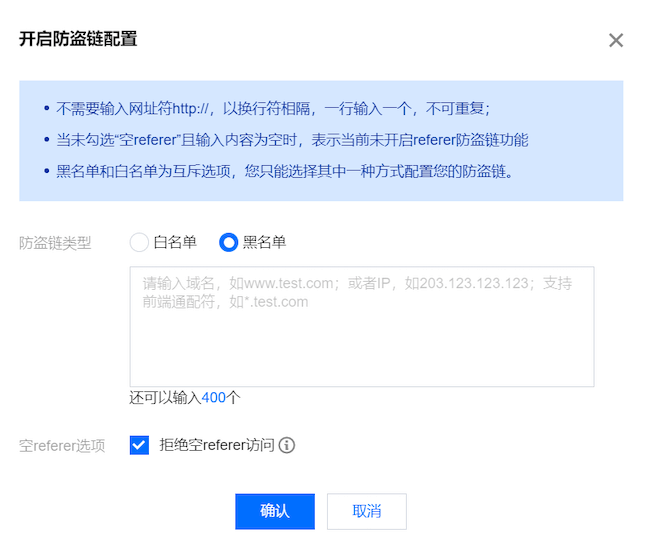
+
-不过,如果站点的防盗链配置允许 Referer 为空的话,通过隐藏 Referer,可以直接绕开防盗链。
+However, if the site's anti-hotlinking configuration allows a blank Referer, it is possible to bypass the anti-hotlinking by hiding the Referer.
-通常情况下,我们会配合其他机制来确保静态资源被盗用,一种常用的机制是 **时间戳防盗链** 。相比之下,**时间戳防盗链** 的安全性更强一些。时间戳防盗链加密的 URL 具有时效性,过期之后就无法再被允许访问。
+Usually, we combine other mechanisms to ensure the static resources are not misused. A commonly used mechanism is **timestamp anti-hotlinking**. Compared to the simple Referer-based approach, **timestamp anti-hotlinking** offers stronger security. The encrypted URL in timestamp anti-hotlinking is time-sensitive, and once it expires, access is no longer permitted.
-时间戳防盗链的 URL 通常会有两个参数一个是签名字符串,一个是过期时间。签名字符串一般是通过对用户设定的加密字符串、请求路径、过期时间通过 MD5 哈希算法取哈希的方式获得。
+The URL for timestamp anti-hotlinking typically includes two parameters: a signature string and an expiration time. The signature string is generally obtained by executing an MD5 hash on a user-defined encrypted string, request path, and expiration time.
-时间戳防盗链 URL 示例:
+Example URL for timestamp anti-hotlinking:
```plain
-http://cdn.wangsu.com/4/123.mp3? wsSecret=79aead3bd7b5db4adeffb93a010298b5&wsTime=1601026312
+http://cdn.wangsu.com/4/123.mp3?wsSecret=79aead3bd7b5db4adeffb93a010298b5&wsTime=1601026312
```
-- `wsSecret`:签名字符串。
-- `wsTime`: 过期时间。
+- `wsSecret`: Signature string.
+- `wsTime`: Expiration time.
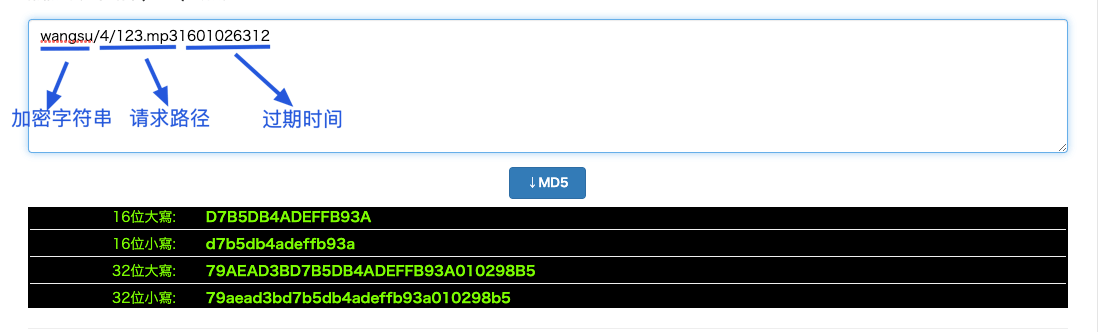
-时间戳防盗链的实现也比较简单,并且可靠性较高,推荐使用。并且,绝大部分 CDN 服务提供商都提供了开箱即用的时间戳防盗链机制。
+The implementation of timestamp anti-hotlinking is relatively simple and highly reliable, making it a recommended option. Additionally, most CDN service providers offer plug-and-play timestamp anti-hotlinking mechanisms.
-
+
-除了 Referer 防盗链和时间戳防盗链之外,你还可以 IP 黑白名单配置、IP 访问限频配置等机制来防盗刷。
+In addition to Referer anti-hotlinking and timestamp anti-hotlinking, you can also utilize IP black and white list configurations, IP access rate limiting configurations, and other mechanisms to prevent misuse.
-## 总结
+## Summary
-- CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。
-- 基于成本、稳定性和易用性考虑,建议直接选择专业的云厂商(比如阿里云、腾讯云、华为云、青云)或者 CDN 厂商(比如网宿、蓝汛)提供的开箱即用的 CDN 服务。
-- GSLB (Global Server Load Balance,全局负载均衡)是 CDN 的大脑,负责多个 CDN 节点之间相互协作,最常用的是基于 DNS 的 GSLB。CDN 会通过 GSLB 找到最合适的 CDN 节点。
-- 为了防止静态资源被盗用,我们可以利用 **Referer 防盗链** + **时间戳防盗链** 。
+- CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.
+- Considering cost, stability, and usability, it is advisable to choose ready-to-use CDN services offered by professional cloud vendors (such as Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, QingCloud) or CDN providers (such as Wangsu, Blue boolean).
+- GSLB (Global Server Load Balance) is the brain of the CDN, responsible for the cooperation among multiple CDN nodes. The most common implementation is DNS-based GSLB. CDN utilizes GSLB to find the most suitable CDN node.
+- To prevent the misuse of static resources, we can use **Referer anti-hotlinking** combined with **timestamp anti-hotlinking**.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 时间戳防盗链 - 七牛云 CDN:
-- CDN 是个啥玩意?一文说个明白:
-- 《透视 HTTP 协议》- 37 | CDN:加速我们的网络服务:
+- Timestamp Anti-Hotlinking - Qiniu Cloud CDN:
+- What on Earth is CDN? A Clear Explanation:
+- "Understanding HTTP Protocol" - 37 | CDN: Accelerating Our Network Services:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md b/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
index d7ae70c2bfd..436b68af621 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
@@ -1,68 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 数据冷热分离详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of Data Hot and Cold Separation
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: 数据冷热分离,冷数据迁移,冷数据存储
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 数据冷热分离是指根据数据的访问频率和业务重要性,将数据分为冷数据和热数据,冷数据一般存储在存储在低成本、低性能的介质中,热数据高性能存储介质中。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Data hot and cold separation, cold data migration, cold data storage
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: Data hot and cold separation refers to dividing data into cold and hot data based on access frequency and business importance. Cold data is generally stored in low-cost, low-performance media, while hot data is stored in high-performance media.
---
-## 什么是数据冷热分离?
+## What is Data Hot and Cold Separation?
-数据冷热分离是指根据数据的访问频率和业务重要性,将数据分为冷数据和热数据,冷数据一般存储在存储在低成本、低性能的介质中,热数据高性能存储介质中。
+Data hot and cold separation refers to dividing data into cold and hot data based on access frequency and business importance. Cold data is generally stored in low-cost, low-performance media, while hot data is stored in high-performance media.
-### 冷数据和热数据
+### Cold Data and Hot Data
-热数据是指经常被访问和修改且需要快速访问的数据,冷数据是指不经常访问,对当前项目价值较低,但需要长期保存的数据。
+Hot data refers to data that is frequently accessed and modified and requires quick access, while cold data refers to data that is infrequently accessed, has lower current project value, but needs to be stored for the long term.
-冷热数据到底如何区分呢?有两个常见的区分方法:
+How do we distinguish between hot and cold data? There are two common methods of distinction:
-1. **时间维度区分**:按照数据的创建时间、更新时间、过期时间等,将一定时间段内的数据视为热数据,超过该时间段的数据视为冷数据。例如,订单系统可以将 1 年前的订单数据作为冷数据,1 年内的订单数据作为热数据。这种方法适用于数据的访问频率和时间有较强的相关性的场景。
-2. **访问频率区分**:将高频访问的数据视为热数据,低频访问的数据视为冷数据。例如,内容系统可以将浏览量非常低的文章作为冷数据,浏览量较高的文章作为热数据。这种方法需要记录数据的访问频率,成本较高,适合访问频率和数据本身有较强的相关性的场景。
+1. **Time Dimension Distinction**: Data is classified as hot or cold based on its creation time, update time, expiration time, etc. Data within a certain time frame is considered hot, while data beyond that time frame is considered cold. For example, an order system might classify order data from one year ago as cold data and order data within the last year as hot data. This method is suitable for scenarios where access frequency is strongly correlated with time.
+1. **Access Frequency Distinction**: Data that is accessed frequently is considered hot, while data that is accessed infrequently is considered cold. For example, a content system might classify articles with very low views as cold data and articles with higher views as hot data. This method requires tracking data access frequency, which can be costly, and is suitable for scenarios where access frequency is strongly correlated with the data itself.
-几年前的数据并不一定都是冷数据,例如一些优质文章发表几年后依然有很多人访问,大部分普通用户新发表的文章却基本没什么人访问。
+Data from a few years ago is not necessarily all cold data; for instance, some high-quality articles may still receive many visits years after publication, while most newly published articles by ordinary users may hardly be accessed.
-这两种区分冷热数据的方法各有优劣,实际项目中,可以将两者结合使用。
+Both methods of distinguishing hot and cold data have their pros and cons, and in actual projects, they can be used in combination.
-### 冷热分离的思想
+### The Concept of Hot and Cold Separation
-冷热分离的思想非常简单,就是对数据进行分类,然后分开存储。冷热分离的思想可以应用到很多领域和场景中,而不仅仅是数据存储,例如:
+The concept of hot and cold separation is quite simple: classify data and then store it separately. This concept can be applied in many fields and scenarios, not just data storage, such as:
-- 邮件系统中,可以将近期的比较重要的邮件放在收件箱,将比较久远的不太重要的邮件存入归档。
-- 日常生活中,可以将常用的物品放在显眼的位置,不常用的物品放入储藏室或者阁楼。
-- 图书馆中,可以将最受欢迎和最常借阅的图书单独放在一个显眼的区域,将较少借阅的书籍放在不起眼的位置。
+- In an email system, important recent emails can be placed in the inbox, while less important older emails can be archived.
+- In daily life, frequently used items can be placed in prominent locations, while less frequently used items can be stored in a storage room or attic.
+- In a library, the most popular and frequently borrowed books can be placed in a prominent area, while less borrowed books can be placed in less noticeable locations.
- ……
-### 数据冷热分离的优缺点
+### Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Hot and Cold Separation
-- 优点:热数据的查询性能得到优化(用户的绝大部分操作体验会更好)、节约成本(可以冷热数据的不同存储需求,选择对应的数据库类型和硬件配置,比如将热数据放在 SSD 上,将冷数据放在 HDD 上)
-- 缺点:系统复杂性和风险增加(需要分离冷热数据,数据错误的风险增加)、统计效率低(统计的时候可能需要用到冷库的数据)。
+- Advantages: The query performance of hot data is optimized (the user experience for most operations will be better), and costs are saved (different storage requirements for hot and cold data allow for the selection of appropriate database types and hardware configurations, such as placing hot data on SSDs and cold data on HDDs).
+- Disadvantages: Increased system complexity and risk (the need to separate hot and cold data increases the risk of data errors), and lower statistical efficiency (cold storage data may be needed for statistics).
-## 冷数据如何迁移?
+## How to Migrate Cold Data?
-冷数据迁移方案:
+Cold data migration solutions:
-1. 业务层代码实现:当有对数据进行写操作时,触发冷热分离的逻辑,判断数据是冷数据还是热数据,冷数据就入冷库,热数据就入热库。这种方案会影响性能且冷热数据的判断逻辑不太好确定,还需要修改业务层代码,因此一般不会使用。
-2. 任务调度:可以利用 xxl-job 或者其他分布式任务调度平台定时去扫描数据库,找出满足冷数据条件的数据,然后批量地将其复制到冷库中,并从热库中删除。这种方法修改的代码非常少,非常适合按照时间区分冷热数据的场景。
-3. 监听数据库的变更日志 binlog :将满足冷数据条件的数据从 binlog 中提取出来,然后复制到冷库中,并从热库中删除。这种方法可以不用修改代码,但不适合按照时间维度区分冷热数据的场景。
+1. **Business Layer Code Implementation**: When there is a write operation on the data, trigger the logic for hot and cold separation to determine whether the data is cold or hot. Cold data goes to cold storage, while hot data goes to hot storage. This solution can impact performance, and the logic for determining hot and cold data can be difficult to establish, plus it requires modifying business layer code, so it is generally not used.
+1. **Task Scheduling**: You can use xxl-job or other distributed task scheduling platforms to periodically scan the database, identify data that meets the cold data criteria, and then batch copy it to cold storage while deleting it from hot storage. This method requires very little code modification and is very suitable for scenarios where cold and hot data are distinguished by time.
+1. **Listening to Database Change Logs (binlog)**: Extract data that meets the cold data criteria from the binlog, then copy it to cold storage and delete it from hot storage. This method does not require code modification but is not suitable for scenarios where hot and cold data are distinguished by time.
-如果你的公司有 DBA 的话,也可以让 DBA 进行冷数据的人工迁移,一次迁移完成冷数据到冷库。然后,再搭配上面介绍的方案实现后续冷数据的迁移工作。
+If your company has a DBA, you can also have the DBA perform manual migration of cold data to cold storage in one go. Then, you can use the solutions mentioned above to implement subsequent cold data migration work.
-## 冷数据如何存储?
+## How to Store Cold Data?
-冷数据的存储要求主要是容量大,成本低,可靠性高,访问速度可以适当牺牲。
-
-冷数据存储方案:
-
-- 中小厂:直接使用 MySQL/PostgreSQL 即可(不改变数据库选型和项目当前使用的数据库保持一致),比如新增一张表来存储某个业务的冷数据或者使用单独的冷库来存放冷数据(涉及跨库查询,增加了系统复杂性和维护难度)
-- 大厂:Hbase(常用)、RocksDB、Doris、Cassandra
-
-如果公司成本预算足的话,也可以直接上 TiDB 这种分布式关系型数据库,直接一步到位。TiDB 6.0 正式支持数据冷热存储分离,可以降低 SSD 使用成本。使用 TiDB 6.0 的数据放置功能,可以在同一个集群实现海量数据的冷热存储,将新的热数据存入 SSD,历史冷数据存入 HDD。
-
-## 案例分享
-
-- [如何快速优化几千万数据量的订单表 - 程序员济癫 - 2023](https://www.cnblogs.com/fulongyuanjushi/p/17910420.html)
-- [海量数据冷热分离方案与实践 - 字节跳动技术团队 - 2022](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZKRkZP6rLHuTE1wvnqmAPQ)
+The storage requirements for cold data mainly include large capacity, low cost, high
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md b/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
index 0d39e627cef..4aaf6a61f15 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
@@ -1,140 +1,140 @@
---
-title: 深度分页介绍及优化建议
-category: 高性能
+title: Introduction to Deep Pagination and Optimization Suggestions
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: 深度分页
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 查询偏移量过大的场景我们称为深度分页,这会导致查询性能较低。深度分页可以采用范围查询、子查询、INNER JOIN 延迟关联、覆盖索引等方法进行优化。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Deep Pagination
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: The scenario where the query offset is excessively large is referred to as deep pagination, which leads to lower query performance. Deep pagination can be optimized using techniques such as range queries, subqueries, INNER JOIN lazy association, and covering indexes.
---
-## 深度分页介绍
+## Introduction to Deep Pagination
-查询偏移量过大的场景我们称为深度分页,这会导致查询性能较低,例如:
+The scenario where the query offset is excessively large is referred to as deep pagination, which leads to lower query performance. For example:
```sql
-# MySQL 在无法利用索引的情况下跳过1000000条记录后,再获取10条记录
+# MySQL skips 1,000,000 records without utilizing the index, then retrieves 10 records.
SELECT * FROM t_order ORDER BY id LIMIT 1000000, 10
```
-## 深度分页问题的原因
+## Reasons for Deep Pagination Issues
-当查询偏移量过大时,MySQL 的查询优化器可能会选择全表扫描而不是利用索引来优化查询。这是因为扫描索引和跳过大量记录可能比直接全表扫描更耗费资源。
+When the query offset is too large, the MySQL query optimizer may choose a full table scan instead of using the index to optimize the query. This is because scanning the index and skipping a large number of records may be more resource-intensive than performing a direct full table scan.
-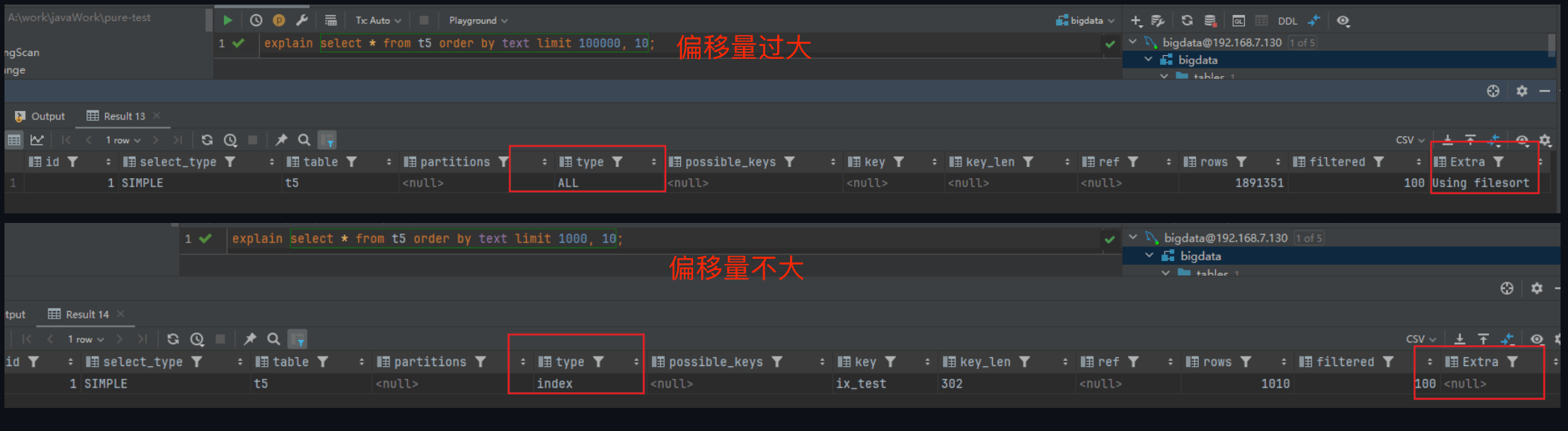
+
-不同机器上这个查询偏移量过大的临界点可能不同,取决于多个因素,包括硬件配置(如 CPU 性能、磁盘速度)、表的大小、索引的类型和统计信息等。
+The critical point for this excessively large query offset may vary between different machines, depending on multiple factors, including hardware configuration (such as CPU performance, disk speed), table size, index types, and statistical information.
-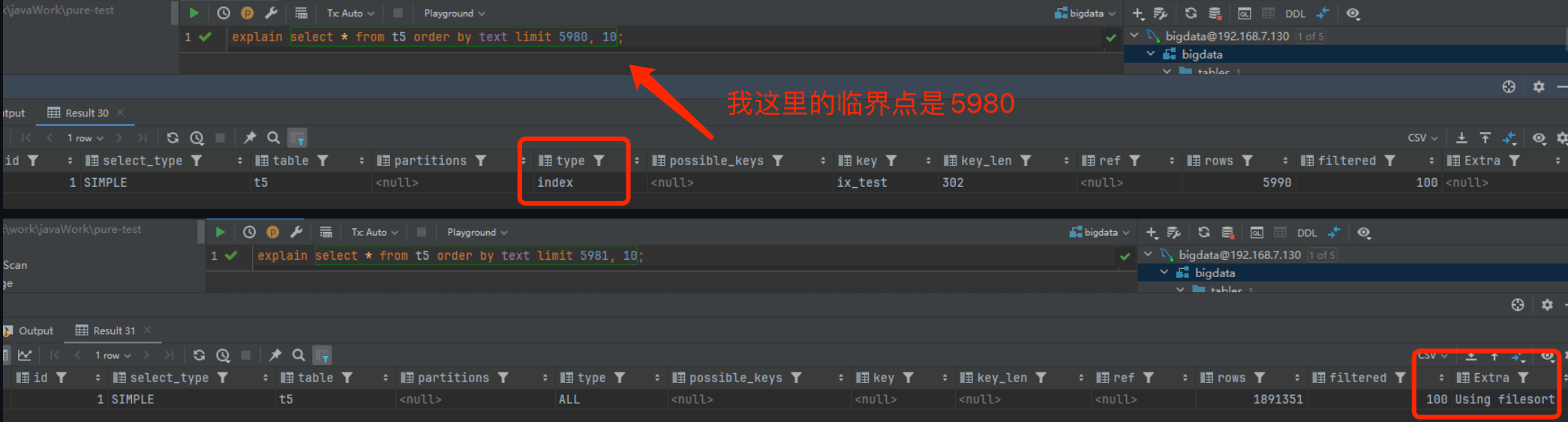
+
-MySQL 的查询优化器采用基于成本的策略来选择最优的查询执行计划。它会根据 CPU 和 I/O 的成本来决定是否使用索引扫描或全表扫描。如果优化器认为全表扫描的成本更低,它就会放弃使用索引。不过,即使偏移量很大,如果查询中使用了覆盖索引(covering index),MySQL 仍然可能会使用索引,避免回表操作。
+MySQL’s query optimizer employs a cost-based strategy to select the optimal query execution plan. It determines whether to use index scanning or full table scanning based on the costs of CPU and I/O. If the optimizer decides that the cost of a full table scan is lower, it will forgo using the index. However, even with a large offset, if a covering index is used in the query, MySQL might still utilize the index, avoiding the need to access the data rows again.
-## 深度分页优化建议
+## Optimization Suggestions for Deep Pagination
-这里以 MySQL 数据库为例介绍一下如何优化深度分页。
+Taking the MySQL database as an example, here are some ways to optimize deep pagination.
-### 范围查询
+### Range Query
-当可以保证 ID 的连续性时,根据 ID 范围进行分页是比较好的解决方案:
+When continuity of IDs can be ensured, using ID ranges for pagination is a good solution:
```sql
-# 查询指定 ID 范围的数据
+# Query data within a specified ID range
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id > 100000 AND id <= 100010 ORDER BY id
-# 也可以通过记录上次查询结果的最后一条记录的ID进行下一页的查询:
+# You can also query the next page using the ID of the last record from the previous query:
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id > 100000 LIMIT 10
```
-这种基于 ID 范围的深度分页优化方式存在很大限制:
+This ID range-based deep pagination optimization method has significant limitations:
-1. **ID 连续性要求高**: 实际项目中,数据库自增 ID 往往因为各种原因(例如删除数据、事务回滚等)导致 ID 不连续,难以保证连续性。
-2. **排序问题**: 如果查询需要按照其他字段(例如创建时间、更新时间等)排序,而不是按照 ID 排序,那么这种方法就不再适用。
-3. **并发场景**: 在高并发场景下,单纯依赖记录上次查询的最后一条记录的 ID 进行分页,容易出现数据重复或遗漏的问题。
+1. **High Requirement for ID Continuity**: In actual projects, database auto-increment IDs often become non-continuous for various reasons (such as data deletion, transaction rollbacks), making it difficult to ensure continuity.
+1. **Sorting Issues**: If the query needs to be sorted by other fields (such as creation time, update time, etc.) instead of sorting by ID, then this method is no longer applicable.
+1. **Concurrent Scenarios**: In high concurrency scenarios, relying solely on the ID of the last record from the previous query for pagination can easily lead to data duplication or omission issues.
-### 子查询
+### Subquery
-我们先查询出 limit 第一个参数对应的主键值,再根据这个主键值再去过滤并 limit,这样效率会更快一些。
+We can first retrieve the primary key values corresponding to the first parameter of limit, and then filter and limit based on this primary key value, which will be more efficient.
-阿里巴巴《Java 开发手册》中也有对应的描述:
+The Alibaba "Java Development Handbook" also describes this:
-> 利用延迟关联或者子查询优化超多分页场景。
+> Use lazy association or subqueries to optimize excessive pagination scenarios.
>
> 
```sql
-# 通过子查询来获取 id 的起始值,把 limit 1000000 的条件转移到子查询
+# Use a subquery to get the starting value of id, transferring the LIMIT 1000000 condition to the subquery
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= (SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1) LIMIT 10;
```
-**工作原理**:
+**How It Works**:
-1. 子查询 `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1)` 会利用主键索引快速定位到第 1000001 条记录,并返回其 ID 值。
-2. 主查询 `SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= ... LIMIT 10` 将子查询返回的起始 ID 作为过滤条件,使用 `id >=` 获取从该 ID 开始的后续 10 条记录。
+1. The subquery `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1)` quickly locates the 1,000,001st record using the primary key index and returns its ID value.
+1. The main query `SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= ... LIMIT 10` uses the starting ID returned from the subquery as a filter condition, using `id >=` to retrieve the subsequent 10 records starting from that ID.
-不过,子查询的结果会产生一张新表,会影响性能,应该尽量避免大量使用子查询。并且,这种方法只适用于 ID 是正序的。在复杂分页场景,往往需要通过过滤条件,筛选到符合条件的 ID,此时的 ID 是离散且不连续的。
+However, the result of the subquery generates a temporary table, which can impact performance. Therefore, large-scale use of subqueries should be avoided. Moreover, this method is only suitable when IDs are in ascending order. In complex pagination scenarios, filtering conditions may be needed to identify matching IDs, resulting in discrete and non-continuous IDs.
-当然,我们也可以利用子查询先去获取目标分页的 ID 集合,然后再根据 ID 集合获取内容,但这种写法非常繁琐,不如使用 INNER JOIN 延迟关联。
+Of course, we can also use subqueries to retrieve the target page's set of IDs and then fetch content based on this ID set, but this approach is very cumbersome compared to using INNER JOIN for lazy association.
-### 延迟关联
+### Lazy Association
-延迟关联与子查询的优化思路类似,都是通过将 `LIMIT` 操作转移到主键索引树上,减少回表次数。相比直接使用子查询,延迟关联通过 `INNER JOIN` 将子查询结果集成到主查询中,避免了子查询可能产生的临时表。在执行 `INNER JOIN` 时,MySQL 优化器能够利用索引进行高效的连接操作(如索引扫描或其他优化策略),因此在深度分页场景下,性能通常优于直接使用子查询。
+Lazy association is similar to the optimization idea of subqueries, where `LIMIT` operations are moved to the primary key index tree to reduce the number of back-table operations. Compared to directly using subqueries, lazy association integrates the subquery results into the main query through `INNER JOIN`, avoiding the potential creation of temporary tables by subqueries. When executing `INNER JOIN`, the MySQL optimizer can utilize indexes for efficient join operations (like index scanning or other optimization strategies), thus usually achieving better performance in deep pagination scenarios than directly using subqueries.
```sql
--- 使用 INNER JOIN 进行延迟关联
+-- Use INNER JOIN for lazy association
SELECT t1.*
FROM t_order t1
INNER JOIN (SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10) t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;
```
-**工作原理**:
+**How It Works**:
-1. 子查询 `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10)` 利用主键索引快速定位目标分页的 10 条记录的 ID。
-2. 通过 `INNER JOIN` 将子查询结果与主表 `t_order` 关联,获取完整的记录数据。
+1. The subquery `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10)` quickly locates the IDs of the 10 target records using the primary key index.
+1. Using `INNER JOIN`, the subquery results are associated with the main table `t_order`, retrieving complete record data.
-除了使用 INNER JOIN 之外,还可以使用逗号连接子查询。
+In addition to using INNER JOIN, you can also connect subqueries with commas.
```sql
--- 使用逗号进行延迟关联
+-- Use a comma for lazy association
SELECT t1.* FROM t_order t1,
(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10) t2
WHERE t1.id = t2.id;
```
-**注意**: 虽然逗号连接子查询也能实现类似的效果,但为了代码可读性和可维护性,建议使用更规范的 `INNER JOIN` 语法。
+[!NOTE]
+Although connecting subqueries with commas can achieve similar effects, it is recommended to use the more standardized `INNER JOIN` syntax for code readability and maintainability.
+### Covering Index
-### 覆盖索引
+A query method where all required fields are included in the index is known as a covering index.
-索引中已经包含了所有需要获取的字段的查询方式称为覆盖索引。
+**Benefits of Covering Index**:
-**覆盖索引的好处:**
-
-- **避免 InnoDB 表进行索引的二次查询,也就是回表操作:** InnoDB 是以聚集索引的顺序来存储的,对于 InnoDB 来说,二级索引在叶子节点中所保存的是行的主键信息,如果是用二级索引查询数据的话,在查找到相应的键值后,还要通过主键进行二次查询才能获取我们真实所需要的数据。而在覆盖索引中,二级索引的键值中可以获取所有的数据,避免了对主键的二次查询(回表),减少了 IO 操作,提升了查询效率。
-- **可以把随机 IO 变成顺序 IO 加快查询效率:** 由于覆盖索引是按键值的顺序存储的,对于 IO 密集型的范围查找来说,对比随机从磁盘读取每一行的数据 IO 要少的多,因此利用覆盖索引在访问时也可以把磁盘的随机读取的 IO 转变成索引查找的顺序 IO。
+- **Avoids InnoDB tables from performing second index queries, which is a back-table operation**: InnoDB stores data in the order of the clustered index. For InnoDB, the secondary index stores the primary key information in its leaf nodes. If data is queried using the secondary index, after finding the corresponding key value, a secondary query via the primary key is still required to retrieve the actual data we need. However, in covering indexes, all data can be accessed from the secondary index's key values, avoiding the need for a secondary query (back-table access), thereby reducing I/O operations and improving query efficiency.
+- **Transforms random I/O into sequential I/O, speeding up query efficiency**: Since covering indexes are stored in key value order, for I/O intensive range queries, it significantly reduces the I/O involved in randomly reading each row of data from disk, thus making disk random reads into index lookups in sequential order.
```sql
-# 如果只需要查询 id, code, type 这三列,可建立 code 和 type 的覆盖索引
+# If only the id, code, and type columns are needed, a covering index can be established for code and type
SELECT id, code, type FROM t_order
ORDER BY code
LIMIT 1000000, 10;
```
-**⚠️注意**:
+**⚠️Note**:
-- 当查询的结果集占表的总行数的很大一部分时,MySQL 查询优化器可能选择放弃使用索引,自动转换为全表扫描。
-- 虽然可以使用 `FORCE INDEX` 强制查询优化器走索引,但这种方式可能会导致查询优化器无法选择更优的执行计划,效果并不总是理想。
+- When the result set of a query accounts for a large proportion of the total rows in the table, MySQL’s query optimizer may opt to forgo using the index, automatically switching to a full table scan.
+- While you can use `FORCE INDEX` to compel the query optimizer to use the index, this might lead to the optimizer being unable to select a better execution plan, and the outcome may not always be ideal.
-## 总结
+## Conclusion
-本文总结了几种常见的深度分页优化方案:
+This article summarizes several common optimization schemes for deep pagination:
-1. **范围查询**: 基于 ID 连续性进行分页,通过记录上一页最后一条记录的 ID 来获取下一页数据。适合 ID 连续且按 ID 查询的场景,但在 ID 不连续或需要按其他字段排序时存在局限。
-2. **子查询**: 先通过子查询获取分页的起始主键值,再根据主键进行筛选分页。利用主键索引提高效率,但子查询会生成临时表,复杂场景下性能不佳。
-3. **延迟关联 (INNER JOIN)**: 使用 `INNER JOIN` 将分页操作转移到主键索引上,减少回表次数。相比子查询,延迟关联的性能更优,适合大数据量的分页查询。
-4. **覆盖索引**: 通过索引直接获取所需字段,避免回表操作,减少 IO 开销,适合查询特定字段的场景。但当结果集较大时,MySQL 可能会选择全表扫描。
+1. **Range Query**: Pagination based on ID continuity, using the ID of the last record from the previous page to fetch data for the next page. Suitable for scenarios where IDs are continuous and queries are sorted by ID, but limited in cases where IDs are non-continuous or sorted by other fields.
+1. **Subquery**: First, the starting primary key value for pagination is retrieved through a subquery, then filtered based on the primary key for pagination. It utilizes primary key indexing to improve efficiency, but subqueries create temporary tables, which may lead to poor performance in complex scenarios.
+1. **Lazy Association (INNER JOIN)**: Utilizing `INNER JOIN` to shift pagination operations to the primary key index, reducing the incidence of back-table operations. Lazy association typically performs better than subqueries, making it suitable for pagination queries involving large data volumes.
+1. **Covering Index**: Directly retrieving required fields through an index, avoiding back-table operations and minimizing I/O overhead, suitable for queries that target specific fields. However, when the result set is large, MySQL may choose a full table scan.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 聊聊如何解决 MySQL 深分页问题 - 捡田螺的小男孩:
-- 数据库深分页介绍及优化方案 - 京东零售技术:
-- MySQL 深分页优化 - 得物技术:
+- Discussing how to solve MySQL deep pagination issues - A Boy Who Picks Snails:
+- Introduction to deep pagination in databases and optimization schemes - JD Retail Technology:
+- MySQL deep pagination optimization - Dewu Technology:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md b/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
index 619df980574..50b4db93623 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
@@ -1,208 +1,208 @@
---
-title: 负载均衡原理及算法详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of Load Balancing Principles and Algorithms
+category: High Performance
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: 客户端负载均衡,服务负载均衡,Nginx,负载均衡算法,七层负载均衡,DNS解析
+ content: Client-side Load Balancing, Server-side Load Balancing, Nginx, Load Balancing Algorithms, Layer 7 Load Balancing, DNS Resolution
- - meta
- name: description
- content: 负载均衡指的是将用户请求分摊到不同的服务器上处理,以提高系统整体的并发处理能力。负载均衡可以简单分为服务端负载均衡和客户端负载均衡 这两种。服务端负载均衡涉及到的知识点更多,工作中遇到的也比较多,因为,我会花更多时间来介绍。
+ content: Load balancing refers to distributing user requests across different servers to improve the overall concurrency and reliability of the system. Load balancing can be simply divided into two types: server-side load balancing and client-side load balancing. Server-side load balancing involves more knowledge points and is encountered more frequently in work, thus, I will spend more time introducing it.
---
-## 什么是负载均衡?
+## What is Load Balancing?
-**负载均衡** 指的是将用户请求分摊到不同的服务器上处理,以提高系统整体的并发处理能力以及可靠性。负载均衡服务可以有由专门的软件或者硬件来完成,一般情况下,硬件的性能更好,软件的价格更便宜(后文会详细介绍到)。
+**Load balancing** refers to distributing user requests across different servers to enhance the overall concurrency capacity and reliability of a system. Load balancing services can be implemented by specialized software or hardware. Generally, hardware has better performance, while software is cheaper (which will be discussed in detail later).
-下图是[《Java 面试指北》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247519384&idx=1&sn=bc7e71af75350b755f04ca4178395b1a&chksm=cea1c353f9d64a458f797696d4144b4d6e58639371a4612b8e4d106d83a66d2289e7b2cd7431&token=660789642&lang=zh_CN&scene=21#wechat_redirect) 「高并发篇」中的一篇文章的配图,从图中可以看出,系统的商品服务部署了多份在不同的服务器上,为了实现访问商品服务请求的分流,我们用到了负载均衡。
+The following image is from an article in the "High Concurrency" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247519384&idx=1&sn=bc7e71af75350b755f04ca4178395b1a&chksm=cea1c353f9d64a458f797696d4144b4d6e58639371a4612b8e4d106d83a66d2289e7b2cd7431&token=660789642&lang=zh_CN&scene=21#wechat_redirect). From the image, we can see that the system's product service is deployed across multiple servers, and to achieve request sharding for accessing the product service, we utilize load balancing.
-
+
-负载均衡是一种比较常用且实施起来较为简单的提高系统并发能力和可靠性的手段,不论是单体架构的系统还是微服务架构的系统几乎都会用到。
+Load balancing is a commonly used and relatively simple means of enhancing system concurrency and reliability. It is utilized in nearly all systems, whether they are monolithic architectures or microservice architectures.
-## 负载均衡分为哪几种?
+## What Types of Load Balancing Are There?
-负载均衡可以简单分为 **服务端负载均衡** 和 **客户端负载均衡** 这两种。
+Load balancing can be simply divided into **server-side load balancing** and **client-side load balancing**.
-服务端负载均衡涉及到的知识点更多,工作中遇到的也比较多,因此,我会花更多时间来介绍。
+Server-side load balancing involves more knowledge points and is encountered more frequently in work, hence I will spend more time introducing it.
-### 服务端负载均衡
+### Server-side Load Balancing
-**服务端负载均衡** 主要应用在 **系统外部请求** 和 **网关层** 之间,可以使用 **软件** 或者 **硬件** 实现。
+**Server-side load balancing** is mainly applied between **external system requests** and the **gateway layer** and can be implemented using **software** or **hardware**.
-下图是我画的一个简单的基于 Nginx 的服务端负载均衡示意图:
+The following diagram illustrates a simple server-side load balancing setup based on Nginx:
-
+
-**硬件负载均衡** 通过专门的硬件设备(比如 **F5、A10、Array** )实现负载均衡功能。
+**Hardware load balancing** is achieved via specialized hardware devices (such as **F5, A10, Array**).
-硬件负载均衡的优势是性能很强且稳定,缺点就是实在是太贵了。像基础款的 F5 最低也要 20 多万,绝大部分公司是根本负担不起的,业务量不大的话,真没必要非要去弄个硬件来做负载均衡,用软件负载均衡就足够了!
+The advantage of hardware load balancing is its strong and stable performance; however, the downside is that it is quite expensive. For instance, a basic model of F5 starts from over 200,000 yuan, which most companies cannot afford. If the business volume is not high, it is unnecessary to invest in hardware for load balancing; software load balancing suffices!
-在我们日常开发中,一般很难接触到硬件负载均衡,接触的比较多的还是 **软件负载均衡** 。软件负载均衡通过软件(比如 **LVS、Nginx、HAproxy** )实现负载均衡功能,性能虽然差一些,但价格便宜啊!像基础款的 Linux 服务器也就几千,性能好一点的 2~3 万的就很不错了。
+In our daily development, we generally have limited exposure to hardware load balancing, as we encounter **software load balancing** more frequently. Software load balancing uses software (such as **LVS, Nginx, HAProxy**) to implement load balancing functionality; while its performance is slightly lower, it is more cost-effective! For instance, a basic Linux server can be just a few thousand yuan, and a slightly better one might cost around 20,000 to 30,000 yuan.
-根据 OSI 模型,服务端负载均衡还可以分为:
+According to the OSI model, server-side load balancing can also be categorized into:
-- 二层负载均衡
-- 三层负载均衡
-- 四层负载均衡
-- 七层负载均衡
+- Layer 2 Load Balancing
+- Layer 3 Load Balancing
+- Layer 4 Load Balancing
+- Layer 7 Load Balancing
-最常见的是四层和七层负载均衡,因此,本文也是重点介绍这两种负载均衡。
+The most common types are Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing, thus this article will primarily focus on these two types.
-> Nginx 官网对四层负载和七层负载均衡均衡做了详细介绍,感兴趣的可以看看。
+> The Nginx official website provides a detailed introduction to Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing. If you're interested, you can check it out.
>
> - [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/)
> - [What Is Layer 7 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-7-load-balancing/)
-
+
-- **四层负载均衡** 工作在 OSI 模型第四层,也就是传输层,这一层的主要协议是 TCP/UDP,负载均衡器在这一层能够看到数据包里的源端口地址以及目的端口地址,会基于这些信息通过一定的负载均衡算法将数据包转发到后端真实服务器。也就是说,四层负载均衡的核心就是 IP+端口层面的负载均衡,不涉及具体的报文内容。
-- **七层负载均衡** 工作在 OSI 模型第七层,也就是应用层,这一层的主要协议是 HTTP 。这一层的负载均衡比四层负载均衡路由网络请求的方式更加复杂,它会读取报文的数据部分(比如说我们的 HTTP 部分的报文),然后根据读取到的数据内容(如 URL、Cookie)做出负载均衡决策。也就是说,七层负载均衡器的核心是报文内容(如 URL、Cookie)层面的负载均衡,执行第七层负载均衡的设备通常被称为 **反向代理服务器** 。
+- **Layer 4 load balancing** operates at the fourth layer of the OSI model, which is the transport layer. The main protocols at this layer are TCP/UDP. The load balancer at this layer can see the source and destination port addresses in the data packets and will forward the packets to the backend real servers based on this information using specific load balancing algorithms. In other words, the core of Layer 4 load balancing is IP + port level load balancing without involving the actual content of the messages.
+- **Layer 7 load balancing** functions at the seventh layer of the OSI model, which is the application layer. The main protocol at this layer is HTTP. The load balancing at this layer is more complex than at Layer 4, as it reads the message data section (for instance, the HTTP portion of messages), and makes load balancing decisions based on the content read (such as URL, Cookie). In other words, the core of Layer 7 load balancers is load balancing at the message content level (such as URL, Cookie), and devices performing Layer 7 load balancing are usually referred to as **reverse proxy servers**.
-七层负载均衡比四层负载均衡会消耗更多的性能,不过,也相对更加灵活,能够更加智能地路由网络请求,比如说你可以根据请求的内容进行优化如缓存、压缩、加密。
+Layer 7 load balancing consumes more performance than Layer 4 load balancing, but it is also relatively more flexible and capable of routing network requests more intelligently. For example, you can optimize based on request content, such as caching, compression, and encryption.
-简单来说,**四层负载均衡性能很强,七层负载均衡功能更强!** 不过,对于绝大部分业务场景来说,四层负载均衡和七层负载均衡的性能差异基本可以忽略不计的。
+In short, **Layer 4 load balancing has strong performance, while Layer 7 load balancing has more powerful functionalities!** However, for most business scenarios, the performance difference between Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing can generally be negligible.
-下面这段话摘自 Nginx 官网的 [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/) 这篇文章。
+The following excerpt is from the Nginx official article [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/).
> Layer 4 load balancing was a popular architectural approach to traffic handling when commodity hardware was not as powerful as it is now, and the interaction between clients and application servers was much less complex. It requires less computation than more sophisticated load balancing methods (such as Layer 7), but CPU and memory are now sufficiently fast and cheap that the performance advantage for Layer 4 load balancing has become negligible or irrelevant in most situations.
>
> 第 4 层负载平衡是一种流行的流量处理体系结构方法,当时商用硬件没有现在这么强大,客户端和应用程序服务器之间的交互也不那么复杂。它比更复杂的负载平衡方法(如第 7 层)需要更少的计算量,但是 CPU 和内存现在足够快和便宜,在大多数情况下,第 4 层负载平衡的性能优势已经变得微不足道或无关紧要。
-在工作中,我们通常会使用 **Nginx** 来做七层负载均衡,LVS(Linux Virtual Server 虚拟服务器, Linux 内核的 4 层负载均衡)来做四层负载均衡。
+In practice, we usually use **Nginx** for Layer 7 load balancing and LVS (Linux Virtual Server, a Layer 4 load balancer in the Linux kernel) for Layer 4 load balancing.
-关于 Nginx 的常见知识点总结,[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 中「技术面试题篇」中已经有对应的内容了,感兴趣的小伙伴可以去看看。
+For a summary of common knowledge about Nginx, corresponding content is already available in the "Technical Interview Questions" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html). Interested readers can take a look.
-不过,LVS 这个绝大部分公司真用不上,像阿里、百度、腾讯、eBay 等大厂才会使用到,用的最多的还是 Nginx。
+However, most companies do not need to use LVS; it is typically used by large companies like Alibaba, Baidu, Tencent, eBay, etc. The most commonly used solution remains Nginx.
-### 客户端负载均衡
+### Client-side Load Balancing
-**客户端负载均衡** 主要应用于系统内部的不同的服务之间,可以使用现成的负载均衡组件来实现。
+**Client-side load balancing** is mainly applied between different services within the system and can be implemented using existing load balancing components.
-在客户端负载均衡中,客户端会自己维护一份服务器的地址列表,发送请求之前,客户端会根据对应的负载均衡算法来选择具体某一台服务器处理请求。
+In client-side load balancing, the client maintains its own list of server addresses. Before sending a request, the client selects a specific server to handle the request based on the corresponding load balancing algorithm.
-客户端负载均衡器和服务运行在同一个进程或者说 Java 程序里,不存在额外的网络开销。不过,客户端负载均衡的实现会受到编程语言的限制,比如说 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 就只能用于 Java 语言。
+The client load balancer and the services run within the same process or Java program, eliminating additional network overhead. However, the implementation of client-side load balancing may be constrained by the programming language; for instance, Spring Cloud Load Balancer can only be used with Java.
-Java 领域主流的微服务框架 Dubbo、Spring Cloud 等都内置了开箱即用的客户端负载均衡实现。Dubbo 属于是默认自带了负载均衡功能,Spring Cloud 是通过组件的形式实现的负载均衡,属于可选项,比较常用的是 Spring Cloud Load Balancer(官方,推荐) 和 Ribbon(Netflix,已被弃用)。
+Mainstream microservice frameworks in the Java field, such as Dubbo and Spring Cloud, come with out-of-the-box client-side load balancing implementations. Dubbo has load balancing functionality built in by default, while Spring Cloud implements load balancing through components; it is optional, with Spring Cloud Load Balancer (official, recommended) and Ribbon (Netflix, deprecated) being the more commonly used options.
-下图是我画的一个简单的基于 Spring Cloud Load Balancer(Ribbon 也类似) 的客户端负载均衡示意图:
+The following diagram illustrates a simple client-side load balancing setup based on Spring Cloud Load Balancer (Ribbon is similar):
-## 负载均衡常见的算法有哪些?
+## What Are the Common Algorithms for Load Balancing?
-### 随机法
+### Random Method
-**随机法** 是最简单粗暴的负载均衡算法。
+**Random method** is the simplest and most brute-force load balancing algorithm.
-如果没有配置权重的话,所有的服务器被访问到的概率都是相同的。如果配置权重的话,权重越高的服务器被访问的概率就越大。
+If weights are not configured, all servers have the same probability of being accessed. If weights are configured, servers with higher weights are more likely to be accessed.
-未加权重的随机算法适合于服务器性能相近的集群,其中每个服务器承载相同的负载。加权随机算法适合于服务器性能不等的集群,权重的存在可以使请求分配更加合理化。
+The unweighted random algorithm is suitable for clusters with similar server performance, where each server bears the same load. The weighted random algorithm is suitable for clusters with unequal server performance, where the presence of weights allows for a more rational request distribution.
-不过,随机算法有一个比较明显的缺陷:部分机器在一段时间之内无法被随机到,毕竟是概率算法,就算是大家权重一样, 也可能会出现这种情况。
+However, the random algorithm has a notable flaw: some machines may not be randomly selected for a period of time due to the nature of probability algorithms. Even if everyone has the same weight, such situations can still occur.
-于是,**轮询法** 来了!
+Thus, the **Round Robin method** comes into play!
-### 轮询法
+### Round Robin Method
-轮询法是挨个轮询服务器处理,也可以设置权重。
+The Round Robin method involves polling each server for processing, and weights can also be set.
-如果没有配置权重的话,每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的服务器处理。如果配置权重的话,权重越高的服务器被访问的次数就越多。
+If weights are not configured, each request is distributed sequentially to different servers based on time. If weights are configured, the server with the higher weight will be accessed more frequently.
-未加权重的轮询算法适合于服务器性能相近的集群,其中每个服务器承载相同的负载。加权轮询算法适合于服务器性能不等的集群,权重的存在可以使请求分配更加合理化。
+The unweighted round robin algorithm is suitable for clusters with similar server performance, where each server bears the same load. The weighted round robin algorithm is suitable for clusters with unequal server performance, where the presence of weights allows for a more rational request distribution.
-在加权轮询的基础上,还有进一步改进得到的负载均衡算法,比如平滑的加权轮训算法。
+On the basis of weighted round robin, further improved load balancing algorithms may arise, such as the smooth weighted round robin algorithm.
-平滑的加权轮训算法最早是在 Nginx 中被实现,可以参考这个 commit:。如果你认真学习过 Dubbo 负载均衡策略的话,就会发现 Dubbo 的加权轮询就借鉴了该算法实现并进一步做了优化。
+The smooth weighted round robin algorithm was first implemented in Nginx; you can refer to this commit: . If you have studied Dubbo's load balancing strategies seriously, you will find that Dubbo's weighted round robin borrowed from this algorithm and further optimized it.
-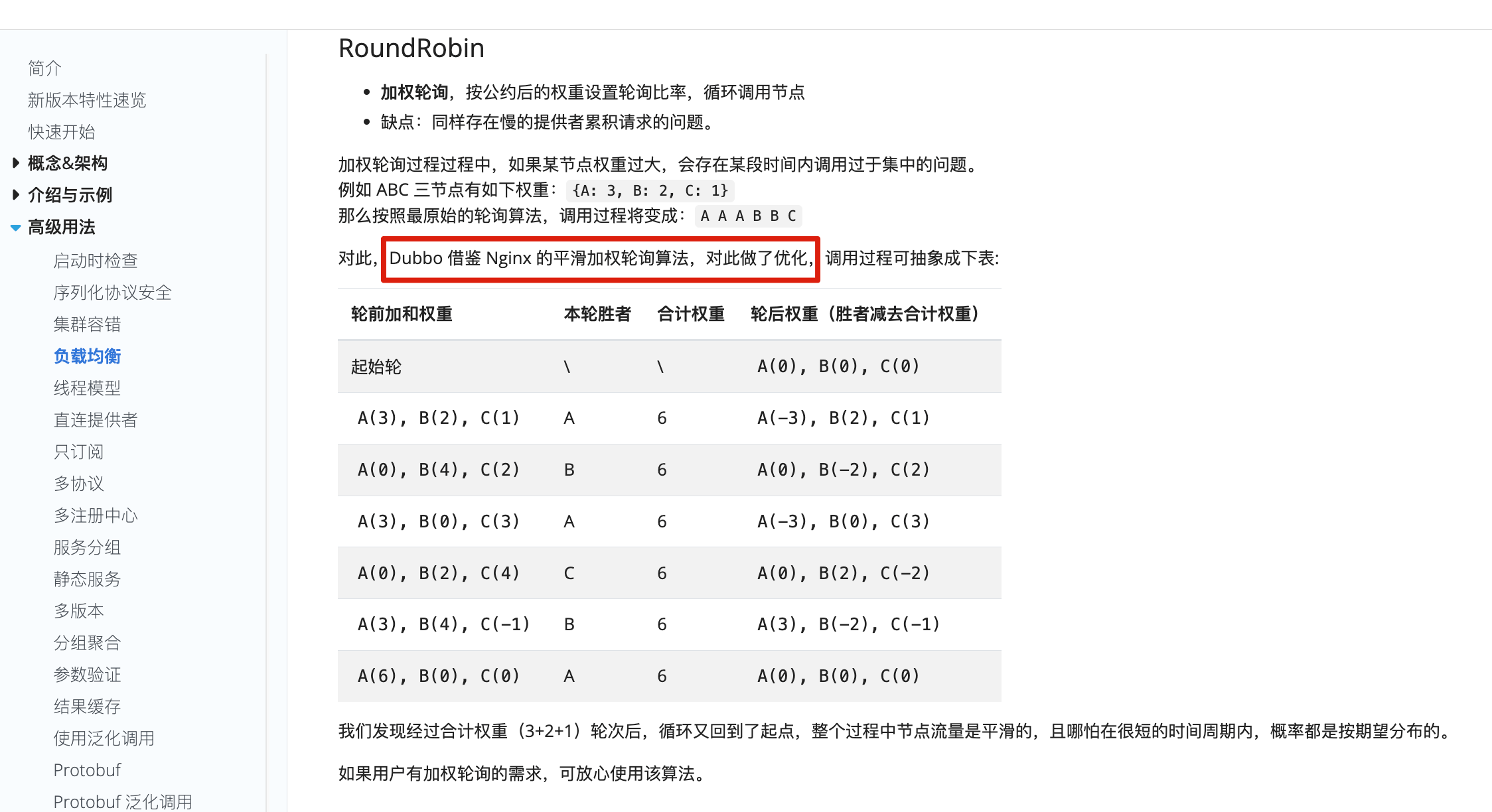
+
-### 两次随机法
+### Two-time Random Method
-两次随机法在随机法的基础上多增加了一次随机,多选出一个服务器。随后再根据两台服务器的负载等情况,从其中选择出一个最合适的服务器。
+The two-time random method adds an additional round of randomness on the basis of the random method by selecting an extra server. Then, based on the load conditions of these two servers, one is chosen as the most suitable for processing.
-两次随机法的好处是可以动态地调节后端节点的负载,使其更加均衡。如果只使用一次随机法,可能会导致某些服务器过载,而某些服务器空闲。
+The benefit of the two-time random method is that it can dynamically adjust the load of backend nodes to achieve better balance. Relying solely on the single random method may lead to certain servers being overloaded while others remain idle.
-### 哈希法
+### Hash Method
-将请求的参数信息通过哈希函数转换成一个哈希值,然后根据哈希值来决定请求被哪一台服务器处理。
+The request parameters are transformed into a hash value using a hash function, and the request is then directed to the server based on this hash value.
-在服务器数量不变的情况下,相同参数的请求总是发到同一台服务器处理,比如同个 IP 的请求、同一个用户的请求。
+When the number of servers remains the same, requests with the same parameters will always be sent to the same server, such as requests from the same IP address or requests from the same user.
-### 一致性 Hash 法
+### Consistent Hash Method
-和哈希法类似,一致性 Hash 法也可以让相同参数的请求总是发到同一台服务器处理。不过,它解决了哈希法存在的一些问题。
+Similar to the hash method, the consistent hash method also allows requests with the same parameters to be consistently sent to the same server. However, it addresses some issues present in the hash method.
-常规哈希法在服务器数量变化时,哈希值会重新落在不同的服务器上,这明显违背了使用哈希法的本意。而一致性哈希法的核心思想是将数据和节点都映射到一个哈希环上,然后根据哈希值的顺序来确定数据属于哪个节点。当服务器增加或删除时,只影响该服务器的哈希,而不会导致整个服务集群的哈希键值重新分布。
+Conventional hash methods reassign hash values to different servers when the number of servers changes, which clearly defeats the purpose of using the hash method. The core idea of consistent hashing is to map both data and nodes onto a hash ring and determine the respective nodes based on the order of hash values. When servers are added or removed, only the hash of the related servers is affected, without causing a complete redistribution of the hash keys across the service cluster.
-### 最小连接法
+### Least Connections Method
-当有新的请求出现时,遍历服务器节点列表并选取其中连接数最小的一台服务器来响应当前请求。相同连接的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+When a new request arrives, the load balancer traverses the server node list and selects the one with the least number of connections to handle the current request. In the case of equal connections, weighted random methods may be employed.
-最少连接数基于一个服务器连接数越多,负载就越高这一理想假设。然而, 实际情况是连接数并不能代表服务器的实际负载,有些连接耗费系统资源更多,有些连接不怎么耗费系统资源。
+The least connected method is based on the ideal assumption that a higher number of connections indicates a higher load on the server. In practice, however, the number of connections does not accurately represent the server's actual load, as some connections may consume more system resources than others.
-### 最少活跃法
+### Least Active Method
-最少活跃法和最小连接法类似,但要更科学一些。最少活跃法以活动连接数为标准,活动连接数可以理解为当前正在处理的请求数。活跃数越低,说明处理能力越强,这样就可以使处理能力强的服务器处理更多请求。相同活跃数的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+The least active method is similar to the least connections method but is more scientific. The least active method uses the number of active connections as the standard; active connections could be understood as the current number of requests being processed. The lower the active connection count, the stronger the processing capacity, allowing more requests to be handled by stronger servers. In the case of the same number of active connections, weighted random methods can be employed.
-### 最快响应时间法
+### Fastest Response Time Method
-不同于最小连接法和最少活跃法,最快响应时间法以响应时间为标准来选择具体是哪一台服务器处理。客户端会维持每个服务器的响应时间,每次请求挑选响应时间最短的。相同响应时间的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+Differing from the least connections and least active methods, the fastest response time method selects the appropriate server based on the response time. The client maintains the response times for each server and chooses the one with the shortest response time for each request. In the case of equal response times, weighted random methods may be employed.
-这种算法可以使得请求被更快处理,但可能会造成流量过于集中于高性能服务器的问题。
+This algorithm ensures that requests are processed more quickly, but it may lead to an excessive concentration of traffic on high-performance servers.
-## 七层负载均衡可以怎么做?
+## How Can Layer 7 Load Balancing Be Achieved?
-简单介绍两种项目中常用的七层负载均衡解决方案:DNS 解析和反向代理。
+Let’s briefly introduce two commonly used Layer 7 load balancing solutions: DNS resolution and reverse proxy.
-除了我介绍的这两种解决方案之外,HTTP 重定向等手段也可以用来实现负载均衡,不过,相对来说,还是 DNS 解析和反向代理用的更多一些,也更推荐一些。
+Apart from the two solutions introduced, other methods such as HTTP redirection can also achieve load balancing; however, DNS resolution and reverse proxy are generally used more and are recommended.
-### DNS 解析
+### DNS Resolution
-DNS 解析是比较早期的七层负载均衡实现方式,非常简单。
+DNS resolution is an early implementation of Layer 7 load balancing; it is very simple.
-DNS 解析实现负载均衡的原理是这样的:在 DNS 服务器中为同一个主机记录配置多个 IP 地址,这些 IP 地址对应不同的服务器。当用户请求域名的时候,DNS 服务器采用轮询算法返回 IP 地址,这样就实现了轮询版负载均衡。
+The principle of DNS resolution for achieving load balancing is as follows: Multiple IP addresses corresponding to different servers are configured in the DNS server for the same host record. When a user requests a domain name, the DNS server uses a round-robin algorithm to return an IP address, thereby achieving round-robin load balancing.
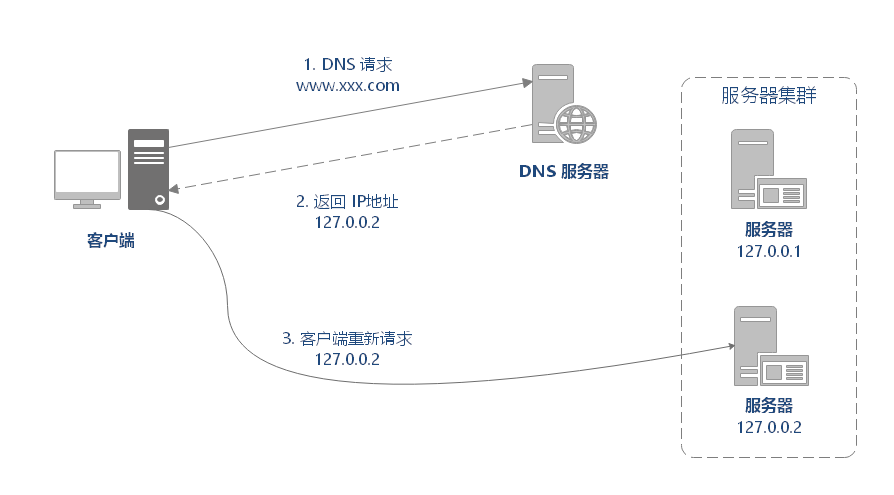
-现在的 DNS 解析几乎都支持 IP 地址的权重配置,这样的话,在服务器性能不等的集群中请求分配会更加合理化。像我自己目前正在用的阿里云 DNS 就支持权重配置。
+Most modern DNS resolutions support the configuration of weight for IP addresses, making request distribution in clusters with unequal server performance more rational. For instance, Alibaba Cloud DNS, which I am currently using, supports weight configuration.
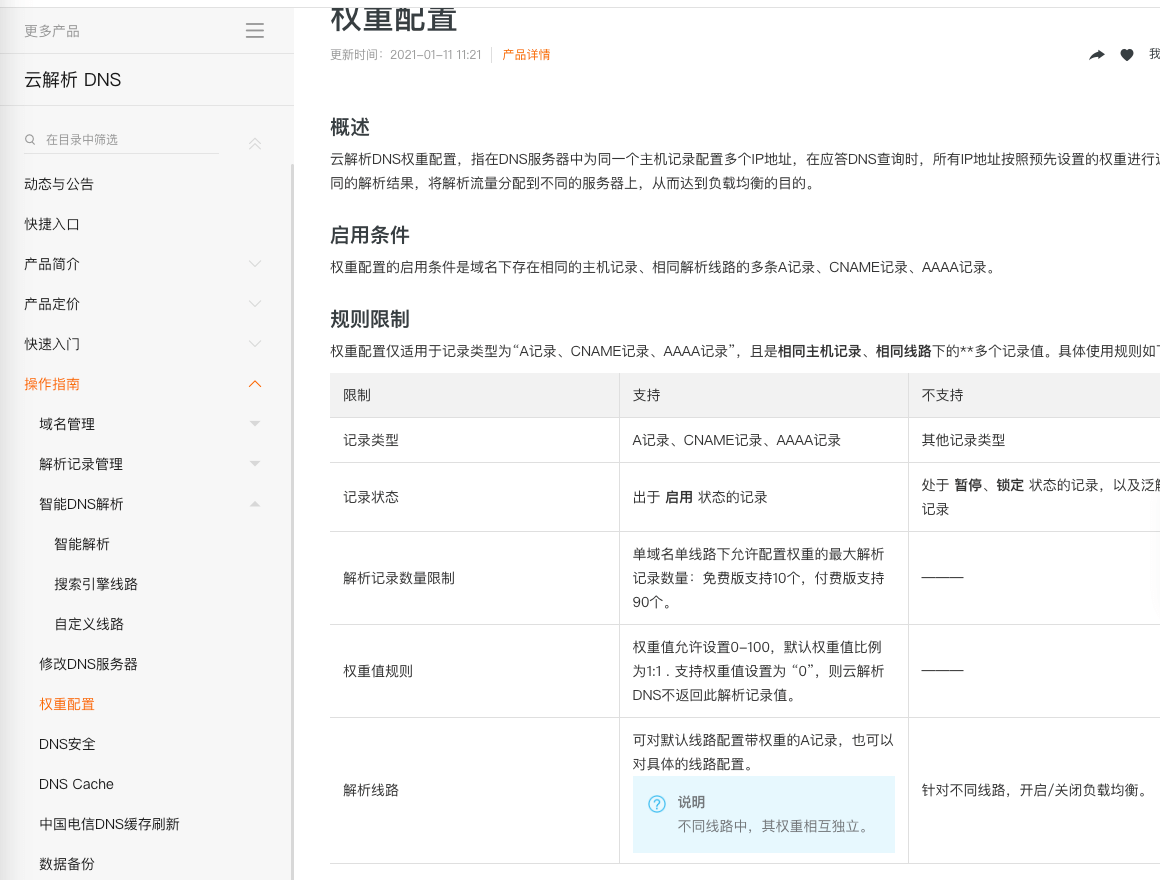
-### 反向代理
+### Reverse Proxy
-客户端将请求发送到反向代理服务器,由反向代理服务器去选择目标服务器,获取数据后再返回给客户端。对外暴露的是反向代理服务器地址,隐藏了真实服务器 IP 地址。反向代理“代理”的是目标服务器,这一个过程对于客户端而言是透明的。
+Clients send requests to the reverse proxy server, which then selects the target server. After obtaining the data, it is returned to the client. The external address exposed is the reverse proxy server's address, concealing the real server IP addresses. The reverse proxy "proxies" the target server, and this process is transparent to the client.
-Nginx 就是最常用的反向代理服务器,它可以将接收到的客户端请求以一定的规则(负载均衡策略)均匀地分配到这个服务器集群中所有的服务器上。
+Nginx is the most commonly used reverse proxy server, capable of evenly distributing incoming client requests across all servers in the server cluster based on certain rules (load balancing strategies).
-反向代理负载均衡同样属于七层负载均衡。
+Reverse proxy load balancing also falls under Layer 7 load balancing.

-## 客户端负载均衡通常是怎么做的?
+## How Is Client-side Load Balancing Usually Implemented?
-我们上面也说了,客户端负载均衡可以使用现成的负载均衡组件来实现。
+As mentioned earlier, client-side load balancing can be implemented using existing load balancing components.
-**Netflix Ribbon** 和 **Spring Cloud Load Balancer** 就是目前 Java 生态最流行的两个负载均衡组件。
+**Netflix Ribbon** and **Spring Cloud Load Balancer** are currently the two most popular load balancing components in the Java ecosystem.
-Ribbon 是老牌负载均衡组件,由 Netflix 开发,功能比较全面,支持的负载均衡策略也比较多。 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 是 Spring 官方为了取代 Ribbon 而推出的,功能相对更简单一些,支持的负载均衡也少一些。
+Ribbon is an established load balancing component developed by Netflix, offering comprehensive features and supporting various load balancing strategies. Spring Cloud Load Balancer is launched by Spring as a replacement for Ribbon, featuring a relatively simpler function set and fewer supported load balancing strategies.
-Ribbon 支持的 7 种负载均衡策略:
+The 7 load balancing strategies supported by Ribbon include:
-- `RandomRule`:随机策略。
-- `RoundRobinRule`(默认):轮询策略
-- `WeightedResponseTimeRule`:权重(根据响应时间决定权重)策略
-- `BestAvailableRule`:最小连接数策略
-- `RetryRule`:重试策略(按照轮询策略来获取服务,如果获取的服务实例为 null 或已经失效,则在指定的时间之内不断地进行重试来获取服务,如果超过指定时间依然没获取到服务实例则返回 null)
-- `AvailabilityFilteringRule`:可用敏感性策略(先过滤掉非健康的服务实例,然后再选择连接数较小的服务实例)
-- `ZoneAvoidanceRule`:区域敏感性策略(根据服务所在区域的性能和服务的可用性来选择服务实例)
+- `RandomRule`: Random strategy.
+- `RoundRobinRule` (default): Round-robin strategy
+- `WeightedResponseTimeRule`: Weighted strategy (determining weights based on response time)
+- `BestAvailableRule`: Least connections strategy
+- `RetryRule`: Retry strategy (fetching services based on round-robin strategy; if the obtained service instance is null or already invalid, it keeps retrying within the specified time; if it still cannot fetch a service instance beyond the specified time, it returns null)
+- `AvailabilityFilteringRule`: Availability sensitivity strategy (first filtering out unhealthy service instances, then choosing the one with a lesser number of connections)
+- `ZoneAvoidanceRule`: Zone sensitivity strategy (selecting service instances based on performance and availability of the service's operating zone)
-Spring Cloud Load Balancer 支持的 2 种负载均衡策略:
+The 2 load balancing strategies supported by Spring Cloud Load Balancer include:
-- `RandomLoadBalancer`:随机策略
-- `RoundRobinLoadBalancer`(默认):轮询策略
+- `RandomLoadBalancer`: Random strategy
+- `RoundRobinLoadBalancer` (default): Round-robin strategy
```java
public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
@@ -218,16 +218,16 @@ public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
}
```
-不过,Spring Cloud Load Balancer 支持的负载均衡策略其实不止这两种,`ServiceInstanceListSupplier` 的实现类同样可以让其支持类似于 Ribbon 的负载均衡策略。这个应该是后续慢慢完善引入的,不看官方文档还真发现不了,所以说阅读官方文档真的很重要!
+However, the load balancing strategies supported by Spring Cloud Load Balancer extend beyond just these two; the implementation class of `ServiceInstanceListSupplier` can also be configured to support loading balancing strategies similar to those of Ribbon. This should be gradually improved and introduced in future updates. Without looking at the official documentation, one might not realize this, which underscores the importance of reading official documentation!
-这里举两个官方的例子:
+Here are two official examples:
-- `ZonePreferenceServiceInstanceListSupplier`:实现基于区域的负载平衡
-- `HintBasedServiceInstanceListSupplier`:实现基于 hint 提示的负载均衡
+- `ZonePreferenceServiceInstanceListSupplier`: Implements region-based load balancing
+- `HintBasedServiceInstanceListSupplier`: Implements hint-based load balancing
```java
public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
- // 使用基于区域的负载平衡方法
+ // Using region-based loading balancing method
@Bean
public ServiceInstanceListSupplier discoveryClientServiceInstanceListSupplier(
ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
@@ -240,28 +240,28 @@ public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
}
```
-关于 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 更详细更新的介绍,推荐大家看看官方文档: ,一切以官方文档为主。
+For a more detailed and updated introduction to Spring Cloud Load Balancer, I recommend checking the official documentation: , everything is based on the official documentation.
-轮询策略基本可以满足绝大部分项目的需求,我们的实际项目中如果没有特殊需求的话,通常使用的就是默认的轮询策略。并且,Ribbon 和 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 都支持自定义负载均衡策略。
+The round-robin strategy can meet the needs of the vast majority of projects. In our actual projects, if there are no special requirements, we usually just use the default round-robin strategy. Moreover, both Ribbon and Spring Cloud Load Balancer support custom load balancing strategies.
-个人建议如非必需 Ribbon 某个特有的功能或者负载均衡策略的话,就优先选择 Spring 官方提供的 Spring Cloud Load Balancer。
+Personally, I suggest opting for Spring Cloud Load Balancer first unless you specifically need a unique feature or load balancing strategy from Ribbon.
-最后再说说为什么我不太推荐使用 Ribbon 。
+Lastly, let's discuss why I do not recommend using Ribbon much.
-Spring Cloud 2020.0.0 版本移除了 Netflix 除 Eureka 外的所有组件。Spring Cloud Hoxton.M2 是第一个支持 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 来替代 Netfix Ribbon 的版本。
+Spring Cloud 2020.0.0 version removed all Netflix components except for Eureka. Spring Cloud Hoxton.M2 was the first version to support Spring Cloud Load Balancer in place of Netflix Ribbon.
-我们早期学习微服务,肯定接触过 Netflix 公司开源的 Feign、Ribbon、Zuul、Hystrix、Eureka 等知名的微服务系统构建所必须的组件,直到现在依然有非常非常多的公司在使用这些组件。不夸张地说,Netflix 公司引领了 Java 技术栈下的微服务发展。
+When we were learning about microservices, we certainly came across well-known components necessary for building microservices systems, such as Feign, Ribbon, Zuul, Hystrix, and Eureka from Netflix. Even now, many companies are still using these components. It is not an exaggeration to say that Netflix has led the development of microservices in the Java technology stack.
-**那为什么 Spring Cloud 这么急着移除 Netflix 的组件呢?** 主要是因为在 2018 年的时候,Netflix 宣布其开源的核心组件 Hystrix、Ribbon、Zuul、Eureka 等进入维护状态,不再进行新特性开发,只修 BUG。于是,Spring 官方不得不考虑移除 Netflix 的组件。
+**So why is Spring Cloud so eager to remove Netflix components?** The main reason is that in 2018, Netflix announced that its core open-source components such as Hystrix, Ribbon, Zuul, and Eureka would enter maintenance mode, ceasing new feature developments and focusing solely on bug fixes. Therefore, Spring had to consider removing Netflix components.
-**Spring Cloud Alibaba** 是一个不错的选择,尤其是对于国内的公司和个人开发者来说。
+**Spring Cloud Alibaba** is a good choice, especially for domestic companies and individual developers.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 干货 | eBay 的 4 层软件负载均衡实现:
-- HTTP Load Balancing(Nginx 官方文档):
-- 深入浅出负载均衡 - vivo 互联网技术:
+- Practical Guide | eBay's Layer 4 Software Load Balancing Implementation:
+- HTTP Load Balancing (Nginx Official Documentation):
+- In-depth Understanding of Load Balancing - Vivo Internet Technology:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md b/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
index 1881f6c2c79..ca3185ec15f 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
@@ -1,140 +1,140 @@
---
-title: Disruptor常见问题总结
-category: 高性能
+title: Summary of Common Questions About Disruptor
+category: High Performance
tag:
- - 消息队列
+ - Message Queue
---
-Disruptor 是一个相对冷门一些的知识点,不过,如果你的项目经历中用到了 Disruptor 的话,那面试中就很可能会被问到。
+Disruptor is a relatively niche topic, but if you've used Disruptor in your project experience, it's likely you'll be asked about it in an interview.
-一位球友之前投稿的面经(社招)中就涉及一些 Disruptor 的问题,文章传送门:[圆梦!顺利拿到字节、淘宝、拼多多等大厂 offer!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/C5QMjwEb6pzXACqZsyqC4A) 。
+A fellow player previously submitted an interview experience (for external recruitment) that included some Disruptor-related questions. You can find the article here: [Achieved my dream! Successfully received offers from major companies like ByteDance, Taobao, and Pinduoduo!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/C5QMjwEb6pzXACqZsyqC4A).

-这篇文章可以看作是对 Disruptor 做的一个简单总结,每个问题都不会扯太深入,主要针对面试或者速览 Disruptor。
+This article can be seen as a simple summary of Disruptor. Each question does not delve too deeply and is mainly focused on interviews or a quick overview of Disruptor.
-## Disruptor 是什么?
+## What is Disruptor?
-Disruptor 是一个开源的高性能内存队列,诞生初衷是为了解决内存队列的性能和内存安全问题,由英国外汇交易公司 LMAX 开发。
+Disruptor is an open-source high-performance memory queue, originally developed to solve performance and memory safety issues associated with memory queues by LMAX, a foreign exchange trading company in the UK.
-根据 Disruptor 官方介绍,基于 Disruptor 开发的系统 LMAX(新的零售金融交易平台),单线程就能支撑每秒 600 万订单。Martin Fowler 在 2011 年写的一篇文章 [The LMAX Architecture](https://martinfowler.com/articles/lmax.html) 中专门介绍过这个 LMAX 系统的架构,感兴趣的可以看看这篇文章。。
+According to the official introduction of Disruptor, the LMAX system developed based on Disruptor (a new retail financial trading platform) can support 6 million orders per second with a single thread. Martin Fowler wrote an article in 2011 [The LMAX Architecture](https://martinfowler.com/articles/lmax.html) specifically introducing the architecture of this LMAX system, which may be of interest.
-LMAX 公司 2010 年在 QCon 演讲后,Disruptor 获得了业界关注,并获得了 2011 年的 Oracle 官方的 Duke's Choice Awards(Duke 选择大奖)。
+After LMAX’s presentation at QCon in 2010, Disruptor received attention from the industry and won the Oracle official Duke's Choice Award in 2011.

-> “Duke 选择大奖”旨在表彰过去一年里全球个人或公司开发的、最具影响力的 Java 技术应用,由甲骨文公司主办。含金量非常高!
+> The "Duke's Choice Award" aims to recognize the most influential Java technology applications developed by individuals or companies worldwide in the past year, and is hosted by Oracle. It holds significant value!
-我专门找到了 Oracle 官方当年颁布获得 Duke's Choice Awards 项目的那篇文章(文章地址: 。从文中可以看出,同年获得此大奖荣誉的还有大名鼎鼎的 Netty、JRebel 等项目。
+I specifically found the Oracle official article announcing the Duke's Choice Award winners that year (article link: ). From the text, it can be seen that other well-known projects such as Netty and JRebel also received this award that year.
-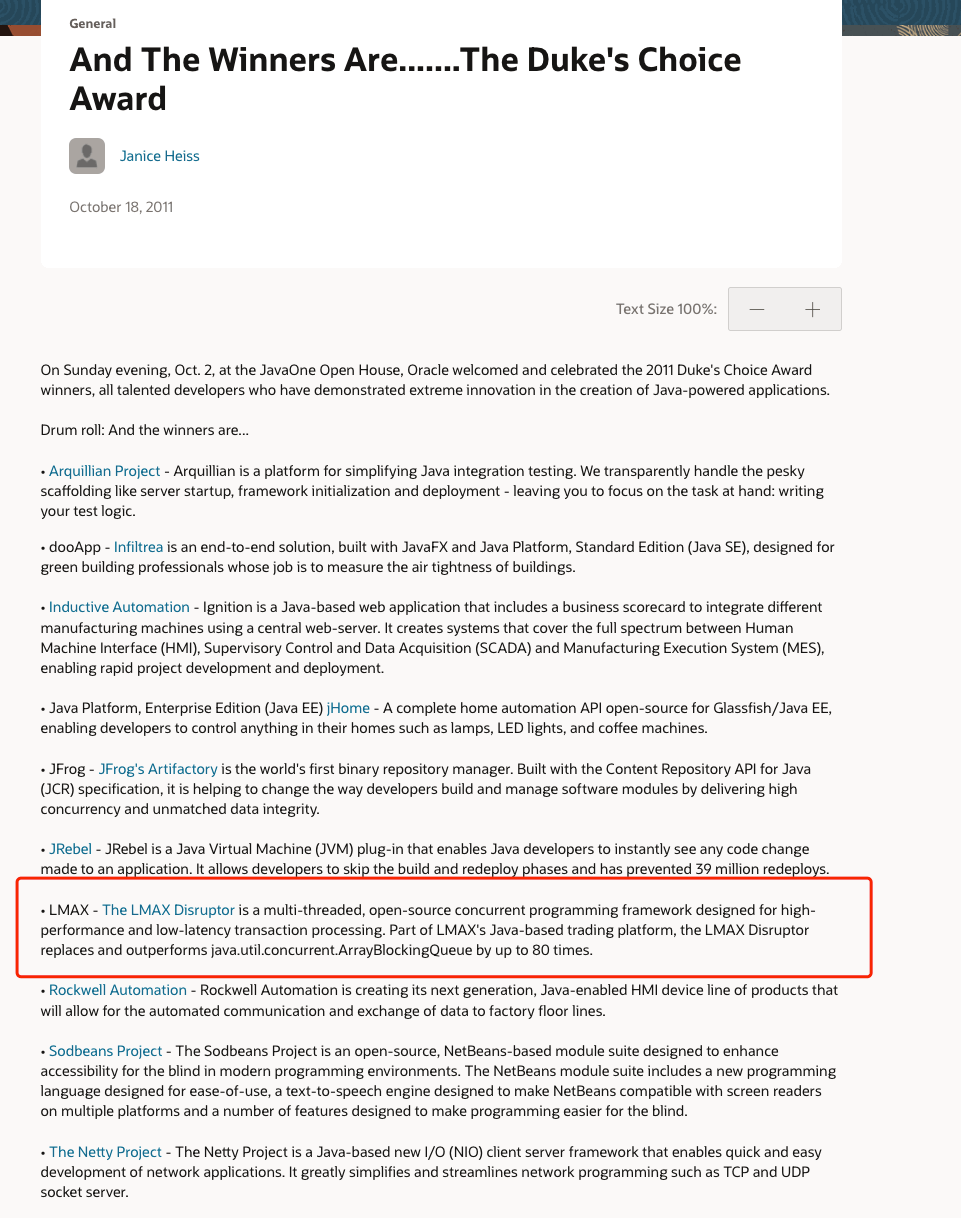
+
-Disruptor 提供的功能优点类似于 Kafka、RocketMQ 这类分布式队列,不过,其作为范围是 JVM(内存)。
+The capabilities provided by Disruptor are similar to those of distributed queues like Kafka and RocketMQ, but its scope is JVM (memory).
-- Github 地址:
-- 官方教程:
+- GitHub link:
+- Official tutorial:
-关于如何在 Spring Boot 项目中使用 Disruptor,可以看这篇文章:[Spring Boot + Disruptor 实战入门](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0iG5brK3bYF0BgSjX4jRiA) 。
+To learn how to use Disruptor in a Spring Boot project, you can refer to this article: [Spring Boot + Disruptor Practical Introduction](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0iG5brK3bYF0BgSjX4jRiA).
-## 为什么要用 Disruptor?
+## Why Use Disruptor?
-Disruptor 主要解决了 JDK 内置线程安全队列的性能和内存安全问题。
+Disruptor mainly addresses the performance and memory safety issues of the JDK's built-in thread-safe queues.
-**JDK 中常见的线程安全的队列如下**:
+**The commonly used thread-safe queues in the JDK are as follows**:
-| 队列名字 | 锁 | 是否有界 |
-| ----------------------- | ----------------------- | -------- |
-| `ArrayBlockingQueue` | 加锁(`ReentrantLock`) | 有界 |
-| `LinkedBlockingQueue` | 加锁(`ReentrantLock`) | 有界 |
-| `LinkedTransferQueue` | 无锁(`CAS`) | 无界 |
-| `ConcurrentLinkedQueue` | 无锁(`CAS`) | 无界 |
+| Queue Name | Lock | Bounded/Unbounded |
+| ----------------------- | ------------------------ | ----------------- |
+| `ArrayBlockingQueue` | Locked (`ReentrantLock`) | Bounded |
+| `LinkedBlockingQueue` | Locked (`ReentrantLock`) | Bounded |
+| `LinkedTransferQueue` | Lock-Free (`CAS`) | Unbounded |
+| `ConcurrentLinkedQueue` | Lock-Free (`CAS`) | Unbounded |
-从上表中可以看出:这些队列要不就是加锁有界,要不就是无锁无界。而加锁的的队列势必会影响性能,无界的队列又存在内存溢出的风险。
+As can be seen from the table above, these queues are either bounded and locked or unbounded and lock-free. The locked queues inevitably affect performance, while unbounded queues face the risk of memory overflow.
-因此,一般情况下,我们都是不建议使用 JDK 内置线程安全队列。
+Therefore, in general, we do not recommend using the JDK's built-in thread-safe queues.
-**Disruptor 就不一样了!它在无锁的情况下还能保证队列有界,并且还是线程安全的。**
+**Disruptor is different! It guarantees that the queue is bounded while being lock-free, and it is still thread-safe.**
-下面这张图是 Disruptor 官网提供的 Disruptor 和 ArrayBlockingQueue 的延迟直方图对比。
+The following image is a comparison of latency histograms between Disruptor and ArrayBlockingQueue provided by the Disruptor official website.
-Disruptor 真的很快,关于它为什么这么快这个问题,会在后文介绍到。
+Disruptor is indeed very fast, and we will introduce why it is so fast later.
-此外,Disruptor 还提供了丰富的扩展功能比如支持批量操作、支持多种等待策略。
+Additionally, Disruptor also provides a rich set of extension capabilities, such as supporting batch operations and multiple wait strategies.
-## Kafka 和 Disruptor 什么区别?
+## What Are the Differences Between Kafka and Disruptor?
-- **Kafka**:分布式消息队列,一般用在系统或者服务之间的消息传递,还可以被用作流式处理平台。
-- **Disruptor**:内存级别的消息队列,一般用在系统内部中线程间的消息传递。
+- **Kafka**: A distributed message queue typically used for message transmission between systems or services and can also be used as a stream processing platform.
+- **Disruptor**: A memory-level message queue commonly used for message transmission between threads within a system.
-## 哪些组件用到了 Disruptor?
+## Which Components Use Disruptor?
-用到 Disruptor 的开源项目还是挺多的,这里简单举几个例子:
+There are quite a few open-source projects that utilize Disruptor. Here are a few examples:
-- **Log4j2**:Log4j2 是一款常用的日志框架,它基于 Disruptor 来实现异步日志。
-- **SOFATracer**:SOFATracer 是蚂蚁金服开源的分布式应用链路追踪工具,它基于 Disruptor 来实现异步日志。
-- **Storm** : Storm 是一个开源的分布式实时计算系统,它基于 Disruptor 来实现工作进程内发生的消息传递(同一 Storm 节点上的线程间,无需网络通信)。
-- **HBase**:HBase 是一个分布式列存储数据库系统,它基于 Disruptor 来提高写并发性能。
+- **Log4j2**: Log4j2 is a commonly used logging framework that implements asynchronous logging based on Disruptor.
+- **SOFATracer**: SOFATracer is an open-source distributed application tracing tool developed by Ant Financial, which uses Disruptor for asynchronous logging.
+- **Storm**: Storm is an open-source distributed real-time computation system that uses Disruptor for message passing within the same worker process (between threads on the same Storm node, without the need for network communication).
+- **HBase**: HBase is a distributed column storage database system that uses Disruptor to improve write concurrency performance.
- ……
-## Disruptor 核心概念有哪些?
+## What Are the Core Concepts of Disruptor?
-- **Event**:你可以把 Event 理解为存放在队列中等待消费的消息对象。
-- **EventFactory**:事件工厂用于生产事件,我们在初始化 `Disruptor` 类的时候需要用到。
-- **EventHandler**:Event 在对应的 Handler 中被处理,你可以将其理解为生产消费者模型中的消费者。
-- **EventProcessor**:EventProcessor 持有特定消费者(Consumer)的 Sequence,并提供用于调用事件处理实现的事件循环(Event Loop)。
-- **Disruptor**:事件的生产和消费需要用到 `Disruptor` 对象。
-- **RingBuffer**:RingBuffer(环形数组)用于保存事件。
-- **WaitStrategy**:等待策略。决定了没有事件可以消费的时候,事件消费者如何等待新事件的到来。
-- **Producer**:生产者,只是泛指调用 `Disruptor` 对象发布事件的用户代码,Disruptor 没有定义特定接口或类型。
-- **ProducerType**:指定是单个事件发布者模式还是多个事件发布者模式(发布者和生产者的意思类似,我个人比较喜欢用发布者)。
-- **Sequencer**:Sequencer 是 Disruptor 的真正核心。此接口有两个实现类 `SingleProducerSequencer`、`MultiProducerSequencer` ,它们定义在生产者和消费者之间快速、正确地传递数据的并发算法。
+- **Event**: You can think of an Event as a message object that is stored in the queue waiting to be consumed.
+- **EventFactory**: The event factory is used to produce events that we need when initializing the `Disruptor` class.
+- **EventHandler**: Events are processed in the corresponding Handler, which can be understood as the consumer in the producer-consumer model.
+- **EventProcessor**: EventProcessor holds the sequence of a specific consumer and provides an event loop for invoking the implementation of event processing.
+- **Disruptor**: The production and consumption of events require the `Disruptor` object.
+- **RingBuffer**: RingBuffer (circular array) is used to store events.
+- **WaitStrategy**: The wait strategy determines how the event consumers wait for new events to arrive when there are no events to consume.
+- **Producer**: The producer refers generically to user code that calls the `Disruptor` object to publish events; Disruptor does not define a specific interface or type.
+- **ProducerType**: Specifies whether it is a single event publisher mode or multiple event publisher mode (the term publisher is similar to producer, and I personally prefer to use publisher).
+- **Sequencer**: The Sequencer is the true core of Disruptor. This interface has two implementation classes: `SingleProducerSequencer` and `MultiProducerSequencer`, which define a concurrent algorithm for fast and correct data transmission between producers and consumers.
-下面这张图摘自 Disruptor 官网,展示了 LMAX 系统使用 Disruptor 的示例。
+The following image is extracted from the Disruptor official website and shows an example of using Disruptor in the LMAX system.
-
+
-## Disruptor 等待策略有哪些?
+## What Are the Wait Strategies of Disruptor?
-**等待策略(WaitStrategy)** 决定了没有事件可以消费的时候,事件消费者如何等待新事件的到来。
+**WaitStrategy** determines how event consumers wait for new events to arrive when there are no events to consume.
-常见的等待策略有下面这些:
+Common wait strategies include the following:
-
+
-- `BlockingWaitStrategy`:基于 `ReentrantLock`+`Condition` 来实现等待和唤醒操作,实现代码非常简单,是 Disruptor 默认的等待策略。虽然最慢,但也是 CPU 使用率最低和最稳定的选项生产环境推荐使用;
-- `BusySpinWaitStrategy`:性能很好,存在持续自旋的风险,使用不当会造成 CPU 负载 100%,慎用;
-- `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`:基于 `BlockingWaitStrategy` 的轻量级等待策略,在没有锁竞争的时候会省去唤醒操作,但是作者说测试不充分,因此不建议使用;
-- `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`:带超时的等待策略,超时后会执行业务指定的处理逻辑;
-- `LiteTimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`:基于`TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`的策略,当没有锁竞争的时候会省去唤醒操作;
-- `SleepingWaitStrategy`:三段式策略,第一阶段自旋,第二阶段执行 Thread.yield 让出 CPU,第三阶段睡眠执行时间,反复的睡眠;
-- `YieldingWaitStrategy`:二段式策略,第一阶段自旋,第二阶段执行 Thread.yield 交出 CPU;
-- `PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy`:四段式策略,第一阶段自旋指定次数,第二阶段自旋指定时间,第三阶段执行 `Thread.yield` 交出 CPU,第四阶段调用成员变量的`waitFor`方法,该成员变量可以被设置为`BlockingWaitStrategy`、`LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`、`SleepingWaitStrategy`三个中的一个。
+- `BlockingWaitStrategy`: Implemented using `ReentrantLock` + `Condition` for waiting and waking operations. The implementation code is quite simple and is the default wait strategy of Disruptor. Although it is the slowest, it is also the option with the lowest and most stable CPU usage and is recommended for production environments.
+- `BusySpinWaitStrategy`: Provides good performance but has the risk of continuous spinning, which can cause the CPU load to reach 100% if used improperly, so caution is advised.
+- `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`: A lightweight wait strategy based on `BlockingWaitStrategy` that skips the waking operation when there is no lock contention, but the author mentions that testing is insufficient and therefore it's not recommended for use.
+- `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`: A wait strategy with a timeout that executes specified processing logic after the timeout.
+- `LiteTimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`: A strategy based on `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy` that skips wakening operations when there is no lock contention.
+- `SleepingWaitStrategy`: A three-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins; in the second phase, it executes Thread.yield to give up the CPU; in the third phase, it sleeps for a specific time, repeating the sleep.
+- `YieldingWaitStrategy`: A two-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins; in the second phase, it executes Thread.yield to yield the CPU.
+- `PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy`: A four-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins a specified number of times; in the second phase, it spins for a specified duration; in the third phase, it executes `Thread.yield` to yield the CPU; in the fourth phase, it calls the member variable's `waitFor` method, which can be set to one of `BlockingWaitStrategy`, `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`, or `SleepingWaitStrategy`.
-## Disruptor 为什么这么快?
+## Why is Disruptor So Fast?
-- **RingBuffer(环形数组)** : Disruptor 内部的 RingBuffer 是通过数组实现的。由于这个数组中的所有元素在初始化时一次性全部创建,因此这些元素的内存地址一般来说是连续的。这样做的好处是,当生产者不断往 RingBuffer 中插入新的事件对象时,这些事件对象的内存地址就能够保持连续,从而利用 CPU 缓存的局部性原理,将相邻的事件对象一起加载到缓存中,提高程序的性能。这类似于 MySQL 的预读机制,将连续的几个页预读到内存里。除此之外,RingBuffer 基于数组还支持批量操作(一次处理多个元素)、还可以避免频繁的内存分配和垃圾回收(RingBuffer 是一个固定大小的数组,当向数组中添加新元素时,如果数组已满,则新元素将覆盖掉最旧的元素)。
-- **避免了伪共享问题**:CPU 缓存内部是按照 Cache Line(缓存行)管理的,一般的 Cache Line 大小在 64 字节左右。Disruptor 为了确保目标字段独占一个 Cache Line,会在目标字段前后增加字节填充(前 56 个字节和后 56 个字节),这样可以避免 Cache Line 的伪共享(False Sharing)问题。同时,为了让 RingBuffer 存放数据的数组独占缓存行,数组的设计为 无效填充(128 字节)+ 有效数据。
-- **无锁设计**:Disruptor 采用无锁设计,避免了传统锁机制带来的竞争和延迟。Disruptor 的无锁实现起来比较复杂,主要是基于 CAS、内存屏障(Memory Barrier)、RingBuffer 等技术实现的。
+- **RingBuffer (Circular Array)**: The internal RingBuffer of Disruptor is implemented via an array. Since all elements of this array are created at once during initialization, these element memory addresses are generally continuous. The benefit of this is that as the producer continuously inserts new event objects into the RingBuffer, the memory addresses of these event objects can remain contiguous, thus utilizing the locality principle of CPU caches and loading adjacent event objects into the cache together to improve program performance. This is similar to MySQL's pre-read mechanism, which pre-loads several continuous pages into memory. Additionally, the RingBuffer, based on the array, supports batch operations (processing multiple elements at once) and avoids frequent memory allocation and garbage collection (the RingBuffer is a fixed-size array, so when a new element is added to the array, if the array is full, the new element will overwrite the oldest element).
+- **Avoided False Sharing Issues**: CPU caches are managed according to Cache Lines, with a typical Cache Line size around 64 bytes. Disruptor ensures that the target field occupies a single Cache Line by adding byte padding (56 bytes before and after the target field), thereby avoiding the false sharing problem. Additionally, to ensure that the array storing the data in the RingBuffer occupies a cache line, the design of the array includes invalid padding (128 bytes) plus valid data.
+- **Lock-Free Design**: Disruptor employs a lock-free design, eliminating the competition and delays associated with traditional locking mechanisms. The lock-free implementation of Disruptor is relatively complex and is primarily based on technologies such as CAS, memory barriers, and RingBuffer.
-综上所述,Disruptor 之所以能够如此快,是基于一系列优化策略的综合作用,既充分利用了现代 CPU 缓存结构的特点,又避免了常见的并发问题和性能瓶颈。
+In summary, the rapid performance of Disruptor stems from a comprehensive series of optimization strategies, effectively utilizing the characteristics of modern CPU cache structures while avoiding common concurrency issues and performance bottlenecks.
-关于 Disruptor 高性能队列原理的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章:[Disruptor 高性能队列原理浅析](https://qin.news/disruptor/) (参考了美团技术团队的[高性能队列——Disruptor](https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html)这篇文章)。
+For a detailed introduction to the principles of Disruptor's high-performance queue, refer to this article: [Analysis of Disruptor High-Performance Queue Principles](https://qin.news/disruptor/) (which references the Meituan tech team's article on [High-Performance Queue - Disruptor](https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html)).
-🌈 这里额外补充一点:**数组中对象元素地址连续为什么可以提高性能?**
+🌈 As an additional note: **Why does having contiguous memory addresses for object elements in an array improve performance?**
-CPU 缓存是通过将最近使用的数据存储在高速缓存中来实现更快的读取速度,并使用预取机制提前加载相邻内存的数据以利用局部性原理。
+CPU caches enable faster reading speeds by storing recently used data in high-speed caches and using prefetching mechanisms to load adjacent memory data ahead of time, leveraging the principle of locality.
-在计算机系统中,CPU 主要访问高速缓存和内存。高速缓存是一种速度非常快、容量相对较小的内存,通常被分为多级缓存,其中 L1、L2、L3 分别表示一级缓存、二级缓存、三级缓存。越靠近 CPU 的缓存,速度越快,容量也越小。相比之下,内存容量相对较大,但速度较慢。
+In computer systems, the CPU primarily accesses high-speed caches and memory. Caches are very fast and relatively small in capacity, usually organized into multiple levels, denoted as L1, L2, and L3 (representing levels of cache). The closer the cache is to the CPU, the faster and smaller its capacity tends to be. In contrast, memory has a relatively large capacity but slower speeds.
-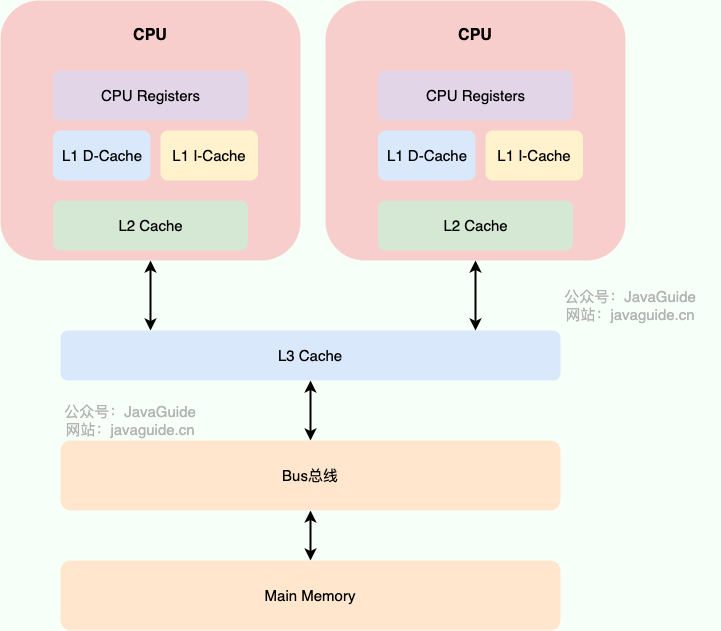
+
-为了加速数据的读取过程,CPU 会先将数据从内存中加载到高速缓存中,如果下一次需要访问相同的数据,就可以直接从高速缓存中读取,而不需要再次访问内存。这就是所谓的 **缓存命中** 。另外,为了利用 **局部性原理** ,CPU 还会根据之前访问的内存地址预取相邻的内存数据,因为在程序中,连续的内存地址通常会被频繁访问到,这样做可以提高数据的缓存命中率,进而提高程序的性能。
+To accelerate data reading, the CPU first loads data from memory into the cache; if the same data needs to be accessed again, it can be read directly from the cache without needing to access memory again. This is known as a **cache hit**. Additionally, to utilize **locality**, the CPU will prefetch adjacent memory data based on previously accessed memory addresses, as consecutive memory addresses are usually accessed frequently in programs; this increases the cache hit rate and, consequently, improves program performance.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Disruptor 高性能之道-等待策略:< 高性能之道-等待策略/>
-- 《Java 并发编程实战》- 40 | 案例分析(三):高性能队列 Disruptor:
-
-每种方式都有各自的优势,根据实际场景选择最合适的才是王道。下面再对这三种方式做一个简单的对比,以供大家实际开发中选择正确的存放时间的数据类型:
-
-| 类型 | 存储空间 | 日期格式 | 日期范围 | 是否带时区信息 |
-| ------------ | -------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------- |
-| DATETIME | 5~8 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1000-01-01 00:00:00[.000000] ~ 9999-12-31 23:59:59[.999999] | 否 |
-| TIMESTAMP | 4~7 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1970-01-01 00:00:01[.000000] ~ 2038-01-19 03:14:07[.999999] | 是 |
-| 数值型时间戳 | 4 字节 | 全数字如 1578707612 | 1970-01-01 00:00:01 之后的时间 | 否 |
-
-**选择建议小结:**
-
-- `TIMESTAMP` 的核心优势在于其内建的时区处理能力。数据库负责 UTC 存储和基于会话时区的自动转换,简化了需要处理多时区应用的开发。如果应用需要处理多时区,或者希望数据库能自动管理时区转换,`TIMESTAMP` 是自然的选择(注意其时间范围限制,也就是 2038 年问题)。
-- 如果应用场景不涉及时区转换,或者希望应用程序完全控制时区逻辑,并且需要表示 2038 年之后的时间,`DATETIME` 是更稳妥的选择。
-- 如果极度关注比较性能,或者需要频繁跨系统传递时间数据,并且可以接受可读性的牺牲(或总是在应用层转换),数值时间戳是一个强大的选项。
-
-
+Insert a
diff --git a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
index 52ad40f4a47..46b60051291 100644
--- a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
+++ b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
@@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
---
-title: MySQL事务隔离级别详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of MySQL Transaction Isolation Levels
+category: Database
tag:
- MySQL
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [guang19](https://github.com/guang19) 共同完成。
+> This article is co-authored by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [guang19](https://github.com/guang19).
-关于事务基本概览的介绍,请看这篇文章的介绍:[MySQL 常见知识点&面试题总结](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-事务)
+For an overview of transactions, please refer to this article: [Summary of Common MySQL Knowledge Points & Interview Questions](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-%E4%BA%8B%E5%8A%A1)
-## 事务隔离级别总结
+## Summary of Transaction Isolation Levels
-SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别:
+The SQL standard defines four isolation levels:
-- **READ-UNCOMMITTED(读取未提交)** :最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读。
-- **READ-COMMITTED(读取已提交)** :允许读取并发事务已经提交的数据,可以阻止脏读,但是幻读或不可重复读仍有可能发生。
-- **REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)** :对同一字段的多次读取结果都是一致的,除非数据是被本身事务自己所修改,可以阻止脏读和不可重复读,但幻读仍有可能发生。
-- **SERIALIZABLE(可串行化)** :最高的隔离级别,完全服从 ACID 的隔离级别。所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。
+- **READ-UNCOMMITTED**: The lowest isolation level, allowing reading of uncommitted data changes, which may lead to dirty reads, phantom reads, or non-repeatable reads.
+- **READ-COMMITTED**: Allows reading of data that has been committed by concurrent transactions, preventing dirty reads, but phantom reads or non-repeatable reads may still occur.
+- **REPEATABLE-READ**: Ensures that multiple reads of the same field yield consistent results unless the data is modified by the transaction itself. It prevents dirty reads and non-repeatable reads, but phantom reads may still occur.
+- **SERIALIZABLE**: The highest isolation level, fully compliant with the ACID isolation level. All transactions are executed sequentially, preventing any interference between transactions, meaning this level can prevent dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads.
----
+______________________________________________________________________
-| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
-| :--------------: | :--: | :--------: | :--: |
-| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
-| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
-| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
-| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
+| Isolation Level | Dirty Read | Non-repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
+| :--------------: | :--------: | :-----------------: | :----------: |
+| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
+| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
+| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
+| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
-MySQL InnoDB 存储引擎的默认支持的隔离级别是 **REPEATABLE-READ(可重读)**。我们可以通过`SELECT @@tx_isolation;`命令来查看,MySQL 8.0 该命令改为`SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
+The default isolation level supported by the MySQL InnoDB storage engine is **REPEATABLE-READ**. We can check this using the command `SELECT @@tx_isolation;`, which in MySQL 8.0 has changed to `SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
```sql
MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
@@ -38,78 +38,34 @@ MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
```
-从上面对 SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别的介绍可以看出,标准的 SQL 隔离级别定义里,REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)是不可以防止幻读的。
+From the introduction above regarding the four isolation levels defined by the SQL standard, it can be seen that the standard SQL isolation level definition does not prevent phantom reads for REPEATABLE-READ.
-但是!InnoDB 实现的 REPEATABLE-READ 隔离级别其实是可以解决幻读问题发生的,主要有下面两种情况:
+However! The REPEATABLE-READ isolation level implemented by InnoDB can actually resolve the issue of phantom reads, mainly in the following two situations:
-- **快照读**:由 MVCC 机制来保证不出现幻读。
-- **当前读**:使用 Next-Key Lock 进行加锁来保证不出现幻读,Next-Key Lock 是行锁(Record Lock)和间隙锁(Gap Lock)的结合,行锁只能锁住已经存在的行,为了避免插入新行,需要依赖间隙锁。
+- **Snapshot Read**: Ensured by the MVCC mechanism to prevent phantom reads.
+- **Current Read**: Uses Next-Key Lock for locking to prevent phantom reads. Next-Key Lock is a combination of row locks (Record Lock) and gap locks (Gap Lock). Row locks can only lock existing rows, and to prevent the insertion of new rows, gap locks are relied upon.
-因为隔离级别越低,事务请求的锁越少,所以大部分数据库系统的隔离级别都是 **READ-COMMITTED** ,但是你要知道的是 InnoDB 存储引擎默认使用 **REPEATABLE-READ** 并不会有任何性能损失。
+Since lower isolation levels require fewer locks for transaction requests, most database systems use **READ-COMMITTED** as the default isolation level. However, it is important to note that the InnoDB storage engine's default use of **REPEATABLE-READ** does not incur any performance loss.
-InnoDB 存储引擎在分布式事务的情况下一般会用到 SERIALIZABLE 隔离级别。
+In distributed transactions, the InnoDB storage engine generally uses the SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
-《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎(第 2 版)》7.7 章这样写到:
+Chapter 7.7 of "MySQL Internals: InnoDB Storage Engine (2nd Edition)" states:
-> InnoDB 存储引擎提供了对 XA 事务的支持,并通过 XA 事务来支持分布式事务的实现。分布式事务指的是允许多个独立的事务资源(transactional resources)参与到一个全局的事务中。事务资源通常是关系型数据库系统,但也可以是其他类型的资源。全局事务要求在其中的所有参与的事务要么都提交,要么都回滚,这对于事务原有的 ACID 要求又有了提高。另外,在使用分布式事务时,InnoDB 存储引擎的事务隔离级别必须设置为 SERIALIZABLE。
+> The InnoDB storage engine provides support for XA transactions and uses XA transactions to support the implementation of distributed transactions. Distributed transactions allow multiple independent transactional resources to participate in a global transaction. Transactional resources are typically relational database systems, but can also include other types of resources. A global transaction requires that all participating transactions either commit or roll back, which raises the original ACID requirements for transactions. Additionally, when using distributed transactions, the transaction isolation level of the InnoDB storage engine must be set to SERIALIZABLE.
-## 实际情况演示
+## Practical Demonstration
-在下面我会使用 2 个命令行 MySQL ,模拟多线程(多事务)对同一份数据的脏读问题。
+Below, I will use two MySQL command line instances to simulate the dirty read problem with multiple threads (multiple transactions) on the same data.
-MySQL 命令行的默认配置中事务都是自动提交的,即执行 SQL 语句后就会马上执行 COMMIT 操作。如果要显式地开启一个事务需要使用命令:`START TRANSACTION`。
+In the default configuration of the MySQL command line, transactions are automatically committed, meaning that after executing an SQL statement, a COMMIT operation is immediately performed. To explicitly start a transaction, the command `START TRANSACTION` is used.
-我们可以通过下面的命令来设置隔离级别。
+We can set the isolation level using the following command:
```sql
SET [SESSION|GLOBAL] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL [READ UNCOMMITTED|READ COMMITTED|REPEATABLE READ|SERIALIZABLE]
```
-我们再来看一下我们在下面实际操作中使用到的一些并发控制语句:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` |`BEGIN`:显式地开启一个事务。
-- `COMMIT`:提交事务,使得对数据库做的所有修改成为永久性。
-- `ROLLBACK`:回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的修改。
-
-### 脏读(读未提交)
-
-![]()
-
-### 避免脏读(读已提交)
-
-
-
-### 不可重复读
-
-还是刚才上面的读已提交的图,虽然避免了读未提交,但是却出现了,一个事务还没有结束,就发生了 不可重复读问题。
-
-
-
-### 可重复读
-
-
-
-### 幻读
-
-#### 演示幻读出现的情况
-
-
-
-SQL 脚本 1 在第一次查询工资为 500 的记录时只有一条,SQL 脚本 2 插入了一条工资为 500 的记录,提交之后;SQL 脚本 1 在同一个事务中再次使用当前读查询发现出现了两条工资为 500 的记录这种就是幻读。
-
-#### 解决幻读的方法
-
-解决幻读的方式有很多,但是它们的核心思想就是一个事务在操作某张表数据的时候,另外一个事务不允许新增或者删除这张表中的数据了。解决幻读的方式主要有以下几种:
-
-1. 将事务隔离级别调整为 `SERIALIZABLE` 。
-2. 在可重复读的事务级别下,给事务操作的这张表添加表锁。
-3. 在可重复读的事务级别下,给事务操作的这张表添加 `Next-key Lock(Record Lock+Gap Lock)`。
-
-### 参考
-
-- 《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎》
--
-- [Mysql 锁:灵魂七拷问](https://tech.youzan.com/seven-questions-about-the-lock-of-MySQL/)
-- [Innodb 中的事务隔离级别和锁的关系](https://tech.meituan.com/2014/08/20/innodb-lock.html)
+Next, let's look at some concurrency control statements we will use in the practical operations below:
-
+- `START TRANSACTION` | `BEGIN`: Explicitly starts a transaction.
+- \`COMMIT
diff --git a/docs/database/nosql.md b/docs/database/nosql.md
index d5ca59698bd..17bf3fa7070 100644
--- a/docs/database/nosql.md
+++ b/docs/database/nosql.md
@@ -1,61 +1,61 @@
---
-title: NoSQL基础知识总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of NoSQL Fundamentals
+category: Database
tag:
- NoSQL
- MongoDB
- Redis
---
-## NoSQL 是什么?
+## What is NoSQL?
-NoSQL(Not Only SQL 的缩写)泛指非关系型的数据库,主要针对的是键值、文档以及图形类型数据存储。并且,NoSQL 数据库天生支持分布式,数据冗余和数据分片等特性,旨在提供可扩展的高可用高性能数据存储解决方案。
+NoSQL (Not Only SQL) refers to non-relational databases that primarily target key-value, document, and graph data storage. Moreover, NoSQL databases naturally support distributed features, data redundancy, and data partitioning, aiming to provide scalable, high-availability, and high-performance data storage solutions.
-一个常见的误解是 NoSQL 数据库或非关系型数据库不能很好地存储关系型数据。NoSQL 数据库可以存储关系型数据—它们与关系型数据库的存储方式不同。
+A common misconception is that NoSQL databases or non-relational databases cannot store relational data well. NoSQL databases can store relational data—they just have a different storage method compared to relational databases.
-NoSQL 数据库代表:HBase、Cassandra、MongoDB、Redis。
+Examples of NoSQL databases include: HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB, Redis.

-## SQL 和 NoSQL 有什么区别?
+## What are the differences between SQL and NoSQL?
-| | SQL 数据库 | NoSQL 数据库 |
-| :----------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| 数据存储模型 | 结构化存储,具有固定行和列的表格 | 非结构化存储。文档:JSON 文档,键值:键值对,宽列:包含行和动态列的表,图:节点和边 |
-| 发展历程 | 开发于 1970 年代,重点是减少数据重复 | 开发于 2000 年代后期,重点是提升可扩展性,减少大规模数据的存储成本 |
-| 例子 | Oracle、MySQL、Microsoft SQL Server、PostgreSQL | 文档:MongoDB、CouchDB,键值:Redis、DynamoDB,宽列:Cassandra、 HBase,图表:Neo4j、 Amazon Neptune、Giraph |
-| ACID 属性 | 提供原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性 (ACID) 属性 | 通常不支持 ACID 事务,为了可扩展、高性能进行了权衡,少部分支持比如 MongoDB 。不过,MongoDB 对 ACID 事务 的支持和 MySQL 还是有所区别的。 |
-| 性能 | 性能通常取决于磁盘子系统。要获得最佳性能,通常需要优化查询、索引和表结构。 | 性能通常由底层硬件集群大小、网络延迟以及调用应用程序来决定。 |
-| 扩展 | 垂直(使用性能更强大的服务器进行扩展)、读写分离、分库分表 | 横向(增加服务器的方式横向扩展,通常是基于分片机制) |
-| 用途 | 普通企业级的项目的数据存储 | 用途广泛比如图数据库支持分析和遍历连接数据之间的关系、键值数据库可以处理大量数据扩展和极高的状态变化 |
-| 查询语法 | 结构化查询语言 (SQL) | 数据访问语法可能因数据库而异 |
+| | SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases |
+| :------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| Data Storage Model | Structured storage with tables that have fixed rows and columns | Unstructured storage. Documents: JSON documents, Key-Value: Key-Value pairs, Wide Column: Tables with rows and dynamic columns, Graph: Nodes and edges |
+| Development History | Developed in the 1970s, focusing on reducing data duplication | Developed in the late 2000s, focusing on improving scalability and reducing storage costs for massive amounts of data |
+| Examples | Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL | Documents: MongoDB, CouchDB; Key-Value: Redis, DynamoDB; Wide Column: Cassandra, HBase; Graph: Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, Giraph |
+| ACID Properties | Provides Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID) properties | Generally does not support ACID transactions, making trade-offs for scalability and high performance; some, like MongoDB, support them, but differently than MySQL. |
+| Performance | Performance typically depends on the disk subsystem. To achieve optimal performance, optimizing queries, indexes, and table structures is often necessary. | Performance is usually determined by the size of the underlying hardware cluster, network latency, and the application calling. |
+| Scalability | Vertical (scaling up using more powerful servers), read-write separation, database sharding | Horizontal (scaling out by adding servers, usually based on sharding mechanisms) |
+| Use Cases | Data storage for typical enterprise-level projects | Wide-ranging uses, for example, graph databases support analysis and traversing relationships between connected data; key-value databases can handle massive data scaling and extreme state changes. |
+| Query Language | Structured Query Language (SQL) | Data access syntax may vary by database |
-## NoSQL 数据库有什么优势?
+## What are the advantages of NoSQL databases?
-NoSQL 数据库非常适合许多现代应用程序,例如移动、Web 和游戏等应用程序,它们需要灵活、可扩展、高性能和功能强大的数据库以提供卓越的用户体验。
+NoSQL databases are particularly suitable for many modern applications, such as mobile, web, and gaming applications, which require flexible, scalable, high-performance, and powerful databases to provide excellent user experiences.
-- **灵活性:** NoSQL 数据库通常提供灵活的架构,以实现更快速、更多的迭代开发。灵活的数据模型使 NoSQL 数据库成为半结构化和非结构化数据的理想之选。
-- **可扩展性:** NoSQL 数据库通常被设计为通过使用分布式硬件集群来横向扩展,而不是通过添加昂贵和强大的服务器来纵向扩展。
-- **高性能:** NoSQL 数据库针对特定的数据模型和访问模式进行了优化,这与尝试使用关系数据库完成类似功能相比可实现更高的性能。
-- **强大的功能:** NoSQL 数据库提供功能强大的 API 和数据类型,专门针对其各自的数据模型而构建。
+- **Flexibility:** NoSQL databases often provide flexible architectures for faster and more iterative development. Their flexible data models make NoSQL databases ideal for semi-structured and unstructured data.
+- **Scalability:** NoSQL databases are generally designed to scale horizontally by utilizing distributed hardware clusters rather than vertically scaling by adding expensive and powerful servers.
+- **High Performance:** NoSQL databases are optimized for specific data models and access patterns, achieving higher performance compared to trying to accomplish similar functions with a relational database.
+- **Powerful Features:** NoSQL databases offer powerful APIs and data types designed specifically for their respective data models.
-## NoSQL 数据库有哪些类型?
+## What types of NoSQL databases are there?
-NoSQL 数据库主要可以分为下面四种类型:
+NoSQL databases can primarily be divided into the following four types:
-- **键值**:键值数据库是一种较简单的数据库,其中每个项目都包含键和值。这是极为灵活的 NoSQL 数据库类型,因为应用可以完全控制 value 字段中存储的内容,没有任何限制。Redis 和 DynanoDB 是两款非常流行的键值数据库。
-- **文档**:文档数据库中的数据被存储在类似于 JSON(JavaScript 对象表示法)对象的文档中,非常清晰直观。每个文档包含成对的字段和值。这些值通常可以是各种类型,包括字符串、数字、布尔值、数组或对象等,并且它们的结构通常与开发者在代码中使用的对象保持一致。MongoDB 就是一款非常流行的文档数据库。
-- **图形**:图形数据库旨在轻松构建和运行与高度连接的数据集一起使用的应用程序。图形数据库的典型使用案例包括社交网络、推荐引擎、欺诈检测和知识图形。Neo4j 和 Giraph 是两款非常流行的图形数据库。
-- **宽列**:宽列存储数据库非常适合需要存储大量的数据。Cassandra 和 HBase 是两款非常流行的宽列存储数据库。
+- **Key-Value:** Key-value databases are a simpler type of database where each item consists of a key and a value. This is a very flexible type of NoSQL database because applications have complete control over the content stored in the value field, with no restrictions. Redis and DynamoDB are two popular key-value databases.
+- **Document:** Data in document databases is stored in documents resembling JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) objects, which are very clear and intuitive. Each document contains paired fields and values. These values can typically be of various types, including strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or objects, and their structure often aligns with the objects developers use in code. MongoDB is a very popular document database.
+- **Graph:** Graph databases are designed to make it easy to build and run applications that work with highly connected datasets. Typical use cases for graph databases include social networks, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and knowledge graphs. Neo4j and Giraph are two well-known graph databases.
+- **Wide Column:** Wide-column store databases are well-suited for scenarios requiring the storage of massive amounts of data. Cassandra and HBase are two popular wide-column storage databases.
-下面这张图片来源于 [微软的官方文档 | 关系数据与 NoSQL 数据](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/relational-vs-nosql-data)。
+The image below is sourced from [Microsoft's official documentation | Relational Data vs. NoSQL Data](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/relational-vs-nosql-data).
-
+
-## 参考
+## References
-- NoSQL 是什么?- MongoDB 官方文档:
-- 什么是 NoSQL? - AWS:
-- NoSQL vs. SQL Databases - MongoDB 官方文档:
+- What is NoSQL? - MongoDB Official Documentation:
+- What is NoSQL? - AWS:
+- NoSQL vs. SQL Databases - MongoDB Official Documentation:
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md b/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
index 7ad88958704..ce2d47640e9 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.md
@@ -1,118 +1,87 @@
---
-title: 3种常用的缓存读写策略详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 3 Common Cache Read/Write Strategies
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-看到很多小伙伴简历上写了“**熟练使用缓存**”,但是被我问到“**缓存常用的 3 种读写策略**”的时候却一脸懵逼。
+I've seen many friends list "**proficient in using cache**" on their resumes, but when I ask them about the "**3 common read/write strategies for cache**," they often look confused.
-在我看来,造成这个问题的原因是我们在学习 Redis 的时候,可能只是简单写了一些 Demo,并没有去关注缓存的读写策略,或者说压根不知道这回事。
+In my opinion, this issue arises because when we learn Redis, we might only write some simple demos without paying attention to cache read/write strategies, or we might not even be aware of them.
-但是,搞懂 3 种常见的缓存读写策略对于实际工作中使用缓存以及面试中被问到缓存都是非常有帮助的!
+However, understanding the 3 common cache read/write strategies is very helpful for using cache in real work and for interview questions about cache!
-**下面介绍到的三种模式各有优劣,不存在最佳模式,根据具体的业务场景选择适合自己的缓存读写模式。**
+**The three patterns introduced below each have their pros and cons; there is no best pattern. Choose a cache read/write pattern that suits your specific business scenario.**
-### Cache Aside Pattern(旁路缓存模式)
+### Cache Aside Pattern
-**Cache Aside Pattern 是我们平时使用比较多的一个缓存读写模式,比较适合读请求比较多的场景。**
+**The Cache Aside Pattern is a commonly used cache read/write pattern, particularly suitable for scenarios with a high volume of read requests.**
-Cache Aside Pattern 中服务端需要同时维系 db 和 cache,并且是以 db 的结果为准。
+In the Cache Aside Pattern, the server needs to maintain both the database (db) and the cache, with the db results being the authoritative source.
-下面我们来看一下这个策略模式下的缓存读写步骤。
+Let's take a look at the steps for reading and writing cache under this strategy.
-**写**:
+**Write:**
-- 先更新 db
-- 然后直接删除 cache 。
+- First, update the db.
+- Then, delete the cache directly.
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解写的步骤。
+Here’s a simple diagram to help you understand the writing steps.

-**读** :
+**Read:**
-- 从 cache 中读取数据,读取到就直接返回
-- cache 中读取不到的话,就从 db 中读取数据返回
-- 再把数据放到 cache 中。
+- Read data from the cache; if found, return it directly.
+- If not found in the cache, read the data from the db and return it.
+- Then, place the data into the cache.
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解读的步骤。
+Here’s a simple diagram to help you understand the reading steps.

-你仅仅了解了上面这些内容的话是远远不够的,我们还要搞懂其中的原理。
+If you only understand the above content, it is far from enough; we also need to grasp the underlying principles.
-比如说面试官很可能会追问:“**在写数据的过程中,可以先删除 cache ,后更新 db 么?**”
+For example, the interviewer might follow up with: "**During the data writing process, can we delete the cache first and then update the db?**"
-**答案:** 那肯定是不行的!因为这样可能会造成 **数据库(db)和缓存(Cache)数据不一致**的问题。
+**Answer:** Absolutely not! Because this could lead to the problem of **inconsistency between the database (db) and the cache.**
-举例:请求 1 先写数据 A,请求 2 随后读数据 A 的话,就很有可能产生数据不一致性的问题。
+For instance: If request 1 writes data A first, and request 2 subsequently reads data A, it is very likely to cause data inconsistency.
-这个过程可以简单描述为:
+This process can be simply described as:
-> 请求 1 先把 cache 中的 A 数据删除 -> 请求 2 从 db 中读取数据->请求 1 再把 db 中的 A 数据更新
+> Request 1 deletes data A from the cache -> Request 2 reads data from the db -> Request 1 updates data A in the db.
-当你这样回答之后,面试官可能会紧接着就追问:“**在写数据的过程中,先更新 db,后删除 cache 就没有问题了么?**”
+After you answer this, the interviewer might immediately ask: "**During the data writing process, is it okay to update the db first and then delete the cache?**"
-**答案:** 理论上来说还是可能会出现数据不一致性的问题,不过概率非常小,因为缓存的写入速度是比数据库的写入速度快很多。
+**Answer:** Theoretically, there could still be a problem with data inconsistency, but the probability is very low because the write speed of the cache is much faster than that of the database.
-举例:请求 1 先读数据 A,请求 2 随后写数据 A,并且数据 A 在请求 1 请求之前不在缓存中的话,也有可能产生数据不一致性的问题。
+For example: If request 1 reads data A first, and request 2 subsequently writes data A, and data A is not in the cache before request 1, there could still be a problem with data inconsistency.
-这个过程可以简单描述为:
+This process can be simply described as:
-> 请求 1 从 db 读数据 A-> 请求 2 更新 db 中的数据 A(此时缓存中无数据 A ,故不用执行删除缓存操作 ) -> 请求 1 将数据 A 写入 cache
+> Request 1 reads data A from the db -> Request 2 updates data A in the db (at this point, there is no data A in the cache, so no cache deletion is needed) -> Request 1 writes data A into the cache.
-现在我们再来分析一下 **Cache Aside Pattern 的缺陷**。
+Now let's analyze the **deficiencies of the Cache Aside Pattern**.
-**缺陷 1:首次请求数据一定不在 cache 的问题**
+**Deficiency 1: The issue that the first request for data is definitely not in the cache.**
-解决办法:可以将热点数据可以提前放入 cache 中。
+Solution: Hot data can be preloaded into the cache.
-**缺陷 2:写操作比较频繁的话导致 cache 中的数据会被频繁被删除,这样会影响缓存命中率 。**
+**Deficiency 2: Frequent write operations can lead to data being frequently deleted from the cache, which affects the cache hit rate.**
-解决办法:
+Solutions:
-- 数据库和缓存数据强一致场景:更新 db 的时候同样更新 cache,不过我们需要加一个锁/分布式锁来保证更新 cache 的时候不存在线程安全问题。
-- 可以短暂地允许数据库和缓存数据不一致的场景:更新 db 的时候同样更新 cache,但是给缓存加一个比较短的过期时间,这样的话就可以保证即使数据不一致的话影响也比较小。
+- For scenarios requiring strong consistency between the database and cache: Update the cache when updating the db, but we need to add a lock/distributed lock to ensure thread safety when updating the cache.
+- For scenarios where temporary inconsistency between the database and cache is acceptable: Update the cache when updating the db, but set a relatively short expiration time for the cache, which can ensure that even if data is inconsistent, the impact is minimal.
-### Read/Write Through Pattern(读写穿透)
+### Read/Write Through Pattern
-Read/Write Through Pattern 中服务端把 cache 视为主要数据存储,从中读取数据并将数据写入其中。cache 服务负责将此数据读取和写入 db,从而减轻了应用程序的职责。
+In the Read/Write Through Pattern, the server treats the cache as the primary data store, reading data from it and writing data into it. The cache service is responsible for reading and writing this data to the db, thereby reducing the responsibilities of the application.
-这种缓存读写策略小伙伴们应该也发现了在平时在开发过程中非常少见。抛去性能方面的影响,大概率是因为我们经常使用的分布式缓存 Redis 并没有提供 cache 将数据写入 db 的功能。
+This cache read/write strategy is also rarely seen in our development process. Aside from performance impacts, it is likely because the distributed cache we often use, Redis, does not provide the functionality for the cache to write data to the db.
-**写(Write Through):**
+**Write (Write Through):**
-- 先查 cache,cache 中不存在,直接更新 db。
-- cache 中存在,则先更新 cache,然后 cache 服务自己更新 db(**同步更新 cache 和 db**)。
-
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解写的步骤。
-
-
-
-**读(Read Through):**
-
-- 从 cache 中读取数据,读取到就直接返回 。
-- 读取不到的话,先从 db 加载,写入到 cache 后返回响应。
-
-简单画了一张图帮助大家理解读的步骤。
-
-
-
-Read-Through Pattern 实际只是在 Cache-Aside Pattern 之上进行了封装。在 Cache-Aside Pattern 下,发生读请求的时候,如果 cache 中不存在对应的数据,是由客户端自己负责把数据写入 cache,而 Read Through Pattern 则是 cache 服务自己来写入缓存的,这对客户端是透明的。
-
-和 Cache Aside Pattern 一样, Read-Through Pattern 也有首次请求数据一定不再 cache 的问题,对于热点数据可以提前放入缓存中。
-
-### Write Behind Pattern(异步缓存写入)
-
-Write Behind Pattern 和 Read/Write Through Pattern 很相似,两者都是由 cache 服务来负责 cache 和 db 的读写。
-
-但是,两个又有很大的不同:**Read/Write Through 是同步更新 cache 和 db,而 Write Behind 则是只更新缓存,不直接更新 db,而是改为异步批量的方式来更新 db。**
-
-很明显,这种方式对数据一致性带来了更大的挑战,比如 cache 数据可能还没异步更新 db 的话,cache 服务可能就就挂掉了。
-
-这种策略在我们平时开发过程中也非常非常少见,但是不代表它的应用场景少,比如消息队列中消息的异步写入磁盘、MySQL 的 Innodb Buffer Pool 机制都用到了这种策略。
-
-Write Behind Pattern 下 db 的写性能非常高,非常适合一些数据经常变化又对数据一致性要求没那么高的场景,比如浏览量、点赞量。
-
-
+- First, check the cache; if it does not exist, directly update the db.
+- If it exists in the cache, first update the cache, then the
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md b/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
index 391e5bec82d..b82a91c1d3d 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/cache-basics.md
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: 缓存基础常见面试题总结(付费)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Interview Questions on Cache Basics (Paid)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-**缓存基础** 相关的面试题为我的 [知识星球](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)中。
+Interview questions related to **cache basics** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md) (click the link to view detailed introduction and joining method), and have been organized into [“Java Interview Guide”](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md).

diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
index e3ef2efd04c..480596dd84b 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-cluster.md
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: Redis集群详解(付费)
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Clusters (Paid)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-**Redis 集群** 相关的面试题为我的 [知识星球](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md)中。
+The interview questions related to **Redis Clusters** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](../../about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.md) (click the link for a detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled in [《Java Interview Guide》](../../zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.md).

diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
index 9aec17fc0cc..62342697a2d 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md
@@ -1,146 +1,144 @@
---
-title: Redis常见阻塞原因总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Blocking Reasons in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-> 本文整理完善自: ,作者:阿 Q 说代码
+> This article is compiled and perfected from: , author: A Q Talks Code
-这篇文章会详细总结一下可能导致 Redis 阻塞的情况,这些情况也是影响 Redis 性能的关键因素,使用 Redis 的时候应该格外注意!
+This article will summarize in detail the situations that may cause Redis blocking, which are also key factors affecting Redis performance. Care should be taken when using Redis!
-## O(n) 命令
+## O(n) Commands
-Redis 中的大部分命令都是 O(1)时间复杂度,但也有少部分 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令,例如:
+Most commands in Redis have an O(1) time complexity, but there are also a few commands with O(n) time complexity, such as:
-- `KEYS *`:会返回所有符合规则的 key。
-- `HGETALL`:会返回一个 Hash 中所有的键值对。
-- `LRANGE`:会返回 List 中指定范围内的元素。
-- `SMEMBERS`:返回 Set 中的所有元素。
-- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`:计算多个 Set 的交集/并集/差集。
+- `KEYS *`: Returns all keys that match the rules.
+- `HGETALL`: Returns all key-value pairs in a Hash.
+- `LRANGE`: Returns elements within a specified range in a List.
+- `SMEMBERS`: Returns all elements in a Set.
+- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`: Calculates the intersection/union/difference of multiple Sets.
- ……
-由于这些命令时间复杂度是 O(n),有时候也会全表扫描,随着 n 的增大,执行耗时也会越长,从而导致客户端阻塞。不过, 这些命令并不是一定不能使用,但是需要明确 N 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
+Due to the O(n) time complexity of these commands, sometimes a full table scan occurs. As n increases, the execution time will also increase, leading to client blocking. However, these commands are not entirely unusable, but the value of N needs to be clarified. If there is a need for traversal, `HSCAN`, `SSCAN`, or `ZSCAN` can be used instead.
-除了这些 O(n)时间复杂度的命令可能会导致阻塞之外, 还有一些时间复杂度可能在 O(N) 以上的命令,例如:
+In addition to these O(n) time complexity commands that may cause blocking, there are also commands with time complexities potentially greater than O(N), such as:
-- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`:返回指定 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量, m 为返回的元素数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`:移除 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围/指定 score 范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量, m 被删除元素的数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
+- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`: Returns all elements within a specified ranking range in a Sorted Set. The time complexity is O(log(n)+m), where n is the total number of elements and m is the number of elements returned. When m and n are relatively large, the time complexity O(n) is smaller.
+- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`: Removes all elements within a specified ranking range/specified score range in a Sorted Set. The time complexity is O(log(n)+m), where n is the total number of elements and m is the number of deleted elements. When m and n are relatively large, the time complexity O(n) is smaller.
- ……
-## SAVE 创建 RDB 快照
+## SAVE Creating RDB Snapshots
-Redis 提供了两个命令来生成 RDB 快照文件:
+Redis provides two commands to generate RDB snapshot files:
-- `save` : 同步保存操作,会阻塞 Redis 主线程;
-- `bgsave` : fork 出一个子进程,子进程执行,不会阻塞 Redis 主线程,默认选项。
+- `save`: Synchronously saves operations and blocks the Redis main thread.
+- `bgsave`: Forks a child process to execute, which does not block the Redis main thread, the default option.
-默认情况下,Redis 默认配置会使用 `bgsave` 命令。如果手动使用 `save` 命令生成 RDB 快照文件的话,就会阻塞主线程。
+By default, Redis will use the `bgsave` command. If you manually use the `save` command to generate RDB snapshot files, it will block the main thread.
## AOF
-### AOF 日志记录阻塞
+### AOF Log Record Blocking
-Redis AOF 持久化机制是在执行完命令之后再记录日志,这和关系型数据库(如 MySQL)通常都是执行命令之前记录日志(方便故障恢复)不同。
+Redis's AOF persistence mechanism records logs after executing commands, differing from relational databases (like MySQL), which usually log before executing commands for recovery purposes.
-
+
-**为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志呢?**
+**Why record logs after executing commands?**
-- 避免额外的检查开销,AOF 记录日志不会对命令进行语法检查;
-- 在命令执行完之后再记录,不会阻塞当前的命令执行。
+- To avoid extra checking overhead, AOF log recording does not perform syntax checking on commands.
+- Logging after command execution does not block the current command execution.
-这样也带来了风险(我在前面介绍 AOF 持久化的时候也提到过):
+This also brings risks (which I mentioned when introducing AOF persistence):
-- 如果刚执行完命令 Redis 就宕机会导致对应的修改丢失;
-- **可能会阻塞后续其他命令的执行(AOF 记录日志是在 Redis 主线程中进行的)**。
+- If Redis crashes right after executing a command, the corresponding modifications may be lost.
+- **It may block the execution of subsequent commands (AOF log recording is conducted in the Redis main thread).**
-### AOF 刷盘阻塞
+### AOF Flush Blocking
-开启 AOF 持久化后每执行一条会更改 Redis 中的数据的命令,Redis 就会将该命令写入到 AOF 缓冲区 `server.aof_buf` 中,然后再根据 `appendfsync` 配置来决定何时将其同步到硬盘中的 AOF 文件。
+After enabling AOF persistence, every command that changes data in Redis will write that command to the AOF buffer `server.aof_buf`, and then according to the `appendfsync` configuration, it decides when to synchronize it to the AOF file on the hard disk.
-在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式( `fsync`策略),它们分别是:
+There are three different AOF persistence methods (fsync strategy) in Redis's configuration file:
-1. `appendfsync always`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后,后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)立即会调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件(刷盘),`fsync` 完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低 Redis 的性能(`write` + `fsync`)。
-2. `appendfsync everysec`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,由后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)每秒钟调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用)同步一次 AOF 文件(`write`+`fsync`,`fsync`间隔为 1 秒)
-3. `appendfsync no`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,让操作系统决定何时进行同步,Linux 下一般为 30 秒一次(`write`但不`fsync`,`fsync` 的时机由操作系统决定)。
+1. `appendfsync always`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation, after which the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) immediately calls the `fsync` function to sync the AOF file (flush). After `fsync` completes, the thread returns; this will severely decrease Redis's performance (write + fsync).
+1. `appendfsync everysec`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation and immediately returns, with the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) calling the `fsync` function once every second to sync the AOF file (write + fsync, the fsync interval is 1 second).
+1. `appendfsync no`: The main thread calls `write` to perform a write operation and immediately returns, allowing the operating system to decide when to sync, which is usually once every 30 seconds on Linux (write but no fsync; the timing of fsync is determined by the operating system).
-当后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件时,需要等待,直到写入完成。当磁盘压力太大的时候,会导致 `fsync` 操作发生阻塞,主线程调用 `write` 函数时也会被阻塞。`fsync` 完成后,主线程执行 `write` 才能成功返回。
+When the background thread (`aof_fsync` thread) calls the `fsync` function to sync the AOF file, it needs to wait until the writing is complete. When there is too much disk pressure, blocking may occur during the `fsync` operation, and the main thread calling `write` will also be blocked. The main thread can only return successfully after `fsync` completes.
-关于 AOF 工作流程的详细介绍可以查看:[Redis 持久化机制详解](./redis-persistence.md),有助于理解 AOF 刷盘阻塞。
+For a detailed introduction to the AOF workflow, you can refer to: [Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanism](./redis-persistence.md), which helps understand AOF flush blocking.
-### AOF 重写阻塞
+### AOF Rewrite Blocking
-1. fork 出一条子线程来将文件重写,在执行 `BGREWRITEAOF` 命令时,Redis 服务器会维护一个 AOF 重写缓冲区,该缓冲区会在子线程创建新 AOF 文件期间,记录服务器执行的所有写命令。
-2. 当子线程完成创建新 AOF 文件的工作之后,服务器会将重写缓冲区中的所有内容追加到新 AOF 文件的末尾,使得新的 AOF 文件保存的数据库状态与现有的数据库状态一致。
-3. 最后,服务器用新的 AOF 文件替换旧的 AOF 文件,以此来完成 AOF 文件重写操作。
+1. A child thread is forked to rewrite the file. When executing the `BGREWRITEAOF` command, the Redis server maintains an AOF rewrite buffer that records all write commands executed by the server during the child thread's creation of the new AOF file.
+1. After the child thread completes the task of creating the new AOF file, the server appends all content from the rewrite buffer to the end of the new AOF file, ensuring that the new AOF file preserves the database state consistent with the existing database state.
+1. Finally, the server replaces the old AOF file with the new AOF file to complete the AOF file rewrite operation.
-阻塞就是出现在第 2 步的过程中,将缓冲区中新数据写到新文件的过程中会产生**阻塞**。
+Blocking occurs during the process of step 2 when writing new data from the buffer to the new file, causing a **block**.
-相关阅读:[Redis AOF 重写阻塞问题分析](https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1633077)。
+For further reading: [Analysis of Redis AOF Rewrite Blocking Issues](https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1633077).
-## 大 Key
+## Big Key
-如果一个 key 对应的 value 所占用的内存比较大,那这个 key 就可以看作是 bigkey。具体多大才算大呢?有一个不是特别精确的参考标准:
+If the value corresponding to a key occupies a large amount of memory, that key can be considered a big key. What exactly counts as large? There is a rather imprecise reference standard:
-- string 类型的 value 超过 1MB
-- 复合类型(列表、哈希、集合、有序集合等)的 value 包含的元素超过 5000 个(对于复合类型的 value 来说,不一定包含的元素越多,占用的内存就越多)。
+- String-type values exceeding 1MB.
+- Composite types (lists, hashes, sets, sorted sets, etc.) whose values contain more than 5000 elements (for composite types, having more elements does not necessarily mean occupying more memory).
-大 key 造成的阻塞问题如下:
+The blocking issues caused by big keys are as follows:
-- 客户端超时阻塞:由于 Redis 执行命令是单线程处理,然后在操作大 key 时会比较耗时,那么就会阻塞 Redis,从客户端这一视角看,就是很久很久都没有响应。
-- 引发网络阻塞:每次获取大 key 产生的网络流量较大,如果一个 key 的大小是 1 MB,每秒访问量为 1000,那么每秒会产生 1000MB 的流量,这对于普通千兆网卡的服务器来说是灾难性的。
-- 阻塞工作线程:如果使用 del 删除大 key 时,会阻塞工作线程,这样就没办法处理后续的命令。
+- Client timeout blocking: Since Redis executes commands in a single-threaded manner, operations on big keys can be time-consuming, causing Redis to block, resulting in the client not responding for an extended period.
+- Causing network blocking: The network traffic generated when retrieving big keys is relatively large. If a key's size is 1MB and the access frequency is 1000 per second, it will generate 1000MB of traffic per second, which is disastrous for a typical gigabit network card server.
+- Blocking worker threads: If deleting a big key using del, it will block worker threads, preventing subsequent commands from being processed.
-### 查找大 key
+### Finding Big Keys
-当我们在使用 Redis 自带的 `--bigkeys` 参数查找大 key 时,最好选择在从节点上执行该命令,因为主节点上执行时,会**阻塞**主节点。
+When using Redis's built-in `--bigkeys` parameter to find big keys, it is best to execute the command on a slave node, as executing it on the master node will **block** the master node.
-- 我们还可以使用 SCAN 命令来查找大 key;
+- We can also use the SCAN command to find big keys;
+- Analyzing RDB files to identify big keys requires that Redis is using RDB persistence. There are tools available online:
+ - redis-rdb-tools: A Python tool for analyzing Redis RDB snapshot files.
+ - rdb_bigkeys: A Go tool for analyzing Redis RDB snapshot files, which performs better.
-- 通过分析 RDB 文件来找出 big key,这种方案的前提是 Redis 采用的是 RDB 持久化。网上有现成的工具:
+### Deleting Big Keys
-- - redis-rdb-tools:Python 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具
- - rdb_bigkeys:Go 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具,性能更好。
+The essence of the delete operation is to free the memory space occupied by key-value pairs.
-### 删除大 key
+Freeing memory is just the first step. To manage memory space more efficiently, when an application releases memory, **the operating system needs to insert the released memory blocks into a linked list of free memory blocks** for subsequent management and reallocation. This process itself requires some time and can **block** the current application that is freeing memory.
-删除操作的本质是要释放键值对占用的内存空间。
+Therefore, if a large amount of memory is released at once, the time required for managing the linked list of free memory blocks will increase, consequently causing blocking in the Redis main thread. If the main thread becomes blocked, all other requests may timeout, leading to increasing timeouts that can exhaust Redis connections and generate various exceptions.
-释放内存只是第一步,为了更加高效地管理内存空间,在应用程序释放内存时,**操作系统需要把释放掉的内存块插入一个空闲内存块的链表**,以便后续进行管理和再分配。这个过程本身需要一定时间,而且会**阻塞**当前释放内存的应用程序。
+When deleting big keys, it is recommended to use batch deletions and asynchronous deletions.
-所以,如果一下子释放了大量内存,空闲内存块链表操作时间就会增加,相应地就会造成 Redis 主线程的阻塞,如果主线程发生了阻塞,其他所有请求可能都会超时,超时越来越多,会造成 Redis 连接耗尽,产生各种异常。
+## Clearing the Database
-删除大 key 时建议采用分批次删除和异步删除的方式进行。
+Clearing the database is similar to the deletion of big keys; `flushdb` and `flushall` involve the deletion and release of all key-value pairs, which are also blocking points in Redis.
-## 清空数据库
+## Cluster Expansion
-清空数据库和上面 bigkey 删除也是同样道理,`flushdb`、`flushall` 也涉及到删除和释放所有的键值对,也是 Redis 的阻塞点。
+Redis clusters can dynamically scale up and down nodes. This process is currently semi-automated and requires manual intervention.
-## 集群扩容
+During the expansion or contraction, data migration is needed. Redis ensures the consistency of migration; all migration operations are synchronous.
-Redis 集群可以进行节点的动态扩容缩容,这一过程目前还处于半自动状态,需要人工介入。
+During migration, both ends of Redis will enter a blocking state for varying durations. For small keys, this time can be negligible, but if a key's memory usage is too large, it can trigger failover within the cluster, causing unnecessary switching.
-在扩缩容的时候,需要进行数据迁移。而 Redis 为了保证迁移的一致性,迁移所有操作都是同步操作。
+## Swap
-执行迁移时,两端的 Redis 均会进入时长不等的阻塞状态,对于小 Key,该时间可以忽略不计,但如果一旦 Key 的内存使用过大,严重的时候会触发集群内的故障转移,造成不必要的切换。
+**What is Swap?** Swap refers to the exchange, and in Linux, Swap is often called memory swapping or swap partition. Similar to virtual memory in Windows, it solves memory shortages by virtualizing some hard disk space to be used as memory. Thus, the purpose of the Swap partition is to sacrifice hard disk space to increase memory and address the issue of insufficient or overloaded VPS memory.
-## Swap(内存交换)
+Swap can be very detrimental to Redis. One important premise for Redis to ensure high performance is that all data exists in memory. If the operating system swaps out some of the memory used by Redis to the hard disk, the read and write speeds of memory and hard disk differ by several orders of magnitude, leading to a drastic decline in Redis performance after the swap.
-**什么是 Swap?** Swap 直译过来是交换的意思,Linux 中的 Swap 常被称为内存交换或者交换分区。类似于 Windows 中的虚拟内存,就是当内存不足的时候,把一部分硬盘空间虚拟成内存使用,从而解决内存容量不足的情况。因此,Swap 分区的作用就是牺牲硬盘,增加内存,解决 VPS 内存不够用或者爆满的问题。
+Here are methods to check if Redis is experiencing Swap:
-Swap 对于 Redis 来说是非常致命的,Redis 保证高性能的一个重要前提是所有的数据在内存中。如果操作系统把 Redis 使用的部分内存换出硬盘,由于内存与硬盘的读写速度差几个数量级,会导致发生交换后的 Redis 性能急剧下降。
-
-识别 Redis 发生 Swap 的检查方法如下:
-
-1、查询 Redis 进程号
+1. Query the Redis process ID
```bash
redis-cli -p 6383 info server | grep process_id
process_id: 4476
```
-2、根据进程号查询内存交换信息
+2. Check memory swap information based on the process ID
```bash
cat /proc/4476/smaps | grep Swap
@@ -152,27 +150,27 @@ Swap: 0kB
.....
```
-如果交换量都是 0KB 或者个别的是 4KB,则正常。
+If the swap amounts are all 0KB or a few are 4KB, it is normal.
-预防内存交换的方法:
+Methods to prevent memory swapping:
-- 保证机器充足的可用内存
-- 确保所有 Redis 实例设置最大可用内存(maxmemory),防止极端情况 Redis 内存不可控的增长
-- 降低系统使用 swap 优先级,如`echo 10 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness`
+- Ensure ample available memory on the machine.
+- Ensure all Redis instances set a maximum available memory (maxmemory) to prevent uncontrolled growth of Redis memory in extreme situations.
+- Lower the system's swap priority, such as `echo 10 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness`.
-## CPU 竞争
+## CPU Competition
-Redis 是典型的 CPU 密集型应用,不建议和其他多核 CPU 密集型服务部署在一起。当其他进程过度消耗 CPU 时,将严重影响 Redis 的吞吐量。
+Redis is a typical CPU-intensive application and should not be deployed alongside other multi-core CPU-intensive services. When other processes excessively consume CPU, it will severely affect Redis's throughput.
-可以通过`redis-cli --stat`获取当前 Redis 使用情况。通过`top`命令获取进程对 CPU 的利用率等信息 通过`info commandstats`统计信息分析出命令不合理开销时间,查看是否是因为高算法复杂度或者过度的内存优化问题。
+You can use `redis-cli --stat` to get the current Redis usage. The `top` command can be used to get information on processes' CPU utilization, and `info commandstats` can provide statistics to analyze unreasonable command overhead, checking if it is due to high algorithm complexity or excessive memory optimization issues.
-## 网络问题
+## Network Issues
-连接拒绝、网络延迟,网卡软中断等网络问题也可能会导致 Redis 阻塞。
+Connection refusals, network delays, software interrupts on network cards, and other network issues might also lead to Redis blocking.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Redis 阻塞的 6 大类场景分析与总结:
-- Redis 开发与运维笔记-Redis 的噩梦-阻塞:
+- Analysis and Summary of 6 Major Scenarios of Redis Blocking:
+- Redis Development and Operation Notes - The Nightmare of Redis - Blocking:
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
index 9dfb0c3eaa5..0e7d5a4d03f 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.md
@@ -1,69 +1,69 @@
---
-title: Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 5 Basic Data Types in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis常见数据类型
+ content: Common data types in Redis
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis基础数据类型总结:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)
+ content: Summary of Redis basic data types: String, List, Set, Hash, Zset
---
-Redis 共有 5 种基本数据类型:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)。
+Redis has a total of 5 basic data types: String, List, Set, Hash, and Zset.
-这 5 种数据类型是直接提供给用户使用的,是数据的保存形式,其底层实现主要依赖这 8 种数据结构:简单动态字符串(SDS)、LinkedList(双向链表)、Dict(哈希表/字典)、SkipList(跳跃表)、Intset(整数集合)、ZipList(压缩列表)、QuickList(快速列表)。
+These 5 data types are directly provided for user use and represent the form of data storage. Their underlying implementation mainly relies on these 8 data structures: Simple Dynamic Strings (SDS), LinkedList, Dict (hash table/dictionary), SkipList, Intset (integer set), ZipList (compressed list), and QuickList.
-Redis 5 种基本数据类型对应的底层数据结构实现如下表所示:
+The underlying data structure implementations corresponding to the 5 basic data types in Redis are shown in the table below:
| String | List | Hash | Set | Zset |
| :----- | :--------------------------- | :------------ | :----------- | :---------------- |
-| SDS | LinkedList/ZipList/QuickList | Dict、ZipList | Dict、Intset | ZipList、SkipList |
+| SDS | LinkedList/ZipList/QuickList | Dict, ZipList | Dict, Intset | ZipList, SkipList |
-Redis 3.2 之前,List 底层实现是 LinkedList 或者 ZipList。 Redis 3.2 之后,引入了 LinkedList 和 ZipList 的结合 QuickList,List 的底层实现变为 QuickList。从 Redis 7.0 开始, ZipList 被 ListPack 取代。
+Before Redis 3.2, the underlying implementation of List was LinkedList or ZipList. After Redis 3.2, QuickList, a combination of LinkedList and ZipList, was introduced, and the underlying implementation of List changed to QuickList. Starting from Redis 7.0, ZipList has been replaced by ListPack.
-你可以在 Redis 官网上找到 Redis 数据类型/结构非常详细的介绍:
+You can find a very detailed introduction to Redis data types/structures on the official Redis website:
- [Redis Data Structures](https://redis.com/redis-enterprise/data-structures/)
- [Redis Data types tutorial](https://redis.io/docs/manual/data-types/data-types-tutorial/)
-未来随着 Redis 新版本的发布,可能会有新的数据结构出现,通过查阅 Redis 官网对应的介绍,你总能获取到最靠谱的信息。
+In the future, with the release of new versions of Redis, new data structures may appear. By consulting the corresponding introductions on the Redis official website, you can always obtain the most reliable information.

-## String(字符串)
+## String
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-String 是 Redis 中最简单同时也是最常用的一个数据类型。
+String is the simplest and most commonly used data type in Redis.
-String 是一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。
+String is a binary-safe data type that can be used to store any type of data, such as strings, integers, floating-point numbers, images (base64 encoding or decoding of images or image paths), and serialized objects.

-虽然 Redis 是用 C 语言写的,但是 Redis 并没有使用 C 的字符串表示,而是自己构建了一种 **简单动态字符串**(Simple Dynamic String,**SDS**)。相比于 C 的原生字符串,Redis 的 SDS 不光可以保存文本数据还可以保存二进制数据,并且获取字符串长度复杂度为 O(1)(C 字符串为 O(N)),除此之外,Redis 的 SDS API 是安全的,不会造成缓冲区溢出。
+Although Redis is written in C, it does not use C's string representation but instead constructs a **Simple Dynamic String** (SDS). Compared to C's native strings, Redis's SDS can not only store text data but also binary data, and the complexity of obtaining the string length is O(1) (C strings are O(N)). In addition, Redis's SDS API is safe and does not cause buffer overflows.
-### 常用命令
+### Common Commands
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------- | -------------------------------- |
-| SET key value | 设置指定 key 的值 |
-| SETNX key value | 只有在 key 不存在时设置 key 的值 |
-| GET key | 获取指定 key 的值 |
-| MSET key1 value1 key2 value2 …… | 设置一个或多个指定 key 的值 |
-| MGET key1 key2 ... | 获取一个或多个指定 key 的值 |
-| STRLEN key | 返回 key 所储存的字符串值的长度 |
-| INCR key | 将 key 中储存的数字值增一 |
-| DECR key | 将 key 中储存的数字值减一 |
-| EXISTS key | 判断指定 key 是否存在 |
-| DEL key(通用) | 删除指定的 key |
-| EXPIRE key seconds(通用) | 给指定 key 设置过期时间 |
+| Command | Description |
+| -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------- |
+| SET key value | Set the value of the specified key |
+| SETNX key value | Set the value of the key only if it does not exist |
+| GET key | Get the value of the specified key |
+| MSET key1 value1 key2 value2 ... | Set the values of one or more specified keys |
+| MGET key1 key2 ... | Get the values of one or more specified keys |
+| STRLEN key | Return the length of the string value stored at key |
+| INCR key | Increment the numeric value stored at key by one |
+| DECR key | Decrement the numeric value stored at key by one |
+| EXISTS key | Determine if the specified key exists |
+| DEL key (general) | Delete the specified key |
+| EXPIRE key seconds (general) | Set an expiration time for the specified key |
-更多 Redis String 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
+For more Redis String commands and detailed usage guides, please refer to the corresponding introduction on the Redis official website: .
-**基本操作**:
+**Basic Operations**:
```bash
> SET key value
@@ -80,424 +80,22 @@ OK
(nil)
```
-**批量设置**:
+**Batch Setting**:
```bash
> MSET key1 value1 key2 value2
OK
-> MGET key1 key2 # 批量获取多个 key 对应的 value
+> MGET key1 key2 # Batch get the values corresponding to multiple keys
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
```
-**计数器(字符串的内容为整数的时候可以使用):**
+**Counter (when the content of the string is an integer)**:
```bash
> SET number 1
OK
-> INCR number # 将 key 中储存的数字值增一
+> INCR number # Increment the numeric value stored at key by one
(integer) 2
> GET number
-"2"
-> DECR number # 将 key 中储存的数字值减一
-(integer) 1
-> GET number
-"1"
-```
-
-**设置过期时间(默认为永不过期)**:
-
-```bash
-> EXPIRE key 60
-(integer) 1
-> SETEX key 60 value # 设置值并设置过期时间
-OK
-> TTL key
-(integer) 56
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要存储常规数据的场景**
-
-- 举例:缓存 Session、Token、图片地址、序列化后的对象(相比较于 Hash 存储更节省内存)。
-- 相关命令:`SET`、`GET`。
-
-**需要计数的场景**
-
-- 举例:用户单位时间的请求数(简单限流可以用到)、页面单位时间的访问数。
-- 相关命令:`SET`、`GET`、 `INCR`、`DECR` 。
-
-**分布式锁**
-
-利用 `SETNX key value` 命令可以实现一个最简易的分布式锁(存在一些缺陷,通常不建议这样实现分布式锁)。
-
-## List(列表)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 List 其实就是链表数据结构的实现。我在 [线性数据结构 :数组、链表、栈、队列](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/linear-data-structure.html) 这篇文章中详细介绍了链表这种数据结构,我这里就不多做介绍了。
-
-许多高级编程语言都内置了链表的实现比如 Java 中的 `LinkedList`,但是 C 语言并没有实现链表,所以 Redis 实现了自己的链表数据结构。Redis 的 List 的实现为一个 **双向链表**,即可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了部分额外的内存开销。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
-| RPUSH key value1 value2 ... | 在指定列表的尾部(右边)添加一个或多个元素 |
-| LPUSH key value1 value2 ... | 在指定列表的头部(左边)添加一个或多个元素 |
-| LSET key index value | 将指定列表索引 index 位置的值设置为 value |
-| LPOP key | 移除并获取指定列表的第一个元素(最左边) |
-| RPOP key | 移除并获取指定列表的最后一个元素(最右边) |
-| LLEN key | 获取列表元素数量 |
-| LRANGE key start end | 获取列表 start 和 end 之间 的元素 |
-
-更多 Redis List 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP`实现队列**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList value1
-(integer) 1
-> RPUSH myList value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> LPOP myList
-"value1"
-> LRANGE myList 0 1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value3"
-> LRANGE myList 0 -1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value3"
-```
-
-**通过 `RPUSH/RPOP`或者`LPUSH/LPOP` 实现栈**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList2 value1 value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> RPOP myList2 # 将 list的最右边的元素取出
-"value3"
-```
-
-我专门画了一个图方便大家理解 `RPUSH` , `LPOP` , `lpush` , `RPOP` 命令:
-
-
-
-**通过 `LRANGE` 查看对应下标范围的列表元素**:
-
-```bash
-> RPUSH myList value1 value2 value3
-(integer) 3
-> LRANGE myList 0 1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> LRANGE myList 0 -1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-3) "value3"
-```
-
-通过 `LRANGE` 命令,你可以基于 List 实现分页查询,性能非常高!
-
-**通过 `LLEN` 查看链表长度**:
-
-```bash
-> LLEN myList
-(integer) 3
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**信息流展示**
-
-- 举例:最新文章、最新动态。
-- 相关命令:`LPUSH`、`LRANGE`。
-
-**消息队列**
-
-`List` 可以用来做消息队列,只是功能过于简单且存在很多缺陷,不建议这样做。
-
-相对来说,Redis 5.0 新增加的一个数据结构 `Stream` 更适合做消息队列一些,只是功能依然非常简陋。和专业的消息队列相比,还是有很多欠缺的地方比如消息丢失和堆积问题不好解决。
-
-## Hash(哈希)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 Hash 是一个 String 类型的 field-value(键值对) 的映射表,特别适合用于存储对象,后续操作的时候,你可以直接修改这个对象中的某些字段的值。
-
-Hash 类似于 JDK1.8 前的 `HashMap`,内部实现也差不多(数组 + 链表)。不过,Redis 的 Hash 做了更多优化。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ----------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
-| HSET key field value | 设置指定哈希表中指定字段的值 |
-| HSETNX key field value | 只有指定字段不存在时设置指定字段的值 |
-| HMSET key field1 value1 field2 value2 ... | 同时将一个或多个 field-value (域-值)对设置到指定哈希表中 |
-| HGET key field | 获取指定哈希表中指定字段的值 |
-| HMGET key field1 field2 ... | 获取指定哈希表中一个或者多个指定字段的值 |
-| HGETALL key | 获取指定哈希表中所有的键值对 |
-| HEXISTS key field | 查看指定哈希表中指定的字段是否存在 |
-| HDEL key field1 field2 ... | 删除一个或多个哈希表字段 |
-| HLEN key | 获取指定哈希表中字段的数量 |
-| HINCRBY key field increment | 对指定哈希中的指定字段做运算操作(正数为加,负数为减) |
-
-更多 Redis Hash 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**模拟对象数据存储**:
-
-```bash
-> HMSET userInfoKey name "guide" description "dev" age 24
-OK
-> HEXISTS userInfoKey name # 查看 key 对应的 value中指定的字段是否存在。
-(integer) 1
-> HGET userInfoKey name # 获取存储在哈希表中指定字段的值。
-"guide"
-> HGET userInfoKey age
-"24"
-> HGETALL userInfoKey # 获取在哈希表中指定 key 的所有字段和值
-1) "name"
-2) "guide"
-3) "description"
-4) "dev"
-5) "age"
-6) "24"
-> HSET userInfoKey name "GuideGeGe"
-> HGET userInfoKey name
-"GuideGeGe"
-> HINCRBY userInfoKey age 2
-(integer) 26
```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**对象数据存储场景**
-
-- 举例:用户信息、商品信息、文章信息、购物车信息。
-- 相关命令:`HSET` (设置单个字段的值)、`HMSET`(设置多个字段的值)、`HGET`(获取单个字段的值)、`HMGET`(获取多个字段的值)。
-
-## Set(集合)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Redis 中的 Set 类型是一种无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。当你需要存储一个列表数据,又不希望出现重复数据时,Set 是一个很好的选择,并且 Set 提供了判断某个元素是否在一个 Set 集合内的重要接口,这个也是 List 所不能提供的。
-
-你可以基于 Set 轻易实现交集、并集、差集的操作,比如你可以将一个用户所有的关注人存在一个集合中,将其所有粉丝存在一个集合。这样的话,Set 可以非常方便的实现如共同关注、共同粉丝、共同喜好等功能。这个过程也就是求交集的过程。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------- |
-| SADD key member1 member2 ... | 向指定集合添加一个或多个元素 |
-| SMEMBERS key | 获取指定集合中的所有元素 |
-| SCARD key | 获取指定集合的元素数量 |
-| SISMEMBER key member | 判断指定元素是否在指定集合中 |
-| SINTER key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的交集 |
-| SINTERSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的交集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SUNION key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的并集 |
-| SUNIONSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的并集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SDIFF key1 key2 ... | 获取给定所有集合的差集 |
-| SDIFFSTORE destination key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有集合的差集存储在 destination 中 |
-| SPOP key count | 随机移除并获取指定集合中一个或多个元素 |
-| SRANDMEMBER key count | 随机获取指定集合中指定数量的元素 |
-
-更多 Redis Set 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> SADD mySet value1 value2
-(integer) 2
-> SADD mySet value1 # 不允许有重复元素,因此添加失败
-(integer) 0
-> SMEMBERS mySet
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> SCARD mySet
-(integer) 2
-> SISMEMBER mySet value1
-(integer) 1
-> SADD mySet2 value2 value3
-(integer) 2
-```
-
-- `mySet` : `value1`、`value2` 。
-- `mySet2`:`value2`、`value3` 。
-
-**求交集**:
-
-```bash
-> SINTERSTORE mySet3 mySet mySet2
-(integer) 1
-> SMEMBERS mySet3
-1) "value2"
-```
-
-**求并集**:
-
-```bash
-> SUNION mySet mySet2
-1) "value3"
-2) "value2"
-3) "value1"
-```
-
-**求差集**:
-
-```bash
-> SDIFF mySet mySet2 # 差集是由所有属于 mySet 但不属于 A 的元素组成的集合
-1) "value1"
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要存放的数据不能重复的场景**
-
-- 举例:网站 UV 统计(数据量巨大的场景还是 `HyperLogLog`更适合一些)、文章点赞、动态点赞等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SCARD`(获取集合数量) 。
-
-
-
-**需要获取多个数据源交集、并集和差集的场景**
-
-- 举例:共同好友(交集)、共同粉丝(交集)、共同关注(交集)、好友推荐(差集)、音乐推荐(差集)、订阅号推荐(差集+交集) 等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SINTER`(交集)、`SINTERSTORE` (交集)、`SUNION` (并集)、`SUNIONSTORE`(并集)、`SDIFF`(差集)、`SDIFFSTORE` (差集)。
-
-
-
-**需要随机获取数据源中的元素的场景**
-
-- 举例:抽奖系统、随机点名等场景。
-- 相关命令:`SPOP`(随机获取集合中的元素并移除,适合不允许重复中奖的场景)、`SRANDMEMBER`(随机获取集合中的元素,适合允许重复中奖的场景)。
-
-## Sorted Set(有序集合)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Sorted Set 类似于 Set,但和 Set 相比,Sorted Set 增加了一个权重参数 `score`,使得集合中的元素能够按 `score` 进行有序排列,还可以通过 `score` 的范围来获取元素的列表。有点像是 Java 中 `HashMap` 和 `TreeSet` 的结合体。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| ZADD key score1 member1 score2 member2 ... | 向指定有序集合添加一个或多个元素 |
-| ZCARD KEY | 获取指定有序集合的元素数量 |
-| ZSCORE key member | 获取指定有序集合中指定元素的 score 值 |
-| ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 将给定所有有序集合的交集存储在 destination 中,对相同元素对应的 score 值进行 SUM 聚合操作,numkeys 为集合数量 |
-| ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 求并集,其它和 ZINTERSTORE 类似 |
-| ZDIFFSTORE destination numkeys key1 key2 ... | 求差集,其它和 ZINTERSTORE 类似 |
-| ZRANGE key start end | 获取指定有序集合 start 和 end 之间的元素(score 从低到高) |
-| ZREVRANGE key start end | 获取指定有序集合 start 和 end 之间的元素(score 从高到底) |
-| ZREVRANK key member | 获取指定有序集合中指定元素的排名(score 从大到小排序) |
-
-更多 Redis Sorted Set 命令以及详细使用指南,请查看 Redis 官网对应的介绍: 。
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> ZADD myZset 2.0 value1 1.0 value2
-(integer) 2
-> ZCARD myZset
-2
-> ZSCORE myZset value1
-2.0
-> ZRANGE myZset 0 1
-1) "value2"
-2) "value1"
-> ZREVRANGE myZset 0 1
-1) "value1"
-2) "value2"
-> ZADD myZset2 4.0 value2 3.0 value3
-(integer) 2
-
-```
-
-- `myZset` : `value1`(2.0)、`value2`(1.0) 。
-- `myZset2`:`value2` (4.0)、`value3`(3.0) 。
-
-**获取指定元素的排名**:
-
-```bash
-> ZREVRANK myZset value1
-0
-> ZREVRANK myZset value2
-1
-```
-
-**求交集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZINTERSTORE myZset3 2 myZset myZset2
-1
-> ZRANGE myZset3 0 1 WITHSCORES
-value2
-5
-```
-
-**求并集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZUNIONSTORE myZset4 2 myZset myZset2
-3
-> ZRANGE myZset4 0 2 WITHSCORES
-value1
-2
-value3
-3
-value2
-5
-```
-
-**求差集**:
-
-```bash
-> ZDIFF 2 myZset myZset2 WITHSCORES
-value1
-2
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要随机获取数据源中的元素根据某个权重进行排序的场景**
-
-- 举例:各种排行榜比如直播间送礼物的排行榜、朋友圈的微信步数排行榜、王者荣耀中的段位排行榜、话题热度排行榜等等。
-- 相关命令:`ZRANGE` (从小到大排序)、 `ZREVRANGE` (从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK` (指定元素排名)。
-
-
-
-[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 的「技术面试题篇」就有一篇文章详细介绍如何使用 Sorted Set 来设计制作一个排行榜。
-
-
-
-**需要存储的数据有优先级或者重要程度的场景** 比如优先级任务队列。
-
-- 举例:优先级任务队列。
-- 相关命令:`ZRANGE` (从小到大排序)、 `ZREVRANGE` (从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK` (指定元素排名)。
-
-## 总结
-
-| 数据类型 | 说明 |
-| -------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| String | 一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。 |
-| List | Redis 的 List 的实现为一个双向链表,即可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了部分额外的内存开销。 |
-| Hash | 一个 String 类型的 field-value(键值对) 的映射表,特别适合用于存储对象,后续操作的时候,你可以直接修改这个对象中的某些字段的值。 |
-| Set | 无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。 |
-| Zset | 和 Set 相比,Sorted Set 增加了一个权重参数 `score`,使得集合中的元素能够按 `score` 进行有序排列,还可以通过 `score` 的范围来获取元素的列表。有点像是 Java 中 `HashMap` 和 `TreeSet` 的结合体。 |
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis Data Structures: 。
-- Redis Commands: 。
-- Redis Data types tutorial: 。
-- Redis 存储对象信息是用 Hash 还是 String :
-
-
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
index 9e5fbcee59b..835b5f8b8be 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.md
@@ -1,48 +1,48 @@
---
-title: Redis 3 种特殊数据类型详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of 3 Special Data Types in Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis常见数据类型
+ content: Common data types in Redis
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis特殊数据类型总结:HyperLogLogs(基数统计)、Bitmap (位存储)、Geospatial (地理位置)。
+ content: Summary of Redis special data types: HyperLogLogs (cardinality statistics), Bitmap (bit storage), Geospatial (geolocation).
---
-除了 5 种基本的数据类型之外,Redis 还支持 3 种特殊的数据类型:Bitmap、HyperLogLog、GEO。
+In addition to the 5 basic data types, Redis also supports 3 special data types: Bitmap, HyperLogLog, and GEO.
-## Bitmap (位图)
+## Bitmap
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-根据官网介绍:
+According to the official website:
> Bitmaps are not an actual data type, but a set of bit-oriented operations defined on the String type which is treated like a bit vector. Since strings are binary safe blobs and their maximum length is 512 MB, they are suitable to set up to 2^32 different bits.
>
-> Bitmap 不是 Redis 中的实际数据类型,而是在 String 类型上定义的一组面向位的操作,将其视为位向量。由于字符串是二进制安全的块,且最大长度为 512 MB,它们适合用于设置最多 2^32 个不同的位。
+> Bitmap is not an actual data type in Redis, but a set of bit-oriented operations defined on the String type, treated as a bit vector. Since strings are binary safe blobs and their maximum length is 512 MB, they are suitable for setting up to 2^32 different bits.
-Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap, 只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身 。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。
+Bitmaps store continuous binary numbers (0 and 1). With Bitmap, only one bit is needed to represent the value or state of a corresponding element, where the key is the element itself. We know that 8 bits can form one byte, so Bitmap can greatly save storage space.
-你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。
+You can think of Bitmap as an array that stores binary numbers (0 and 1), where each element's index is called an offset.

-### 常用命令
+### Common Commands
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| SETBIT key offset value | 设置指定 offset 位置的值 |
-| GETBIT key offset | 获取指定 offset 位置的值 |
-| BITCOUNT key start end | 获取 start 和 end 之间值为 1 的元素个数 |
-| BITOP operation destkey key1 key2 ... | 对一个或多个 Bitmap 进行运算,可用运算符有 AND, OR, XOR 以及 NOT |
+| Command | Description |
+| ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| SETBIT key offset value | Set the value at the specified offset position |
+| GETBIT key offset | Get the value at the specified offset position |
+| BITCOUNT key start end | Get the number of elements with a value of 1 between start and end |
+| BITOP operation destkey key1 key2 ... | Perform operations on one or more Bitmaps, with operators AND, OR, XOR, and NOT |
-**Bitmap 基本操作演示**:
+**Basic Bitmap Operations Demonstration**:
```bash
-# SETBIT 会返回之前位的值(默认是 0)这里会生成 7 个位
+# SETBIT will return the previous value of the bit (default is 0), generating 7 bits
> SETBIT mykey 7 1
(integer) 0
> SETBIT mykey 7 0
@@ -53,174 +53,35 @@ Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap, 只需
(integer) 0
> SETBIT mykey 8 1
(integer) 0
-# 通过 bitcount 统计被被设置为 1 的位的数量。
+# Count the number of bits set to 1 using bitcount.
> BITCOUNT mykey
(integer) 2
```
-### 应用场景
+### Application Scenarios
-**需要保存状态信息(0/1 即可表示)的场景**
+**Scenarios that require saving state information (0/1 can represent)**
-- 举例:用户签到情况、活跃用户情况、用户行为统计(比如是否点赞过某个视频)。
-- 相关命令:`SETBIT`、`GETBIT`、`BITCOUNT`、`BITOP`。
+- Example: User sign-in status, active user status, user behavior statistics (e.g., whether a user has liked a certain video).
+- Related commands: `SETBIT`, `GETBIT`, `BITCOUNT`, `BITOP`.
-## HyperLogLog(基数统计)
+## HyperLogLog
-### 介绍
+### Introduction
-HyperLogLog 是一种有名的基数计数概率算法 ,基于 LogLog Counting(LLC)优化改进得来,并不是 Redis 特有的,Redis 只是实现了这个算法并提供了一些开箱即用的 API。
+HyperLogLog is a well-known probabilistic algorithm for cardinality counting, optimized from LogLog Counting (LLC). It is not unique to Redis; Redis simply implements this algorithm and provides some out-of-the-box APIs.
-Redis 提供的 HyperLogLog 占用空间非常非常小,只需要 12k 的空间就能存储接近`2^64`个不同元素。这是真的厉害,这就是数学的魅力么!并且,Redis 对 HyperLogLog 的存储结构做了优化,采用两种方式计数:
+The HyperLogLog provided by Redis occupies a very small space, requiring only 12k of space to store nearly `2^64` different elements. This is truly impressive; this is the charm of mathematics! Additionally, Redis has optimized the storage structure of HyperLogLog, using two counting methods:
-- **稀疏矩阵**:计数较少的时候,占用空间很小。
-- **稠密矩阵**:计数达到某个阈值的时候,占用 12k 的空间。
+- **Sparse Matrix**: When the count is low, it occupies very little space.
+- **Dense Matrix**: When the count reaches a certain threshold, it occupies 12k of space.
-Redis 官方文档中有对应的详细说明:
+The official Redis documentation provides detailed explanations:

-基数计数概率算法为了节省内存并不会直接存储元数据,而是通过一定的概率统计方法预估基数值(集合中包含元素的个数)。因此, HyperLogLog 的计数结果并不是一个精确值,存在一定的误差(标准误差为 `0.81%` )。
+The cardinality counting probabilistic algorithm does not directly store metadata to save memory; instead, it estimates the cardinality value (the number of elements in the set) through certain probabilistic statistical methods. Therefore, the counting result of HyperLogLog is not an exact value and has a certain margin of error (standard error is `0.81%`).

-HyperLogLog 的使用非常简单,但原理非常复杂。HyperLogLog 的原理以及在 Redis 中的实现可以看这篇文章:[HyperLogLog 算法的原理讲解以及 Redis 是如何应用它的](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903785744056333) 。
-
-再推荐一个可以帮助理解 HyperLogLog 原理的工具:[Sketch of the Day: HyperLogLog — Cornerstone of a Big Data Infrastructure](http://content.research.neustar.biz/blog/hll.html) 。
-
-除了 HyperLogLog 之外,Redis 还提供了其他的概率数据结构,对应的官方文档地址: 。
-
-### 常用命令
-
-HyperLogLog 相关的命令非常少,最常用的也就 3 个。
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ----------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| PFADD key element1 element2 ... | 添加一个或多个元素到 HyperLogLog 中 |
-| PFCOUNT key1 key2 | 获取一个或者多个 HyperLogLog 的唯一计数。 |
-| PFMERGE destkey sourcekey1 sourcekey2 ... | 将多个 HyperLogLog 合并到 destkey 中,destkey 会结合多个源,算出对应的唯一计数。 |
-
-**HyperLogLog 基本操作演示**:
-
-```bash
-> PFADD hll foo bar zap
-(integer) 1
-> PFADD hll zap zap zap
-(integer) 0
-> PFADD hll foo bar
-(integer) 0
-> PFCOUNT hll
-(integer) 3
-> PFADD some-other-hll 1 2 3
-(integer) 1
-> PFCOUNT hll some-other-hll
-(integer) 6
-> PFMERGE desthll hll some-other-hll
-"OK"
-> PFCOUNT desthll
-(integer) 6
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**数量巨大(百万、千万级别以上)的计数场景**
-
-- 举例:热门网站每日/每周/每月访问 ip 数统计、热门帖子 uv 统计。
-- 相关命令:`PFADD`、`PFCOUNT` 。
-
-## Geospatial (地理位置)
-
-### 介绍
-
-Geospatial index(地理空间索引,简称 GEO) 主要用于存储地理位置信息,基于 Sorted Set 实现。
-
-通过 GEO 我们可以轻松实现两个位置距离的计算、获取指定位置附近的元素等功能。
-
-
-
-### 常用命令
-
-| 命令 | 介绍 |
-| ------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| GEOADD key longitude1 latitude1 member1 ... | 添加一个或多个元素对应的经纬度信息到 GEO 中 |
-| GEOPOS key member1 member2 ... | 返回给定元素的经纬度信息 |
-| GEODIST key member1 member2 M/KM/FT/MI | 返回两个给定元素之间的距离 |
-| GEORADIUS key longitude latitude radius distance | 获取指定位置附近 distance 范围内的其他元素,支持 ASC(由近到远)、DESC(由远到近)、Count(数量) 等参数 |
-| GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius distance | 类似于 GEORADIUS 命令,只是参照的中心点是 GEO 中的元素 |
-
-**基本操作**:
-
-```bash
-> GEOADD personLocation 116.33 39.89 user1 116.34 39.90 user2 116.35 39.88 user3
-3
-> GEOPOS personLocation user1
-116.3299986720085144
-39.89000061669732844
-> GEODIST personLocation user1 user2 km
-1.4018
-```
-
-通过 Redis 可视化工具查看 `personLocation` ,果不其然,底层就是 Sorted Set。
-
-GEO 中存储的地理位置信息的经纬度数据通过 GeoHash 算法转换成了一个整数,这个整数作为 Sorted Set 的 score(权重参数)使用。
-
-
-
-**获取指定位置范围内的其他元素**:
-
-```bash
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 3 km
-user3
-user1
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 2 km
-> GEORADIUS personLocation 116.33 39.87 5 km
-user3
-user1
-user2
-> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER personLocation user1 5 km
-user3
-user1
-user2
-> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER personLocation user1 2 km
-user1
-user2
-```
-
-`GEORADIUS` 命令的底层原理解析可以看看阿里的这篇文章:[Redis 到底是怎么实现“附近的人”这个功能的呢?](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903966061363207) 。
-
-**移除元素**:
-
-GEO 底层是 Sorted Set ,你可以对 GEO 使用 Sorted Set 相关的命令。
-
-```bash
-> ZREM personLocation user1
-1
-> ZRANGE personLocation 0 -1
-user3
-user2
-> ZSCORE personLocation user2
-4069879562983946
-```
-
-### 应用场景
-
-**需要管理使用地理空间数据的场景**
-
-- 举例:附近的人。
-- 相关命令: `GEOADD`、`GEORADIUS`、`GEORADIUSBYMEMBER` 。
-
-## 总结
-
-| 数据类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| Bitmap | 你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。通过 Bitmap, 只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身 。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。 |
-| HyperLogLog | Redis 提供的 HyperLogLog 占用空间非常非常小,只需要 12k 的空间就能存储接近`2^64`个不同元素。不过,HyperLogLog 的计数结果并不是一个精确值,存在一定的误差(标准误差为 `0.81%` )。 |
-| Geospatial index | Geospatial index(地理空间索引,简称 GEO) 主要用于存储地理位置信息,基于 Sorted Set 实现。 |
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis Data Structures: 。
-- 《Redis 深度历险:核心原理与应用实践》1.6 四两拨千斤——HyperLogLog
-- 布隆过滤器,位图,HyperLogLog:
-
-
+Using HyperLogLog is very simple, but the principle is quite complex. You can read this article for an explanation of the principle of HyperLogLog and how it is applied in Redis: \[Explanation of the Principle of HyperLogLog Algorithm and How Redis Applies It\](https://juejin.cn/post/684490378574
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
index 35f9304321f..acfebfbb9d6 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-delayed-task.md
@@ -1,82 +1,82 @@
---
-title: 如何基于Redis实现延时任务
-category: 数据库
+title: How to Implement Delayed Tasks Based on Redis
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-基于 Redis 实现延时任务的功能无非就下面两种方案:
+The functionality of implementing delayed tasks based on Redis consists of the following two solutions:
-1. Redis 过期事件监听
-2. Redisson 内置的延时队列
+1. Redis Expiration Event Listening
+1. Built-in Delayed Queue in Redisson
-面试的时候,你可以先说自己考虑了这两种方案,但最后发现 Redis 过期事件监听这种方案存在很多问题,因此你最终选择了 Redisson 内置的 DelayedQueue 这种方案。
+During the interview, you can first mention that you considered these two solutions, but ultimately found that the Redis expiration event listening approach has many issues, which led you to choose the built-in DelayedQueue in Redisson.
-这个时候面试官可能会追问你一些相关的问题,我们后面会提到,提前准备就好了。
+At this point, the interviewer may ask you some related questions, which we will cover later, so it's good to prepare in advance.
-另外,除了下面介绍到的这些问题之外,Redis 相关的常见问题建议你都复习一遍,不排除面试官会顺带问你一些 Redis 的其他问题。
+Additionally, besides the issues mentioned below, it is recommended that you review all common issues related to Redis, as the interviewer may also ask some other questions about Redis.
-### Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能的原理?
+### What is the Principle of Implementing Delayed Task Functionality through Redis Expiration Event Listening?
-Redis 2.0 引入了发布订阅 (pub/sub) 功能。在 pub/sub 中,引入了一个叫做 **channel(频道)** 的概念,有点类似于消息队列中的 **topic(主题)**。
+Redis 2.0 introduced the publish/subscribe (pub/sub) feature. In pub/sub, a concept called **channel** is introduced, which is somewhat similar to **topic** in message queues.
-pub/sub 涉及发布者(publisher)和订阅者(subscriber,也叫消费者)两个角色:
+pub/sub involves two roles: publisher and subscriber (also known as consumers):
-- 发布者通过 `PUBLISH` 投递消息给指定 channel。
-- 订阅者通过`SUBSCRIBE`订阅它关心的 channel。并且,订阅者可以订阅一个或者多个 channel。
+- The publisher delivers messages to a specified channel using `PUBLISH`.
+- Subscribers subscribe to the channels of their interest using `SUBSCRIBE`, and they can subscribe to one or more channels.
-
+
-在 pub/sub 模式下,生产者需要指定消息发送到哪个 channel 中,而消费者则订阅对应的 channel 以获取消息。
+In the pub/sub model, the producer needs to specify which channel the message is sent to, while consumers subscribe to the corresponding channel to receive messages.
-Redis 中有很多默认的 channel,这些 channel 是由 Redis 本身向它们发送消息的,而不是我们自己编写的代码。其中,`__keyevent@0__:expired` 就是一个默认的 channel,负责监听 key 的过期事件。也就是说,当一个 key 过期之后,Redis 会发布一个 key 过期的事件到`__keyevent@__:expired`这个 channel 中。
+Redis has many default channels, which are messages sent by Redis itself rather than our own code. One of them, `__keyevent@0__:expired`, is a default channel responsible for listening to the expiration events of keys. This means that when a key expires, Redis will publish an expiration event to the channel `__keyevent@__:expired`.
-我们只需要监听这个 channel,就可以拿到过期的 key 的消息,进而实现了延时任务功能。
+We only need to listen to this channel to receive messages about expired keys, thus achieving the delayed task functionality.
-这个功能被 Redis 官方称为 **keyspace notifications** ,作用是实时监控 Redis 键和值的变化。
+This feature is officially referred to as **keyspace notifications** by Redis, which serves to monitor changes in Redis keys and values in real-time.
-### Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能有什么缺陷?
+### What Are the Defects of Implementing Delayed Task Functionality through Redis Expiration Event Listening?
-**1、时效性差**
+**1. Poor Timeliness**
-官方文档的一段介绍解释了时效性差的原因,地址: 。
+A paragraph in the official documentation explains the reason for poor timeliness, reference: .
-
+
-这段话的核心是:过期事件消息是在 Redis 服务器删除 key 时发布的,而不是一个 key 过期之后就会就会直接发布。
+The core of this statement is that expiration event messages are published when the Redis server deletes the key, not immediately when a key expires.
-我们知道常用的过期数据的删除策略就两个:
+We know there are two common strategies for deleting expired data:
-1. **惰性删除**:只会在取出 key 的时候才对数据进行过期检查。这样对 CPU 最友好,但是可能会造成太多过期 key 没有被删除。
-2. **定期删除**:每隔一段时间抽取一批 key 执行删除过期 key 操作。并且,Redis 底层会通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对 CPU 时间的影响。
+1. **Lazy Deletion**: It only checks for expiration when the key is accessed. This is friendly to the CPU but may result in many expired keys not being deleted.
+1. **Periodic Deletion**: A batch of keys is randomly selected to execute the deletion of expired keys at intervals. Moreover, Redis limits the duration and frequency of deletion operations to reduce the impact on CPU time.
-定期删除对内存更加友好,惰性删除对 CPU 更加友好。两者各有千秋,所以 Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 。
+Periodic deletion is more memory-friendly, while lazy deletion is more CPU-friendly. Each has its advantages, which is why Redis adopts **periodic deletion combined with lazy/eager deletion**.
-因此,就会存在我设置了 key 的过期时间,但到了指定时间 key 还未被删除,进而没有发布过期事件的情况。
+Therefore, there might be scenarios where I set an expiration time for a key, but the key has not been deleted by the specified time and thus did not publish an expiration event.
-**2、丢消息**
+**2. Message Loss**
-Redis 的 pub/sub 模式中的消息并不支持持久化,这与消息队列不同。在 Redis 的 pub/sub 模式中,发布者将消息发送给指定的频道,订阅者监听相应的频道以接收消息。当没有订阅者时,消息会被直接丢弃,在 Redis 中不会存储该消息。
+Messages in Redis's pub/sub mode do not support persistence, which is different from message queues. In Redis's pub/sub mode, the publisher sends messages to a specified channel, and subscribers listen to the corresponding channel to receive messages. When there are no subscribers, messages are directly discarded and will not be stored in Redis.
-**3、多服务实例下消息重复消费**
+**3. Message Duplicate Consumption in Multiple Service Instances**
-Redis 的 pub/sub 模式目前只有广播模式,这意味着当生产者向特定频道发布一条消息时,所有订阅相关频道的消费者都能够收到该消息。
+Redis's pub/sub mode currently only supports broadcasting, which means that when a producer publishes a message to a specific channel, all consumers listening to that channel can receive it.
-这个时候,我们需要注意多个服务实例重复处理消息的问题,这会增加代码开发量和维护难度。
+In this case, we need to be aware of the issue of multiple service instances processing messages repeatedly, which increases both code development and maintenance difficulty.
-### Redisson 延迟队列原理是什么?有什么优势?
+### What Is the Principle of Redisson Delayed Queue? What Are Its Advantages?
-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,比如多种分布式锁的实现、延时队列。
+Redisson is an open-source Redis client for the Java language, providing many out-of-the-box features, such as various implementations of distributed locks and delayed queues.
-我们可以借助 Redisson 内置的延时队列 RDelayedQueue 来实现延时任务功能。
+We can use Redisson's built-in delayed queue RDelayedQueue to implement the delayed task functionality.
-Redisson 的延迟队列 RDelayedQueue 是基于 Redis 的 SortedSet 来实现的。SortedSet 是一个有序集合,其中的每个元素都可以设置一个分数,代表该元素的权重。Redisson 利用这一特性,将需要延迟执行的任务插入到 SortedSet 中,并给它们设置相应的过期时间作为分数。
+Redisson's delayed queue RDelayedQueue is implemented based on Redis's SortedSet. SortedSet is an ordered collection where each element can have a score set that represents the weight of that element. Redisson uses this feature to insert tasks that need to be executed with a delay into the SortedSet and sets their corresponding expiration time as the score.
-Redisson 定期使用 `zrangebyscore` 命令扫描 SortedSet 中过期的元素,然后将这些过期元素从 SortedSet 中移除,并将它们加入到就绪消息列表中。就绪消息列表是一个阻塞队列,有消息进入就会被消费者监听到。这样做可以避免消费者对整个 SortedSet 进行轮询,提高了执行效率。
+Redisson periodically uses the `zrangebyscore` command to scan for expired elements in the SortedSet, then removes these expired elements from the SortedSet and adds them to the ready message list. The ready message list is a blocking queue that consumers can listen to when new messages enter. This avoids consumers polling the entire SortedSet, thereby improving execution efficiency.
-相比于 Redis 过期事件监听实现延时任务功能,这种方式具备下面这些优势:
+Compared to the Redis expiration event listening method for implementing delayed tasks, this approach has the following advantages:
-1. **减少了丢消息的可能**:DelayedQueue 中的消息会被持久化,即使 Redis 宕机了,根据持久化机制,也只可能丢失一点消息,影响不大。当然了,你也可以使用扫描数据库的方法作为补偿机制。
-2. **消息不存在重复消费问题**:每个客户端都是从同一个目标队列中获取任务的,不存在重复消费的问题。
+1. **Reduced Possibility of Message Loss**: Messages in the DelayedQueue are persisted, so even if Redis crashes, based on the persistence mechanism, only a small number of messages may be lost, which has a minimal impact. Of course, you can also use database scanning as a compensation mechanism.
+1. **No Duplicate Consumption Issue**: Every client retrieves tasks from the same target queue, eliminating the issue of duplicate consumption.
-跟 Redisson 内置的延时队列相比,消息队列可以通过保障消息消费的可靠性、控制消息生产者和消费者的数量等手段来实现更高的吞吐量和更强的可靠性,实际项目中首选使用消息队列的延时消息这种方案。
+Compared to Redisson's built-in delayed queue, message queues can achieve higher throughput and stronger reliability by ensuring message consumption reliability and controlling the number of message producers and consumers, making delayed messages in message queues the preferred solution in practical projects.
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
index cb2da7476d1..97a731c3291 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.md
@@ -1,37 +1,37 @@
---
-title: Redis内存碎片详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Memory Fragmentation
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-## 什么是内存碎片?
+## What is Memory Fragmentation?
-你可以将内存碎片简单地理解为那些不可用的空闲内存。
+You can simply understand memory fragmentation as the unusable free memory.
-举个例子:操作系统为你分配了 32 字节的连续内存空间,而你存储数据实际只需要使用 24 字节内存空间,那这多余出来的 8 字节内存空间如果后续没办法再被分配存储其他数据的话,就可以被称为内存碎片。
+For example, if the operating system allocates a continuous memory space of 32 bytes for you, but you only need to use 24 bytes of that space to store data, then the extra 8 bytes of memory, if it cannot be allocated for other data later, can be referred to as memory fragmentation.
-
+
-Redis 内存碎片虽然不会影响 Redis 性能,但是会增加内存消耗。
+Although Redis memory fragmentation does not affect Redis performance, it does increase memory consumption.
-## 为什么会有 Redis 内存碎片?
+## Why Does Redis Memory Fragmentation Occur?
-Redis 内存碎片产生比较常见的 2 个原因:
+There are two common reasons for Redis memory fragmentation:
-**1、Redis 存储数据的时候向操作系统申请的内存空间可能会大于数据实际需要的存储空间。**
+**1. The memory space requested by Redis from the operating system when storing data may be larger than the actual storage space needed.**
-以下是这段 Redis 官方的原话:
+Here is the original statement from the Redis official documentation:
> To store user keys, Redis allocates at most as much memory as the `maxmemory` setting enables (however there are small extra allocations possible).
-Redis 使用 `zmalloc` 方法(Redis 自己实现的内存分配方法)进行内存分配的时候,除了要分配 `size` 大小的内存之外,还会多分配 `PREFIX_SIZE` 大小的内存。
+When Redis allocates memory using the `zmalloc` method (a memory allocation method implemented by Redis itself), it not only allocates memory of size `size`, but also allocates additional memory of size `PREFIX_SIZE`.
-`zmalloc` 方法源码如下(源码地址:
+The source code for the `zmalloc` method is as follows (source link: ):
```java
void *zmalloc(size_t size) {
- // 分配指定大小的内存
+ // Allocate memory of the specified size
void *ptr = malloc(size+PREFIX_SIZE);
if (!ptr) zmalloc_oom_handler(size);
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOC_SIZE
@@ -45,80 +45,39 @@ void *zmalloc(size_t size) {
}
```
-另外,Redis 可以使用多种内存分配器来分配内存( libc、jemalloc、tcmalloc),默认使用 [jemalloc](https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc),而 jemalloc 按照一系列固定的大小(8 字节、16 字节、32 字节……)来分配内存的。jemalloc 划分的内存单元如下图所示:
+Additionally, Redis can use various memory allocators to allocate memory (libc, jemalloc, tcmalloc), with the default being [jemalloc](https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc), which allocates memory based on a series of fixed sizes (8 bytes, 16 bytes, 32 bytes, etc.). The memory units allocated by jemalloc are shown in the following diagram:
-
+
-当程序申请的内存最接近某个固定值时,jemalloc 会给它分配相应大小的空间,就比如说程序需要申请 17 字节的内存,jemalloc 会直接给它分配 32 字节的内存,这样会导致有 15 字节内存的浪费。不过,jemalloc 专门针对内存碎片问题做了优化,一般不会存在过度碎片化的问题。
+When the memory requested by the program is closest to a fixed value, jemalloc allocates the corresponding size of space. For example, if the program requests 17 bytes of memory, jemalloc will allocate 32 bytes, resulting in a waste of 15 bytes of memory. However, jemalloc has been optimized specifically for memory fragmentation issues, so excessive fragmentation is generally not a problem.
-**2、频繁修改 Redis 中的数据也会产生内存碎片。**
+**2. Frequent modifications to data in Redis can also lead to memory fragmentation.**
-当 Redis 中的某个数据删除时,Redis 通常不会轻易释放内存给操作系统。
+When a piece of data in Redis is deleted, Redis typically does not readily release memory back to the operating system.
-这个在 Redis 官方文档中也有对应的原话:
+This is also mentioned in the official Redis documentation:

-文档地址: 。
+Documentation link: .
-## 如何查看 Redis 内存碎片的信息?
+## How to Check Redis Memory Fragmentation Information?
-使用 `info memory` 命令即可查看 Redis 内存相关的信息。下图中每个参数具体的含义,Redis 官方文档有详细的介绍: 。
+You can use the `info memory` command to view Redis memory-related information. The specific meanings of each parameter in the following image are detailed in the Redis official documentation: .

-Redis 内存碎片率的计算公式:`mem_fragmentation_ratio` (内存碎片率)= `used_memory_rss` (操作系统实际分配给 Redis 的物理内存空间大小)/ `used_memory`(Redis 内存分配器为了存储数据实际申请使用的内存空间大小)
+The formula for calculating Redis memory fragmentation ratio: `mem_fragmentation_ratio` (memory fragmentation ratio) = `used_memory_rss` (the actual physical memory space allocated to Redis by the operating system) / `used_memory` (the actual memory space requested by the Redis memory allocator for storing data).
-也就是说,`mem_fragmentation_ratio` (内存碎片率)的值越大代表内存碎片率越严重。
+In other words, a larger value of `mem_fragmentation_ratio` indicates a more serious memory fragmentation issue.
-一定不要误认为`used_memory_rss` 减去 `used_memory`值就是内存碎片的大小!!!这不仅包括内存碎片,还包括其他进程开销,以及共享库、堆栈等的开销。
+Do not mistakenly think that the value of `used_memory_rss` minus `used_memory` is the size of memory fragmentation!!! This includes not only memory fragmentation but also overhead from other processes, as well as shared libraries, stacks, etc.
-很多小伙伴可能要问了:“多大的内存碎片率才是需要清理呢?”。
+Many may ask, "What level of memory fragmentation ratio requires cleanup?"
-通常情况下,我们认为 `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` 的话才需要清理内存碎片。 `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` 意味着你使用 Redis 存储实际大小 2G 的数据需要使用大于 3G 的内存。
+Generally, we consider that a `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` indicates the need to clean up memory fragmentation. A `mem_fragmentation_ratio > 1.5` means that you need more than 3G of memory to store an actual size of 2G of data in Redis.
-如果想要快速查看内存碎片率的话,你还可以通过下面这个命令:
+If you want to quickly check the memory fragmentation ratio, you can use the following command:
```bash
-> redis-cli -p 6379 info | grep mem_fragmentation_ratio
-```
-
-另外,内存碎片率可能存在小于 1 的情况。这种情况我在日常使用中还没有遇到过,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看这篇文章 [故障分析 | Redis 内存碎片率太低该怎么办?- 爱可生开源社区](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/drlDvp7bfq5jt2M5pTqJCw) 。
-
-## 如何清理 Redis 内存碎片?
-
-Redis4.0-RC3 版本以后自带了内存整理,可以避免内存碎片率过大的问题。
-
-直接通过 `config set` 命令将 `activedefrag` 配置项设置为 `yes` 即可。
-
-```bash
-config set activedefrag yes
-```
-
-具体什么时候清理需要通过下面两个参数控制:
-
-```bash
-# 内存碎片占用空间达到 500mb 的时候开始清理
-config set active-defrag-ignore-bytes 500mb
-# 内存碎片率大于 1.5 的时候开始清理
-config set active-defrag-threshold-lower 50
-```
-
-通过 Redis 自动内存碎片清理机制可能会对 Redis 的性能产生影响,我们可以通过下面两个参数来减少对 Redis 性能的影响:
-
-```bash
-# 内存碎片清理所占用 CPU 时间的比例不低于 20%
-config set active-defrag-cycle-min 20
-# 内存碎片清理所占用 CPU 时间的比例不高于 50%
-config set active-defrag-cycle-max 50
-```
-
-另外,重启节点可以做到内存碎片重新整理。如果你采用的是高可用架构的 Redis 集群的话,你可以将碎片率过高的主节点转换为从节点,以便进行安全重启。
-
-## 参考
-
-- Redis 官方文档:
-- Redis 核心技术与实战 - 极客时间 - 删除数据后,为什么内存占用率还是很高?:
-- Redis 源码解析——内存分配:< 源码解析——内存管理>
-
-
+> redis-cli -p 637
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
index c17fe7db316..1929e74c349 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-persistence.md
@@ -1,217 +1,74 @@
---
-title: Redis持久化机制详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanisms
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: Redis持久化机制详解
+ content: Detailed Explanation of Redis Persistence Mechanisms
- - meta
- name: description
- content: Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:快照(snapshotting,RDB)、只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)、RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)。
+ content: One important difference between Redis and Memcached is that Redis supports persistence, and it supports three types of persistence methods: snapshots (snapshotting, RDB), append-only files (append-only file, AOF), and hybrid persistence of RDB and AOF (new in Redis 4.0).
---
-使用缓存的时候,我们经常需要对内存中的数据进行持久化也就是将内存中的数据写入到硬盘中。大部分原因是为了之后重用数据(比如重启机器、机器故障之后恢复数据),或者是为了做数据同步(比如 Redis 集群的主从节点通过 RDB 文件同步数据)。
+When using caching, we often need to persist data in memory, which means writing the data in memory to disk. The main reasons are to reuse data later (for example, to recover data after restarting the machine or after a machine failure) or to synchronize data (for example, Redis cluster master-slave nodes synchronize data through RDB files).
-Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:
+One important difference between Redis and Memcached is that Redis supports persistence, and it supports three types of persistence methods:
-- 快照(snapshotting,RDB)
-- 只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)
-- RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)
+- Snapshots (snapshotting, RDB)
+- Append-only files (append-only file, AOF)
+- Hybrid persistence of RDB and AOF (new in Redis 4.0)
-官方文档地址: 。
+Official documentation link: .

-## RDB 持久化
+## RDB Persistence
-### 什么是 RDB 持久化?
+### What is RDB Persistence?
-Redis 可以通过创建快照来获得存储在内存里面的数据在 **某个时间点** 上的副本。Redis 创建快照之后,可以对快照进行备份,可以将快照复制到其他服务器从而创建具有相同数据的服务器副本(Redis 主从结构,主要用来提高 Redis 性能),还可以将快照留在原地以便重启服务器的时候使用。
+Redis can create snapshots to obtain a copy of the data stored in memory at **a certain point in time**. After Redis creates a snapshot, it can back it up, copy the snapshot to other servers to create replicas with the same data (the Redis master-slave structure, mainly used to improve Redis performance), or keep the snapshot in place for use when restarting the server.
-快照持久化是 Redis 默认采用的持久化方式,在 `redis.conf` 配置文件中默认有此下配置:
+Snapshot persistence is the default persistence method used by Redis, and the following configuration is present by default in the `redis.conf` configuration file:
```clojure
-save 900 1 #在900秒(15分钟)之后,如果至少有1个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 900 1 # After 900 seconds (15 minutes), if at least 1 key has changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
-save 300 10 #在300秒(5分钟)之后,如果至少有10个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 300 10 # After 300 seconds (5 minutes), if at least 10 keys have changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
-save 60 10000 #在60秒(1分钟)之后,如果至少有10000个key发生变化,Redis就会自动触发bgsave命令创建快照。
+save 60 10000 # After 60 seconds (1 minute), if at least 10000 keys have changed, Redis will automatically trigger the bgsave command to create a snapshot.
```
-### RDB 创建快照时会阻塞主线程吗?
+### Does RDB Block the Main Thread When Creating Snapshots?
-Redis 提供了两个命令来生成 RDB 快照文件:
+Redis provides two commands to generate RDB snapshot files:
-- `save` : 同步保存操作,会阻塞 Redis 主线程;
-- `bgsave` : fork 出一个子进程,子进程执行,不会阻塞 Redis 主线程,默认选项。
+- `save`: A synchronous save operation that blocks the Redis main thread;
+- `bgsave`: Forks a child process to execute, which does not block the Redis main thread, the default option.
-> 这里说 Redis 主线程而不是主进程的主要是因为 Redis 启动之后主要是通过单线程的方式完成主要的工作。如果你想将其描述为 Redis 主进程,也没毛病。
+> Here, we refer to the Redis main thread rather than the main process mainly because Redis primarily completes its main work in a single-threaded manner after startup. If you want to describe it as the Redis main process, that is also acceptable.
-## AOF 持久化
+## AOF Persistence
-### 什么是 AOF 持久化?
+### What is AOF Persistence?
-与快照持久化相比,AOF 持久化的实时性更好。默认情况下 Redis 没有开启 AOF(append only file)方式的持久化(Redis 6.0 之后已经默认是开启了),可以通过 `appendonly` 参数开启:
+Compared to snapshot persistence, AOF persistence has better real-time performance. By default, Redis does not enable AOF (append-only file) persistence (it has been enabled by default since Redis 6.0), and it can be enabled through the `appendonly` parameter:
```bash
appendonly yes
```
-开启 AOF 持久化后每执行一条会更改 Redis 中的数据的命令,Redis 就会将该命令写入到 AOF 缓冲区 `server.aof_buf` 中,然后再写入到 AOF 文件中(此时还在系统内核缓存区未同步到磁盘),最后再根据持久化方式( `fsync`策略)的配置来决定何时将系统内核缓存区的数据同步到硬盘中的。
+After enabling AOF persistence, every command that modifies data in Redis will write that command to the AOF buffer `server.aof_buf`, and then write it to the AOF file (at this point, it is still in the system kernel cache and has not been synchronized to disk). Finally, it decides when to synchronize the data in the system kernel cache to the hard disk based on the persistence method (`fsync` strategy) configuration.
-只有同步到磁盘中才算持久化保存了,否则依然存在数据丢失的风险,比如说:系统内核缓存区的数据还未同步,磁盘机器就宕机了,那这部分数据就算丢失了。
+Only when synchronized to disk is it considered persistently saved; otherwise, there is still a risk of data loss. For example, if the data in the system kernel cache has not been synchronized and the disk machine crashes, that portion of data will be lost.
-AOF 文件的保存位置和 RDB 文件的位置相同,都是通过 `dir` 参数设置的,默认的文件名是 `appendonly.aof`。
+The AOF file's save location is the same as that of the RDB file, both set by the `dir` parameter, and the default filename is `appendonly.aof`.
-### AOF 工作基本流程是怎样的?
+### What is the Basic Workflow of AOF?
-AOF 持久化功能的实现可以简单分为 5 步:
+The implementation of AOF persistence can be simply divided into 5 steps:
-1. **命令追加(append)**:所有的写命令会追加到 AOF 缓冲区中。
-2. **文件写入(write)**:将 AOF 缓冲区的数据写入到 AOF 文件中。这一步需要调用`write`函数(系统调用),`write`将数据写入到了系统内核缓冲区之后直接返回了(延迟写)。注意!!!此时并没有同步到磁盘。
-3. **文件同步(fsync)**:AOF 缓冲区根据对应的持久化方式( `fsync` 策略)向硬盘做同步操作。这一步需要调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用), `fsync` 针对单个文件操作,对其进行强制硬盘同步,`fsync` 将阻塞直到写入磁盘完成后返回,保证了数据持久化。
-4. **文件重写(rewrite)**:随着 AOF 文件越来越大,需要定期对 AOF 文件进行重写,达到压缩的目的。
-5. **重启加载(load)**:当 Redis 重启时,可以加载 AOF 文件进行数据恢复。
-
-> Linux 系统直接提供了一些函数用于对文件和设备进行访问和控制,这些函数被称为 **系统调用(syscall)**。
-
-这里对上面提到的一些 Linux 系统调用再做一遍解释:
-
-- `write`:写入系统内核缓冲区之后直接返回(仅仅是写到缓冲区),不会立即同步到硬盘。虽然提高了效率,但也带来了数据丢失的风险。同步硬盘操作通常依赖于系统调度机制,Linux 内核通常为 30s 同步一次,具体值取决于写出的数据量和 I/O 缓冲区的状态。
-- `fsync`:`fsync`用于强制刷新系统内核缓冲区(同步到到磁盘),确保写磁盘操作结束才会返回。
-
-AOF 工作流程图如下:
-
-
-
-### AOF 持久化方式有哪些?
-
-在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式( `fsync`策略),它们分别是:
-
-1. `appendfsync always`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后,后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)立即会调用 `fsync` 函数同步 AOF 文件(刷盘),`fsync` 完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低 Redis 的性能(`write` + `fsync`)。
-2. `appendfsync everysec`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,由后台线程( `aof_fsync` 线程)每秒钟调用 `fsync` 函数(系统调用)同步一次 AOF 文件(`write`+`fsync`,`fsync`间隔为 1 秒)
-3. `appendfsync no`:主线程调用 `write` 执行写操作后立即返回,让操作系统决定何时进行同步,Linux 下一般为 30 秒一次(`write`但不`fsync`,`fsync` 的时机由操作系统决定)。
-
-可以看出:**这 3 种持久化方式的主要区别在于 `fsync` 同步 AOF 文件的时机(刷盘)**。
-
-为了兼顾数据和写入性能,可以考虑 `appendfsync everysec` 选项 ,让 Redis 每秒同步一次 AOF 文件,Redis 性能受到的影响较小。而且这样即使出现系统崩溃,用户最多只会丢失一秒之内产生的数据。当硬盘忙于执行写入操作的时候,Redis 还会优雅的放慢自己的速度以便适应硬盘的最大写入速度。
-
-从 Redis 7.0.0 开始,Redis 使用了 **Multi Part AOF** 机制。顾名思义,Multi Part AOF 就是将原来的单个 AOF 文件拆分成多个 AOF 文件。在 Multi Part AOF 中,AOF 文件被分为三种类型,分别为:
-
-- BASE:表示基础 AOF 文件,它一般由子进程通过重写产生,该文件最多只有一个。
-- INCR:表示增量 AOF 文件,它一般会在 AOFRW 开始执行时被创建,该文件可能存在多个。
-- HISTORY:表示历史 AOF 文件,它由 BASE 和 INCR AOF 变化而来,每次 AOFRW 成功完成时,本次 AOFRW 之前对应的 BASE 和 INCR AOF 都将变为 HISTORY,HISTORY 类型的 AOF 会被 Redis 自动删除。
-
-Multi Part AOF 不是重点,了解即可,详细介绍可以看看阿里开发者的[Redis 7.0 Multi Part AOF 的设计和实现](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/467217082) 这篇文章。
-
-**相关 issue**:[Redis 的 AOF 方式 #783](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/783)。
-
-### AOF 为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志?
-
-关系型数据库(如 MySQL)通常都是执行命令之前记录日志(方便故障恢复),而 Redis AOF 持久化机制是在执行完命令之后再记录日志。
-
-
-
-**为什么是在执行完命令之后记录日志呢?**
-
-- 避免额外的检查开销,AOF 记录日志不会对命令进行语法检查;
-- 在命令执行完之后再记录,不会阻塞当前的命令执行。
-
-这样也带来了风险(我在前面介绍 AOF 持久化的时候也提到过):
-
-- 如果刚执行完命令 Redis 就宕机会导致对应的修改丢失;
-- 可能会阻塞后续其他命令的执行(AOF 记录日志是在 Redis 主线程中进行的)。
-
-### AOF 重写了解吗?
-
-当 AOF 变得太大时,Redis 能够在后台自动重写 AOF 产生一个新的 AOF 文件,这个新的 AOF 文件和原有的 AOF 文件所保存的数据库状态一样,但体积更小。
-
-
-
-> AOF 重写(rewrite) 是一个有歧义的名字,该功能是通过读取数据库中的键值对来实现的,程序无须对现有 AOF 文件进行任何读入、分析或者写入操作。
-
-由于 AOF 重写会进行大量的写入操作,为了避免对 Redis 正常处理命令请求造成影响,Redis 将 AOF 重写程序放到子进程里执行。
-
-AOF 文件重写期间,Redis 还会维护一个 **AOF 重写缓冲区**,该缓冲区会在子进程创建新 AOF 文件期间,记录服务器执行的所有写命令。当子进程完成创建新 AOF 文件的工作之后,服务器会将重写缓冲区中的所有内容追加到新 AOF 文件的末尾,使得新的 AOF 文件保存的数据库状态与现有的数据库状态一致。最后,服务器用新的 AOF 文件替换旧的 AOF 文件,以此来完成 AOF 文件重写操作。
-
-开启 AOF 重写功能,可以调用 `BGREWRITEAOF` 命令手动执行,也可以设置下面两个配置项,让程序自动决定触发时机:
-
-- `auto-aof-rewrite-min-size`:如果 AOF 文件大小小于该值,则不会触发 AOF 重写。默认值为 64 MB;
-- `auto-aof-rewrite-percentage`:执行 AOF 重写时,当前 AOF 大小(aof_current_size)和上一次重写时 AOF 大小(aof_base_size)的比值。如果当前 AOF 文件大小增加了这个百分比值,将触发 AOF 重写。将此值设置为 0 将禁用自动 AOF 重写。默认值为 100。
-
-Redis 7.0 版本之前,如果在重写期间有写入命令,AOF 可能会使用大量内存,重写期间到达的所有写入命令都会写入磁盘两次。
-
-Redis 7.0 版本之后,AOF 重写机制得到了优化改进。下面这段内容摘自阿里开发者的[从 Redis7.0 发布看 Redis 的过去与未来](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RnoPPL7jiFSKkx3G4p57Pg) 这篇文章。
-
-> AOF 重写期间的增量数据如何处理一直是个问题,在过去写期间的增量数据需要在内存中保留,写结束后再把这部分增量数据写入新的 AOF 文件中以保证数据完整性。可以看出来 AOF 写会额外消耗内存和磁盘 IO,这也是 Redis AOF 写的痛点,虽然之前也进行过多次改进但是资源消耗的本质问题一直没有解决。
->
-> 阿里云的 Redis 企业版在最初也遇到了这个问题,在内部经过多次迭代开发,实现了 Multi-part AOF 机制来解决,同时也贡献给了社区并随此次 7.0 发布。具体方法是采用 base(全量数据)+inc(增量数据)独立文件存储的方式,彻底解决内存和 IO 资源的浪费,同时也支持对历史 AOF 文件的保存管理,结合 AOF 文件中的时间信息还可以实现 PITR 按时间点恢复(阿里云企业版 Tair 已支持),这进一步增强了 Redis 的数据可靠性,满足用户数据回档等需求。
-
-**相关 issue**:[Redis AOF 重写描述不准确 #1439](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1439)。
-
-### AOF 校验机制了解吗?
-
-纯 AOF 模式下,Redis 不会对整个 AOF 文件使用校验和(如 CRC64),而是通过逐条解析文件中的命令来验证文件的有效性。如果解析过程中发现语法错误(如命令不完整、格式错误),Redis 会终止加载并报错,从而避免错误数据载入内存。
-
-在 **混合持久化模式**(Redis 4.0 引入)下,AOF 文件由两部分组成:
-
-- **RDB 快照部分**:文件以固定的 `REDIS` 字符开头,存储某一时刻的内存数据快照,并在快照数据末尾附带一个 CRC64 校验和(位于 RDB 数据块尾部、AOF 增量部分之前)。
-- **AOF 增量部分**:紧随 RDB 快照部分之后,记录 RDB 快照生成后的增量写命令。这部分增量命令以 Redis 协议格式逐条记录,无整体或全局校验和。
-
-RDB 文件结构的核心部分如下:
-
-| **字段** | **解释** |
-| ----------------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
-| `"REDIS"` | 固定以该字符串开始 |
-| `RDB_VERSION` | RDB 文件的版本号 |
-| `DB_NUM` | Redis 数据库编号,指明数据需要存放到哪个数据库 |
-| `KEY_VALUE_PAIRS` | Redis 中具体键值对的存储 |
-| `EOF` | RDB 文件结束标志 |
-| `CHECK_SUM` | 8 字节确保 RDB 完整性的校验和 |
-
-Redis 启动并加载 AOF 文件时,首先会校验文件开头 RDB 快照部分的数据完整性,即计算该部分数据的 CRC64 校验和,并与紧随 RDB 数据之后、AOF 增量部分之前存储的 CRC64 校验和值进行比较。如果 CRC64 校验和不匹配,Redis 将拒绝启动并报告错误。
-
-RDB 部分校验通过后,Redis 随后逐条解析 AOF 部分的增量命令。如果解析过程中出现错误(如不完整的命令或格式错误),Redis 会停止继续加载后续命令,并报告错误,但此时 Redis 已经成功加载了 RDB 快照部分的数据。
-
-## Redis 4.0 对于持久化机制做了什么优化?
-
-由于 RDB 和 AOF 各有优势,于是,Redis 4.0 开始支持 RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(默认关闭,可以通过配置项 `aof-use-rdb-preamble` 开启)。
-
-如果把混合持久化打开,AOF 重写的时候就直接把 RDB 的内容写到 AOF 文件开头。这样做的好处是可以结合 RDB 和 AOF 的优点, 快速加载同时避免丢失过多的数据。当然缺点也是有的, AOF 里面的 RDB 部分是压缩格式不再是 AOF 格式,可读性较差。
-
-官方文档地址:
-
-
-
-## 如何选择 RDB 和 AOF?
-
-关于 RDB 和 AOF 的优缺点,官网上面也给了比较详细的说明[Redis persistence](https://redis.io/docs/manual/persistence/),这里结合自己的理解简单总结一下。
-
-**RDB 比 AOF 优秀的地方**:
-
-- RDB 文件存储的内容是经过压缩的二进制数据, 保存着某个时间点的数据集,文件很小,适合做数据的备份,灾难恢复。AOF 文件存储的是每一次写命令,类似于 MySQL 的 binlog 日志,通常会比 RDB 文件大很多。当 AOF 变得太大时,Redis 能够在后台自动重写 AOF。新的 AOF 文件和原有的 AOF 文件所保存的数据库状态一样,但体积更小。不过, Redis 7.0 版本之前,如果在重写期间有写入命令,AOF 可能会使用大量内存,重写期间到达的所有写入命令都会写入磁盘两次。
-- 使用 RDB 文件恢复数据,直接解析还原数据即可,不需要一条一条地执行命令,速度非常快。而 AOF 则需要依次执行每个写命令,速度非常慢。也就是说,与 AOF 相比,恢复大数据集的时候,RDB 速度更快。
-
-**AOF 比 RDB 优秀的地方**:
-
-- RDB 的数据安全性不如 AOF,没有办法实时或者秒级持久化数据。生成 RDB 文件的过程是比较繁重的, 虽然 BGSAVE 子进程写入 RDB 文件的工作不会阻塞主线程,但会对机器的 CPU 资源和内存资源产生影响,严重的情况下甚至会直接把 Redis 服务干宕机。AOF 支持秒级数据丢失(取决 fsync 策略,如果是 everysec,最多丢失 1 秒的数据),仅仅是追加命令到 AOF 文件,操作轻量。
-- RDB 文件是以特定的二进制格式保存的,并且在 Redis 版本演进中有多个版本的 RDB,所以存在老版本的 Redis 服务不兼容新版本的 RDB 格式的问题。
-- AOF 以一种易于理解和解析的格式包含所有操作的日志。你可以轻松地导出 AOF 文件进行分析,你也可以直接操作 AOF 文件来解决一些问题。比如,如果执行`FLUSHALL`命令意外地刷新了所有内容后,只要 AOF 文件没有被重写,删除最新命令并重启即可恢复之前的状态。
-
-**综上**:
-
-- Redis 保存的数据丢失一些也没什么影响的话,可以选择使用 RDB。
-- 不建议单独使用 AOF,因为时不时地创建一个 RDB 快照可以进行数据库备份、更快的重启以及解决 AOF 引擎错误。
-- 如果保存的数据要求安全性比较高的话,建议同时开启 RDB 和 AOF 持久化或者开启 RDB 和 AOF 混合持久化。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- Redis persistence - Redis 官方文档:
-- The difference between AOF and RDB persistence:
-- Redis AOF 持久化详解 - 程序员历小冰:
-- Redis RDB 与 AOF 持久化 · Analyze:
-
-
+1. **Command Append (append)**: All write commands are appended to the AOF buffer.
+1. **File Write (write)**: The data in the AOF buffer is written to the AOF file. This step requires calling the `write` function (system call), and `write` returns directly after writing the data to the system kernel buffer (delayed write). Note!!! At this point, it has not been synchronized to disk.
+1. \*\*File Synchron
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
index 7102985b9a5..ead2803acfb 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-01.md
@@ -1,874 +1,57 @@
---
-title: Redis常见面试题总结(上)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Redis Interview Questions (Part 1)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: Redis基础,Redis常见数据结构,Redis线程模型,Redis内存管理,Redis事务,Redis性能优化
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 一篇文章总结Redis常见的知识点和面试题,涵盖Redis基础、Redis常见数据结构、Redis线程模型、Redis内存管理、Redis事务、Redis性能优化等内容。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Redis Basics, Common Redis Data Structures, Redis Thread Model, Redis Memory Management, Redis Transactions, Redis Performance Optimization
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: An article summarizing common knowledge points and interview questions about Redis, covering Redis basics, common data structures, thread model, memory management, transactions, performance optimization, and more.
---
-## Redis 基础
+## Redis Basics
-### 什么是 Redis?
+### What is Redis?
-[Redis](https://redis.io/) (**RE**mote **DI**ctionary **S**erver)是一个基于 C 语言开发的开源 NoSQL 数据库(BSD 许可)。与传统数据库不同的是,Redis 的数据是保存在内存中的(内存数据库,支持持久化),因此读写速度非常快,被广泛应用于分布式缓存方向。并且,Redis 存储的是 KV 键值对数据。
+[Redis](https://redis.io/) (**RE**mote **DI**ctionary **S**erver) is an open-source NoSQL database developed in C language (BSD license). Unlike traditional databases, Redis stores data in memory (in-memory database, supports persistence), which allows for very fast read and write speeds, making it widely used in distributed caching. Additionally, Redis stores data as key-value pairs (KV).
-为了满足不同的业务场景,Redis 内置了多种数据类型实现(比如 String、Hash、Sorted Set、Bitmap、HyperLogLog、GEO)。并且,Redis 还支持事务、持久化、Lua 脚本、发布订阅模型、多种开箱即用的集群方案(Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster)。
+To meet different business scenarios, Redis has built-in implementations of various data types (such as String, Hash, Sorted Set, Bitmap, HyperLogLog, GEO). Furthermore, Redis supports transactions, persistence, Lua scripting, a publish-subscribe model, and various out-of-the-box clustering solutions (Redis Sentinel, Redis Cluster).
-
+
-Redis 没有外部依赖,Linux 和 OS X 是 Redis 开发和测试最多的两个操作系统,官方推荐生产环境使用 Linux 部署 Redis。
+Redis has no external dependencies, and Linux and OS X are the two operating systems where Redis is developed and tested the most. The official recommendation is to deploy Redis in a production environment using Linux.
-个人学习的话,你可以自己本机安装 Redis 或者通过 Redis 官网提供的[在线 Redis 环境](https://try.redis.io/)(少部分命令无法使用)来实际体验 Redis。
+For personal learning, you can install Redis on your local machine or use the [online Redis environment](https://try.redis.io/) provided by the Redis official website (some commands may not be available) to experience Redis in practice.

-全世界有非常多的网站使用到了 Redis,[techstacks.io](https://techstacks.io/) 专门维护了一个[使用 Redis 的热门站点列表](https://techstacks.io/tech/redis),感兴趣的话可以看看。
+Many websites around the world use Redis, and [techstacks.io](https://techstacks.io/) maintains a [list of popular sites using Redis](https://techstacks.io/tech/redis). If you're interested, you can take a look.
-### Redis 为什么这么快?
+### Why is Redis so fast?
-Redis 内部做了非常多的性能优化,比较重要的有下面 4 点:
+Redis has implemented many performance optimizations internally, with the following four points being particularly important:
-1. **纯内存操作 (Memory-Based Storage)** :这是最主要的原因。Redis 数据读写操作都发生在内存中,访问速度是纳秒级别,而传统数据库频繁读写磁盘的速度是毫秒级别,两者相差数个数量级。
-2. **高效的 I/O 模型 (I/O Multiplexing & Single-Threaded Event Loop)** :Redis 使用单线程事件循环配合 I/O 多路复用技术,让单个线程可以同时处理多个网络连接上的 I/O 事件(如读写),避免了多线程模型中的上下文切换和锁竞争问题。虽然是单线程,但结合内存操作的高效性和 I/O 多路复用,使得 Redis 能轻松处理大量并发请求(Redis 线程模型会在后文中详细介绍到)。
-3. **优化的内部数据结构 (Optimized Data Structures)** :Redis 提供多种数据类型(如 String, List, Hash, Set, Sorted Set 等),其内部实现采用高度优化的编码方式(如 ziplist, quicklist, skiplist, hashtable 等)。Redis 会根据数据大小和类型动态选择最合适的内部编码,以在性能和空间效率之间取得最佳平衡。
-4. **简洁高效的通信协议 (Simple Protocol - RESP)** :Redis 使用的是自己设计的 RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) 协议。这个协议实现简单、解析性能好,并且是二进制安全的。客户端和服务端之间通信的序列化/反序列化开销很小,有助于提升整体的交互速度。
+1. **Memory-Based Storage**: This is the primary reason. Redis read and write operations occur in memory, with access speeds at the nanosecond level, while traditional databases frequently read and write to disk at the millisecond level, resulting in several orders of magnitude difference.
+1. **Efficient I/O Model (I/O Multiplexing & Single-Threaded Event Loop)**: Redis uses a single-threaded event loop combined with I/O multiplexing technology, allowing a single thread to handle multiple I/O events (such as read and write) on multiple network connections simultaneously, avoiding context switching and lock contention issues in multi-threaded models. Although it is single-threaded, the efficiency of memory operations and I/O multiplexing allows Redis to easily handle a large number of concurrent requests (the Redis thread model will be introduced in detail later).
+1. **Optimized Internal Data Structures**: Redis provides various data types (such as String, List, Hash, Set, Sorted Set, etc.), and its internal implementation uses highly optimized encoding methods (such as ziplist, quicklist, skiplist, hashtable, etc.). Redis dynamically selects the most suitable internal encoding based on data size and type to achieve the best balance between performance and space efficiency.
+1. **Simple and Efficient Communication Protocol (Simple Protocol - RESP)**: Redis uses its own designed RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) protocol. This protocol is simple to implement, has good parsing performance, and is binary safe. The serialization/deserialization overhead for communication between the client and server is minimal, which helps improve overall interaction speed.
-> 下面这张图片总结的挺不错的,分享一下,出自 [Why is Redis so fast?](https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1498703822528544770)。
+> The image below summarizes this well, shared from [Why is Redis so fast?](https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1498703822528544770).

-那既然都这么快了,为什么不直接用 Redis 当主数据库呢?主要是因为内存成本太高,并且 Redis 提供的数据持久化仍然有数据丢失的风险。
+Since Redis is so fast, why not use it as the primary database? The main reason is that memory costs are too high, and the data persistence provided by Redis still carries the risk of data loss.
-### 除了 Redis,你还知道其他分布式缓存方案吗?
+### Besides Redis, do you know other distributed caching solutions?
-如果面试中被问到这个问题的话,面试官主要想看看:
+If asked this question in an interview, the interviewer mainly wants to see:
-1. 你在选择 Redis 作为分布式缓存方案时,是否是经过严谨的调研和思考,还是只是因为 Redis 是当前的“热门”技术。
-2. 你在分布式缓存方向的技术广度。
+1. Whether your choice of Redis as a distributed caching solution was based on rigorous research and thought, or just because Redis is currently a "hot" technology.
+1. Your breadth of knowledge in distributed caching technologies.
-如果你了解其他方案,并且能解释为什么最终选择了 Redis(更进一步!),这会对你面试表现加分不少!
-
-下面简单聊聊常见的分布式缓存技术选型。
-
-分布式缓存的话,比较老牌同时也是使用的比较多的还是 **Memcached** 和 **Redis**。不过,现在基本没有看过还有项目使用 **Memcached** 来做缓存,都是直接用 **Redis**。
-
-Memcached 是分布式缓存最开始兴起的那会,比较常用的。后来,随着 Redis 的发展,大家慢慢都转而使用更加强大的 Redis 了。
-
-有一些大厂也开源了类似于 Redis 的分布式高性能 KV 存储数据库,例如,腾讯开源的 [**Tendis**](https://github.com/Tencent/Tendis)。Tendis 基于知名开源项目 [RocksDB](https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb) 作为存储引擎 ,100% 兼容 Redis 协议和 Redis4.0 所有数据模型。关于 Redis 和 Tendis 的对比,腾讯官方曾经发过一篇文章:[Redis vs Tendis:冷热混合存储版架构揭秘](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/MeYkfOIdnU6LYlsGb24KjQ),可以简单参考一下。
-
-不过,从 Tendis 这个项目的 Github 提交记录可以看出,Tendis 开源版几乎已经没有被维护更新了,加上其关注度并不高,使用的公司也比较少。因此,不建议你使用 Tendis 来实现分布式缓存。
-
-目前,比较业界认可的 Redis 替代品还是下面这两个开源分布式缓存(都是通过碰瓷 Redis 火的):
-
-- [Dragonfly](https://github.com/dragonflydb/dragonfly):一种针对现代应用程序负荷需求而构建的内存数据库,完全兼容 Redis 和 Memcached 的 API,迁移时无需修改任何代码,号称全世界最快的内存数据库。
-- [KeyDB](https://github.com/Snapchat/KeyDB):Redis 的一个高性能分支,专注于多线程、内存效率和高吞吐量。
-
-不过,个人还是建议分布式缓存首选 Redis,毕竟经过了这么多年的考验,生态非常优秀,资料也很全面!
-
-PS:篇幅问题,我这并没有对上面提到的分布式缓存选型做详细介绍和对比,感兴趣的话,可以自行研究一下。
-
-### 说一下 Redis 和 Memcached 的区别和共同点
-
-现在公司一般都是用 Redis 来实现缓存,而且 Redis 自身也越来越强大了!不过,了解 Redis 和 Memcached 的区别和共同点,有助于我们在做相应的技术选型的时候,能够做到有理有据!
-
-**共同点**:
-
-1. 都是基于内存的数据库,一般都用来当做缓存使用。
-2. 都有过期策略。
-3. 两者的性能都非常高。
-
-**区别**:
-
-1. **数据类型**:Redis 支持更丰富的数据类型(支持更复杂的应用场景)。Redis 不仅仅支持简单的 k/v 类型的数据,同时还提供 list、set、zset、hash 等数据结构的存储;而 Memcached 只支持最简单的 k/v 数据类型。
-2. **数据持久化**:Redis 支持数据的持久化,可以将内存中的数据保持在磁盘中,重启的时候可以再次加载进行使用;而 Memcached 把数据全部存在内存之中。也就是说,Redis 有灾难恢复机制,而 Memcached 没有。
-3. **集群模式支持**:Memcached 没有原生的集群模式,需要依靠客户端来实现往集群中分片写入数据;而 Redis 自 3.0 版本起是原生支持集群模式的。
-4. **线程模型**:Memcached 是多线程、非阻塞 IO 复用的网络模型;而 Redis 使用单线程的多路 IO 复用模型(Redis 6.0 针对网络数据的读写引入了多线程)。
-5. **特性支持**:Redis 支持发布订阅模型、Lua 脚本、事务等功能,而 Memcached 不支持。并且,Redis 支持更多的编程语言。
-6. **过期数据删除**:Memcached 过期数据的删除策略只用了惰性删除,而 Redis 同时使用了惰性删除与定期删除。
-
-相信看了上面的对比之后,我们已经没有什么理由可以选择使用 Memcached 来作为自己项目的分布式缓存了。
-
-### 为什么要用 Redis?
-
-**1、访问速度更快**
-
-传统数据库数据保存在磁盘,而 Redis 基于内存,内存的访问速度比磁盘快很多。引入 Redis 之后,我们可以把一些高频访问的数据放到 Redis 中,这样下次就可以直接从内存中读取,速度可以提升几十倍甚至上百倍。
-
-**2、高并发**
-
-一般像 MySQL 这类的数据库的 QPS 大概都在 4k 左右(4 核 8g),但是使用 Redis 缓存之后很容易达到 5w+,甚至能达到 10w+(就单机 Redis 的情况,Redis 集群的话会更高)。
-
-> QPS(Query Per Second):服务器每秒可以执行的查询次数;
-
-由此可见,直接操作缓存能够承受的数据库请求数量是远远大于直接访问数据库的,所以我们可以考虑把数据库中的部分数据转移到缓存中去,这样用户的一部分请求会直接到缓存这里而不用经过数据库。进而,我们也就提高了系统整体的并发。
-
-**3、功能全面**
-
-Redis 除了可以用作缓存之外,还可以用于分布式锁、限流、消息队列、延时队列等场景,功能强大!
-
-### 为什么用 Redis 而不用本地缓存呢?
-
-| 特性 | 本地缓存 | Redis |
-| ------------ | ------------------------------------ | -------------------------------- |
-| 数据一致性 | 多服务器部署时存在数据不一致问题 | 数据一致 |
-| 内存限制 | 受限于单台服务器内存 | 独立部署,内存空间更大 |
-| 数据丢失风险 | 服务器宕机数据丢失 | 可持久化,数据不易丢失 |
-| 管理维护 | 分散,管理不便 | 集中管理,提供丰富的管理工具 |
-| 功能丰富性 | 功能有限,通常只提供简单的键值对存储 | 功能丰富,支持多种数据结构和功能 |
-
-### 常见的缓存读写策略有哪些?
-
-关于常见的缓存读写策略的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[3 种常用的缓存读写策略详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/3-commonly-used-cache-read-and-write-strategies.html)。
-
-### 什么是 Redis Module?有什么用?
-
-Redis 从 4.0 版本开始,支持通过 Module 来扩展其功能以满足特殊的需求。这些 Module 以动态链接库(so 文件)的形式被加载到 Redis 中,这是一种非常灵活的动态扩展功能的实现方式,值得借鉴学习!
-
-我们每个人都可以基于 Redis 去定制化开发自己的 Module,比如实现搜索引擎功能、自定义分布式锁和分布式限流。
-
-目前,被 Redis 官方推荐的 Module 有:
-
-- [RediSearch](https://github.com/RediSearch/RediSearch):用于实现搜索引擎的模块。
-- [RedisJSON](https://github.com/RedisJSON/RedisJSON):用于处理 JSON 数据的模块。
-- [RedisGraph](https://github.com/RedisGraph/RedisGraph):用于实现图形数据库的模块。
-- [RedisTimeSeries](https://github.com/RedisTimeSeries/RedisTimeSeries):用于处理时间序列数据的模块。
-- [RedisBloom](https://github.com/RedisBloom/RedisBloom):用于实现布隆过滤器的模块。
-- [RedisAI](https://github.com/RedisAI/RedisAI):用于执行深度学习/机器学习模型并管理其数据的模块。
-- [RedisCell](https://github.com/brandur/redis-cell):用于实现分布式限流的模块。
-- ……
-
-关于 Redis 模块的详细介绍,可以查看官方文档:。
-
-## Redis 应用
-
-### Redis 除了做缓存,还能做什么?
-
-- **分布式锁**:通过 Redis 来做分布式锁是一种比较常见的方式。通常情况下,我们都是基于 Redisson 来实现分布式锁。关于 Redis 实现分布式锁的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock.html)。
-- **限流**:一般是通过 Redis + Lua 脚本的方式来实现限流。如果不想自己写 Lua 脚本的话,也可以直接利用 Redisson 中的 `RRateLimiter` 来实现分布式限流,其底层实现就是基于 Lua 代码+令牌桶算法。
-- **消息队列**:Redis 自带的 List 数据结构可以作为一个简单的队列使用。Redis 5.0 中增加的 Stream 类型的数据结构更加适合用来做消息队列。它比较类似于 Kafka,有主题和消费组的概念,支持消息持久化以及 ACK 机制。
-- **延时队列**:Redisson 内置了延时队列(基于 Sorted Set 实现的)。
-- **分布式 Session**:利用 String 或者 Hash 数据类型保存 Session 数据,所有的服务器都可以访问。
-- **复杂业务场景**:通过 Redis 以及 Redis 扩展(比如 Redisson)提供的数据结构,我们可以很方便地完成很多复杂的业务场景,比如通过 Bitmap 统计活跃用户、通过 Sorted Set 维护排行榜、通过 HyperLogLog 统计网站 UV 和 PV。
-- ……
-
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现分布式锁?
-
-关于 Redis 实现分布式锁的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.html)。
-
-### Redis 可以做消息队列么?
-
-> 实际项目中使用 Redis 来做消息队列的非常少,毕竟有更成熟的消息队列中间件可以用。
-
-先说结论:**可以是可以,但不建议使用 Redis 来做消息队列。和专业的消息队列相比,还是有很多欠缺的地方。**
-
-**Redis 2.0 之前,如果想要使用 Redis 来做消息队列的话,只能通过 List 来实现。**
-
-通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP` 即可实现简易版消息队列:
-
-```bash
-# 生产者生产消息
-> RPUSH myList msg1 msg2
-(integer) 2
-> RPUSH myList msg3
-(integer) 3
-# 消费者消费消息
-> LPOP myList
-"msg1"
-```
-
-不过,通过 `RPUSH/LPOP` 或者 `LPUSH/RPOP` 这样的方式存在性能问题,我们需要不断轮询去调用 `RPOP` 或 `LPOP` 来消费消息。当 List 为空时,大部分的轮询的请求都是无效请求,这种方式大量浪费了系统资源。
-
-因此,Redis 还提供了 `BLPOP`、`BRPOP` 这种阻塞式读取的命令(带 B-Blocking 的都是阻塞式),并且还支持一个超时参数。如果 List 为空,Redis 服务端不会立刻返回结果,它会等待 List 中有新数据后再返回或者是等待最多一个超时时间后返回空。如果将超时时间设置为 0 时,即可无限等待,直到弹出消息
-
-```bash
-# 超时时间为 10s
-# 如果有数据立刻返回,否则最多等待10秒
-> BRPOP myList 10
-null
-```
-
-**List 实现消息队列功能太简单,像消息确认机制等功能还需要我们自己实现,最要命的是没有广播机制,消息也只能被消费一次。**
-
-**Redis 2.0 引入了发布订阅 (pub/sub) 功能,解决了 List 实现消息队列没有广播机制的问题。**
-
-
-
-pub/sub 中引入了一个概念叫 **channel(频道)**,发布订阅机制的实现就是基于这个 channel 来做的。
-
-pub/sub 涉及发布者(Publisher)和订阅者(Subscriber,也叫消费者)两个角色:
-
-- 发布者通过 `PUBLISH` 投递消息给指定 channel。
-- 订阅者通过`SUBSCRIBE`订阅它关心的 channel。并且,订阅者可以订阅一个或者多个 channel。
-
-我们这里启动 3 个 Redis 客户端来简单演示一下:
-
-
-
-pub/sub 既能单播又能广播,还支持 channel 的简单正则匹配。不过,消息丢失(客户端断开连接或者 Redis 宕机都会导致消息丢失)、消息堆积(发布者发布消息的时候不会管消费者的具体消费能力如何)等问题依然没有一个比较好的解决办法。
-
-为此,Redis 5.0 新增加的一个数据结构 `Stream` 来做消息队列。`Stream` 支持:
-
-- 发布 / 订阅模式;
-- 按照消费者组进行消费(借鉴了 Kafka 消费者组的概念);
-- 消息持久化( RDB 和 AOF);
-- ACK 机制(通过确认机制来告知已经成功处理了消息);
-- 阻塞式获取消息。
-
-`Stream` 的结构如下:
-
-
-
-这是一个有序的消息链表,每个消息都有一个唯一的 ID 和对应的内容。ID 是一个时间戳和序列号的组合,用来保证消息的唯一性和递增性。内容是一个或多个键值对(类似 Hash 基本数据类型),用来存储消息的数据。
-
-这里再对图中涉及到的一些概念,进行简单解释:
-
-- `Consumer Group`:消费者组用于组织和管理多个消费者。消费者组本身不处理消息,而是再将消息分发给消费者,由消费者进行真正的消费。
-- `last_delivered_id`:标识消费者组当前消费位置的游标,消费者组中任意一个消费者读取了消息都会使 last_delivered_id 往前移动。
-- `pending_ids`:记录已经被客户端消费但没有 ack 的消息的 ID。
-
-下面是`Stream` 用作消息队列时常用的命令:
-
-- `XADD`:向流中添加新的消息。
-- `XREAD`:从流中读取消息。
-- `XREADGROUP`:从消费组中读取消息。
-- `XRANGE`:根据消息 ID 范围读取流中的消息。
-- `XREVRANGE`:与 `XRANGE` 类似,但以相反顺序返回结果。
-- `XDEL`:从流中删除消息。
-- `XTRIM`:修剪流的长度,可以指定修建策略(`MAXLEN`/`MINID`)。
-- `XLEN`:获取流的长度。
-- `XGROUP CREATE`:创建消费者组。
-- `XGROUP DESTROY`:删除消费者组。
-- `XGROUP DELCONSUMER`:从消费者组中删除一个消费者。
-- `XGROUP SETID`:为消费者组设置新的最后递送消息 ID。
-- `XACK`:确认消费组中的消息已被处理。
-- `XPENDING`:查询消费组中挂起(未确认)的消息。
-- `XCLAIM`:将挂起的消息从一个消费者转移到另一个消费者。
-- `XINFO`:获取流(`XINFO STREAM`)、消费组(`XINFO GROUPS`)或消费者(`XINFO CONSUMERS`)的详细信息。
-
-`Stream` 使用起来相对要麻烦一些,这里就不演示了。
-
-总的来说,`Stream` 已经可以满足一个消息队列的基本要求了。不过,`Stream` 在实际使用中依然会有一些小问题不太好解决,比如在 Redis 发生故障恢复后不能保证消息至少被消费一次。
-
-综上,和专业的消息队列相比,使用 Redis 来实现消息队列还是有很多欠缺的地方,比如消息丢失和堆积问题不好解决。因此,我们通常建议不要使用 Redis 来做消息队列,你完全可以选择市面上比较成熟的一些消息队列,比如 RocketMQ、Kafka。不过,如果你就是想要用 Redis 来做消息队列的话,那我建议你优先考虑 `Stream`,这是目前相对最优的 Redis 消息队列实现。
-
-相关阅读:[Redis 消息队列发展历程 - 阿里开发者 - 2022](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gCUT5TcCQRAxYkTJfTRjJw)。
-
-### Redis 可以做搜索引擎么?
-
-Redis 是可以实现全文搜索引擎功能的,需要借助 **RediSearch**,这是一个基于 Redis 的搜索引擎模块。
-
-RediSearch 支持中文分词、聚合统计、停用词、同义词、拼写检查、标签查询、向量相似度查询、多关键词搜索、分页搜索等功能,算是一个功能比较完善的全文搜索引擎了。
-
-相比较于 Elasticsearch 来说,RediSearch 主要在下面两点上表现更优异一些:
-
-1. 性能更优秀:依赖 Redis 自身的高性能,基于内存操作(Elasticsearch 基于磁盘)。
-2. 较低内存占用实现快速索引:RediSearch 内部使用压缩的倒排索引,所以可以用较低的内存占用来实现索引的快速构建。
-
-对于小型项目的简单搜索场景来说,使用 RediSearch 来作为搜索引擎还是没有问题的(搭配 RedisJSON 使用)。
-
-对于比较复杂或者数据规模较大的搜索场景,还是不太建议使用 RediSearch 来作为搜索引擎,主要是因为下面这些限制和问题:
-
-1. 数据量限制:Elasticsearch 可以支持 PB 级别的数据量,可以轻松扩展到多个节点,利用分片机制提高可用性和性能。RedisSearch 是基于 Redis 实现的,其能存储的数据量受限于 Redis 的内存容量,不太适合存储大规模的数据(内存昂贵,扩展能力较差)。
-2. 分布式能力较差:Elasticsearch 是为分布式环境设计的,可以轻松扩展到多个节点。虽然 RedisSearch 支持分布式部署,但在实际应用中可能会面临一些挑战,如数据分片、节点间通信、数据一致性等问题。
-3. 聚合功能较弱:Elasticsearch 提供了丰富的聚合功能,而 RediSearch 的聚合功能相对较弱,只支持简单的聚合操作。
-4. 生态较差:Elasticsearch 可以轻松和常见的一些系统/软件集成比如 Hadoop、Spark、Kibana,而 RedisSearch 则不具备该优势。
-
-Elasticsearch 适用于全文搜索、复杂查询、实时数据分析和聚合的场景,而 RediSearch 适用于快速数据存储、缓存和简单查询的场景。
-
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现延时任务?
-
-> 类似的问题:
->
-> - 订单在 10 分钟后未支付就失效,如何用 Redis 实现?
-> - 红包 24 小时未被查收自动退还,如何用 Redis 实现?
-
-基于 Redis 实现延时任务的功能无非就下面两种方案:
-
-1. Redis 过期事件监听。
-2. Redisson 内置的延时队列。
-
-Redis 过期事件监听存在时效性较差、丢消息、多服务实例下消息重复消费等问题,不被推荐使用。
-
-Redisson 内置的延时队列具备下面这些优势:
-
-1. **减少了丢消息的可能**:DelayedQueue 中的消息会被持久化,即使 Redis 宕机了,根据持久化机制,也只可能丢失一点消息,影响不大。当然了,你也可以使用扫描数据库的方法作为补偿机制。
-2. **消息不存在重复消费问题**:每个客户端都是从同一个目标队列中获取任务的,不存在重复消费的问题。
-
-关于 Redis 实现延时任务的详细介绍,可以看我写的这篇文章:[如何基于 Redis 实现延时任务?](./redis-delayed-task.md)。
-
-## Redis 数据类型
-
-关于 Redis 5 种基础数据类型和 3 种特殊数据类型的详细介绍请看下面这两篇文章以及 [Redis 官方文档](https://redis.io/docs/data-types/):
-
-- [Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.html)
-- [Redis 3 种特殊数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-02.html)
-
-### Redis 常用的数据类型有哪些?
-
-Redis 中比较常见的数据类型有下面这些:
-
-- **5 种基础数据类型**:String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)。
-- **3 种特殊数据类型**:HyperLogLog(基数统计)、Bitmap (位图)、Geospatial (地理位置)。
-
-除了上面提到的之外,还有一些其他的比如 [Bloom filter(布隆过滤器)](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/bloom-filter.html)、Bitfield(位域)。
-
-### String 的应用场景有哪些?
-
-String 是 Redis 中最简单同时也是最常用的一个数据类型。它是一种二进制安全的数据类型,可以用来存储任何类型的数据比如字符串、整数、浮点数、图片(图片的 base64 编码或者解码或者图片的路径)、序列化后的对象。
-
-String 的常见应用场景如下:
-
-- 常规数据(比如 Session、Token、序列化后的对象、图片的路径)的缓存;
-- 计数比如用户单位时间的请求数(简单限流可以用到)、页面单位时间的访问数;
-- 分布式锁(利用 `SETNX key value` 命令可以实现一个最简易的分布式锁);
-- ……
-
-关于 String 的详细介绍请看这篇文章:[Redis 5 种基本数据类型详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-data-structures-01.html)。
-
-### String 还是 Hash 存储对象数据更好呢?
-
-简单对比一下二者:
-
-- **对象存储方式**:String 存储的是序列化后的对象数据,存放的是整个对象,操作简单直接。Hash 是对对象的每个字段单独存储,可以获取部分字段的信息,也可以修改或者添加部分字段,节省网络流量。如果对象中某些字段需要经常变动或者经常需要单独查询对象中的个别字段信息,Hash 就非常适合。
-- **内存消耗**:Hash 通常比 String 更节省内存,特别是在字段较多且字段长度较短时。Redis 对小型 Hash 进行优化(如使用 ziplist 存储),进一步降低内存占用。
-- **复杂对象存储**:String 在处理多层嵌套或复杂结构的对象时更方便,因为无需处理每个字段的独立存储和操作。
-- **性能**:String 的操作通常具有 O(1) 的时间复杂度,因为它存储的是整个对象,操作简单直接,整体读写的性能较好。Hash 由于需要处理多个字段的增删改查操作,在字段较多且经常变动的情况下,可能会带来额外的性能开销。
-
-总结:
-
-- 在绝大多数情况下,**String** 更适合存储对象数据,尤其是当对象结构简单且整体读写是主要操作时。
-- 如果你需要频繁操作对象的部分字段或节省内存,**Hash** 可能是更好的选择。
-
-### String 的底层实现是什么?
-
-Redis 是基于 C 语言编写的,但 Redis 的 String 类型的底层实现并不是 C 语言中的字符串(即以空字符 `\0` 结尾的字符数组),而是自己编写了 [SDS](https://github.com/antirez/sds)(Simple Dynamic String,简单动态字符串)来作为底层实现。
-
-SDS 最早是 Redis 作者为日常 C 语言开发而设计的 C 字符串,后来被应用到了 Redis 上,并经过了大量的修改完善以适合高性能操作。
-
-Redis7.0 的 SDS 的部分源码如下():
-
-```c
-/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
- * However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
- uint8_t len; /* used */
- uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
- uint16_t len; /* used */
- uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
- uint32_t len; /* used */
- uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
- uint64_t len; /* used */
- uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
- unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
- char buf[];
-};
-```
-
-通过源码可以看出,SDS 共有五种实现方式:SDS_TYPE_5(并未用到)、SDS_TYPE_8、SDS_TYPE_16、SDS_TYPE_32、SDS_TYPE_64,其中只有后四种实际用到。Redis 会根据初始化的长度决定使用哪种类型,从而减少内存的使用。
-
-| 类型 | 字节 | 位 |
-| -------- | ---- | --- |
-| sdshdr5 | < 1 | <8 |
-| sdshdr8 | 1 | 8 |
-| sdshdr16 | 2 | 16 |
-| sdshdr32 | 4 | 32 |
-| sdshdr64 | 8 | 64 |
-
-对于后四种实现都包含了下面这 4 个属性:
-
-- `len`:字符串的长度也就是已经使用的字节数。
-- `alloc`:总共可用的字符空间大小,alloc-len 就是 SDS 剩余的空间大小。
-- `buf[]`:实际存储字符串的数组。
-- `flags`:低三位保存类型标志。
-
-SDS 相比于 C 语言中的字符串有如下提升:
-
-1. **可以避免缓冲区溢出**:C 语言中的字符串被修改(比如拼接)时,一旦没有分配足够长度的内存空间,就会造成缓冲区溢出。SDS 被修改时,会先根据 len 属性检查空间大小是否满足要求,如果不满足,则先扩展至所需大小再进行修改操作。
-2. **获取字符串长度的复杂度较低**:C 语言中的字符串的长度通常是经过遍历计数来实现的,时间复杂度为 O(n)。SDS 的长度获取直接读取 len 属性即可,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
-3. **减少内存分配次数**:为了避免修改(增加/减少)字符串时,每次都需要重新分配内存(C 语言的字符串是这样的),SDS 实现了空间预分配和惰性空间释放两种优化策略。当 SDS 需要增加字符串时,Redis 会为 SDS 分配好内存,并且根据特定的算法分配多余的内存,这样可以减少连续执行字符串增长操作所需的内存重分配次数。当 SDS 需要减少字符串时,这部分内存不会立即被回收,会被记录下来,等待后续使用(支持手动释放,有对应的 API)。
-4. **二进制安全**:C 语言中的字符串以空字符 `\0` 作为字符串结束的标识,这存在一些问题,像一些二进制文件(比如图片、视频、音频)就可能包括空字符,C 字符串无法正确保存。SDS 使用 len 属性判断字符串是否结束,不存在这个问题。
-
-🤐 多提一嘴,很多文章里 SDS 的定义是下面这样的:
-
-```c
-struct sdshdr {
- unsigned int len;
- unsigned int free;
- char buf[];
-};
-```
-
-这个也没错,Redis 3.2 之前就是这样定义的。后来,由于这种方式的定义存在问题,`len` 和 `free` 的定义用了 4 个字节,造成了浪费。Redis 3.2 之后,Redis 改进了 SDS 的定义,将其划分为了现在的 5 种类型。
-
-### 购物车信息用 String 还是 Hash 存储更好呢?
-
-由于购物车中的商品频繁修改和变动,购物车信息建议使用 Hash 存储:
-
-- 用户 id 为 key
-- 商品 id 为 field,商品数量为 value
-
-
-
-那用户购物车信息的维护具体应该怎么操作呢?
-
-- 用户添加商品就是往 Hash 里面增加新的 field 与 value;
-- 查询购物车信息就是遍历对应的 Hash;
-- 更改商品数量直接修改对应的 value 值(直接 set 或者做运算皆可);
-- 删除商品就是删除 Hash 中对应的 field;
-- 清空购物车直接删除对应的 key 即可。
-
-这里只是以业务比较简单的购物车场景举例,实际电商场景下,field 只保存一个商品 id 是没办法满足需求的。
-
-### 使用 Redis 实现一个排行榜怎么做?
-
-Redis 中有一个叫做 `Sorted Set`(有序集合)的数据类型经常被用在各种排行榜的场景,比如直播间送礼物的排行榜、朋友圈的微信步数排行榜、王者荣耀中的段位排行榜、话题热度排行榜等等。
-
-相关的一些 Redis 命令:`ZRANGE`(从小到大排序)、`ZREVRANGE`(从大到小排序)、`ZREVRANK`(指定元素排名)。
-
-
-
-[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 的「技术面试题篇」就有一篇文章详细介绍如何使用 Sorted Set 来设计制作一个排行榜,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
-
-
-
-### Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+ 树?
-
-这道面试题很多大厂比较喜欢问,难度还是有点大的。
-
-- 平衡树 vs 跳表:平衡树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)**。对于范围查询来说,平衡树也可以通过中序遍历的方式达到和跳表一样的效果。但是它的每一次插入或者删除操作都需要保证整颗树左右节点的绝对平衡,只要不平衡就要通过旋转操作来保持平衡,这个过程是比较耗时的。跳表诞生的初衷就是为了克服平衡树的一些缺点。跳表使用概率平衡而不是严格强制的平衡,因此,跳表中的插入和删除算法比平衡树的等效算法简单得多,速度也快得多。
-- 红黑树 vs 跳表:相比较于红黑树来说,跳表的实现也更简单一些,不需要通过旋转和染色(红黑变换)来保证黑平衡。并且,按照区间来查找数据这个操作,红黑树的效率没有跳表高。
-- B+ 树 vs 跳表:B+ 树更适合作为数据库和文件系统中常用的索引结构之一,它的核心思想是通过可能少的 IO 定位到尽可能多的索引来获得查询数据。对于 Redis 这种内存数据库来说,它对这些并不感冒,因为 Redis 作为内存数据库它不可能存储大量的数据,所以对于索引不需要通过 B+ 树这种方式进行维护,只需按照概率进行随机维护即可,节约内存。而且使用跳表实现 zset 时相较前者来说更简单一些,在进行插入时只需通过索引将数据插入到链表中合适的位置再随机维护一定高度的索引即可,也不需要像 B+ 树那样插入时发现失衡时还需要对节点分裂与合并。
-
-另外,我还单独写了一篇文章从有序集合的基本使用到跳表的源码分析和实现,让你会对 Redis 的有序集合底层实现的跳表有着更深刻的理解和掌握:[Redis 为什么用跳表实现有序集合](./redis-skiplist.md)。
-
-### Set 的应用场景是什么?
-
-Redis 中 `Set` 是一种无序集合,集合中的元素没有先后顺序但都唯一,有点类似于 Java 中的 `HashSet` 。
-
-`Set` 的常见应用场景如下:
-
-- 存放的数据不能重复的场景:网站 UV 统计(数据量巨大的场景还是 `HyperLogLog` 更适合一些)、文章点赞、动态点赞等等。
-- 需要获取多个数据源交集、并集和差集的场景:共同好友(交集)、共同粉丝(交集)、共同关注(交集)、好友推荐(差集)、音乐推荐(差集)、订阅号推荐(差集+交集)等等。
-- 需要随机获取数据源中的元素的场景:抽奖系统、随机点名等等。
-
-### 使用 Set 实现抽奖系统怎么做?
-
-如果想要使用 `Set` 实现一个简单的抽奖系统的话,直接使用下面这几个命令就可以了:
-
-- `SADD key member1 member2 ...`:向指定集合添加一个或多个元素。
-- `SPOP key count`:随机移除并获取指定集合中一个或多个元素,适合不允许重复中奖的场景。
-- `SRANDMEMBER key count`:随机获取指定集合中指定数量的元素,适合允许重复中奖的场景。
-
-### 使用 Bitmap 统计活跃用户怎么做?
-
-Bitmap 存储的是连续的二进制数字(0 和 1),通过 Bitmap,只需要一个 bit 位来表示某个元素对应的值或者状态,key 就是对应元素本身。我们知道 8 个 bit 可以组成一个 byte,所以 Bitmap 本身会极大的节省储存空间。
-
-你可以将 Bitmap 看作是一个存储二进制数字(0 和 1)的数组,数组中每个元素的下标叫做 offset(偏移量)。
-
-
-
-如果想要使用 Bitmap 统计活跃用户的话,可以使用日期(精确到天)作为 key,然后用户 ID 为 offset,如果当日活跃过就设置为 1。
-
-初始化数据:
-
-```bash
-> SETBIT 20210308 1 1
-(integer) 0
-> SETBIT 20210308 2 1
-(integer) 0
-> SETBIT 20210309 1 1
-(integer) 0
-```
-
-统计 20210308~20210309 总活跃用户数:
-
-```bash
-> BITOP and desk1 20210308 20210309
-(integer) 1
-> BITCOUNT desk1
-(integer) 1
-```
-
-统计 20210308~20210309 在线活跃用户数:
-
-```bash
-> BITOP or desk2 20210308 20210309
-(integer) 1
-> BITCOUNT desk2
-(integer) 2
-```
-
-### 使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV 怎么做?
-
-使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV 主要需要用到下面这两个命令:
-
-- `PFADD key element1 element2 ...`:添加一个或多个元素到 HyperLogLog 中。
-- `PFCOUNT key1 key2`:获取一个或者多个 HyperLogLog 的唯一计数。
-
-1、将访问指定页面的每个用户 ID 添加到 `HyperLogLog` 中。
-
-```bash
-PFADD PAGE_1:UV USER1 USER2 ...... USERn
-```
-
-2、统计指定页面的 UV。
-
-```bash
-PFCOUNT PAGE_1:UV
-```
-
-## Redis 持久化机制(重要)
-
-Redis 持久化机制(RDB 持久化、AOF 持久化、RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化)相关的问题比较多,也比较重要,于是我单独抽了一篇文章来总结 Redis 持久化机制相关的知识点和问题:[Redis 持久化机制详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-persistence.html)。
-
-## Redis 线程模型(重要)
-
-对于读写命令来说,Redis 一直是单线程模型。不过,在 Redis 4.0 版本之后引入了多线程来执行一些大键值对的异步删除操作,Redis 6.0 版本之后引入了多线程来处理网络请求(提高网络 IO 读写性能)。
-
-### Redis 单线程模型了解吗?
-
-**Redis 基于 Reactor 模式设计开发了一套高效的事件处理模型**(Netty 的线程模型也基于 Reactor 模式,Reactor 模式不愧是高性能 IO 的基石),这套事件处理模型对应的是 Redis 中的文件事件处理器(file event handler)。由于文件事件处理器(file event handler)是单线程方式运行的,所以我们一般都说 Redis 是单线程模型。
-
-《Redis 设计与实现》有一段话是这样介绍文件事件处理器的,我觉得写得挺不错。
-
-> Redis 基于 Reactor 模式开发了自己的网络事件处理器:这个处理器被称为文件事件处理器(file event handler)。
->
-> - 文件事件处理器使用 I/O 多路复用(multiplexing)程序来同时监听多个套接字,并根据套接字目前执行的任务来为套接字关联不同的事件处理器。
-> - 当被监听的套接字准备好执行连接应答(accept)、读取(read)、写入(write)、关 闭(close)等操作时,与操作相对应的文件事件就会产生,这时文件事件处理器就会调用套接字之前关联好的事件处理器来处理这些事件。
->
-> **虽然文件事件处理器以单线程方式运行,但通过使用 I/O 多路复用程序来监听多个套接字**,文件事件处理器既实现了高性能的网络通信模型,又可以很好地与 Redis 服务器中其他同样以单线程方式运行的模块进行对接,这保持了 Redis 内部单线程设计的简单性。
-
-**既然是单线程,那怎么监听大量的客户端连接呢?**
-
-Redis 通过 **IO 多路复用程序** 来监听来自客户端的大量连接(或者说是监听多个 socket),它会将感兴趣的事件及类型(读、写)注册到内核中并监听每个事件是否发生。
-
-这样的好处非常明显:**I/O 多路复用技术的使用让 Redis 不需要额外创建多余的线程来监听客户端的大量连接,降低了资源的消耗**(和 NIO 中的 `Selector` 组件很像)。
-
-文件事件处理器(file event handler)主要是包含 4 个部分:
-
-- 多个 socket(客户端连接)
-- IO 多路复用程序(支持多个客户端连接的关键)
-- 文件事件分派器(将 socket 关联到相应的事件处理器)
-- 事件处理器(连接应答处理器、命令请求处理器、命令回复处理器)
-
-
-
-相关阅读:[Redis 事件机制详解](http://remcarpediem.net/article/1aa2da89/)。
-
-### Redis6.0 之前为什么不使用多线程?
-
-虽然说 Redis 是单线程模型,但实际上,**Redis 在 4.0 之后的版本中就已经加入了对多线程的支持。**
-
-不过,Redis 4.0 增加的多线程主要是针对一些大键值对的删除操作的命令,使用这些命令就会使用主线程之外的其他线程来“异步处理”,从而减少对主线程的影响。
-
-为此,Redis 4.0 之后新增了几个异步命令:
-
-- `UNLINK`:可以看作是 `DEL` 命令的异步版本。
-- `FLUSHALL ASYNC`:用于清空所有数据库的所有键,不限于当前 `SELECT` 的数据库。
-- `FLUSHDB ASYNC`:用于清空当前 `SELECT` 数据库中的所有键。
-
-
-
-总的来说,直到 Redis 6.0 之前,Redis 的主要操作仍然是单线程处理的。
-
-**那 Redis6.0 之前为什么不使用多线程?** 我觉得主要原因有 3 点:
-
-- 单线程编程容易并且更容易维护;
-- Redis 的性能瓶颈不在 CPU,主要在内存和网络;
-- 多线程就会存在死锁、线程上下文切换等问题,甚至会影响性能。
-
-相关阅读:[为什么 Redis 选择单线程模型?](https://draveness.me/whys-the-design-redis-single-thread/)。
-
-### Redis6.0 之后为何引入了多线程?
-
-**Redis6.0 引入多线程主要是为了提高网络 IO 读写性能**,因为这个算是 Redis 中的一个性能瓶颈(Redis 的瓶颈主要受限于内存和网络)。
-
-虽然,Redis6.0 引入了多线程,但是 Redis 的多线程只是在网络数据的读写这类耗时操作上使用了,执行命令仍然是单线程顺序执行。因此,你也不需要担心线程安全问题。
-
-Redis6.0 的多线程默认是禁用的,只使用主线程。如需开启需要设置 IO 线程数 > 1,需要修改 redis 配置文件 `redis.conf`:
-
-```bash
-io-threads 4 #设置1的话只会开启主线程,官网建议4核的机器建议设置为2或3个线程,8核的建议设置为6个线程
-```
-
-另外:
-
-- io-threads 的个数一旦设置,不能通过 config 动态设置。
-- 当设置 ssl 后,io-threads 将不工作。
-
-开启多线程后,默认只会使用多线程进行 IO 写入 writes,即发送数据给客户端,如果需要开启多线程 IO 读取 reads,同样需要修改 redis 配置文件 `redis.conf`:
-
-```bash
-io-threads-do-reads yes
-```
-
-但是官网描述开启多线程读并不能有太大提升,因此一般情况下并不建议开启。
-
-相关阅读:
-
-- [Redis 6.0 新特性-多线程连环 13 问!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FZu3acwK6zrCBZQ_3HoUgw)
-- [Redis 多线程网络模型全面揭秘](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039223696)(推荐)
-
-### Redis 后台线程了解吗?
-
-我们虽然经常说 Redis 是单线程模型(主要逻辑是单线程完成的),但实际还有一些后台线程用于执行一些比较耗时的操作:
-
-- 通过 `bio_close_file` 后台线程来释放 AOF / RDB 等过程中产生的临时文件资源。
-- 通过 `bio_aof_fsync` 后台线程调用 `fsync` 函数将系统内核缓冲区还未同步到到磁盘的数据强制刷到磁盘(AOF 文件)。
-- 通过 `bio_lazy_free` 后台线程释放大对象(已删除)占用的内存空间.
-
-在`bio.h` 文件中有定义(Redis 6.0 版本,源码地址:):
-
-```java
-#ifndef __BIO_H
-#define __BIO_H
-
-/* Exported API */
-void bioInit(void);
-void bioCreateBackgroundJob(int type, void *arg1, void *arg2, void *arg3);
-unsigned long long bioPendingJobsOfType(int type);
-unsigned long long bioWaitStepOfType(int type);
-time_t bioOlderJobOfType(int type);
-void bioKillThreads(void);
-
-/* Background job opcodes */
-#define BIO_CLOSE_FILE 0 /* Deferred close(2) syscall. */
-#define BIO_AOF_FSYNC 1 /* Deferred AOF fsync. */
-#define BIO_LAZY_FREE 2 /* Deferred objects freeing. */
-#define BIO_NUM_OPS 3
-
-#endif
-```
-
-关于 Redis 后台线程的详细介绍可以查看 [Redis 6.0 后台线程有哪些?](https://juejin.cn/post/7102780434739626014) 这篇就文章。
-
-## Redis 内存管理
-
-### Redis 给缓存数据设置过期时间有什么用?
-
-一般情况下,我们设置保存的缓存数据的时候都会设置一个过期时间。为什么呢?
-
-内存是有限且珍贵的,如果不对缓存数据设置过期时间,那内存占用就会一直增长,最终可能会导致 OOM 问题。通过设置合理的过期时间,Redis 会自动删除暂时不需要的数据,为新的缓存数据腾出空间。
-
-Redis 自带了给缓存数据设置过期时间的功能,比如:
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> expire key 60 # 数据在 60s 后过期
-(integer) 1
-127.0.0.1:6379> setex key 60 value # 数据在 60s 后过期 (setex:[set] + [ex]pire)
-OK
-127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key # 查看数据还有多久过期
-(integer) 56
-```
-
-注意 ⚠️:Redis 中除了字符串类型有自己独有设置过期时间的命令 `setex` 外,其他方法都需要依靠 `expire` 命令来设置过期时间 。另外,`persist` 命令可以移除一个键的过期时间。
-
-**过期时间除了有助于缓解内存的消耗,还有什么其他用么?**
-
-很多时候,我们的业务场景就是需要某个数据只在某一时间段内存在,比如我们的短信验证码可能只在 1 分钟内有效,用户登录的 Token 可能只在 1 天内有效。
-
-如果使用传统的数据库来处理的话,一般都是自己判断过期,这样更麻烦并且性能要差很多。
-
-### Redis 是如何判断数据是否过期的呢?
-
-Redis 通过一个叫做过期字典(可以看作是 hash 表)来保存数据过期的时间。过期字典的键指向 Redis 数据库中的某个 key(键),过期字典的值是一个 long long 类型的整数,这个整数保存了 key 所指向的数据库键的过期时间(毫秒精度的 UNIX 时间戳)。
-
-
-
-过期字典是存储在 redisDb 这个结构里的:
-
-```c
-typedef struct redisDb {
- ...
-
- dict *dict; //数据库键空间,保存着数据库中所有键值对
- dict *expires // 过期字典,保存着键的过期时间
- ...
-} redisDb;
-```
-
-在查询一个 key 的时候,Redis 首先检查该 key 是否存在于过期字典中(时间复杂度为 O(1)),如果不在就直接返回,在的话需要判断一下这个 key 是否过期,过期直接删除 key 然后返回 null。
-
-### Redis 过期 key 删除策略了解么?
-
-如果假设你设置了一批 key 只能存活 1 分钟,那么 1 分钟后,Redis 是怎么对这批 key 进行删除的呢?
-
-常用的过期数据的删除策略就下面这几种:
-
-1. **惰性删除**:只会在取出/查询 key 的时候才对数据进行过期检查。这种方式对 CPU 最友好,但是可能会造成太多过期 key 没有被删除。
-2. **定期删除**:周期性地随机从设置了过期时间的 key 中抽查一批,然后逐个检查这些 key 是否过期,过期就删除 key。相比于惰性删除,定期删除对内存更友好,对 CPU 不太友好。
-3. **延迟队列**:把设置过期时间的 key 放到一个延迟队列里,到期之后就删除 key。这种方式可以保证每个过期 key 都能被删除,但维护延迟队列太麻烦,队列本身也要占用资源。
-4. **定时删除**:每个设置了过期时间的 key 都会在设置的时间到达时立即被删除。这种方法可以确保内存中不会有过期的键,但是它对 CPU 的压力最大,因为它需要为每个键都设置一个定时器。
-
-**Redis 采用的是那种删除策略呢?**
-
-Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 结合的策略,这也是大部分缓存框架的选择。定期删除对内存更加友好,惰性删除对 CPU 更加友好。两者各有千秋,结合起来使用既能兼顾 CPU 友好,又能兼顾内存友好。
-
-下面是我们详细介绍一下 Redis 中的定期删除具体是如何做的。
-
-Redis 的定期删除过程是随机的(周期性地随机从设置了过期时间的 key 中抽查一批),所以并不保证所有过期键都会被立即删除。这也就解释了为什么有的 key 过期了,并没有被删除。并且,Redis 底层会通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对 CPU 时间的影响。
-
-另外,定期删除还会受到执行时间和过期 key 的比例的影响:
-
-- 执行时间已经超过了阈值,那么就中断这一次定期删除循环,以避免使用过多的 CPU 时间。
-- 如果这一批过期的 key 比例超过一个比例,就会重复执行此删除流程,以更积极地清理过期 key。相应地,如果过期的 key 比例低于这个比例,就会中断这一次定期删除循环,避免做过多的工作而获得很少的内存回收。
-
-Redis 7.2 版本的执行时间阈值是 **25ms**,过期 key 比例设定值是 **10%**。
-
-```c
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 1000 /* Microseconds. */
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 25 /* Max % of CPU to use. */
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE 10 /* % of stale keys after which
- we do extra efforts. */
-```
-
-**每次随机抽查数量是多少?**
-
-`expire.c` 中定义了每次随机抽查的数量,Redis 7.2 版本为 20,也就是说每次会随机选择 20 个设置了过期时间的 key 判断是否过期。
-
-```c
-#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP 20 /* Keys for each DB loop. */
-```
-
-**如何控制定期删除的执行频率?**
-
-在 Redis 中,定期删除的频率是由 **hz** 参数控制的。hz 默认为 10,代表每秒执行 10 次,也就是每秒钟进行 10 次尝试来查找并删除过期的 key。
-
-hz 的取值范围为 1~500。增大 hz 参数的值会提升定期删除的频率。如果你想要更频繁地执行定期删除任务,可以适当增加 hz 的值,但这会增加 CPU 的使用率。根据 Redis 官方建议,hz 的值不建议超过 100,对于大部分用户使用默认的 10 就足够了。
-
-下面是 hz 参数的官方注释,我翻译了其中的重要信息(Redis 7.2 版本)。
-
-
-
-类似的参数还有一个 **dynamic-hz**,这个参数开启之后 Redis 就会在 hz 的基础上动态计算一个值。Redis 提供并默认启用了使用自适应 hz 值的能力,
-
-这两个参数都在 Redis 配置文件 `redis.conf` 中:
-
-```properties
-# 默认为 10
-hz 10
-# 默认开启
-dynamic-hz yes
-```
-
-多提一嘴,除了定期删除过期 key 这个定期任务之外,还有一些其他定期任务例如关闭超时的客户端连接、更新统计信息,这些定期任务的执行频率也是通过 hz 参数决定。
-
-**为什么定期删除不是把所有过期 key 都删除呢?**
-
-这样会对性能造成太大的影响。如果我们 key 数量非常庞大的话,挨个遍历检查是非常耗时的,会严重影响性能。Redis 设计这种策略的目的是为了平衡内存和性能。
-
-**为什么 key 过期之后不立马把它删掉呢?这样不是会浪费很多内存空间吗?**
-
-因为不太好办到,或者说这种删除方式的成本太高了。假如我们使用延迟队列作为删除策略,这样存在下面这些问题:
-
-1. 队列本身的开销可能很大:key 多的情况下,一个延迟队列可能无法容纳。
-2. 维护延迟队列太麻烦:修改 key 的过期时间就需要调整期在延迟队列中的位置,并且还需要引入并发控制。
-
-### 大量 key 集中过期怎么办?
-
-当 Redis 中存在大量 key 在同一时间点集中过期时,可能会导致以下问题:
-
-- **请求延迟增加**:Redis 在处理过期 key 时需要消耗 CPU 资源,如果过期 key 数量庞大,会导致 Redis 实例的 CPU 占用率升高,进而影响其他请求的处理速度,造成延迟增加。
-- **内存占用过高**:过期的 key 虽然已经失效,但在 Redis 真正删除它们之前,仍然会占用内存空间。如果过期 key 没有及时清理,可能会导致内存占用过高,甚至引发内存溢出。
-
-为了避免这些问题,可以采取以下方案:
-
-1. **尽量避免 key 集中过期**:在设置键的过期时间时尽量随机一点。
-2. **开启 lazy free 机制**:修改 `redis.conf` 配置文件,将 `lazyfree-lazy-expire` 参数设置为 `yes`,即可开启 lazy free 机制。开启 lazy free 机制后,Redis 会在后台异步删除过期的 key,不会阻塞主线程的运行,从而降低对 Redis 性能的影响。
-
-### Redis 内存淘汰策略了解么?
-
-> 相关问题:MySQL 里有 2000w 数据,Redis 中只存 20w 的数据,如何保证 Redis 中的数据都是热点数据?
-
-Redis 的内存淘汰策略只有在运行内存达到了配置的最大内存阈值时才会触发,这个阈值是通过 `redis.conf` 的 `maxmemory` 参数来定义的。64 位操作系统下,`maxmemory` 默认为 0,表示不限制内存大小。32 位操作系统下,默认的最大内存值是 3GB。
-
-你可以使用命令 `config get maxmemory` 来查看 `maxmemory` 的值。
-
-```bash
-> config get maxmemory
-maxmemory
-0
-```
-
-Redis 提供了 6 种内存淘汰策略:
-
-1. **volatile-lru(least recently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰。
-2. **volatile-ttl**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选将要过期的数据淘汰。
-3. **volatile-random**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中任意选择数据淘汰。
-4. **allkeys-lru(least recently used)**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中移除最近最少使用的数据淘汰。
-5. **allkeys-random**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中任意选择数据淘汰。
-6. **no-eviction**(默认内存淘汰策略):禁止驱逐数据,当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,新写入操作会报错。
-
-4.0 版本后增加以下两种:
-
-7. **volatile-lfu(least frequently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-8. **allkeys-lfu(least frequently used)**:从数据集(`server.db[i].dict`)中移除最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-
-`allkeys-xxx` 表示从所有的键值中淘汰数据,而 `volatile-xxx` 表示从设置了过期时间的键值中淘汰数据。
-
-`config.c` 中定义了内存淘汰策略的枚举数组:
-
-```c
-configEnum maxmemory_policy_enum[] = {
- {"volatile-lru", MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU},
- {"volatile-lfu", MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LFU},
- {"volatile-random",MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM},
- {"volatile-ttl",MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL},
- {"allkeys-lru",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU},
- {"allkeys-lfu",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LFU},
- {"allkeys-random",MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM},
- {"noeviction",MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION},
- {NULL, 0}
-};
-```
-
-你可以使用 `config get maxmemory-policy` 命令来查看当前 Redis 的内存淘汰策略。
-
-```bash
-> config get maxmemory-policy
-maxmemory-policy
-noeviction
-```
-
-可以通过 `config set maxmemory-policy 内存淘汰策略` 命令修改内存淘汰策略,立即生效,但这种方式重启 Redis 之后就失效了。修改 `redis.conf` 中的 `maxmemory-policy` 参数不会因为重启而失效,不过,需要重启之后修改才能生效。
-
-```properties
-maxmemory-policy noeviction
-```
-
-关于淘汰策略的详细说明可以参考 Redis 官方文档:。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 开发与运维》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- 《Redis 核心原理与实战》
-- Redis 命令手册:
-- RedisSearch 终极使用指南,你值得拥有!:
-- WHY Redis choose single thread (vs multi threads): [https://medium.com/@jychen7/sharing-redis-single-thread-vs-multi-threads-5870bd44d153](https://medium.com/@jychen7/sharing-redis-single-thread-vs-multi-threads-5870bd44d153)
-
-
+If you are familiar with other solutions and can explain why you ultimately chose Redis (even better!), this will significantly enhance your interview performance
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
index 37ef43ea72a..9a391821bf5 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-questions-02.md
@@ -1,34 +1,34 @@
---
-title: Redis常见面试题总结(下)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common Redis Interview Questions (Part 2)
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: Redis基础,Redis常见数据结构,Redis线程模型,Redis内存管理,Redis事务,Redis性能优化
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 一篇文章总结Redis常见的知识点和面试题,涵盖Redis基础、Redis常见数据结构、Redis线程模型、Redis内存管理、Redis事务、Redis性能优化等内容。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Redis Basics, Common Redis Data Structures, Redis Thread Model, Redis Memory Management, Redis Transactions, Redis Performance Optimization
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: An article summarizing common knowledge points and interview questions about Redis, covering Redis basics, common data structures, thread model, memory management, transactions, and performance optimization.
---
-## Redis 事务
+## Redis Transactions
-### 什么是 Redis 事务?
+### What is a Redis Transaction?
-你可以将 Redis 中的事务理解为:**Redis 事务提供了一种将多个命令请求打包的功能。然后,再按顺序执行打包的所有命令,并且不会被中途打断。**
+You can understand a transaction in Redis as: **Redis transactions provide a way to package multiple command requests together. Then, all the packaged commands are executed in order without being interrupted.**
-Redis 事务实际开发中使用的非常少,功能比较鸡肋,不要将其和我们平时理解的关系型数据库的事务混淆了。
+In actual development, Redis transactions are used very rarely, and their functionality is somewhat limited. Do not confuse them with transactions in relational databases as we usually understand them.
-除了不满足原子性和持久性之外,事务中的每条命令都会与 Redis 服务器进行网络交互,这是比较浪费资源的行为。明明一次批量执行多个命令就可以了,这种操作实在是看不懂。
+In addition to not satisfying atomicity and durability, each command in a transaction interacts with the Redis server over the network, which is a resource-wasting behavior. Clearly, multiple commands can be executed in a batch, so this operation is hard to understand.
-因此,Redis 事务是不建议在日常开发中使用的。
+Therefore, Redis transactions are not recommended for use in daily development.
-### 如何使用 Redis 事务?
+### How to Use Redis Transactions?
-Redis 可以通过 **`MULTI`、`EXEC`、`DISCARD` 和 `WATCH`** 等命令来实现事务(Transaction)功能。
+Redis can implement transaction functionality through commands like **`MULTI`, `EXEC`, `DISCARD`, and `WATCH`**.
```bash
> MULTI
@@ -42,15 +42,15 @@ QUEUED
2) "JavaGuide"
```
-[`MULTI`](https://redis.io/commands/multi) 命令后可以输入多个命令,Redis 不会立即执行这些命令,而是将它们放到队列,当调用了 [`EXEC`](https://redis.io/commands/exec) 命令后,再执行所有的命令。
+After the [`MULTI`](https://redis.io/commands/multi) command, you can input multiple commands. Redis will not execute these commands immediately but will queue them. When the [`EXEC`](https://redis.io/commands/exec) command is called, all commands are executed.
-这个过程是这样的:
+The process is as follows:
-1. 开始事务(`MULTI`);
-2. 命令入队(批量操作 Redis 的命令,先进先出(FIFO)的顺序执行);
-3. 执行事务(`EXEC`)。
+1. Start the transaction (`MULTI`);
+1. Queue commands (commands for batch operations on Redis are executed in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order);
+1. Execute the transaction (`EXEC`).
-你也可以通过 [`DISCARD`](https://redis.io/commands/discard) 命令取消一个事务,它会清空事务队列中保存的所有命令。
+You can also cancel a transaction using the [`DISCARD`](https://redis.io/commands/discard) command, which will clear all commands saved in the transaction queue.
```bash
> MULTI
@@ -63,10 +63,10 @@ QUEUED
OK
```
-你可以通过[`WATCH`](https://redis.io/commands/watch) 命令监听指定的 Key,当调用 `EXEC` 命令执行事务时,如果一个被 `WATCH` 命令监视的 Key 被 **其他客户端/Session** 修改的话,整个事务都不会被执行。
+You can use the [`WATCH`](https://redis.io/commands/watch) command to monitor a specified key. When the `EXEC` command is called to execute the transaction, if a key being monitored by the `WATCH` command is modified by **another client/session**, the entire transaction will not be executed.
```bash
-# 客户端 1
+# Client 1
> SET PROJECT "RustGuide"
OK
> WATCH PROJECT
@@ -76,21 +76,21 @@ OK
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
QUEUED
-# 客户端 2
-# 在客户端 1 执行 EXEC 命令提交事务之前修改 PROJECT 的值
+# Client 2
+# Modifies the value of PROJECT before Client 1 executes the EXEC command to submit the transaction
> SET PROJECT "GoGuide"
-# 客户端 1
-# 修改失败,因为 PROJECT 的值被客户端2修改了
+# Client 1
+# Modification fails because the value of PROJECT was changed by Client 2
> EXEC
(nil)
> GET PROJECT
"GoGuide"
```
-不过,如果 **WATCH** 与 **事务** 在同一个 Session 里,并且被 **WATCH** 监视的 Key 被修改的操作发生在事务内部,这个事务是可以被执行成功的(相关 issue:[WATCH 命令碰到 MULTI 命令时的不同效果](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1714))。
+However, if **WATCH** and **transaction** are in the same session, and the operation that modifies the monitored key occurs within the transaction, the transaction can be successfully executed (related issue: [Different Effects of WATCH Command When Encountering MULTI Command](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1714)).
-事务内部修改 WATCH 监视的 Key:
+Modifying the WATCH monitored key inside the transaction:
```bash
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ QUEUED
"JavaGuide3"
```
-事务外部修改 WATCH 监视的 Key:
+Modifying the WATCH monitored key outside the transaction:
```bash
> SET PROJECT "JavaGuide"
@@ -130,670 +130,10 @@ QUEUED
(nil)
```
-Redis 官网相关介绍 [https://redis.io/topics/transactions](https://redis.io/topics/transactions) 如下:
+The official Redis website provides related information [https://redis.io/topics/transactions](https://redis.io/topics/transactions) as follows:
-
+
-### Redis 事务支持原子性吗?
+### Does Redis Transactions Support Atomicity?
-Redis 的事务和我们平时理解的关系型数据库的事务不同。我们知道事务具有四大特性:**1. 原子性**,**2. 隔离性**,**3. 持久性**,**4. 一致性**。
-
-1. **原子性(Atomicity)**:事务是最小的执行单位,不允许分割。事务的原子性确保动作要么全部完成,要么完全不起作用;
-2. **隔离性(Isolation)**:并发访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不被其他事务所干扰,各并发事务之间数据库是独立的;
-3. **持久性(Durability)**:一个事务被提交之后。它对数据库中数据的改变是持久的,即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响;
-4. **一致性(Consistency)**:执行事务前后,数据保持一致,多个事务对同一个数据读取的结果是相同的。
-
-Redis 事务在运行错误的情况下,除了执行过程中出现错误的命令外,其他命令都能正常执行。并且,Redis 事务是不支持回滚(roll back)操作的。因此,Redis 事务其实是不满足原子性的。
-
-Redis 官网也解释了自己为啥不支持回滚。简单来说就是 Redis 开发者们觉得没必要支持回滚,这样更简单便捷并且性能更好。Redis 开发者觉得即使命令执行错误也应该在开发过程中就被发现而不是生产过程中。
-
-
-
-**相关 issue**:
-
-- [issue#452: 关于 Redis 事务不满足原子性的问题](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/452)。
-- [Issue#491:关于 Redis 没有事务回滚?](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/491)。
-
-### Redis 事务支持持久性吗?
-
-Redis 不同于 Memcached 的很重要一点就是,Redis 支持持久化,而且支持 3 种持久化方式:
-
-- 快照(snapshotting,RDB);
-- 只追加文件(append-only file,AOF);
-- RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化(Redis 4.0 新增)。
-
-与 RDB 持久化相比,AOF 持久化的实时性更好。在 Redis 的配置文件中存在三种不同的 AOF 持久化方式(`fsync` 策略),它们分别是:
-
-```bash
-appendfsync always #每次有数据修改发生时,都会调用fsync函数同步AOF文件,fsync完成后线程返回,这样会严重降低Redis的速度
-appendfsync everysec #每秒钟调用fsync函数同步一次AOF文件
-appendfsync no #让操作系统决定何时进行同步,一般为30秒一次
-```
-
-AOF 持久化的 `fsync` 策略为 no、everysec 时都会存在数据丢失的情况。always 下可以基本是可以满足持久性要求的,但性能太差,实际开发过程中不会使用。
-
-因此,Redis 事务的持久性也是没办法保证的。
-
-### 如何解决 Redis 事务的缺陷?
-
-Redis 从 2.6 版本开始支持执行 Lua 脚本,它的功能和事务非常类似。我们可以利用 Lua 脚本来批量执行多条 Redis 命令,这些 Redis 命令会被提交到 Redis 服务器一次性执行完成,大幅减小了网络开销。
-
-一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰。
-
-不过,如果 Lua 脚本运行时出错并中途结束,出错之后的命令是不会被执行的。并且,出错之前执行的命令是无法被撤销的,无法实现类似关系型数据库执行失败可以回滚的那种原子性效果。因此,**严格来说的话,通过 Lua 脚本来批量执行 Redis 命令实际也是不完全满足原子性的。**
-
-如果想要让 Lua 脚本中的命令全部执行,必须保证语句语法和命令都是对的。
-
-另外,Redis 7.0 新增了 [Redis functions](https://redis.io/docs/manual/programmability/functions-intro/) 特性,你可以将 Redis functions 看作是比 Lua 更强大的脚本。
-
-## Redis 性能优化(重要)
-
-除了下面介绍的内容之外,再推荐两篇不错的文章:
-
-- [你的 Redis 真的变慢了吗?性能优化如何做 - 阿里开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/nNEuYw0NlYGhuKKKKoWfcQ)。
-- [Redis 常见阻塞原因总结 - JavaGuide](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.html)。
-
-### 使用批量操作减少网络传输
-
-一个 Redis 命令的执行可以简化为以下 4 步:
-
-1. 发送命令;
-2. 命令排队;
-3. 命令执行;
-4. 返回结果。
-
-其中,第 1 步和第 4 步耗费时间之和称为 **Round Trip Time(RTT,往返时间)**,也就是数据在网络上传输的时间。
-
-使用批量操作可以减少网络传输次数,进而有效减小网络开销,大幅减少 RTT。
-
-另外,除了能减少 RTT 之外,发送一次命令的 socket I/O 成本也比较高(涉及上下文切换,存在 `read()` 和 `write()` 系统调用),批量操作还可以减少 socket I/O 成本。这个在官方对 pipeline 的介绍中有提到:。
-
-#### 原生批量操作命令
-
-Redis 中有一些原生支持批量操作的命令,比如:
-
-- `MGET`(获取一个或多个指定 key 的值)、`MSET`(设置一个或多个指定 key 的值)、
-- `HMGET`(获取指定哈希表中一个或者多个指定字段的值)、`HMSET`(同时将一个或多个 field-value 对设置到指定哈希表中)、
-- `SADD`(向指定集合添加一个或多个元素)
-- ……
-
-不过,在 Redis 官方提供的分片集群解决方案 Redis Cluster 下,使用这些原生批量操作命令可能会存在一些小问题需要解决。就比如说 `MGET` 无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上,`MGET`可能还是需要多次网络传输,原子操作也无法保证了。不过,相较于非批量操作,还是可以节省不少网络传输次数。
-
-整个步骤的简化版如下(通常由 Redis 客户端实现,无需我们自己再手动实现):
-
-1. 找到 key 对应的所有 hash slot;
-2. 分别向对应的 Redis 节点发起 `MGET` 请求获取数据;
-3. 等待所有请求执行结束,重新组装结果数据,保持跟入参 key 的顺序一致,然后返回结果。
-
-如果想要解决这个多次网络传输的问题,比较常用的办法是自己维护 key 与 slot 的关系。不过这样不太灵活,虽然带来了性能提升,但同样让系统复杂性提升。
-
-> Redis Cluster 并没有使用一致性哈希,采用的是 **哈希槽分区**,每一个键值对都属于一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)**。当客户端发送命令请求的时候,需要先根据 key 通过上面的计算公式找到的对应的哈希槽,然后再查询哈希槽和节点的映射关系,即可找到目标 Redis 节点。
->
-> 我在 [Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html) 这篇文章中详细介绍了 Redis Cluster 这部分的内容,感兴趣地可以看看。
-
-#### pipeline
-
-对于不支持批量操作的命令,我们可以利用 **pipeline(流水线)** 将一批 Redis 命令封装成一组,这些 Redis 命令会被一次性提交到 Redis 服务器,只需要一次网络传输。不过,需要注意控制一次批量操作的 **元素个数**(例如 500 以内,实际也和元素字节数有关),避免网络传输的数据量过大。
-
-与 `MGET`、`MSET` 等原生批量操作命令一样,pipeline 同样在 Redis Cluster 上使用会存在一些小问题。原因类似,无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上。如果想要使用的话,客户端需要自己维护 key 与 slot 的关系。
-
-原生批量操作命令和 pipeline 的是有区别的,使用的时候需要注意:
-
-- 原生批量操作命令是原子操作,pipeline 是非原子操作。
-- pipeline 可以打包不同的命令,原生批量操作命令不可以。
-- 原生批量操作命令是 Redis 服务端支持实现的,而 pipeline 需要服务端和客户端的共同实现。
-
-顺带补充一下 pipeline 和 Redis 事务的对比:
-
-- 事务是原子操作,pipeline 是非原子操作。两个不同的事务不会同时运行,而 pipeline 可以同时以交错方式执行。
-- Redis 事务中每个命令都需要发送到服务端,而 Pipeline 只需要发送一次,请求次数更少。
-
-> 事务可以看作是一个原子操作,但其实并不满足原子性。当我们提到 Redis 中的原子操作时,主要指的是这个操作(比如事务、Lua 脚本)不会被其他操作(比如其他事务、Lua 脚本)打扰,并不能完全保证这个操作中的所有写命令要么都执行要么都不执行。这主要也是因为 Redis 是不支持回滚操作。
-
-
-
-另外,pipeline 不适用于执行顺序有依赖关系的一批命令。就比如说,你需要将前一个命令的结果给后续的命令使用,pipeline 就没办法满足你的需求了。对于这种需求,我们可以使用 **Lua 脚本**。
-
-#### Lua 脚本
-
-Lua 脚本同样支持批量操作多条命令。一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,可以看作是 **原子操作**。也就是说,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰,这是 pipeline 所不具备的。
-
-并且,Lua 脚本中支持一些简单的逻辑处理比如使用命令读取值并在 Lua 脚本中进行处理,这同样是 pipeline 所不具备的。
-
-不过, Lua 脚本依然存在下面这些缺陷:
-
-- 如果 Lua 脚本运行时出错并中途结束,之后的操作不会进行,但是之前已经发生的写操作不会撤销,所以即使使用了 Lua 脚本,也不能实现类似数据库回滚的原子性。
-- Redis Cluster 下 Lua 脚本的原子操作也无法保证了,原因同样是无法保证所有的 key 都在同一个 **hash slot(哈希槽)** 上。
-
-### 大量 key 集中过期问题
-
-我在前面提到过:对于过期 key,Redis 采用的是 **定期删除+惰性/懒汉式删除** 策略。
-
-定期删除执行过程中,如果突然遇到大量过期 key 的话,客户端请求必须等待定期清理过期 key 任务线程执行完成,因为这个这个定期任务线程是在 Redis 主线程中执行的。这就导致客户端请求没办法被及时处理,响应速度会比较慢。
-
-**如何解决呢?** 下面是两种常见的方法:
-
-1. 给 key 设置随机过期时间。
-2. 开启 lazy-free(惰性删除/延迟释放)。lazy-free 特性是 Redis 4.0 开始引入的,指的是让 Redis 采用异步方式延迟释放 key 使用的内存,将该操作交给单独的子线程处理,避免阻塞主线程。
-
-个人建议不管是否开启 lazy-free,我们都尽量给 key 设置随机过期时间。
-
-### Redis bigkey(大 Key)
-
-#### 什么是 bigkey?
-
-简单来说,如果一个 key 对应的 value 所占用的内存比较大,那这个 key 就可以看作是 bigkey。具体多大才算大呢?有一个不是特别精确的参考标准:
-
-- String 类型的 value 超过 1MB
-- 复合类型(List、Hash、Set、Sorted Set 等)的 value 包含的元素超过 5000 个(不过,对于复合类型的 value 来说,不一定包含的元素越多,占用的内存就越多)。
-
-
-
-#### bigkey 是怎么产生的?有什么危害?
-
-bigkey 通常是由于下面这些原因产生的:
-
-- 程序设计不当,比如直接使用 String 类型存储较大的文件对应的二进制数据。
-- 对于业务的数据规模考虑不周到,比如使用集合类型的时候没有考虑到数据量的快速增长。
-- 未及时清理垃圾数据,比如哈希中冗余了大量的无用键值对。
-
-bigkey 除了会消耗更多的内存空间和带宽,还会对性能造成比较大的影响。
-
-在 [Redis 常见阻塞原因总结](./redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.md) 这篇文章中我们提到:大 key 还会造成阻塞问题。具体来说,主要体现在下面三个方面:
-
-1. 客户端超时阻塞:由于 Redis 执行命令是单线程处理,然后在操作大 key 时会比较耗时,那么就会阻塞 Redis,从客户端这一视角看,就是很久很久都没有响应。
-2. 网络阻塞:每次获取大 key 产生的网络流量较大,如果一个 key 的大小是 1 MB,每秒访问量为 1000,那么每秒会产生 1000MB 的流量,这对于普通千兆网卡的服务器来说是灾难性的。
-3. 工作线程阻塞:如果使用 del 删除大 key 时,会阻塞工作线程,这样就没办法处理后续的命令。
-
-大 key 造成的阻塞问题还会进一步影响到主从同步和集群扩容。
-
-综上,大 key 带来的潜在问题是非常多的,我们应该尽量避免 Redis 中存在 bigkey。
-
-#### 如何发现 bigkey?
-
-**1、使用 Redis 自带的 `--bigkeys` 参数来查找。**
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli -p 6379 --bigkeys
-
-# Scanning the entire keyspace to find biggest keys as well as
-# average sizes per key type. You can use -i 0.1 to sleep 0.1 sec
-# per 100 SCAN commands (not usually needed).
-
-[00.00%] Biggest string found so far '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' with 4437 bytes
-[00.00%] Biggest list found so far '"my-list"' with 17 items
-
--------- summary -------
-
-Sampled 5 keys in the keyspace!
-Total key length in bytes is 264 (avg len 52.80)
-
-Biggest list found '"my-list"' has 17 items
-Biggest string found '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' has 4437 bytes
-
-1 lists with 17 items (20.00% of keys, avg size 17.00)
-0 hashs with 0 fields (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-4 strings with 4831 bytes (80.00% of keys, avg size 1207.75)
-0 streams with 0 entries (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-0 sets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
-0 zsets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00
-```
-
-从这个命令的运行结果,我们可以看出:这个命令会扫描(Scan)Redis 中的所有 key,会对 Redis 的性能有一点影响。并且,这种方式只能找出每种数据结构 top 1 bigkey(占用内存最大的 String 数据类型,包含元素最多的复合数据类型)。然而,一个 key 的元素多并不代表占用内存也多,需要我们根据具体的业务情况来进一步判断。
-
-在线上执行该命令时,为了降低对 Redis 的影响,需要指定 `-i` 参数控制扫描的频率。`redis-cli -p 6379 --bigkeys -i 3` 表示扫描过程中每次扫描后休息的时间间隔为 3 秒。
-
-**2、使用 Redis 自带的 SCAN 命令**
-
-`SCAN` 命令可以按照一定的模式和数量返回匹配的 key。获取了 key 之后,可以利用 `STRLEN`、`HLEN`、`LLEN` 等命令返回其长度或成员数量。
-
-| 数据结构 | 命令 | 复杂度 | 结果(对应 key) |
-| ---------- | ------ | ------ | ------------------ |
-| String | STRLEN | O(1) | 字符串值的长度 |
-| Hash | HLEN | O(1) | 哈希表中字段的数量 |
-| List | LLEN | O(1) | 列表元素数量 |
-| Set | SCARD | O(1) | 集合元素数量 |
-| Sorted Set | ZCARD | O(1) | 有序集合的元素数量 |
-
-对于集合类型还可以使用 `MEMORY USAGE` 命令(Redis 4.0+),这个命令会返回键值对占用的内存空间。
-
-**3、借助开源工具分析 RDB 文件。**
-
-通过分析 RDB 文件来找出 big key。这种方案的前提是你的 Redis 采用的是 RDB 持久化。
-
-网上有现成的代码/工具可以直接拿来使用:
-
-- [redis-rdb-tools](https://github.com/sripathikrishnan/redis-rdb-tools):Python 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具。
-- [rdb_bigkeys](https://github.com/weiyanwei412/rdb_bigkeys):Go 语言写的用来分析 Redis 的 RDB 快照文件用的工具,性能更好。
-
-**4、借助公有云的 Redis 分析服务。**
-
-如果你用的是公有云的 Redis 服务的话,可以看看其是否提供了 key 分析功能(一般都提供了)。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持 bigkey 实时分析、发现,文档地址:。
-
-
-
-#### 如何处理 bigkey?
-
-bigkey 的常见处理以及优化办法如下(这些方法可以配合起来使用):
-
-- **分割 bigkey**:将一个 bigkey 分割为多个小 key。例如,将一个含有上万字段数量的 Hash 按照一定策略(比如二次哈希)拆分为多个 Hash。
-- **手动清理**:Redis 4.0+ 可以使用 `UNLINK` 命令来异步删除一个或多个指定的 key。Redis 4.0 以下可以考虑使用 `SCAN` 命令结合 `DEL` 命令来分批次删除。
-- **采用合适的数据结构**:例如,文件二进制数据不使用 String 保存、使用 HyperLogLog 统计页面 UV、Bitmap 保存状态信息(0/1)。
-- **开启 lazy-free(惰性删除/延迟释放)**:lazy-free 特性是 Redis 4.0 开始引入的,指的是让 Redis 采用异步方式延迟释放 key 使用的内存,将该操作交给单独的子线程处理,避免阻塞主线程。
-
-### Redis hotkey(热 Key)
-
-#### 什么是 hotkey?
-
-如果一个 key 的访问次数比较多且明显多于其他 key 的话,那这个 key 就可以看作是 **hotkey(热 Key)**。例如在 Redis 实例的每秒处理请求达到 5000 次,而其中某个 key 的每秒访问量就高达 2000 次,那这个 key 就可以看作是 hotkey。
-
-hotkey 出现的原因主要是某个热点数据访问量暴增,如重大的热搜事件、参与秒杀的商品。
-
-#### hotkey 有什么危害?
-
-处理 hotkey 会占用大量的 CPU 和带宽,可能会影响 Redis 实例对其他请求的正常处理。此外,如果突然访问 hotkey 的请求超出了 Redis 的处理能力,Redis 就会直接宕机。这种情况下,大量请求将落到后面的数据库上,可能会导致数据库崩溃。
-
-因此,hotkey 很可能成为系统性能的瓶颈点,需要单独对其进行优化,以确保系统的高可用性和稳定性。
-
-#### 如何发现 hotkey?
-
-**1、使用 Redis 自带的 `--hotkeys` 参数来查找。**
-
-Redis 4.0.3 版本中新增了 `hotkeys` 参数,该参数能够返回所有 key 的被访问次数。
-
-使用该方案的前提条件是 Redis Server 的 `maxmemory-policy` 参数设置为 LFU 算法,不然就会出现如下所示的错误。
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli -p 6379 --hotkeys
-
-# Scanning the entire keyspace to find hot keys as well as
-# average sizes per key type. You can use -i 0.1 to sleep 0.1 sec
-# per 100 SCAN commands (not usually needed).
-
-Error: ERR An LFU maxmemory policy is not selected, access frequency not tracked. Please note that when switching between policies at runtime LRU and LFU data will take some time to adjust.
-```
-
-Redis 中有两种 LFU 算法:
-
-1. **volatile-lfu(least frequently used)**:从已设置过期时间的数据集(`server.db[i].expires`)中挑选最不经常使用的数据淘汰。
-2. **allkeys-lfu(least frequently used)**:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在键空间中,移除最不经常使用的 key。
-
-以下是配置文件 `redis.conf` 中的示例:
-
-```properties
-# 使用 volatile-lfu 策略
-maxmemory-policy volatile-lfu
-
-# 或者使用 allkeys-lfu 策略
-maxmemory-policy allkeys-lfu
-```
-
-需要注意的是,`hotkeys` 参数命令也会增加 Redis 实例的 CPU 和内存消耗(全局扫描),因此需要谨慎使用。
-
-**2、使用 `MONITOR` 命令。**
-
-`MONITOR` 命令是 Redis 提供的一种实时查看 Redis 的所有操作的方式,可以用于临时监控 Redis 实例的操作情况,包括读写、删除等操作。
-
-由于该命令对 Redis 性能的影响比较大,因此禁止长时间开启 `MONITOR`(生产环境中建议谨慎使用该命令)。
-
-```bash
-# redis-cli
-127.0.0.1:6379> MONITOR
-OK
-1683638260.637378 [0 172.17.0.1:61516] "ping"
-1683638267.144236 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638268.941863 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638269.551671 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638270.646256 [0 172.17.0.1:61516] "ping"
-1683638270.849551 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638271.926945 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-1683638274.276599 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet2"
-1683638276.327234 [0 172.17.0.1:61518] "smembers" "mySet"
-```
-
-在发生紧急情况时,我们可以选择在合适的时机短暂执行 `MONITOR` 命令并将输出重定向至文件,在关闭 `MONITOR` 命令后通过对文件中请求进行归类分析即可找出这段时间中的 hotkey。
-
-**3、借助开源项目。**
-
-京东零售的 [hotkey](https://gitee.com/jd-platform-opensource/hotkey) 这个项目不光支持 hotkey 的发现,还支持 hotkey 的处理。
-
-
-
-**4、根据业务情况提前预估。**
-
-可以根据业务情况来预估一些 hotkey,比如参与秒杀活动的商品数据等。不过,我们无法预估所有 hotkey 的出现,比如突发的热点新闻事件等。
-
-**5、业务代码中记录分析。**
-
-在业务代码中添加相应的逻辑对 key 的访问情况进行记录分析。不过,这种方式会让业务代码的复杂性增加,一般也不会采用。
-
-**6、借助公有云的 Redis 分析服务。**
-
-如果你用的是公有云的 Redis 服务的话,可以看看其是否提供了 key 分析功能(一般都提供了)。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持 hotkey 实时分析、发现,文档地址:。
-
-
-
-#### 如何解决 hotkey?
-
-hotkey 的常见处理以及优化办法如下(这些方法可以配合起来使用):
-
-- **读写分离**:主节点处理写请求,从节点处理读请求。
-- **使用 Redis Cluster**:将热点数据分散存储在多个 Redis 节点上。
-- **二级缓存**:hotkey 采用二级缓存的方式进行处理,将 hotkey 存放一份到 JVM 本地内存中(可以用 Caffeine)。
-
-除了这些方法之外,如果你使用的公有云的 Redis 服务话,还可以留意其提供的开箱即用的解决方案。
-
-这里以阿里云 Redis 为例说明,它支持通过代理查询缓存功能(Proxy Query Cache)优化热点 Key 问题。
-
-
-
-### 慢查询命令
-
-#### 为什么会有慢查询命令?
-
-我们知道一个 Redis 命令的执行可以简化为以下 4 步:
-
-1. 发送命令;
-2. 命令排队;
-3. 命令执行;
-4. 返回结果。
-
-Redis 慢查询统计的是命令执行这一步骤的耗时,慢查询命令也就是那些命令执行时间较长的命令。
-
-Redis 为什么会有慢查询命令呢?
-
-Redis 中的大部分命令都是 O(1) 时间复杂度,但也有少部分 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令,例如:
-
-- `KEYS *`:会返回所有符合规则的 key。
-- `HGETALL`:会返回一个 Hash 中所有的键值对。
-- `LRANGE`:会返回 List 中指定范围内的元素。
-- `SMEMBERS`:返回 Set 中的所有元素。
-- `SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF`:计算多个 Set 的交集/并集/差集。
-- ……
-
-由于这些命令时间复杂度是 O(n),有时候也会全表扫描,随着 n 的增大,执行耗时也会越长。不过, 这些命令并不是一定不能使用,但是需要明确 N 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
-
-除了这些 O(n) 时间复杂度的命令可能会导致慢查询之外,还有一些时间复杂度可能在 O(N) 以上的命令,例如:
-
-- `ZRANGE`/`ZREVRANGE`:返回指定 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量,m 为返回的元素数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- `ZREMRANGEBYRANK`/`ZREMRANGEBYSCORE`:移除 Sorted Set 中指定排名范围/指定 score 范围内的所有元素。时间复杂度为 O(log(n)+m),n 为所有元素的数量,m 被删除元素的数量,当 m 和 n 相当大时,O(n) 的时间复杂度更小。
-- ……
-
-#### 如何找到慢查询命令?
-
-在 `redis.conf` 文件中,我们可以使用 `slowlog-log-slower-than` 参数设置耗时命令的阈值,并使用 `slowlog-max-len` 参数设置耗时命令的最大记录条数。
-
-当 Redis 服务器检测到执行时间超过 `slowlog-log-slower-than` 阈值的命令时,就会将该命令记录在慢查询日志(slow log)中,这点和 MySQL 记录慢查询语句类似。当慢查询日志超过设定的最大记录条数之后,Redis 会把最早的执行命令依次舍弃。
-
-⚠️注意:由于慢查询日志会占用一定内存空间,如果设置最大记录条数过大,可能会导致内存占用过高的问题。
-
-`slowlog-log-slower-than` 和 `slowlog-max-len` 的默认配置如下(可以自行修改):
-
-```properties
-# The following time is expressed in microseconds, so 1000000 is equivalent
-# to one second. Note that a negative number disables the slow log, while
-# a value of zero forces the logging of every command.
-slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
-
-# There is no limit to this length. Just be aware that it will consume memory.
-# You can reclaim memory used by the slow log with SLOWLOG RESET.
-slowlog-max-len 128
-```
-
-除了修改配置文件之外,你也可以直接通过 `CONFIG` 命令直接设置:
-
-```bash
-# 命令执行耗时超过 10000 微妙(即10毫秒)就会被记录
-CONFIG SET slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
-# 只保留最近 128 条耗时命令
-CONFIG SET slowlog-max-len 128
-```
-
-获取慢查询日志的内容很简单,直接使用 `SLOWLOG GET` 命令即可。
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG GET #慢日志查询
- 1) 1) (integer) 5
- 2) (integer) 1684326682
- 3) (integer) 12000
- 4) 1) "KEYS"
- 2) "*"
- 5) "172.17.0.1:61152"
- 6) ""
- // ...
-```
-
-慢查询日志中的每个条目都由以下六个值组成:
-
-1. 唯一渐进的日志标识符。
-2. 处理记录命令的 Unix 时间戳。
-3. 执行所需的时间量,以微秒为单位。
-4. 组成命令参数的数组。
-5. 客户端 IP 地址和端口。
-6. 客户端名称。
-
-`SLOWLOG GET` 命令默认返回最近 10 条的的慢查询命令,你也自己可以指定返回的慢查询命令的数量 `SLOWLOG GET N`。
-
-下面是其他比较常用的慢查询相关的命令:
-
-```bash
-# 返回慢查询命令的数量
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG LEN
-(integer) 128
-# 清空慢查询命令
-127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG RESET
-OK
-```
-
-### Redis 内存碎片
-
-**相关问题**:
-
-1. 什么是内存碎片?为什么会有 Redis 内存碎片?
-2. 如何清理 Redis 内存碎片?
-
-**参考答案**:[Redis 内存碎片详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-memory-fragmentation.html)。
-
-## Redis 生产问题(重要)
-
-### 缓存穿透
-
-#### 什么是缓存穿透?
-
-缓存穿透说简单点就是大量请求的 key 是不合理的,**根本不存在于缓存中,也不存在于数据库中**。这就导致这些请求直接到了数据库上,根本没有经过缓存这一层,对数据库造成了巨大的压力,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-
-
-举个例子:某个黑客故意制造一些非法的 key 发起大量请求,导致大量请求落到数据库,结果数据库上也没有查到对应的数据。也就是说这些请求最终都落到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-最基本的就是首先做好参数校验,一些不合法的参数请求直接抛出异常信息返回给客户端。比如查询的数据库 id 不能小于 0、传入的邮箱格式不对的时候直接返回错误消息给客户端等等。
-
-**1)缓存无效 key**
-
-如果缓存和数据库都查不到某个 key 的数据,就写一个到 Redis 中去并设置过期时间,具体命令如下:`SET key value EX 10086`。这种方式可以解决请求的 key 变化不频繁的情况,如果黑客恶意攻击,每次构建不同的请求 key,会导致 Redis 中缓存大量无效的 key。很明显,这种方案并不能从根本上解决此问题。如果非要用这种方式来解决穿透问题的话,尽量将无效的 key 的过期时间设置短一点,比如 1 分钟。
-
-另外,这里多说一嘴,一般情况下我们是这样设计 key 的:`表名:列名:主键名:主键值`。
-
-如果用 Java 代码展示的话,差不多是下面这样的:
-
-```java
-public Object getObjectInclNullById(Integer id) {
- // 从缓存中获取数据
- Object cacheValue = cache.get(id);
- // 缓存为空
- if (cacheValue == null) {
- // 从数据库中获取
- Object storageValue = storage.get(key);
- // 缓存空对象
- cache.set(key, storageValue);
- // 如果存储数据为空,需要设置一个过期时间(300秒)
- if (storageValue == null) {
- // 必须设置过期时间,否则有被攻击的风险
- cache.expire(key, 60 * 5);
- }
- return storageValue;
- }
- return cacheValue;
-}
-```
-
-**2)布隆过滤器**
-
-布隆过滤器是一个非常神奇的数据结构,通过它我们可以非常方便地判断一个给定数据是否存在于海量数据中。我们可以把它看作由二进制向量(或者说位数组)和一系列随机映射函数(哈希函数)两部分组成的数据结构。相比于我们平时常用的 List、Map、Set 等数据结构,它占用空间更少并且效率更高,但是缺点是其返回的结果是概率性的,而不是非常准确的。理论情况下添加到集合中的元素越多,误报的可能性就越大。并且,存放在布隆过滤器的数据不容易删除。
-
-
-
-Bloom Filter 会使用一个较大的 bit 数组来保存所有的数据,数组中的每个元素都只占用 1 bit ,并且每个元素只能是 0 或者 1(代表 false 或者 true),这也是 Bloom Filter 节省内存的核心所在。这样来算的话,申请一个 100w 个元素的位数组只占用 1000000Bit / 8 = 125000 Byte = 125000/1024 KB ≈ 122KB 的空间。
-
-
-
-具体是这样做的:把所有可能存在的请求的值都存放在布隆过滤器中,当用户请求过来,先判断用户发来的请求的值是否存在于布隆过滤器中。不存在的话,直接返回请求参数错误信息给客户端,存在的话才会走下面的流程。
-
-加入布隆过滤器之后的缓存处理流程图如下:
-
-
-
-更多关于布隆过滤器的详细介绍可以看看我的这篇原创:[不了解布隆过滤器?一文给你整的明明白白!](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/bloom-filter.html),强烈推荐。
-
-**3)接口限流**
-
-根据用户或者 IP 对接口进行限流,对于异常频繁的访问行为,还可以采取黑名单机制,例如将异常 IP 列入黑名单。
-
-后面提到的缓存击穿和雪崩都可以配合接口限流来解决,毕竟这些问题的关键都是有很多请求落到了数据库上造成数据库压力过大。
-
-限流的具体方案可以参考这篇文章:[服务限流详解](https://javaguide.cn/high-availability/limit-request.html)。
-
-### 缓存击穿
-
-#### 什么是缓存击穿?
-
-缓存击穿中,请求的 key 对应的是 **热点数据**,该数据 **存在于数据库中,但不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)**。这就可能会导致瞬时大量的请求直接打到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-
-
-举个例子:秒杀进行过程中,缓存中的某个秒杀商品的数据突然过期,这就导致瞬时大量对该商品的请求直接落到数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-1. **永不过期**(不推荐):设置热点数据永不过期或者过期时间比较长。
-2. **提前预热**(推荐):针对热点数据提前预热,将其存入缓存中并设置合理的过期时间比如秒杀场景下的数据在秒杀结束之前不过期。
-3. **加锁**(看情况):在缓存失效后,通过设置互斥锁确保只有一个请求去查询数据库并更新缓存。
-
-#### 缓存穿透和缓存击穿有什么区别?
-
-缓存穿透中,请求的 key 既不存在于缓存中,也不存在于数据库中。
-
-缓存击穿中,请求的 key 对应的是 **热点数据** ,该数据 **存在于数据库中,但不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)** 。
-
-### 缓存雪崩
-
-#### 什么是缓存雪崩?
-
-我发现缓存雪崩这名字起的有点意思,哈哈。
-
-实际上,缓存雪崩描述的就是这样一个简单的场景:**缓存在同一时间大面积的失效,导致大量的请求都直接落到了数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。** 这就好比雪崩一样,摧枯拉朽之势,数据库的压力可想而知,可能直接就被这么多请求弄宕机了。
-
-另外,缓存服务宕机也会导致缓存雪崩现象,导致所有的请求都落到了数据库上。
-
-
-
-举个例子:缓存中的大量数据在同一时间过期,这个时候突然有大量的请求需要访问这些过期的数据。这就导致大量的请求直接落到数据库上,对数据库造成了巨大的压力。
-
-#### 有哪些解决办法?
-
-**针对 Redis 服务不可用的情况**:
-
-1. **Redis 集群**:采用 Redis 集群,避免单机出现问题整个缓存服务都没办法使用。Redis Cluster 和 Redis Sentinel 是两种最常用的 Redis 集群实现方案,详细介绍可以参考:[Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html)。
-2. **多级缓存**:设置多级缓存,例如本地缓存+Redis 缓存的二级缓存组合,当 Redis 缓存出现问题时,还可以从本地缓存中获取到部分数据。
-
-**针对大量缓存同时失效的情况**:
-
-1. **设置随机失效时间**(可选):为缓存设置随机的失效时间,例如在固定过期时间的基础上加上一个随机值,这样可以避免大量缓存同时到期,从而减少缓存雪崩的风险。
-2. **提前预热**(推荐):针对热点数据提前预热,将其存入缓存中并设置合理的过期时间,比如秒杀场景下的数据在秒杀结束之前不过期。
-3. **持久缓存策略**(看情况):虽然一般不推荐设置缓存永不过期,但对于某些关键性和变化不频繁的数据,可以考虑这种策略。
-
-#### 缓存预热如何实现?
-
-常见的缓存预热方式有两种:
-
-1. 使用定时任务,比如 xxl-job,来定时触发缓存预热的逻辑,将数据库中的热点数据查询出来并存入缓存中。
-2. 使用消息队列,比如 Kafka,来异步地进行缓存预热,将数据库中的热点数据的主键或者 ID 发送到消息队列中,然后由缓存服务消费消息队列中的数据,根据主键或者 ID 查询数据库并更新缓存。
-
-#### 缓存雪崩和缓存击穿有什么区别?
-
-缓存雪崩和缓存击穿比较像,但缓存雪崩导致的原因是缓存中的大量或者所有数据失效,缓存击穿导致的原因主要是某个热点数据不存在于缓存中(通常是因为缓存中的那份数据已经过期)。
-
-### 如何保证缓存和数据库数据的一致性?
-
-细说的话可以扯很多,但是我觉得其实没太大必要(小声 BB:很多解决方案我也没太弄明白)。我个人觉得引入缓存之后,如果为了短时间的不一致性问题,选择让系统设计变得更加复杂的话,完全没必要。
-
-下面单独对 **Cache Aside Pattern(旁路缓存模式)** 来聊聊。
-
-Cache Aside Pattern 中遇到写请求是这样的:更新数据库,然后直接删除缓存。
-
-如果更新数据库成功,而删除缓存这一步失败的情况的话,简单说有两个解决方案:
-
-1. **缓存失效时间变短**(不推荐,治标不治本):我们让缓存数据的过期时间变短,这样的话缓存就会从数据库中加载数据。另外,这种解决办法对于先操作缓存后操作数据库的场景不适用。
-2. **增加缓存更新重试机制**(常用):如果缓存服务当前不可用导致缓存删除失败的话,我们就隔一段时间进行重试,重试次数可以自己定。不过,这里更适合引入消息队列实现异步重试,将删除缓存重试的消息投递到消息队列,然后由专门的消费者来重试,直到成功。虽然说多引入了一个消息队列,但其整体带来的收益还是要更高一些。
-
-相关文章推荐:[缓存和数据库一致性问题,看这篇就够了 - 水滴与银弹](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIyOTYxNDI5OA==&mid=2247487312&idx=1&sn=fa19566f5729d6598155b5c676eee62d&chksm=e8beb8e5dfc931f3e35655da9da0b61c79f2843101c130cf38996446975014f958a6481aacf1&scene=178&cur_album_id=1699766580538032128#rd)。
-
-### 哪些情况可能会导致 Redis 阻塞?
-
-单独抽了一篇文章来总结可能会导致 Redis 阻塞的情况:[Redis 常见阻塞原因总结](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-common-blocking-problems-summary.html)。
-
-## Redis 集群
-
-**Redis Sentinel**:
-
-1. 什么是 Sentinel? 有什么用?
-2. Sentinel 如何检测节点是否下线?主观下线与客观下线的区别?
-3. Sentinel 是如何实现故障转移的?
-4. 为什么建议部署多个 sentinel 节点(哨兵集群)?
-5. Sentinel 如何选择出新的 master(选举机制)?
-6. 如何从 Sentinel 集群中选择出 Leader?
-7. Sentinel 可以防止脑裂吗?
-
-**Redis Cluster**:
-
-1. 为什么需要 Redis Cluster?解决了什么问题?有什么优势?
-2. Redis Cluster 是如何分片的?
-3. 为什么 Redis Cluster 的哈希槽是 16384 个?
-4. 如何确定给定 key 的应该分布到哪个哈希槽中?
-5. Redis Cluster 支持重新分配哈希槽吗?
-6. Redis Cluster 扩容缩容期间可以提供服务吗?
-7. Redis Cluster 中的节点是怎么进行通信的?
-
-**参考答案**:[Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html)。
-
-## Redis 使用规范
-
-实际使用 Redis 的过程中,我们尽量要准守一些常见的规范,比如:
-
-1. 使用连接池:避免频繁创建关闭客户端连接。
-2. 尽量不使用 O(n) 指令,使用 O(n) 命令时要关注 n 的数量:像 `KEYS *`、`HGETALL`、`LRANGE`、`SMEMBERS`、`SINTER`/`SUNION`/`SDIFF` 等 O(n) 命令并非不能使用,但是需要明确 n 的值。另外,有遍历的需求可以使用 `HSCAN`、`SSCAN`、`ZSCAN` 代替。
-3. 使用批量操作减少网络传输:原生批量操作命令(比如 `MGET`、`MSET` 等等)、pipeline、Lua 脚本。
-4. 尽量不使用 Redis 事务:Redis 事务实现的功能比较鸡肋,可以使用 Lua 脚本代替。
-5. 禁止长时间开启 monitor:对性能影响比较大。
-6. 控制 key 的生命周期:避免 Redis 中存放了太多不经常被访问的数据。
-7. ……
-
-相关文章推荐:[阿里云 Redis 开发规范](https://developer.aliyun.com/article/531067)。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《Redis 开发与运维》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-- Redis Transactions:
-- What is Redis Pipeline:
-- 一文详解 Redis 中 BigKey、HotKey 的发现与处理:
-- Bigkey 问题的解决思路与方式探索:
-- Redis 延迟问题全面排障指南:
-
-
+Redis transactions are different from what we usually understand as transactions in relational databases. We know that transactions have four major characteristics: **1. Atomicity**, **2. Isolation**, **3. Durability**,
diff --git a/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md b/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
index 1194f736374..e62a788c1c3 100644
--- a/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
+++ b/docs/database/redis/redis-skiplist.md
@@ -1,28 +1,27 @@
---
-title: Redis为什么用跳表实现有序集合
-category: 数据库
+title: Why Redis Uses Skip Lists to Implement Sorted Sets
+category: Database
tag:
- Redis
---
-## 前言
+## Introduction
-近几年针对 Redis 面试时会涉及常见数据结构的底层设计,其中就有这么一道比较有意思的面试题:“Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+树?”。
+In recent years, common data structure design questions have been frequently asked in Redis interviews. One interesting interview question is: "Why does Redis use skip lists for its sorted sets instead of balanced trees, red-black trees, or B+ trees?"
-本文就以这道大厂常问的面试题为切入点,带大家详细了解一下跳表这个数据结构。
+This article will use this commonly asked interview question as a starting point to provide a detailed understanding of the skip list data structure.
-本文整体脉络如下图所示,笔者会从有序集合的基本使用到跳表的源码分析和实现,让你会对 Redis 的有序集合底层实现的跳表有着更深刻的理解和掌握。
+The overall structure of this article is illustrated in the following diagram. I will guide you from the basic usage of sorted sets to the source code analysis and implementation of skip lists, giving you a deeper understanding and mastery of the skip list used in the underlying implementation of Redis's sorted sets.

-## 跳表在 Redis 中的运用
+## The Use of Skip Lists in Redis
-这里我们需要先了解一下 Redis 用到跳表的数据结构有序集合的使用,Redis 有个比较常用的数据结构叫**有序集合(sorted set,简称 zset)**,正如其名它是一个可以保证有序且元素唯一的集合,所以它经常用于排行榜等需要进行统计排列的场景。
+First, we need to understand the usage of the skip list data structure in Redis's sorted sets. Redis has a commonly used data structure called **sorted set (zset)**. As the name suggests, it is a collection that guarantees order and uniqueness of elements, making it frequently used in scenarios like leaderboards that require statistical ranking.
-这里我们通过命令行的形式演示一下排行榜的实现,可以看到笔者分别输入 3 名用户:**xiaoming**、**xiaohong**、**xiaowang**,它们的**score**分别是 60、80、60,最终按照成绩升级降序排列。
+Here, we will demonstrate the implementation of a leaderboard using command line. We can see that I entered three users: **xiaoming**, **xiaohong**, and **xiaowang**, with their **scores** being 60, 80, and 60, respectively, and they are finally ranked in descending order of their scores.
```bash
-
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 60 xiaoming
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 80 xiaohong
@@ -30,7 +29,7 @@ tag:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 60 xiaowang
(integer) 1
-# 返回有序集中指定区间内的成员,通过索引,分数从高到低
+# Return members in the specified range of the sorted set, indexed, with scores from high to low
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGE rankList 0 100 WITHSCORES
1) "xiaohong"
2) "80"
@@ -40,734 +39,42 @@ tag:
6) "60"
```
-此时我们通过 `object` 指令查看 zset 的数据结构,可以看到当前有序集合存储的还是**ziplist(压缩列表)**。
+At this point, we can check the data structure of the zset using the `object` command, and we can see that the current sorted set is still stored as a **ziplist**.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding rankList
"ziplist"
```
-因为设计者考虑到 Redis 数据存放于内存,为了节约宝贵的内存空间,在有序集合元素小于 64 字节且个数小于 128 的时候,会使用 ziplist,而这个阈值的默认值的设置就来自下面这两个配置项。
+The designer considered that Redis stores data in memory, and to save precious memory space, when the number of elements in the sorted set is less than 128 and each element is less than 64 bytes, it will use a ziplist. The default threshold for this setting comes from the following two configuration items.
```bash
zset-max-ziplist-value 64
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128
```
-一旦有序集合中的某个元素超出这两个其中的一个阈值它就会转为 **skiplist**(实际是 dict+skiplist,还会借用字典来提高获取指定元素的效率)。
+Once an element in the sorted set exceeds one of these two thresholds, it will switch to a **skiplist** (actually a dict + skiplist, which also uses a dictionary to improve the efficiency of retrieving specific elements).
-我们不妨在添加一个大于 64 字节的元素,可以看到有序集合的底层存储转为 skiplist。
+Let's add an element greater than 64 bytes and see that the underlying storage of the sorted set switches to a skiplist.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd rankList 90 yigemingzihuichaoguo64zijiedeyonghumingchengyongyuceshitiaobiaodeshijiyunyong
(integer) 1
-# 超过阈值,转为跳表
+# Exceeds the threshold, switches to skiplist
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding rankList
"skiplist"
```
-也就是说,ZSet 有两种不同的实现,分别是 ziplist 和 skiplist,具体使用哪种结构进行存储的规则如下:
-
-- 当有序集合对象同时满足以下两个条件时,使用 ziplist:
- 1. ZSet 保存的键值对数量少于 128 个;
- 2. 每个元素的长度小于 64 字节。
-- 如果不满足上述两个条件,那么使用 skiplist 。
-
-## 手写一个跳表
-
-为了更好的回答上述问题以及更好的理解和掌握跳表,这里可以通过手写一个简单的跳表的形式来帮助读者理解跳表这个数据结构。
-
-我们都知道有序链表在添加、查询、删除的平均时间复杂都都是 **O(n)** 即线性增长,所以一旦节点数量达到一定体量后其性能表现就会非常差劲。而跳表我们完全可以理解为在原始链表基础上,建立多级索引,通过多级索引检索定位将增删改查的时间复杂度变为 **O(log n)** 。
-
-可能这里说的有些抽象,我们举个例子,以下图跳表为例,其原始链表存储按序存储 1-10,有 2 级索引,每级索引的索引个数都是基于下层元素个数的一半。
-
-
-
-假如我们需要查询元素 6,其工作流程如下:
-
-1. 从 2 级索引开始,先来到节点 4。
-2. 查看 4 的后继节点,是 8 的 2 级索引,这个值大于 6,说明 2 级索引后续的索引都是大于 6 的,没有再往后搜寻的必要,我们索引向下查找。
-3. 来到 4 的 1 级索引,比对其后继节点为 6,查找结束。
-
-相较于原始有序链表需要 6 次,我们的跳表通过建立多级索引,我们只需两次就直接定位到了目标元素,其查寻的复杂度被直接优化为**O(log n)**。
-
-
-
-对应的添加也是一个道理,假如我们需要在这个有序集合中添加一个元素 7,那么我们就需要通过跳表找到**小于元素 7 的最大值**,也就是下图元素 6 的位置,将其插入到元素 6 的后面,让元素 6 的索引指向新插入的节点 7,其工作流程如下:
-
-1. 从 2 级索引开始定位到了元素 4 的索引。
-2. 查看索引 4 的后继索引为 8,索引向下推进。
-3. 来到 1 级索引,发现索引 4 后继索引为 6,小于插入元素 7,指针推进到索引 6 位置。
-4. 继续比较 6 的后继节点为索引 8,大于元素 7,索引继续向下。
-5. 最终我们来到 6 的原始节点,发现其后继节点为 7,指针没有继续向下的空间,自此我们可知元素 6 就是小于插入元素 7 的最大值,于是便将元素 7 插入。
-
-
-
-这里我们又面临一个问题,我们是否需要为元素 7 建立索引,索引多高合适?
-
-我们上文提到,理想情况是每一层索引是下一层元素个数的二分之一,假设我们的总共有 16 个元素,对应各级索引元素个数应该是:
-
-```bash
-1. 一级索引:16/2=8
-2. 二级索引:8/2 =4
-3. 三级索引:4/2=2
-```
-
-由此我们用数学归纳法可知:
-
-```bash
-1. 一级索引:16/2=16/2^1=8
-2. 二级索引:8/2 => 16/2^2 =4
-3. 三级索引:4/2=>16/2^3=2
-```
-
-假设元素个数为 n,那么对应 k 层索引的元素个数 r 计算公式为:
-
-```bash
-r=n/2^k
-```
-
-同理我们再来推断以下索引的最大高度,一般来说最高级索引的元素个数为 2,我们设元素总个数为 n,索引高度为 h,代入上述公式可得:
-
-```bash
-2= n/2^h
-=> 2*2^h=n
-=> 2^(h+1)=n
-=> h+1=log2^n
-=> h=log2^n -1
-```
-
-而 Redis 又是内存数据库,我们假设元素最大个数是**65536**,我们把**65536**代入上述公式可知最大高度为 16。所以我们建议添加一个元素后为其建立的索引高度不超过 16。
-
-因为我们要求尽可能保证每一个上级索引都是下级索引的一半,在实现高度生成算法时,我们可以这样设计:
-
-1. 跳表的高度计算从原始链表开始,即默认情况下插入的元素的高度为 1,代表没有索引,只有元素节点。
-2. 设计一个为插入元素生成节点索引高度 level 的方法。
-3. 进行一次随机运算,随机数值范围为 0-1 之间。
-4. 如果随机数大于 0.5 则为当前元素添加一级索引,自此我们保证生成一级索引的概率为 **50%** ,这也就保证了 1 级索引理想情况下只有一半的元素会生成索引。
-5. 同理后续每次随机算法得到的值大于 0.5 时,我们的索引高度就加 1,这样就可以保证节点生成的 2 级索引概率为 **25%** ,3 级索引为 **12.5%** ……
-
-我们回过头,上述插入 7 之后,我们通过随机算法得到 2,即要为其建立 1 级索引:
-
-
-
-最后我们再来说说删除,假设我们这里要删除元素 10,我们必须定位到当前跳表**各层**元素小于 10 的最大值,索引执行步骤为:
-
-1. 2 级索引 4 的后继节点为 8,指针推进。
-2. 索引 8 无后继节点,该层无要删除的元素,指针直接向下。
-3. 1 级索引 8 后继节点为 10,说明 1 级索引 8 在进行删除时需要将自己的指针和 1 级索引 10 断开联系,将 10 删除。
-4. 1 级索引完成定位后,指针向下,后继节点为 9,指针推进。
-5. 9 的后继节点为 10,同理需要让其指向 null,将 10 删除。
-
-
-
-### 模板定义
-
-有了整体的思路之后,我们可以开始实现一个跳表了,首先定义一下跳表中的节点**Node**,从上文的演示中可以看出每一个**Node**它都包含以下几个元素:
-
-1. 存储的**value**值。
-2. 后继节点的地址。
-3. 多级索引。
-
-为了更方便统一管理**Node**后继节点地址和多级索引指向的元素地址,笔者在**Node**中设置了一个**forwards**数组,用于记录原始链表节点的后继节点和多级索引的后继节点指向。
-
-以下图为例,我们**forwards**数组长度为 5,其中**索引 0**记录的是原始链表节点的后继节点地址,而其余自底向上表示从 1 级索引到 4 级索引的后继节点指向。
-
-
-
-于是我们的就有了这样一个代码定义,可以看出笔者对于数组的长度设置为固定的 16**(上文的推算最大高度建议是 16)**,默认**data**为-1,节点最大高度**maxLevel**初始化为 1,注意这个**maxLevel**的值代表原始链表加上索引的总高度。
-
-```java
-/**
- * 跳表索引最大高度为16
- */
-private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
-
-class Node {
- private int data = -1;
- private Node[] forwards = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
- private int maxLevel = 0;
-
-}
-```
-
-### 元素添加
-
-定义好节点之后,我们先实现以下元素的添加,添加元素时首先自然是设置**data**这一步我们直接根据将传入的**value**设置到**data**上即可。
-
-然后就是高度**maxLevel**的设置 ,我们在上文也已经给出了思路,默认高度为 1,即只有一个原始链表节点,通过随机算法每次大于 0.5 索引高度加 1,由此我们得出高度计算的算法`randomLevel()`:
-
-```java
-/**
- * 理论来讲,一级索引中元素个数应该占原始数据的 50%,二级索引中元素个数占 25%,三级索引12.5% ,一直到最顶层。
- * 因为这里每一层的晋升概率是 50%。对于每一个新插入的节点,都需要调用 randomLevel 生成一个合理的层数。
- * 该 randomLevel 方法会随机生成 1~MAX_LEVEL 之间的数,且 :
- * 50%的概率返回 1
- * 25%的概率返回 2
- * 12.5%的概率返回 3 ...
- * @return
- */
-private int randomLevel() {
- int level = 1;
- while (Math.random() > PROB && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
- ++level;
- }
- return level;
-}
-```
-
-然后再设置当前要插入的**Node**和**Node**索引的后继节点地址,这一步稍微复杂一点,我们假设当前节点的高度为 4,即 1 个节点加 3 个索引,所以我们创建一个长度为 4 的数组**maxOfMinArr** ,遍历各级索引节点中小于当前**value**的最大值。
-
-假设我们要插入的**value**为 5,我们的数组查找结果当前节点的前驱节点和 1 级索引、2 级索引的前驱节点都为 4,三级索引为空。
-
-
-
-然后我们基于这个数组**maxOfMinArr** 定位到各级的后继节点,让插入的元素 5 指向这些后继节点,而**maxOfMinArr**指向 5,结果如下图:
-
-
-
-转化成代码就是下面这个形式,是不是很简单呢?我们继续:
-
-```java
-/**
- * 默认情况下的高度为1,即只有自己一个节点
- */
-private int levelCount = 1;
-
-/**
- * 跳表最底层的节点,即头节点
- */
-private Node h = new Node();
-
-public void add(int value) {
-
- //随机生成高度
- int level = randomLevel();
-
- Node newNode = new Node();
- newNode.data = value;
- newNode.maxLevel = level;
-
- //创建一个node数组,用于记录小于当前value的最大值
- Node[] maxOfMinArr = new Node[level];
- //默认情况下指向头节点
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- maxOfMinArr[i] = h;
- }
-
- //基于上述结果拿到当前节点的后继节点
- Node p = h;
- for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- maxOfMinArr[i] = p;
- }
-
- //更新前驱节点的后继节点为当前节点newNode
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- newNode.forwards[i] = maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i];
- maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
- }
-
- //如果当前newNode高度大于跳表最高高度则更新levelCount
- if (levelCount < level) {
- levelCount = level;
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-### 元素查询
-
-查询逻辑比较简单,从跳表最高级的索引开始定位找到小于要查的 value 的最大值,以下图为例,我们希望查找到节点 8:
-
-1. 跳表的 3 级索引首先找找到 5 的索引,5 的 3 级索引 **forwards[3]** 指向空,索引直接向下。
-2. 来到 5 的 2 级索引,其后继 **forwards[2]** 指向 8,继续向下。
-3. 5 的 1 级索引 **forwards[1]** 指向索引 6,继续向前。
-4. 索引 6 的 **forwards[1]** 指向索引 8,继续向下。
-5. 我们在原始节点向前找到节点 7。
-6. 节点 7 后续就是节点 8,继续向前为节点 8,无法继续向下,结束搜寻。
-7. 判断 7 的前驱,等于 8,查找结束。
-
-
-
-所以我们的代码实现也很上述步骤差不多,从最高级索引开始向前查找,如果不为空且小于要查找的值,则继续向前搜寻,遇到不小于的节点则继续向下,如此往复,直到得到当前跳表中小于查找值的最大节点,查看其前驱是否等于要查找的值:
-
-```java
-public Node get(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到小于value的最大值
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- }
- //如果p的前驱节点等于value则直接返回
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- return p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- return null;
-}
-```
-
-### 元素删除
-
-最后是删除逻辑,需要查找各层级小于要删除节点的最大值,假设我们要删除 10:
-
-1. 3 级索引得到小于 10 的最大值为 5,继续向下。
-2. 2 级索引从索引 5 开始查找,发现小于 10 的最大值为 8,继续向下。
-3. 同理 1 级索引得到 8,继续向下。
-4. 原始节点找到 9。
-5. 从最高级索引开始,查看每个小于 10 的节点后继节点是否为 10,如果等于 10,则让这个节点指向 10 的后继节点,将节点 10 及其索引交由 GC 回收。
-
-
-
-```java
-/**
- * 删除
- *
- * @param value
- */
-public void delete(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到各级节点小于value的最大值
- Node[] updateArr = new Node[levelCount];
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- updateArr[i] = p;
- }
- //查看原始层节点前驱是否等于value,若等于则说明存在要删除的值
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- //从最高级索引开始查看其前驱是否等于value,若等于则将当前节点指向value节点的后继节点
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (updateArr[i].forwards[i] != null && updateArr[i].forwards[i].data == value) {
- updateArr[i].forwards[i] = updateArr[i].forwards[i].forwards[i];
- }
- }
- }
-
- //从最高级开始查看是否有一级索引为空,若为空则层级减1
- while (levelCount > 1 && h.forwards[levelCount - 1] == null) {
- levelCount--;
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-### 完整代码以及测试
-
-完整代码如下,读者可自行参阅:
-
-```java
-public class SkipList {
-
- /**
- * 跳表索引最大高度为16
- */
- private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
-
- /**
- * 每个节点添加一层索引高度的概率为二分之一
- */
- private static final float PROB = 0.5 f;
-
- /**
- * 默认情况下的高度为1,即只有自己一个节点
- */
- private int levelCount = 1;
-
- /**
- * 跳表最底层的节点,即头节点
- */
- private Node h = new Node();
-
- public SkipList() {}
-
- public class Node {
- private int data = -1;
- /**
- *
- */
- private Node[] forwards = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
- private int maxLevel = 0;
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Node{" +
- "data=" + data +
- ", maxLevel=" + maxLevel +
- '}';
- }
- }
-
- public void add(int value) {
-
- //随机生成高度
- int level = randomLevel();
-
- Node newNode = new Node();
- newNode.data = value;
- newNode.maxLevel = level;
-
- //创建一个node数组,用于记录小于当前value的最大值
- Node[] maxOfMinArr = new Node[level];
- //默认情况下指向头节点
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- maxOfMinArr[i] = h;
- }
-
- //基于上述结果拿到当前节点的后继节点
- Node p = h;
- for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- maxOfMinArr[i] = p;
- }
-
- //更新前驱节点的后继节点为当前节点newNode
- for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
- newNode.forwards[i] = maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i];
- maxOfMinArr[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
- }
-
- //如果当前newNode高度大于跳表最高高度则更新levelCount
- if (levelCount < level) {
- levelCount = level;
- }
-
- }
-
- /**
- * 理论来讲,一级索引中元素个数应该占原始数据的 50%,二级索引中元素个数占 25%,三级索引12.5% ,一直到最顶层。
- * 因为这里每一层的晋升概率是 50%。对于每一个新插入的节点,都需要调用 randomLevel 生成一个合理的层数。
- * 该 randomLevel 方法会随机生成 1~MAX_LEVEL 之间的数,且 :
- * 50%的概率返回 1
- * 25%的概率返回 2
- * 12.5%的概率返回 3 ...
- * @return
- */
- private int randomLevel() {
- int level = 1;
- while (Math.random() > PROB && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
- ++level;
- }
- return level;
- }
-
- public Node get(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到小于value的最大值
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- }
- //如果p的前驱节点等于value则直接返回
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- return p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- return null;
- }
-
- /**
- * 删除
- *
- * @param value
- */
- public void delete(int value) {
- Node p = h;
- //找到各级节点小于value的最大值
- Node[] updateArr = new Node[levelCount];
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
- p = p.forwards[i];
- }
- updateArr[i] = p;
- }
- //查看原始层节点前驱是否等于value,若等于则说明存在要删除的值
- if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
- //从最高级索引开始查看其前驱是否等于value,若等于则将当前节点指向value节点的后继节点
- for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (updateArr[i].forwards[i] != null && updateArr[i].forwards[i].data == value) {
- updateArr[i].forwards[i] = updateArr[i].forwards[i].forwards[i];
- }
- }
- }
-
- //从最高级开始查看是否有一级索引为空,若为空则层级减1
- while (levelCount > 1 && h.forwards[levelCount - 1] == null) {
- levelCount--;
- }
-
- }
-
- public void printAll() {
- Node p = h;
- //基于最底层的非索引层进行遍历,只要后继节点不为空,则速速出当前节点,并移动到后继节点
- while (p.forwards[0] != null) {
- System.out.println(p.forwards[0]);
- p = p.forwards[0];
- }
-
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-对应测试代码和输出结果如下:
-
-```java
-public static void main(String[] args) {
- SkipList skipList = new SkipList();
- for (int i = 0; i < 24; i++) {
- skipList.add(i);
- }
-
- System.out.println("**********输出添加结果**********");
- skipList.printAll();
-
- SkipList.Node node = skipList.get(22);
- System.out.println("**********查询结果:" + node+" **********");
-
- skipList.delete(22);
- System.out.println("**********删除结果**********");
- skipList.printAll();
-
-
- }
-```
-
-输出结果:
-
-```bash
-**********输出添加结果**********
-Node{data=0, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=1, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=2, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=3, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=4, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=5, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=6, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=7, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=8, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=9, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=10, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=11, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=12, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=13, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=14, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=15, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=16, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=17, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=18, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=19, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=20, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=21, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=22, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=23, maxLevel=1}
-**********查询结果:Node{data=22, maxLevel=1} **********
-**********删除结果**********
-Node{data=0, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=1, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=2, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=3, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=4, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=5, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=6, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=7, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=8, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=9, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=10, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=11, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=12, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=13, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=14, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=15, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=16, maxLevel=4}
-Node{data=17, maxLevel=2}
-Node{data=18, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=19, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=20, maxLevel=1}
-Node{data=21, maxLevel=3}
-Node{data=23, maxLevel=1}
-```
-
-**Redis 跳表的特点**:
-
-1. 采用**双向链表**,不同于上面的示例,存在一个回退指针。主要用于简化操作,例如删除某个元素时,还需要找到该元素的前驱节点,使用回退指针会非常方便。
-2. `score` 值可以重复,如果 `score` 值一样,则按照 ele(节点存储的值,为 sds)字典排序
-3. Redis 跳跃表默认允许最大的层数是 32,被源码中 `ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL` 定义。
-
-## 和其余三种数据结构的比较
-
-最后,我们再来回答一下文章开头的那道面试题: “Redis 的有序集合底层为什么要用跳表,而不用平衡树、红黑树或者 B+树?”。
-
-### 平衡树 vs 跳表
-
-先来说说它和平衡树的比较,平衡树我们又会称之为 **AVL 树**,是一个严格的平衡二叉树,平衡条件必须满足(所有节点的左右子树高度差不超过 1,即平衡因子为范围为 `[-1,1]`)。平衡树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)** 。
-
-对于范围查询来说,它也可以通过中序遍历的方式达到和跳表一样的效果。但是它的每一次插入或者删除操作都需要保证整颗树左右节点的绝对平衡,只要不平衡就要通过旋转操作来保持平衡,这个过程是比较耗时的。
-
-
-
-跳表诞生的初衷就是为了克服平衡树的一些缺点,跳表的发明者在论文[《Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees》](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2018/papers/08-oltpindexes1/pugh-skiplists-cacm1990.pdf)中有详细提到:
-
-
-
-> Skip lists are a data structure that can be used in place of balanced trees. Skip lists use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing and as a result the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
->
-> 跳表是一种可以用来代替平衡树的数据结构。跳表使用概率平衡而不是严格强制的平衡,因此,跳表中的插入和删除算法比平衡树的等效算法简单得多,速度也快得多。
-
-笔者这里也贴出了 AVL 树插入操作的核心代码,可以看出每一次添加操作都需要进行一次递归定位插入位置,然后还需要根据回溯到根节点检查沿途的各层节点是否失衡,再通过旋转节点的方式进行调整。
-
-```java
-// 向二分搜索树中添加新的元素(key, value)
-public void add(K key, V value) {
- root = add(root, key, value);
-}
-
-// 向以node为根的二分搜索树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法
-// 返回插入新节点后二分搜索树的根
-private Node add(Node node, K key, V value) {
-
- if (node == null) {
- size++;
- return new Node(key, value);
- }
-
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
- node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
- else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
- node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
- else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
- node.value = value;
-
- node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right));
-
- int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node);
-
- // LL型需要右旋
- if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
- return rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //RR型失衡需要左旋
- if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
- return leftRotate(node);
- }
-
- //LR需要先左旋成LL型,然后再右旋
- if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) < 0) {
- node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
- return rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //RL
- if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) > 0) {
- node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
- return leftRotate(node);
- }
- return node;
-}
-```
-
-### 红黑树 vs 跳表
-
-红黑树(Red Black Tree)也是一种自平衡二叉查找树,它的查询性能略微逊色于 AVL 树,但插入和删除效率更高。红黑树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 **O(log n)** 。
-
-红黑树是一个**黑平衡树**,即从任意节点到另外一个叶子叶子节点,它所经过的黑节点是一样的。当对它进行插入操作时,需要通过旋转和染色(红黑变换)来保证黑平衡。不过,相较于 AVL 树为了维持平衡的开销要小一些。关于红黑树的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章:[红黑树](https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/data-structure/red-black-tree.html)。
-
-相比较于红黑树来说,跳表的实现也更简单一些。并且,按照区间来查找数据这个操作,红黑树的效率没有跳表高。
-
-
-
-对应红黑树添加的核心代码如下,读者可自行参阅理解:
-
-```java
-private Node < K, V > add(Node < K, V > node, K key, V val) {
-
- if (node == null) {
- size++;
- return new Node(key, val);
-
- }
-
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0) {
- node.left = add(node.left, key, val);
- } else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0) {
- node.right = add(node.right, key, val);
- } else {
- node.val = val;
- }
-
- //左节点不为红,右节点为红,左旋
- if (isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)) {
- node = leftRotate(node);
- }
-
- //左链右旋
- if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)) {
- node = rightRotate(node);
- }
-
- //颜色翻转
- if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)) {
- flipColors(node);
- }
-
- return node;
-}
-```
-
-### B+树 vs 跳表
-
-想必使用 MySQL 的读者都知道 B+树这个数据结构,B+树是一种常用的数据结构,具有以下特点:
-
-1. **多叉树结构**:它是一棵多叉树,每个节点可以包含多个子节点,减小了树的高度,查询效率高。
-2. **存储效率高**:其中非叶子节点存储多个 key,叶子节点存储 value,使得每个节点更够存储更多的键,根据索引进行范围查询时查询效率更高。-
-3. **平衡性**:它是绝对的平衡,即树的各个分支高度相差不大,确保查询和插入时间复杂度为 **O(log n)** 。
-4. **顺序访问**:叶子节点间通过链表指针相连,范围查询表现出色。
-5. **数据均匀分布**:B+树插入时可能会导致数据重新分布,使得数据在整棵树分布更加均匀,保证范围查询和删除效率。
-
-
-
-所以,B+树更适合作为数据库和文件系统中常用的索引结构之一,它的核心思想是通过可能少的 IO 定位到尽可能多的索引来获得查询数据。对于 Redis 这种内存数据库来说,它对这些并不感冒,因为 Redis 作为内存数据库它不可能存储大量的数据,所以对于索引不需要通过 B+树这种方式进行维护,只需按照概率进行随机维护即可,节约内存。而且使用跳表实现 zset 时相较前者来说更简单一些,在进行插入时只需通过索引将数据插入到链表中合适的位置再随机维护一定高度的索引即可,也不需要像 B+树那样插入时发现失衡时还需要对节点分裂与合并。
-
-### Redis 作者给出的理由
-
-当然我们也可以通过 Redis 的作者自己给出的理由:
-
-> There are a few reasons:
-> 1、They are not very memory intensive. It's up to you basically. Changing parameters about the probability of a node to have a given number of levels will make then less memory intensive than btrees.
-> 2、A sorted set is often target of many ZRANGE or ZREVRANGE operations, that is, traversing the skip list as a linked list. With this operation the cache locality of skip lists is at least as good as with other kind of balanced trees.
-> 3、They are simpler to implement, debug, and so forth. For instance thanks to the skip list simplicity I received a patch (already in Redis master) with augmented skip lists implementing ZRANK in O(log(N)). It required little changes to the code.
-
-翻译过来的意思就是:
-
-> 有几个原因:
->
-> 1、它们不是很占用内存。这主要取决于你。改变节点拥有给定层数的概率的参数,会使它们比 B 树更节省内存。
->
-> 2、有序集合经常是许多 ZRANGE 或 ZREVRANGE 操作的目标,也就是说,以链表的方式遍历跳表。通过这种操作,跳表的缓存局部性至少和其他类型的平衡树一样好。
->
-> 3、它们更容易实现、调试等等。例如,由于跳表的简单性,我收到了一个补丁(已经在 Redis 主分支中),用增强的跳表实现了 O(log(N))的 ZRANK。它只需要对代码做很少的修改。
+In other words, ZSet has two different implementations: ziplist and skiplist. The specific rules for which structure to use for storage are as follows:
-## 小结
+- Use ziplist when the sorted set object meets both of the following conditions:
+ 1. The number of key-value pairs in ZSet is less than 128.
+ 1. The length of each element is less than 64 bytes.
+- If the above two conditions are not met, then use skiplist.
-本文通过大量篇幅介绍跳表的工作原理和实现,帮助读者更进一步的熟悉跳表这一数据结构的优劣,最后再结合各个数据结构操作的特点进行比对,从而帮助读者更好的理解这道面试题,建议读者实现理解跳表时,尽可能配合执笔模拟来了解跳表的增删改查详细过程。
+## Implementing a Skip List
-## 参考
+To better answer the above question and to understand and master skip lists, we can help readers understand this data structure by implementing a simple skip list.
-- 为啥 redis 使用跳表(skiplist)而不是使用 red-black?:
-- Skip List--跳表(全网最详细的跳表文章没有之一):
-- Redis 对象与底层数据结构详解:
-- Redis 有序集合(sorted set):
-- 红黑树和跳表比较:
-- 为什么 redis 的 zset 用跳跃表而不用 b+ tree?:
+We all know that the average time complexity for adding, querying, and deleting in a sorted linked list is **O(n)**, which grows linearly. Therefore, once the number of nodes reaches a certain size, its performance will be very poor. A skip list can be understood as building multiple levels of indexes on top of the original linked list, allowing for a time complexity of **O(log n)** for search, insert
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
index 4bf08f0fa0b..56510ad1b2c 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-01.md
@@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(1)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (1)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 必知必会](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=298)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Essentials](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=298)
-## 检索数据
+## Data Retrieval
-`SELECT` 用于从数据库中查询数据。
+`SELECT` is used to query data from the database.
-### 从 Customers 表中检索所有的 ID
+### Retrieve all IDs from the Customers table
-现有表 `Customers` 如下:
+The existing `Customers` table is as follows:
| cust_id |
| ------- |
@@ -22,18 +22,18 @@ tag:
| B |
| C |
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Customers` 表中检索所有的 `cust_id`。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve all `cust_id` from the `Customers` table.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_id
FROM Customers
```
-### 检索并列出已订购产品的清单
+### Retrieve and list the ordered product list
-表 `OrderItems` 含有非空的列 `prod_id` 代表商品 id,包含了所有已订购的商品(有些已被订购多次)。
+The `OrderItems` table contains a non-null column `prod_id` representing the product ID, which includes all ordered products (some may have been ordered multiple times).
| prod_id |
| ------- |
@@ -45,20 +45,20 @@ FROM Customers
| a6 |
| a7 |
-编写 SQL 语句,检索并列出所有已订购商品(`prod_id`)的去重后的清单。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve and list all distinct ordered products (`prod_id`).
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT DISTINCT prod_id
FROM OrderItems
```
-知识点:`DISTINCT` 用于返回列中的唯一不同值。
+Knowledge point: `DISTINCT` is used to return unique different values in a column.
-### 检索所有列
+### Retrieve all columns
-现在有 `Customers` 表(表中含有列 `cust_id` 代表客户 id,`cust_name` 代表客户姓名)
+Now there is a `Customers` table (which contains the column `cust_id` representing customer ID and `cust_name` representing customer name)
| cust_id | cust_name |
| ------- | --------- |
@@ -70,22 +70,22 @@ FROM OrderItems
| a6 | lee |
| a7 | hex |
-需要编写 SQL 语句,检索所有列。
+You need to write an SQL statement to retrieve all columns.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_id, cust_name
FROM Customers
```
-## 排序检索数据
+## Sorting Data Retrieval
-`ORDER BY` 用于对结果集按照一个列或者多个列进行排序。默认按照升序对记录进行排序,如果需要按照降序对记录进行排序,可以使用 `DESC` 关键字。
+`ORDER BY` is used to sort the result set by one or more columns. By default, records are sorted in ascending order; to sort records in descending order, you can use the `DESC` keyword.
-### 检索顾客名称并且排序
+### Retrieve customer names and sort
-有表 `Customers`,`cust_id` 代表客户 id,`cust_name` 代表客户姓名。
+There is a `Customers` table, where `cust_id` represents customer ID and `cust_name` represents customer name.
| cust_id | cust_name |
| ------- | --------- |
@@ -97,9 +97,9 @@ FROM Customers
| a6 | lee |
| a7 | hex |
-从 `Customers` 中检索所有的顾客名称(`cust_name`),并按从 Z 到 A 的顺序显示结果。
+Retrieve all customer names (`cust_name`) from `Customers` and display the results in descending order from Z to A.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT cust_name
@@ -107,9 +107,9 @@ FROM Customers
ORDER BY cust_name DESC
```
-### 对顾客 ID 和日期排序
+### Sort by customer ID and date
-有 `Orders` 表:
+There is an `Orders` table:
| cust_id | order_num | order_date |
| ------- | --------- | ------------------- |
@@ -118,23 +118,23 @@ ORDER BY cust_name DESC
| bob | cccc | 2021-01-10 12:00:00 |
| dick | dddd | 2021-01-11 00:00:00 |
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Orders` 表中检索顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单号(`order_num`),并先按顾客 ID 对结果进行排序,再按订单日期倒序排列。
+Write an SQL statement to retrieve customer ID (`cust_id`) and order number (`order_num`) from the `Orders` table, first sorting the results by customer ID, then sorting by order date in descending order.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
-# 根据列名排序
-# 注意:是 order_date 降序,而不是 order_num
+# Sort by column name
+# Note: order_date is in descending order, not order_num
SELECT cust_id, order_num
FROM Orders
-ORDER BY cust_id,order_date DESC
+ORDER BY cust_id, order_date DESC
```
-知识点:`order by` 对多列排序的时候,先排序的列放前面,后排序的列放后面。并且,不同的列可以有不同的排序规则。
+Knowledge point: When sorting multiple columns with `ORDER BY`, the first column to be sorted is placed first, and the subsequent columns follow. Different columns can have different sorting rules.
-### 按照数量和价格排序
+### Sort by quantity and price
-假设有一个 `OrderItems` 表:
+Assuming there is an `OrderItems` table:
| quantity | item_price |
| -------- | ---------- |
@@ -142,1687 +142,21 @@ ORDER BY cust_id,order_date DESC
| 10 | 1003 |
| 2 | 500 |
-编写 SQL 语句,显示 `OrderItems` 表中的数量(`quantity`)和价格(`item_price`),并按数量由多到少、价格由高到低排序。
+Write an SQL statement to display the quantity (`quantity`) and price (`item_price`) from the `OrderItems` table, sorted by quantity in descending order and price in descending order.
-答案:
+Answer:
```sql
SELECT quantity, item_price
FROM OrderItems
-ORDER BY quantity DESC,item_price DESC
+ORDER BY quantity DESC, item_price DESC
```
-### 检查 SQL 语句
+### Check SQL statement
-有 `Vendors` 表:
+There is a `Vendors` table:
| vend_name |
| --------- |
-| 海底捞 |
-| 小龙坎 |
-| 大龙燚 |
-
-下面的 SQL 语句有问题吗?尝试将它改正确,使之能够正确运行,并且返回结果根据`vend_name` 逆序排列。
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name,
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER vend_name DESC
-```
-
-改正后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vend_name DESC
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 逗号作用是用来隔开列与列之间的。
-- ORDER BY 是有 BY 的,需要撰写完整,且位置正确。
-
-## 过滤数据
-
-`WHERE` 可以过滤返回的数据。
-
-下面的运算符可以在 `WHERE` 子句中使用:
-
-| 运算符 | 描述 |
-| :------ | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
-| = | 等于 |
-| <> | 不等于。 **注释:** 在 SQL 的一些版本中,该操作符可被写成 != |
-| > | 大于 |
-| < | 小于 |
-| >= | 大于等于 |
-| <= | 小于等于 |
-| BETWEEN | 在某个范围内 |
-| LIKE | 搜索某种模式 |
-| IN | 指定针对某个列的多个可能值 |
-
-### 返回固定价格的产品
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | -------------- | ---------- |
-| a0018 | sockets | 9.49 |
-| a0019 | iphone13 | 600 |
-| b0018 | gucci t-shirts | 1000 |
-
-【问题】从 `Products` 表中检索产品 ID(`prod_id`)和产品名称(`prod_name`),只返回价格为 9.49 美元的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price = 9.49
-```
-
-### 返回更高价格的产品
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | -------------- | ---------- |
-| a0018 | sockets | 9.49 |
-| a0019 | iphone13 | 600 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts | 1000 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品 ID(`prod_id`)和产品名称(`prod_name`),只返回价格为 9 美元或更高的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 9
-```
-
-### 返回产品并且按照价格排序
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | --------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | egg | 3 |
-| a0019 | sockets | 4 |
-| b0019 | coffee | 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 `Products` 表中所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称(`prod_name`)和价格(`prod_price`),然后按价格对结果进行排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price BETWEEN 3 AND 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-
-# 或者
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 3 AND prod_price <= 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-```
-
-### 返回更多的产品
-
-`OrderItems` 表含有:订单号 `order_num`,`quantity`产品数量
-
-| order_num | quantity |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 200 |
-| a4 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 19 |
-| a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】从 `OrderItems` 表中检索出所有不同且不重复的订单号(`order_num`),其中每个订单都要包含 100 个或更多的产品。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING SUM(quantity) >= 100
-```
-
-## 高级数据过滤
-
-`AND` 和 `OR` 运算符用于基于一个以上的条件对记录进行过滤,两者可以结合使用。`AND` 必须 2 个条件都成立,`OR`只要 2 个条件中的一个成立即可。
-
-### 检索供应商名称
-
-`Vendors` 表有字段供应商名称(`vend_name`)、供应商国家(`vend_country`)、供应商州(`vend_state`)
-
-| vend_name | vend_country | vend_state |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- |
-| apple | USA | CA |
-| vivo | CNA | shenzhen |
-| huawei | CNA | xian |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Vendors` 表中检索供应商名称(`vend_name`),仅返回加利福尼亚州的供应商(这需要按国家[USA]和州[CA]进行过滤,没准其他国家也存在一个 CA)
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
-```
-
-### 检索并列出已订购产品的清单
-
-`OrderItems` 表包含了所有已订购的产品(有些已被订购多次)。
-
-| prod_id | order_num | quantity |
-| ------- | --------- | -------- |
-| BR01 | a1 | 105 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 1100 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 200 |
-| BR03 | a4 | 1121 |
-| BR017 | a5 | 10 |
-| BR02 | a2 | 19 |
-| BR017 | a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,查找所有订购了数量至少 100 个的 `BR01`、`BR02` 或 `BR03` 的订单。你需要返回 `OrderItems` 表的订单号(`order_num`)、产品 ID(`prod_id`)和数量(`quantity`),并按产品 ID 和数量进行过滤。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id IN ('BR01', 'BR02', 'BR03') AND quantity >= 100
-```
-
-### 返回所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称和价格
-
-有表 `Products`:
-
-| prod_id | prod_name | prod_price |
-| ------- | --------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | egg | 3 |
-| a0019 | sockets | 4 |
-| b0019 | coffee | 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回所有价格在 3 美元到 6 美元之间的产品的名称(`prod_name`)和价格(`prod_price`),使用 AND 操作符,然后按价格对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price >= 3 and prod_price <= 6
-ORDER BY prod_price
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-供应商表 `Vendors` 有字段供应商名称 `vend_name`、供应商国家 `vend_country`、供应商省份 `vend_state`
-
-| vend_name | vend_country | vend_state |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- |
-| apple | USA | CA |
-| vivo | CNA | shenzhen |
-| huawei | CNA | xian |
-
-【问题】修改正确下面 sql,使之正确返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vend_name
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA';
-```
-
-修改后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_name
-FROM Vendors
-WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
-ORDER BY vend_name
-```
-
-`ORDER BY` 语句必须放在 `WHERE` 之后。
-
-## 用通配符进行过滤
-
-SQL 通配符必须与 `LIKE` 运算符一起使用
-
-在 SQL 中,可使用以下通配符:
-
-| 通配符 | 描述 |
-| :------------------------------- | :------------------------- |
-| `%` | 代表零个或多个字符 |
-| `_` | 仅替代一个字符 |
-| `[charlist]` | 字符列中的任何单一字符 |
-| `[^charlist]` 或者 `[!charlist]` | 不在字符列中的任何单一字符 |
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(一)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | -------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中包含 `toy` 一词的产品名称。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%'
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(二)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | -------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中未出现 `toy` 一词的产品,最后按”产品名称“对结果进行排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc NOT LIKE '%toy%'
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(三)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego carrots toy |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索产品名称(`prod_name`)和描述(`prod_desc`),仅返回描述中同时出现 `toy` 和 `carrots` 的产品。有好几种方法可以执行此操作,但对于这个挑战题,请使用 `AND` 和两个 `LIKE` 比较。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%' AND prod_desc LIKE "%carrots%"
-```
-
-### 检索产品名称和描述(四)
-
-`Products` 表如下:
-
-| prod_name | prod_desc |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| a0011 | usb |
-| a0019 | iphone13 |
-| b0019 | gucci t-shirts |
-| c0019 | gucci toy |
-| d0019 | lego toy carrots |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 Products 表中检索产品名称(prod_name)和描述(prod_desc),仅返回在描述中以**先后顺序**同时出现 toy 和 carrots 的产品。提示:只需要用带有三个 `%` 符号的 `LIKE` 即可。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, prod_desc
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_desc LIKE '%toy%carrots%'
-```
-
-## 创建计算字段
-
-### 别名
-
-别名的常见用法是在检索出的结果中重命名表的列字段(为了符合特定的报表要求或客户需求)。有表 `Vendors` 代表供应商信息,`vend_id` 供应商 id、`vend_name` 供应商名称、`vend_address` 供应商地址、`vend_city` 供应商城市。
-
-| vend_id | vend_name | vend_address | vend_city |
-| ------- | ------------- | ------------ | --------- |
-| a001 | tencent cloud | address1 | shenzhen |
-| a002 | huawei cloud | address2 | dongguan |
-| a003 | aliyun cloud | address3 | hangzhou |
-| a003 | netease cloud | address4 | guangzhou |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Vendors` 表中检索 `vend_id`、`vend_name`、`vend_address` 和 `vend_city`,将 `vend_name` 重命名为 `vname`,将 `vend_city` 重命名为 `vcity`,将 `vend_address` 重命名为 `vaddress`,按供应商名称对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_id, vend_name AS vname, vend_address AS vaddress, vend_city AS vcity
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vname
-# as 可以省略
-SELECT vend_id, vend_name vname, vend_address vaddress, vend_city vcity
-FROM Vendors
-ORDER BY vname
-```
-
-### 打折
-
-我们的示例商店正在进行打折促销,所有产品均降价 10%。`Products` 表包含 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_price` 产品价格。
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中返回 `prod_id`、`prod_price` 和 `sale_price`。`sale_price` 是一个包含促销价格的计算字段。提示:可以乘以 0.9,得到原价的 90%(即 10%的折扣)。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_price, prod_price * 0.9 AS sale_price
-FROM Products
-```
-
-注意:`sale_price` 是对计算结果的命名,而不是原有的列名。
-
-## 使用函数处理数据
-
-### 顾客登录名
-
-我们的商店已经上线了,正在创建顾客账户。所有用户都需要登录名,默认登录名是其名称和所在城市的组合。
-
-给出 `Customers` 表 如下:
-
-| cust_id | cust_name | cust_contact | cust_city |
-| ------- | --------- | ------------ | --------- |
-| a1 | Andy Li | Andy Li | Oak Park |
-| a2 | Ben Liu | Ben Liu | Oak Park |
-| a3 | Tony Dai | Tony Dai | Oak Park |
-| a4 | Tom Chen | Tom Chen | Oak Park |
-| a5 | An Li | An Li | Oak Park |
-| a6 | Lee Chen | Lee Chen | Oak Park |
-| a7 | Hex Liu | Hex Liu | Oak Park |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回顾客 ID(`cust_id`)、顾客名称(`cust_name`)和登录名(`user_login`),其中登录名全部为大写字母,并由顾客联系人的前两个字符(`cust_contact`)和其所在城市的前三个字符(`cust_city`)组成。提示:需要使用函数、拼接和别名。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_id, cust_name, UPPER(CONCAT(SUBSTRING(cust_contact, 1, 2), SUBSTRING(cust_city, 1, 3))) AS user_login
-FROM Customers
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 截取函数`SUBSTRING()`:截取字符串,`substring(str ,n ,m)`(n 表示起始截取位置,m 表示要截取的字符个数)表示返回字符串 str 从第 n 个字符开始截取 m 个字符;
-- 拼接函数`CONCAT()`:将两个或多个字符串连接成一个字符串,select concat(A,B):连接字符串 A 和 B。
-
-- 大写函数 `UPPER()`:将指定字符串转换为大写。
-
-### 返回 2020 年 1 月的所有订单的订单号和订单日期
-
-`Orders` 订单表如下:
-
-| order_num | order_date |
-| --------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | 2020-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | 2020-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0003 | 2020-01-01 12:00:00 |
-| a0004 | 2020-02-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0005 | 2020-03-01 00:00:00 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 2020 年 1 月的所有订单的订单号(`order_num`)和订单日期(`order_date`),并按订单日期升序排序
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE month(order_date) = '01' AND YEAR(order_date) = '2020'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-也可以用通配符来做:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_date LIKE '2020-01%'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- 日期格式:`YYYY-MM-DD`
-- 时间格式:`HH:MM:SS`
-
-日期和时间处理相关的常用函数:
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------------- | ------------------------------ |
-| `ADDDATE()` | 增加一个日期(天、周等) |
-| `ADDTIME()` | 增加一个时间(时、分等) |
-| `CURDATE()` | 返回当前日期 |
-| `CURTIME()` | 返回当前时间 |
-| `DATE()` | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
-| `DATEDIFF` | 计算两个日期之差 |
-| `DATE_FORMAT()` | 返回一个格式化的日期或时间串 |
-| `DAY()` | 返回一个日期的天数部分 |
-| `DAYOFWEEK()` | 对于一个日期,返回对应的星期几 |
-| `HOUR()` | 返回一个时间的小时部分 |
-| `MINUTE()` | 返回一个时间的分钟部分 |
-| `MONTH()` | 返回一个日期的月份部分 |
-| `NOW()` | 返回当前日期和时间 |
-| `SECOND()` | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
-| `TIME()` | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
-| `YEAR()` | 返回一个日期的年份部分 |
-
-## 汇总数据
-
-汇总数据相关的函数:
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| `AVG()` | 返回某列的平均值 |
-| `COUNT()` | 返回某列的行数 |
-| `MAX()` | 返回某列的最大值 |
-| `MIN()` | 返回某列的最小值 |
-| `SUM()` | 返回某列值之和 |
-
-### 确定已售出产品的总数
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表售出的产品,`quantity` 代表售出商品数量。
-
-| quantity |
-| -------- |
-| 10 |
-| 100 |
-| 1000 |
-| 10001 |
-| 2 |
-| 15 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,确定已售出产品的总数。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Sum(quantity) AS items_ordered
-FROM OrderItems
-```
-
-### 确定已售出产品项 BR01 的总数
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表售出的产品,`quantity` 代表售出商品数量,产品项为 `prod_id`。
-
-| quantity | prod_id |
-| -------- | ------- |
-| 10 | AR01 |
-| 100 | AR10 |
-| 1000 | BR01 |
-| 10001 | BR010 |
-
-【问题】修改创建的语句,确定已售出产品项(`prod_id`)为"BR01"的总数。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Sum(quantity) AS items_ordered
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 确定 Products 表中价格不超过 10 美元的最贵产品的价格
-
-`Products` 表如下,`prod_price` 代表商品的价格。
-
-| prod_price |
-| ---------- |
-| 9.49 |
-| 600 |
-| 1000 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,确定 `Products` 表中价格不超过 10 美元的最贵产品的价格(`prod_price`)。将计算所得的字段命名为 `max_price`。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT Max(prod_price) AS max_price
-FROM Products
-WHERE prod_price <= 10
-```
-
-## 分组数据
-
-`GROUP BY`:
-
-- `GROUP BY` 子句将记录分组到汇总行中。
-- `GROUP BY` 为每个组返回一个记录。
-- `GROUP BY` 通常还涉及聚合`COUNT`,`MAX`,`SUM`,`AVG` 等。
-- `GROUP BY` 可以按一列或多列进行分组。
-- `GROUP BY` 按分组字段进行排序后,`ORDER BY` 可以以汇总字段来进行排序。
-
-`HAVING`:
-
-- `HAVING` 用于对汇总的 `GROUP BY` 结果进行过滤。
-- `HAVING` 必须要与 `GROUP BY` 连用。
-- `WHERE` 和 `HAVING` 可以在相同的查询中。
-
-`HAVING` vs `WHERE`:
-
-- `WHERE`:过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。
-- `HAVING`:过滤分组,必须要与 `GROUP BY` 连用,不能单独使用。
-
-### 返回每个订单号各有多少行数
-
-`OrderItems` 表包含每个订单的每个产品
-
-| order_num |
-| --------- |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a004 |
-| a007 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回每个订单号(`order_num`)各有多少行数(`order_lines`),并按 `order_lines` 对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, Count(order_num) AS order_lines
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-ORDER BY order_lines
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-1. `count(*)`,`count(列名)`都可以,区别在于,`count(列名)`是统计非 NULL 的行数;
-2. `order by` 最后执行,所以可以使用列别名;
-3. 分组聚合一定不要忘记加上 `group by` ,不然只会有一行结果。
-
-### 每个供应商成本最低的产品
-
-有 `Products` 表,含有字段 `prod_price` 代表产品价格,`vend_id` 代表供应商 id
-
-| vend_id | prod_price |
-| ------- | ---------- |
-| a0011 | 100 |
-| a0019 | 0.1 |
-| b0019 | 1000 |
-| b0019 | 6980 |
-| b0019 | 20 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回名为 `cheapest_item` 的字段,该字段包含每个供应商成本最低的产品(使用 `Products` 表中的 `prod_price`),然后从最低成本到最高成本对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT vend_id, Min(prod_price) AS cheapest_item
-FROM Products
-GROUP BY vend_id
-ORDER BY cheapest_item
-```
-
-### 返回订单数量总和不小于 100 的所有订单的订单号
-
-`OrderItems` 代表订单商品表,包括:订单号 `order_num` 和订单数量 `quantity`。
-
-| order_num | quantity |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 200 |
-| a4 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 19 |
-| a7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】请编写 SQL 语句,返回订单数量总和不小于 100 的所有订单号,最后结果按照订单号升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 直接聚合
-SELECT order_num
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING Sum(quantity) >= 100
-ORDER BY order_num
-
-# 子查询
-SELECT a.order_num
-FROM (SELECT order_num, Sum(quantity) AS sum_num
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY order_num
- HAVING sum_num >= 100) a
-ORDER BY a.order_num
-```
-
-知识点:
-
-- `where`:过滤过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。
-- `having`:过滤分组,与 `group by` 连用,不能单独使用。
-
-### 计算总和
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,包括字段:订单号 `order_num` 和 `item_price` 商品售出价格、`quantity` 商品数量。
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 10 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 1 | 200 |
-| a4 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 | 19 |
-| a7 | 7 | 5 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,根据订单号聚合,返回订单总价不小于 1000 的所有订单号,最后的结果按订单号进行升序排序。
-
-提示:总价 = item_price 乘以 quantity
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, Sum(item_price * quantity) AS total_price
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING total_price >= 1000
-ORDER BY order_num
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-`OrderItems` 表含有 `order_num` 订单号
-
-| order_num |
-| --------- |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a002 |
-| a004 |
-| a007 |
-
-【问题】将下面代码修改正确后执行
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, COUNT(*) AS items
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY items
-HAVING COUNT(*) >= 3
-ORDER BY items, order_num;
-```
-
-修改后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT order_num, COUNT(*) AS items
-FROM OrderItems
-GROUP BY order_num
-HAVING items >= 3
-ORDER BY items, order_num;
-```
-
-## 使用子查询
-
-子查询是嵌套在较大查询中的 SQL 查询,也称内部查询或内部选择,包含子查询的语句也称为外部查询或外部选择。简单来说,子查询就是指将一个 `SELECT` 查询(子查询)的结果作为另一个 SQL 语句(主查询)的数据来源或者判断条件。
-
-子查询可以嵌入 `SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 语句中,也可以和 `=`、`<`、`>`、`IN`、`BETWEEN`、`EXISTS` 等运算符一起使用。
-
-子查询常用在 `WHERE` 子句和 `FROM` 子句后边:
-
-- 当用于 `WHERE` 子句时,根据不同的运算符,子查询可以返回单行单列、多行单列、单行多列数据。子查询就是要返回能够作为 WHERE 子句查询条件的值。
-- 当用于 `FROM` 子句时,一般返回多行多列数据,相当于返回一张临时表,这样才符合 `FROM` 后面是表的规则。这种做法能够实现多表联合查询。
-
-> 注意:MySQL 数据库从 4.1 版本才开始支持子查询,早期版本是不支持的。
-
-用于 `WHERE` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM table1 [, table2 ]
-WHERE column_name operator
-(SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM table1 [, table2 ]
-[WHERE])
-```
-
-- 子查询需要放在括号`( )`内。
-- `operator` 表示用于 `WHERE` 子句的运算符,可以是比较运算符(如 `=`, `<`, `>`, `<>` 等)或逻辑运算符(如 `IN`, `NOT IN`, `EXISTS`, `NOT EXISTS` 等),具体根据需求来确定。
-
-用于 `FROM` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
-FROM (SELECT column_name [, column_name ]
- FROM table1 [, table2 ]
- [WHERE]) AS temp_table_name [, ...]
-[JOIN type JOIN table_name ON condition]
-WHERE condition;
-```
-
-- 用于 `FROM` 的子查询返回的结果相当于一张临时表,所以需要使用 AS 关键字为该临时表起一个名字。
-- 子查询需要放在括号 `( )` 内。
-- 可以指定多个临时表名,并使用 `JOIN` 语句连接这些表。
-
-### 返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表
-
-`OrderItems` 表示订单商品表,含有字段订单号:`order_num`、订单价格:`item_price`;`Orders` 表代表订单信息表,含有顾客 `id:cust_id` 和订单号:`order_num`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| order_num | item_price |
-| --------- | ---------- |
-| a1 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a4 | 2 |
-| a5 | 5 |
-| a2 | 1 |
-| a7 | 7 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | ------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a4 | cust2 |
-| a5 | cust5 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a7 | cust7 |
-
-【问题】使用子查询,返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表,结果无需排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_id
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN (SELECT DISTINCT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- where item_price >= 10)
-```
-
-### 确定哪些订单购买了 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品(一)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 `OrderItems` 中)购买了 `prod_id` 为 "BR01" 的产品,然后从 `Orders` 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单日期(`order_date`),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_id,order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN
- (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01' )
-ORDER BY order_date;
-
-# 写法 2: 连接表
-SELECT b.cust_id, b.order_date
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num AND a.prod_id = 'BR01'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-### 返回购买 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(一)
-
-你想知道订购 BR01 产品的日期,有表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`;`Customers` 表含有 `cust_email` 顾客邮件和 `cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息,`cust_id` 为顾客 id,`cust_email` 为顾客 email
-
-| cust_id | cust_email |
-| ------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | |
-| cust1 | |
-| cust2 | |
-
-【问题】返回购买 `prod_id` 为 `BR01` 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_email`),结果无需排序。
-
-提示:这涉及 `SELECT` 语句,最内层的从 `OrderItems` 表返回 `order_num`,中间的从 `Customers` 表返回 `cust_id`。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id
- FROM Orders
- WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01'))
-
-# 写法 2: 连接表(inner join)
-SELECT c.cust_email
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b,Customers c
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num AND b.cust_id = c.cust_id AND a.prod_id = 'BR01'
-
-# 写法 3:连接表(left join)
-SELECT c.cust_email
-FROM Orders a LEFT JOIN
- OrderItems b ON a.order_num = b.order_num LEFT JOIN
- Customers c ON a.cust_id = c.cust_id
-WHERE b.prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 返回每个顾客不同订单的总金额
-
-我们需要一个顾客 ID 列表,其中包含他们已订购的总金额。
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,`OrderItems` 表有订单号:`order_num` 和商品售出价格:`item_price`、商品数量:`quantity`。
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 10 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a0002 | 1 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 5 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 1 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 7 | 5 |
-
-`Orders` 表订单号:`order_num`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | ------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 |
-| a0002 | cust1 |
-| a0003 | cust1 |
-| a0013 | cust2 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,返回顾客 ID(`Orders` 表中的 `cust_id`),并使用子查询返回 `total_ordered` 以便返回每个顾客的订单总数,将结果按金额从大到小排序。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT o.cust_id, SUM(tb.total_ordered) AS `total_ordered`
-FROM (SELECT order_num, SUM(item_price * quantity) AS total_ordered
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY order_num) AS tb,
- Orders o
-WHERE tb.order_num = o.order_num
-GROUP BY o.cust_id
-ORDER BY total_ordered DESC;
-
-# 写法 2:连接表
-SELECT b.cust_id, Sum(a.quantity * a.item_price) AS total_ordered
-FROM OrderItems a,Orders b
-WHERE a.order_num = b.order_num
-GROUP BY cust_id
-ORDER BY total_ordered DESC
-```
-
-关于写法一详细介绍可以参考: [issue#2402:写法 1 存在的错误以及修改方法](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/2402)。
-
-### 从 Products 表中检索所有的产品名称以及对应的销售总数
-
-`Products` 表中检索所有的产品名称:`prod_name`、产品 id:`prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-
-`OrderItems` 代表订单商品表,订单产品:`prod_id`、售出数量:`quantity`
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 1100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,从 `Products` 表中检索所有的产品名称(`prod_name`),以及名为 `quant_sold` 的计算列,其中包含所售产品的总数(在 `OrderItems` 表上使用子查询和 `SUM(quantity)` 检索)。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT p.prod_name, tb.quant_sold
-FROM (SELECT prod_id, Sum(quantity) AS quant_sold
- FROM OrderItems
- GROUP BY prod_id) AS tb,
- Products p
-WHERE tb.prod_id = p.prod_id
-
-# 写法 2:连接表
-SELECT p.prod_name, Sum(o.quantity) AS quant_sold
-FROM Products p,
- OrderItems o
-WHERE p.prod_id = o.prod_id
-GROUP BY p.prod_name(这里不能用 p.prod_id,会报错)
-```
-
-## 连接表
-
-JOIN 是“连接”的意思,顾名思义,SQL JOIN 子句用于将两个或者多个表联合起来进行查询。
-
-连接表时需要在每个表中选择一个字段,并对这些字段的值进行比较,值相同的两条记录将合并为一条。**连接表的本质就是将不同表的记录合并起来,形成一张新表。当然,这张新表只是临时的,它仅存在于本次查询期间**。
-
-使用 `JOIN` 连接两个表的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT table1.column1, table2.column2...
-FROM table1
-JOIN table2
-ON table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2;
-```
-
-`table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2` 是连接条件,只有满足此条件的记录才会合并为一行。您可以使用多个运算符来连接表,例如 =、>、<、<>、<=、>=、!=、`between`、`like` 或者 `not`,但是最常见的是使用 =。
-
-当两个表中有同名的字段时,为了帮助数据库引擎区分是哪个表的字段,在书写同名字段名时需要加上表名。当然,如果书写的字段名在两个表中是唯一的,也可以不使用以上格式,只写字段名即可。
-
-另外,如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用 `USING`子句来代替 `ON`,举个例子:
-
-```sql
-# join....on
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-ON c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-
-# 如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用USING子句:JOIN....USING()
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-```
-
-**`ON` 和 `WHERE` 的区别**:
-
-- 连接表时,SQL 会根据连接条件生成一张新的临时表。`ON` 就是连接条件,它决定临时表的生成。
-- `WHERE` 是在临时表生成以后,再对临时表中的数据进行过滤,生成最终的结果集,这个时候已经没有 JOIN-ON 了。
-
-所以总结来说就是:**SQL 先根据 ON 生成一张临时表,然后再根据 WHERE 对临时表进行筛选**。
-
-SQL 允许在 `JOIN` 左边加上一些修饰性的关键词,从而形成不同类型的连接,如下表所示:
-
-| 连接类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| INNER JOIN 内连接 | (默认连接方式)只有当两个表都存在满足条件的记录时才会返回行。 |
-| LEFT JOIN / LEFT OUTER JOIN 左(外)连接 | 返回左表中的所有行,即使右表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| RIGHT JOIN / RIGHT OUTER JOIN 右(外)连接 | 返回右表中的所有行,即使左表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| FULL JOIN / FULL OUTER JOIN 全(外)连接 | 只要其中有一个表存在满足条件的记录,就返回行。 |
-| SELF JOIN | 将一个表连接到自身,就像该表是两个表一样。为了区分两个表,在 SQL 语句中需要至少重命名一个表。 |
-| CROSS JOIN | 交叉连接,从两个或者多个连接表中返回记录集的笛卡尔积。 |
-
-下图展示了 LEFT JOIN、RIGHT JOIN、INNER JOIN、OUTER JOIN 相关的 7 种用法。
-
-
-
-如果不加任何修饰词,只写 `JOIN`,那么默认为 `INNER JOIN`
-
-对于 `INNER JOIN` 来说,还有一种隐式的写法,称为 “**隐式内连接**”,也就是没有 `INNER JOIN` 关键字,使用 `WHERE` 语句实现内连接的功能
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c,Orders o
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name
-
-# 显式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name;
-```
-
-### 返回顾客名称和相关订单号
-
-`Customers` 表有字段顾客名称 `cust_name`、顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 订单信息表,含有字段 `order_num` 订单号、`cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)和 `Orders` 表中的相关订单号(`order_num`),并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。你可以尝试用两个不同的写法,一个使用简单的等连接语法,另外一个使用 INNER JOIN。
-
-答案:
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c,Orders o
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num
-
-# 显式内连接
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num
-FROM Customers c
-INNER JOIN Orders o
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num;
-```
-
-### 返回顾客名称和相关订单号以及每个订单的总价
-
-`Customers` 表有字段,顾客名称:`cust_name`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 订单信息表,含有字段,订单号:`order_num`、顾客 id:`cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-`OrderItems` 表有字段,商品订单号:`order_num`、商品数量:`quantity`、商品价格:`item_price`
-
-| order_num | quantity | item_price |
-| --------- | -------- | ---------- |
-| a1 | 1000 | 10 |
-| a2 | 200 | 10 |
-| a3 | 10 | 15 |
-| a4 | 25 | 50 |
-| a5 | 15 | 25 |
-| a7 | 7 | 7 |
-
-【问题】除了返回顾客名称和订单号,返回 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)和 `Orders` 表中的相关订单号(`order_num`),添加第三列 `OrderTotal`,其中包含每个订单的总价,并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-# 简单的等连接语法
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num, SUM(quantity * item_price) AS OrderTotal
-FROM Customers c,Orders o,OrderItems oi
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id AND o.order_num = oi.order_num
-GROUP BY c.cust_name, o.order_num
-ORDER BY c.cust_name, o.order_num
-```
-
-注意,可能有小伙伴会这样写:
-
-```sql
-SELECT c.cust_name, o.order_num, SUM(quantity * item_price) AS OrderTotal
-FROM Customers c,Orders o,OrderItems oi
-WHERE c.cust_id = o.cust_id AND o.order_num = oi.order_num
-GROUP BY c.cust_name
-ORDER BY c.cust_name,o.order_num
-```
-
-这是错误的!只对 `cust_name` 进行聚类确实符合题意,但是不符合 `GROUP BY` 的语法。
-
-select 语句中,如果没有 `GROUP BY` 语句,那么 `cust_name`、`order_num` 会返回若干个值,而 `sum(quantity * item_price)` 只返回一个值,通过 `group by` `cust_name` 可以让 `cust_name` 和 `sum(quantity * item_price)` 一一对应起来,或者说**聚类**,所以同样的,也要对 `order_num` 进行聚类。
-
-> **一句话,select 中的字段要么都聚类,要么都不聚类**
-
-### 确定哪些订单购买了 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品(二)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-【问题】
-
-编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 `OrderItems` 中)购买了 `prod_id` 为 "BR01" 的产品,然后从 `Orders` 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(`cust_id`)和订单日期(`order_date`),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
-
-提示:这一次使用连接和简单的等连接语法。
-
-```sql
-# 写法 1:子查询
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders
-WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01')
-ORDER BY order_date
-
-# 写法 2:连接表 inner join
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders o INNER JOIN
- (SELECT order_num
- FROM OrderItems
- WHERE prod_id = 'BR01') tb ON o.order_num = tb.order_num
-ORDER BY order_date
-
-# 写法 3:写法 2 的简化版
-SELECT cust_id, order_date
-FROM Orders
-INNER JOIN OrderItems USING(order_num)
-WHERE OrderItems.prod_id = 'BR01'
-ORDER BY order_date
-```
-
-### 返回购买 prod_id 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(二)
-
-有表 `OrderItems` 代表订单商品信息表,`prod_id` 为产品 id;`Orders` 表代表订单表有 `cust_id` 代表顾客 id 和订单日期 `order_date`;`Customers` 表含有 `cust_email` 顾客邮件和 cust_id 顾客 id
-
-`OrderItems` 表:
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| BR01 | a0001 |
-| BR01 | a0002 |
-| BR02 | a0003 |
-| BR02 | a0013 |
-
-`Orders` 表:
-
-| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
-| --------- | ------- | ------------------- |
-| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
-| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
-| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
-| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息,`cust_id` 为顾客 id,`cust_email` 为顾客 email
-
-| cust_id | cust_email |
-| ------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | |
-| cust1 | |
-| cust2 | |
-
-【问题】返回购买 `prod_id` 为 BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_email`),结果无需排序。
-
-提示:涉及到 `SELECT` 语句,最内层的从 `OrderItems` 表返回 `order_num`,中间的从 `Customers` 表返回 `cust_id`,但是必须使用 INNER JOIN 语法。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_email
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders using(cust_id)
-INNER JOIN OrderItems using(order_num)
-WHERE OrderItems.prod_id = 'BR01'
-```
-
-### 确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(二)
-
-`OrderItems` 表代表订单信息,确定最佳顾客的另一种方式是看他们花了多少钱,`OrderItems` 表有订单号 `order_num` 和 `item_price` 商品售出价格、`quantity` 商品数量
-
-| order_num | item_price | quantity |
-| --------- | ---------- | -------- |
-| a1 | 10 | 105 |
-| a2 | 1 | 1100 |
-| a2 | 1 | 200 |
-| a4 | 2 | 1121 |
-| a5 | 5 | 10 |
-| a2 | 1 | 19 |
-| a7 | 7 | 5 |
-
-`Orders` 表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号、`cust_id` 顾客 id
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-顾客表 `Customers` 有字段 `cust_id` 客户 id、`cust_name` 客户姓名
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回订单总价不小于 1000 的客户名称和总额(`OrderItems` 表中的 `order_num`)。
-
-提示:需要计算总和(`item_price` 乘以 `quantity`)。按总额对结果进行排序,请使用 `INNER JOIN`语法。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, SUM(item_price * quantity) AS total_price
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders USING(cust_id)
-INNER JOIN OrderItems USING(order_num)
-GROUP BY cust_name
-HAVING total_price >= 1000
-ORDER BY total_price
-```
-
-## 创建高级连接
-
-### 检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(一)
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息含有顾客 id `cust_id` 和 顾客名称 `cust_name`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-
-`Orders` 表代表订单信息含有订单号 `order_num` 和顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-【问题】使用 INNER JOIN 编写 SQL 语句,检索每个顾客的名称(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_name`)和所有的订单号(`Orders` 表中的 `order_num`),最后根据顾客姓名 `cust_name` 升序返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, order_num
-FROM Customers
-INNER JOIN Orders
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY cust_name
-```
-
-### 检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(二)
-
-`Orders` 表代表订单信息含有订单号 `order_num` 和顾客 id `cust_id`
-
-| order_num | cust_id |
-| --------- | -------- |
-| a1 | cust10 |
-| a2 | cust1 |
-| a3 | cust2 |
-| a4 | cust22 |
-| a5 | cust221 |
-| a7 | cust2217 |
-
-`Customers` 表代表顾客信息含有顾客 id `cust_id` 和 顾客名称 `cust_name`
-
-| cust_id | cust_name |
-| -------- | --------- |
-| cust10 | andy |
-| cust1 | ben |
-| cust2 | tony |
-| cust22 | tom |
-| cust221 | an |
-| cust2217 | hex |
-| cust40 | ace |
-
-【问题】检索每个顾客的名称(`Customers` 表中的 `cust_name`)和所有的订单号(Orders 表中的 `order_num`),列出所有的顾客,即使他们没有下过订单。最后根据顾客姓名 `cust_name` 升序返回。
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, order_num
-FROM Customers
-LEFT JOIN Orders
-USING(cust_id)
-ORDER BY cust_name
-```
-
-### 返回产品名称和与之相关的订单号
-
-`Products` 表为产品信息表含有字段 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_name` 产品名称
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-| a0023 | soda |
-
-`OrderItems` 表为订单信息表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号和产品 id `prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | a105 |
-| a0002 | a1100 |
-| a0002 | a200 |
-| a0013 | a1121 |
-| a0003 | a10 |
-| a0003 | a19 |
-| a0003 | a5 |
-
-【问题】使用外连接(left join、 right join、full join)联结 `Products` 表和 `OrderItems` 表,返回产品名称(`prod_name`)和与之相关的订单号(`order_num`)的列表,并按照产品名称升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, order_num
-FROM Products
-LEFT JOIN OrderItems
-USING(prod_id)
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 返回产品名称和每一项产品的总订单数
-
-`Products` 表为产品信息表含有字段 `prod_id` 产品 id、`prod_name` 产品名称
-
-| prod_id | prod_name |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | sockets |
-| a0013 | coffee |
-| a0003 | cola |
-| a0023 | soda |
-
-`OrderItems` 表为订单信息表含有字段 `order_num` 订单号和产品 id `prod_id`
-
-| prod_id | order_num |
-| ------- | --------- |
-| a0001 | a105 |
-| a0002 | a1100 |
-| a0002 | a200 |
-| a0013 | a1121 |
-| a0003 | a10 |
-| a0003 | a19 |
-| a0003 | a5 |
-
-【问题】
-
-使用 OUTER JOIN 联结 `Products` 表和 `OrderItems` 表,返回产品名称(`prod_name`)和每一项产品的总订单数(不是订单号),并按产品名称升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name, COUNT(order_num) AS orders
-FROM Products
-LEFT JOIN OrderItems
-USING(prod_id)
-GROUP BY prod_name
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 列出供应商及其可供产品的数量
-
-有 `Vendors` 表含有 `vend_id` (供应商 id)
-
-| vend_id |
-| ------- |
-| a0002 |
-| a0013 |
-| a0003 |
-| a0010 |
-
-有 `Products` 表含有 `vend_id`(供应商 id)和 prod_id(供应产品 id)
-
-| vend_id | prod_id |
-| ------- | -------------------- |
-| a0001 | egg |
-| a0002 | prod_id_iphone |
-| a00113 | prod_id_tea |
-| a0003 | prod_id_vivo phone |
-| a0010 | prod_id_huawei phone |
-
-【问题】列出供应商(`Vendors` 表中的 `vend_id`)及其可供产品的数量,包括没有产品的供应商。你需要使用 OUTER JOIN 和 COUNT()聚合函数来计算 `Products` 表中每种产品的数量,最后根据 vend_id 升序排序。
-
-注意:`vend_id` 列会显示在多个表中,因此在每次引用它时都需要完全限定它。
-
-```sql
-SELECT v.vend_id, COUNT(prod_id) AS prod_id
-FROM Vendors v
-LEFT JOIN Products p
-USING(vend_id)
-GROUP BY v.vend_id
-ORDER BY v.vend_id
-```
-
-## 组合查询
-
-`UNION` 运算符将两个或更多查询的结果组合起来,并生成一个结果集,其中包含来自 `UNION` 中参与查询的提取行。
-
-`UNION` 基本规则:
-
-- 所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- 每个查询中涉及表的列的数据类型必须相同或兼容。
-- 通常返回的列名取自第一个查询。
-
-默认地,`UNION` 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 `UNION ALL`。
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
-UNION ALL
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;
-```
-
-`UNION` 结果集中的列名总是等于 `UNION` 中第一个 `SELECT` 语句中的列名。
-
-`JOIN` vs `UNION`:
-
-- `JOIN` 中连接表的列可能不同,但在 `UNION` 中,所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- `UNION` 将查询之后的行放在一起(垂直放置),但 `JOIN` 将查询之后的列放在一起(水平放置),即它构成一个笛卡尔积。
-
-### 将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来(一)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 包含订单产品信息,字段 `prod_id` 代表产品 id、`quantity` 代表产品数量
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-| BNBG | 10002 |
-
-【问题】将两个 `SELECT` 语句结合起来,以便从 `OrderItems` 表中检索产品 id(`prod_id`)和 `quantity`。其中,一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE quantity = 100
-UNION
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE prod_id LIKE 'BNBG%'
-```
-
-### 将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来(二)
-
-表 `OrderItems` 包含订单产品信息,字段 `prod_id` 代表产品 id、`quantity` 代表产品数量。
-
-| prod_id | quantity |
-| ------- | -------- |
-| a0001 | 105 |
-| a0002 | 100 |
-| a0002 | 200 |
-| a0013 | 1121 |
-| a0003 | 10 |
-| a0003 | 19 |
-| a0003 | 5 |
-| BNBG | 10002 |
-
-【问题】将两个 `SELECT` 语句结合起来,以便从 `OrderItems` 表中检索产品 id(`prod_id`)和 `quantity`。其中,一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 `SELECT` 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。 注意:**这次仅使用单个 SELECT 语句。**
-
-答案:
-
-要求只用一条 select 语句,那就用 `or` 不用 `union` 了。
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, quantity
-FROM OrderItems
-WHERE quantity = 100 OR prod_id LIKE 'BNBG%'
-```
-
-### 组合 Products 表中的产品名称和 Customers 表中的顾客名称
-
-`Products` 表含有字段 `prod_name` 代表产品名称
-
-| prod_name |
-| --------- |
-| flower |
-| rice |
-| ring |
-| umbrella |
-
-Customers 表代表顾客信息,cust_name 代表顾客名称
-
-| cust_name |
-| --------- |
-| andy |
-| ben |
-| tony |
-| tom |
-| an |
-| lee |
-| hex |
-
-【问题】编写 SQL 语句,组合 `Products` 表中的产品名称(`prod_name`)和 `Customers` 表中的顾客名称(`cust_name`)并返回,然后按产品名称对结果进行升序排序。
-
-```sql
-# UNION 结果集中的列名总是等于 UNION 中第一个 SELECT 语句中的列名。
-SELECT prod_name
-FROM Products
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name
-FROM Customers
-ORDER BY prod_name
-```
-
-### 检查 SQL 语句
-
-表 `Customers` 含有字段 `cust_name` 顾客名、`cust_contact` 顾客联系方式、`cust_state` 顾客州、`cust_email` 顾客 `email`
-
-| cust_name | cust_contact | cust_state | cust_email |
-| --------- | ------------ | ---------- | ----------------- |
-| cust10 | 8695192 | MI | |
-| cust1 | 8695193 | MI | |
-| cust2 | 8695194 | IL | |
-
-【问题】修正下面错误的 SQL
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'IL'ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-修正后:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
-UNION
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'IL'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-使用 `union` 组合查询时,只能使用一条 `order by` 字句,他必须位于最后一条 `select` 语句之后
-
-或者直接用 `or` 来做:
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_state = 'MI' or cust_state = 'IL'
-ORDER BY cust_name;
-```
-
-
+| Haidilao |
+| Xia |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
index 2a4a3e496c6..2f88a9c173f 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-02.md
@@ -1,354 +1,354 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(2)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (2)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of the question: [Niuke Problem Boss - Advanced SQL Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-## 增删改操作
+## Insert, Delete, and Update Operations
-SQL 插入记录的方式汇总:
+Summary of SQL methods for inserting records:
-- **普通插入(全字段)** :`INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
-- **普通插入(限定字段)** :`INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
-- **多条一次性插入** :`INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...`
-- **从另一个表导入** :`INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]`
-- **带更新的插入** :`REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`(注意这种原理是检测到主键或唯一性索引键重复就删除原记录后重新插入)
+- **Normal Insert (All Fields)**: `INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
+- **Normal Insert (Specified Fields)**: `INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...)`
+- **Insert Multiple Records at Once**: `INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1_1, value1_2, ...), (value2_1, value2_2, ...), ...`
+- **Import from Another Table**: `INSERT INTO table_name SELECT * FROM table_name2 [WHERE key=value]`
+- **Insert with Update**: `REPLACE INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, ...)` (Note that this method deletes the original record if a primary key or unique index key duplicate is detected, then reinserts it)
-### 插入记录(一)
+### Inserting Records (1)
-**描述**:牛客后台会记录每个用户的试卷作答记录到 `exam_record` 表,现在有两个用户的作答记录详情如下:
+**Description**: The Niuke backend records each user's exam record in the `exam_record` table. Two users' exam records are as follows:
-- 用户 1001 在 2021 年 9 月 1 日晚上 10 点 11 分 12 秒开始作答试卷 9001,并在 50 分钟后提交,得了 90 分;
-- 用户 1002 在 2021 年 9 月 4 日上午 7 点 1 分 2 秒开始作答试卷 9002,并在 10 分钟后退出了平台。
+- User 1001 started the exam 9001 at 10:11:12 PM on September 1, 2021, and submitted it after 50 minutes, scoring 90 points;
+- User 1002 started the exam 9002 at 7:01:02 AM on September 4, 2021, and left the platform after 10 minutes.
-试卷作答记录表`exam_record`中,表已建好,其结构如下,请用一条语句将这两条记录插入表中。
+The structure of the `exam_record` table is already established as follows; please use a single statement to insert these two records into the table.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-// 存在自增主键,无需手动赋值
+-- Auto-incrementing primary key, no manual assignment required
INSERT INTO exam_record (uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score) VALUES
(1001, 9001, '2021-09-01 22:11:12', '2021-09-01 23:01:12', 90),
(1002, 9002, '2021-09-04 07:01:02', NULL, NULL);
```
-### 插入记录(二)
+### Inserting Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表`exam_record`,结构如下表,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,由于数据越来越多,维护难度越来越大,需要对数据表内容做精简,历史数据做备份。
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing user exam records for many years. Due to the increasing amount of data, maintenance difficulty is getting higher, and the content of the data table needs to be simplified, with historical data backed up.
-表`exam_record`:
+Table `exam_record`:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-我们已经创建了一张新表`exam_record_before_2021`用来备份 2021 年之前的试题作答记录,结构和`exam_record`表一致,请将 2021 年之前的已完成了的试题作答纪录导入到该表。
+We have created a new table `exam_record_before_2021` to back up exam records before 2021, which has the same structure as the `exam_record` table. Please import the completed exam records before 2021 into this new table.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
INSERT INTO exam_record_before_2021 (uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score)
-SELECT uid,exam_id,start_time,submit_time,score
+SELECT uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score
FROM exam_record
WHERE YEAR(submit_time) < 2021;
```
-### 插入记录(三)
+### Inserting Records (3)
-**描述**:现在有一套 ID 为 9003 的高难度 SQL 试卷,时长为一个半小时,请你将 2021-01-01 00:00:00 作为发布时间插入到试题信息表`examination_info`,不管该 ID 试卷是否存在,都要插入成功,请尝试插入它。
+**Description**: There is a difficult SQL exam with ID 9003, which lasts for one and a half hours. Please insert the release time `2021-01-01 00:00:00` into the `examination_info` table, regardless of whether this ID exam exists or not.
-试题信息表`examination_info`:
+Table `examination_info`:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ------------ | ----------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ------------ |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| tag | varchar(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | 类别标签 |
-| difficulty | varchar(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | 难度 |
-| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 时长(分钟数) |
-| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 发布时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ------------ | ----------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ------------------ |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| tag | varchar(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | Category Tag |
+| difficulty | varchar(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | Difficulty |
+| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Duration (minutes) |
+| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Release Time |
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
REPLACE INTO examination_info VALUES
(NULL, 9003, "SQL", "hard", 90, "2021-01-01 00:00:00");
```
-### 更新记录(一)
+### Updating Records (1)
-**描述**:现在有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`, 表结构如下图所示:
+**Description**: There is an `examination_info` table. The table structure is as follows:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ------------ | -------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| tag | char(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | 类别标签 |
-| difficulty | char(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | 难度 |
-| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 时长 |
-| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 发布时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ------------ | -------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | UNI | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| tag | char(32) | YES | | | (NULL) | Category Tag |
+| difficulty | char(8) | YES | | | (NULL) | Difficulty |
+| duration | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Duration |
+| release_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Release Time |
-请把**examination_info**表中`tag`为`PYTHON`的`tag`字段全部修改为`Python`。
+Please change all `tag` fields of `tag` equal to `PYTHON` in the `examination_info` table to `Python`.
-**思路**:这题有两种解题思路,最容易想到的是直接`update + where`来指定条件更新,第二种就是根据要修改的字段进行查找替换
+**Thought Process**: There are two ways to solve this problem. The most straightforward approach is to directly use `update + where` to specify the conditional update. The second method is to find and replace based on the field that needs to be modified.
-**答案一**:
+**Answer 1**:
```sql
UPDATE examination_info SET tag = 'Python' WHERE tag='PYTHON'
```
-**答案二**:
+**Answer 2**:
```sql
UPDATE examination_info
SET tag = REPLACE(tag,'PYTHON','Python')
-# REPLACE (目标字段,"查找内容","替换内容")
+# REPLACE (Target Field, "Search Content", "Replacement Content")
```
-### 更新记录(二)
+### Updating Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 exam_record,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:作答记录表 `exam_record`: **`submit_time`** 为 完成时间 (注意这句话)
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table, which contains years of user exam records. The table structure is as follows: The **`submit_time`** is the completion time (Note this statement).
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**题目要求**:请把 `exam_record` 表中 2021 年 9 月 1 日==之前==开始作答的==未完成==记录全部改为被动完成,即:将完成时间改为'2099-01-01 00:00:00',分数改为 0。
+**Requirement**: Please change all uncompleted records in the `exam_record` table that started before September 1, 2021, to be marked as completed. Specifically: Set the completion time to '2099-01-01 00:00:00' and the score to 0.
-**思路**:注意题干中的关键字(已经高亮) `" xxx 时间 "`之前这个条件, 那么这里马上就要想到要进行时间的比较 可以直接 `xxx_time < "2021-09-01 00:00:00",` 也可以采用`date()`函数来进行比较;第二个条件就是 `"未完成"`, 即完成时间为 NULL,也就是题目中的提交时间 ----- `submit_time 为 NULL`。
+**Thought Process**: Pay attention to the key phrases in the problem statement (highlighted) regarding "xxx time" before this condition. This suggests that we need to perform a time comparison using either `xxx_time < "2021-09-01 00:00:00"` or using the `date()` function for comparison. The second condition is "uncompleted", meaning the submission time is NULL; hence, `submit_time IS NULL`.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
UPDATE exam_record SET submit_time = '2099-01-01 00:00:00', score = 0 WHERE DATE(start_time) < "2021-09-01" AND submit_time IS null
```
-### 删除记录(一)
+### Deleting Records (1)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing many years of user records as follows:
-作答记录表`exam_record:` **`start_time`** 是试卷开始时间`submit_time` 是交卷,即结束时间。
+The exam record table `exam_record`: **`start_time`** is the start time and `submit_time` is the submission/end time.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 得分 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---- | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中作答时间小于 5 分钟整且分数不及格(及格线为 60 分)的记录;
+**Requirement**: Delete records in the `exam_record` table where the exam duration is less than 5 minutes and the score is failing (the passing score is 60).
-**思路**:这一题虽然是练习删除,仔细看确是考察对时间函数的用法,这里提及的分钟数比较,常用的函数有 **`TIMEDIFF`**和**`TIMESTAMPDIFF`** ,两者用法稍有区别,后者更为灵活,这都是看个人习惯。
+**Thought Process**: While this question practices deletion, it exactly tests the usage of time functions. Two common functions for minute comparison are **`TIMEDIFF`** and **`TIMESTAMPDIFF`**, both with slightly different usages, with the latter being more flexible.
-1. `TIMEDIFF`:两个时间之间的差值
+1. `TIMEDIFF`: The time difference between two times
```sql
TIMEDIFF(time1, time2)
```
-两者参数都是必须的,都是一个时间或者日期时间表达式。如果指定的参数不合法或者是 NULL,那么函数将返回 NULL。
+Both parameters are required and must be a time or datetime expression. If either is invalid or NULL, the function returns NULL.
-对于这题而言,可以用在 minute 函数里面,因为 TIMEDIFF 计算出来的是时间的差值,在外面套一个 MINUTE 函数,计算出来的就是分钟数。
+For this problem, it can be applied within the minute function because the TIMEDIFF result gives the time difference, and wrapping this in a MINUTE function gives the minutes.
-2. `TIMESTAMPDIFF`:用于计算两个日期的时间差
+2. `TIMESTAMPDIFF`: Used to calculate the time difference between two dates
```sql
-TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit,datetime_expr1,datetime_expr2)
-# 参数说明
-#unit: 日期比较返回的时间差单位,常用可选值如下:
-SECOND:秒
-MINUTE:分钟
-HOUR:小时
-DAY:天
-WEEK:星期
-MONTH:月
-QUARTER:季度
-YEAR:年
-# TIMESTAMPDIFF函数返回datetime_expr2 - datetime_expr1的结果(人话: 后面的 - 前面的 即2-1),其中datetime_expr1和datetime_expr2可以是DATE或DATETIME类型值(人话:可以是“2023-01-01”, 也可以是“2023-01-01- 00:00:00”)
+TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit, datetime_expr1, datetime_expr2)
+# Parameter description
+# unit: Common optional values for the time difference returned:
+SECOND: seconds
+MINUTE: minutes
+HOUR: hours
+DAY: days
+WEEK: weeks
+MONTH: months
+QUARTER: quarters
+YEAR: years
+# The TIMESTAMPDIFF function returns the result of datetime_expr2 - datetime_expr1 (in simple terms: the latter - the former, i.e., 2-1), where datetime_expr1 and datetime_expr2 can be DATE or DATETIME type values.
```
-这题需要进行分钟的比较,那么就是 TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, 开始时间, 结束时间) < 5
+This question requires minute comparison, hence `TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5`.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE MINUTE (TIMEDIFF(submit_time , start_time)) < 5 AND score < 60
+DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE MINUTE (TIMEDIFF(submit_time, start_time)) < 5 AND score < 60
```
```sql
DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5 AND score < 60
```
-### 删除记录(二)
+### Deleting Records (2)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表`exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table that includes numerous user exam records, structured as follows:
-作答记录表`exam_record`:`start_time` 是试卷开始时间,`submit_time` 是交卷时间,即结束时间,如果未完成的话,则为空。
+Exam record table `exam_record`: `start_time` is the exam start time, and `submit_time` is the submission time. If incomplete, it is NULL.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 分数 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中未完成作答==或==作答时间小于 5 分钟整的记录中,开始作答时间最早的 3 条记录。
+**Requirement**: Delete the earliest 3 records among those that are either uncompleted or have an exam duration of less than 5 minutes.
-**思路**:这题比较简单,但是要注意题干中给出的信息,结束时间,如果未完成的话,则为空,这个其实就是一个条件
+**Thought Process**: This problem is relatively simple, but be sure to note the information given in the prompt. The end time, if incomplete, is NULL, which means this is one condition.
-还有一个条件就是小于 5 分钟,跟上题类似,但是这里是**或**,即两个条件满足一个就行;另外就是稍微考察到了排序和 limit 的用法。
+Another condition is being less than 5 minutes, similar to the previous question, but here it is **or**, so either condition suffices. Lastly, this tests sorting and the use of limit.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS null OR TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5
+DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS NULL OR TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5
ORDER BY start_time
LIMIT 3
-# 默认就是asc, desc是降序排列
+# The default is ascending, desc is descending order
```
-### 删除记录(三)
+### Deleting Records (3)
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 exam_record,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录,结构如下表:
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing multi-year user exam records structured as follows:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
-| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 用户 ID |
-| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | 试卷 ID |
-| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | 开始时间 |
-| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | 提交时间 |
-| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | 分数 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Extra | Default | Comment |
+| ----------- | ---------- | :--: | --- | -------------- | ------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | auto_increment | (NULL) | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | User ID |
+| exam_id | int(11) | NO | | | (NULL) | Exam ID |
+| start_time | datetime | NO | | | (NULL) | Start Time |
+| submit_time | datetime | YES | | | (NULL) | Submit Time |
+| score | tinyint(4) | YES | | | (NULL) | Score |
-**要求**:请删除`exam_record`表中所有记录,==并重置自增主键==
+**Requirement**: Delete all records in the `exam_record` table and reset the auto-incrementing primary key.
-**思路**:这题考察对三种删除语句的区别,注意高亮部分,要求重置主键;
+**Thought Process**: This question tests the differences between three delete statements. Note the highlighted part about resetting the primary key:
-- `DROP`: 清空表,删除表结构,不可逆
-- `TRUNCATE`: 格式化表,不删除表结构,不可逆
-- `DELETE`:删除数据,可逆
+- `DROP`: Deletes the table and its structure and is irreversible.
+- `TRUNCATE`: Clears the table but does not delete the structure. It is irreversible.
+- `DELETE`: Deletes data and is reversible.
-这里选用`TRUNCATE`的原因是:TRUNCATE 只能作用于表;`TRUNCATE`会清空表中的所有行,但表结构及其约束、索引等保持不变;`TRUNCATE`会重置表的自增值;使用`TRUNCATE`后会使表和索引所占用的空间会恢复到初始大小。
+In this case, `TRUNCATE` is chosen because it only affects the table; `TRUNCATE` clears all rows from the table but keeps the structure, constraints, indexes, etc.; `TRUNCATE` resets the auto-increment value; after using `TRUNCATE`, the space occupied by the table and indexes reverts to the initial size.
-这题也可以采用`DELETE`来做,但是在删除后,还需要手动`ALTER`表结构来设置主键初始值;
+This problem can also be approached with `DELETE`, but would require a manual `ALTER` after deleting to set the primary key initial value.
-同理也可以采用`DROP`来做,直接删除整张表,包括表结构,然后再新建表即可。
+Similarly, `DROP` could be used but involves deleting the entire table, including its structure and then recreating it.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
-TRUNCATE exam_record;
+TRUNCATE exam_record;
```
-## 表与索引操作
+## Table and Index Operations
-### 创建一张新表
+### Creating a New Table
-**描述**:现有一张用户信息表,其中包含多年来在平台注册过的用户信息,随着牛客平台的不断壮大,用户量飞速增长,为了高效地为高活跃用户提供服务,现需要将部分用户拆分出一张新表。
+**Description**: There is a user information table that contains user information registered on the platform over the years. As the Niuke platform continues to grow, the user base is rapidly increasing. To efficiently serve high-activity users, there is a need to split some users into a new table.
-原来的用户信息表:
+Original user information table:
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-作为数据分析师,请**创建一张优质用户信息表 user_info_vip**,表结构和用户信息表一致。
+As a data analyst, please **create a quality user information table named user_info_vip** with the same structure as the user information table.
-你应该返回的输出如下表格所示,请写出建表语句将表格中所有限制和说明记录到表里。
+The output you should return should match the table structure shown below. Please write the create table statement to include all constraints and comments.
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-**思路**:如果这题给出了旧表的名称,可直接`create table 新表 as select * from 旧表;` 但是这题并没有给出旧表名称,所以需要自己创建,注意默认值和键的创建即可,比较简单。(注意:如果是在牛客网上面执行,请注意 comment 中要和题目中的 comment 保持一致,包括大小写,否则不通过,还有字符也要设置)
+**Thought Process**: If the old table name was provided, one could simply use `create table new_table as select * from old_table;` However, since the name is not given, it needs to be created manually, paying attention to defaults and key creation. This is relatively simple (Note: if executed on Niuke.com, ensure the comment matches the requirement, including case sensitivity, otherwise it will fail).
-答案:
+**Answer**:
```sql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_info_vip(
- id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT'自增ID',
- uid INT(11) UNIQUE NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
- nick_name VARCHAR(64) COMMENT'昵称',
- achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '成就值',
- `level` INT(11) COMMENT '用户等级',
- job VARCHAR(32) COMMENT '职业方向',
- register_time DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '注册时间'
-)CHARACTER SET UTF8
+ id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Auto-increment ID',
+ uid INT(11) UNIQUE NOT NULL COMMENT 'User ID',
+ nick_name VARCHAR(64) COMMENT 'Nickname',
+ achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 'Achievement Value',
+ `level` INT(11) COMMENT 'User Level',
+ job VARCHAR(32) COMMENT 'Career Direction',
+ register_time DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT 'Registration Time'
+) CHARACTER SET UTF8
```
-### 修改表
+### Modifying a Table
-**描述**: 现有一张用户信息表`user_info`,其中包含多年来在平台注册过的用户信息。
+**Description**: There is a user information table `user_info` which contains user information registered on the platform over the years.
-**用户信息表 `user_info`:**
+**User Information Table `user_info`:**
-| Filed | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
-| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | -------- |
-| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | 自增 ID |
-| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | 用户 ID |
-| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | 昵称 |
-| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | 成就值 |
-| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | 用户等级 |
-| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | 职业方向 |
-| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | 注册时间 |
+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Comment |
+| ------------- | ----------- | ---- | --- | ----------------- | -------------- | ----------------- |
+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | auto_increment | Auto-increment ID |
+| uid | int(11) | NO | UNI | (NULL) | | User ID |
+| nick_name | varchar(64) | YES | | (NULL) | | Nickname |
+| achievement | int(11) | YES | | 0 | | Achievement Value |
+| level | int(11) | YES | | (NULL) | | User Level |
+| job | varchar(32) | YES | | (NULL) | | Career Direction |
+| register_time | datetime | YES | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | Registration Time |
-**要求:**请在用户信息表,字段 `level` 的后面增加一列最多可保存 15 个汉字的字段 `school`;并将表中 `job` 列名改为 `profession`,同时 `varchar` 字段长度变为 10;`achievement` 的默认值设置为 0。
+**Requirement**: Please add a new column `school` that can store a maximum of 15 Chinese characters after the `level` column in the user information table; rename the `job` column to `profession` while also changing the `varchar` field length to 10; set the default value of `achievement` to 0.
-**思路**:首先做这题之前,需要了解 ALTER 语句的基本用法:
+**Thought Process**: Before answering, one should understand the basic usage of the ALTER statement:
-- 添加一列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD COLUMN 列名 类型 【first | after 字段名】;`(first : 在某列之前添加,after 反之)
-- 修改列的类型或约束:`ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY COLUMN 列名 新类型 【新约束】;`
-- 修改列名:`ALTER TABLE 表名 change COLUMN 旧列名 新列名 类型;`
-- 删除列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 drop COLUMN 列名;`
-- 修改表名:`ALTER TABLE 表名 rename 【to】 新表名;`
-- 将某一列放到第一列:`ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY COLUMN 列名 类型 first;`
+- Add a column: `ALTER TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN column_name type [first | after column_name];` (first: add before a certain column, after is the opposite)
+- Modify the column type or constraints: `ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name new_type [new_constraints];`
+- Rename the column: `ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE COLUMN old_column_name new_column_name type;`
+- Delete a column: `ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;`
+- Rename a table: `ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME [TO] new_table_name;`
+- Move a column to the first position: `ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name type FIRST;`
-`COLUMN` 关键字其实可以省略不写,这里基于规范还是罗列出来了。
+The `COLUMN` keyword can actually be omitted, but it is listed here for clarity in format.
-在修改时,如果有多个修改项,可以写到一起,但要注意格式
+When making modifications, if there are multiple changes, they can be combined, but formatting is essential.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
ALTER TABLE user_info
@@ -357,15 +357,15 @@ ALTER TABLE user_info
MODIFY achievement INT(11) DEFAULT 0;
```
-### 删除表
+### Deleting a Table
-**描述**:现有一张试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,其中包含多年来的用户作答试卷记录。一般每年都会为 `exam_record` 表建立一张备份表 `exam_record_{YEAR},{YEAR}` 为对应年份。
+**Description**: There is an `exam_record` table containing numerous user exam records over the years. Every year, a backup table named `exam_record_{YEAR}` is created, where `{YEAR}` corresponds to the year.
-现在随着数据越来越多,存储告急,请你把很久前的(2011 到 2014 年)备份表都删掉(如果存在的话)。
+Now, due to increasing data, storage is running low, so please delete the old backup tables from 2011 to 2014 (if they exist).
-**思路**:这题很简单,直接删就行,如果嫌麻烦,可以将要删除的表用逗号隔开,写到一行;这里肯定会有小伙伴问:如果要删除很多张表呢?放心,如果要删除很多张表,可以写脚本来进行删除。
+**Thought Process**: This question is straightforward; just delete them. To avoid additional complexity, you can list the tables to be deleted separated by commas in one line; one might ask: What if there are many tables to delete? No worries, scripts can be written to delete multiple tables.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2011;
@@ -374,13 +374,13 @@ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2013;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2014;
```
-### 创建索引
+### Creating an Index
-**描述**:现有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`,其中包含各种类型试卷的信息。为了对表更方便快捷地查询,需要在 `examination_info` 表创建以下索引,
+**Description**: There is an `examination_info` table containing information on various types of exams. To facilitate quicker queries on this table, the following indexes need to be created in the `examination_info` table:
-规则如下:在 `duration` 列创建普通索引 `idx_duration`、在 `exam_id` 列创建唯一性索引 `uniq_idx_exam_id`、在 `tag` 列创建全文索引 `full_idx_tag`。
+The rules are as follows: create a normal index `idx_duration` on the `duration` column, create a unique index `uniq_idx_exam_id` on the `exam_id` column, and a full-text index `full_idx_tag` on the `tag` column.
-根据题意,将返回如下结果:
+Based on the question, the expected output is as follows:
| examination_info | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | | | | BTREE |
| ---------------- | --- | ---------------- | --- | -------- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | -------- |
@@ -388,32 +388,18 @@ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS exam_record_2014;
| examination_info | 1 | idx_duration | 1 | duration | A | 0 | | | | BTREE |
| examination_info | 1 | full_idx_tag | 1 | tag | | 0 | | | YES | FULLTEXT |
-备注:后台会通过 `SHOW INDEX FROM examination_info` 语句来对比输出结果
+Note: The backend will compare the output using `SHOW INDEX FROM examination_info`.
-**思路**:做这题首先需要了解常见的索引类型:
+**Thought Process**: Before answering, one needs to understand common index types:
-- B-Tree 索引:B-Tree(或称为平衡树)索引是最常见和默认的索引类型。它适用于各种查询条件,可以快速定位到符合条件的数据。B-Tree 索引适用于普通的查找操作,支持等值查询、范围查询和排序。
-- 唯一索引:唯一索引与普通的 B-Tree 索引类似,不同之处在于它要求被索引的列的值是唯一的。这意味着在插入或更新数据时,MySQL 会验证索引列的唯一性。
-- 主键索引:主键索引是一种特殊的唯一索引,它用于唯一标识表中的每一行数据。每个表只能有一个主键索引,它可以帮助提高数据的访问速度和数据完整性。
-- 全文索引:全文索引用于在文本数据中进行全文搜索。它支持在文本字段中进行关键字搜索,而不仅仅是简单的等值或范围查找。全文索引适用于需要进行全文搜索的应用场景。
+- B-Tree Index: The B-Tree (or balanced tree) index is the most common and default type. It's suitable for various query conditions and can quickly locate the data that meets the condition. It's typically used for ordinary queries supporting equality, range queries, and sorting.
+- Unique Index: Similar to the ordinary B-Tree index, but it requires the indexed column’s values to be unique, which means MySQL will check for uniqueness during insertion and updates.
+- Primary Key Index: This is a special type of unique index used to uniquely identify every row in a table. Each table can only have one primary key index, which helps enhance access speed and data integrity.
+- Full-Text Index: A full-text index is used for full-text searches within text data. It supports keyword searches in text fields, not just simple equality or range queries. It's suitable for applications needing full-text search.
-```sql
--- 示例:
--- 添加B-Tree索引:
- CREATE INDEX idx_name(索引名) ON 表名 (字段名); -- idx_name为索引名,以下都是
--- 创建唯一索引:
- CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_name ON 表名 (字段名);
--- 创建一个主键索引:
- ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD PRIMARY KEY (字段名);
--- 创建一个全文索引
- ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD FULLTEXT INDEX idx_name (字段名);
-
--- 通过以上示例,可以看出create 和 alter 都可以添加索引
-```
-
-有了以上的基础知识之后,该题答案也就浮出水面了。
+With this foundational knowledge, the answer to this question is now clear.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
ALTER TABLE examination_info
@@ -422,25 +408,25 @@ ALTER TABLE examination_info
ADD FULLTEXT INDEX full_idx_tag(tag);
```
-### 删除索引
+### Deleting an Index
-**描述**:请删除`examination_info`表上的唯一索引 uniq_idx_exam_id 和全文索引 full_idx_tag。
+**Description**: Please delete the unique index `uniq_idx_exam_id` and the full-text index `full_idx_tag` on the `examination_info` table.
-**思路**:该题考察删除索引的基本语法:
+**Thought Process**: This question tests the basic syntax for deleting an index:
```sql
--- 使用 DROP INDEX 删除索引
-DROP INDEX idx_name ON 表名;
+-- Using DROP INDEX to delete an index
+DROP INDEX idx_name ON table_name;
--- 使用 ALTER TABLE 删除索引
-ALTER TABLE employees DROP INDEX idx_email;
+-- Using ALTER TABLE to delete an index
+ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX idx_name;
```
-这里需要注意的是:在 MySQL 中,一次删除多个索引的操作是不支持的。每次删除索引时,只能指定一个索引名称进行删除。
+It is important to note that in MySQL, multiple indexes cannot be deleted in a single operation. Each operation can only specify one index name for deletion.
-而且 **DROP** 命令需要慎用!!!
+Additionally, **DROP** commands should be used with caution!
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
```sql
DROP INDEX uniq_idx_exam_id ON examination_info;
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
index f5acd8fc5c8..fe478879d90 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-03.md
@@ -1,31 +1,31 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(3)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (3)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+You can decide whether to skip difficult or challenging questions based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 聚合函数
+## Aggregate Functions
-### SQL 类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(较难)
+### Truncated Average Score of High-Difficulty SQL Papers (Difficult)
-**描述**: 牛客的运营同学想要查看大家在 SQL 类别中高难度试卷的得分情况。
+**Description**: The operations team at Niuke wants to see the score situation of users on high-difficulty SQL papers.
-请你帮她从`exam_record`数据表中计算所有用户完成 SQL 类别高难度试卷得分的截断平均值(去掉一个最大值和一个最小值后的平均值)。
+Please help her calculate the truncated average score (the average after removing one maximum and one minimum score) of all users who completed high-difficulty SQL papers from the `exam_record` data table.
-示例数据:`examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间)
+Sample data: `examination_info` (`exam_id` Paper ID, `tag` Paper Category, `difficulty` Paper Difficulty, `duration` Exam Duration, `release_time` Release Time)
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
+| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
+| --- | ------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | Algorithm | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-示例数据:`exam_record`(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分)
+Sample data: `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Paper ID, `start_time` Start Time, `submit_time` Submit Time, `score` Score)
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
@@ -40,1262 +40,16 @@ tag:
| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 50 |
| 10 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-根据输入你的查询结果如下:
+Based on your input, your query result is as follows:
| tag | difficulty | clip_avg_score |
| --- | ---------- | -------------- |
| SQL | hard | 81.7 |
-从`examination_info`表可知,试卷 9001 为高难度 SQL 试卷,该试卷被作答的得分有[80,81,84,90,50],去除最高分和最低分后为[80,81,84],平均分为 81.6666667,保留一位小数后为 81.7
+From the `examination_info` table, it can be seen that paper 9001 is a high-difficulty SQL paper, and the scores for this paper are [80, 81, 84, 90, 50]. After removing the highest and lowest scores, we have [80, 81, 84], and the average score is 81.6666667, which rounds to 81.7 when keeping one decimal place.
-**输入描述:**
+**Input Description:**
-输入数据中至少有 3 个有效分数
+The input data must contain at least 3 valid scores.
-**思路一:** 要找出高难度 sql 试卷,肯定需要联 examination_info 这张表,然后找出高难度的课程,由 examination_info 得知,高难度 sql 的 exam_id 为 9001,那么等下就以 exam_id = 9001 作为条件去查询;
-
-先找出 9001 号考试 `select * from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-然后,找出最高分 `select max(score) 最高分 from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-接着,找出最低分 `select min(score) 最低分 from exam_record where exam_id = 9001`
-
-在查询出来的分数结果集当中,去掉最高分和最低分,最直观能想到的就是 NOT IN 或者 用 NOT EXISTS 也行,这里以 NOT IN 来做
-
-首先将主体写出来`select tag, difficulty, round(avg(score), 1) clip_avg_score from examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record`
-
-**小 tips** : MYSQL 的 `ROUND()` 函数 ,`ROUND(X)`返回参数 X 最近似的整数 `ROUND(X,D)`返回 X ,其值保留到小数点后 D 位,第 D 位的保留方式为四舍五入。
-
-再将上面的 "碎片" 语句拼凑起来即可, 注意在 NOT IN 中两个子查询用 UNION ALL 来关联,用 union 把 max 和 min 的结果集中在一行当中,这样形成一列多行的效果。
-
-**答案一:**
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag, difficulty, ROUND(AVG(score), 1) clip_avg_score
- FROM examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record
- WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND record.exam_id = 9001
- AND record.score NOT IN(
- SELECT MAX(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id = 9001
- UNION ALL
- SELECT MIN(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id = 9001
- )
-```
-
-这是最直观,也是最容易想到的解法,但是还有待改进,这算是投机取巧过关,其实严格按照题目要求应该这么写:
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- difficulty,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 1) clip_avg_score
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND record.exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' )
- AND record.score NOT IN
- (SELECT MAX(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' )
- UNION ALL SELECT MIN(score)
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE exam_id =
- (SELECT examination_info.exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard' ) )
-```
-
-然而你会发现,重复的语句非常多,所以可以利用`WITH`来抽取公共部分
-
-**`WITH` 子句介绍**:
-
-`WITH` 子句,也称为公共表表达式(Common Table Expression,CTE),是在 SQL 查询中定义临时表的方式。它可以让我们在查询中创建一个临时命名的结果集,并且可以在同一查询中引用该结果集。
-
-基本用法:
-
-```sql
-WITH cte_name (column1, column2, ..., columnN) AS (
- -- 查询体
- SELECT ...
- FROM ...
- WHERE ...
-)
--- 主查询
-SELECT ...
-FROM cte_name
-WHERE ...
-```
-
-`WITH` 子句由以下几个部分组成:
-
-- `cte_name`: 给临时表起一个名称,可以在主查询中引用。
-- `(column1, column2, ..., columnN)`: 可选,指定临时表的列名。
-- `AS`: 必需,表示开始定义临时表。
-- `CTE 查询体`: 实际的查询语句,用于定义临时表中的数据。
-
-`WITH` 子句的主要用途之一是增强查询的可读性和可维护性,尤其在涉及多个嵌套子查询或需要重复使用相同的查询逻辑时。通过将这些逻辑放在一个命名的临时表中,我们可以更清晰地组织查询,并消除重复代码。
-
-此外,`WITH` 子句还可以在复杂的查询中实现递归查询。递归查询允许我们在单个查询中执行对同一表的多次迭代,逐步构建结果集。这在处理层次结构数据、组织结构和树状结构等场景中非常有用。
-
-**小细节**:MySQL 5.7 版本以及之前的版本不支持在 `WITH` 子句中直接使用别名。
-
-下面是改进后的答案:
-
-```sql
-WITH t1 AS
- (SELECT record.*,
- info.tag,
- info.difficulty
- FROM exam_record record
- INNER JOIN examination_info info ON record.exam_id = info.exam_id
- WHERE info.tag = "SQL"
- AND info.difficulty = "hard" )
-SELECT tag,
- difficulty,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 1)
-FROM t1
-WHERE score NOT IN
- (SELECT max(score)
- FROM t1
- UNION SELECT min(score)
- FROM t1)
-```
-
-**思路二:**
-
-- 筛选 SQL 高难度试卷:`where tag="SQL" and difficulty="hard"`
-- 计算截断平均值:`(和-最大值-最小值) / (总个数-2)`:
- - `(sum(score) - max(score) - min(score)) / (count(score) - 2)`
- - 有一个缺点就是,如果最大值和最小值有多个,这个方法就很难筛选出来, 但是题目中说了----->**`去掉一个最大值和一个最小值后的平均值`**, 所以这里可以用这个公式。
-
-**答案二:**
-
-```sql
-SELECT info.tag,
- info.difficulty,
- ROUND((SUM(record.score)- MIN(record.score)- MAX(record.score)) / (COUNT(record.score)- 2), 1) AS clip_avg_score
-FROM examination_info info,
- exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND info.tag = "SQL"
- AND info.difficulty = "hard";
-```
-
-### 统计作答次数
-
-有一个试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`,请从中统计出总作答次数 `total_pv`、试卷已完成作答数 `complete_pv`、已完成的试卷数 `complete_exam_cnt`。
-
-示例数据 `exam_record` 表(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | 2021-05-02 10:30:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:31:01 | 84 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 50 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-示例输出:
-
-| total_pv | complete_pv | complete_exam_cnt |
-| -------- | ----------- | ----------------- |
-| 10 | 7 | 2 |
-
-解释:表示截止当前,有 10 次试卷作答记录,已完成的作答次数为 7 次(中途退出的为未完成状态,其交卷时间和份数为 NULL),已完成的试卷有 9001 和 9002 两份。
-
-**思路**: 这题一看到统计次数,肯定第一时间就要想到用`COUNT`这个函数来解决,问题是要统计不同的记录,该怎么来写?使用子查询就能解决这个题目(这题用 case when 也能写出来,解法类似,逻辑不同而已);首先在做这个题之前,让我们先来了解一下`COUNT`的基本用法;
-
-`COUNT()` 函数的基本语法如下所示:
-
-```sql
-COUNT(expression)
-```
-
-其中,`expression` 可以是列名、表达式、常量或通配符。下面是一些常见的用法示例:
-
-1. 计算表中所有行的数量:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-2. 计算特定列非空(不为 NULL)值的数量:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-3. 计算满足条件的行数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name WHERE condition;
-```
-
-4. 结合 `GROUP BY` 使用,计算分组后每个组的行数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name;
-```
-
-5. 计算不同列组合的唯一组合数:
-
-```sql
-SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column_name1, column_name2) FROM table_name;
-```
-
-在使用 `COUNT()` 函数时,如果不指定任何参数或者使用 `COUNT(*)`,将会计算所有行的数量。而如果使用列名,则只会计算该列非空值的数量。
-
-另外,`COUNT()` 函数的结果是一个整数值。即使结果是零,也不会返回 NULL,这点需要谨记。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- count(*) total_pv,
- ( SELECT count(*) FROM exam_record WHERE submit_time IS NOT NULL ) complete_pv,
- ( SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT exam_id, score IS NOT NULL OR NULL ) FROM exam_record ) complete_exam_cnt
-FROM
- exam_record
-```
-
-这里着重说一下`COUNT( DISTINCT exam_id, score IS NOT NULL OR NULL )`这一句,判断 score 是否为 null ,如果是即为真,如果不是返回 null;注意这里如果不加 `or null` 在不是 null 的情况下只会返回 false 也就是返回 0;
-
-`COUNT`本身是不可以对多列求行数的,`distinct`的加入是的多列成为一个整体,可以求出现的行数了;`count distinct`在计算时只返回非 null 的行, 这个也要注意;
-
-另外通过本题 get 到了------>count 加条件常用句式`count( 列判断 or null)`
-
-### 得分不小于平均分的最低分
-
-**描述**: 请从试卷作答记录表中找到 SQL 试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分。
-
-示例数据 exam_record 表(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-`examination_info` 表(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间)
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-示例输出数据:
-
-| min_score_over_avg |
-| ------------------ |
-| 87 |
-
-**解释**:试卷 9001 和 9002 为 SQL 类别,作答这两份试卷的得分有[80,89,87,90],平均分为 86.5,不小于平均分的最小分数为 87
-
-**思路**:这类题目第一眼看确实很复杂, 因为不知道从哪入手,但是当我们仔细读题审题后,要学会抓住题干中的关键信息。以本题为例:`请从试卷作答记录表中找到SQL试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分。`你能一眼从中提取哪些有效信息来作为解题思路?
-
-第一条:找到==SQL==试卷得分
-
-第二条:该类试卷==平均得分==
-
-第三条:该类试卷的==用户最低得分==
-
-然后中间的 “桥梁” 就是==不小于==
-
-将条件拆分后,先逐步完成
-
-```sql
--- 找出tag为‘SQL’的得分 【80, 89,87,90】
--- 再算出这一组的平均得分
-select ROUND(AVG(score), 1) from examination_info info INNER JOIN exam_record record
- where info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- and tag= 'SQL'
-```
-
-然后再找出该类试卷的最低得分,接着将结果集`【80, 89,87,90】` 去和平均分数作比较,方可得出最终答案。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT MIN(score) AS min_score_over_avg
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND tag= 'SQL'
- AND score >=
- (SELECT ROUND(AVG(score), 1)
- FROM examination_info info
- INNER JOIN exam_record record
- WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND tag= 'SQL' )
-```
-
-其实这类题目给出的要求看似很 “绕”,但其实仔细梳理一遍,将大条件拆分成小条件,逐个拆分完以后,最后将所有条件拼凑起来。反正只要记住:**抓主干,理分支**,问题便迎刃而解。
-
-## 分组查询
-
-### 平均活跃天数和月活人数
-
-**描述**:用户在牛客试卷作答区作答记录存储在表 `exam_record` 中,内容如下:
-
-`exam_record` 表(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分)
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-07-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 19:01:01 | 2021-07-02 19:30:01 | 82 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-05 18:01:01 | 2021-07-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 13 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-09-02 12:11:01 | 2020-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请计算 2021 年每个月里试卷作答区用户平均月活跃天数 `avg_active_days` 和月度活跃人数 `mau`,上面数据的示例输出如下:
-
-| month | avg_active_days | mau |
-| ------ | --------------- | --- |
-| 202107 | 1.50 | 2 |
-| 202109 | 1.25 | 4 |
-
-**解释**:2021 年 7 月有 2 人活跃,共活跃了 3 天(1001 活跃 1 天,1002 活跃 2 天),平均活跃天数 1.5;2021 年 9 月有 4 人活跃,共活跃了 5 天,平均活跃天数 1.25,结果保留 2 位小数。
-
-注:此处活跃指有==交卷==行为。
-
-**思路**:读完题先注意高亮部分;一般求天数和月活跃人数马上就要想到相关的日期函数;这一题我们同样来进行拆分,把问题细化再解决;首先求活跃人数,肯定要用到`COUNT()`,那这里首先就有一个坑,不知道大家注意了没有?用户 1002 在 9 月份做了两种不同的试卷,所以这里要注意去重,不然在统计的时候,活跃人数是错的;第二个就是要知道日期的格式化,如上表,题目要求以`202107`这种日期格式展现,要用到`DATE_FORMAT`来进行格式化。
-
-基本用法:
-
-`DATE_FORMAT(date_value, format)`
-
-- `date_value` 参数是待格式化的日期或时间值。
-- `format` 参数是指定的日期或时间格式(这个和 Java 里面的日期格式一样)。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m') MONTH,
- round(count(DISTINCT UID, DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m%d')) / count(DISTINCT UID), 2) avg_active_days,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) mau
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE YEAR (submit_time) = 2021
-GROUP BY MONTH
-```
-
-这里多说一句, 使用`COUNT(DISTINCT uid, DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m%d'))` 可以统计在 `uid` 列和 `submit_time` 列按照年份、月份和日期进行格式化后的组合值的数量。
-
-### 月总刷题数和日均刷题数
-
-**描述**:现有一张题目练习记录表 `practice_record`,示例内容如下:
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请从中统计出 2021 年每个月里用户的月总刷题数 `month_q_cnt` 和日均刷题数 `avg_day_q_cnt`(按月份升序排序)以及该年的总体情况,示例数据输出如下:
-
-| submit_month | month_q_cnt | avg_day_q_cnt |
-| ------------ | ----------- | ------------- |
-| 202108 | 2 | 0.065 |
-| 202109 | 3 | 0.100 |
-| 2021 汇总 | 5 | 0.161 |
-
-**解释**:2021 年 8 月共有 2 次刷题记录,日均刷题数为 2/31=0.065(保留 3 位小数);2021 年 9 月共有 3 次刷题记录,日均刷题数为 3/30=0.100;2021 年共有 5 次刷题记录(年度汇总平均无实际意义,这里我们按照 31 天来算 5/31=0.161)
-
-> 牛客已经采用最新的 Mysql 版本,如果您运行结果出现错误:ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,意思是:对于 GROUP BY 聚合操作,如果在 SELECT 中的列,没有在 GROUP BY 中出现,那么这个 SQL 是不合法的,因为列不在 GROUP BY 从句中,也就是说查出来的列必须在 group by 后面出现否则就会报错,或者这个字段出现在聚合函数里面。
-
-**思路:**
-
-看到实例数据就要马上联想到相关的函数,比如`submit_month`就要用到`DATE_FORMAT`来格式化日期。然后查出每月的刷题数量。
-
-每月的刷题数量
-
-```sql
-SELECT MONTH ( submit_time ), COUNT( question_id )
-FROM
- practice_record
-GROUP BY
- MONTH (submit_time)
-```
-
-接着第三列这里要用到`DAY(LAST_DAY(date_value))`函数来查找给定日期的月份中的天数。
-
-示例代码如下:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY('2023-07-08')) AS days_in_month;
--- 输出:31
-
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY('2023-02-01')) AS days_in_month;
--- 输出:28 (闰年中的二月份)
-
-SELECT DAY(LAST_DAY(NOW())) AS days_in_current_month;
--- 输出:31 (当前月份的天数)
-```
-
-使用 `LAST_DAY()` 函数获取给定日期的当月最后一天,然后使用 `DAY()` 函数提取该日期的天数。这样就能获得指定月份的天数。
-
-需要注意的是,`LAST_DAY()` 函数返回的是日期值,而 `DAY()` 函数用于提取日期值中的天数部分。
-
-有了上述的分析之后,即可马上写出答案,这题复杂就复杂在处理日期上,其中的逻辑并不难。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y%m') submit_month,
- count(question_id) month_q_cnt,
- ROUND(COUNT(question_id) / DAY (LAST_DAY(submit_time)), 3) avg_day_q_cnt
-FROM practice_record
-WHERE DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y') = '2021'
-GROUP BY submit_month
-UNION ALL
-SELECT '2021汇总' AS submit_month,
- count(question_id) month_q_cnt,
- ROUND(COUNT(question_id) / 31, 3) avg_day_q_cnt
-FROM practice_record
-WHERE DATE_FORMAT(submit_time, '%Y') = '2021'
-ORDER BY submit_month
-```
-
-在实例数据输出中因为最后一行需要得出汇总数据,所以这里要 `UNION ALL`加到结果集中;别忘了最后要排序!
-
-### 未完成试卷数大于 1 的有效用户(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-07-02 09:21:01 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 19:01:01 | 2021-07-02 19:30:01 | 82 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-05 18:01:01 | 2021-07-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 13 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-09-02 12:11:01 | 2020-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-还有一张试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-请统计 2021 年每个未完成试卷作答数大于 1 的有效用户的数据(有效用户指完成试卷作答数至少为 1 且未完成数小于 5),输出用户 ID、未完成试卷作答数、完成试卷作答数、作答过的试卷 tag 集合,按未完成试卷数量由多到少排序。示例数据的输出结果如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | complete_cnt | detail |
-| ---- | -------------- | ------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| 1002 | 2 | 4 | 2021-09-01:算法;2021-07-02:SQL;2021-09-02:SQL;2021-09-05:SQL;2021-07-05:SQL |
-
-**解释**:2021 年的作答记录中,除了 1004,其他用户均满足有效用户定义,但只有 1002 未完成试卷数大于 1,因此只输出 1002,detail 中是 1002 作答过的试卷{日期:tag}集合,日期和 tag 间用 **:** 连接,多元素间用 **;** 连接。
-
-**思路:**
-
-仔细读题后,分析出:首先要联表,因为后面要输出`tag`;
-
-筛选出 2021 年的数据
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM exam_record er
-LEFT JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR (er.start_time)= 2021
-```
-
-根据 uid 进行分组,然后对每个用户进行条件进行判断,题目中要求`完成试卷数至少为1,未完成试卷数要大于1,小于5`
-
-那么等会儿写 sql 的时候条件应该是:`未完成 > 1 and 已完成 >=1 and 未完成 < 5`
-
-因为最后要用到字符串的拼接,而且还要组合拼接,这个可以用`GROUP_CONCAT`函数,下面简单介绍一下该函数的用法:
-
-基本格式:
-
-```sql
-GROUP_CONCAT([DISTINCT] expr [ORDER BY {unsigned_integer | col_name | expr} [ASC | DESC] [, ...]] [SEPARATOR sep])
-```
-
-- `expr`:要连接的列或表达式。
-- `DISTINCT`:可选参数,用于去重。当指定了 `DISTINCT`,相同的值只会出现一次。
-- `ORDER BY`:可选参数,用于排序连接后的值。可以选择升序 (`ASC`) 或降序 (`DESC`) 排序。
-- `SEPARATOR sep`:可选参数,用于设置连接后的值的分隔符。(本题要用这个参数设置 ; 号 )
-
-`GROUP_CONCAT()` 函数常用于 `GROUP BY` 子句中,将一组行的值连接为一个字符串,并在结果集中以聚合的形式返回。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.uid,
- SUM(CASE
- WHEN a.submit_time IS NULL THEN 1
- END) AS incomplete_cnt,
- SUM(CASE
- WHEN a.submit_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1
- END) AS complete_cnt,
- GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT CONCAT(DATE_FORMAT(a.start_time, '%Y-%m-%d'), ':', b.tag)
- ORDER BY start_time SEPARATOR ";") AS detail
-FROM exam_record a
-LEFT JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR (a.start_time)= 2021
-GROUP BY a.uid
-HAVING incomplete_cnt > 1
-AND complete_cnt >= 1
-AND incomplete_cnt < 5
-ORDER BY incomplete_cnt DESC
-```
-
-- `SUM(CASE WHEN a.submit_time IS NULL THEN 1 END)` 统计了每个用户未完成的记录数量。
-- `SUM(CASE WHEN a.submit_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1 END)` 统计了每个用户已完成的记录数量。
-- `GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT CONCAT(DATE_FORMAT(a.start_time, '%Y-%m-%d'), ':', b.tag) ORDER BY a.start_time SEPARATOR ';')` 将每个用户的考试日期和标签以逗号分隔的形式连接成一个字符串,并按考试开始时间进行排序。
-
-## 嵌套子查询
-
-### 月均完成试卷数不小于 3 的用户爱作答的类别(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid`:用户 ID, `exam_id`:试卷 ID, `start_time`:开始作答时间, `submit_time`:交卷时间,没提交的话为 NULL, `score`:得分),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 13:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 12 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 13 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id`:试卷 ID, `tag`:试卷类别, `difficulty`:试卷难度, `duration`:考试时长, `release_time`:发布时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-请从表中统计出 “当月均完成试卷数”不小于 3 的用户们爱作答的类别及作答次数,按次数降序输出,示例输出如下:
-
-| tag | tag_cnt |
-| ---- | ------- |
-| C++ | 4 |
-| SQL | 2 |
-| 算法 | 1 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1002 和 1005 在 2021 年 09 月的完成试卷数目均为 3,其他用户均小于 3;然后用户 1002 和 1005 作答过的试卷 tag 分布结果按作答次数降序排序依次为 C++、SQL、算法。
-
-**思路**:这题考察联合子查询,重点在于`月均回答>=3`, 但是个人认为这里没有表述清楚,应该直接说查 9 月的就容易理解多了;这里不是每个月都要>=3 或者是所有答题次数/答题月份。不要理解错误了。
-
-先查询出哪些用户月均答题大于三次
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID
-FROM exam_record record
-GROUP BY UID,
- MONTH (start_time)
-HAVING count(submit_time) >= 3
-```
-
-有了这一步之后再进行深入,只要能理解上一步(我的意思是不被题目中的月均所困扰),然后再套一个子查询,查哪些用户包含其中,然后查出题目中所需的列即可。记得排序!!
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- count(start_time) AS tag_cnt
-FROM exam_record record
-INNER JOIN examination_info info ON record.exam_id = info.exam_id
-WHERE UID IN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM exam_record record
- GROUP BY UID,
- MONTH (start_time)
- HAVING count(submit_time) >= 3)
-GROUP BY tag
-ORDER BY tag_cnt DESC
-```
-
-### 试卷发布当天作答人数和平均分
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间),示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 1500 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1100 | 4 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-**释义**:用户 1001 昵称为牛客 1 号,成就值为 3100,用户等级是 7 级,职业方向为算法,注册时间 2020-01-01 10:00:00
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间) 示例数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-08-02 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分) 示例数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-07-02 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 70 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 12:01:01 | 2021-08-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-08-02 12:01:01 | 2021-08-02 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-07-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 11 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 13:01:01 | 2021-09-01 13:41:01 | 70 |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 16 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请计算每张 SQL 类别试卷发布后,当天 5 级以上的用户作答的人数 `uv` 和平均分 `avg_score`,按人数降序,相同人数的按平均分升序,示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | uv | avg_score |
-| ------- | --- | --------- |
-| 9001 | 3 | 81.3 |
-
-解释:只有一张 SQL 类别的试卷,试卷 ID 为 9001,发布当天(2021-09-01)有 1001、1002、1003、1005 作答过,但是 1003 是 5 级用户,其他 3 位为 5 级以上,他们三的得分有[70,80,85,90],平均分为 81.3(保留 1 位小数)。
-
-**思路**:这题看似很复杂,但是先逐步将“外边”条件拆分,然后合拢到一起,答案就出来,多表查询反正记住:由外向里,抽丝剥茧。
-
-先把三种表连起来,同时给定一些条件,比如题目中要求`等级> 5`的用户,那么可以先查出来
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT u_info.uid
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND u_info.LEVEL > 5
-```
-
-接着注意题目中要求:`每张sql类别试卷发布后,当天作答用户`,注意其中的==当天==,那我们马上就要想到要用到时间的比较。
-
-对试卷发布日期和开始考试日期进行比较:`DATE(e_info.release_time) = DATE(record.start_time)`;不用担心`submit_time` 为 null 的问题,后续在 where 中会给过滤掉。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT record.exam_id AS exam_id,
- COUNT(DISTINCT u_info.uid) AS uv,
- ROUND(SUM(record.score) / COUNT(u_info.uid), 1) AS avg_score
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND DATE (e_info.release_time) = DATE (record.start_time)
- AND submit_time IS NOT NULL
- AND tag = 'SQL'
- AND u_info.LEVEL > 5
-GROUP BY record.exam_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- avg_score ASC
-```
-
-注意最后的分组排序!先按人数排,若一致,按平均分排。
-
-### 作答试卷得分大于过 80 的人的用户等级分布
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 1500 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1100 | 4 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答信息表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 79 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 12:01:01 | 2021-08-01 12:21:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 86 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 11 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 13:01:01 | 2021-09-01 13:41:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 88 |
-| 16 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | 2021-09-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-
-统计作答 SQL 类别的试卷得分大于过 80 的人的用户等级分布,按数量降序排序(保证数量都不同)。示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| level | level_cnt |
-| ----- | --------- |
-| 6 | 2 |
-| 5 | 1 |
-
-解释:9001 为 SQL 类试卷,作答该试卷大于 80 分的人有 1002、1003、1005 共 3 人,6 级两人,5 级一人。
-
-**思路:**这题和上一题都是一样的数据,只是查询条件改变了而已,上一题理解了,这题分分钟做出来。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT u_info.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- count(u_info.uid) AS level_cnt
-FROM examination_info e_info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-INNER JOIN user_info u_info
-WHERE e_info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND u_info.uid = record.uid
- AND record.score > 80
- AND submit_time IS NOT NULL
- AND tag = 'SQL'
-GROUP BY LEVEL
-ORDER BY level_cnt DESC
-```
-
-## 合并查询
-
-### 每个题目和每份试卷被作答的人数和次数
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:41:01 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 80 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 85 |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-题目练习表 practice_record(uid 用户 ID, question_id 题目 ID, submit_time 提交时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请统计每个题目和每份试卷被作答的人数和次数,分别按照"试卷"和"题目"的 uv & pv 降序显示,示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tid | uv | pv |
-| ---- | --- | --- |
-| 9001 | 3 | 3 |
-| 9002 | 1 | 3 |
-| 8001 | 3 | 5 |
-| 8002 | 2 | 2 |
-
-**解释**:“试卷”有 3 人共练习 3 次试卷 9001,1 人作答 3 次 9002;“刷题”有 3 人刷 5 次 8001,有 2 人刷 2 次 8002
-
-**思路**:这题的难点和易错点在于`UNION`和`ORDER BY` 同时使用的问题
-
-有以下几种情况:使用`union`和多个`order by`不加括号,报错!
-
-`order by`在`union`连接的子句中不起作用;
-
-比如不加括号:
-
-```sql
-SELECT exam_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) AS uv,
- COUNT(UID) AS pv
-FROM exam_record
-GROUP BY exam_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- pv DESC
-UNION
-SELECT question_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT UID) AS uv,
- COUNT(UID) AS pv
-FROM practice_record
-GROUP BY question_id
-ORDER BY uv DESC,
- pv DESC
-```
-
-直接报语法错误,如果没有括号,只能有一个`order by`
-
-还有一种`order by`不起作用的情况,但是能在子句的子句中起作用,这里的解决方案就是在外面再套一层查询。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM
- (SELECT exam_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT exam_record.uid) uv,
- COUNT(*) pv
- FROM exam_record
- GROUP BY exam_id
- ORDER BY uv DESC, pv DESC) t1
-UNION
-SELECT *
-FROM
- (SELECT question_id AS tid,
- COUNT(DISTINCT practice_record.uid) uv,
- COUNT(*) pv
- FROM practice_record
- GROUP BY question_id
- ORDER BY uv DESC, pv DESC) t2;
-```
-
-### 分别满足两个活动的人
-
-**描述**: 为了促进更多用户在牛客平台学习和刷题进步,我们会经常给一些既活跃又表现不错的用户发放福利。假使以前我们有两拨运营活动,分别给每次试卷得分都能到 85 分的人(activity1)、至少有一次用了一半时间就完成高难度试卷且分数大于 80 的人(activity2)发了福利券。
-
-现在,需要你一次性将这两个活动满足的人筛选出来,交给运营同学。请写出一个 SQL 实现:输出 2021 年里,所有每次试卷得分都能到 85 分的人以及至少有一次用了一半时间就完成高难度试卷且分数大于 80 的人的 id 和活动号,按用户 ID 排序输出。
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 70 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | **86** |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-
-示例数据输出结果:
-
-| uid | activity |
-| ---- | --------- |
-| 1001 | activity2 |
-| 1003 | activity1 |
-| 1004 | activity1 |
-| 1004 | activity2 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1001 最小分数 81 不满足活动 1,但 29 分 59 秒完成了 60 分钟长的试卷得分 81,满足活动 2;1003 最小分数 86 满足活动 1,完成时长都大于试卷时长的一半,不满足活动 2;用户 1004 刚好用了一半时间(30 分钟整)完成了试卷得分 85,满足活动 1 和活动 2。
-
-**思路**: 这一题需要涉及到时间的减法,需要用到 `TIMESTAMPDIFF()` 函数计算两个时间戳之间的分钟差值。
-
-下面我们来看一下基本用法
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, end_time)
-```
-
-`TIMESTAMPDIFF()` 函数的第一个参数是时间单位,这里我们选择 `MINUTE` 表示返回分钟差值。第二个参数是较早的时间戳,第三个参数是较晚的时间戳。函数会返回它们之间的分钟差值
-
-了解了这个函数的用法之后,我们再回过头来看`activity1`的要求,求分数大于 85 即可,那我们还是先把这个写出来,后续思路就会清晰很多
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT UID
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE score >= 85
- AND YEAR (start_time) = '2021'
-```
-
-根据条件 2,接着写出`在一半时间内完成高难度试卷且分数大于80的人`
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID
-FROM examination_info info
-INNER JOIN exam_record record
-WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
- AND (TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time)) < (info.duration / 2)
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND score >= 80
-```
-
-然后再把两者`UNION` 起来即可。(这里特别要注意括号问题和`order by`位置,具体用法在上一篇中已提及)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT UID UID,
- 'activity1' activity
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE UID not in
- (SELECT UID
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE score<85
- AND YEAR(submit_time) = 2021 )
-UNION
-SELECT DISTINCT UID UID,
- 'activity2' activity
-FROM exam_record e_r
-LEFT JOIN examination_info e_i ON e_r.exam_id = e_i.exam_id
-WHERE YEAR(submit_time) = 2021
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND TIMESTAMPDIFF(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) <= duration *30
- AND score>80
-ORDER BY UID
-```
-
-## 连接查询
-
-### 满足条件的用户的试卷完成数和题目练习数(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 user_info(uid 用户 ID,nick_name 昵称, achievement 成就值, level 等级, job 职业方向, register_time 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2300 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 2500 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 2000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 examination_info(exam_id 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, difficulty 试卷难度, duration 考试时长, release_time 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 86 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 80 |
-
-题目练习记录表 practice_record(uid 用户 ID, question_id 题目 ID, submit_time 提交时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 8 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:58:01 | 94 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 11 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1004 | 8003 | 2021-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请你找到高难度 SQL 试卷得分平均值大于 80 并且是 7 级的红名大佬,统计他们的 2021 年试卷总完成次数和题目总练习次数,只保留 2021 年有试卷完成记录的用户。结果按试卷完成数升序,按题目练习数降序。
-
-示例数据输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_cnt | question_cnt |
-| ---- | -------- | ------------ |
-| 1001 | 1 | 2 |
-| 1003 | 2 | 0 |
-
-解释:用户 1001、1003、1004、1006 满足高难度 SQL 试卷得分平均值大于 80,但只有 1001、1003 是 7 级红名大佬;1001 完成了 1 次试卷 1001,练习了 2 次题目;1003 完成了 2 次试卷 9001、9002,未练习题目(因此计数为 0)
-
-**思路:**
-
-先将条件进行初步筛选,比如先查出做过高难度 sql 试卷的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- record.uid
-FROM
- exam_record record
- INNER JOIN examination_info e_info ON record.exam_id = e_info.exam_id
- JOIN user_info u_info ON record.uid = u_info.uid
-WHERE
- e_info.tag = 'SQL'
- AND e_info.difficulty = 'hard'
-```
-
-然后根据题目要求,接着再往里叠条件即可;
-
-但是这里又要注意:
-
-第一:不能`YEAR(submit_time)= 2021`这个条件放到最后,要在`ON`条件里,因为左连接存在返回左表全部行,右表为 null 的情形,放在 `JOIN`条件的 `ON` 子句中的目的是为了确保在连接两个表时,只有满足年份条件的记录会进行连接。这样可以避免其他年份的记录被包含在结果中。即 1001 做过 2021 年的试卷,但没有练习过,如果把条件放到最后,就会排除掉这种情况。
-
-第二,必须是`COUNT(distinct er.exam_id) exam_cnt, COUNT(distinct pr.id) question_cnt,`要加 distinct,因为有左连接产生很多重复值。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT er.uid AS UID,
- count(DISTINCT er.exam_id) AS exam_cnt,
- count(DISTINCT pr.id) AS question_cnt
-FROM exam_record er
-LEFT JOIN practice_record pr ON er.uid = pr.uid
-AND YEAR (er.submit_time)= 2021
-AND YEAR (pr.submit_time)= 2021
-WHERE er.uid IN
- (SELECT er.uid
- FROM exam_record er
- LEFT JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
- LEFT JOIN user_info ui ON er.uid = ui.uid
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- AND difficulty = 'hard'
- AND LEVEL = 7
- GROUP BY er.uid
- HAVING avg(score) > 80)
-GROUP BY er.uid
-ORDER BY exam_cnt,
- question_cnt DESC
-```
-
-可能细心的小伙伴会发现,为什么明明将条件限制了`tag = 'SQL' AND difficulty = 'hard'`,但是用户 1003 仍然能查出两条考试记录,其中一条的考试`tag`为 `C++`; 这是由于`LEFT JOIN`的特性,即使没有与右表匹配的行,左表的所有记录仍然会被保留。
-
-### 每个 6/7 级用户活跃情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3100 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2300 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 | 2500 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 1200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 1600 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 2600 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | easy | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:59 | 84 |
-| 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 2020-09-01 13:01:01 | 2020-09-01 13:41:01 | 81 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-题目练习记录表 `practice_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `question_id` 题目 ID, `submit_time` 提交时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 1004 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1001 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 8002 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1006 | 8002 | 2021-08-04 19:58:01 | 94 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2021-08-03 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2021-08-02 19:48:01 | 90 |
-| 1006 | 8003 | 2020-08-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请统计每个 6/7 级用户总活跃月份数、2021 年活跃天数、2021 年试卷作答活跃天数、2021 年答题活跃天数,按照总活跃月份数、2021 年活跃天数降序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | act_month_total | act_days_2021 | act_days_2021_exam |
-| ---- | --------------- | ------------- | ------------------ |
-| 1006 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
-| 1001 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
-| 1005 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
-
-**解释**:6/7 级用户共有 5 个,其中 1006 在 202109、202108、202008 共 3 个月活跃过,2021 年活跃的日期有 20210907、20210804、20210803、20210802 共 4 天,2021 年在试卷作答区 20210907 活跃 1 天,在题目练习区活跃了 3 天。
-
-**思路:**
-
-这题的关键在于`CASE WHEN THEN`的使用,不然要写很多的`left join` 因为会产生很多的结果集。
-
-`CASE WHEN THEN`语句是一种条件表达式,用于在 SQL 中根据条件执行不同的操作或返回不同的结果。
-
-语法结构如下:
-
-```sql
-CASE
- WHEN condition1 THEN result1
- WHEN condition2 THEN result2
- ...
- ELSE result
-END
-```
-
-在这个结构中,可以根据需要添加多个`WHEN`子句,每个`WHEN`子句后面跟着一个条件(condition)和一个结果(result)。条件可以是任何逻辑表达式,如果满足条件,将返回对应的结果。
-
-最后的`ELSE`子句是可选的,用于指定当所有前面的条件都不满足时的默认返回结果。如果没有提供`ELSE`子句,则默认返回`NULL`。
-
-例如:
-
-```sql
-SELECT score,
- CASE
- WHEN score >= 90 THEN '优秀'
- WHEN score >= 80 THEN '良好'
- WHEN score >= 60 THEN '及格'
- ELSE '不及格'
- END AS grade
-FROM student_scores;
-```
-
-在上述示例中,根据学生成绩(score)的不同范围,使用 CASE WHEN THEN 语句返回相应的等级(grade)。如果成绩大于等于 90,则返回"优秀";如果成绩大于等于 80,则返回"良好";如果成绩大于等于 60,则返回"及格";否则返回"不及格"。
-
-那了解到了上述的用法之后,回过头看看该题,要求列出不同的活跃天数。
-
-```sql
-count(distinct act_month) as act_month_total,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021'then act_day end) as act_days_2021,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021' and tag='exam' then act_day end) as act_days_2021_exam,
-count(distinct case when year(act_time)='2021' and tag='question'then act_day end) as act_days_2021_question
-```
-
-这里的 tag 是先给标记,方便对查询进行区分,将考试和答题分开。
-
-找出试卷作答区的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- exam_id AS ans_id,
- start_time AS act_time,
- date_format( start_time, '%Y%m' ) AS act_month,
- date_format( start_time, '%Y%m%d' ) AS act_day,
- 'exam' AS tag
- FROM
- exam_record
-```
-
-紧接着就是答题作答区的用户
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- question_id AS ans_id,
- submit_time AS act_time,
- date_format( submit_time, '%Y%m' ) AS act_month,
- date_format( submit_time, '%Y%m%d' ) AS act_day,
- 'question' AS tag
- FROM
- practice_record
-```
-
-最后将两个结果进行`UNION` 最后别忘了将结果进行排序 (这题有点类似于分治法的思想)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT user_info.uid,
- count(DISTINCT act_month) AS act_month_total,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021'
- AND tag = 'exam' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021_exam,
- count(DISTINCT CASE
- WHEN YEAR (act_time)= '2021'
- AND tag = 'question' THEN act_day
- END) AS act_days_2021_question
-FROM
- (SELECT UID,
- exam_id AS ans_id,
- start_time AS act_time,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS act_month,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') AS act_day,
- 'exam' AS tag
- FROM exam_record
- UNION ALL SELECT UID,
- question_id AS ans_id,
- submit_time AS act_time,
- date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m') AS act_month,
- date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m%d') AS act_day,
- 'question' AS tag
- FROM practice_record) total
-RIGHT JOIN user_info ON total.uid = user_info.uid
-WHERE user_info.LEVEL IN (6,
- 7)
-GROUP BY user_info.uid
-ORDER BY act_month_total DESC,
- act_days_2021 DESC
-```
-
-
+**Approach 1:** To find high-difficulty SQL papers, you need to join the `examination_info` table and find the high-difficulty courses. From `examination_info`, we know that the exam_id for high-difficulty SQL is 900
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
index 84f1a2b3c8c..8d60b4e8ecc 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-04.md
@@ -1,55 +1,55 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(4)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (4)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of the questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+For more difficult questions, you can decide whether to skip them based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 专用窗口函数
+## Specialized Window Functions
-MySQL 8.0 版本引入了窗口函数的支持,下面是 MySQL 中常见的窗口函数及其用法:
+MySQL 8.0 introduced support for window functions. Below are common window functions in MySQL and their usage:
-1. `ROW_NUMBER()`: 为查询结果集中的每一行分配一个唯一的整数值。
+1. `ROW_NUMBER()`: Assigns a unique integer value to each row in the result set.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS row_num
FROM table;
```
-2. `RANK()`: 计算每一行在排序结果中的排名。
+2. `RANK()`: Calculates the rank of each row in the sorted result.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY col1 DESC) AS ranking
FROM table;
```
-3. `DENSE_RANK()`: 计算每一行在排序结果中的排名,保留相同的排名。
+3. `DENSE_RANK()`: Calculates the rank of each row in the sorted result, preserving the same rank for ties.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY col1 DESC) AS ranking
FROM table;
```
-4. `NTILE(n)`: 将结果分成 n 个基本均匀的桶,并为每个桶分配一个标识号。
+4. `NTILE(n)`: Divides the result into n evenly distributed buckets and assigns an identifier to each bucket.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS bucket
FROM table;
```
-5. `SUM()`, `AVG()`,`COUNT()`, `MIN()`, `MAX()`: 这些聚合函数也可以与窗口函数结合使用,计算窗口内指定列的汇总、平均值、计数、最小值和最大值。
+5. `SUM()`, `AVG()`, `COUNT()`, `MIN()`, `MAX()`: These aggregate functions can also be used with window functions to calculate the sum, average, count, minimum, and maximum of specified columns within the window.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, SUM(col1) OVER () AS sum_col
FROM table;
```
-6. `LEAD()` 和 `LAG()`: LEAD 函数用于获取当前行之后的某个偏移量的行的值,而 LAG 函数用于获取当前行之前的某个偏移量的行的值。
+6. `LEAD()` and `LAG()`: The LEAD function is used to get the value of a row at a specified offset after the current row, while the LAG function is used to get the value of a row at a specified offset before the current row.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, LEAD(col1, 1) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS next_col1,
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ SELECT col1, col2, LEAD(col1, 1) OVER (ORDER BY col1) AS next_col1,
FROM table;
```
-7. `FIRST_VALUE()` 和 `LAST_VALUE()`: FIRST_VALUE 函数用于获取窗口内指定列的第一个值,LAST_VALUE 函数用于获取窗口内指定列的最后一个值。
+7. `FIRST_VALUE()` and `LAST_VALUE()`: The FIRST_VALUE function retrieves the first value of a specified column within the window, while the LAST_VALUE function retrieves the last value of a specified column within the window.
```sql
SELECT col1, col2, FIRST_VALUE(col2) OVER (PARTITION BY col1 ORDER BY col2) AS first_val,
@@ -65,768 +65,24 @@ SELECT col1, col2, FIRST_VALUE(col2) OVER (PARTITION BY col1 ORDER BY col2) AS f
FROM table;
```
-窗口函数通常需要配合 OVER 子句一起使用,用于定义窗口的大小、排序规则和分组方式。
+Window functions typically need to be used in conjunction with the OVER clause to define the size of the window, sorting rules, and grouping methods.
-### 每类试卷得分前三名
+### Top Three Scores for Each Exam Type
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
+There is an exam information table `examination_info` (`exam_id` Exam ID, `tag` Exam Category, `difficulty` Exam Difficulty, `duration` Exam Duration, `release_time` Release Time):
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
+| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
+| --- | ------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
+| 3 | 9003 | Algorithm | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:40:01 | 86 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1005 | 9003 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到每类试卷得分的前 3 名,如果两人最大分数相同,选择最小分数大者,如果还相同,选择 uid 大者。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tid | uid | ranking |
-| ---- | ---- | ------- |
-| SQL | 1003 | 1 |
-| SQL | 1004 | 2 |
-| SQL | 1002 | 3 |
-| 算法 | 1005 | 1 |
-| 算法 | 1006 | 2 |
-| 算法 | 1003 | 3 |
-
-**解释**:有作答得分记录的试卷 tag 有 SQL 和算法,SQL 试卷用户 1001、1002、1003、1004 有作答得分,最高得分分别为 81、81、89、85,最低得分分别为 78、81、86、40,因此先按最高得分排名再按最低得分排名取前三为 1003、1004、1002。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT tag,
- UID,
- ranking
-FROM
- (SELECT b.tag AS tag,
- a.uid AS UID,
- ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY b.tag
- ORDER BY b.tag,
- max(a.score) DESC,
- min(a.score) DESC,
- a.uid DESC) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
- GROUP BY b.tag,
- a.uid) t
-WHERE ranking <= 3
-```
-
-### 第二快/慢用时之差大于试卷时长一半的试卷(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2021-09-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| ---- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:51:01 | 78 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:59:01 | 86 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:51 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 19:01:01 | 2021-09-01 19:30:01 | 85 |
-| 7 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:02 | 85 |
-| 8 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:02:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:01 | 84 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-08 12:01:01 | 2021-09-08 12:11:01 | 40 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 14:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-09-08 15:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到第二快和第二慢用时之差大于试卷时长的一半的试卷信息,按试卷 ID 降序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | duration | release_time |
-| ------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 9001 | 60 | 2021-09-01 06:00:00 |
-
-**解释**:试卷 9001 被作答用时有 50 分钟、58 分钟、30 分 1 秒、19 分钟、10 分钟,第二快和第二慢用时之差为 50 分钟-19 分钟=31 分钟,试卷时长为 60 分钟,因此满足大于试卷时长一半的条件,输出试卷 ID、时长、发布时间。
-
-**思路:**
-
-第一步,找到每张试卷完成时间的顺序排名和倒序排名 也就是表 a;
-
-第二步,与通过试卷信息表 b 建立内连接,并根据试卷 id 分组,利用`having`筛选排名为第二个数据,将秒转化为分钟并进行比较,最后再根据试卷 id 倒序排序就行
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.exam_id,
- b.duration,
- b.release_time
-FROM
- (SELECT exam_id,
- row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) DESC) rn1,
- row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) ASC) rn2,
- timestampdiff(SECOND, start_time, submit_time) timex
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE score IS NOT NULL ) a
-INNER JOIN examination_info b ON a.exam_id = b.exam_id
-GROUP BY a.exam_id
-HAVING (max(IF (rn1 = 2, a.timex, 0))- max(IF (rn2 = 2, a.timex, 0)))/ 60 > b.duration / 2
-ORDER BY a.exam_id DESC
-```
-
-### 连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗(较难)
-
-**描述**
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:21:02 | 84 |
-| 2 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 12:11:01 | 2021-09-01 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | 2021-09-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1005 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 10:01:01 | 2021-09-05 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 10:31:01 | 2021-09-05 10:51:01 | 81 |
-
-请计算在 2021 年至少有两天作答过试卷的人中,计算该年连续两次作答试卷的最大时间窗 `days_window`,那么根据该年的历史规律他在 `days_window` 天里平均会做多少套试卷,按最大时间窗和平均做答试卷套数倒序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | days_window | avg_exam_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------- | ------------ |
-| 1006 | 6 | 2.57 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1006 分别在 20210901、20210906、20210907 作答过 3 次试卷,连续两次作答最大时间窗为 6 天(1 号到 6 号),他 1 号到 7 号这 7 天里共做了 3 张试卷,平均每天 3/7=0.428571 张,那么 6 天里平均会做 0.428571\*6=2.57 张试卷(保留两位小数);用户 1005 在 20210905 做了两张试卷,但是只有一天的作答记录,过滤掉。
-
-**思路:**
-
-上面这个解释中提示要对作答记录去重,千万别被骗了,不要去重!去重就通不过测试用例。注意限制时间是 2021 年;
-
-而且要注意时间差要+1 天;还要注意==没交卷也算在内==!!!! (反正感觉这题描述不清,出的不是很好)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- max(datediff(next_time, start_time)) + 1 AS days_window,
- round(count(start_time)/(datediff(max(start_time), min(start_time))+ 1) * (max(datediff(next_time, start_time))+ 1), 2) AS avg_exam_cnt
-FROM
- (SELECT UID,
- start_time,
- lead(start_time, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY start_time) AS next_time
- FROM exam_record
- WHERE YEAR (start_time) = '2021' ) a
-GROUP BY UID
-HAVING count(DISTINCT date(start_time)) > 1
-ORDER BY days_window DESC,
- avg_exam_cnt DESC
-```
-
-### 近三个月未完成为 0 的用户完成情况
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid`:用户 ID, `exam_id`:试卷 ID, `start_time`:开始作答时间, `submit_time`:交卷时间,为空的话则代表未完成, `score`:得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1006 | 9003 | 2021-09-06 10:01:01 | 2021-09-06 10:21:02 | 84 |
-| 2 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-08-02 12:11:01 | 2021-08-02 12:31:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-06-06 10:01:01 | 2021-06-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 4 | 1006 | 9002 | 2021-05-06 10:01:01 | 2021-05-06 10:21:01 | 81 |
-| 5 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-05-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-05 10:31:01 | 2021-09-05 10:51:01 | 81 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-08-01 09:01:01 | 2021-08-01 09:51:11 | 78 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 09:01:01 | 2021-07-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | 2021-07-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 10 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-07-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-找到每个人近三个有试卷作答记录的月份中没有试卷是未完成状态的用户的试卷作答完成数,按试卷完成数和用户 ID 降序排名。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_complete_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------------- |
-| 1006 | 3 |
-
-**解释**:用户 1006 近三个有作答试卷的月份为 202109、202108、202106,作答试卷数为 3,全部完成;用户 1001 近三个有作答试卷的月份为 202109、202108、202107,作答试卷数为 5,完成试卷数为 4,因为有未完成试卷,故过滤掉。
-
-**思路:**
-
-1. `找到每个人近三个有试卷作答记录的月份中没有试卷是未完成状态的用户的试卷作答完成数`首先看这句话,肯定要先根据人进行分组
-2. 最近三个月,可以采用连续重复排名,倒序排列,排名<=3
-3. 统计作答数
-4. 拼装剩余条件
-5. 排序
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- count(score) exam_complete_cnt
-FROM
- (SELECT *, DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) dr
- FROM exam_record) t1
-WHERE dr <= 3
-GROUP BY UID
-HAVING count(dr)= count(score)
-ORDER BY exam_complete_cnt DESC,
- UID DESC
-```
-
-### 未完成率较高的 50%用户近三个月答卷情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 3200 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 15 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 18:01:01 | 2020-01-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 13 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | | |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | | |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | | |
-| 6 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | | |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 14 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | | |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | | |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 17 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-05-05 18:01:01 | | |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-05-06 12:01:01 | | |
-
-请统计 SQL 试卷上未完成率较高的 50%用户中,6 级和 7 级用户在有试卷作答记录的近三个月中,每个月的答卷数目和完成数目。按用户 ID、月份升序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | start_month | total_cnt | complete_cnt |
-| ---- | ----------- | --------- | ------------ |
-| 1002 | 202002 | 3 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 202003 | 2 | 1 |
-| 1002 | 202005 | 2 | 1 |
-
-解释:各个用户对 SQL 试卷的未完成数、作答总数、未完成率如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | total_cnt | incomplete_rate |
-| ---- | -------------- | --------- | --------------- |
-| 1001 | 3 | 7 | 0.4286 |
-| 1002 | 4 | 8 | 0.5000 |
-| 1003 | 1 | 1 | 1.0000 |
-
-1001、1002、1003 分别排在 1.0、0.5、0.0 的位置,因此较高的 50%用户(排位<=0.5)为 1002、1003;
-
-1003 不是 6 级或 7 级;
-
-有试卷作答记录的近三个月为 202005、202003、202002;
-
-这三个月里 1002 的作答题数分别为 3、2、2,完成数目分别为 1、1、1。
-
-**思路:**
-
-注意点:这题注意求的是所有的答题次数和完成次数,而 sql 类别的试卷是限制未完成率排名,6, 7 级用户限制的是做题记录。
-
-先求出未完成率的排名
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- count(submit_time IS NULL
- OR NULL)/ count(start_time) AS num,
- PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
- ORDER BY count(submit_time IS NULL
- OR NULL)/ count(start_time)) AS ranking
-FROM exam_record
-LEFT JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
-WHERE tag = 'SQL'
-GROUP BY UID
-```
-
-再求出最近三个月的练习记录
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS month_d,
- submit_time,
- exam_id,
- dense_rank() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) AS ranking
-FROM exam_record
-LEFT JOIN user_info USING (UID)
-WHERE LEVEL IN (6,7)
-```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT t1.uid,
- t1.month_d,
- count(*) AS total_cnt,
- count(t1.submit_time) AS complete_cnt
-FROM-- 先求出未完成率的排名
-
- (SELECT UID,
- count(submit_time IS NULL OR NULL)/ count(start_time) AS num,
- PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
- ORDER BY count(submit_time IS NULL OR NULL)/ count(start_time)) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record
- LEFT JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
- WHERE tag = 'SQL'
- GROUP BY UID) t
-INNER JOIN
- (-- 再求出近三个月的练习记录
- SELECT UID,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS month_d,
- submit_time,
- exam_id,
- dense_rank() OVER (PARTITION BY UID
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') DESC) AS ranking
- FROM exam_record
- LEFT JOIN user_info USING (UID)
- WHERE LEVEL IN (6,7) ) t1 USING (UID)
-WHERE t1.ranking <= 3 AND t.ranking >= 0.5 -- 使用限制找到符合条件的记录
-
-GROUP BY t1.uid,
- t1.month_d
-ORDER BY t1.uid,
- t1.month_d
-```
-
-### 试卷完成数同比 2020 年的增长率及排名变化(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
+There is an exam record table `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Exam ID, `start_time` Start Time, `submit_time` Submit Time, `score` Score):
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-08-02 10:01:01 | 2020-08-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-04-01 18:01:01 | 2020-04-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-04-01 09:01:01 | 2020-04-01 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-03-02 19:01:01 | 2021-03-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 12:01:01 | 2021-05-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | | |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 18 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | | |
-| 4 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-01-20 10:01:01 | 2021-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-04-02 19:01:01 | 2021-04-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 15 | 1002 | 9003 | 2021-01-01 18:01:01 | 2021-01-01 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1004 | 9004 | 2020-05-02 12:01:01 | 2020-05-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-02 12:11:01 | | |
-| 14 | 1002 | 9004 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-
-请计算 2021 年上半年各类试卷的做完次数相比 2020 年上半年同期的增长率(百分比格式,保留 1 位小数),以及做完次数排名变化,按增长率和 21 年排名降序输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tag | exam_cnt_20 | exam_cnt_21 | growth_rate | exam_cnt_rank_20 | exam_cnt_rank_21 | rank_delta |
-| --- | ----------- | ----------- | ----------- | ---------------- | ---------------- | ---------- |
-| SQL | 3 | 2 | -33.3% | 1 | 2 | 1 |
-
-解释:2020 年上半年有 3 个 tag 有作答完成的记录,分别是 C++、SQL、PYTHON,它们被做完的次数分别是 3、3、2,做完次数排名为 1、1(并列)、3;
-
-2021 年上半年有 2 个 tag 有作答完成的记录,分别是算法、SQL,它们被做完的次数分别是 3、2,做完次数排名为 1、2;具体如下:
-
-| tag | start_year | exam_cnt | exam_cnt_rank |
-| ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------- |
-| C++ | 2020 | 3 | 1 |
-| SQL | 2020 | 3 | 1 |
-| PYTHON | 2020 | 2 | 3 |
-| 算法 | 2021 | 3 | 1 |
-| SQL | 2021 | 2 | 2 |
-
-因此能输出同比结果的 tag 只有 SQL,从 2020 到 2021 年,做完次数 3=>2,减少 33.3%(保留 1 位小数);排名 1=>2,后退 1 名。
-
-**思路:**
-
-本题难点在于长整型的数据类型要求不能有负号产生,用 cast 函数转换数据类型为 signed。
-
-以及用到的`增长率计算公式:(exam_cnt_21-exam_cnt_20)/exam_cnt_20`
-
-做完次数排名变化(2021 年和 2020 年比排名升了或者降了多少)
-
-计算公式:`exam_cnt_rank_21 - exam_cnt_rank_20`
-
-在 MySQL 中,`CAST()` 函数用于将一个表达式的数据类型转换为另一个数据类型。它的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-CAST(expression AS data_type)
-
--- 将一个字符串转换成整数
-SELECT CAST('123' AS INT);
-```
-
-示例就不一一举例了,这个函数很简单
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- tag,
- exam_cnt_20,
- exam_cnt_21,
- concat(
- round(
- 100 * (exam_cnt_21 - exam_cnt_20) / exam_cnt_20,
- 1
- ),
- '%'
- ) AS growth_rate,
- exam_cnt_rank_20,
- exam_cnt_rank_21,
- cast(exam_cnt_rank_21 AS signed) - cast(exam_cnt_rank_20 AS signed) AS rank_delta
-FROM
- (
- #2020年、2021年上半年各类试卷的做完次数和做完次数排名
- SELECT
- tag,
- count(
- IF (
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') BETWEEN '20200101'
- AND '20200630',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) AS exam_cnt_20,
- count(
- IF (
- substring(start_time, 1, 10) BETWEEN '2021-01-01'
- AND '2021-06-30',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) AS exam_cnt_21,
- rank() over (
- ORDER BY
- count(
- IF (
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m%d') BETWEEN '20200101'
- AND '20200630',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) DESC
- ) AS exam_cnt_rank_20,
- rank() over (
- ORDER BY
- count(
- IF (
- substring(start_time, 1, 10) BETWEEN '2021-01-01'
- AND '2021-06-30',
- start_time,
- NULL
- )
- ) DESC
- ) AS exam_cnt_rank_21
- FROM
- examination_info
- JOIN exam_record USING (exam_id)
- WHERE
- submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY
- tag
- ) main
-WHERE
- exam_cnt_21 * exam_cnt_20 <> 0
-ORDER BY
- growth_rate DESC,
- exam_cnt_rank_21 DESC
-```
-
-## 聚合窗口函数
-
-### 对试卷得分做 min-max 归一化
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ------ | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | PYTHON | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 9 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 19:01:01 | 2020-01-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 5 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9004 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9005 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-在物理学及统计学数据计算时,有个概念叫 min-max 标准化,也被称为离差标准化,是对原始数据的线性变换,使结果值映射到[0 - 1]之间。
-
-转换函数为:
-
-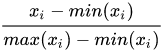
-
-请你将用户作答高难度试卷的得分在每份试卷作答记录内执行 min-max 归一化后缩放到[0,100]区间,并输出用户 ID、试卷 ID、归一化后分数平均值;最后按照试卷 ID 升序、归一化分数降序输出。(注:得分区间默认为[0,100],如果某个试卷作答记录中只有一个得分,那么无需使用公式,归一化并缩放后分数仍为原分数)。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | avg_new_score |
-| ---- | ------- | ------------- |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 98 |
-| 1003 | 9001 | 0 |
-| 1002 | 9002 | 88 |
-| 1003 | 9002 | 75 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 70 |
-| 1004 | 9002 | 0 |
-
-解释:高难度试卷有 9001、9002、9003;
-
-作答了 9001 的记录有 3 条,分数分别为 68、89、90,按给定公式归一化后分数为:0、95、100,而后两个得分都是用户 1001 作答的,因此用户 1001 对试卷 9001 的新得分为(95+100)/2≈98(只保留整数部分),用户 1003 对于试卷 9001 的新得分为 0。最后结果按照试卷 ID 升序、归一化分数降序输出。
-
-**思路:**
-
-注意点:
-
-1. 将高难度的试卷,按每类试卷的得分,利用 max/min (col) over()窗口函数求得各组内最大最小值,然后进行归一化公式计算,缩放区间为[0,100],即 min_max\*100
-2. 若某类试卷只有一个得分,则无需使用归一化公式,因只有一个分 max_score=min_score,score,公式后结果可能会变成 0。
-3. 最后结果按 uid、exam_id 分组求归一化后均值,score 为 NULL 的要过滤掉。
-
-最后就是仔细看上面公式 (说实话,这题看起来就很绕)
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
- exam_id,
- round(sum(min_max) / count(score), 0) AS avg_new_score
-FROM
- (
- SELECT
- *,
- IF (
- max_score = min_score,
- score,
- (score - min_score) / (max_score - min_score) * 100
- ) AS min_max
- FROM
- (
- SELECT
- uid,
- a.exam_id,
- score,
- max(score) over (PARTITION BY a.exam_id) AS max_score,
- min(score) over (PARTITION BY a.exam_id) AS min_score
- FROM
- exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN examination_info b USING (exam_id)
- WHERE
- difficulty = 'hard'
- ) t
- WHERE
- score IS NOT NULL
- ) t1
-GROUP BY
- uid,
- exam_id
-ORDER BY
- exam_id ASC,
- avg_new_score DESC;
-```
-
-### 每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数
-
-**描述:**
-
-现有试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-请输出每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数。
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | start_month | month_cnt | cum_exam_cnt |
-| ------- | ----------- | --------- | ------------ |
-| 9001 | 202001 | 2 | 2 |
-| 9001 | 202002 | 1 | 3 |
-| 9001 | 202003 | 3 | 6 |
-| 9001 | 202005 | 1 | 7 |
-| 9002 | 202001 | 1 | 1 |
-| 9002 | 202002 | 3 | 4 |
-| 9002 | 202003 | 1 | 5 |
-
-解释:试卷 9001 在 202001、202002、202003、202005 共 4 个月有被作答记录,每个月被作答数分别为 2、1、3、1,截止当月累积作答总数为 2、3、6、7。
-
-**思路:**
-
-这题就两个关键点:统计截止当月的作答总数、输出每份试卷每月作答数和截止当月的作答总数
-
-这个是关键`**sum(count(*)) over(partition by exam_id order by date_format(start_time,'%Y%m'))**`
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT exam_id,
- date_format(start_time, '%Y%m') AS start_month,
- count(*) AS month_cnt,
- sum(count(*)) OVER (PARTITION BY exam_id
- ORDER BY date_format(start_time, '%Y%m')) AS cum_exam_cnt
-FROM exam_record
-GROUP BY exam_id,
- start_month
-```
-
-### 每月及截止当月的答题情况(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 90 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 89 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1003 | 9001 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 90 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:59:01 | 69 |
-| 9 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 68 |
-| 11 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1001 | 9002 | 2020-03-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-
-请输出自从有用户作答记录以来,每月的试卷作答记录中月活用户数、新增用户数、截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数。结果按月份升序输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| start_month | mau | month_add_uv | max_month_add_uv | cum_sum_uv |
-| ----------- | --- | ------------ | ---------------- | ---------- |
-| 202001 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
-| 202002 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
-| 202003 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
-| 202005 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
-
-| month | 1001 | 1002 | 1003 | 1004 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 202001 | 1 | 1 | | |
-| 202002 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-| 202003 | 1 | | 1 | 1 |
-| 202005 | | 1 | | |
-
-由上述矩阵可以看出,2020 年 1 月有 2 个用户活跃(mau=2),当月新增用户数为 2;
-
-2020 年 2 月有 4 个用户活跃,当月新增用户数为 2,最大单月新增用户数为 2,当前累积用户数为 4。
-
-**思路:**
-
-难点:
-
-1.如何求每月新增用户
-
-2.截至当月的答题情况
-
-大致流程:
-
-(1)统计每个人的首次登陆月份 `min()`
-
-(2)统计每月的月活和新增用户数:先得到每个人的首次登陆月份,再对首次登陆月份分组求和是该月份的新增人数
-
-(3)统计截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数 ,最终按照按月份升序输出
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
--- 截止当月的单月最大新增用户数、截止当月的累积用户数,按月份升序输出
-SELECT
- start_month,
- mau,
- month_add_uv,
- max( month_add_uv ) over ( ORDER BY start_month ),
- sum( month_add_uv ) over ( ORDER BY start_month )
-FROM
- (
- -- 统计每月的月活和新增用户数
- SELECT
- date_format( a.start_time, '%Y%m' ) AS start_month,
- count( DISTINCT a.uid ) AS mau,
- count( DISTINCT b.uid ) AS month_add_uv
- FROM
- exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN (
- -- 统计每个人的首次登陆月份
- SELECT uid, min( date_format( start_time, '%Y%m' )) AS first_month FROM exam_record GROUP BY uid ) b ON date_format( a.start_time, '%Y%m' ) = b.first_month
- GROUP BY
- start_month
- ) main
-ORDER BY
- start_month
-```
-
-
+| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 78 |
+| 2 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-01 09:01:01 | 2021-09-01 09:31:00 | 81 |
+| 3 | 1002 | 900 | | | |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
index c20af2cad39..7475e377940 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-questions-05.md
@@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
---
-title: SQL常见面试题总结(5)
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Common SQL Interview Questions (5)
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 题目来源于:[牛客题霸 - SQL 进阶挑战](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
+> Source of questions: [Niuke Question Bank - SQL Advanced Challenge](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=SQL%E7%AF%87&topicId=240)
-较难或者困难的题目可以根据自身实际情况和面试需要来决定是否要跳过。
+Difficult or challenging questions can be skipped based on your actual situation and interview needs.
-## 空值处理
+## Handling Null Values
-### 统计有未完成状态的试卷的未完成数和未完成率
+### Count the number of unfinished exams and the unfinished rate for exams with an unfinished status
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),数据如下:
+There is an exam record table `exam_record` (`uid` User ID, `exam_id` Exam ID, `start_time` Start time, `submit_time` Submission time, `score` Score), with the following data:
| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
@@ -24,21 +24,21 @@ tag:
| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | 2021-05-02 10:30:01 | 81 |
| 3 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-请统计有未完成状态的试卷的未完成数 incomplete_cnt 和未完成率 incomplete_rate。由示例数据结果输出如下:
+Please count the number of unfinished exams `incomplete_cnt` and the unfinished rate `incomplete_rate` for exams with an unfinished status. The output based on the example data is as follows:
| exam_id | incomplete_cnt | complete_rate |
| ------- | -------------- | ------------- |
| 9001 | 1 | 0.333 |
-解释:试卷 9001 有 3 次被作答的记录,其中两次完成,1 次未完成,因此未完成数为 1,未完成率为 0.333(保留 3 位小数)
+Explanation: Exam 9001 has 3 records, of which two are completed and one is unfinished, so the number of unfinished exams is 1, and the unfinished rate is 0.333 (retaining 3 decimal places).
-**思路**:
+**Thought Process**:
-这题只需要注意一个是有条件限制,一个是没条件限制的;要么分别查询条件,然后合并;要么直接在 select 里面进行条件判断。
+This question only requires attention to one condition with restrictions and one without; you can either query the conditions separately and then merge them, or directly perform conditional checks in the select statement.
-**答案**:
+**Answer**:
-写法 1:
+Method 1:
```sql
SELECT exam_id,
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ GROUP BY exam_id
HAVING incomplete_cnt <> 0
```
-写法 2:
+Method 2:
```sql
SELECT exam_id,
@@ -60,954 +60,22 @@ GROUP BY exam_id
HAVING incomplete_cnt <> 0
```
-两种写法都可以,只有中间的写法不一样,一个是对符合条件的才`COUNT`,一个是直接上`IF`,后者更为直观,最后这个`having`解释一下, 无论是 `complete_rate` 还是 `incomplete_cnt`,只要不为 0 即可,不为 0 就意味着有未完成的。
+Both methods are valid; only the middle part differs, one counts only those that meet the condition, while the other uses `IF` directly, which is more intuitive. Finally, this `HAVING` clause explains that as long as either `complete_rate` or `incomplete_cnt` is not 0, it means there are unfinished exams.
-### 0 级用户高难度试卷的平均用时和平均得分
+### Average time and average score for level 0 users on difficult exams
-**描述**:
+**Description**:
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间),数据如下:
+There is a user information table `user_info` (`uid` User ID, `nick_name` Nickname, `achievement` Achievement value, `level` Level, `job` Job direction, `register_time` Registration time), with the following data:
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 10 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 2100 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
+| --- | ---- | --------- | ----------- | ----- | --------- | ------------------- |
+| 1 | 1001 | Niuke 1 | 10 | 0 | Algorithm | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 1002 | Niuke 2 | 2100 | 6 | Algorithm | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间),数据如下:
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9004 | 算法 | medium | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分),数据如下:
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-
-请输出每个 0 级用户所有的高难度试卷考试平均用时和平均得分,未完成的默认试卷最大考试时长和 0 分处理。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | avg_score | avg_time_took |
-| ---- | --------- | ------------- |
-| 1001 | 33 | 36.7 |
-
-解释:0 级用户有 1001,高难度试卷有 9001,1001 作答 9001 的记录有 3 条,分别用时 20 分钟、未完成(试卷时长 60 分钟)、30 分钟(未满 31 分钟),分别得分为 80 分、未完成(0 分处理)、20 分。因此他的平均用时为 110/3=36.7(保留一位小数),平均得分为 33 分(取整)
-
-**思路**:这题用`IF`是判断的最方便的,因为涉及到 NULL 值的判断。当然 `case when`也可以,大同小异。这题的难点就在于空值的处理,其他的这些查询条件什么的,我相信难不倒大家。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- round(avg(new_socre)) AS avg_score,
- round(avg(time_diff), 1) AS avg_time_took
-FROM
- (SELECT er.uid,
- IF (er.submit_time IS NOT NULL, TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time), ef.duration) AS time_diff,
- IF (er.submit_time IS NOT NULL,er.score,0) AS new_socre
- FROM exam_record er
- LEFT JOIN user_info uf ON er.uid = uf.uid
- LEFT JOIN examination_info ef ON er.exam_id = ef.exam_id
- WHERE uf.LEVEL = 0 AND ef.difficulty = 'hard' ) t
-GROUP BY UID
-ORDER BY UID
-```
-
-## 高级条件语句
-
-### 筛选限定昵称成就值活跃日期的用户(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 1000 | 2 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 进击的 3 号 | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5 号 | 3000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 13 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | 2021-09-06 12:21:01 | 80 |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 18 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-08-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-| 15 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-
-题目练习记录表 `practice_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `question_id` 题目 ID, `submit_time` 提交时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | question_id | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 8001 | 2021-08-02 11:41:01 | 60 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:30:01 | 50 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 8001 | 2021-09-02 19:20:01 | 70 |
-| 4 | 1002 | 8002 | 2021-09-02 19:38:01 | 70 |
-| 5 | 1003 | 8002 | 2021-09-01 19:38:01 | 80 |
-
-请找到昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾、成就值在 1200~2500 之间,且最近一次活跃(答题或作答试卷)在 2021 年 9 月的用户信息。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name | achievement |
-| ---- | --------- | ----------- |
-| 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 |
-
-**解释**:昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾且成就值在 1200~2500 之间的有 1002、1004;
-
-1002 最近一次试卷区活跃为 2021 年 9 月,最近一次题目区活跃为 2021 年 9 月;1004 最近一次试卷区活跃为 2021 年 8 月,题目区未活跃。
-
-因此最终满足条件的只有 1002。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先根据条件列出主要查询语句
-
-昵称以『牛客』开头『号』结尾: `nick_name LIKE "牛客%号"`
-
-成就值在 1200~2500 之间:`achievement BETWEEN 1200 AND 2500`
-
-第三个条件因为限定了为 9 月,所以直接写就行:`( date_format( record.submit_time, '%Y%m' )= 202109 OR date_format( pr.submit_time, '%Y%m' )= 202109 )`
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT u_info.uid,
- u_info.nick_name,
- u_info.achievement
-FROM user_info u_info
-LEFT JOIN exam_record record ON record.uid = u_info.uid
-LEFT JOIN practice_record pr ON u_info.uid = pr.uid
-WHERE u_info.nick_name LIKE "牛客%号"
- AND u_info.achievement BETWEEN 1200
- AND 2500
- AND (date_format(record.submit_time, '%Y%m')= 202109
- OR date_format(pr.submit_time, '%Y%m')= 202109)
-GROUP BY u_info.uid
-```
-
-### 筛选昵称规则和试卷规则的作答记录(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 1900 | 2 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2200 | 5 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2500 | 6 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
+There is an exam information table `examination_info` (`exam_id` Exam ID, `tag` Exam category, `difficulty` Exam difficulty, `duration` Exam duration, `release_time` Release time), with the following data:
| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
| --- | ------- | --- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | C++ | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | c# | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 81 |
-| 16 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | 2021-09-06 12:21:01 | 80 |
-| 17 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 18 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | 2021-05-05 18:59:02 | 90 |
-| 12 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 13 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 9 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-| 8 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1004 | 9002 | 2021-08-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 14 | 1005 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-02-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-| 15 | 1006 | 9001 | 2021-02-01 11:01:01 | 2021-09-01 11:31:01 | 84 |
-
-找到昵称以"牛客"+纯数字+"号"或者纯数字组成的用户对于字母 c 开头的试卷类别(如 C,C++,c#等)的已完成的试卷 ID 和平均得分,按用户 ID、平均分升序排序。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | avg_score |
-| ---- | ------- | --------- |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 81 |
-| 1002 | 9002 | 85 |
-| 1005 | 9001 | 84 |
-| 1006 | 9001 | 84 |
-
-解释:昵称满足条件的用户有 1002、1004、1005、1006;
-
-c 开头的试卷有 9001、9002;
-
-满足上述条件的作答记录中,1002 完成 9001 的得分有 81、80,平均分为 81(80.5 取整四舍五入得 81);
-
-1002 完成 9002 的得分有 90、82、83,平均分为 85;
-
-**思路**:
-
-还是老样子,既然给出了条件,就先把各个条件先写出来
-
-找到昵称以"牛客"+纯数字+"号"或者纯数字组成的用户: 我最开始是这么写的:`nick_name LIKE '牛客%号' OR nick_name REGEXP '^[0-9]+$'`,如果表中有个 “牛客 H 号” ,那也能通过。
-
-所以这里还得用正则: `nick_name LIKE '^牛客[0-9]+号'`
-
-对于字母 c 开头的试卷类别: `e_info.tag LIKE 'c%'` 或者 `tag regexp '^c|^C'` 第一个也能匹配到大写 C
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT UID,
- exam_id,
- ROUND(AVG(score), 0) avg_score
-FROM exam_record
-WHERE UID IN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM user_info
- WHERE nick_name RLIKE "^牛客[0-9]+号 $"
- OR nick_name RLIKE "^[0-9]+$")
- AND exam_id IN
- (SELECT exam_id
- FROM examination_info
- WHERE tag RLIKE "^[cC]")
- AND score IS NOT NULL
-GROUP BY UID,exam_id
-ORDER BY UID,avg_score;
-```
-
-### 根据指定记录是否存在输出不同情况(困难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ----------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 进击的 3 号 | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 87 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-03 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 7 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 99 |
-| 8 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 9 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9002 | 2021-05-05 18:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9001 | 2021-09-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 12 | 1003 | 9003 | 2021-02-06 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1003 | 9001 | 2021-09-07 10:01:01 | 2021-09-07 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-请你筛选表中的数据,当有任意一个 0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2 时,输出每个 0 级用户的试卷未完成数和未完成率(保留 3 位小数);若不存在这样的用户,则输出所有有作答记录的用户的这两个指标。结果按未完成率升序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | incomplete_cnt | incomplete_rate |
-| ---- | -------------- | --------------- |
-| 1004 | 0 | 0.000 |
-| 1003 | 1 | 0.500 |
-| 1001 | 4 | 0.667 |
-
-**解释**:0 级用户有 1001、1003、1004;他们作答试卷数和未完成数分别为:6:4、2:1、0:0;
-
-存在 1001 这个 0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2,因此输出这三个用户的未完成数和未完成率(1004 未作答过试卷,未完成率默认填 0,保留 3 位小数后是 0.000);
-
-结果按照未完成率升序排序。
-
-附:如果 1001 不满足『未完成试卷数大于 2』,则需要输出 1001、1002、1003 的这两个指标,因为试卷作答记录表里只有这三个用户的作答记录。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先把可能满足条件**“0 级用户未完成试卷数大于 2”**的 SQL 写出来
-
-```sql
-SELECT ui.uid UID
-FROM user_info ui
-LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
-WHERE ui.uid IN
- (SELECT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 )
-GROUP BY ui.uid
-HAVING sum(IF(er.submit_time IS NULL, 1, 0)) > 2
-```
-
-然后再分别写出两种情况的 SQL 查询语句:
-
-情况 1. 查询存在条件要求的 0 级用户的试卷未完成率
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- tmp1.uid uid,
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 )) incomplete_cnt,
- round(
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 ))/ count( tmp1.uid ),
- 3
- ) incomplete_rate
-FROM
- (
- SELECT DISTINCT
- ui.uid
- FROM
- user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE
- er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0
- ) tmp1
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON tmp1.uid = er.uid
-GROUP BY
- tmp1.uid
-ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate
-```
-
-情况 2. 查询不存在条件要求时所有有作答记录的 yong 用户的试卷未完成率
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- ui.uid uid,
- sum( CASE WHEN er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1 ELSE 0 END ) incomplete_cnt,
- round(
- sum(
- IF
- ( er.submit_time IS NULL AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0 ))/ count( ui.uid ),
- 3
- ) incomplete_rate
-FROM
- user_info ui
- JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
-GROUP BY
- ui.uid
-ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate
-```
-
-拼在一起,就是答案
-
-```sql
-WITH host_user AS
- (SELECT ui.uid UID
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE ui.uid IN
- (SELECT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 )
- GROUP BY ui.uid
- HAVING sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL, 1, 0))> 2),
- tt1 AS
- (SELECT tmp1.uid UID,
- sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0)) incomplete_cnt,
- round(sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0))/ count(tmp1.uid), 3) incomplete_rate
- FROM
- (SELECT DISTINCT ui.uid
- FROM user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- WHERE er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND ui.LEVEL = 0 ) tmp1
- LEFT JOIN exam_record er ON tmp1.uid = er.uid
- GROUP BY tmp1.uid
- ORDER BY incomplete_rate),
- tt2 AS
- (SELECT ui.uid UID,
- sum(CASE
- WHEN er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL THEN 1
- ELSE 0
- END) incomplete_cnt,
- round(sum(IF (er.submit_time IS NULL
- AND er.start_time IS NOT NULL, 1, 0))/ count(ui.uid), 3) incomplete_rate
- FROM user_info ui
- JOIN exam_record er ON ui.uid = er.uid
- GROUP BY ui.uid
- ORDER BY incomplete_rate)
- (SELECT tt1.*
- FROM tt1
- LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM host_user) t1 ON 1 = 1
- WHERE t1.uid IS NOT NULL )
-UNION ALL
- (SELECT tt2.*
- FROM tt2
- LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT UID
- FROM host_user) t2 ON 1 = 1
- WHERE t2.uid IS NULL)
-```
-
-V2 版本(根据上面做出的改进,答案缩短了,逻辑更强):
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- ui.uid,
- SUM(
- IF
- ( start_time IS NOT NULL AND score IS NULL, 1, 0 )) AS incomplete_cnt,#3.试卷未完成数
- ROUND( AVG( IF ( start_time IS NOT NULL AND score IS NULL, 1, 0 )), 3 ) AS incomplete_rate #4.未完成率
-
-FROM
- user_info ui
- LEFT JOIN exam_record USING ( uid )
-WHERE
-CASE
-
- WHEN (#1.当有任意一个0级用户未完成试卷数大于2时
- SELECT
- MAX( lv0_incom_cnt )
- FROM
- (
- SELECT
- SUM(
- IF
- ( score IS NULL, 1, 0 )) AS lv0_incom_cnt
- FROM
- user_info
- JOIN exam_record USING ( uid )
- WHERE
- LEVEL = 0
- GROUP BY
- uid
- ) table1
- )> 2 THEN
- uid IN ( #1.1找出每个0级用户
- SELECT uid FROM user_info WHERE LEVEL = 0 ) ELSE uid IN ( #2.若不存在这样的用户,找出有作答记录的用户
- SELECT DISTINCT uid FROM exam_record )
- END
- GROUP BY
- ui.uid
- ORDER BY
- incomplete_rate #5.结果按未完成率升序排序
-```
-
-### 各用户等级的不同得分表现占比(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 2000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 exam_record(uid 用户 ID, exam_id 试卷 ID, start_time 开始作答时间, submit_time 交卷时间, score 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-05-02 10:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 3 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-02-02 19:01:01 | 2021-02-02 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 4 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-01 12:01:01 | 2021-09-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 5 | 1001 | 9003 | 2021-09-02 12:01:01 | 2021-09-02 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 6 | 1001 | 9001 | 2021-06-02 19:01:01 | 2021-06-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 7 | 1001 | 9002 | 2021-09-05 19:01:01 | 2021-09-05 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 8 | 1001 | 9004 | 2021-09-03 12:01:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 9 | 1002 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-01 12:01:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 11 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-02-02 12:11:01 | 2020-02-02 12:41:01 | 76 |
-
-为了得到用户试卷作答的定性表现,我们将试卷得分按分界点[90,75,60]分为优良中差四个得分等级(分界点划分到左区间),请统计不同用户等级的人在完成过的试卷中各得分等级占比(结果保留 3 位小数),未完成过试卷的用户无需输出,结果按用户等级降序、占比降序排序。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| level | score_grade | ratio |
-| ----- | ----------- | ----- |
-| 3 | 良 | 0.667 |
-| 3 | 优 | 0.333 |
-| 0 | 良 | 0.500 |
-| 0 | 中 | 0.167 |
-| 0 | 优 | 0.167 |
-| 0 | 差 | 0.167 |
-
-解释:完成过试卷的用户有 1001、1002;完成了的试卷对应的用户等级和分数等级如下:
-
-| uid | exam_id | score | level | score_grade |
-| ---- | ------- | ----- | ----- | ----------- |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 80 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 75 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 60 | 0 | 中 |
-| 1001 | 9003 | 90 | 0 | 优 |
-| 1001 | 9001 | 20 | 0 | 差 |
-| 1001 | 9002 | 89 | 0 | 良 |
-| 1002 | 9001 | 99 | 3 | 优 |
-| 1002 | 9003 | 82 | 3 | 良 |
-| 1002 | 9003 | 76 | 3 | 良 |
-
-因此 0 级用户(只有 1001)的各分数等级比例为:优 1/6,良 1/6,中 1/6,差 3/6;3 级用户(只有 1002)各分数等级比例为:优 1/3,良 2/3。结果保留 3 位小数。
-
-**思路**:
-
-先把 **“将试卷得分按分界点[90,75,60]分为优良中差四个得分等级”**这个条件写出来,这里可以用到`case when`
-
-```sql
-CASE
- WHEN a.score >= 90 THEN
- '优'
- WHEN a.score < 90 AND a.score >= 75 THEN
- '良'
- WHEN a.score < 75 AND a.score >= 60 THEN
- '中' ELSE '差'
-END
-```
-
-这题的关键点就在于这,其他剩下的就是条件拼接了
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT a.LEVEL,
- a.score_grade,
- ROUND(a.cur_count / b.total_num, 3) AS ratio
-FROM
- (SELECT b.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- (CASE
- WHEN a.score >= 90 THEN '优'
- WHEN a.score < 90
- AND a.score >= 75 THEN '良'
- WHEN a.score < 75
- AND a.score >= 60 THEN '中'
- ELSE '差'
- END) AS score_grade,
- count(1) AS cur_count
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN user_info b ON a.uid = b.uid
- WHERE a.submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY b.LEVEL,
- score_grade) a
-LEFT JOIN
- (SELECT b.LEVEL AS LEVEL,
- count(b.LEVEL) AS total_num
- FROM exam_record a
- LEFT JOIN user_info b ON a.uid = b.uid
- WHERE a.submit_time IS NOT NULL
- GROUP BY b.LEVEL) b ON a.LEVEL = b.LEVEL
-ORDER BY a.LEVEL DESC,
- ratio DESC
-```
-
-## 限量查询
-
-### 注册时间最早的三个人
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 号 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-02-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 4000 | 7 | C++ | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-11-01 10:00:00 |
-
-请从中找到注册时间最早的 3 个人。由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name | register_time |
-| ---- | ------------ | ------------------- |
-| 1001 | 牛客 1 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-| 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-
-解释:按注册时间排序后选取前三名,输出其用户 ID、昵称、注册时间。
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT uid, nick_name, register_time
- FROM user_info
- ORDER BY register_time
- LIMIT 3
-```
-
-### 注册当天就完成了试卷的名单第三页(较难)
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ------------ | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 555 号 | 4000 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 6 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 7 | 1007 | 牛客 7 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 8 | 1008 | 牛客 8 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 9 | 1009 | 牛客 9 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 10 | 1010 | 牛客 10 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-| 11 | 1011 | 666666 | 3000 | 6 | C++ | 2020-01-02 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷信息表 examination_info(exam_id 试卷 ID, tag 试卷类别, difficulty 试卷难度, duration 考试时长, release_time 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答记录表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ----- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 09:01:01 | 2020-01-02 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 2020-01-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 19:01:01 | 2020-01-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2020-01-01 12:01:01 | 2020-01-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1007 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1008 | 9003 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1008 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 11 | 1009 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:31:01 | 82 |
-| 12 | 1010 | 9002 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | 2020-01-02 12:41:01 | 76 |
-| 13 | 1011 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 10:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-
-
-找到求职方向为算法工程师,且注册当天就完成了算法类试卷的人,按参加过的所有考试最高得分排名。排名榜很长,我们将采用分页展示,每页 3 条,现在需要你取出第 3 页(页码从 1 开始)的人的信息。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | level | register_time | max_score |
-| ---- | ----- | ------------------- | --------- |
-| 1010 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 76 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 75 |
-| 1004 | 0 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 | 60 |
-
-解释:除了 1011 其他用户的求职方向都为算法工程师;算法类试卷有 9001 和 9002,11 个用户注册当天都完成了算法类试卷;计算他们的所有考试最大分时,只有 1002 和 1008 完成了两次考试,其他人只完成了一场考试,1002 两场考试最高分为 81,1008 最高分为 99。
-
-按最高分排名如下:
-
-| uid | level | register_time | max_score |
-| ---- | ----- | ------------------- | --------- |
-| 1008 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 99 |
-| 1005 | 7 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 90 |
-| 1007 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 89 |
-| 1002 | 3 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 83 |
-| 1009 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 82 |
-| 1001 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 80 |
-| 1010 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 76 |
-| 1003 | 0 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 | 75 |
-| 1004 | 0 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 | 60 |
-| 1006 | 0 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 | 20 |
-
-每页 3 条,第三页也就是第 7~9 条,返回 1010、1003、1004 的行记录即可。
-
-**思路**:
-
-1. 每页三条,即需要取出第三页的人的信息,要用到`limit`
-
-2. 统计求职方向为算法工程师且注册当天就完成了算法类试卷的人的**信息和每次记录的得分**,先求满足条件的用户,后用 left join 做连接查找信息和每次记录的得分
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT t1.uid,
- LEVEL,
- register_time,
- max(score) AS max_score
-FROM exam_record t
-JOIN examination_info USING (exam_id)
-JOIN user_info t1 ON t.uid = t1.uid
-AND date(t.submit_time) = date(t1.register_time)
-WHERE job = '算法'
- AND tag = '算法'
-GROUP BY t1.uid,
- LEVEL,
- register_time
-ORDER BY max_score DESC
-LIMIT 6,3
-```
-
-## 文本转换函数
-
-### 修复串列了的记录
-
-**描述**:现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | -------------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | 算法 | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | 算法,medium,80 | | 0 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-录题同学有一次手误将部分记录的试题类别 tag、难度、时长同时录入到了 tag 字段,请帮忙找出这些录错了的记录,并拆分后按正确的列类型输出。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration |
-| ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- |
-| 9004 | 算法 | medium | 80 |
-
-**思路**:
-
-先来学习下本题要用到的函数
-
-`SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数用于提取字符串中指定分隔符的部分。它接受三个参数:原始字符串、分隔符和指定要返回的部分的数量。
-
-以下是 `SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数的语法:
-
-```sql
-SUBSTRING_INDEX(str, delimiter, count)
-```
-
-- `str`:要进行分割的原始字符串。
-- `delimiter`:用作分割的字符串或字符。
-- `count`:指定要返回的部分的数量。
- - 如果 `count` 大于 0,则返回从左边开始的前 `count` 个部分(以分隔符为界)。
- - 如果 `count` 小于 0,则返回从右边开始的前 `count` 个部分(以分隔符为界),即从右侧向左计数。
-
-下面是一些示例,演示了 `SUBSTRING_INDEX` 函数的使用:
-
-1. 提取字符串中的第一个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', 1);
- -- 输出结果:'apple'
- ```
-
-2. 提取字符串中的最后一个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', -1);
- -- 输出结果:'cherry'
- ```
-
-3. 提取字符串中的前两个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', 2);
- -- 输出结果:'apple,banana'
- ```
-
-4. 提取字符串中的最后两个部分:
-
- ```sql
- SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('apple,banana,cherry', ',', -2);
- -- 输出结果:'banana,cherry'
- ```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- exam_id,
- substring_index( tag, ',', 1 ) tag,
- substring_index( substring_index( tag, ',', 2 ), ',',- 1 ) difficulty,
- substring_index( tag, ',',- 1 ) duration
-FROM
- examination_info
-WHERE
- difficulty = ''
-```
-
-### 对过长的昵称截取处理
-
-**描述**:现有用户信息表 `user_info`(`uid` 用户 ID,`nick_name` 昵称, `achievement` 成就值, `level` 等级, `job` 职业方向, `register_time` 注册时间):
-
-| id | uid | nick_name | achievement | level | job | register_time |
-| --- | ---- | ---------------------- | ----------- | ----- | ---- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 1001 | 牛客 1 | 19 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 牛客 2 号 | 1200 | 3 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 1003 | 牛客 3 号 ♂ | 22 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 1004 | 牛客 4 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-01 11:00:00 |
-| 5 | 1005 | 牛客 5678901234 号 | 4000 | 7 | 算法 | 2020-01-11 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 1006 | 牛客 67890123456789 号 | 25 | 0 | 算法 | 2020-01-02 11:00:00 |
-
-有的用户的昵称特别长,在一些展示场景会导致样式混乱,因此需要将特别长的昵称转换一下再输出,请输出字符数大于 10 的用户信息,对于字符数大于 13 的用户输出前 10 个字符然后加上三个点号:『...』。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| uid | nick_name |
-| ---- | ------------------ |
-| 1005 | 牛客 5678901234 号 |
-| 1006 | 牛客 67890123... |
-
-解释:字符数大于 10 的用户有 1005 和 1006,长度分别为 13、17;因此需要对 1006 的昵称截断输出。
-
-**思路**:
-
-这题涉及到字符的计算,要计算字符串的字符数(即字符串的长度),可以使用 `LENGTH` 函数或 `CHAR_LENGTH` 函数。这两个函数的区别在于对待多字节字符的方式。
-
-1. `LENGTH` 函数:它返回给定字符串的字节数。对于包含多字节字符的字符串,每个字符都会被当作一个字节来计算。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-SELECT LENGTH('你好'); -- 输出结果:6,因为 '你好' 中的每个汉字每个占3个字节
-```
-
-1. `CHAR_LENGTH` 函数:它返回给定字符串的字符数。对于包含多字节字符的字符串,每个字符会被当作一个字符来计算。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-SELECT CHAR_LENGTH('你好'); -- 输出结果:2,因为 '你好' 中有两个字符,即两个汉字
-```
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-SELECT
- uid,
-CASE
-
- WHEN CHAR_LENGTH( nick_name ) > 13 THEN
- CONCAT( SUBSTR( nick_name, 1, 10 ), '...' ) ELSE nick_name
- END AS nick_name
-FROM
- user_info
-WHERE
- CHAR_LENGTH( nick_name ) > 10
-GROUP BY
- uid;
-```
-
-### 大小写混乱时的筛选统计(较难)
-
-**描述**:
-
-现有试卷信息表 `examination_info`(`exam_id` 试卷 ID, `tag` 试卷类别, `difficulty` 试卷难度, `duration` 考试时长, `release_time` 发布时间):
-
-| id | exam_id | tag | difficulty | duration | release_time |
-| --- | ------- | ---- | ---------- | -------- | ------------------- |
-| 1 | 9001 | 算法 | hard | 60 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 2 | 9002 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 3 | 9003 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 4 | 9004 | sql | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 5 | 9005 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 6 | 9006 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 7 | 9007 | C++ | hard | 80 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 8 | 9008 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 9 | 9009 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-| 10 | 9010 | SQL | medium | 70 | 2021-01-01 10:00:00 |
-
-试卷作答信息表 `exam_record`(`uid` 用户 ID, `exam_id` 试卷 ID, `start_time` 开始作答时间, `submit_time` 交卷时间, `score` 得分):
-
-| id | uid | exam_id | start_time | submit_time | score |
-| --- | ---- | ------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------ |
-| 1 | 1001 | 9001 | 2020-01-01 09:01:01 | 2020-01-01 09:21:59 | 80 |
-| 2 | 1002 | 9003 | 2020-01-20 10:01:01 | 2020-01-20 10:10:01 | 81 |
-| 3 | 1002 | 9002 | 2020-02-01 12:11:01 | 2020-02-01 12:31:01 | 83 |
-| 4 | 1003 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 19:01:01 | 2020-03-01 19:30:01 | 75 |
-| 5 | 1004 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:11:01 | 60 |
-| 6 | 1005 | 9002 | 2020-03-01 12:01:01 | 2020-03-01 12:41:01 | 90 |
-| 7 | 1006 | 9001 | 2020-05-02 19:01:01 | 2020-05-02 19:32:00 | 20 |
-| 8 | 1007 | 9003 | 2020-01-02 19:01:01 | 2020-01-02 19:40:01 | 89 |
-| 9 | 1008 | 9004 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:20:01 | 99 |
-| 10 | 1008 | 9001 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-02-02 12:31:01 | 98 |
-| 11 | 1009 | 9002 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 12:43:01 | 81 |
-| 12 | 1010 | 9001 | 2020-01-02 12:11:01 | (NULL) | (NULL) |
-| 13 | 1010 | 9001 | 2020-02-02 12:01:01 | 2020-01-02 10:31:01 | 89 |
-
-试卷的类别 tag 可能出现大小写混乱的情况,请先筛选出试卷作答数小于 3 的类别 tag,统计将其转换为大写后对应的原本试卷作答数。
-
-如果转换后 tag 并没有发生变化,不输出该条结果。
-
-由示例数据结果输出如下:
-
-| tag | answer_cnt |
-| --- | ---------- |
-| C++ | 6 |
-
-解释:被作答过的试卷有 9001、9002、9003、9004,他们的 tag 和被作答次数如下:
-
-| exam_id | tag | answer_cnt |
-| ------- | ---- | ---------- |
-| 9001 | 算法 | 4 |
-| 9002 | C++ | 6 |
-| 9003 | c++ | 2 |
-| 9004 | sql | 2 |
-
-作答次数小于 3 的 tag 有 c++和 sql,而转为大写后只有 C++本来就有作答数,于是输出 c++转化大写后的作答次数为 6。
-
-**思路**:
-
-首先,这题有点混乱,9004 根据示例数据查出来只有 1 次,这里显示有 2 次。
-
-先看一下大小写转换函数:
-
-1.`UPPER(s)`或`UCASE(s)`函数可以将字符串 s 中的字母字符全部转换成大写字母;
-
-2.`LOWER(s)`或者`LCASE(s)`函数可以将字符串 s 中的字母字符全部转换成小写字母。
-
-难点在于相同表做连接要查询不同的值
-
-**答案**:
-
-```sql
-WITH a AS
- (SELECT tag,
- COUNT(start_time) AS answer_cnt
- FROM exam_record er
- JOIN examination_info ei ON er.exam_id = ei.exam_id
- GROUP BY tag)
-SELECT a.tag,
- b.answer_cnt
-FROM a
-INNER JOIN a AS b ON UPPER(a.tag)= b.tag #a小写 b大写
-AND a.tag != b.tag
-WHERE a.answer_cnt < 3;
-```
-
-
+| 1 | 9001 | SQL | hard | 60 | 2020-01-01 10:00:00 |
+| 2 | 9002 | SQL | easy | 60 | 2020-01-01 |
diff --git a/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md b/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
index cff0b931495..c11eadd7bd9 100644
--- a/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
+++ b/docs/database/sql/sql-syntax-summary.md
@@ -1,1212 +1,100 @@
---
-title: SQL语法基础知识总结
-category: 数据库
+title: Summary of Basic SQL Syntax
+category: Database
tag:
- - 数据库基础
+ - Database Basics
- SQL
---
-> 本文整理完善自下面这两份资料:
+> This article is organized and improved based on the following two resources:
>
-> - [SQL 语法速成手册](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903790571700231)
-> - [MySQL 超全教程](https://www.begtut.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html)
+> - [SQL Syntax Quick Reference](https://juejin.cn/post/6844903790571700231)
+> - [Comprehensive MySQL Tutorial](https://www.begtut.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html)
-## 基本概念
+## Basic Concepts
-### 数据库术语
+### Database Terminology
-- `数据库(database)` - 保存有组织的数据的容器(通常是一个文件或一组文件)。
-- `数据表(table)` - 某种特定类型数据的结构化清单。
-- `模式(schema)` - 关于数据库和表的布局及特性的信息。模式定义了数据在表中如何存储,包含存储什么样的数据,数据如何分解,各部分信息如何命名等信息。数据库和表都有模式。
-- `列(column)` - 表中的一个字段。所有表都是由一个或多个列组成的。
-- `行(row)` - 表中的一个记录。
-- `主键(primary key)` - 一列(或一组列),其值能够唯一标识表中每一行。
+- `Database` - A container for storing organized data (usually a file or a set of files).
+- `Table` - A structured list of a specific type of data.
+- `Schema` - Information about the layout and characteristics of the database and tables. The schema defines how data is stored in tables, what types of data are stored, how data is decomposed, and how parts of the information are named. Both databases and tables have schemas.
+- `Column` - A field in a table. All tables consist of one or more columns.
+- `Row` - A record in a table.
+- `Primary Key` - A column (or a set of columns) whose values uniquely identify each row in the table.
-### SQL 语法
+### SQL Syntax
-SQL(Structured Query Language),标准 SQL 由 ANSI 标准委员会管理,从而称为 ANSI SQL。各个 DBMS 都有自己的实现,如 PL/SQL、Transact-SQL 等。
+SQL (Structured Query Language) is managed by the ANSI standards committee, hence it is referred to as ANSI SQL. Each DBMS has its own implementation, such as PL/SQL, Transact-SQL, etc.
-#### SQL 语法结构
+#### SQL Syntax Structure

-SQL 语法结构包括:
+The SQL syntax structure includes:
-- **`子句`** - 是语句和查询的组成成分。(在某些情况下,这些都是可选的。)
-- **`表达式`** - 可以产生任何标量值,或由列和行的数据库表
-- **`谓词`** - 给需要评估的 SQL 三值逻辑(3VL)(true/false/unknown)或布尔真值指定条件,并限制语句和查询的效果,或改变程序流程。
-- **`查询`** - 基于特定条件检索数据。这是 SQL 的一个重要组成部分。
-- **`语句`** - 可以持久地影响纲要和数据,也可以控制数据库事务、程序流程、连接、会话或诊断。
+- **`Clause`** - Components of statements and queries. (In some cases, these are optional.)
+- **`Expression`** - Can produce any scalar value or be derived from columns and rows of a database table.
+- **`Predicate`** - Specifies conditions for evaluating SQL three-valued logic (3VL) (true/false/unknown) or Boolean truth values, and limits the effects of statements and queries or alters program flow.
+- **`Query`** - Retrieves data based on specific conditions. This is an important component of SQL.
+- **`Statement`** - Can permanently affect schemas and data, and can also control database transactions, program flow, connections, sessions, or diagnostics.
-#### SQL 语法要点
+#### Key Points of SQL Syntax
-- **SQL 语句不区分大小写**,但是数据库表名、列名和值是否区分,依赖于具体的 DBMS 以及配置。例如:`SELECT` 与 `select`、`Select` 是相同的。
-- **多条 SQL 语句必须以分号(`;`)分隔**。
-- 处理 SQL 语句时,**所有空格都被忽略**。
+- **SQL statements are case-insensitive**, but whether database table names, column names, and values are case-sensitive depends on the specific DBMS and configuration. For example, `SELECT`, `select`, and `Select` are the same.
+- **Multiple SQL statements must be separated by a semicolon (`;`).**
+- When processing SQL statements, **all whitespace is ignored**.
-SQL 语句可以写成一行,也可以分写为多行。
+SQL statements can be written in a single line or split into multiple lines.
```sql
--- 一行 SQL 语句
+-- Single line SQL statement
UPDATE user SET username='robot', password='robot' WHERE username = 'root';
--- 多行 SQL 语句
+-- Multi-line SQL statement
UPDATE user
SET username='robot', password='robot'
WHERE username = 'root';
```
-SQL 支持三种注释:
+SQL supports three types of comments:
```sql
-## 注释1
--- 注释2
-/* 注释3 */
+## Comment 1
+-- Comment 2
+/* Comment 3 */
```
-### SQL 分类
+### SQL Classification
-#### 数据定义语言(DDL)
+#### Data Definition Language (DDL)
-数据定义语言(Data Definition Language,DDL)是 SQL 语言集中负责数据结构定义与数据库对象定义的语言。
+Data Definition Language (DDL) is the part of SQL responsible for defining data structures and database objects.
-DDL 的主要功能是**定义数据库对象**。
+The main function of DDL is to **define database objects**.
-DDL 的核心指令是 `CREATE`、`ALTER`、`DROP`。
+The core commands of DDL are `CREATE`, `ALTER`, `DROP`.
-#### 数据操纵语言(DML)
+#### Data Manipulation Language (DML)
-数据操纵语言(Data Manipulation Language, DML)是用于数据库操作,对数据库其中的对象和数据运行访问工作的编程语句。
+Data Manipulation Language (DML) is used for database operations, executing access operations on database objects and data.
-DML 的主要功能是 **访问数据**,因此其语法都是以**读写数据库**为主。
+The main function of DML is to **access data**, so its syntax is primarily focused on **reading and writing databases**.
-DML 的核心指令是 `INSERT`、`UPDATE`、`DELETE`、`SELECT`。这四个指令合称 CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete),即增删改查。
+The core commands of DML are `INSERT`, `UPDATE`, `DELETE`, `SELECT`. These four commands are collectively referred to as CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
-#### 事务控制语言(TCL)
+#### Transaction Control Language (TCL)
-事务控制语言 (Transaction Control Language, TCL) 用于**管理数据库中的事务**。这些用于管理由 DML 语句所做的更改。它还允许将语句分组为逻辑事务。
+Transaction Control Language (TCL) is used to **manage transactions in the database**. These manage changes made by DML statements. It also allows grouping statements into logical transactions.
-TCL 的核心指令是 `COMMIT`、`ROLLBACK`。
+The core commands of TCL are `COMMIT`, `ROLLBACK`.
-#### 数据控制语言(DCL)
+#### Data Control Language (DCL)
-数据控制语言 (Data Control Language, DCL) 是一种可对数据访问权进行控制的指令,它可以控制特定用户账户对数据表、查看表、预存程序、用户自定义函数等数据库对象的控制权。
+Data Control Language (DCL) is a set of commands that control data access rights, allowing control over specific user accounts regarding database objects such as tables, views, stored procedures, and user-defined functions.
-DCL 的核心指令是 `GRANT`、`REVOKE`。
+The core commands of DCL are `GRANT`, `REVOKE`.
-DCL 以**控制用户的访问权限**为主,因此其指令作法并不复杂,可利用 DCL 控制的权限有:`CONNECT`、`SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE`、`DELETE`、`EXECUTE`、`USAGE`、`REFERENCES`。
+DCL primarily focuses on **controlling user access rights**, so its commands are not complex. The permissions that can be controlled by DCL include: `CONNECT`, `SELECT`, `INSERT`, `UPDATE`, `DELETE`, `EXECUTE`, `USAGE`, `REFERENCES`.
-根据不同的 DBMS 以及不同的安全性实体,其支持的权限控制也有所不同。
-
-**我们先来介绍 DML 语句用法。 DML 的主要功能是读写数据库实现增删改查。**
-
-## 增删改查
-
-增删改查,又称为 CRUD,数据库基本操作中的基本操作。
-
-### 插入数据
-
-`INSERT INTO` 语句用于向表中插入新记录。
-
-**插入完整的行**
-
-```sql
-# 插入一行
-INSERT INTO user
-VALUES (10, 'root', 'root', 'xxxx@163.com');
-# 插入多行
-INSERT INTO user
-VALUES (10, 'root', 'root', 'xxxx@163.com'), (12, 'user1', 'user1', 'xxxx@163.com'), (18, 'user2', 'user2', 'xxxx@163.com');
-```
-
-**插入行的一部分**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO user(username, password, email)
-VALUES ('admin', 'admin', 'xxxx@163.com');
-```
-
-**插入查询出来的数据**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO user(username)
-SELECT name
-FROM account;
-```
-
-### 更新数据
-
-`UPDATE` 语句用于更新表中的记录。
-
-```sql
-UPDATE user
-SET username='robot', password='robot'
-WHERE username = 'root';
-```
-
-### 删除数据
-
-- `DELETE` 语句用于删除表中的记录。
-- `TRUNCATE TABLE` 可以清空表,也就是删除所有行。说明:`TRUNCATE` 语句不属于 DML 语法而是 DDL 语法。
-
-**删除表中的指定数据**
-
-```sql
-DELETE FROM user
-WHERE username = 'robot';
-```
-
-**清空表中的数据**
-
-```sql
-TRUNCATE TABLE user;
-```
-
-### 查询数据
-
-`SELECT` 语句用于从数据库中查询数据。
-
-`DISTINCT` 用于返回唯一不同的值。它作用于所有列,也就是说所有列的值都相同才算相同。
-
-`LIMIT` 限制返回的行数。可以有两个参数,第一个参数为起始行,从 0 开始;第二个参数为返回的总行数。
-
-- `ASC`:升序(默认)
-- `DESC`:降序
-
-**查询单列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_name
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询多列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询所有列**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products;
-```
-
-**查询不同的值**
-
-```sql
-SELECT DISTINCT
-vend_id FROM products;
-```
-
-**限制查询结果**
-
-```sql
--- 返回前 5 行
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 5;
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 0, 5;
--- 返回第 3 ~ 5 行
-SELECT * FROM mytable LIMIT 2, 3;
-```
-
-## 排序
-
-`order by` 用于对结果集按照一个列或者多个列进行排序。默认按照升序对记录进行排序,如果需要按照降序对记录进行排序,可以使用 `desc` 关键字。
-
-`order by` 对多列排序的时候,先排序的列放前面,后排序的列放后面。并且,不同的列可以有不同的排序规则。
-
-```sql
-SELECT * FROM products
-ORDER BY prod_price DESC, prod_name ASC;
-```
-
-## 分组
-
-**`group by`**:
-
-- `group by` 子句将记录分组到汇总行中。
-- `group by` 为每个组返回一个记录。
-- `group by` 通常还涉及聚合`count`,`max`,`sum`,`avg` 等。
-- `group by` 可以按一列或多列进行分组。
-- `group by` 按分组字段进行排序后,`order by` 可以以汇总字段来进行排序。
-
-**分组**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(cust_address) AS addr_num
-FROM Customers GROUP BY cust_name;
-```
-
-**分组后排序**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(cust_address) AS addr_num
-FROM Customers GROUP BY cust_name
-ORDER BY cust_name DESC;
-```
-
-**`having`**:
-
-- `having` 用于对汇总的 `group by` 结果进行过滤。
-- `having` 一般都是和 `group by` 连用。
-- `where` 和 `having` 可以在相同的查询中。
-
-**使用 WHERE 和 HAVING 过滤数据**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, COUNT(*) AS NumberOfOrders
-FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_email IS NOT NULL
-GROUP BY cust_name
-HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
-```
-
-**`having` vs `where`**:
-
-- `where`:过滤过滤指定的行,后面不能加聚合函数(分组函数)。`where` 在`group by` 前。
-- `having`:过滤分组,一般都是和 `group by` 连用,不能单独使用。`having` 在 `group by` 之后。
-
-## 子查询
-
-子查询是嵌套在较大查询中的 SQL 查询,也称内部查询或内部选择,包含子查询的语句也称为外部查询或外部选择。简单来说,子查询就是指将一个 `select` 查询(子查询)的结果作为另一个 SQL 语句(主查询)的数据来源或者判断条件。
-
-子查询可以嵌入 `SELECT`、`INSERT`、`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 语句中,也可以和 `=`、`<`、`>`、`IN`、`BETWEEN`、`EXISTS` 等运算符一起使用。
-
-子查询常用在 `WHERE` 子句和 `FROM` 子句后边:
-
-- 当用于 `WHERE` 子句时,根据不同的运算符,子查询可以返回单行单列、多行单列、单行多列数据。子查询就是要返回能够作为 `WHERE` 子句查询条件的值。
-- 当用于 `FROM` 子句时,一般返回多行多列数据,相当于返回一张临时表,这样才符合 `FROM` 后面是表的规则。这种做法能够实现多表联合查询。
-
-> 注意:MYSQL 数据库从 4.1 版本才开始支持子查询,早期版本是不支持的。
-
-用于 `WHERE` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select column_name [, column_name ]
-from table1 [, table2 ]
-where column_name operator
- (select column_name [, column_name ]
- from table1 [, table2 ]
- [where])
-```
-
-- 子查询需要放在括号`( )`内。
-- `operator` 表示用于 where 子句的运算符。
-
-用于 `FROM` 子句的子查询的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select column_name [, column_name ]
-from (select column_name [, column_name ]
- from table1 [, table2 ]
- [where]) as temp_table_name
-where condition
-```
-
-用于 `FROM` 的子查询返回的结果相当于一张临时表,所以需要使用 AS 关键字为该临时表起一个名字。
-
-**子查询的子查询**
-
-```sql
-SELECT cust_name, cust_contact
-FROM customers
-WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id
- FROM orders
- WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
- FROM orderitems
- WHERE prod_id = 'RGAN01'));
-```
-
-内部查询首先在其父查询之前执行,以便可以将内部查询的结果传递给外部查询。执行过程可以参考下图:
-
-
-
-### WHERE
-
-- `WHERE` 子句用于过滤记录,即缩小访问数据的范围。
-- `WHERE` 后跟一个返回 `true` 或 `false` 的条件。
-- `WHERE` 可以与 `SELECT`,`UPDATE` 和 `DELETE` 一起使用。
-- 可以在 `WHERE` 子句中使用的操作符。
-
-| 运算符 | 描述 |
-| ------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
-| = | 等于 |
-| <> | 不等于。注释:在 SQL 的一些版本中,该操作符可被写成 != |
-| > | 大于 |
-| < | 小于 |
-| >= | 大于等于 |
-| <= | 小于等于 |
-| BETWEEN | 在某个范围内 |
-| LIKE | 搜索某种模式 |
-| IN | 指定针对某个列的多个可能值 |
-
-**`SELECT` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-SELECT * FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-**`UPDATE` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-UPDATE Customers
-SET cust_name = 'Jack Jones'
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-**`DELETE` 语句中的 `WHERE` 子句**
-
-```ini
-DELETE FROM Customers
-WHERE cust_name = 'Kids Place';
-```
-
-### IN 和 BETWEEN
-
-- `IN` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是在指定的几个特定值中任选一个值。
-- `BETWEEN` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是选取介于某个范围内的值。
-
-**IN 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id IN ('DLL01', 'BRS01');
-```
-
-**BETWEEN 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_price BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
-```
-
-### AND、OR、NOT
-
-- `AND`、`OR`、`NOT` 是用于对过滤条件的逻辑处理指令。
-- `AND` 优先级高于 `OR`,为了明确处理顺序,可以使用 `()`。
-- `AND` 操作符表示左右条件都要满足。
-- `OR` 操作符表示左右条件满足任意一个即可。
-- `NOT` 操作符用于否定一个条件。
-
-**AND 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01' AND prod_price <= 4;
-```
-
-**OR 示例**
-
-```ini
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01' OR vend_id = 'BRS01';
-```
-
-**NOT 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_price NOT BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
-```
-
-### LIKE
-
-- `LIKE` 操作符在 `WHERE` 子句中使用,作用是确定字符串是否匹配模式。
-- 只有字段是文本值时才使用 `LIKE`。
-- `LIKE` 支持两个通配符匹配选项:`%` 和 `_`。
-- 不要滥用通配符,通配符位于开头处匹配会非常慢。
-- `%` 表示任何字符出现任意次数。
-- `_` 表示任何字符出现一次。
-
-**% 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_name LIKE '%bean bag%';
-```
-
-**\_ 示例**
-
-```sql
-SELECT prod_id, prod_name, prod_price
-FROM products
-WHERE prod_name LIKE '__ inch teddy bear';
-```
-
-## 连接
-
-JOIN 是“连接”的意思,顾名思义,SQL JOIN 子句用于将两个或者多个表联合起来进行查询。
-
-连接表时需要在每个表中选择一个字段,并对这些字段的值进行比较,值相同的两条记录将合并为一条。**连接表的本质就是将不同表的记录合并起来,形成一张新表。当然,这张新表只是临时的,它仅存在于本次查询期间**。
-
-使用 `JOIN` 连接两个表的基本语法如下:
-
-```sql
-select table1.column1, table2.column2...
-from table1
-join table2
-on table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2;
-```
-
-`table1.common_column1 = table2.common_column2` 是连接条件,只有满足此条件的记录才会合并为一行。您可以使用多个运算符来连接表,例如 =、>、<、<>、<=、>=、!=、`between`、`like` 或者 `not`,但是最常见的是使用 =。
-
-当两个表中有同名的字段时,为了帮助数据库引擎区分是哪个表的字段,在书写同名字段名时需要加上表名。当然,如果书写的字段名在两个表中是唯一的,也可以不使用以上格式,只写字段名即可。
-
-另外,如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用 `USING`子句来代替 `ON`,举个例子:
-
-```sql
-# join....on
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c
-inner join Orders o
-on c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-order by c.cust_name;
-
-# 如果两张表的关联字段名相同,也可以使用USING子句:join....using()
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c
-inner join Orders o
-using(cust_id)
-order by c.cust_name;
-```
-
-**`ON` 和 `WHERE` 的区别**:
-
-- 连接表时,SQL 会根据连接条件生成一张新的临时表。`ON` 就是连接条件,它决定临时表的生成。
-- `WHERE` 是在临时表生成以后,再对临时表中的数据进行过滤,生成最终的结果集,这个时候已经没有 JOIN-ON 了。
-
-所以总结来说就是:**SQL 先根据 ON 生成一张临时表,然后再根据 WHERE 对临时表进行筛选**。
-
-SQL 允许在 `JOIN` 左边加上一些修饰性的关键词,从而形成不同类型的连接,如下表所示:
-
-| 连接类型 | 说明 |
-| ---------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| INNER JOIN 内连接 | (默认连接方式)只有当两个表都存在满足条件的记录时才会返回行。 |
-| LEFT JOIN / LEFT OUTER JOIN 左(外)连接 | 返回左表中的所有行,即使右表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| RIGHT JOIN / RIGHT OUTER JOIN 右(外)连接 | 返回右表中的所有行,即使左表中没有满足条件的行也是如此。 |
-| FULL JOIN / FULL OUTER JOIN 全(外)连接 | 只要其中有一个表存在满足条件的记录,就返回行。 |
-| SELF JOIN | 将一个表连接到自身,就像该表是两个表一样。为了区分两个表,在 SQL 语句中需要至少重命名一个表。 |
-| CROSS JOIN | 交叉连接,从两个或者多个连接表中返回记录集的笛卡尔积。 |
-
-下图展示了 LEFT JOIN、RIGHT JOIN、INNER JOIN、OUTER JOIN 相关的 7 种用法。
-
-
-
-如果不加任何修饰词,只写 `JOIN`,那么默认为 `INNER JOIN`
-
-对于 `INNER JOIN` 来说,还有一种隐式的写法,称为 “**隐式内连接**”,也就是没有 `INNER JOIN` 关键字,使用 `WHERE` 语句实现内连接的功能
-
-```sql
-# 隐式内连接
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c, Orders o
-where c.cust_id = o.cust_id
-order by c.cust_name;
-
-# 显式内连接
-select c.cust_name, o.order_num
-from Customers c inner join Orders o
-using(cust_id)
-order by c.cust_name;
-```
-
-## 组合
-
-`UNION` 运算符将两个或更多查询的结果组合起来,并生成一个结果集,其中包含来自 `UNION` 中参与查询的提取行。
-
-`UNION` 基本规则:
-
-- 所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- 每个查询中涉及表的列的数据类型必须相同或兼容。
-- 通常返回的列名取自第一个查询。
-
-默认地,`UNION` 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 `UNION ALL`。
-
-```sql
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
-UNION ALL
-SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;
-```
-
-`UNION` 结果集中的列名总是等于 `UNION` 中第一个 `SELECT` 语句中的列名。
-
-`JOIN` vs `UNION`:
-
-- `JOIN` 中连接表的列可能不同,但在 `UNION` 中,所有查询的列数和列顺序必须相同。
-- `UNION` 将查询之后的行放在一起(垂直放置),但 `JOIN` 将查询之后的列放在一起(水平放置),即它构成一个笛卡尔积。
-
-## 函数
-
-不同数据库的函数往往各不相同,因此不可移植。本节主要以 MySQL 的函数为例。
-
-### 文本处理
-
-| 函数 | 说明 |
-| -------------------- | ---------------------- |
-| `LEFT()`、`RIGHT()` | 左边或者右边的字符 |
-| `LOWER()`、`UPPER()` | 转换为小写或者大写 |
-| `LTRIM()`、`RTRIM()` | 去除左边或者右边的空格 |
-| `LENGTH()` | 长度,以字节为单位 |
-| `SOUNDEX()` | 转换为语音值 |
-
-其中, **`SOUNDEX()`** 可以将一个字符串转换为描述其语音表示的字母数字模式。
-
-```sql
-SELECT *
-FROM mytable
-WHERE SOUNDEX(col1) = SOUNDEX('apple')
-```
-
-### 日期和时间处理
-
-- 日期格式:`YYYY-MM-DD`
-- 时间格式:`HH:MM:SS`
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------------- | ------------------------------ |
-| `AddDate()` | 增加一个日期(天、周等) |
-| `AddTime()` | 增加一个时间(时、分等) |
-| `CurDate()` | 返回当前日期 |
-| `CurTime()` | 返回当前时间 |
-| `Date()` | 返回日期时间的日期部分 |
-| `DateDiff()` | 计算两个日期之差 |
-| `Date_Add()` | 高度灵活的日期运算函数 |
-| `Date_Format()` | 返回一个格式化的日期或时间串 |
-| `Day()` | 返回一个日期的天数部分 |
-| `DayOfWeek()` | 对于一个日期,返回对应的星期几 |
-| `Hour()` | 返回一个时间的小时部分 |
-| `Minute()` | 返回一个时间的分钟部分 |
-| `Month()` | 返回一个日期的月份部分 |
-| `Now()` | 返回当前日期和时间 |
-| `Second()` | 返回一个时间的秒部分 |
-| `Time()` | 返回一个日期时间的时间部分 |
-| `Year()` | 返回一个日期的年份部分 |
-
-### 数值处理
-
-| 函数 | 说明 |
-| ------ | ------ |
-| SIN() | 正弦 |
-| COS() | 余弦 |
-| TAN() | 正切 |
-| ABS() | 绝对值 |
-| SQRT() | 平方根 |
-| MOD() | 余数 |
-| EXP() | 指数 |
-| PI() | 圆周率 |
-| RAND() | 随机数 |
-
-### 汇总
-
-| 函 数 | 说 明 |
-| --------- | ---------------- |
-| `AVG()` | 返回某列的平均值 |
-| `COUNT()` | 返回某列的行数 |
-| `MAX()` | 返回某列的最大值 |
-| `MIN()` | 返回某列的最小值 |
-| `SUM()` | 返回某列值之和 |
-
-`AVG()` 会忽略 NULL 行。
-
-使用 `DISTINCT` 可以让汇总函数值汇总不同的值。
-
-```sql
-SELECT AVG(DISTINCT col1) AS avg_col
-FROM mytable
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 DDL 语句用法。DDL 的主要功能是定义数据库对象(如:数据库、数据表、视图、索引等)**
-
-## 数据定义
-
-### 数据库(DATABASE)
-
-#### 创建数据库
-
-```sql
-CREATE DATABASE test;
-```
-
-#### 删除数据库
-
-```sql
-DROP DATABASE test;
-```
-
-#### 选择数据库
-
-```sql
-USE test;
-```
-
-### 数据表(TABLE)
-
-#### 创建数据表
-
-**普通创建**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE user (
- id int(10) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT 'Id',
- username varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '用户名',
- password varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '密码',
- email varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '邮箱'
-) COMMENT='用户表';
-```
-
-**根据已有的表创建新表**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE vip_user AS
-SELECT * FROM user;
-```
-
-#### 删除数据表
-
-```sql
-DROP TABLE user;
-```
-
-#### 修改数据表
-
-**添加列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-ADD age int(3);
-```
-
-**删除列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP COLUMN age;
-```
-
-**修改列**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE `user`
-MODIFY COLUMN age tinyint;
-```
-
-**添加主键**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-ADD PRIMARY KEY (id);
-```
-
-**删除主键**
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP PRIMARY KEY;
-```
-
-### 视图(VIEW)
-
-定义:
-
-- 视图是基于 SQL 语句的结果集的可视化的表。
-- 视图是虚拟的表,本身不包含数据,也就不能对其进行索引操作。对视图的操作和对普通表的操作一样。
-
-作用:
-
-- 简化复杂的 SQL 操作,比如复杂的联结;
-- 只使用实际表的一部分数据;
-- 通过只给用户访问视图的权限,保证数据的安全性;
-- 更改数据格式和表示。
-
-
-
-#### 创建视图
-
-```sql
-CREATE VIEW top_10_user_view AS
-SELECT id, username
-FROM user
-WHERE id < 10;
-```
-
-#### 删除视图
-
-```sql
-DROP VIEW top_10_user_view;
-```
-
-### 索引(INDEX)
-
-**索引是一种用于快速查询和检索数据的数据结构,其本质可以看成是一种排序好的数据结构。**
-
-索引的作用就相当于书的目录。打个比方: 我们在查字典的时候,如果没有目录,那我们就只能一页一页的去找我们需要查的那个字,速度很慢。如果有目录了,我们只需要先去目录里查找字的位置,然后直接翻到那一页就行了。
-
-**优点**:
-
-- 使用索引可以大大加快 数据的检索速度(大大减少检索的数据量), 这也是创建索引的最主要的原因。
-- 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。
-
-**缺点**:
-
-- 创建索引和维护索引需要耗费许多时间。当对表中的数据进行增删改的时候,如果数据有索引,那么索引也需要动态的修改,会降低 SQL 执行效率。
-- 索引需要使用物理文件存储,也会耗费一定空间。
-
-但是,**使用索引一定能提高查询性能吗?**
-
-大多数情况下,索引查询都是比全表扫描要快的。但是如果数据库的数据量不大,那么使用索引也不一定能够带来很大提升。
-
-关于索引的详细介绍,请看我写的 [MySQL 索引详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/mysql/mysql-index.html) 这篇文章。
-
-#### 创建索引
-
-```sql
-CREATE INDEX user_index
-ON user (id);
-```
-
-#### 添加索引
-
-```sql
-ALTER table user ADD INDEX user_index(id)
-```
-
-#### 创建唯一索引
-
-```sql
-CREATE UNIQUE INDEX user_index
-ON user (id);
-```
-
-#### 删除索引
-
-```sql
-ALTER TABLE user
-DROP INDEX user_index;
-```
-
-### 约束
-
-SQL 约束用于规定表中的数据规则。
-
-如果存在违反约束的数据行为,行为会被约束终止。
-
-约束可以在创建表时规定(通过 CREATE TABLE 语句),或者在表创建之后规定(通过 ALTER TABLE 语句)。
-
-约束类型:
-
-- `NOT NULL` - 指示某列不能存储 NULL 值。
-- `UNIQUE` - 保证某列的每行必须有唯一的值。
-- `PRIMARY KEY` - NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合。确保某列(或两个列多个列的结合)有唯一标识,有助于更容易更快速地找到表中的一个特定的记录。
-- `FOREIGN KEY` - 保证一个表中的数据匹配另一个表中的值的参照完整性。
-- `CHECK` - 保证列中的值符合指定的条件。
-- `DEFAULT` - 规定没有给列赋值时的默认值。
-
-创建表时使用约束条件:
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE Users (
- Id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增Id',
- Username VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '用户名',
- Password VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '密码',
- Email VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'default' COMMENT '邮箱地址',
- Enabled TINYINT(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '是否有效',
- PRIMARY KEY (Id)
-) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='用户表';
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 TCL 语句用法。TCL 的主要功能是管理数据库中的事务。**
-
-## 事务处理
-
-不能回退 `SELECT` 语句,回退 `SELECT` 语句也没意义;也不能回退 `CREATE` 和 `DROP` 语句。
-
-**MySQL 默认是隐式提交**,每执行一条语句就把这条语句当成一个事务然后进行提交。当出现 `START TRANSACTION` 语句时,会关闭隐式提交;当 `COMMIT` 或 `ROLLBACK` 语句执行后,事务会自动关闭,重新恢复隐式提交。
-
-通过 `set autocommit=0` 可以取消自动提交,直到 `set autocommit=1` 才会提交;`autocommit` 标记是针对每个连接而不是针对服务器的。
-
-指令:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` - 指令用于标记事务的起始点。
-- `SAVEPOINT` - 指令用于创建保留点。
-- `ROLLBACK TO` - 指令用于回滚到指定的保留点;如果没有设置保留点,则回退到 `START TRANSACTION` 语句处。
-- `COMMIT` - 提交事务。
-
-```sql
--- 开始事务
-START TRANSACTION;
-
--- 插入操作 A
-INSERT INTO `user`
-VALUES (1, 'root1', 'root1', 'xxxx@163.com');
-
--- 创建保留点 updateA
-SAVEPOINT updateA;
-
--- 插入操作 B
-INSERT INTO `user`
-VALUES (2, 'root2', 'root2', 'xxxx@163.com');
-
--- 回滚到保留点 updateA
-ROLLBACK TO updateA;
-
--- 提交事务,只有操作 A 生效
-COMMIT;
-```
-
-**接下来,我们来介绍 DCL 语句用法。DCL 的主要功能是控制用户的访问权限。**
-
-## 权限控制
-
-要授予用户帐户权限,可以用`GRANT`命令。要撤销用户的权限,可以用`REVOKE`命令。这里以 MySQL 为例,介绍权限控制实际应用。
-
-`GRANT`授予权限语法:
-
-```sql
-GRANT privilege,[privilege],.. ON privilege_level
-TO user [IDENTIFIED BY password]
-[REQUIRE tsl_option]
-[WITH [GRANT_OPTION | resource_option]];
-```
-
-简单解释一下:
-
-1. 在`GRANT`关键字后指定一个或多个权限。如果授予用户多个权限,则每个权限由逗号分隔。
-2. `ON privilege_level` 确定权限应用级别。MySQL 支持 global(`*.*`),database(`database.*`),table(`database.table`)和列级别。如果使用列权限级别,则必须在每个权限之后指定一个或逗号分隔列的列表。
-3. `user` 是要授予权限的用户。如果用户已存在,则`GRANT`语句将修改其权限。否则,`GRANT`语句将创建一个新用户。可选子句`IDENTIFIED BY`允许您为用户设置新的密码。
-4. `REQUIRE tsl_option`指定用户是否必须通过 SSL,X059 等安全连接连接到数据库服务器。
-5. 可选 `WITH GRANT OPTION` 子句允许您授予其他用户或从其他用户中删除您拥有的权限。此外,您可以使用`WITH`子句分配 MySQL 数据库服务器的资源,例如,设置用户每小时可以使用的连接数或语句数。这在 MySQL 共享托管等共享环境中非常有用。
-
-`REVOKE` 撤销权限语法:
-
-```sql
-REVOKE privilege_type [(column_list)]
- [, priv_type [(column_list)]]...
-ON [object_type] privilege_level
-FROM user [, user]...
-```
-
-简单解释一下:
-
-1. 在 `REVOKE` 关键字后面指定要从用户撤消的权限列表。您需要用逗号分隔权限。
-2. 指定在 `ON` 子句中撤销特权的特权级别。
-3. 指定要撤消 `FROM` 子句中的权限的用户帐户。
-
-`GRANT` 和 `REVOKE` 可在几个层次上控制访问权限:
-
-- 整个服务器,使用 `GRANT ALL` 和 `REVOKE ALL`;
-- 整个数据库,使用 `ON database.*`;
-- 特定的表,使用 `ON database.table`;
-- 特定的列;
-- 特定的存储过程。
-
-新创建的账户没有任何权限。账户用 `username@host` 的形式定义,`username@%` 使用的是默认主机名。MySQL 的账户信息保存在 mysql 这个数据库中。
-
-```sql
-USE mysql;
-SELECT user FROM user;
-```
-
-下表说明了可用于`GRANT`和`REVOKE`语句的所有允许权限:
-
-| **特权** | **说明** | **级别** | | | | | |
-| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------- | ------ | -------- | -------- | --- | --- |
-| **全局** | 数据库 | **表** | **列** | **程序** | **代理** | | |
-| ALL [PRIVILEGES] | 授予除 GRANT OPTION 之外的指定访问级别的所有权限 | | | | | | |
-| ALTER | 允许用户使用 ALTER TABLE 语句 | X | X | X | | | |
-| ALTER ROUTINE | 允许用户更改或删除存储的例程 | X | X | | | X | |
-| CREATE | 允许用户创建数据库和表 | X | X | X | | | |
-| CREATE ROUTINE | 允许用户创建存储的例程 | X | X | | | | |
-| CREATE TABLESPACE | 允许用户创建,更改或删除表空间和日志文件组 | X | | | | | |
-| CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES | 允许用户使用 CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE 创建临时表 | X | X | | | | |
-| CREATE USER | 允许用户使用 CREATE USER,DROP USER,RENAME USER 和 REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES 语句。 | X | | | | | |
-| CREATE VIEW | 允许用户创建或修改视图。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| DELETE | 允许用户使用 DELETE | X | X | X | | | |
-| DROP | 允许用户删除数据库,表和视图 | X | X | X | | | |
-| EVENT | 启用事件计划程序的事件使用。 | X | X | | | | |
-| EXECUTE | 允许用户执行存储的例程 | X | X | X | | | |
-| FILE | 允许用户读取数据库目录中的任何文件。 | X | | | | | |
-| GRANT OPTION | 允许用户拥有授予或撤消其他帐户权限的权限。 | X | X | X | | X | X |
-| INDEX | 允许用户创建或删除索引。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| INSERT | 允许用户使用 INSERT 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| LOCK TABLES | 允许用户对具有 SELECT 权限的表使用 LOCK TABLES | X | X | | | | |
-| PROCESS | 允许用户使用 SHOW PROCESSLIST 语句查看所有进程。 | X | | | | | |
-| PROXY | 启用用户代理。 | | | | | | |
-| REFERENCES | 允许用户创建外键 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| RELOAD | 允许用户使用 FLUSH 操作 | X | | | | | |
-| REPLICATION CLIENT | 允许用户查询以查看主服务器或从属服务器的位置 | X | | | | | |
-| REPLICATION SLAVE | 允许用户使用复制从属从主服务器读取二进制日志事件。 | X | | | | | |
-| SELECT | 允许用户使用 SELECT 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| SHOW DATABASES | 允许用户显示所有数据库 | X | | | | | |
-| SHOW VIEW | 允许用户使用 SHOW CREATE VIEW 语句 | X | X | X | | | |
-| SHUTDOWN | 允许用户使用 mysqladmin shutdown 命令 | X | | | | | |
-| SUPER | 允许用户使用其他管理操作,例如 CHANGE MASTER TO,KILL,PURGE BINARY LOGS,SET GLOBAL 和 mysqladmin 命令 | X | | | | | |
-| TRIGGER | 允许用户使用 TRIGGER 操作。 | X | X | X | | | |
-| UPDATE | 允许用户使用 UPDATE 语句 | X | X | X | X | | |
-| USAGE | 相当于“没有特权” | | | | | | |
-
-### 创建账户
-
-```sql
-CREATE USER myuser IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
-```
-
-### 修改账户名
-
-```sql
-UPDATE user SET user='newuser' WHERE user='myuser';
-FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
-```
-
-### 删除账户
-
-```sql
-DROP USER myuser;
-```
-
-### 查看权限
-
-```sql
-SHOW GRANTS FOR myuser;
-```
-
-### 授予权限
-
-```sql
-GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON *.* TO myuser;
-```
-
-### 删除权限
-
-```sql
-REVOKE SELECT, INSERT ON *.* FROM myuser;
-```
-
-### 更改密码
-
-```sql
-SET PASSWORD FOR myuser = 'mypass';
-```
-
-## 存储过程
-
-存储过程可以看成是对一系列 SQL 操作的批处理。存储过程可以由触发器,其他存储过程以及 Java, Python,PHP 等应用程序调用。
-
-
-
-使用存储过程的好处:
-
-- 代码封装,保证了一定的安全性;
-- 代码复用;
-- 由于是预先编译,因此具有很高的性能。
-
-创建存储过程:
-
-- 命令行中创建存储过程需要自定义分隔符,因为命令行是以 `;` 为结束符,而存储过程中也包含了分号,因此会错误把这部分分号当成是结束符,造成语法错误。
-- 包含 `in`、`out` 和 `inout` 三种参数。
-- 给变量赋值都需要用 `select into` 语句。
-- 每次只能给一个变量赋值,不支持集合的操作。
-
-需要注意的是:**阿里巴巴《Java 开发手册》强制禁止使用存储过程。因为存储过程难以调试和扩展,更没有移植性。**
-
-
-
-至于到底要不要在项目中使用,还是要看项目实际需求,权衡好利弊即可!
-
-### 创建存储过程
-
-```sql
-DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `proc_adder`;
-DELIMITER ;;
-CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `proc_adder`(IN a int, IN b int, OUT sum int)
-BEGIN
- DECLARE c int;
- if a is null then set a = 0;
- end if;
-
- if b is null then set b = 0;
- end if;
-
- set sum = a + b;
-END
-;;
-DELIMITER ;
-```
-
-### 使用存储过程
-
-```less
-set @b=5;
-call proc_adder(2,@b,@s);
-select @s as sum;
-```
-
-## 游标
-
-游标(cursor)是一个存储在 DBMS 服务器上的数据库查询,它不是一条 `SELECT` 语句,而是被该语句检索出来的结果集。
-
-在存储过程中使用游标可以对一个结果集进行移动遍历。
-
-游标主要用于交互式应用,其中用户需要滚动屏幕上的数据,并对数据进行浏览或做出更改。
-
-使用游标的几个明确步骤:
-
-- 在使用游标前,必须声明(定义)它。这个过程实际上没有检索数据, 它只是定义要使用的 `SELECT` 语句和游标选项。
-
-- 一旦声明,就必须打开游标以供使用。这个过程用前面定义的 SELECT 语句把数据实际检索出来。
-
-- 对于填有数据的游标,根据需要取出(检索)各行。
-
-- 在结束游标使用时,必须关闭游标,可能的话,释放游标(有赖于具
-
- 体的 DBMS)。
-
-```sql
-DELIMITER $
-CREATE PROCEDURE getTotal()
-BEGIN
- DECLARE total INT;
- -- 创建接收游标数据的变量
- DECLARE sid INT;
- DECLARE sname VARCHAR(10);
- -- 创建总数变量
- DECLARE sage INT;
- -- 创建结束标志变量
- DECLARE done INT DEFAULT false;
- -- 创建游标
- DECLARE cur CURSOR FOR SELECT id,name,age from cursor_table where age>30;
- -- 指定游标循环结束时的返回值
- DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = true;
- SET total = 0;
- OPEN cur;
- FETCH cur INTO sid, sname, sage;
- WHILE(NOT done)
- DO
- SET total = total + 1;
- FETCH cur INTO sid, sname, sage;
- END WHILE;
-
- CLOSE cur;
- SELECT total;
-END $
-DELIMITER ;
-
--- 调用存储过程
-call getTotal();
-```
-
-## 触发器
-
-触发器是一种与表操作有关的数据库对象,当触发器所在表上出现指定事件时,将调用该对象,即表的操作事件触发表上的触发器的执行。
-
-我们可以使用触发器来进行审计跟踪,把修改记录到另外一张表中。
-
-使用触发器的优点:
-
-- SQL 触发器提供了另一种检查数据完整性的方法。
-- SQL 触发器可以捕获数据库层中业务逻辑中的错误。
-- SQL 触发器提供了另一种运行计划任务的方法。通过使用 SQL 触发器,您不必等待运行计划任务,因为在对表中的数据进行更改之前或之后会自动调用触发器。
-- SQL 触发器对于审计表中数据的更改非常有用。
-
-使用触发器的缺点:
-
-- SQL 触发器只能提供扩展验证,并且不能替换所有验证。必须在应用程序层中完成一些简单的验证。例如,您可以使用 JavaScript 在客户端验证用户的输入,或者使用服务器端脚本语言(如 JSP,PHP,ASP.NET,Perl)在服务器端验证用户的输入。
-- 从客户端应用程序调用和执行 SQL 触发器是不可见的,因此很难弄清楚数据库层中发生了什么。
-- SQL 触发器可能会增加数据库服务器的开销。
-
-MySQL 不允许在触发器中使用 CALL 语句 ,也就是不能调用存储过程。
-
-> 注意:在 MySQL 中,分号 `;` 是语句结束的标识符,遇到分号表示该段语句已经结束,MySQL 可以开始执行了。因此,解释器遇到触发器执行动作中的分号后就开始执行,然后会报错,因为没有找到和 BEGIN 匹配的 END。
->
-> 这时就会用到 `DELIMITER` 命令(DELIMITER 是定界符,分隔符的意思)。它是一条命令,不需要语句结束标识,语法为:`DELIMITER new_delimiter`。`new_delimiter` 可以设为 1 个或多个长度的符号,默认的是分号 `;`,我们可以把它修改为其他符号,如 `$` - `DELIMITER $` 。在这之后的语句,以分号结束,解释器不会有什么反应,只有遇到了 `$`,才认为是语句结束。注意,使用完之后,我们还应该记得把它给修改回来。
-
-在 MySQL 5.7.2 版之前,可以为每个表定义最多六个触发器。
-
-- `BEFORE INSERT` - 在将数据插入表格之前激活。
-- `AFTER INSERT` - 将数据插入表格后激活。
-- `BEFORE UPDATE` - 在更新表中的数据之前激活。
-- `AFTER UPDATE` - 更新表中的数据后激活。
-- `BEFORE DELETE` - 在从表中删除数据之前激活。
-- `AFTER DELETE` - 从表中删除数据后激活。
-
-但是,从 MySQL 版本 5.7.2+开始,可以为同一触发事件和操作时间定义多个触发器。
-
-**`NEW` 和 `OLD`**:
-
-- MySQL 中定义了 `NEW` 和 `OLD` 关键字,用来表示触发器的所在表中,触发了触发器的那一行数据。
-- 在 `INSERT` 型触发器中,`NEW` 用来表示将要(`BEFORE`)或已经(`AFTER`)插入的新数据;
-- 在 `UPDATE` 型触发器中,`OLD` 用来表示将要或已经被修改的原数据,`NEW` 用来表示将要或已经修改为的新数据;
-- 在 `DELETE` 型触发器中,`OLD` 用来表示将要或已经被删除的原数据;
-- 使用方法:`NEW.columnName` (columnName 为相应数据表某一列名)
-
-### 创建触发器
-
-> 提示:为了理解触发器的要点,有必要先了解一下创建触发器的指令。
-
-`CREATE TRIGGER` 指令用于创建触发器。
-
-语法:
-
-```sql
-CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
-trigger_time
-trigger_event
-ON table_name
-FOR EACH ROW
-BEGIN
- trigger_statements
-END;
-```
-
-说明:
-
-- `trigger_name`:触发器名
-- `trigger_time` : 触发器的触发时机。取值为 `BEFORE` 或 `AFTER`。
-- `trigger_event` : 触发器的监听事件。取值为 `INSERT`、`UPDATE` 或 `DELETE`。
-- `table_name` : 触发器的监听目标。指定在哪张表上建立触发器。
-- `FOR EACH ROW`: 行级监视,Mysql 固定写法,其他 DBMS 不同。
-- `trigger_statements`: 触发器执行动作。是一条或多条 SQL 语句的列表,列表内的每条语句都必须用分号 `;` 来结尾。
-
-当触发器的触发条件满足时,将会执行 `BEGIN` 和 `END` 之间的触发器执行动作。
-
-示例:
-
-```sql
-DELIMITER $
-CREATE TRIGGER `trigger_insert_user`
-AFTER INSERT ON `user`
-FOR EACH ROW
-BEGIN
- INSERT INTO `user_history`(user_id, operate_type, operate_time)
- VALUES (NEW.id, 'add a user', now());
-END $
-DELIMITER ;
-```
-
-### 查看触发器
-
-```sql
-SHOW TRIGGERS;
-```
-
-### 删除触发器
-
-```sql
-DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trigger_insert_user;
-```
-
-## 文章推荐
-
-- [后端程序员必备:SQL 高性能优化指南!35+条优化建议立马 GET!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/I-ZT3zGTNBZ6egS7T09jyQ)
-- [后端程序员必备:书写高质量 SQL 的 30 条建议](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247486461&idx=1&sn=60a22279196d084cc398936fe3b37772&chksm=cea24436f9d5cd20a4fa0e907590f3e700d7378b3f608d7b33bb52cfb96f503b7ccb65a1deed&token=1987003517&lang=zh_CN#rd)
-
-
+The supported permission controls may vary depending on different DBMS and security entities.
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md b/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
index e9b9f27e6dd..4ab33311d2c 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/api-gateway.md
@@ -1,63 +1,63 @@
---
-title: API网关基础知识总结
-category: 分布式
+title: API Gateway Basic Knowledge Summary
+category: Distributed
---
-## 什么是网关?
+## What is a Gateway?
-微服务背景下,一个系统被拆分为多个服务,但是像安全认证,流量控制,日志,监控等功能是每个服务都需要的,没有网关的话,我们就需要在每个服务中单独实现,这使得我们做了很多重复的事情并且没有一个全局的视图来统一管理这些功能。
+In the context of microservices, a system is split into multiple services, but features such as security authentication, traffic control, logging, and monitoring are required by each service. Without a gateway, we would need to implement these features individually in each service, leading to a lot of duplication and lacking a global view to manage these functions uniformly.
-
+
-一般情况下,网关可以为我们提供请求转发、安全认证(身份/权限认证)、流量控制、负载均衡、降级熔断、日志、监控、参数校验、协议转换等功能。
+Generally, a gateway can provide us with features such as request forwarding, security authentication (identity/authorization authentication), traffic control, load balancing, circuit breaking, logging, monitoring, parameter validation, and protocol conversion.
-上面介绍了这么多功能,实际上,网关主要做了两件事情:**请求转发** + **请求过滤**。
+Despite all these features, the gateway mainly does two things: **request forwarding** + **request filtering**.
-由于引入网关之后,会多一步网络转发,因此性能会有一点影响(几乎可以忽略不计,尤其是内网访问的情况下)。 另外,我们需要保障网关服务的高可用,避免单点风险。
+Since introducing a gateway adds a step of network forwarding, performance may be slightly affected (virtually negligible, especially in the case of internal network access). Additionally, we need to ensure high availability of the gateway service to avoid single points of failure.
-如下图所示,网关服务外层通过 Nginx(其他负载均衡设备/软件也行) 进⾏负载转发以达到⾼可⽤。Nginx 在部署的时候,尽量也要考虑高可用,避免单点风险。
+As shown in the figure below, the outer layer of the gateway service uses Nginx (other load balancing devices/software can also be used) for load forwarding to achieve high availability. When deploying Nginx, considerations for high availability should be made to avoid single points of risk.
-
+
-## 网关能提供哪些功能?
+## What Functions Can a Gateway Provide?
-绝大部分网关可以提供下面这些功能(有一些功能需要借助其他框架或者中间件):
+Most gateways can provide the following functions (some functions may require the assistance of other frameworks or middleware):
-- **请求转发**:将请求转发到目标微服务。
-- **负载均衡**:根据各个微服务实例的负载情况或者具体的负载均衡策略配置对请求实现动态的负载均衡。
-- **安全认证**:对用户请求进行身份验证并仅允许可信客户端访问 API,并且还能够使用类似 RBAC 等方式来授权。
-- **参数校验**:支持参数映射与校验逻辑。
-- **日志记录**:记录所有请求的行为日志供后续使用。
-- **监控告警**:从业务指标、机器指标、JVM 指标等方面进行监控并提供配套的告警机制。
-- **流量控制**:对请求的流量进行控制,也就是限制某一时刻内的请求数。
-- **熔断降级**:实时监控请求的统计信息,达到配置的失败阈值后,自动熔断,返回默认值。
-- **响应缓存**:当用户请求获取的是一些静态的或更新不频繁的数据时,一段时间内多次请求获取到的数据很可能是一样的。对于这种情况可以将响应缓存起来。这样用户请求可以直接在网关层得到响应数据,无需再去访问业务服务,减轻业务服务的负担。
-- **响应聚合**:某些情况下用户请求要获取的响应内容可能会来自于多个业务服务。网关作为业务服务的调用方,可以把多个服务的响应整合起来,再一并返回给用户。
-- **灰度发布**:将请求动态分流到不同的服务版本(最基本的一种灰度发布)。
-- **异常处理**:对于业务服务返回的异常响应,可以在网关层在返回给用户之前做转换处理。这样可以把一些业务侧返回的异常细节隐藏,转换成用户友好的错误提示返回。
-- **API 文档:** 如果计划将 API 暴露给组织以外的开发人员,那么必须考虑使用 API 文档,例如 Swagger 或 OpenAPI。
-- **协议转换**:通过协议转换整合后台基于 REST、AMQP、Dubbo 等不同风格和实现技术的微服务,面向 Web Mobile、开放平台等特定客户端提供统一服务。
-- **证书管理**:将 SSL 证书部署到 API 网关,由一个统一的入口管理接口,降低了证书更换时的复杂度。
+- **Request Forwarding**: Forward requests to the target microservice.
+- **Load Balancing**: Implement dynamic load balancing based on the load of each microservice instance or specific load balancing strategy configurations.
+- **Security Authentication**: Verify user requests and only allow trusted clients to access the API, and authorization can be done using methods like RBAC.
+- **Parameter Validation**: Support parameter mapping and validation logic.
+- **Logging**: Record the behavior logs of all requests for future use.
+- **Monitoring and Alerts**: Monitor from operational metrics, machine metrics, JVM metrics, etc., and provide a corresponding alert mechanism.
+- **Traffic Control**: Control the traffic of requests, limiting the number of requests at a certain time.
+- **Circuit Breaking**: Monitor request statistics in real-time, and when the configured failure threshold is reached, automatically break the circuit and return default values.
+- **Response Caching**: When user requests are for some static or infrequently updated data, multiple requests for data within a certain time period may yield the same result. In such cases, responses can be cached. This way, user requests can directly receive response data at the gateway layer without going through the business service, reducing the load on the business service.
+- **Response Aggregation**: In some cases, the response content that user requests may come from multiple business services. The gateway, as the caller of the business services, can aggregate the responses from multiple services and return them to the user together.
+- **Gray Release**: Dynamically divert requests to different service versions (a basic form of gray release).
+- **Exception Handling**: For exception responses returned by business services, the gateway layer can transform them before returning them to the user. This can obscure some details of the exceptions returned from the business side, converting them into user-friendly error messages.
+- **API Documentation**: If planning to expose APIs to developers outside the organization, it's necessary to consider using API documentation tools like Swagger or OpenAPI.
+- **Protocol Conversion**: Through protocol conversion, integrate backend microservices based on REST, AMQP, Dubbo, etc., providing unified services for specific clients like Web Mobile and open platforms.
+- **Certificate Management**: Deploy SSL certificates to the API gateway, managing interfaces through a unified entry point, reducing the complexity during certificate replacement.
-下图来源于[百亿规模 API 网关服务 Shepherd 的设计与实现 - 美团技术团队 - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iITqdIiHi3XGKq6u6FRVdg)这篇文章。
+The following diagram is sourced from [Design and Implementation of the Billion-scale API Gateway Service Shepherd - Meituan Technical Team - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iITqdIiHi3XGKq6u6FRVdg).

-## 有哪些常见的网关系统?
+## What Common Gateway Systems Are There?
### Netflix Zuul
-Zuul 是 Netflix 开发的一款提供动态路由、监控、弹性、安全的网关服务,基于 Java 技术栈开发,可以和 Eureka、Ribbon、Hystrix 等组件配合使用。
+Zuul is a gateway service developed by Netflix that provides dynamic routing, monitoring, elasticity, and security, developed on the Java technology stack and can be used with components like Eureka, Ribbon, and Hystrix.
-Zuul 核心架构如下:
+The core architecture of Zuul is as follows:
-
+
-Zuul 主要通过过滤器(类似于 AOP)来过滤请求,从而实现网关必备的各种功能。
+Zuul mainly uses filters (similar to AOP) to filter requests, thereby implementing various necessary functions of a gateway.
-
+
-我们可以自定义过滤器来处理请求,并且,Zuul 生态本身就有很多现成的过滤器供我们使用。就比如限流可以直接用国外朋友写的 [spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit](https://github.com/marcosbarbero/spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit) (这里只是举例说明,一般是配合 hystrix 来做限流):
+We can customize filters to handle requests, and the Zuul ecosystem already has many ready-made filters for us to use. For instance, rate limiting can directly use a repository written by overseas friends called [spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit](https://github.com/marcosbarbero/spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit) (this is just an example; generally, it is used in conjunction with Hystrix for rate limiting):
```xml
@@ -71,60 +71,60 @@ Zuul 主要通过过滤器(类似于 AOP)来过滤请求,从而实现网
```
-[Zuul 1.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/announcing-zuul-edge-service-in-the-cloud-ab3af5be08ee) 基于同步 IO,性能较差。[Zuul 2.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/open-sourcing-zuul-2-82ea476cb2b3) 基于 Netty 实现了异步 IO,性能得到了大幅改进。
+[Zuul 1.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/announcing-zuul-edge-service-in-the-cloud-ab3af5be08ee) is based on synchronous I/O, which performs poorly. [Zuul 2.x](https://netflixtechblog.com/open-sourcing-zuul-2-82ea476cb2b3) implements asynchronous I/O based on Netty, significantly improving performance.
-
+
-- GitHub 地址:
-- 官方 Wiki:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Wiki:
### Spring Cloud Gateway
-SpringCloud Gateway 属于 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,其诞生的目标是为了替代老牌网关 **Zuul**。准确点来说,应该是 Zuul 1.x。SpringCloud Gateway 起步要比 Zuul 2.x 更早。
+Spring Cloud Gateway is a gateway in the Spring Cloud ecosystem born to replace the legacy gateway **Zuul**. More precisely, it should be Zuul 1.x. Spring Cloud Gateway started earlier than Zuul 2.x.
-为了提升网关的性能,SpringCloud Gateway 基于 Spring WebFlux 。Spring WebFlux 使用 Reactor 库来实现响应式编程模型,底层基于 Netty 实现同步非阻塞的 I/O。
+To enhance gateway performance, Spring Cloud Gateway is built on Spring WebFlux. Spring WebFlux uses the Reactor library to implement a reactive programming model, based on Netty for synchronous, non-blocking I/O.

-Spring Cloud Gateway 不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,限流。
+Spring Cloud Gateway provides not only a unified routing method but also offers basic gateway functionalities based on a filter chain, such as security, monitoring/metrics, and rate limiting.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 和 Zuul 2.x 的差别不大,也是通过过滤器来处理请求。不过,目前更加推荐使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 而非 Zuul,Spring Cloud 生态对其支持更加友好。
+There aren't many differences between Spring Cloud Gateway and Zuul 2.x, both use filters to process requests. However, Spring Cloud Gateway is currently more recommended over Zuul, as the Spring Cloud ecosystem supports it more favorably.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### OpenResty
-根据官方介绍:
+According to the official introduction:
-> OpenResty 是一个基于 Nginx 与 Lua 的高性能 Web 平台,其内部集成了大量精良的 Lua 库、第三方模块以及大多数的依赖项。用于方便地搭建能够处理超高并发、扩展性极高的动态 Web 应用、Web 服务和动态网关。
+> OpenResty is a high-performance web platform based on Nginx and Lua, which integrates numerous high-quality Lua libraries, third-party modules, and most dependencies. It is used to conveniently build dynamic web applications, web services, and dynamic gateways that can handle ultra-high concurrency with high scalability.
-
+
-OpenResty 基于 Nginx,主要还是看中了其优秀的高并发能力。不过,由于 Nginx 采用 C 语言开发,二次开发门槛较高。如果想在 Nginx 上实现一些自定义的逻辑或功能,就需要编写 C 语言的模块,并重新编译 Nginx。
+OpenResty is based on Nginx, primarily due to its excellent high concurrency capability. However, because Nginx is developed in C language, the barrier to secondary development is relatively high. If you want to implement some custom logic or functionality on Nginx, it requires writing C language modules and recompiling Nginx.
-为了解决这个问题,OpenResty 通过实现 `ngx_lua` 和 `stream_lua` 等 Nginx 模块,把 Lua/LuaJIT 完美地整合进了 Nginx,从而让我们能够在 Nginx 内部里嵌入 Lua 脚本,使得可以通过简单的 Lua 语言来扩展网关的功能,比如实现自定义的路由规则、过滤器、缓存策略等。
+To solve this problem, OpenResty integrates Lua/LuaJIT perfectly into Nginx by implementing `ngx_lua` and `stream_lua` modules, allowing us to embed Lua scripts inside Nginx. This makes it possible to extend the gateway's functionality using simple Lua language, such as implementing custom routing rules, filters, caching strategies, etc.
-> Lua 是一种非常快速的动态脚本语言,它的运行速度接近于 C 语言。LuaJIT 是 Lua 的一个即时编译器,它可以显著提高 Lua 代码的执行效率。LuaJIT 将一些常用的 Lua 函数和工具库预编译并缓存,这样在下次调用时就可以直接使用缓存的字节码,从而大大加快了执行速度。
+> Lua is a very fast dynamic scripting language, with running speeds close to those of C language. LuaJIT is a just-in-time compiler for Lua that can significantly improve the execution efficiency of Lua code. LuaJIT precompiles and caches commonly used Lua functions and tool libraries, so they can be directly reused in the next call, greatly speeding up execution.
-关于 OpenResty 的入门以及网关安全实战推荐阅读这篇文章:[每个后端都应该了解的 OpenResty 入门以及网关安全实战](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3HglZs06W95vF3tSa3KrXw)。
+For an introduction to OpenResty and practical gateway security, it is recommended to read this article: [OpenResty Introduction and Gateway Security Practices Every Backend Should Know](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3HglZs06W95vF3tSa3KrXw).
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### Kong
-Kong 是一款基于 [OpenResty](https://github.com/openresty/) (Nginx + Lua)的高性能、云原生、可扩展、生态丰富的网关系统,主要由 3 个组件组成:
+Kong is a high-performance, cloud-native, scalable, and rich ecosystem gateway system based on [OpenResty](https://github.com/openresty/) (Nginx + Lua), mainly consisting of three components:
-- Kong Server:基于 Nginx 的服务器,用来接收 API 请求。
-- Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL:用来存储操作数据。
-- Kong Dashboard:官方推荐 UI 管理工具,当然,也可以使用 RESTful 方式 管理 Admin api。
+- Kong Server: A server based on Nginx, used to receive API requests.
+- Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL: Used to store operational data.
+- Kong Dashboard: Officially recommended UI management tool. Alternatively, RESTful methods can be used to manage the Admin API.

-由于默认使用 Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL 存储数据,Kong 的整个架构比较臃肿,并且会带来高可用的问题。
+Due to the default use of Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL for data storage, Kong's entire architecture can be somewhat bulky and may introduce high availability issues.
-Kong 提供了插件机制来扩展其功能,插件在 API 请求响应循环的生命周期中被执行。比如在服务上启用 Zipkin 插件:
+Kong offers a plugin mechanism to extend its functionality, executed during the API request-response lifecycle. For example, to enable the Zipkin plugin on a service:
```shell
$ curl -X POST http://kong:8001/services/{service}/plugins \
@@ -133,79 +133,79 @@ $ curl -X POST http://kong:8001/services/{service}/plugins \
--data "config.sample_ratio=0.001"
```
-Kong 本身就是一个 Lua 应用程序,并且是在 Openresty 的基础之上做了一层封装的应用。归根结底就是利用 Lua 嵌入 Nginx 的方式,赋予了 Nginx 可编程的能力,这样以插件的形式在 Nginx 这一层能够做到无限想象的事情。例如限流、安全访问策略、路由、负载均衡等等。编写一个 Kong 插件,就是按照 Kong 插件编写规范,写一个自己自定义的 Lua 脚本,然后加载到 Kong 中,最后引用即可。
+Kong itself is a Lua application, but it is also an encapsulated application built on top of OpenResty. Ultimately, it empowers Nginx with programmable capabilities using the embedded Lua approach, enabling endless possibilities through plugins for things like rate limiting, security access policies, routing, load balancing, and so on. Writing a Kong plugin involves creating a custom Lua script following the Kong plugin development standards and loading it into Kong.

-除了 Lua,Kong 还可以基于 Go 、JavaScript、Python 等语言开发插件,得益于对应的 PDK(插件开发工具包)。
+In addition to Lua, Kong can also develop plugins based on Go, JavaScript, Python, and other languages, thanks to the corresponding PDK (Plugin Development Kit).
-关于 Kong 插件的详细介绍,推荐阅读官方文档:,写的比较详细。
+For a detailed introduction to Kong plugins, it is recommended to read the official documentation: , which is quite comprehensive.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
### APISIX
-APISIX 是一款基于 OpenResty 和 etcd 的高性能、云原生、可扩展的网关系统。
+APISIX is a high-performance, cloud-native, scalable gateway system based on OpenResty and etcd.
-> etcd 是使用 Go 语言开发的一个开源的、高可用的分布式 key-value 存储系统,使用 Raft 协议做分布式共识。
+> etcd is an open-source, high-availability distributed key-value store system developed using Go, utilizing the Raft protocol for distributed consensus.
-与传统 API 网关相比,APISIX 具有动态路由和插件热加载,特别适合微服务系统下的 API 管理。并且,APISIX 与 SkyWalking(分布式链路追踪系统)、Zipkin(分布式链路追踪系统)、Prometheus(监控系统) 等 DevOps 生态工具对接都十分方便。
+Compared to traditional API gateways, APISIX has dynamic routing and hot plugin loading, making it especially suitable for API management in microservice systems. Additionally, APISIX integrates easily with various DevOps tools such as SkyWalking (distributed tracing system), Zipkin (distributed tracing system), and Prometheus (monitoring system).
-
+
-作为 Nginx 和 Kong 的替代项目,APISIX 目前已经是 Apache 顶级开源项目,并且是最快毕业的国产开源项目。国内目前已经有很多知名企业(比如金山、有赞、爱奇艺、腾讯、贝壳)使用 APISIX 处理核心的业务流量。
+As an alternative project to Nginx and Kong, APISIX is currently an Apache top-level open-source project and is the fastest domestic open-source project to graduate. Many well-known domestic enterprises (such as Kingsoft, Youzan, iQIYI, Tencent, and Beike) are using APISIX to handle core business traffic.
-根据官网介绍:“APISIX 已经生产可用,功能、性能、架构全面优于 Kong”。
+According to the official site: "APISIX is already production-ready and has comprehensive features, performance, and architecture surpassing Kong."
-APISIX 同样支持定制化的插件开发。开发者除了能够使用 Lua 语言开发插件,还能通过下面两种方式开发来避开 Lua 语言的学习成本:
+APISIX also supports customizable plugin development. Developers can create plugins using Lua, and they can also do so in the following two ways to avoid the learning cost of Lua:
-- 通过 Plugin Runner 来支持更多的主流编程语言(比如 Java、Python、Go 等等)。通过这样的方式,可以让后端工程师通过本地 RPC 通信,使用熟悉的编程语言开发 APISIX 的插件。这样做的好处是减少了开发成本,提高了开发效率,但是在性能上会有一些损失。
-- 使用 Wasm(WebAssembly) 开发插件。Wasm 被嵌入到了 APISIX 中,用户可以使用 Wasm 去编译成 Wasm 的字节码在 APISIX 中运行。
+- Use Plugin Runner to support more mainstream programming languages (such as Java, Python, Go, etc.). This allows backend engineers to develop APISIX plugins using familiar programming languages via local RPC communication. This approach reduces development costs and improves efficiency, although there will be some performance losses.
+- Use Wasm (WebAssembly) to develop plugins. Wasm is embedded in APISIX, allowing users to compile their code into Wasm bytecode to run in APISIX.
-> Wasm 是基于堆栈的虚拟机的二进制指令格式,一种低级汇编语言,旨在非常接近已编译的机器代码,并且非常接近本机性能。Wasm 最初是为浏览器构建的,但是随着技术的成熟,在服务器端看到了越来越多的用例。
+> Wasm is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine, a low-level assembly language designed to be very close to compiled machine code and very close to native performance. Originally built for browsers, as the technology matured, more use cases for server-side applications have emerged.

-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
-相关阅读:
+Related articles:
-- [为什么说 Apache APISIX 是最好的 API 网关?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j8ggPGEHFu3x5ekJZyeZnA)
-- [有了 NGINX 和 Kong,为什么还需要 Apache APISIX](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog/why-we-need-Apache-APISIX)
-- [APISIX 技术博客](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog)
-- [APISIX 用户案例](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/usercases)(推荐)
+- [Why Apache APISIX is the Best API Gateway?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j8ggPGEHFu3x5ekJZyeZnA)
+- [With NGINX and Kong, Why Do We Still Need Apache APISIX](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog/why-we-need-Apache-APISIX)
+- [APISIX Technical Blog](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/blog)
+- [APISIX User Cases](https://www.apiseven.com/zh/usercases) (Recommended)
### Shenyu
-Shenyu 是一款基于 WebFlux 的可扩展、高性能、响应式网关,Apache 顶级开源项目。
+Shenyu is an extensible, high-performance, and reactive gateway based on WebFlux, and is an Apache top-level open-source project.
-
+
-Shenyu 通过插件扩展功能,插件是 ShenYu 的灵魂,并且插件也是可扩展和热插拔的。不同的插件实现不同的功能。Shenyu 自带了诸如限流、熔断、转发、重写、重定向、和路由监控等插件。
+Shenyu extends its functionality through plugins, which are the soul of Shenyu, and the plugins are also extensible and hot-swappable. Different plugins implement different features. Shenyu comes with built-in plugins for rate limiting, circuit breaking, forwarding, rewriting, redirection, and routing monitoring.
-- Github 地址:
-- 官网地址:
+- GitHub Address:
+- Official Site:
-## 如何选择?
+## How to Choose?
-上面介绍的几个常见的网关系统,最常用的是 Spring Cloud Gateway、Kong、APISIX 这三个。
+Among the common gateway systems introduced above, the three most commonly used are Spring Cloud Gateway, Kong, and APISIX.
-对于公司业务以 Java 为主要开发语言的情况下,Spring Cloud Gateway 通常是个不错的选择,其优点有:简单易用、成熟稳定、与 Spring Cloud 生态系统兼容、Spring 社区成熟等等。不过,Spring Cloud Gateway 也有一些局限性和不足之处, 一般还需要结合其他网关一起使用比如 OpenResty。并且,其性能相比较于 Kong 和 APISIX,还是差一些。如果对性能要求比较高的话,Spring Cloud Gateway 不是一个好的选择。
+For companies where Java is the primary development language, Spring Cloud Gateway is typically a good choice, with advantages such as: simplicity, maturity and stability, compatibility with the Spring Cloud ecosystem, and a mature Spring community, etc. However, Spring Cloud Gateway also has some limitations and shortcomings, generally requiring it to be used in conjunction with other gateways like OpenResty. Moreover, its performance is still somewhat inferior compared to Kong and APISIX. If performance is a significant concern, Spring Cloud Gateway is not a good choice.
-Kong 和 APISIX 功能更丰富,性能更强大,技术架构更贴合云原生。Kong 是开源 API 网关的鼻祖,生态丰富,用户群体庞大。APISIX 属于后来者,更优秀一些,根据 APISIX 官网介绍:“APISIX 已经生产可用,功能、性能、架构全面优于 Kong”。下面简单对比一下二者:
+Kong and APISIX offer more robust functionality, with stronger performance and a technology architecture more aligned with cloud-native principles. Kong is the pioneer of open-source API gateways, with a rich ecosystem and a large user base. APISIX, as a later entrant, is even better; according to its official site: "APISIX is already production-ready, with functionality, performance, and architecture comprehensively superior to Kong." Below is a brief comparison between the two:
-- APISIX 基于 etcd 来做配置中心,不存在单点问题,云原生友好;而 Kong 基于 Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL ,存在单点风险,需要额外的基础设施保障做高可用。
-- APISIX 支持热更新,并且实现了毫秒级别的热更新响应;而 Kong 不支持热更新。
-- APISIX 的性能要优于 Kong 。
-- APISIX 支持的插件更多,功能更丰富。
+- APISIX uses etcd as a configuration center, avoiding single point issues and is cloud-native friendly; whereas Kong relies on Apache Cassandra/PostgreSQL, which has single point risks and requires additional infrastructure for high availability.
+- APISIX supports hot updates and achieves milliseconds-level hot update response; while Kong does not support hot updates.
+- APISIX exhibits superior performance compared to Kong.
+- APISIX supports a greater number of plugins, with richer functionalities.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Kong 插件开发教程[通俗易懂]:
-- API 网关 Kong 实战:
-- Spring Cloud Gateway 原理介绍和应用:
-- 微服务为什么要用到 API 网关?:
+- Kong Plugin Development Tutorial \[Easy to Understand\]:
+- API Gateway Kong Practical Application:
+- Introduction to Spring Cloud Gateway Principles and Applications:
+- Why Do Microservices Need an API Gateway?:
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
index 2e00aec70a3..1759140bcd6 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-configuration-center.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
---
-title: 分布式配置中心常见问题总结(付费)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Issues in Distributed Configuration Centers (Paid)
+category: Distributed
---
-**分布式配置中心** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了《Java 面试指北》中。
+The interview questions related to **Distributed Configuration Centers** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to see the detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled into the "Java Interview Guide."

diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
index 5b737f34593..8d545e4cfb9 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id-design.md
@@ -1,173 +1,62 @@
---
-title: 分布式ID设计指南
-category: 分布式
+title: Distributed ID Design Guide
+category: Distributed
---
::: tip
-看到百度 Geek 说的一篇结合具体场景聊分布式 ID 设计的文章,感觉挺不错的。于是,我将这篇文章的部分内容整理到了这里。原文传送门:[分布式 ID 生成服务的技术原理和项目实战](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bFDLb6U6EgI-DvCdLTq_QA) 。
+I came across an article by Baidu Geek discussing the design of distributed IDs in specific scenarios, and I found it quite insightful. Therefore, I have organized some of the content from this article here. You can find the original article here: [Technical Principles and Project Practice of Distributed ID Generation Service](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bFDLb6U6EgI-DvCdLTq_QA).
:::
-网上绝大多数的分布式 ID 生成服务,一般着重于技术原理剖析,很少见到根据具体的业务场景去选型 ID 生成服务的文章。
+Most distributed ID generation services available online generally focus on technical principles and rarely discuss how to choose ID generation services based on specific business scenarios.
-本文结合一些使用场景,进一步探讨业务场景中对 ID 有哪些具体的要求。
+This article explores the specific requirements for IDs in various business scenarios.
-## 场景一:订单系统
+## Scenario 1: Order System
-我们在商场买东西一码付二维码,下单生成的订单号,使用到的优惠券码,联合商品兑换券码,这些是在网上购物经常使用到的单号,那么为什么有些单号那么长,有些只有几位数?有些单号一看就知道年月日的信息,有些却看不出任何意义?下面展开分析下订单系统中不同场景的 id 服务的具体实现。
+When we shop in a mall, we often use a QR code for payment, and the order number generated upon placing an order, along with the coupon codes and product exchange codes, are frequently used identifiers in online shopping. So why are some order numbers so long while others are only a few digits? Some order numbers clearly indicate the date, while others seem meaningless. Below, we analyze the specific implementations of ID services in different scenarios within the order system.
-### 1、一码付
+### 1. One-Code Payment
-我们常见的一码付,指的是一个二维码可以使用支付宝或者微信进行扫码支付。
+The common one-code payment refers to a QR code that can be scanned using Alipay or WeChat for payment.
-二维码的本质是一个字符串。聚合码的本质就是一个链接地址。用户使用支付宝微信直接扫一个码付钱,不用担心拿支付宝扫了微信的收款码或者用微信扫了支付宝的收款码,这极大减少了用户扫码支付的时间。
+The essence of a QR code is a string. The aggregation code is essentially a link. Users can directly scan a code with Alipay or WeChat to make payments without worrying about scanning the wrong payment code, which greatly reduces the time taken for users to complete the payment.
-实现原理是当客户用 APP 扫码后,网站后台就会判断客户的扫码环境。(微信、支付宝、QQ 钱包、京东支付、云闪付等)。
+The implementation principle is that when a customer scans the code with the app, the website backend determines the customer's scanning environment (WeChat, Alipay, QQ Wallet, JD Pay, UnionPay, etc.).
-判断扫码环境的原理就是根据打开链接浏览器的 HTTP header。任何浏览器打开 http 链接时,请求的 header 都会有 User-Agent(UA、用户代理)信息。
+The principle for determining the scanning environment is based on the HTTP header of the browser that opens the link. Any browser that opens an HTTP link will have a User-Agent (UA) information in the request header.
-UA 是一个特殊字符串头,服务器依次可以识别出客户使用的操作系统及版本、CPU 类型、浏览器及版本、浏览器渲染引擎、浏览器语言、浏览器插件等很多信息。
+The UA is a special string header that allows the server to identify the customer's operating system and version, CPU type, browser and version, browser rendering engine, browser language, browser plugins, and much more.
-各渠道对应支付产品的名称不一样,一定要仔细看各支付产品的 API 介绍。
+The names of payment products vary across different channels, so it is essential to carefully review the API documentation for each payment product.
-1. 微信支付:JSAPI 支付支付
-2. 支付宝:手机网站支付
-3. QQ 钱包:公众号支付
+1. WeChat Pay: JSAPI Payment
+1. Alipay: Mobile Website Payment
+1. QQ Wallet: Public Account Payment
-其本质均为在 APP 内置浏览器中实现 HTML5 支付。
+Essentially, they all implement HTML5 payment within the app's built-in browser.
-
+
-文库的研发同学在这个思路上,做了优化迭代。动态生成一码付的二维码预先绑定用户所选的商品信息和价格,根据用户所选的商品动态更新。这样不仅支持一码多平台调起支付,而且不用用户选择商品输入金额,即可完成订单支付的功能,很丝滑。用户在真正扫码后,服务端才通过前端获取用户 UID,结合二维码绑定的商品信息,真正的生成订单,发送支付信息到第三方(qq、微信、支付宝),第三方生成支付订单推给用户设备,从而调起支付。
+The development team at the library has optimized this approach. They dynamically generate a one-code payment QR code that is pre-bound to the product information and price selected by the user, updating dynamically based on the user's selection. This not only supports multi-platform payment initiation but also allows users to complete order payments without selecting products or entering amounts, providing a smooth experience. Only after the user scans the code does the server obtain the user's UID from the frontend, combine it with the product information bound to the QR code, truly generate the order, and send the payment information to third parties (QQ, WeChat, Alipay), which then generate the payment order and push it to the user's device to initiate payment.
-区别于固定的一码付,在文库的应用中,使用到了动态二维码,二维码本质是一个短网址,ID 服务提供短网址的唯一标志参数。唯一的短网址映射的 ID 绑定了商品的订单信息,技术和业务的深度结合,缩短了支付流程,提升用户的支付体验。
+Unlike fixed one-code payments, the library's application uses dynamic QR codes, where the QR code is essentially a short URL, and the ID service provides a unique identifier for the short URL. The unique short URL maps to the ID bound to the product's order information, deeply integrating technology and business, shortening the payment process, and enhancing the user's payment experience.
-### 2、订单号
+### 2. Order Number
-订单号在实际的业务过程中作为一个订单的唯一标识码存在,一般实现以下业务场景:
+In actual business processes, the order number serves as a unique identifier for an order and generally fulfills the following business scenarios:
-1. 用户订单遇到问题,需要找客服进行协助;
-2. 对订单进行操作,如线下收款,订单核销;
-3. 下单,改单,成单,退单,售后等系统内部的订单流程处理和跟进。
+1. Users encounter issues with their orders and need to contact customer service for assistance.
+1. Operations on the order, such as offline payments and order verification.
+1. Internal order processing and follow-up for placing, modifying, completing, canceling, and after-sales orders.
-很多时候搜索订单相关信息的时候都是以订单 ID 作为唯一标识符,这是由于订单号的生成规则的唯一性决定的。从技术角度看,除了 ID 服务必要的特性之外,在订单号的设计上需要体现几个特性:
+Often, when searching for order-related information, the order ID is used as a unique identifier, which is determined by the uniqueness of the order number generation rules. From a technical perspective, in addition to the necessary characteristics of the ID service, the design of the order number needs to reflect several features:
-**(1)信息安全**
+**(1) Information Security**
-编号不能透露公司的运营情况,比如日销、公司流水号等信息,以及商业信息和用户手机号,身份证等隐私信息。并且不能有明显的整体规律(可以有局部规律),任意修改一个字符就能查询到另一个订单信息,这也是不允许的。
+The numbering should not reveal the company's operational status, such as daily sales, company serial numbers, or any commercial information and user privacy information like phone numbers and ID numbers. Additionally, there should not be any obvious overall patterns (local patterns are acceptable), and modifying a single character should not allow access to another order's information.
-类比于我们高考时候的考生编号的生成规则,一定不能是连号的,否则只需要根据顺序往下查询就能搜索到别的考生的成绩,这是绝对不可允许。
+This is akin to the generation rules for student numbers during our college entrance examination, which must not be sequential; otherwise, one could easily search for another student's scores based on the order.
-**(2)部分可读**
-
-位数要便于操作,因此要求订单号的位数适中,且局部有规律。这样可以方便在订单异常,或者退货时客服查询。
-
-过长的订单号或易读性差的订单号会导致客服输入困难且易错率较高,影响用户体验的售后体验。因此在实际的业务场景中,订单号的设计通常都会适当携带一些允许公开的对使用场景有帮助的信息,如时间,星期,类型等等,这个主要根据所涉及的编号对应的使用场景来。
-
-而且像时间、星期这些自增长的属于作为订单号的设计的一部分元素,有助于解决业务累积而导致的订单号重复的问题。
-
-**(3)查询效率**
-
-常见的电商平台订单号大多是纯数字组成,兼具可读性的同时,int 类型相对 varchar 类型的查询效率更高,对在线业务更加友好。
-
-### 3、优惠券和兑换券
-
-优惠券、兑换券是运营推广最常用的促销工具之一,合理使用它们,可以让买家得到实惠,商家提升商品销量。常见场景有:
-
-1. 在文库购买【文库 VIP+QQ 音乐年卡】联合商品,支付成功后会得到 QQ 音乐年卡的兑换码,可以去 QQ 音乐 App 兑换音乐会员年卡;
-2. 疫情期间,部分地方政府发放的消费券;
-3. 瓶装饮料经常会出现输入优惠编码兑换奖品。
-
-
-
-从技术角度看,有些场景适合 ID 即时生成,比如电商平台购物领取的优惠券,只需要在用户领取时分配优惠券信息即可。有些线上线下结合的场景,比如疫情优惠券,瓶盖开奖,京东卡,超市卡这种,则需要预先生成,预先生成的券码具备以下特性:
-
-1.预先生成,在活动正式开始前提供出来进行活动预热;
-
-2.优惠券体量大,以万为单位,通常在 10 万级别以上;
-
-3.不可破解、仿制券码;
-
-4.支持用后核销;
-
-5.优惠券、兑换券属于广撒网的策略,所以利用率低,也就不适合使用数据库进行存储 **(占空间,有效的数据又少)**。
-
-设计思路上,需要设计一种有效的兑换码生成策略,支持预先生成,支持校验,内容简洁,生成的兑换码都具有唯一性,那么这种策略就是一种特殊的编解码策略,按照约定的编解码规则支撑上述需求。
-
-既然是一种编解码规则,那么需要约定编码空间(也就是用户看到的组成兑换码的字符),编码空间由字符 a-z,A-Z,数字 0-9 组成,为了增强兑换码的可识别度,剔除大写字母 O 以及 I,可用字符如下所示,共 60 个字符:
-
-abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXZY0123456789
-
-之前说过,兑换码要求尽可能简洁,那么设计时就需要考虑兑换码的字符数,假设上限为 12 位,而字符空间有 60 位,那么可以表示的空间范围为 60^12=130606940160000000000000(也就是可以 12 位的兑换码可以生成天量,应该够运营同学挥霍了),转换成 2 进制:
-
-1001000100000000101110011001101101110011000000000000000000000(61 位)
-
-**兑换码组成成分分析**
-
-兑换码可以预先生成,并且不需要额外的存储空间保存这些信息,每一个优惠方案都有独立的一组兑换码(指运营同学组织的每一场运营活动都有不同的兑换码,不能混合使用, 例如双 11 兑换码不能使用在双 12 活动上),每个兑换码有自己的编号,防止重复,为了保证兑换码的有效性,对兑换码的数据需要进行校验,当前兑换码的数据组成如下所示:
-
-优惠方案 ID + 兑换码序列号 i + 校验码
-
-**编码方案**
-
-1. 兑换码序列号 i,代表当前兑换码是当前活动中第 i 个兑换码,兑换码序列号的空间范围决定了优惠活动可以发行的兑换码数目,当前采用 30 位 bit 位表示,可表示范围:1073741824(10 亿个券码)。
-2. 优惠方案 ID, 代表当前优惠方案的 ID 号,优惠方案的空间范围决定了可以组织的优惠活动次数,当前采用 15 位表示,可以表示范围:32768(考虑到运营活动的频率,以及 ID 的初始值 10000,15 位足够,365 天每天有运营活动,可以使用 54 年)。
-3. 校验码,校验兑换码是否有效,主要为了快捷的校验兑换码信息的是否正确,其次可以起到填充数据的目的,增强数据的散列性,使用 13 位表示校验位,其中分为两部分,前 6 位和后 7 位。
-
-深耕业务还会有区分通用券和单独券的情况,分别具备以下特点,技术实现需要因地制宜地思考。
-
-1. 通用券:多个玩家都可以输入兑换,然后有总量限制,期限限制。
-2. 单独券:运营同学可以在后台设置兑换码的奖励物品、期限、个数,然后由后台生成兑换码的列表,兑换之后核销。
-
-## 场景二:Tracing
-
-### 1、日志跟踪
-
-在分布式服务架构下,一个 Web 请求从网关流入,有可能会调用多个服务对请求进行处理,拿到最终结果。这个过程中每个服务之间的通信又是单独的网络请求,无论请求经过的哪个服务出了故障或者处理过慢都会对前端造成影响。
-
-处理一个 Web 请求要调用的多个服务,为了能更方便的查询哪个环节的服务出现了问题,现在常用的解决方案是为整个系统引入分布式链路跟踪。
-
-
-
-在分布式链路跟踪中有两个重要的概念:跟踪(trace)和 跨度( span)。trace 是请求在分布式系统中的整个链路视图,span 则代表整个链路中不同服务内部的视图,span 组合在一起就是整个 trace 的视图。
-
-在整个请求的调用链中,请求会一直携带 traceid 往下游服务传递,每个服务内部也会生成自己的 spanid 用于生成自己的内部调用视图,并和 traceid 一起传递给下游服务。
-
-### 2、TraceId 生成规则
-
-这种场景下,生成的 ID 除了要求唯一之外,还要求生成的效率高、吞吐量大。traceid 需要具备接入层的服务器实例自主生成的能力,如果每个 trace 中的 ID 都需要请求公共的 ID 服务生成,纯纯的浪费网络带宽资源。且会阻塞用户请求向下游传递,响应耗时上升,增加了没必要的风险。所以需要服务器实例最好可以自行计算 tracid,spanid,避免依赖外部服务。
-
-产生规则:服务器 IP + ID 产生的时间 + 自增序列 + 当前进程号 ,比如:
-
-0ad1348f1403169275002100356696
-
-前 8 位 0ad1348f 即产生 TraceId 的机器的 IP,这是一个十六进制的数字,每两位代表 IP 中的一段,我们把这个数字,按每两位转成 10 进制即可得到常见的 IP 地址表示方式 10.209.52.143,您也可以根据这个规律来查找到请求经过的第一个服务器。
-
-后面的 13 位 1403169275002 是产生 TraceId 的时间。之后的 4 位 1003 是一个自增的序列,从 1000 涨到 9000,到达 9000 后回到 1000 再开始往上涨。最后的 5 位 56696 是当前的进程 ID,为了防止单机多进程出现 TraceId 冲突的情况,所以在 TraceId 末尾添加了当前的进程 ID。
-
-### 3、SpanId 生成规则
-
-span 是层的意思,比如在第一个实例算是第一层, 请求代理或者分流到下一个实例处理,就是第二层,以此类推。通过层,SpanId 代表本次调用在整个调用链路树中的位置。
-
-假设一个 服务器实例 A 接收了一次用户请求,代表是整个调用的根节点,那么 A 层处理这次请求产生的非服务调用日志记录 spanid 的值都是 0,A 层需要通过 RPC 依次调用 B、C、D 三个服务器实例,那么在 A 的日志中,SpanId 分别是 0.1,0.2 和 0.3,在 B、C、D 中,SpanId 也分别是 0.1,0.2 和 0.3;如果 C 系统在处理请求的时候又调用了 E,F 两个服务器实例,那么 C 系统中对应的 spanid 是 0.2.1 和 0.2.2,E、F 两个系统对应的日志也是 0.2.1 和 0.2.2。
-
-根据上面的描述可以知道,如果把一次调用中所有的 SpanId 收集起来,可以组成一棵完整的链路树。
-
-**spanid 的生成本质:在跨层传递透传的同时,控制大小版本号的自增来实现的。**
-
-## 场景三:短网址
-
-短网址主要功能包括网址缩短与还原两大功能。相对于长网址,短网址可以更方便地在电子邮件,社交网络,微博和手机上传播,例如原来很长的网址通过短网址服务即可生成相应的短网址,避免折行或超出字符限制。
-
-
-
-常用的 ID 生成服务比如:MySQL ID 自增、 Redis 键自增、号段模式,生成的 ID 都是一串数字。短网址服务把客户的长网址转换成短网址,
-
-实际是在 dwz.cn 域名后面拼接新产生的数字类型 ID,直接用数字 ID,网址长度也有些长,服务可以通过数字 ID 转更高进制的方式压缩长度。这种算法在短网址的技术实现上越来越多了起来,它可以进一步压缩网址长度。转进制的压缩算法在生活中有广泛的应用场景,举例:
-
-- 客户的长网址:
-- ID 映射的短网址: (演示使用,可能无法正确打开)
-- 转进制后的短网址: (演示使用,可能无法正确打开)
-
-
+\*\*(2) Partial
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
index 9920f8f7753..e23a8336dbf 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-id.md
@@ -1,65 +1,65 @@
---
-title: 分布式ID介绍&实现方案总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Introduction to Distributed ID & Summary of Implementation Solutions
+category: Distributed
---
-## 分布式 ID 介绍
+## Introduction to Distributed ID
-### 什么是 ID?
+### What is an ID?
-日常开发中,我们需要对系统中的各种数据使用 ID 唯一表示,比如用户 ID 对应且仅对应一个人,商品 ID 对应且仅对应一件商品,订单 ID 对应且仅对应一个订单。
+In daily development, we need to uniquely represent various data in the system using IDs. For example, a user ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one person, a product ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one product, and an order ID corresponds to and only corresponds to one order.
-我们现实生活中也有各种 ID,比如身份证 ID 对应且仅对应一个人、地址 ID 对应且仅对应一个地址。
+In real life, we also have various IDs, such as an ID card ID that corresponds to and only corresponds to one person, and an address ID that corresponds to and only corresponds to one address.
-简单来说,**ID 就是数据的唯一标识**。
+In simple terms, **an ID is a unique identifier for data**.
-### 什么是分布式 ID?
+### What is a Distributed ID?
-分布式 ID 是分布式系统下的 ID。分布式 ID 不存在与现实生活中,属于计算机系统中的一个概念。
+A distributed ID is an ID used in a distributed system. Distributed IDs do not exist in real life; they are a concept within computer systems.
-我简单举一个分库分表的例子。
+Let me give a simple example of sharding.
-我司的一个项目,使用的是单机 MySQL 。但是,没想到的是,项目上线一个月之后,随着使用人数越来越多,整个系统的数据量将越来越大。单机 MySQL 已经没办法支撑了,需要进行分库分表(推荐 Sharding-JDBC)。
+In one of our projects, we used a standalone MySQL database. However, unexpectedly, after the project went live for a month, as the number of users increased, the data volume of the entire system grew larger. The standalone MySQL could no longer support it, and we needed to implement sharding (recommended Sharding-JDBC).
-在分库之后, 数据遍布在不同服务器上的数据库,数据库的自增主键已经没办法满足生成的主键唯一了。**我们如何为不同的数据节点生成全局唯一主键呢?**
+After sharding, the data is distributed across databases on different servers, and the auto-incrementing primary key of the database can no longer guarantee the uniqueness of the generated primary key. **How do we generate a globally unique primary key for different data nodes?**
-这个时候就需要生成**分布式 ID**了。
+At this point, we need to generate **distributed IDs**.

-### 分布式 ID 需要满足哪些要求?
+### What Requirements Must Distributed IDs Meet?

-分布式 ID 作为分布式系统中必不可少的一环,很多地方都要用到分布式 ID。
+As an essential part of a distributed system, distributed IDs are needed in many places.
-一个最基本的分布式 ID 需要满足下面这些要求:
+A basic distributed ID must meet the following requirements:
-- **全局唯一**:ID 的全局唯一性肯定是首先要满足的!
-- **高性能**:分布式 ID 的生成速度要快,对本地资源消耗要小。
-- **高可用**:生成分布式 ID 的服务要保证可用性无限接近于 100%。
-- **方便易用**:拿来即用,使用方便,快速接入!
+- **Globally Unique**: The global uniqueness of the ID must be guaranteed!
+- **High Performance**: The generation speed of distributed IDs must be fast, with minimal local resource consumption.
+- **High Availability**: The service generating distributed IDs must ensure availability close to 100%.
+- **Convenient and Easy to Use**: It should be ready to use, easy to implement, and quickly integrated!
-除了这些之外,一个比较好的分布式 ID 还应保证:
+In addition to these, a good distributed ID should also ensure:
-- **安全**:ID 中不包含敏感信息。
-- **有序递增**:如果要把 ID 存放在数据库的话,ID 的有序性可以提升数据库写入速度。并且,很多时候 ,我们还很有可能会直接通过 ID 来进行排序。
-- **有具体的业务含义**:生成的 ID 如果能有具体的业务含义,可以让定位问题以及开发更透明化(通过 ID 就能确定是哪个业务)。
-- **独立部署**:也就是分布式系统单独有一个发号器服务,专门用来生成分布式 ID。这样就生成 ID 的服务可以和业务相关的服务解耦。不过,这样同样带来了网络调用消耗增加的问题。总的来说,如果需要用到分布式 ID 的场景比较多的话,独立部署的发号器服务还是很有必要的。
+- **Security**: The ID should not contain sensitive information.
+- **Ordered Increment**: If IDs are to be stored in a database, the order of IDs can improve database write speed. Moreover, many times, we may directly sort by ID.
+- **Specific Business Meaning**: If the generated ID has specific business meaning, it can make problem identification and development more transparent (the ID can indicate which business it belongs to).
+- **Independent Deployment**: This means that the distributed system has a separate ID generator service specifically for generating distributed IDs. This decouples the ID generation service from business-related services. However, this also increases the overhead of network calls. Overall, if there are many scenarios requiring distributed IDs, an independently deployed ID generator service is still very necessary.
-## 分布式 ID 常见解决方案
+## Common Solutions for Distributed IDs
-### 数据库
+### Database
-#### 数据库主键自增
+#### Auto-Incrementing Database Primary Key
-这种方式就比较简单直白了,就是通过关系型数据库的自增主键产生来唯一的 ID。
+This method is quite straightforward; it generates a unique ID through the auto-incrementing primary key of a relational database.
-
+
-以 MySQL 举例,我们通过下面的方式即可。
+Taking MySQL as an example, we can do it as follows.
-**1.创建一个数据库表。**
+**1. Create a database table.**
```sql
CREATE TABLE `sequence_id` (
@@ -70,9 +70,9 @@ CREATE TABLE `sequence_id` (
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
```
-`stub` 字段无意义,只是为了占位,便于我们插入或者修改数据。并且,给 `stub` 字段创建了唯一索引,保证其唯一性。
+The `stub` field is meaningless; it is just a placeholder to facilitate data insertion or modification. Additionally, a unique index is created for the `stub` field to ensure its uniqueness.
-**2.通过 `replace into` 来插入数据。**
+**2. Insert data using `replace into`.**
```java
BEGIN;
@@ -81,315 +81,11 @@ SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
COMMIT;
```
-插入数据这里,我们没有使用 `insert into` 而是使用 `replace into` 来插入数据,具体步骤是这样的:
+In this data insertion, we use `replace into` instead of `insert into`. The specific steps are as follows:
-- 第一步:尝试把数据插入到表中。
+- Step 1: Attempt to insert data into the table.
+- Step 2: If a duplicate data error occurs due to the primary key or unique index field, delete the conflicting row containing the duplicate key value from the table, and then attempt to insert the data again.
-- 第二步:如果主键或唯一索引字段出现重复数据错误而插入失败时,先从表中删除含有重复关键字值的冲突行,然后再次尝试把数据插入到表中。
+The advantages and disadvantages of this method are also quite clear:
-这种方式的优缺点也比较明显:
-
-- **优点**:实现起来比较简单、ID 有序递增、存储消耗空间小
-- **缺点**:支持的并发量不大、存在数据库单点问题(可以使用数据库集群解决,不过增加了复杂度)、ID 没有具体业务含义、安全问题(比如根据订单 ID 的递增规律就能推算出每天的订单量,商业机密啊! )、每次获取 ID 都要访问一次数据库(增加了对数据库的压力,获取速度也慢)
-
-#### 数据库号段模式
-
-数据库主键自增这种模式,每次获取 ID 都要访问一次数据库,ID 需求比较大的时候,肯定是不行的。
-
-如果我们可以批量获取,然后存在在内存里面,需要用到的时候,直接从内存里面拿就舒服了!这也就是我们说的 **基于数据库的号段模式来生成分布式 ID。**
-
-数据库的号段模式也是目前比较主流的一种分布式 ID 生成方式。像滴滴开源的[Tinyid](https://github.com/didi/tinyid/wiki/tinyid原理介绍) 就是基于这种方式来做的。不过,TinyId 使用了双号段缓存、增加多 db 支持等方式来进一步优化。
-
-以 MySQL 举例,我们通过下面的方式即可。
-
-**1. 创建一个数据库表。**
-
-```sql
-CREATE TABLE `sequence_id_generator` (
- `id` int(10) NOT NULL,
- `current_max_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '当前最大id',
- `step` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '号段的长度',
- `version` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '版本号',
- `biz_type` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '业务类型',
- PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
-) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-```
-
-`current_max_id` 字段和`step`字段主要用于获取批量 ID,获取的批量 id 为:`current_max_id ~ current_max_id+step`。
-
-
-
-`version` 字段主要用于解决并发问题(乐观锁),`biz_type` 主要用于表示业务类型。
-
-**2. 先插入一行数据。**
-
-```sql
-INSERT INTO `sequence_id_generator` (`id`, `current_max_id`, `step`, `version`, `biz_type`)
-VALUES
- (1, 0, 100, 0, 101);
-```
-
-**3. 通过 SELECT 获取指定业务下的批量唯一 ID**
-
-```sql
-SELECT `current_max_id`, `step`,`version` FROM `sequence_id_generator` where `biz_type` = 101
-```
-
-结果:
-
-```plain
-id current_max_id step version biz_type
-1 0 100 0 101
-```
-
-**4. 不够用的话,更新之后重新 SELECT 即可。**
-
-```sql
-UPDATE sequence_id_generator SET current_max_id = 0+100, version=version+1 WHERE version = 0 AND `biz_type` = 101
-SELECT `current_max_id`, `step`,`version` FROM `sequence_id_generator` where `biz_type` = 101
-```
-
-结果:
-
-```plain
-id current_max_id step version biz_type
-1 100 100 1 101
-```
-
-相比于数据库主键自增的方式,**数据库的号段模式对于数据库的访问次数更少,数据库压力更小。**
-
-另外,为了避免单点问题,你可以从使用主从模式来提高可用性。
-
-**数据库号段模式的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:ID 有序递增、存储消耗空间小
-- **缺点**:存在数据库单点问题(可以使用数据库集群解决,不过增加了复杂度)、ID 没有具体业务含义、安全问题(比如根据订单 ID 的递增规律就能推算出每天的订单量,商业机密啊! )
-
-#### NoSQL
-
-
-
-一般情况下,NoSQL 方案使用 Redis 多一些。我们通过 Redis 的 `incr` 命令即可实现对 id 原子顺序递增。
-
-```bash
-127.0.0.1:6379> set sequence_id_biz_type 1
-OK
-127.0.0.1:6379> incr sequence_id_biz_type
-(integer) 2
-127.0.0.1:6379> get sequence_id_biz_type
-"2"
-```
-
-为了提高可用性和并发,我们可以使用 Redis Cluster。Redis Cluster 是 Redis 官方提供的 Redis 集群解决方案(3.0+版本)。
-
-除了 Redis Cluster 之外,你也可以使用开源的 Redis 集群方案[Codis](https://github.com/CodisLabs/codis) (大规模集群比如上百个节点的时候比较推荐)。
-
-除了高可用和并发之外,我们知道 Redis 基于内存,我们需要持久化数据,避免重启机器或者机器故障后数据丢失。Redis 支持两种不同的持久化方式:**快照(snapshotting,RDB)**、**只追加文件(append-only file, AOF)**。 并且,Redis 4.0 开始支持 **RDB 和 AOF 的混合持久化**(默认关闭,可以通过配置项 `aof-use-rdb-preamble` 开启)。
-
-关于 Redis 持久化,我这里就不过多介绍。不了解这部分内容的小伙伴,可以看看 [Redis 持久化机制详解](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-persistence.html)这篇文章。
-
-**Redis 方案的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:性能不错并且生成的 ID 是有序递增的
-- **缺点**:和数据库主键自增方案的缺点类似
-
-除了 Redis 之外,MongoDB ObjectId 经常也会被拿来当做分布式 ID 的解决方案。
-
-
-
-MongoDB ObjectId 一共需要 12 个字节存储:
-
-- 0~3:时间戳
-- 3~6:代表机器 ID
-- 7~8:机器进程 ID
-- 9~11:自增值
-
-**MongoDB 方案的优缺点:**
-
-- **优点**:性能不错并且生成的 ID 是有序递增的
-- **缺点**:需要解决重复 ID 问题(当机器时间不对的情况下,可能导致会产生重复 ID)、有安全性问题(ID 生成有规律性)
-
-### 算法
-
-#### UUID
-
-UUID 是 Universally Unique Identifier(通用唯一标识符) 的缩写。UUID 包含 32 个 16 进制数字(8-4-4-4-12)。
-
-JDK 就提供了现成的生成 UUID 的方法,一行代码就行了。
-
-```java
-//输出示例:cb4a9ede-fa5e-4585-b9bb-d60bce986eaa
-UUID.randomUUID()
-```
-
-[RFC 4122](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4122) 中关于 UUID 的示例是这样的:
-
-
-
-我们这里重点关注一下这个 Version(版本),不同的版本对应的 UUID 的生成规则是不同的。
-
-8 种不同的 Version(版本)值分别对应的含义(参考[维基百科对于 UUID 的介绍](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/通用唯一识别码)):
-
-- **版本 1 (基于时间和节点 ID)** : 基于时间戳(通常是当前时间)和节点 ID(通常为设备的 MAC 地址)生成。当包含 MAC 地址时,可以保证全球唯一性,但也因此存在隐私泄露的风险。
-- **版本 2 (基于标识符、时间和节点 ID)** : 与版本 1 类似,也基于时间和节点 ID,但额外包含了本地标识符(例如用户 ID 或组 ID)。
-- **版本 3 (基于命名空间和名称的 MD5 哈希)**:使用 MD5 哈希算法,将命名空间标识符(一个 UUID)和名称字符串组合计算得到。相同的命名空间和名称总是生成相同的 UUID(**确定性生成**)。
-- **版本 4 (基于随机数)**:几乎完全基于随机数生成,通常使用伪随机数生成器(PRNG)或加密安全随机数生成器(CSPRNG)来生成。 虽然理论上存在碰撞的可能性,但理论上碰撞概率极低(2^122 的可能性),可以认为在实际应用中是唯一的。
-- **版本 5 (基于命名空间和名称的 SHA-1 哈希)**:类似于版本 3,但使用 SHA-1 哈希算法。
-- **版本 6 (基于时间戳、计数器和节点 ID)**:改进了版本 1,将时间戳放在最高有效位(Most Significant Bit,MSB),使得 UUID 可以直接按时间排序。
-- **版本 7 (基于时间戳和随机数据)**:基于 Unix 时间戳和随机数据生成。 由于时间戳位于最高有效位,因此支持按时间排序。并且,不依赖 MAC 地址或节点 ID,避免了隐私问题。
-- **版本 8 (自定义)**:允许用户根据自己的需求定义 UUID 的生成方式。其结构和内容由用户决定,提供更大的灵活性。
-
-下面是 Version 1 版本下生成的 UUID 的示例:
-
-
-
-JDK 中通过 `UUID` 的 `randomUUID()` 方法生成的 UUID 的版本默认为 4。
-
-```java
-UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
-int version = uuid.version();// 4
-```
-
-另外,Variant(变体)也有 4 种不同的值,这种值分别对应不同的含义。这里就不介绍了,貌似平时也不怎么需要关注。
-
-需要用到的时候,去看看维基百科对于 UUID 的 Variant(变体) 相关的介绍即可。
-
-从上面的介绍中可以看出,UUID 可以保证唯一性,因为其生成规则包括 MAC 地址、时间戳、名字空间(Namespace)、随机或伪随机数、时序等元素,计算机基于这些规则生成的 UUID 是肯定不会重复的。
-
-虽然,UUID 可以做到全局唯一性,但是,我们一般很少会使用它。
-
-比如使用 UUID 作为 MySQL 数据库主键的时候就非常不合适:
-
-- 数据库主键要尽量越短越好,而 UUID 的消耗的存储空间比较大(32 个字符串,128 位)。
-- UUID 是无顺序的,InnoDB 引擎下,数据库主键的无序性会严重影响数据库性能。
-
-最后,我们再简单分析一下 **UUID 的优缺点** (面试的时候可能会被问到的哦!) :
-
-- **优点**:生成速度通常比较快、简单易用
-- **缺点**:存储消耗空间大(32 个字符串,128 位)、 不安全(基于 MAC 地址生成 UUID 的算法会造成 MAC 地址泄露)、无序(非自增)、没有具体业务含义、需要解决重复 ID 问题(当机器时间不对的情况下,可能导致会产生重复 ID)
-
-#### Snowflake(雪花算法)
-
-Snowflake 是 Twitter 开源的分布式 ID 生成算法。Snowflake 由 64 bit 的二进制数字组成,这 64bit 的二进制被分成了几部分,每一部分存储的数据都有特定的含义:
-
-
-
-- **sign(1bit)**:符号位(标识正负),始终为 0,代表生成的 ID 为正数。
-- **timestamp (41 bits)**:一共 41 位,用来表示时间戳,单位是毫秒,可以支撑 2 ^41 毫秒(约 69 年)
-- **datacenter id + worker id (10 bits)**:一般来说,前 5 位表示机房 ID,后 5 位表示机器 ID(实际项目中可以根据实际情况调整)。这样就可以区分不同集群/机房的节点。
-- **sequence (12 bits)**:一共 12 位,用来表示序列号。 序列号为自增值,代表单台机器每毫秒能够产生的最大 ID 数(2^12 = 4096),也就是说单台机器每毫秒最多可以生成 4096 个 唯一 ID。
-
-在实际项目中,我们一般也会对 Snowflake 算法进行改造,最常见的就是在 Snowflake 算法生成的 ID 中加入业务类型信息。
-
-我们再来看看 Snowflake 算法的优缺点:
-
-- **优点**:生成速度比较快、生成的 ID 有序递增、比较灵活(可以对 Snowflake 算法进行简单的改造比如加入业务 ID)
-- **缺点**:需要解决重复 ID 问题(ID 生成依赖时间,在获取时间的时候,可能会出现时间回拨的问题,也就是服务器上的时间突然倒退到之前的时间,进而导致会产生重复 ID)、依赖机器 ID 对分布式环境不友好(当需要自动启停或增减机器时,固定的机器 ID 可能不够灵活)。
-
-如果你想要使用 Snowflake 算法的话,一般不需要你自己再造轮子。有很多基于 Snowflake 算法的开源实现比如美团 的 Leaf、百度的 UidGenerator(后面会提到),并且这些开源实现对原有的 Snowflake 算法进行了优化,性能更优秀,还解决了 Snowflake 算法的时间回拨问题和依赖机器 ID 的问题。
-
-并且,Seata 还提出了“改良版雪花算法”,针对原版雪花算法进行了一定的优化改良,解决了时间回拨问题,大幅提高的 QPS。具体介绍和改进原理,可以参考下面这两篇文章:
-
-- [Seata 基于改良版雪花算法的分布式 UUID 生成器分析](https://seata.io/zh-cn/blog/seata-analysis-UUID-generator.html)
-- [在开源项目中看到一个改良版的雪花算法,现在它是你的了。](https://www.cnblogs.com/thisiswhy/p/17611163.html)
-
-### 开源框架
-
-#### UidGenerator(百度)
-
-[UidGenerator](https://github.com/baidu/uid-generator) 是百度开源的一款基于 Snowflake(雪花算法)的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-不过,UidGenerator 对 Snowflake(雪花算法)进行了改进,生成的唯一 ID 组成如下:
-
-
-
-- **sign(1bit)**:符号位(标识正负),始终为 0,代表生成的 ID 为正数。
-- **delta seconds (28 bits)**:当前时间,相对于时间基点"2016-05-20"的增量值,单位:秒,最多可支持约 8.7 年
-- **worker id (22 bits)**:机器 id,最多可支持约 420w 次机器启动。内置实现为在启动时由数据库分配,默认分配策略为用后即弃,后续可提供复用策略。
-- **sequence (13 bits)**:每秒下的并发序列,13 bits 可支持每秒 8192 个并发。
-
-可以看出,和原始 Snowflake(雪花算法)生成的唯一 ID 的组成不太一样。并且,上面这些参数我们都可以自定义。
-
-UidGenerator 官方文档中的介绍如下:
-
-
-
-自 18 年后,UidGenerator 就基本没有再维护了,我这里也不过多介绍。想要进一步了解的朋友,可以看看 [UidGenerator 的官方介绍](https://github.com/baidu/uid-generator/blob/master/README.zh_cn.md)。
-
-#### Leaf(美团)
-
-[Leaf](https://github.com/Meituan-Dianping/Leaf) 是美团开源的一个分布式 ID 解决方案 。这个项目的名字 Leaf(树叶) 起源于德国哲学家、数学家莱布尼茨的一句话:“There are no two identical leaves in the world”(世界上没有两片相同的树叶) 。这名字起得真心挺不错的,有点文艺青年那味了!
-
-Leaf 提供了 **号段模式** 和 **Snowflake(雪花算法)** 这两种模式来生成分布式 ID。并且,它支持双号段,还解决了雪花 ID 系统时钟回拨问题。不过,时钟问题的解决需要弱依赖于 Zookeeper(使用 Zookeeper 作为注册中心,通过在特定路径下读取和创建子节点来管理 workId) 。
-
-Leaf 的诞生主要是为了解决美团各个业务线生成分布式 ID 的方法多种多样以及不可靠的问题。
-
-Leaf 对原有的号段模式进行改进,比如它这里增加了双号段避免获取 DB 在获取号段的时候阻塞请求获取 ID 的线程。简单来说,就是我一个号段还没用完之前,我自己就主动提前去获取下一个号段(图片来自于美团官方文章:[《Leaf——美团点评分布式 ID 生成系统》](https://tech.meituan.com/2017/04/21/mt-leaf.html))。
-
-
-
-根据项目 README 介绍,在 4C8G VM 基础上,通过公司 RPC 方式调用,QPS 压测结果近 5w/s,TP999 1ms。
-
-#### Tinyid(滴滴)
-
-[Tinyid](https://github.com/didi/tinyid) 是滴滴开源的一款基于数据库号段模式的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-数据库号段模式的原理我们在上面已经介绍过了。**Tinyid 有哪些亮点呢?**
-
-为了搞清楚这个问题,我们先来看看基于数据库号段模式的简单架构方案。(图片来自于 Tinyid 的官方 wiki:[《Tinyid 原理介绍》](https://github.com/didi/tinyid/wiki/tinyid%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D))
-
-
-
-在这种架构模式下,我们通过 HTTP 请求向发号器服务申请唯一 ID。负载均衡 router 会把我们的请求送往其中的一台 tinyid-server。
-
-这种方案有什么问题呢?在我看来(Tinyid 官方 wiki 也有介绍到),主要由下面这 2 个问题:
-
-- 获取新号段的情况下,程序获取唯一 ID 的速度比较慢。
-- 需要保证 DB 高可用,这个是比较麻烦且耗费资源的。
-
-除此之外,HTTP 调用也存在网络开销。
-
-Tinyid 的原理比较简单,其架构如下图所示:
-
-
-
-相比于基于数据库号段模式的简单架构方案,Tinyid 方案主要做了下面这些优化:
-
-- **双号段缓存**:为了避免在获取新号段的情况下,程序获取唯一 ID 的速度比较慢。 Tinyid 中的号段在用到一定程度的时候,就会去异步加载下一个号段,保证内存中始终有可用号段。
-- **增加多 db 支持**:支持多个 DB,并且,每个 DB 都能生成唯一 ID,提高了可用性。
-- **增加 tinyid-client**:纯本地操作,无 HTTP 请求消耗,性能和可用性都有很大提升。
-
-Tinyid 的优缺点这里就不分析了,结合数据库号段模式的优缺点和 Tinyid 的原理就能知道。
-
-#### IdGenerator(个人)
-
-和 UidGenerator、Leaf 一样,[IdGenerator](https://github.com/yitter/IdGenerator) 也是一款基于 Snowflake(雪花算法)的唯一 ID 生成器。
-
-IdGenerator 有如下特点:
-
-- 生成的唯一 ID 更短;
-- 兼容所有雪花算法(号段模式或经典模式,大厂或小厂);
-- 原生支持 C#/Java/Go/C/Rust/Python/Node.js/PHP(C 扩展)/SQL/ 等语言,并提供多线程安全调用动态库(FFI);
-- 解决了时间回拨问题,支持手工插入新 ID(当业务需要在历史时间生成新 ID 时,用本算法的预留位能生成 5000 个每秒);
-- 不依赖外部存储系统;
-- 默认配置下,ID 可用 71000 年不重复。
-
-IdGenerator 生成的唯一 ID 组成如下:
-
-
-
-- **timestamp (位数不固定)**:时间差,是生成 ID 时的系统时间减去 BaseTime(基础时间,也称基点时间、原点时间、纪元时间,默认值为 2020 年) 的总时间差(毫秒单位)。初始为 5bits,随着运行时间而增加。如果觉得默认值太老,你可以重新设置,不过要注意,这个值以后最好不变。
-- **worker id (默认 6 bits)**:机器 id,机器码,最重要参数,是区分不同机器或不同应用的唯一 ID,最大值由 `WorkerIdBitLength`(默认 6)限定。如果一台服务器部署多个独立服务,需要为每个服务指定不同的 WorkerId。
-- **sequence (默认 6 bits)**:序列数,是每毫秒下的序列数,由参数中的 `SeqBitLength`(默认 6)限定。增加 `SeqBitLength` 会让性能更高,但生成的 ID 也会更长。
-
-Java 语言使用示例:。
-
-## 总结
-
-通过这篇文章,我基本上已经把最常见的分布式 ID 生成方案都总结了一波。
-
-除了上面介绍的方式之外,像 ZooKeeper 这类中间件也可以帮助我们生成唯一 ID。**没有银弹,一定要结合实际项目来选择最适合自己的方案。**
-
-不过,本文主要介绍的是分布式 ID 的理论知识。在实际的面试中,面试官可能会结合具体的业务场景来考察你对分布式 ID 的设计,你可以参考这篇文章:[分布式 ID 设计指南](./distributed-id-design)(对于实际工作中分布式 ID 的设计也非常有帮助)。
-
-
+- **Advantages**: Simple to implement, IDs are ordered and incrementing,
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
index cb4504c4a7a..fbb695d1020 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock-implementations.md
@@ -1,19 +1,19 @@
---
-title: 分布式锁常见实现方案总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Distributed Lock Implementation Solutions
+category: Distributed
---
-通常情况下,我们一般会选择基于 Redis 或者 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁,Redis 用的要更多一点,我这里也先以 Redis 为例介绍分布式锁的实现。
+In general, we usually choose to implement distributed locks based on Redis or ZooKeeper, with Redis being the more commonly used option. Here, I will introduce the implementation of distributed locks using Redis as an example.
-## 基于 Redis 实现分布式锁
+## Implementing Distributed Locks Based on Redis
-### 如何基于 Redis 实现一个最简易的分布式锁?
+### How to Implement a Simple Distributed Lock Using Redis?
-不论是本地锁还是分布式锁,核心都在于“互斥”。
+Whether it's a local lock or a distributed lock, the core concept is "mutual exclusion."
-在 Redis 中, `SETNX` 命令是可以帮助我们实现互斥。`SETNX` 即 **SET** if **N**ot e**X**ists (对应 Java 中的 `setIfAbsent` 方法),如果 key 不存在的话,才会设置 key 的值。如果 key 已经存在, `SETNX` 啥也不做。
+In Redis, the `SETNX` command helps us achieve mutual exclusion. `SETNX` stands for **SET** if **N**ot e**X**ists (corresponding to the `setIfAbsent` method in Java). It sets the key's value only if the key does not exist. If the key already exists, `SETNX` does nothing.
```bash
> SETNX lockKey uniqueValue
@@ -22,19 +22,19 @@ category: 分布式
(integer) 0
```
-释放锁的话,直接通过 `DEL` 命令删除对应的 key 即可。
+To release the lock, simply delete the corresponding key using the `DEL` command.
```bash
> DEL lockKey
(integer) 1
```
-为了防止误删到其他的锁,这里我们建议使用 Lua 脚本通过 key 对应的 value(唯一值)来判断。
+To prevent accidentally deleting other locks, it is recommended to use a Lua script to check the value (unique value) corresponding to the key.
-选用 Lua 脚本是为了保证解锁操作的原子性。因为 Redis 在执行 Lua 脚本时,可以以原子性的方式执行,从而保证了锁释放操作的原子性。
+Using a Lua script ensures the atomicity of the unlock operation. When Redis executes a Lua script, it does so atomically, thus guaranteeing the atomicity of the lock release operation.
```lua
-// 释放锁时,先比较锁对应的 value 值是否相等,避免锁的误释放
+// When releasing the lock, first compare the value of the lock to avoid accidental release
if redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then
return redis.call("del",KEYS[1])
else
@@ -42,340 +42,40 @@ else
end
```
-
+
-这是一种最简易的 Redis 分布式锁实现,实现方式比较简单,性能也很高效。不过,这种方式实现分布式锁存在一些问题。就比如应用程序遇到一些问题比如释放锁的逻辑突然挂掉,可能会导致锁无法被释放,进而造成共享资源无法再被其他线程/进程访问。
+This is a simple implementation of a Redis distributed lock, which is straightforward and efficient. However, this method has some issues. For example, if the application encounters a problem and the logic for releasing the lock suddenly crashes, it may lead to the lock not being released, causing shared resources to be inaccessible to other threads/processes.
-### 为什么要给锁设置一个过期时间?
+### Why Set an Expiration Time for the Lock?
-为了避免锁无法被释放,我们可以想到的一个解决办法就是:**给这个 key(也就是锁) 设置一个过期时间** 。
+To avoid the lock being unreleased, one solution is to **set an expiration time for this key (the lock)**.
```bash
127.0.0.1:6379> SET lockKey uniqueValue EX 3 NX
OK
```
-- **lockKey**:加锁的锁名;
-- **uniqueValue**:能够唯一标识锁的随机字符串;
-- **NX**:只有当 lockKey 对应的 key 值不存在的时候才能 SET 成功;
-- **EX**:过期时间设置(秒为单位)EX 3 标示这个锁有一个 3 秒的自动过期时间。与 EX 对应的是 PX(毫秒为单位),这两个都是过期时间设置。
+- **lockKey**: The name of the lock;
+- **uniqueValue**: A random string that uniquely identifies the lock;
+- **NX**: The SET operation will only succeed if the key corresponding to lockKey does not exist;
+- **EX**: Sets the expiration time (in seconds). EX 3 indicates that this lock has an automatic expiration time of 3 seconds. The counterpart to EX is PX (in milliseconds), and both are used for setting expiration times.
-**一定要保证设置指定 key 的值和过期时间是一个原子操作!!!** 不然的话,依然可能会出现锁无法被释放的问题。
+**It is crucial to ensure that setting the specified key's value and expiration time is an atomic operation!!!** Otherwise, the issue of the lock not being released may still occur.
-这样确实可以解决问题,不过,这种解决办法同样存在漏洞:**如果操作共享资源的时间大于过期时间,就会出现锁提前过期的问题,进而导致分布式锁直接失效。如果锁的超时时间设置过长,又会影响到性能。**
+This indeed solves the problem, but this solution also has vulnerabilities: **If the time taken to operate on the shared resource exceeds the expiration time, the lock may expire prematurely, leading to the distributed lock becoming invalid. If the timeout is set too long, it may affect performance.**
-你或许在想:**如果操作共享资源的操作还未完成,锁过期时间能够自己续期就好了!**
+You might be wondering: **If the operation on the shared resource is not yet complete, it would be great if the lock's expiration time could be renewed automatically!**
-### 如何实现锁的优雅续期?
+### How to Implement Elegant Lock Renewal?
-对于 Java 开发的小伙伴来说,已经有了现成的解决方案:**[Redisson](https://github.com/redisson/redisson)** 。其他语言的解决方案,可以在 Redis 官方文档中找到,地址: 。
+For Java developers, there is already a ready-made solution: **[Redisson](https://github.com/redisson/redisson)**. Solutions for other languages can be found in the official Redis documentation at: .

-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,不仅仅包括多种分布式锁的实现。并且,Redisson 还支持 Redis 单机、Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster 等多种部署架构。
+Redisson is an open-source Redis client for Java that provides many out-of-the-box features, including various implementations of distributed locks. Additionally, Redisson supports multiple deployment architectures such as Redis standalone, Redis Sentinel, and Redis Cluster.
-Redisson 中的分布式锁自带自动续期机制,使用起来非常简单,原理也比较简单,其提供了一个专门用来监控和续期锁的 **Watch Dog( 看门狗)**,如果操作共享资源的线程还未执行完成的话,Watch Dog 会不断地延长锁的过期时间,进而保证锁不会因为超时而被释放。
+The distributed lock in Redisson comes with an automatic renewal mechanism, making it very easy to use. The principle is quite simple: it provides a dedicated **Watch Dog** to monitor and renew the lock. If the thread operating on the shared resource has not completed its execution, the Watch Dog will continuously extend the lock's expiration time, ensuring that the lock is not released due to timeout.
-
+
-看门狗名字的由来于 `getLockWatchdogTimeout()` 方法,这个方法返回的是看门狗给锁续期的过期时间,默认为 30 秒([redisson-3.17.6](https://github.com/redisson/redisson/releases/tag/redisson-3.17.6))。
-
-```java
-//默认 30秒,支持修改
-private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;
-
-public Config setLockWatchdogTimeout(long lockWatchdogTimeout) {
- this.lockWatchdogTimeout = lockWatchdogTimeout;
- return this;
-}
-public long getLockWatchdogTimeout() {
- return lockWatchdogTimeout;
-}
-```
-
-`renewExpiration()` 方法包含了看门狗的主要逻辑:
-
-```java
-private void renewExpiration() {
- //......
- Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
- @Override
- public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
- //......
- // 异步续期,基于 Lua 脚本
- CompletionStage future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
- future.whenComplete((res, e) -> {
- if (e != null) {
- // 无法续期
- log.error("Can't update lock " + getRawName() + " expiration", e);
- EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
- return;
- }
-
- if (res) {
- // 递归调用实现续期
- renewExpiration();
- } else {
- // 取消续期
- cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
- }
- });
- }
- // 延迟 internalLockLeaseTime/3(默认 10s,也就是 30/3) 再调用
- }, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
-
- ee.setTimeout(task);
- }
-```
-
-默认情况下,每过 10 秒,看门狗就会执行续期操作,将锁的超时时间设置为 30 秒。看门狗续期前也会先判断是否需要执行续期操作,需要才会执行续期,否则取消续期操作。
-
-Watch Dog 通过调用 `renewExpirationAsync()` 方法实现锁的异步续期:
-
-```java
-protected CompletionStage renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
- return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
- // 判断是否为持锁线程,如果是就执行续期操作,就锁的过期时间设置为 30s(默认)
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return 1; " +
- "end; " +
- "return 0;",
- Collections.singletonList(getRawName()),
- internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
-}
-```
-
-可以看出, `renewExpirationAsync` 方法其实是调用 Lua 脚本实现的续期,这样做主要是为了保证续期操作的原子性。
-
-我这里以 Redisson 的分布式可重入锁 `RLock` 为例来说明如何使用 Redisson 实现分布式锁:
-
-```java
-// 1.获取指定的分布式锁对象
-RLock lock = redisson.getLock("lock");
-// 2.拿锁且不设置锁超时时间,具备 Watch Dog 自动续期机制
-lock.lock();
-// 3.执行业务
-...
-// 4.释放锁
-lock.unlock();
-```
-
-只有未指定锁超时时间,才会使用到 Watch Dog 自动续期机制。
-
-```java
-// 手动给锁设置过期时间,不具备 Watch Dog 自动续期机制
-lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
-```
-
-如果使用 Redis 来实现分布式锁的话,还是比较推荐直接基于 Redisson 来做的。
-
-### 如何实现可重入锁?
-
-所谓可重入锁指的是在一个线程中可以多次获取同一把锁,比如一个线程在执行一个带锁的方法,该方法中又调用了另一个需要相同锁的方法,则该线程可以直接执行调用的方法即可重入 ,而无需重新获得锁。像 Java 中的 `synchronized` 和 `ReentrantLock` 都属于可重入锁。
-
-**不可重入的分布式锁基本可以满足绝大部分业务场景了,一些特殊的场景可能会需要使用可重入的分布式锁。**
-
-可重入分布式锁的实现核心思路是线程在获取锁的时候判断是否为自己的锁,如果是的话,就不用再重新获取了。为此,我们可以为每个锁关联一个可重入计数器和一个占有它的线程。当可重入计数器大于 0 时,则锁被占有,需要判断占有该锁的线程和请求获取锁的线程是否为同一个。
-
-实际项目中,我们不需要自己手动实现,推荐使用我们上面提到的 **Redisson** ,其内置了多种类型的锁比如可重入锁(Reentrant Lock)、自旋锁(Spin Lock)、公平锁(Fair Lock)、多重锁(MultiLock)、 红锁(RedLock)、 读写锁(ReadWriteLock)。
-
-
-
-### Redis 如何解决集群情况下分布式锁的可靠性?
-
-为了避免单点故障,生产环境下的 Redis 服务通常是集群化部署的。
-
-Redis 集群下,上面介绍到的分布式锁的实现会存在一些问题。由于 Redis 集群数据同步到各个节点时是异步的,如果在 Redis 主节点获取到锁后,在没有同步到其他节点时,Redis 主节点宕机了,此时新的 Redis 主节点依然可以获取锁,所以多个应用服务就可以同时获取到锁。
-
-
-
-针对这个问题,Redis 之父 antirez 设计了 [Redlock 算法](https://redis.io/topics/distlock) 来解决。
-
-
-
-Redlock 算法的思想是让客户端向 Redis 集群中的多个独立的 Redis 实例依次请求申请加锁,如果客户端能够和半数以上的实例成功地完成加锁操作,那么我们就认为,客户端成功地获得分布式锁,否则加锁失败。
-
-即使部分 Redis 节点出现问题,只要保证 Redis 集群中有半数以上的 Redis 节点可用,分布式锁服务就是正常的。
-
-Redlock 是直接操作 Redis 节点的,并不是通过 Redis 集群操作的,这样才可以避免 Redis 集群主从切换导致的锁丢失问题。
-
-Redlock 实现比较复杂,性能比较差,发生时钟变迁的情况下还存在安全性隐患。《数据密集型应用系统设计》一书的作者 Martin Kleppmann 曾经专门发文([How to do distributed locking - Martin Kleppmann - 2016](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2016/02/08/how-to-do-distributed-locking.html))怼过 Redlock,他认为这是一个很差的分布式锁实现。感兴趣的朋友可以看看[Redis 锁从面试连环炮聊到神仙打架](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3NjU3NTkwMQ==&mid=2247505097&idx=1&sn=5c03cb769c4458350f4d4a321ad51f5a&source=41#wechat_redirect)这篇文章,有详细介绍到 antirez 和 Martin Kleppmann 关于 Redlock 的激烈辩论。
-
-实际项目中不建议使用 Redlock 算法,成本和收益不成正比,可以考虑基于 Redis 主从复制+哨兵模式实现分布式锁。
-
-## 基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁
-
-ZooKeeper 相比于 Redis 实现分布式锁,除了提供相对更高的可靠性之外,在功能层面还有一个非常有用的特性:**Watch 机制**。这个机制可以用来实现公平的分布式锁。不过,使用 ZooKeeper 实现的分布式锁在性能方面相对较差,因此如果对性能要求比较高的话,ZooKeeper 可能就不太适合了。
-
-### 如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁?
-
-ZooKeeper 分布式锁是基于 **临时顺序节点** 和 **Watcher(事件监听器)** 实现的。
-
-获取锁:
-
-1. 首先我们要有一个持久节点`/locks`,客户端获取锁就是在`locks`下创建临时顺序节点。
-2. 假设客户端 1 创建了`/locks/lock1`节点,创建成功之后,会判断 `lock1`是否是 `/locks` 下最小的子节点。
-3. 如果 `lock1`是最小的子节点,则获取锁成功。否则,获取锁失败。
-4. 如果获取锁失败,则说明有其他的客户端已经成功获取锁。客户端 1 并不会不停地循环去尝试加锁,而是在前一个节点比如`/locks/lock0`上注册一个事件监听器。这个监听器的作用是当前一个节点释放锁之后通知客户端 1(避免无效自旋),这样客户端 1 就加锁成功了。
-
-释放锁:
-
-1. 成功获取锁的客户端在执行完业务流程之后,会将对应的子节点删除。
-2. 成功获取锁的客户端在出现故障之后,对应的子节点由于是临时顺序节点,也会被自动删除,避免了锁无法被释放。
-3. 我们前面说的事件监听器其实监听的就是这个子节点删除事件,子节点删除就意味着锁被释放。
-
-
-
-实际项目中,推荐使用 Curator 来实现 ZooKeeper 分布式锁。Curator 是 Netflix 公司开源的一套 ZooKeeper Java 客户端框架,相比于 ZooKeeper 自带的客户端 zookeeper 来说,Curator 的封装更加完善,各种 API 都可以比较方便地使用。
-
-`Curator`主要实现了下面四种锁:
-
-- `InterProcessMutex`:分布式可重入排它锁
-- `InterProcessSemaphoreMutex`:分布式不可重入排它锁
-- `InterProcessReadWriteLock`:分布式读写锁
-- `InterProcessMultiLock`:将多个锁作为单个实体管理的容器,获取锁的时候获取所有锁,释放锁也会释放所有锁资源(忽略释放失败的锁)。
-
-```java
-CuratorFramework client = ZKUtils.getClient();
-client.start();
-// 分布式可重入排它锁
-InterProcessLock lock1 = new InterProcessMutex(client, lockPath1);
-// 分布式不可重入排它锁
-InterProcessLock lock2 = new InterProcessSemaphoreMutex(client, lockPath2);
-// 将多个锁作为一个整体
-InterProcessMultiLock lock = new InterProcessMultiLock(Arrays.asList(lock1, lock2));
-
-if (!lock.acquire(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("不能获取多锁");
-}
-System.out.println("已获取多锁");
-System.out.println("是否有第一个锁: " + lock1.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-System.out.println("是否有第二个锁: " + lock2.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-try {
- // 资源操作
- resource.use();
-} finally {
- System.out.println("释放多个锁");
- lock.release();
-}
-System.out.println("是否有第一个锁: " + lock1.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-System.out.println("是否有第二个锁: " + lock2.isAcquiredInThisProcess());
-client.close();
-```
-
-### 为什么要用临时顺序节点?
-
-每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。
-
-我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
-
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。并且,**临时节点只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性。
-
-可以看出,临时节点相比持久节点,最主要的是对会话失效的情况处理不一样,临时节点会话消失则对应的节点消失。这样的话,如果客户端发生异常导致没来得及释放锁也没关系,会话失效节点自动被删除,不会发生死锁的问题。
-
-使用 Redis 实现分布式锁的时候,我们是通过过期时间来避免锁无法被释放导致死锁问题的,而 ZooKeeper 直接利用临时节点的特性即可。
-
-假设不使用顺序节点的话,所有尝试获取锁的客户端都会对持有锁的子节点加监听器。当该锁被释放之后,势必会造成所有尝试获取锁的客户端来争夺锁,这样对性能不友好。使用顺序节点之后,只需要监听前一个节点就好了,对性能更友好。
-
-### 为什么要设置对前一个节点的监听?
-
-> Watcher(事件监听器),是 ZooKeeper 中的一个很重要的特性。ZooKeeper 允许用户在指定节点上注册一些 Watcher,并且在一些特定事件触发的时候,ZooKeeper 服务端会将事件通知到感兴趣的客户端上去,该机制是 ZooKeeper 实现分布式协调服务的重要特性。
-
-同一时间段内,可能会有很多客户端同时获取锁,但只有一个可以获取成功。如果获取锁失败,则说明有其他的客户端已经成功获取锁。获取锁失败的客户端并不会不停地循环去尝试加锁,而是在前一个节点注册一个事件监听器。
-
-这个事件监听器的作用是:**当前一个节点对应的客户端释放锁之后(也就是前一个节点被删除之后,监听的是删除事件),通知获取锁失败的客户端(唤醒等待的线程,Java 中的 `wait/notifyAll` ),让它尝试去获取锁,然后就成功获取锁了。**
-
-### 如何实现可重入锁?
-
-这里以 Curator 的 `InterProcessMutex` 对可重入锁的实现来介绍(源码地址:[InterProcessMutex.java](https://github.com/apache/curator/blob/master/curator-recipes/src/main/java/org/apache/curator/framework/recipes/locks/InterProcessMutex.java))。
-
-当我们调用 `InterProcessMutex#acquire`方法获取锁的时候,会调用`InterProcessMutex#internalLock`方法。
-
-```java
-// 获取可重入互斥锁,直到获取成功为止
-@Override
-public void acquire() throws Exception {
- if (!internalLock(-1, null)) {
- throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);
- }
-}
-```
-
-`internalLock` 方法会先获取当前请求锁的线程,然后从 `threadData`( `ConcurrentMap` 类型)中获取当前线程对应的 `lockData` 。 `lockData` 包含锁的信息和加锁的次数,是实现可重入锁的关键。
-
-第一次获取锁的时候,`lockData`为 `null`。获取锁成功之后,会将当前线程和对应的 `lockData` 放到 `threadData` 中
-
-```java
-private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
- // 获取当前请求锁的线程
- Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
- // 拿对应的 lockData
- LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
- // 第一次获取锁的话,lockData 为 null
- if (lockData != null) {
- // 当前线程获取过一次锁之后
- // 因为当前线程的锁存在, lockCount 自增后返回,实现锁重入.
- lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
- return true;
- }
- // 尝试获取锁
- String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
- if (lockPath != null) {
- LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
- // 获取锁成功之后,将当前线程和对应的 lockData 放到 threadData 中
- threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
- return true;
- }
-
- return false;
-}
-```
-
-`LockData`是 `InterProcessMutex`中的一个静态内部类。
-
-```java
-private final ConcurrentMap threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
-
-private static class LockData
-{
- // 当前持有锁的线程
- final Thread owningThread;
- // 锁对应的子节点
- final String lockPath;
- // 加锁的次数
- final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
-
- private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath)
- {
- this.owningThread = owningThread;
- this.lockPath = lockPath;
- }
-}
-```
-
-如果已经获取过一次锁,后面再来获取锁的话,直接就会在 `if (lockData != null)` 这里被拦下了,然后就会执行`lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();` 将加锁次数加 1。
-
-整个可重入锁的实现逻辑非常简单,直接在客户端判断当前线程有没有获取锁,有的话直接将加锁次数加 1 就可以了。
-
-## 总结
-
-在这篇文章中,我介绍了实现分布式锁的两种常见方式:**Redis** 和 **ZooKeeper**。至于具体选择 Redis 还是 ZooKeeper 来实现分布式锁,还是要根据业务的具体需求来决定。
-
-- 如果对性能要求比较高的话,建议使用 Redis 实现分布式锁。推荐优先选择 **Redisson** 提供的现成分布式锁,而不是自己实现。实际项目中不建议使用 Redlock 算法,成本和收益不成正比,可以考虑基于 Redis 主从复制+哨兵模式实现分布式锁。
-- 如果对可靠性要求比较高,建议使用 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁,推荐基于 **Curator** 框架来实现。不过,现在很多项目都不会用到 ZooKeeper,如果单纯是因为分布式锁而引入 ZooKeeper 的话,那是不太可取的,不建议这样做,为了一个小小的功能增加了系统的复杂度。
-
-需要注意的是,无论选择哪种方式实现分布式锁,包括 Redis、ZooKeeper 或 Etcd(本文没介绍,但也经常用来实现分布式锁),都无法保证 100% 的安全性,特别是在遇到进程垃圾回收(GC)、网络延迟等异常情况下。
-
-为了进一步提高系统的可靠性,建议引入一个兜底机制。例如,可以通过 **版本号(Fencing Token)机制** 来避免并发冲突。
-
-最后,再分享几篇我觉得写的还不错的文章:
-
-- [分布式锁实现原理与最佳实践 - 阿里云开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JzCHpIOiFVmBoAko58ZuGw)
-- [聊聊分布式锁 - 字节跳动技术团队](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-N4x6EkxwAYDGdJhwvmZLw)
-- [Redis、ZooKeeper、Etcd,谁有最好用的分布式锁? - 腾讯云开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yZC6VJGxt1ANZkn0SljZBg)
-
-
+The name "Watch Dog" comes from the \`getLockWatchdog
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
index ba53f443d03..9d6403b1f0e 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-lock.md
@@ -1,84 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 分布式锁介绍
-category: 分布式
+title: Introduction to Distributed Locks
+category: Distributed
---
-网上有很多分布式锁相关的文章,写了一个相对简洁易懂的版本,针对面试和工作应该够用了。
+There are many articles online about distributed locks, and I have written a relatively concise and easy-to-understand version that should be sufficient for interviews and work.
-这篇文章我们先介绍一下分布式锁的基本概念。
+In this article, we will first introduce the basic concepts of distributed locks.
-## 为什么需要分布式锁?
+## Why Do We Need Distributed Locks?
-在多线程环境中,如果多个线程同时访问共享资源(例如商品库存、外卖订单),会发生数据竞争,可能会导致出现脏数据或者系统问题,威胁到程序的正常运行。
+In a multithreaded environment, if multiple threads access shared resources (such as product inventory or food delivery orders) simultaneously, data contention can occur, potentially leading to dirty data or system issues, threatening the normal operation of the program.
-举个例子,假设现在有 100 个用户参与某个限时秒杀活动,每位用户限购 1 件商品,且商品的数量只有 3 个。如果不对共享资源进行互斥访问,就可能出现以下情况:
+For example, suppose there are 100 users participating in a limited-time flash sale, with each user allowed to purchase 1 item, and there are only 3 items available. If mutual exclusion is not applied to the shared resource, the following situation may occur:
-- 线程 1、2、3 等多个线程同时进入抢购方法,每一个线程对应一个用户。
-- 线程 1 查询用户已经抢购的数量,发现当前用户尚未抢购且商品库存还有 1 个,因此认为可以继续执行抢购流程。
-- 线程 2 也执行查询用户已经抢购的数量,发现当前用户尚未抢购且商品库存还有 1 个,因此认为可以继续执行抢购流程。
-- 线程 1 继续执行,将库存数量减少 1 个,然后返回成功。
-- 线程 2 继续执行,将库存数量减少 1 个,然后返回成功。
-- 此时就发生了超卖问题,导致商品被多卖了一份。
+- Threads 1, 2, 3, etc., enter the purchase method simultaneously, with each thread corresponding to a user.
+- Thread 1 queries the number of items the user has already purchased, finds that the current user has not yet purchased and that there is still 1 item in stock, and thus believes it can continue the purchase process.
+- Thread 2 also executes the query for the number of items the user has already purchased, finds that the current user has not yet purchased and that there is still 1 item in stock, and thus believes it can continue the purchase process.
+- Thread 1 continues to execute, reducing the stock quantity by 1, and then returns success.
+- Thread 2 continues to execute, reducing the stock quantity by 1, and then returns success.
+- At this point, an overselling issue occurs, resulting in the product being sold more than once.
-
+
-为了保证共享资源被安全地访问,我们需要使用互斥操作对共享资源进行保护,即同一时刻只允许一个线程访问共享资源,其他线程需要等待当前线程释放后才能访问。这样可以避免数据竞争和脏数据问题,保证程序的正确性和稳定性。
+To ensure that shared resources are accessed safely, we need to use mutual exclusion operations to protect shared resources, allowing only one thread to access the shared resource at any given time, while other threads must wait until the current thread releases it. This can avoid data contention and dirty data issues, ensuring the correctness and stability of the program.
-**如何才能实现共享资源的互斥访问呢?** 锁是一个比较通用的解决方案,更准确点来说是悲观锁。
+**How can we achieve mutual access to shared resources?** Locks are a relatively general solution, more specifically, pessimistic locks.
-悲观锁总是假设最坏的情况,认为共享资源每次被访问的时候就会出现问题(比如共享数据被修改),所以每次在获取资源操作的时候都会上锁,这样其他线程想拿到这个资源就会阻塞直到锁被上一个持有者释放。也就是说,**共享资源每次只给一个线程使用,其它线程阻塞,用完后再把资源转让给其它线程**。
+Pessimistic locks always assume the worst-case scenario, believing that issues will arise every time shared resources are accessed (for example, shared data being modified). Therefore, every time a resource operation is performed, a lock is acquired, causing other threads that want to access this resource to block until the lock is released by the previous holder. In other words, **the shared resource is used by only one thread at a time, while other threads are blocked, and after use, the resource is transferred to other threads**.
-对于单机多线程来说,在 Java 中,我们通常使用 `ReentrantLock` 类、`synchronized` 关键字这类 JDK 自带的 **本地锁** 来控制一个 JVM 进程内的多个线程对本地共享资源的访问。
+For single-machine multithreading, in Java, we typically use the `ReentrantLock` class or the `synchronized` keyword, which are built-in **local locks** provided by the JDK, to control access to local shared resources by multiple threads within a single JVM process.
-下面是我对本地锁画的一张示意图。
+Here is a diagram I created to illustrate local locks.
-
+
-从图中可以看出,这些线程访问共享资源是互斥的,同一时刻只有一个线程可以获取到本地锁访问共享资源。
+From the diagram, it can be seen that these threads access shared resources mutually exclusively, with only one thread able to acquire the local lock to access the shared resource at any given time.
-分布式系统下,不同的服务/客户端通常运行在独立的 JVM 进程上。如果多个 JVM 进程共享同一份资源的话,使用本地锁就没办法实现资源的互斥访问了。于是,**分布式锁** 就诞生了。
+In a distributed system, different services/clients typically run in separate JVM processes. If multiple JVM processes share the same resource, local locks cannot achieve mutual access to the resource. Thus, **distributed locks** were born.
-举个例子:系统的订单服务一共部署了 3 份,都对外提供服务。用户下订单之前需要检查库存,为了防止超卖,这里需要加锁以实现对检查库存操作的同步访问。由于订单服务位于不同的 JVM 进程中,本地锁在这种情况下就没办法正常工作了。我们需要用到分布式锁,这样的话,即使多个线程不在同一个 JVM 进程中也能获取到同一把锁,进而实现共享资源的互斥访问。
+For example: The order service of the system is deployed in 3 instances, all providing services externally. Before a user places an order, they need to check the inventory. To prevent overselling, a lock is needed to synchronize access to the inventory check operation. Since the order service is located in different JVM processes, local locks cannot function properly in this case. We need to use distributed locks, which allow multiple threads, even if they are not in the same JVM process, to acquire the same lock, thereby achieving mutual access to shared resources.
-下面是我对分布式锁画的一张示意图。
+Here is a diagram I created to illustrate distributed locks.
-
+
-从图中可以看出,这些独立的进程中的线程访问共享资源是互斥的,同一时刻只有一个线程可以获取到分布式锁访问共享资源。
+From the diagram, it can be seen that threads in these independent processes access shared resources mutually exclusively, with only one thread able to acquire the distributed lock to access the shared resource at any given time.
-## 分布式锁应该具备哪些条件?
+## What Conditions Should a Distributed Lock Meet?
-一个最基本的分布式锁需要满足:
+A basic distributed lock needs to satisfy the following:
-- **互斥**:任意一个时刻,锁只能被一个线程持有。
-- **高可用**:锁服务是高可用的,当一个锁服务出现问题,能够自动切换到另外一个锁服务。并且,即使客户端的释放锁的代码逻辑出现问题,锁最终一定还是会被释放,不会影响其他线程对共享资源的访问。这一般是通过超时机制实现的。
-- **可重入**:一个节点获取了锁之后,还可以再次获取锁。
-
-除了上面这三个基本条件之外,一个好的分布式锁还需要满足下面这些条件:
-
-- **高性能**:获取和释放锁的操作应该快速完成,并且不应该对整个系统的性能造成过大影响。
-- **非阻塞**:如果获取不到锁,不能无限期等待,避免对系统正常运行造成影响。
-
-## 分布式锁的常见实现方式有哪些?
-
-常见分布式锁实现方案如下:
-
-- 基于关系型数据库比如 MySQL 实现分布式锁。
-- 基于分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁。
-- 基于分布式键值存储系统比如 Redis 、Etcd 实现分布式锁。
-
-关系型数据库的方式一般是通过唯一索引或者排他锁实现。不过,一般不会使用这种方式,问题太多比如性能太差、不具备锁失效机制。
-
-基于 ZooKeeper 或者 Redis 实现分布式锁这两种实现方式要用的更多一些,我专门写了一篇文章来详细介绍这两种方案:[分布式锁常见实现方案总结](./distributed-lock-implementations.md)。
-
-## 总结
-
-这篇文章我们主要介绍了:
-
-- 分布式锁的用途:分布式系统下,不同的服务/客户端通常运行在独立的 JVM 进程上。如果多个 JVM 进程共享同一份资源的话,使用本地锁就没办法实现资源的互斥访问了。
-- 分布式锁的应该具备的条件:互斥、高可用、可重入、高性能、非阻塞。
-- 分布式锁的常见实现方式:关系型数据库比如 MySQL、分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper、分布式键值存储系统比如 Redis 、Etcd 。
-
-
+- **Mutual Exclusion**: At any given time, the lock can only be held by one thread.
+- **High Availability**: The lock service is highly available. When one
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
index af6f3de5a21..e9065b67c9f 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-in-action.md
@@ -1,76 +1,76 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper 实战
-category: 分布式
+title: ZooKeeper Practical Guide
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-这篇文章简单给演示一下 ZooKeeper 常见命令的使用以及 ZooKeeper Java 客户端 Curator 的基本使用。介绍到的内容都是最基本的操作,能满足日常工作的基本需要。
+This article will briefly demonstrate the use of common ZooKeeper commands and the basic usage of the ZooKeeper Java client, Curator. The topics covered are the most basic operations and can meet the basic needs of daily work.
-如果文章有任何需要改善和完善的地方,欢迎在评论区指出,共同进步!
+If there are any areas in the article that need improvement or enhancement, feel free to point them out in the comments section for our mutual progress!
-## ZooKeeper 安装
+## ZooKeeper Installation
-### 使用 Docker 安装 zookeeper
+### Installing ZooKeeper Using Docker
-**a.使用 Docker 下载 ZooKeeper**
+**a. Download ZooKeeper using Docker**
```shell
docker pull zookeeper:3.5.8
```
-**b.运行 ZooKeeper**
+**b. Run ZooKeeper**
```shell
docker run -d --name zookeeper -p 2181:2181 zookeeper:3.5.8
```
-### 连接 ZooKeeper 服务
+### Connecting to the ZooKeeper Service
-**a.进入 ZooKeeper 容器中**
+**a. Enter the ZooKeeper container**
-先使用 `docker ps` 查看 ZooKeeper 的 ContainerID,然后使用 `docker exec -it ContainerID /bin/bash` 命令进入容器中。
+First, use `docker ps` to check the ContainerID of ZooKeeper, and then use the command `docker exec -it ContainerID /bin/bash` to enter the container.
-**b.先进入 bin 目录,然后通过 `./zkCli.sh -server 127.0.0.1:2181`命令连接 ZooKeeper 服务**
+**b. Navigate to the bin directory and connect to the ZooKeeper service using the command `./zkCli.sh -server 127.0.0.1:2181`**
```bash
root@eaf70fc620cb:/apache-zookeeper-3.5.8-bin# cd bin
```
-如果你看到控制台成功打印出如下信息的话,说明你已经成功连接 ZooKeeper 服务。
+If you see the following message successfully printed in the console, it indicates that you have successfully connected to the ZooKeeper service.
-
+
-## ZooKeeper 常用命令演示
+## Common ZooKeeper Commands Demonstration
-### 查看常用命令(help 命令)
+### View Common Commands (help Command)
-通过 `help` 命令查看 ZooKeeper 常用命令
+Use the `help` command to view common ZooKeeper commands.
-### 创建节点(create 命令)
+### Create Node (create Command)
-通过 `create` 命令在根目录创建了 node1 节点,与它关联的字符串是"node1"
+Use the `create` command to create the node1 in the root directory, with the associated string "node1".
```shell
-[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 34] create /node1 “node1”
+[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 34] create /node1 "node1"
```
-通过 `create` 命令在根目录创建了 node1 节点,与它关联的内容是数字 123
+Use the `create` command to create the node1.1 under node1, with the associated content as the number 123.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 1] create /node1/node1.1 123
Created /node1/node1.1
```
-### 更新节点数据内容(set 命令)
+### Update Node Data Content (set Command)
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 11] set /node1 "set node1"
```
-### 获取节点的数据(get 命令)
+### Retrieve Node Data (get Command)
-`get` 命令可以获取指定节点的数据内容和节点的状态,可以看出我们通过 `set` 命令已经将节点数据内容改为 "set node1"。
+The `get` command can retrieve the data content and status of the specified node, showing that we have already changed the node data to "set node1" using the `set` command.
```shell
[zk: zookeeper(CONNECTED) 12] get -s /node1
@@ -86,30 +86,29 @@ aclVersion = 0
ephemeralOwner = 0x0
dataLength = 9
numChildren = 1
-
```
-### 查看某个目录下的子节点(ls 命令)
+### View Subnodes of a Directory (ls Command)
-通过 `ls` 命令查看根目录下的节点
+Use the `ls` command to view the nodes in the root directory.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 37] ls /
[dubbo, ZooKeeper, node1]
```
-通过 `ls` 命令查看 node1 目录下的节点
+Use the `ls` command to view the nodes under the node1 directory.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 5] ls /node1
[node1.1]
```
-ZooKeeper 中的 ls 命令和 linux 命令中的 ls 类似, 这个命令将列出绝对路径 path 下的所有子节点信息(列出 1 级,并不递归)
+The `ls` command in ZooKeeper is similar to the `ls` command in Linux; this command will list all subnode information under the absolute path (only listing 1 level, not recursively).
-### 查看节点状态(stat 命令)
+### View Node Status (stat Command)
-通过 `stat` 命令查看节点状态
+Use the `stat` command to view the node status.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 10] stat /node1
@@ -126,14 +125,14 @@ dataLength = 11
numChildren = 1
```
-上面显示的一些信息比如 cversion、aclVersion、numChildren 等等,我在上面 “[ZooKeeper 相关概念总结(入门)](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.html)” 这篇文章中已经介绍到。
+The information displayed above, such as cversion, aclVersion, numChildren, etc., has been introduced in my previous article “[Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Beginner)](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.html)”.
-### 查看节点信息和状态(ls2 命令)
+### View Node Information and Status (ls2 Command)
-`ls2` 命令更像是 `ls` 命令和 `stat` 命令的结合。 `ls2` 命令返回的信息包括 2 部分:
+The `ls2` command is more like a combination of the `ls` and `stat` commands. The information returned by the `ls2` command includes 2 parts:
-1. 子节点列表
-2. 当前节点的 stat 信息。
+1. List of subnodes
+1. The current node's stat information.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 7] ls2 /node1
@@ -149,28 +148,27 @@ aclVersion = 0
ephemeralOwner = 0x0
dataLength = 11
numChildren = 1
-
```
-### 删除节点(delete 命令)
+### Delete Node (delete Command)
-这个命令很简单,但是需要注意的一点是如果你要删除某一个节点,那么这个节点必须无子节点才行。
+This command is straightforward, but it is crucial to note that if you want to delete a node, that node must have no children.
```shell
[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 3] delete /node1/node1.1
```
-在后面我会介绍到 Java 客户端 API 的使用以及开源 ZooKeeper 客户端 ZkClient 和 Curator 的使用。
+Later, I will introduce the use of the Java client API and the open-source ZooKeeper clients ZkClient and Curator.
-## ZooKeeper Java 客户端 Curator 简单使用
+## Simple Usage of ZooKeeper Java Client Curator
-Curator 是 Netflix 公司开源的一套 ZooKeeper Java 客户端框架,相比于 Zookeeper 自带的客户端 zookeeper 来说,Curator 的封装更加完善,各种 API 都可以比较方便地使用。
+Curator is an open-source ZooKeeper Java client framework developed by Netflix. Compared to the built-in ZooKeeper client, Curator's encapsulation is more comprehensive, allowing various APIs to be used more conveniently.

-下面我们就来简单地演示一下 Curator 的使用吧!
+Now, let's briefly demonstrate the usage of Curator!
-Curator4.0+版本对 ZooKeeper 3.5.x 支持比较好。开始之前,请先将下面的依赖添加进你的项目。
+Curator version 4.0+ has good support for ZooKeeper 3.5.x. Before starting, please add the following dependencies to your project.
```xml
@@ -185,9 +183,9 @@ Curator4.0+版本对 ZooKeeper 3.5.x 支持比较好。开始之前,请先将
```
-### 连接 ZooKeeper 客户端
+### Connecting to ZooKeeper Client
-通过 `CuratorFrameworkFactory` 创建 `CuratorFramework` 对象,然后再调用 `CuratorFramework` 对象的 `start()` 方法即可!
+Create a `CuratorFramework` object through `CuratorFrameworkFactory`, and then call the `start()` method on the `CuratorFramework` object!
```java
private static final int BASE_SLEEP_TIME = 1000;
@@ -203,92 +201,92 @@ CuratorFramework zkClient = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
zkClient.start();
```
-对于一些基本参数的说明:
+Here are explanations of some basic parameters:
-- `baseSleepTimeMs`:重试之间等待的初始时间
-- `maxRetries`:最大重试次数
-- `connectString`:要连接的服务器列表
-- `retryPolicy`:重试策略
+- `baseSleepTimeMs`: The initial time to wait between retries
+- `maxRetries`: The maximum number of retries
+- `connectString`: The list of servers to connect to
+- `retryPolicy`: The retry policy
-### 数据节点的增删改查
+### CRUD Operations on Data Nodes
-#### 创建节点
+#### Create Node
-我们在 [ZooKeeper 常见概念解读](./zookeeper-intro.md) 中介绍到,我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
+As we discussed in [Common Concepts of ZooKeeper](./zookeeper-intro.md), we generally categorize znodes into 4 major types:
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。并且,临时节点 **只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性。
+- **Persistent (PERSISTENT) Nodes**: Once created, they always exist even if the ZooKeeper cluster crashes, until deleted.
+- **Ephemeral (EPHEMERAL) Nodes**: The lifecycle of ephemeral nodes is bound to the **client session**; **the session disappears, and the node disappears**. Moreover, ephemeral nodes **can only be leaf nodes**, and cannot have child nodes.
+- **Persistent Sequential (PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL) Nodes**: In addition to having the characteristics of persistent nodes, the names of child nodes also have order. For example, `/node1/app0000000001`, `/node1/app0000000002`.
+- **Ephemeral Sequential (EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL) Nodes**: In addition to having the characteristics of ephemeral nodes, the names of child nodes also have order.
-你在使用的 ZooKeeper 的时候,会发现 `CreateMode` 类中实际有 7 种 znode 类型 ,但是用的最多的还是上面介绍的 4 种。
+When using ZooKeeper, you will find that the `CreateMode` class has a total of 7 types of znodes, but the most commonly used are the 4 types mentioned above.
-**a.创建持久化节点**
+**a. Create Persistent Node**
-你可以通过下面两种方式创建持久化的节点。
+You can create persistent nodes in the following two ways.
```java
-//注意:下面的代码会报错,下文说了具体原因
+// Note: The following code will cause an error; the specific reason will be explained later
zkClient.create().forPath("/node1/00001");
zkClient.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/node1/00002");
```
-但是,你运行上面的代码会报错,这是因为的父节点`node1`还未创建。
+However, running the above code will raise an error because the parent node `node1` has not been created yet.
-你可以先创建父节点 `node1` ,然后再执行上面的代码就不会报错了。
+You can first create the parent node `node1`, and then the above code will not cause an error.
```java
zkClient.create().forPath("/node1");
```
-更推荐的方式是通过下面这行代码, **`creatingParentsIfNeeded()` 可以保证父节点不存在的时候自动创建父节点,这是非常有用的。**
+A more recommended way is to use the following line of code. **`creatingParentsIfNeeded()` ensures that if the parent node does not exist, it will be created automatically, which is very useful.**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**b.创建临时节点**
+**b. Create Ephemeral Node**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**c.创建节点并指定数据内容**
+**c. Create Node and Specify Data Content**
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001","java".getBytes());
-zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");//获取节点的数据内容,获取到的是 byte数组
+zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");// Retrieve the data content of the node; the result is a byte array
```
-**d.检测节点是否创建成功**
+**d. Check if the Node Was Created Successfully**
```java
-zkClient.checkExists().forPath("/node1/00001");//不为null的话,说明节点创建成功
+zkClient.checkExists().forPath("/node1/00001");// If not null, it indicates that the node was created successfully
```
-#### 删除节点
+#### Delete Node
-**a.删除一个子节点**
+**a. Delete a Child Node**
```java
zkClient.delete().forPath("/node1/00001");
```
-**b.删除一个节点以及其下的所有子节点**
+**b. Delete a Node and All Its Children**
```java
zkClient.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/node1");
```
-#### 获取/更新节点数据内容
+#### Retrieve/Update Node Data Content
```java
zkClient.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/node1/00001","java".getBytes());
-zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");//获取节点的数据内容
-zkClient.setData().forPath("/node1/00001","c++".getBytes());//更新节点数据内容
+zkClient.getData().forPath("/node1/00001");// Retrieve the data content of the node
+zkClient.setData().forPath("/node1/00001","c++".getBytes());// Update the data content of the node
```
-#### 获取某个节点的所有子节点路径
+#### Retrieve All Child Node Paths of a Specific Node
```java
List childrenPaths = zkClient.getChildren().forPath("/node1");
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
index 955c5d2813a..11bebd0d158 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-intro.md
@@ -1,316 +1,52 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper相关概念总结(入门)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Introduction)
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-相信大家对 ZooKeeper 应该不算陌生。但是你真的了解 ZooKeeper 到底有啥用不?如果别人/面试官让你给他讲讲对于 ZooKeeper 的认识,你能回答到什么地步呢?
+I believe everyone is somewhat familiar with ZooKeeper. But do you really understand what ZooKeeper is used for? If someone, like an interviewer, asks you to explain your understanding of ZooKeeper, how far could you go in your answer?
-拿我自己来说吧!我本人在大学曾经使用 Dubbo 来做分布式项目的时候,使用了 ZooKeeper 作为注册中心。为了保证分布式系统能够同步访问某个资源,我还使用 ZooKeeper 做过分布式锁。另外,我在学习 Kafka 的时候,知道 Kafka 很多功能的实现依赖了 ZooKeeper。
+Let me share my own experience! During my university days, I used Dubbo for a distributed project and employed ZooKeeper as the registration center. To ensure that the distributed system could synchronously access a certain resource, I also used ZooKeeper for distributed locking. Additionally, while learning Kafka, I realized that many of Kafka's functionalities depend on ZooKeeper.
-前几天,总结项目经验的时候,我突然问自己 ZooKeeper 到底是个什么东西?想了半天,脑海中只是简单的能浮现出几句话:
+A few days ago, while summarizing project experiences, I suddenly asked myself, what exactly is ZooKeeper? After thinking for a long time, I could only recall a few simple statements:
-1. ZooKeeper 可以被用作注册中心、分布式锁;
-2. ZooKeeper 是 Hadoop 生态系统的一员;
-3. 构建 ZooKeeper 集群的时候,使用的服务器最好是奇数台。
+1. ZooKeeper can be used as a registration center and for distributed locks;
+1. ZooKeeper is a part of the Hadoop ecosystem;
+1. When building a ZooKeeper cluster, it is best to use an odd number of servers.
-由此可见,我对于 ZooKeeper 的理解仅仅是停留在了表面。
+From this, it is clear that my understanding of ZooKeeper was merely superficial.
-所以,通过本文,希望带大家稍微详细的了解一下 ZooKeeper 。如果没有学过 ZooKeeper ,那么本文将会是你进入 ZooKeeper 大门的垫脚砖。如果你已经接触过 ZooKeeper ,那么本文将带你回顾一下 ZooKeeper 的一些基础概念。
+Therefore, through this article, I hope to provide a more detailed understanding of ZooKeeper. If you have never learned about ZooKeeper, this article will serve as a stepping stone for you to enter the world of ZooKeeper. If you have already been exposed to ZooKeeper, this article will help you review some basic concepts.
-另外,本文不光会涉及到 ZooKeeper 的一些概念,后面的文章会介绍到 ZooKeeper 常见命令的使用以及使用 Apache Curator 作为 ZooKeeper 的客户端。
+Moreover, this article will not only cover some concepts of ZooKeeper; subsequent articles will introduce common commands for ZooKeeper and the use of Apache Curator as a client for ZooKeeper.
-_如果文章有任何需要改善和完善的地方,欢迎在评论区指出,共同进步!_
+_If there are any areas in the article that need improvement or enhancement, please feel free to point them out in the comments section for our mutual progress!_
-## ZooKeeper 介绍
+## Introduction to ZooKeeper
-### ZooKeeper 由来
+### Origin of ZooKeeper
-正式介绍 ZooKeeper 之前,我们先来看看 ZooKeeper 的由来,还挺有意思的。
+Before formally introducing ZooKeeper, let's take a look at its origin, which is quite interesting.
-下面这段内容摘自《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper》第四章第一节,推荐大家阅读一下:
+The following excerpt is from Chapter 4, Section 1 of "From Paxos to ZooKeeper," and I recommend everyone read it:
-> ZooKeeper 最早起源于雅虎研究院的一个研究小组。在当时,研究人员发现,在雅虎内部很多大型系统基本都需要依赖一个类似的系统来进行分布式协调,但是这些系统往往都存在分布式单点问题。所以,雅虎的开发人员就试图开发一个通用的无单点问题的分布式协调框架,以便让开发人员将精力集中在处理业务逻辑上。
+> ZooKeeper originated from a research group at Yahoo! Research. At that time, researchers found that many large systems within Yahoo! relied on a similar system for distributed coordination, but these systems often had distributed single point issues. Therefore, Yahoo! developers attempted to create a general-purpose distributed coordination framework without single points of failure, allowing developers to focus on business logic.
>
-> 关于“ZooKeeper”这个项目的名字,其实也有一段趣闻。在立项初期,考虑到之前内部很多项目都是使用动物的名字来命名的(例如著名的 Pig 项目),雅虎的工程师希望给这个项目也取一个动物的名字。时任研究院的首席科学家 RaghuRamakrishnan 开玩笑地说:“在这样下去,我们这儿就变成动物园了!”此话一出,大家纷纷表示就叫动物园管理员吧一一一因为各个以动物命名的分布式组件放在一起,雅虎的整个分布式系统看上去就像一个大型的动物园了,而 ZooKeeper 正好要用来进行分布式环境的协调一一于是,ZooKeeper 的名字也就由此诞生了。
+> Regarding the name "ZooKeeper," there is also an interesting story. In the early stages of the project, considering that many previous internal projects were named after animals (such as the famous Pig project), Yahoo! engineers wanted to give this project an animal name as well. The then chief scientist of the research institute, Raghu Ramakrishnan, jokingly said, "At this rate, we will turn into a zoo!" Once this was said, everyone agreed to call it ZooKeeper—because various distributed components named after animals together made Yahoo!'s entire distributed system look like a large zoo, and ZooKeeper was just meant for coordinating in a distributed environment—thus, the name ZooKeeper was born.
-### ZooKeeper 概览
+### Overview of ZooKeeper
-ZooKeeper 是一个开源的**分布式协调服务**,它的设计目标是将那些复杂且容易出错的分布式一致性服务封装起来,构成一个高效可靠的原语集,并以一系列简单易用的接口提供给用户使用。
+ZooKeeper is an open-source **distributed coordination service** designed to encapsulate complex and error-prone distributed consistency services into a set of efficient and reliable primitives, providing users with a series of simple and easy-to-use interfaces.
-> **原语:** 操作系统或计算机网络用语范畴。是由若干条指令组成的,用于完成一定功能的一个过程。具有不可分割性,即原语的执行必须是连续的,在执行过程中不允许被中断。
+> **Primitive:** A term used in operating systems or computer networks. It is a process composed of several instructions used to accomplish a certain function. It has indivisibility, meaning that the execution of a primitive must be continuous and cannot be interrupted during execution.
-ZooKeeper 为我们提供了高可用、高性能、稳定的分布式数据一致性解决方案,通常被用于实现诸如数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master 选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。这些功能的实现主要依赖于 ZooKeeper 提供的 **数据存储+事件监听** 功能(后文会详细介绍到) 。
+ZooKeeper provides us with a high-availability, high-performance, and stable distributed data consistency solution, commonly used to implement functionalities such as data publishing/subscription, load balancing, naming services, distributed coordination/notification, cluster management, master election, distributed locks, and distributed queues. The implementation of these functionalities mainly relies on the **data storage + event listening** capabilities provided by ZooKeeper (which will be detailed later).
-ZooKeeper 将数据保存在内存中,性能是不错的。 在“读”多于“写”的应用程序中尤其地高性能,因为“写”会导致所有的服务器间同步状态。(“读”多于“写”是协调服务的典型场景)。
+ZooKeeper stores data in memory, resulting in good performance, especially in applications where "reads" outnumber "writes," as "writes" cause synchronization of states among all servers. (The scenario of "reads" outnumbering "writes" is typical for coordination services).
-另外,很多顶级的开源项目都用到了 ZooKeeper,比如:
+Additionally, many top open-source projects utilize ZooKeeper, such as:
-- **Kafka** : ZooKeeper 主要为 Kafka 提供 Broker 和 Topic 的注册以及多个 Partition 的负载均衡等功能。不过,在 Kafka 2.8 之后,引入了基于 Raft 协议的 KRaft 模式,不再依赖 Zookeeper,大大简化了 Kafka 的架构。
-- **Hbase** : ZooKeeper 为 Hbase 提供确保整个集群只有一个 Master 以及保存和提供 regionserver 状态信息(是否在线)等功能。
-- **Hadoop** : ZooKeeper 为 Namenode 提供高可用支持。
-
-### ZooKeeper 特点
-
-- **顺序一致性:** 从同一客户端发起的事务请求,最终将会严格地按照顺序被应用到 ZooKeeper 中去。
-- **原子性:** 所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有机器上的应用情况是一致的,也就是说,要么整个集群中所有的机器都成功应用了某一个事务,要么都没有应用。
-- **单一系统映像:** 无论客户端连到哪一个 ZooKeeper 服务器上,其看到的服务端数据模型都是一致的。
-- **可靠性:** 一旦一次更改请求被应用,更改的结果就会被持久化,直到被下一次更改覆盖。
-- **实时性:** 一旦数据发生变更,其他节点会实时感知到。每个客户端的系统视图都是最新的。
-- **集群部署**:3~5 台(最好奇数台)机器就可以组成一个集群,每台机器都在内存保存了 ZooKeeper 的全部数据,机器之间互相通信同步数据,客户端连接任何一台机器都可以。
-- **高可用:**如果某台机器宕机,会保证数据不丢失。集群中挂掉不超过一半的机器,都能保证集群可用。比如 3 台机器可以挂 1 台,5 台机器可以挂 2 台。
-
-### ZooKeeper 应用场景
-
-ZooKeeper 概览中,我们介绍到使用其通常被用于实现诸如数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master 选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。
-
-下面选 3 个典型的应用场景来专门说说:
-
-1. **命名服务**:可以通过 ZooKeeper 的顺序节点生成全局唯一 ID。
-2. **数据发布/订阅**:通过 **Watcher 机制** 可以很方便地实现数据发布/订阅。当你将数据发布到 ZooKeeper 被监听的节点上,其他机器可通过监听 ZooKeeper 上节点的变化来实现配置的动态更新。
-3. **分布式锁**:通过创建唯一节点获得分布式锁,当获得锁的一方执行完相关代码或者是挂掉之后就释放锁。分布式锁的实现也需要用到 **Watcher 机制** ,我在 [分布式锁详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/distributed-lock.html) 这篇文章中有详细介绍到如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现分布式锁。
-
-实际上,这些功能的实现基本都得益于 ZooKeeper 可以保存数据的功能,但是 ZooKeeper 不适合保存大量数据,这一点需要注意。
-
-## ZooKeeper 重要概念
-
-_破音:拿出小本本,下面的内容非常重要哦!_
-
-### Data model(数据模型)
-
-ZooKeeper 数据模型采用层次化的多叉树形结构,每个节点上都可以存储数据,这些数据可以是数字、字符串或者是二进制序列。并且。每个节点还可以拥有 N 个子节点,最上层是根节点以“/”来代表。每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。并且,每个 znode 都有一个唯一的路径标识。
-
-强调一句:**ZooKeeper 主要是用来协调服务的,而不是用来存储业务数据的,所以不要放比较大的数据在 znode 上,ZooKeeper 给出的每个节点的数据大小上限是 1M 。**
-
-从下图可以更直观地看出:ZooKeeper 节点路径标识方式和 Unix 文件系统路径非常相似,都是由一系列使用斜杠"/"进行分割的路径表示,开发人员可以向这个节点中写入数据,也可以在节点下面创建子节点。这些操作我们后面都会介绍到。
-
-
-
-### znode(数据节点)
-
-介绍了 ZooKeeper 树形数据模型之后,我们知道每个数据节点在 ZooKeeper 中被称为 **znode**,它是 ZooKeeper 中数据的最小单元。你要存放的数据就放在上面,是你使用 ZooKeeper 过程中经常需要接触到的一个概念。
-
-我们通常是将 znode 分为 4 大类:
-
-- **持久(PERSISTENT)节点**:一旦创建就一直存在即使 ZooKeeper 集群宕机,直到将其删除。
-- **临时(EPHEMERAL)节点**:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话(session)** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失**。并且,**临时节点只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- **持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具有持久(PERSISTENT)节点的特性之外, 子节点的名称还具有顺序性。比如 `/node1/app0000000001`、`/node1/app0000000002` 。
-- **临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)节点**:除了具备临时(EPHEMERAL)节点的特性之外,子节点的名称还具有顺序性
-
-每个 znode 由 2 部分组成:
-
-- **stat**:状态信息
-- **data**:节点存放的数据的具体内容
-
-如下所示,我通过 get 命令来获取 根目录下的 dubbo 节点的内容。(get 命令在下面会介绍到)。
-
-```shell
-[zk: 127.0.0.1:2181(CONNECTED) 6] get /dubbo
-# 该数据节点关联的数据内容为空
-null
-# 下面是该数据节点的一些状态信息,其实就是 Stat 对象的格式化输出
-cZxid = 0x2
-ctime = Tue Nov 27 11:05:34 CST 2018
-mZxid = 0x2
-mtime = Tue Nov 27 11:05:34 CST 2018
-pZxid = 0x3
-cversion = 1
-dataVersion = 0
-aclVersion = 0
-ephemeralOwner = 0x0
-dataLength = 0
-numChildren = 1
-```
-
-Stat 类中包含了一个数据节点的所有状态信息的字段,包括事务 ID(cZxid)、节点创建时间(ctime) 和子节点个数(numChildren) 等等。
-
-下面我们来看一下每个 znode 状态信息究竟代表的是什么吧!(下面的内容来源于《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper 分布式一致性原理与实践》,因为 Guide 确实也不是特别清楚,要学会参考资料的嘛! ):
-
-| znode 状态信息 | 解释 |
-| -------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| cZxid | create ZXID,即该数据节点被创建时的事务 id |
-| ctime | create time,即该节点的创建时间 |
-| mZxid | modified ZXID,即该节点最终一次更新时的事务 id |
-| mtime | modified time,即该节点最后一次的更新时间 |
-| pZxid | 该节点的子节点列表最后一次修改时的事务 id,只有子节点列表变更才会更新 pZxid,子节点内容变更不会更新 |
-| cversion | 子节点版本号,当前节点的子节点每次变化时值增加 1 |
-| dataVersion | 数据节点内容版本号,节点创建时为 0,每更新一次节点内容(不管内容有无变化)该版本号的值增加 1 |
-| aclVersion | 节点的 ACL 版本号,表示该节点 ACL 信息变更次数 |
-| ephemeralOwner | 创建该临时节点的会话的 sessionId;如果当前节点为持久节点,则 ephemeralOwner=0 |
-| dataLength | 数据节点内容长度 |
-| numChildren | 当前节点的子节点个数 |
-
-### 版本(version)
-
-在前面我们已经提到,对应于每个 znode,ZooKeeper 都会为其维护一个叫作 **Stat** 的数据结构,Stat 中记录了这个 znode 的三个相关的版本:
-
-- **dataVersion**:当前 znode 节点的版本号
-- **cversion**:当前 znode 子节点的版本
-- **aclVersion**:当前 znode 的 ACL 的版本。
-
-### ACL(权限控制)
-
-ZooKeeper 采用 ACL(AccessControlLists)策略来进行权限控制,类似于 UNIX 文件系统的权限控制。
-
-对于 znode 操作的权限,ZooKeeper 提供了以下 5 种:
-
-- **CREATE** : 能创建子节点
-- **READ**:能获取节点数据和列出其子节点
-- **WRITE** : 能设置/更新节点数据
-- **DELETE** : 能删除子节点
-- **ADMIN** : 能设置节点 ACL 的权限
-
-其中尤其需要注意的是,**CREATE** 和 **DELETE** 这两种权限都是针对 **子节点** 的权限控制。
-
-对于身份认证,提供了以下几种方式:
-
-- **world**:默认方式,所有用户都可无条件访问。
-- **auth** :不使用任何 id,代表任何已认证的用户。
-- **digest** :用户名:密码认证方式:_username:password_ 。
-- **ip** : 对指定 ip 进行限制。
-
-### Watcher(事件监听器)
-
-Watcher(事件监听器),是 ZooKeeper 中的一个很重要的特性。ZooKeeper 允许用户在指定节点上注册一些 Watcher,并且在一些特定事件触发的时候,ZooKeeper 服务端会将事件通知到感兴趣的客户端上去,该机制是 ZooKeeper 实现分布式协调服务的重要特性。
-
-
-
-_破音:非常有用的一个特性,都拿出小本本记好了,后面用到 ZooKeeper 基本离不开 Watcher(事件监听器)机制。_
-
-### 会话(Session)
-
-Session 可以看作是 ZooKeeper 服务器与客户端的之间的一个 TCP 长连接,通过这个连接,客户端能够通过心跳检测与服务器保持有效的会话,也能够向 ZooKeeper 服务器发送请求并接受响应,同时还能够通过该连接接收来自服务器的 Watcher 事件通知。
-
-Session 有一个属性叫做:`sessionTimeout` ,`sessionTimeout` 代表会话的超时时间。当由于服务器压力太大、网络故障或是客户端主动断开连接等各种原因导致客户端连接断开时,只要在`sessionTimeout`规定的时间内能够重新连接上集群中任意一台服务器,那么之前创建的会话仍然有效。
-
-另外,在为客户端创建会话之前,服务端首先会为每个客户端都分配一个 `sessionID`。由于 `sessionID`是 ZooKeeper 会话的一个重要标识,许多与会话相关的运行机制都是基于这个 `sessionID` 的,因此,无论是哪台服务器为客户端分配的 `sessionID`,都务必保证全局唯一。
-
-## ZooKeeper 集群
-
-为了保证高可用,最好是以集群形态来部署 ZooKeeper,这样只要集群中大部分机器是可用的(能够容忍一定的机器故障),那么 ZooKeeper 本身仍然是可用的。通常 3 台服务器就可以构成一个 ZooKeeper 集群了。ZooKeeper 官方提供的架构图就是一个 ZooKeeper 集群整体对外提供服务。
-
-
-
-上图中每一个 Server 代表一个安装 ZooKeeper 服务的服务器。组成 ZooKeeper 服务的服务器都会在内存中维护当前的服务器状态,并且每台服务器之间都互相保持着通信。集群间通过 ZAB 协议(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)来保持数据的一致性。
-
-**最典型集群模式:Master/Slave 模式(主备模式)**。在这种模式中,通常 Master 服务器作为主服务器提供写服务,其他的 Slave 服务器从服务器通过异步复制的方式获取 Master 服务器最新的数据提供读服务。
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群角色
-
-但是,在 ZooKeeper 中没有选择传统的 Master/Slave 概念,而是引入了 Leader、Follower 和 Observer 三种角色。如下图所示
-
-
-
-ZooKeeper 集群中的所有机器通过一个 **Leader 选举过程** 来选定一台称为 “**Leader**” 的机器,Leader 既可以为客户端提供写服务又能提供读服务。除了 Leader 外,**Follower** 和 **Observer** 都只能提供读服务。Follower 和 Observer 唯一的区别在于 Observer 机器不参与 Leader 的选举过程,也不参与写操作的“过半写成功”策略,因此 Observer 机器可以在不影响写性能的情况下提升集群的读性能。
-
-| 角色 | 说明 |
-| -------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-| Leader | 为客户端提供读和写的服务,负责投票的发起和决议,更新系统状态。 |
-| Follower | 为客户端提供读服务,如果是写服务则转发给 Leader。参与选举过程中的投票。 |
-| Observer | 为客户端提供读服务,如果是写服务则转发给 Leader。不参与选举过程中的投票,也不参与“过半写成功”策略。在不影响写性能的情况下提升集群的读性能。此角色于 ZooKeeper3.3 系列新增的角色。 |
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群 Leader 选举过程
-
-当 Leader 服务器出现网络中断、崩溃退出与重启等异常情况时,就会进入 Leader 选举过程,这个过程会选举产生新的 Leader 服务器。
-
-这个过程大致是这样的:
-
-1. **Leader election(选举阶段)**:节点在一开始都处于选举阶段,只要有一个节点得到超半数节点的票数,它就可以当选准 leader。
-2. **Discovery(发现阶段)**:在这个阶段,followers 跟准 leader 进行通信,同步 followers 最近接收的事务提议。
-3. **Synchronization(同步阶段)**:同步阶段主要是利用 leader 前一阶段获得的最新提议历史,同步集群中所有的副本。同步完成之后准 leader 才会成为真正的 leader。
-4. **Broadcast(广播阶段)**:到了这个阶段,ZooKeeper 集群才能正式对外提供事务服务,并且 leader 可以进行消息广播。同时如果有新的节点加入,还需要对新节点进行同步。
-
-ZooKeeper 集群中的服务器状态有下面几种:
-
-- **LOOKING**:寻找 Leader。
-- **LEADING**:Leader 状态,对应的节点为 Leader。
-- **FOLLOWING**:Follower 状态,对应的节点为 Follower。
-- **OBSERVING**:Observer 状态,对应节点为 Observer,该节点不参与 Leader 选举。
-
-### ZooKeeper 集群为啥最好奇数台?
-
-ZooKeeper 集群在宕掉几个 ZooKeeper 服务器之后,如果剩下的 ZooKeeper 服务器个数大于宕掉的个数的话整个 ZooKeeper 才依然可用。假如我们的集群中有 n 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,那么也就是剩下的服务数必须大于 n/2。先说一下结论,2n 和 2n-1 的容忍度是一样的,都是 n-1,大家可以先自己仔细想一想,这应该是一个很简单的数学问题了。
-
-比如假如我们有 3 台,那么最大允许宕掉 1 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,如果我们有 4 台的的时候也同样只允许宕掉 1 台。
-假如我们有 5 台,那么最大允许宕掉 2 台 ZooKeeper 服务器,如果我们有 6 台的的时候也同样只允许宕掉 2 台。
-
-综上,何必增加那一个不必要的 ZooKeeper 呢?
-
-### ZooKeeper 选举的过半机制防止脑裂
-
-**何为集群脑裂?**
-
-对于一个集群,通常多台机器会部署在不同机房,来提高这个集群的可用性。保证可用性的同时,会发生一种机房间网络线路故障,导致机房间网络不通,而集群被割裂成几个小集群。这时候子集群各自选主导致“脑裂”的情况。
-
-举例说明:比如现在有一个由 6 台服务器所组成的一个集群,部署在了 2 个机房,每个机房 3 台。正常情况下只有 1 个 leader,但是当两个机房中间网络断开的时候,每个机房的 3 台服务器都会认为另一个机房的 3 台服务器下线,而选出自己的 leader 并对外提供服务。若没有过半机制,当网络恢复的时候会发现有 2 个 leader。仿佛是 1 个大脑(leader)分散成了 2 个大脑,这就发生了脑裂现象。脑裂期间 2 个大脑都可能对外提供了服务,这将会带来数据一致性等问题。
-
-**过半机制是如何防止脑裂现象产生的?**
-
-ZooKeeper 的过半机制导致不可能产生 2 个 leader,因为少于等于一半是不可能产生 leader 的,这就使得不论机房的机器如何分配都不可能发生脑裂。
-
-## ZAB 协议和 Paxos 算法
-
-Paxos 算法应该可以说是 ZooKeeper 的灵魂了。但是,ZooKeeper 并没有完全采用 Paxos 算法 ,而是使用 ZAB 协议作为其保证数据一致性的核心算法。另外,在 ZooKeeper 的官方文档中也指出,ZAB 协议并不像 Paxos 算法那样,是一种通用的分布式一致性算法,它是一种特别为 Zookeeper 设计的崩溃可恢复的原子消息广播算法。
-
-### ZAB 协议介绍
-
-ZAB(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast,原子广播) 协议是为分布式协调服务 ZooKeeper 专门设计的一种支持崩溃恢复的原子广播协议。 在 ZooKeeper 中,主要依赖 ZAB 协议来实现分布式数据一致性,基于该协议,ZooKeeper 实现了一种主备模式的系统架构来保持集群中各个副本之间的数据一致性。
-
-### ZAB 协议两种基本的模式:崩溃恢复和消息广播
-
-ZAB 协议包括两种基本的模式,分别是
-
-- **崩溃恢复**:当整个服务框架在启动过程中,或是当 Leader 服务器出现网络中断、崩溃退出与重启等异常情况时,ZAB 协议就会进入恢复模式并选举产生新的 Leader 服务器。当选举产生了新的 Leader 服务器,同时集群中已经有过半的机器与该 Leader 服务器完成了状态同步之后,ZAB 协议就会退出恢复模式。其中,**所谓的状态同步是指数据同步,用来保证集群中存在过半的机器能够和 Leader 服务器的数据状态保持一致**。
-- **消息广播**:**当集群中已经有过半的 Follower 服务器完成了和 Leader 服务器的状态同步,那么整个服务框架就可以进入消息广播模式了。** 当一台同样遵守 ZAB 协议的服务器启动后加入到集群中时,如果此时集群中已经存在一个 Leader 服务器在负责进行消息广播,那么新加入的服务器就会自觉地进入数据恢复模式:找到 Leader 所在的服务器,并与其进行数据同步,然后一起参与到消息广播流程中去。
-
-### ZAB 协议&Paxos 算法文章推荐
-
-关于 **ZAB 协议&Paxos 算法** 需要讲和理解的东西太多了,具体可以看下面这几篇文章:
-
-- [Paxos 算法详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.html)
-- [ZooKeeper 与 Zab 协议 · Analyze](https://wingsxdu.com/posts/database/zookeeper/)
-- [Raft 算法详解](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.html)
-
-## ZooKeeper VS ETCD
-
-[ETCD](https://etcd.io/) 是一种强一致性的分布式键值存储,它提供了一种可靠的方式来存储需要由分布式系统或机器集群访问的数据。ETCD 内部采用 [Raft 算法](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.html)作为一致性算法,基于 Go 语言实现。
-
-与 ZooKeeper 类似,ETCD 也可用于数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、分布式锁等场景。那二者如何选择呢?
-
-得物技术的[浅析如何基于 ZooKeeper 实现高可用架构](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pBI3rjv5NdS1124Z7HQ-JA)这篇文章给出了如下的对比表格(我进一步做了优化),可以作为参考:
-
-| | ZooKeeper | ETCD |
-| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
-| **语言** | Java | Go |
-| **协议** | TCP | Grpc |
-| **接口调用** | 必须要使用自己的 client 进行调用 | 可通过 HTTP 传输,即可通过 CURL 等命令实现调用 |
-| **一致性算法** | Zab 协议 | Raft 算法 |
-| **Watcher 机制** | 较局限,一次性触发器 | 一次 Watch 可以监听所有的事件 |
-| **数据模型** | 基于目录的层次模式 | 参考了 zk 的数据模型,是个扁平的 kv 模型 |
-| **存储** | kv 存储,使用的是 ConcurrentHashMap,内存存储,一般不建议存储较多数据 | kv 存储,使用 bbolt 存储引擎,可以处理几个 GB 的数据。 |
-| **MVCC** | 不支持 | 支持,通过两个 B+ Tree 进行版本控制 |
-| **全局 Session** | 存在缺陷 | 实现更灵活,避免了安全性问题 |
-| **权限校验** | ACL | RBAC |
-| **事务能力** | 提供了简易的事务能力 | 只提供了版本号的检查能力 |
-| **部署维护** | 复杂 | 简单 |
-
-ZooKeeper 在存储性能、全局 Session、Watcher 机制等方面存在一定局限性,越来越多的开源项目在替换 ZooKeeper 为 Raft 实现或其它分布式协调服务,例如:[Kafka Needs No Keeper - Removing ZooKeeper Dependency (confluent.io)](https://www.confluent.io/blog/removing-zookeeper-dependency-in-kafka/)、[Moving Toward a ZooKeeper-Less Apache Pulsar (streamnative.io)](https://streamnative.io/blog/moving-toward-zookeeper-less-apache-pulsar)。
-
-ETCD 相对来说更优秀一些,提供了更稳定的高负载读写能力,对 ZooKeeper 暴露的许多问题进行了改进优化。并且,ETCD 基本能够覆盖 ZooKeeper 的所有应用场景,实现对其的替代。
-
-## 总结
-
-1. ZooKeeper 本身就是一个分布式程序(只要半数以上节点存活,ZooKeeper 就能正常服务)。
-2. 为了保证高可用,最好是以集群形态来部署 ZooKeeper,这样只要集群中大部分机器是可用的(能够容忍一定的机器故障),那么 ZooKeeper 本身仍然是可用的。
-3. ZooKeeper 将数据保存在内存中,这也就保证了 高吞吐量和低延迟(但是内存限制了能够存储的容量不太大,此限制也是保持 znode 中存储的数据量较小的进一步原因)。
-4. ZooKeeper 是高性能的。 在“读”多于“写”的应用程序中尤其地明显,因为“写”会导致所有的服务器间同步状态。(“读”多于“写”是协调服务的典型场景。)
-5. ZooKeeper 有临时节点的概念。 当创建临时节点的客户端会话一直保持活动,瞬时节点就一直存在。而当会话终结时,瞬时节点被删除。持久节点是指一旦这个 znode 被创建了,除非主动进行 znode 的移除操作,否则这个 znode 将一直保存在 ZooKeeper 上。
-6. ZooKeeper 底层其实只提供了两个功能:① 管理(存储、读取)用户程序提交的数据;② 为用户程序提供数据节点监听服务。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 《从 Paxos 到 ZooKeeper 分布式一致性原理与实践》
-- 谈谈 ZooKeeper 的局限性:
-
-
+- **Kafka**: ZooKeeper primarily provides registration for Brokers and Topics, as well as load balancing for multiple Partitions. However, after Kafka 2.8, it introduced the KRaft mode based on the Raft protocol, eliminating the dependency on ZooKeeper and greatly simplifying Kafka's architecture.
+- **HBase**: ZooKeeper ensures that there is only one Master in the entire HBase cluster and provides and saves the status information of region servers (whether they are online).
+- **Hadoop**: ZooKeeper provides high availability support for the Namen
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
index 856378a0cd5..ad6193591ea 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-process-coordination/zookeeper/zookeeper-plus.md
@@ -1,386 +1,44 @@
---
-title: ZooKeeper相关概念总结(进阶)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of ZooKeeper Related Concepts (Advanced)
+category: Distributed
tag:
- ZooKeeper
---
-> [FrancisQ](https://juejin.im/user/5c33853851882525ea106810) 投稿。
+> [FrancisQ](https://juejin.im/user/5c33853851882525ea106810) Contribution.
-## 什么是 ZooKeeper
+## What is ZooKeeper
-`ZooKeeper` 由 `Yahoo` 开发,后来捐赠给了 `Apache` ,现已成为 `Apache` 顶级项目。`ZooKeeper` 是一个开源的分布式应用程序协调服务器,其为分布式系统提供一致性服务。其一致性是通过基于 `Paxos` 算法的 `ZAB` 协议完成的。其主要功能包括:配置维护、分布式同步、集群管理等。
+`ZooKeeper` was developed by `Yahoo` and later donated to `Apache`, and it has now become an Apache top-level project. `ZooKeeper` is an open-source distributed application coordination server that provides consistency services for distributed systems. Its consistency is achieved through the `ZAB` protocol based on the `Paxos` algorithm. Its main functions include configuration maintenance, distributed synchronization, cluster management, and more.
-简单来说, `ZooKeeper` 是一个 **分布式协调服务框架** 。分布式?协调服务?这啥玩意?🤔🤔
+In simple terms, `ZooKeeper` is a **distributed coordination service framework**. Distributed? Coordination service? What is that? 🤔🤔
-其实解释到分布式这个概念的时候,我发现有些同学并不是能把 **分布式和集群** 这两个概念很好的理解透。前段时间有同学和我探讨起分布式的东西,他说分布式不就是加机器吗?一台机器不够用再加一台抗压呗。当然加机器这种说法也无可厚非,你一个分布式系统必定涉及到多个机器,但是你别忘了,计算机学科中还有一个相似的概念—— `Cluster` ,集群不也是加机器吗?但是 集群 和 分布式 其实就是两个完全不同的概念。
+When explaining the concept of distribution, I found that some students do not fully understand the difference between **distributed systems and clusters**. Recently, a student discussed distributed systems with me, saying that isn't distributed just about adding machines? If one machine is not enough, just add another to handle the load. Of course, saying "add machines" is not entirely wrong; a distributed system must involve multiple machines. However, don't forget that there is a similar concept in computer science—`Cluster`. Isn't a cluster also about adding machines? But clusters and distributed systems are actually two completely different concepts.
-比如,我现在有一个秒杀服务,并发量太大单机系统承受不住,那我加几台服务器也 **一样** 提供秒杀服务,这个时候就是 **`Cluster` 集群** 。
+For example, I now have a flash sale service, and the concurrency is too high for a single machine to handle. If I add a few servers, I can still provide the flash sale service; this is a **`Cluster`**.

-但是,我现在换一种方式,我将一个秒杀服务 **拆分成多个子服务** ,比如创建订单服务,增加积分服务,扣优惠券服务等等,**然后我将这些子服务都部署在不同的服务器上** ,这个时候就是 **`Distributed` 分布式** 。
+However, if I take a different approach and **split a flash sale service into multiple sub-services**, such as creating an order service, a points service, a coupon deduction service, etc., **and then deploy these sub-services on different servers**, this is a **`Distributed`** system.

-而我为什么反驳同学所说的分布式就是加机器呢?因为我认为加机器更加适用于构建集群,因为它真是只有加机器。而对于分布式来说,你首先需要将业务进行拆分,然后再加机器(不仅仅是加机器那么简单),同时你还要去解决分布式带来的一系列问题。
+Why do I refute the student's claim that distributed means just adding machines? Because I believe that adding machines is more applicable to building a cluster, as it truly only involves adding machines. In contrast, for a distributed system, you first need to split the business, and then add machines (it's not just as simple as adding machines). At the same time, you also need to solve a series of problems brought by distribution.

-比如各个分布式组件如何协调起来,如何减少各个系统之间的耦合度,分布式事务的处理,如何去配置整个分布式系统等等。`ZooKeeper` 主要就是解决这些问题的。
+For example, how various distributed components coordinate, how to reduce coupling between systems, handling distributed transactions, how to configure the entire distributed system, etc. `ZooKeeper` mainly addresses these issues.
-## 一致性问题
+## Consistency Issues
-设计一个分布式系统必定会遇到一个问题—— **因为分区容忍性(partition tolerance)的存在,就必定要求我们需要在系统可用性(availability)和数据一致性(consistency)中做出权衡** 。这就是著名的 `CAP` 定理。
+Designing a distributed system will inevitably encounter a problem—**due to the existence of partition tolerance, we must make trade-offs between system availability and data consistency**. This is the famous `CAP` theorem.
-理解起来其实很简单,比如说把一个班级作为整个系统,而学生是系统中的一个个独立的子系统。这个时候班里的小红小明偷偷谈恋爱被班里的大嘴巴小花发现了,小花欣喜若狂告诉了周围的人,然后小红小明谈恋爱的消息在班级里传播起来了。当在消息的传播(散布)过程中,你抓到一个同学问他们的情况,如果回答你不知道,那么说明整个班级系统出现了数据不一致的问题(因为小花已经知道这个消息了)。而如果他直接不回答你,因为整个班级有消息在进行传播(为了保证一致性,需要所有人都知道才可提供服务),这个时候就出现了系统的可用性问题。
+Understanding it is actually quite simple. For example, consider a class as the entire system, and the students are independent subsystems within the system. At this point, if Xiaohong and Xiaoming in the class are secretly dating and are discovered by the gossiping Xiaohua, who excitedly tells those around her, the news of Xiaohong and Xiaoming's relationship spreads throughout the class. If you catch a student during the spread of the news and ask them about it, if they respond with "I don't know," it indicates that the entire class system has a data inconsistency issue (because Xiaohua already knows this news). If they simply do not answer you, it means that the entire class is in the process of spreading the news (to ensure consistency, everyone must know before services can be provided), and at this point, a system availability issue arises.

-而上述前者就是 `Eureka` 的处理方式,它保证了 AP(可用性),后者就是我们今天所要讲的 `ZooKeeper` 的处理方式,它保证了 CP(数据一致性)。
+The former is the handling method of `Eureka`, which guarantees AP (availability), while the latter is the handling method of `ZooKeeper`, which guarantees CP (data consistency).
-## 一致性协议和算法
+## Consistency Protocols and Algorithms
-而为了解决数据一致性问题,在科学家和程序员的不断探索中,就出现了很多的一致性协议和算法。比如 2PC(两阶段提交),3PC(三阶段提交),Paxos 算法等等。
-
-这时候请你思考一个问题,同学之间如果采用传纸条的方式去传播消息,那么就会出现一个问题——我咋知道我的小纸条有没有传到我想要传递的那个人手中呢?万一被哪个小家伙给劫持篡改了呢,对吧?
-
-
-
-这个时候就引申出一个概念—— **拜占庭将军问题** 。它意指 **在不可靠信道上试图通过消息传递的方式达到一致性是不可能的**, 所以所有的一致性算法的 **必要前提** 就是安全可靠的消息通道。
-
-而为什么要去解决数据一致性的问题?你想想,如果一个秒杀系统将服务拆分成了下订单和加积分服务,这两个服务部署在不同的机器上了,万一在消息的传播过程中积分系统宕机了,总不能你这边下了订单却没加积分吧?你总得保证两边的数据需要一致吧?
-
-### 2PC(两阶段提交)
-
-两阶段提交是一种保证分布式系统数据一致性的协议,现在很多数据库都是采用的两阶段提交协议来完成 **分布式事务** 的处理。
-
-在介绍 2PC 之前,我们先来想想分布式事务到底有什么问题呢?
-
-还拿秒杀系统的下订单和加积分两个系统来举例吧(我想你们可能都吐了 🤮🤮🤮),我们此时下完订单会发个消息给积分系统告诉它下面该增加积分了。如果我们仅仅是发送一个消息也不收回复,那么我们的订单系统怎么能知道积分系统的收到消息的情况呢?如果我们增加一个收回复的过程,那么当积分系统收到消息后返回给订单系统一个 `Response` ,但在中间出现了网络波动,那个回复消息没有发送成功,订单系统是不是以为积分系统消息接收失败了?它是不是会回滚事务?但此时积分系统是成功收到消息的,它就会去处理消息然后给用户增加积分,这个时候就会出现积分加了但是订单没下成功。
-
-所以我们所需要解决的是在分布式系统中,整个调用链中,我们所有服务的数据处理要么都成功要么都失败,即所有服务的 **原子性问题** 。
-
-在两阶段提交中,主要涉及到两个角色,分别是协调者和参与者。
-
-第一阶段:当要执行一个分布式事务的时候,事务发起者首先向协调者发起事务请求,然后协调者会给所有参与者发送 `prepare` 请求(其中包括事务内容)告诉参与者你们需要执行事务了,如果能执行我发的事务内容那么就先执行但不提交,执行后请给我回复。然后参与者收到 `prepare` 消息后,他们会开始执行事务(但不提交),并将 `Undo` 和 `Redo` 信息记入事务日志中,之后参与者就向协调者反馈是否准备好了。
-
-第二阶段:第二阶段主要是协调者根据参与者反馈的情况来决定接下来是否可以进行事务的提交操作,即提交事务或者回滚事务。
-
-比如这个时候 **所有的参与者** 都返回了准备好了的消息,这个时候就进行事务的提交,协调者此时会给所有的参与者发送 **`Commit` 请求** ,当参与者收到 `Commit` 请求的时候会执行前面执行的事务的 **提交操作** ,提交完毕之后将给协调者发送提交成功的响应。
-
-而如果在第一阶段并不是所有参与者都返回了准备好了的消息,那么此时协调者将会给所有参与者发送 **回滚事务的 `rollback` 请求**,参与者收到之后将会 **回滚它在第一阶段所做的事务处理** ,然后再将处理情况返回给协调者,最终协调者收到响应后便给事务发起者返回处理失败的结果。
-
-
-
-个人觉得 2PC 实现得还是比较鸡肋的,因为事实上它只解决了各个事务的原子性问题,随之也带来了很多的问题。
-
-
-
-- **单点故障问题**,如果协调者挂了那么整个系统都处于不可用的状态了。
-- **阻塞问题**,即当协调者发送 `prepare` 请求,参与者收到之后如果能处理那么它将会进行事务的处理但并不提交,这个时候会一直占用着资源不释放,如果此时协调者挂了,那么这些资源都不会再释放了,这会极大影响性能。
-- **数据不一致问题**,比如当第二阶段,协调者只发送了一部分的 `commit` 请求就挂了,那么也就意味着,收到消息的参与者会进行事务的提交,而后面没收到的则不会进行事务提交,那么这时候就会产生数据不一致性问题。
-
-### 3PC(三阶段提交)
-
-因为 2PC 存在的一系列问题,比如单点,容错机制缺陷等等,从而产生了 **3PC(三阶段提交)** 。那么这三阶段又分别是什么呢?
-
-> 千万不要吧 PC 理解成个人电脑了,其实他们是 phase-commit 的缩写,即阶段提交。
-
-1. **CanCommit 阶段**:协调者向所有参与者发送 `CanCommit` 请求,参与者收到请求后会根据自身情况查看是否能执行事务,如果可以则返回 YES 响应并进入预备状态,否则返回 NO 。
-2. **PreCommit 阶段**:协调者根据参与者返回的响应来决定是否可以进行下面的 `PreCommit` 操作。如果上面参与者返回的都是 YES,那么协调者将向所有参与者发送 `PreCommit` 预提交请求,**参与者收到预提交请求后,会进行事务的执行操作,并将 `Undo` 和 `Redo` 信息写入事务日志中** ,最后如果参与者顺利执行了事务则给协调者返回成功的响应。如果在第一阶段协调者收到了 **任何一个 NO** 的信息,或者 **在一定时间内** 并没有收到全部的参与者的响应,那么就会中断事务,它会向所有参与者发送中断请求(abort),参与者收到中断请求之后会立即中断事务,或者在一定时间内没有收到协调者的请求,它也会中断事务。
-3. **DoCommit 阶段**:这个阶段其实和 `2PC` 的第二阶段差不多,如果协调者收到了所有参与者在 `PreCommit` 阶段的 YES 响应,那么协调者将会给所有参与者发送 `DoCommit` 请求,**参与者收到 `DoCommit` 请求后则会进行事务的提交工作**,完成后则会给协调者返回响应,协调者收到所有参与者返回的事务提交成功的响应之后则完成事务。若协调者在 `PreCommit` 阶段 **收到了任何一个 NO 或者在一定时间内没有收到所有参与者的响应** ,那么就会进行中断请求的发送,参与者收到中断请求后则会 **通过上面记录的回滚日志** 来进行事务的回滚操作,并向协调者反馈回滚状况,协调者收到参与者返回的消息后,中断事务。
-
-
-
-> 这里是 `3PC` 在成功的环境下的流程图,你可以看到 `3PC` 在很多地方进行了超时中断的处理,比如协调者在指定时间内未收到全部的确认消息则进行事务中断的处理,这样能 **减少同步阻塞的时间** 。还有需要注意的是,**`3PC` 在 `DoCommit` 阶段参与者如未收到协调者发送的提交事务的请求,它会在一定时间内进行事务的提交**。为什么这么做呢?是因为这个时候我们肯定**保证了在第一阶段所有的协调者全部返回了可以执行事务的响应**,这个时候我们有理由**相信其他系统都能进行事务的执行和提交**,所以**不管**协调者有没有发消息给参与者,进入第三阶段参与者都会进行事务的提交操作。
-
-总之,`3PC` 通过一系列的超时机制很好的缓解了阻塞问题,但是最重要的一致性并没有得到根本的解决,比如在 `DoCommit` 阶段,当一个参与者收到了请求之后其他参与者和协调者挂了或者出现了网络分区,这个时候收到消息的参与者都会进行事务提交,这就会出现数据不一致性问题。
-
-所以,要解决一致性问题还需要靠 `Paxos` 算法 ⭐️ ⭐️ ⭐️ 。
-
-### `Paxos` 算法
-
-`Paxos` 算法是基于**消息传递且具有高度容错特性的一致性算法**,是目前公认的解决分布式一致性问题最有效的算法之一,**其解决的问题就是在分布式系统中如何就某个值(决议)达成一致** 。
-
-在 `Paxos` 中主要有三个角色,分别为 `Proposer提案者`、`Acceptor表决者`、`Learner学习者`。`Paxos` 算法和 `2PC` 一样,也有两个阶段,分别为 `Prepare` 和 `accept` 阶段。
-
-#### prepare 阶段
-
-- `Proposer提案者`:负责提出 `proposal`,每个提案者在提出提案时都会首先获取到一个 **具有全局唯一性的、递增的提案编号 N**,即在整个集群中是唯一的编号 N,然后将该编号赋予其要提出的提案,在**第一阶段是只将提案编号发送给所有的表决者**。
-- `Acceptor表决者`:每个表决者在 `accept` 某提案后,会将该提案编号 N 记录在本地,这样每个表决者中保存的已经被 accept 的提案中会存在一个**编号最大的提案**,其编号假设为 `maxN`。每个表决者仅会 `accept` 编号大于自己本地 `maxN` 的提案,在批准提案时表决者会将以前接受过的最大编号的提案作为响应反馈给 `Proposer` 。
-
-> 下面是 `prepare` 阶段的流程图,你可以对照着参考一下。
-
-
-
-#### accept 阶段
-
-当一个提案被 `Proposer` 提出后,如果 `Proposer` 收到了超过半数的 `Acceptor` 的批准(`Proposer` 本身同意),那么此时 `Proposer` 会给所有的 `Acceptor` 发送真正的提案(你可以理解为第一阶段为试探),这个时候 `Proposer` 就会发送提案的内容和提案编号。
-
-表决者收到提案请求后会再次比较本身已经批准过的最大提案编号和该提案编号,如果该提案编号 **大于等于** 已经批准过的最大提案编号,那么就 `accept` 该提案(此时执行提案内容但不提交),随后将情况返回给 `Proposer` 。如果不满足则不回应或者返回 NO 。
-
-
-
-当 `Proposer` 收到超过半数的 `accept` ,那么它这个时候会向所有的 `acceptor` 发送提案的提交请求。需要注意的是,因为上述仅仅是超过半数的 `acceptor` 批准执行了该提案内容,其他没有批准的并没有执行该提案内容,所以这个时候需要**向未批准的 `acceptor` 发送提案内容和提案编号并让它无条件执行和提交**,而对于前面已经批准过该提案的 `acceptor` 来说 **仅仅需要发送该提案的编号** ,让 `acceptor` 执行提交就行了。
-
-
-
-而如果 `Proposer` 如果没有收到超过半数的 `accept` 那么它将会将 **递增** 该 `Proposal` 的编号,然后 **重新进入 `Prepare` 阶段** 。
-
-> 对于 `Learner` 来说如何去学习 `Acceptor` 批准的提案内容,这有很多方式,读者可以自己去了解一下,这里不做过多解释。
-
-#### paxos 算法的死循环问题
-
-其实就有点类似于两个人吵架,小明说我是对的,小红说我才是对的,两个人据理力争的谁也不让谁 🤬🤬。
-
-比如说,此时提案者 P1 提出一个方案 M1,完成了 `Prepare` 阶段的工作,这个时候 `acceptor` 则批准了 M1,但是此时提案者 P2 同时也提出了一个方案 M2,它也完成了 `Prepare` 阶段的工作。然后 P1 的方案已经不能在第二阶段被批准了(因为 `acceptor` 已经批准了比 M1 更大的 M2),所以 P1 自增方案变为 M3 重新进入 `Prepare` 阶段,然后 `acceptor` ,又批准了新的 M3 方案,它又不能批准 M2 了,这个时候 M2 又自增进入 `Prepare` 阶段。。。
-
-就这样无休无止的永远提案下去,这就是 `paxos` 算法的死循环问题。
-
-
-
-那么如何解决呢?很简单,人多了容易吵架,我现在 **就允许一个能提案** 就行了。
-
-## 引出 ZAB
-
-### Zookeeper 架构
-
-作为一个优秀高效且可靠的分布式协调框架,`ZooKeeper` 在解决分布式数据一致性问题时并没有直接使用 `Paxos` ,而是专门定制了一致性协议叫做 `ZAB(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)` 原子广播协议,该协议能够很好地支持 **崩溃恢复** 。
-
-
-
-### ZAB 中的三个角色
-
-和介绍 `Paxos` 一样,在介绍 `ZAB` 协议之前,我们首先来了解一下在 `ZAB` 中三个主要的角色,`Leader 领导者`、`Follower跟随者`、`Observer观察者` 。
-
-- `Leader`:集群中 **唯一的写请求处理者** ,能够发起投票(投票也是为了进行写请求)。
-- `Follower`:能够接收客户端的请求,如果是读请求则可以自己处理,**如果是写请求则要转发给 `Leader`** 。在选举过程中会参与投票,**有选举权和被选举权** 。
-- `Observer`:就是没有选举权和被选举权的 `Follower` 。
-
-在 `ZAB` 协议中对 `zkServer`(即上面我们说的三个角色的总称) 还有两种模式的定义,分别是 **消息广播** 和 **崩溃恢复** 。
-
-### 消息广播模式
-
-说白了就是 `ZAB` 协议是如何处理写请求的,上面我们不是说只有 `Leader` 能处理写请求嘛?那么我们的 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 是不是也需要 **同步更新数据** 呢?总不能数据只在 `Leader` 中更新了,其他角色都没有得到更新吧?
-
-不就是 **在整个集群中保持数据的一致性** 嘛?如果是你,你会怎么做呢?
-
-废话,第一步肯定需要 `Leader` 将写请求 **广播** 出去呀,让 `Leader` 问问 `Followers` 是否同意更新,如果超过半数以上的同意那么就进行 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 的更新(和 `Paxos` 一样)。当然这么说有点虚,画张图理解一下。
-
-
-
-嗯。。。看起来很简单,貌似懂了 🤥🤥🤥。这两个 `Queue` 哪冒出来的?答案是 **`ZAB` 需要让 `Follower` 和 `Observer` 保证顺序性** 。何为顺序性,比如我现在有一个写请求 A,此时 `Leader` 将请求 A 广播出去,因为只需要半数同意就行,所以可能这个时候有一个 `Follower` F1 因为网络原因没有收到,而 `Leader` 又广播了一个请求 B,因为网络原因,F1 竟然先收到了请求 B 然后才收到了请求 A,这个时候请求处理的顺序不同就会导致数据的不同,从而 **产生数据不一致问题** 。
-
-所以在 `Leader` 这端,它为每个其他的 `zkServer` 准备了一个 **队列** ,采用先进先出的方式发送消息。由于协议是 **通过 `TCP`** 来进行网络通信的,保证了消息的发送顺序性,接受顺序性也得到了保证。
-
-除此之外,在 `ZAB` 中还定义了一个 **全局单调递增的事务 ID `ZXID`** ,它是一个 64 位 long 型,其中高 32 位表示 `epoch` 年代,低 32 位表示事务 id。`epoch` 是会根据 `Leader` 的变化而变化的,当一个 `Leader` 挂了,新的 `Leader` 上位的时候,年代(`epoch`)就变了。而低 32 位可以简单理解为递增的事务 id。
-
-定义这个的原因也是为了顺序性,每个 `proposal` 在 `Leader` 中生成后需要 **通过其 `ZXID` 来进行排序** ,才能得到处理。
-
-### 崩溃恢复模式
-
-说到崩溃恢复我们首先要提到 `ZAB` 中的 `Leader` 选举算法,当系统出现崩溃影响最大应该是 `Leader` 的崩溃,因为我们只有一个 `Leader` ,所以当 `Leader` 出现问题的时候我们势必需要重新选举 `Leader` 。
-
-`Leader` 选举可以分为两个不同的阶段,第一个是我们提到的 `Leader` 宕机需要重新选举,第二则是当 `Zookeeper` 启动时需要进行系统的 `Leader` 初始化选举。下面我先来介绍一下 `ZAB` 是如何进行初始化选举的。
-
-假设我们集群中有 3 台机器,那也就意味着我们需要两台以上同意(超过半数)。比如这个时候我们启动了 `server1` ,它会首先 **投票给自己** ,投票内容为服务器的 `myid` 和 `ZXID` ,因为初始化所以 `ZXID` 都为 0,此时 `server1` 发出的投票为 (1,0)。但此时 `server1` 的投票仅为 1,所以不能作为 `Leader` ,此时还在选举阶段所以整个集群处于 **`Looking` 状态**。
-
-接着 `server2` 启动了,它首先也会将投票选给自己(2,0),并将投票信息广播出去(`server1`也会,只是它那时没有其他的服务器了),`server1` 在收到 `server2` 的投票信息后会将投票信息与自己的作比较。**首先它会比较 `ZXID` ,`ZXID` 大的优先为 `Leader`,如果相同则比较 `myid`,`myid` 大的优先作为 `Leader`**。所以此时`server1` 发现 `server2` 更适合做 `Leader`,它就会将自己的投票信息更改为(2,0)然后再广播出去,之后`server2` 收到之后发现和自己的一样无需做更改,并且自己的 **投票已经超过半数** ,则 **确定 `server2` 为 `Leader`**,`server1` 也会将自己服务器设置为 `Following` 变为 `Follower`。整个服务器就从 `Looking` 变为了正常状态。
-
-当 `server3` 启动发现集群没有处于 `Looking` 状态时,它会直接以 `Follower` 的身份加入集群。
-
-还是前面三个 `server` 的例子,如果在整个集群运行的过程中 `server2` 挂了,那么整个集群会如何重新选举 `Leader` 呢?其实和初始化选举差不多。
-
-首先毫无疑问的是剩下的两个 `Follower` 会将自己的状态 **从 `Following` 变为 `Looking` 状态** ,然后每个 `server` 会向初始化投票一样首先给自己投票(这不过这里的 `zxid` 可能不是 0 了,这里为了方便随便取个数字)。
-
-假设 `server1` 给自己投票为(1,99),然后广播给其他 `server`,`server3` 首先也会给自己投票(3,95),然后也广播给其他 `server`。`server1` 和 `server3` 此时会收到彼此的投票信息,和一开始选举一样,他们也会比较自己的投票和收到的投票(`zxid` 大的优先,如果相同那么就 `myid` 大的优先)。这个时候 `server1` 收到了 `server3` 的投票发现没自己的合适故不变,`server3` 收到 `server1` 的投票结果后发现比自己的合适于是更改投票为(1,99)然后广播出去,最后 `server1` 收到了发现自己的投票已经超过半数就把自己设为 `Leader`,`server3` 也随之变为 `Follower`。
-
-> 请注意 `ZooKeeper` 为什么要设置奇数个结点?比如这里我们是三个,挂了一个我们还能正常工作,挂了两个我们就不能正常工作了(已经没有超过半数的节点数了,所以无法进行投票等操作了)。而假设我们现在有四个,挂了一个也能工作,**但是挂了两个也不能正常工作了**,这是和三个一样的,而三个比四个还少一个,带来的效益是一样的,所以 `Zookeeper` 推荐奇数个 `server` 。
-
-那么说完了 `ZAB` 中的 `Leader` 选举方式之后我们再来了解一下 **崩溃恢复** 是什么玩意?
-
-其实主要就是 **当集群中有机器挂了,我们整个集群如何保证数据一致性?**
-
-如果只是 `Follower` 挂了,而且挂的没超过半数的时候,因为我们一开始讲了在 `Leader` 中会维护队列,所以不用担心后面的数据没接收到导致数据不一致性。
-
-如果 `Leader` 挂了那就麻烦了,我们肯定需要先暂停服务变为 `Looking` 状态然后进行 `Leader` 的重新选举(上面我讲过了),但这个就要分为两种情况了,分别是 **确保已经被 Leader 提交的提案最终能够被所有的 Follower 提交** 和 **跳过那些已经被丢弃的提案** 。
-
-确保已经被 Leader 提交的提案最终能够被所有的 Follower 提交是什么意思呢?
-
-假设 `Leader (server2)` 发送 `commit` 请求(忘了请看上面的消息广播模式),他发送给了 `server3`,然后要发给 `server1` 的时候突然挂了。这个时候重新选举的时候我们如果把 `server1` 作为 `Leader` 的话,那么肯定会产生数据不一致性,因为 `server3` 肯定会提交刚刚 `server2` 发送的 `commit` 请求的提案,而 `server1` 根本没收到所以会丢弃。
-
-
-
-那怎么解决呢?
-
-聪明的同学肯定会质疑,**这个时候 `server1` 已经不可能成为 `Leader` 了,因为 `server1` 和 `server3` 进行投票选举的时候会比较 `ZXID` ,而此时 `server3` 的 `ZXID` 肯定比 `server1` 的大了**。(不理解可以看前面的选举算法)
-
-那么跳过那些已经被丢弃的提案又是什么意思呢?
-
-假设 `Leader (server2)` 此时同意了提案 N1,自身提交了这个事务并且要发送给所有 `Follower` 要 `commit` 的请求,却在这个时候挂了,此时肯定要重新进行 `Leader` 的选举,比如说此时选 `server1` 为 `Leader` (这无所谓)。但是过了一会,这个 **挂掉的 `Leader` 又重新恢复了** ,此时它肯定会作为 `Follower` 的身份进入集群中,需要注意的是刚刚 `server2` 已经同意提交了提案 N1,但其他 `server` 并没有收到它的 `commit` 信息,所以其他 `server` 不可能再提交这个提案 N1 了,这样就会出现数据不一致性问题了,所以 **该提案 N1 最终需要被抛弃掉** 。
-
-
-
-## Zookeeper 的几个理论知识
-
-了解了 `ZAB` 协议还不够,它仅仅是 `Zookeeper` 内部实现的一种方式,而我们如何通过 `Zookeeper` 去做一些典型的应用场景呢?比如说集群管理,分布式锁,`Master` 选举等等。
-
-这就涉及到如何使用 `Zookeeper` 了,但在使用之前我们还需要掌握几个概念。比如 `Zookeeper` 的 **数据模型**、**会话机制**、**ACL**、**Watcher 机制** 等等。
-
-### 数据模型
-
-`zookeeper` 数据存储结构与标准的 `Unix` 文件系统非常相似,都是在根节点下挂很多子节点(树型)。但是 `zookeeper` 中没有文件系统中目录与文件的概念,而是 **使用了 `znode` 作为数据节点** 。`znode` 是 `zookeeper` 中的最小数据单元,每个 `znode` 上都可以保存数据,同时还可以挂载子节点,形成一个树形化命名空间。
-
-
-
-每个 `znode` 都有自己所属的 **节点类型** 和 **节点状态**。
-
-其中节点类型可以分为 **持久节点**、**持久顺序节点**、**临时节点** 和 **临时顺序节点**。
-
-- 持久节点:一旦创建就一直存在,直到将其删除。
-- 持久顺序节点:一个父节点可以为其子节点 **维护一个创建的先后顺序** ,这个顺序体现在 **节点名称** 上,是节点名称后自动添加一个由 10 位数字组成的数字串,从 0 开始计数。
-- 临时节点:临时节点的生命周期是与 **客户端会话** 绑定的,**会话消失则节点消失** 。临时节点 **只能做叶子节点** ,不能创建子节点。
-- 临时顺序节点:父节点可以创建一个维持了顺序的临时节点(和前面的持久顺序性节点一样)。
-
-节点状态中包含了很多节点的属性比如 `czxid`、`mzxid` 等等,在 `zookeeper` 中是使用 `Stat` 这个类来维护的。下面我列举一些属性解释。
-
-- `czxid`:`Created ZXID`,该数据节点被 **创建** 时的事务 ID。
-- `mzxid`:`Modified ZXID`,节点 **最后一次被更新时** 的事务 ID。
-- `ctime`:`Created Time`,该节点被创建的时间。
-- `mtime`:`Modified Time`,该节点最后一次被修改的时间。
-- `version`:节点的版本号。
-- `cversion`:**子节点** 的版本号。
-- `aversion`:节点的 `ACL` 版本号。
-- `ephemeralOwner`:创建该节点的会话的 `sessionID` ,如果该节点为持久节点,该值为 0。
-- `dataLength`:节点数据内容的长度。
-- `numChildre`:该节点的子节点个数,如果为临时节点为 0。
-- `pzxid`:该节点子节点列表最后一次被修改时的事务 ID,注意是子节点的 **列表** ,不是内容。
-
-### 会话
-
-我想这个对于后端开发的朋友肯定不陌生,不就是 `session` 吗?只不过 `zk` 客户端和服务端是通过 **`TCP` 长连接** 维持的会话机制,其实对于会话来说你可以理解为 **保持连接状态** 。
-
-在 `zookeeper` 中,会话还有对应的事件,比如 `CONNECTION_LOSS 连接丢失事件`、`SESSION_MOVED 会话转移事件`、`SESSION_EXPIRED 会话超时失效事件` 。
-
-### ACL
-
-`ACL` 为 `Access Control Lists` ,它是一种权限控制。在 `zookeeper` 中定义了 5 种权限,它们分别为:
-
-- `CREATE`:创建子节点的权限。
-- `READ`:获取节点数据和子节点列表的权限。
-- `WRITE`:更新节点数据的权限。
-- `DELETE`:删除子节点的权限。
-- `ADMIN`:设置节点 ACL 的权限。
-
-### Watcher 机制
-
-`Watcher` 为事件监听器,是 `zk` 非常重要的一个特性,很多功能都依赖于它,它有点类似于订阅的方式,即客户端向服务端 **注册** 指定的 `watcher` ,当服务端符合了 `watcher` 的某些事件或要求则会 **向客户端发送事件通知** ,客户端收到通知后找到自己定义的 `Watcher` 然后 **执行相应的回调方法** 。
-
-
-
-## Zookeeper 的几个典型应用场景
-
-前面说了这么多的理论知识,你可能听得一头雾水,这些玩意有啥用?能干啥事?别急,听我慢慢道来。
-
-
-
-### 选主
-
-还记得上面我们的所说的临时节点吗?因为 `Zookeeper` 的强一致性,能够很好地在保证 **在高并发的情况下保证节点创建的全局唯一性** (即无法重复创建同样的节点)。
-
-利用这个特性,我们可以 **让多个客户端创建一个指定的节点** ,创建成功的就是 `master`。
-
-但是,如果这个 `master` 挂了怎么办???
-
-你想想为什么我们要创建临时节点?还记得临时节点的生命周期吗?`master` 挂了是不是代表会话断了?会话断了是不是意味着这个节点没了?还记得 `watcher` 吗?我们是不是可以 **让其他不是 `master` 的节点监听节点的状态** ,比如说我们监听这个临时节点的父节点,如果子节点个数变了就代表 `master` 挂了,这个时候我们 **触发回调函数进行重新选举** ,或者我们直接监听节点的状态,我们可以通过节点是否已经失去连接来判断 `master` 是否挂了等等。
-
-
-
-总的来说,我们可以完全 **利用 临时节点、节点状态 和 `watcher` 来实现选主的功能**,临时节点主要用来选举,节点状态和`watcher` 可以用来判断 `master` 的活性和进行重新选举。
-
-### 数据发布/订阅
-
-还记得 Zookeeper 的 `Watcher` 机制吗? Zookeeper 通过这种推拉相结合的方式实现客户端与服务端的交互:客户端向服务端注册节点,一旦相应节点的数据变更,服务端就会向“监听”该节点的客户端发送 `Watcher` 事件通知,客户端接收到通知后需要 **主动** 到服务端获取最新的数据。基于这种方式,Zookeeper 实现了 **数据发布/订阅** 功能。
-
-一个典型的应用场景为 **全局配置信息的集中管理**。 客户端在启动时会主动到 Zookeeper 服务端获取配置信息,同时 **在指定节点注册一个** `Watcher` **监听**。当配置信息发生变更,服务端通知所有订阅的客户端重新获取配置信息,实现配置信息的实时更新。
-
-上面所提到的全局配置信息通常包括机器列表信息、运行时的开关配置、数据库配置信息等。需要注意的是,这类全局配置信息通常具备以下特性:
-
-- 数据量较小
-- 数据内容在运行时动态变化
-- 集群中机器共享一致配置
-
-### 负载均衡
-
-可以通过 Zookeeper 的 **临时节点** 实现负载均衡。回顾一下临时节点的特性:当创建节点的客户端与服务端之间断开连接,即客户端会话(session)消失时,对应节点也会自动消失。因此,我们可以使用临时节点来维护 Server 的地址列表,从而保证请求不会被分配到已停机的服务上。
-
-具体地,我们需要在集群的每一个 Server 中都使用 Zookeeper 客户端连接 Zookeeper 服务端,同时用 Server **自身的地址信息**在服务端指定目录下创建临时节点。当客户端请求调用集群服务时,首先通过 Zookeeper 获取该目录下的节点列表 (即所有可用的 Server),随后根据不同的负载均衡策略将请求转发到某一具体的 Server。
-
-### 分布式锁
-
-分布式锁的实现方式有很多种,比如 `Redis`、数据库、`zookeeper` 等。个人认为 `zookeeper` 在实现分布式锁这方面是非常非常简单的。
-
-上面我们已经提到过了 **zk 在高并发的情况下保证节点创建的全局唯一性**,这玩意一看就知道能干啥了。实现互斥锁呗,又因为能在分布式的情况下,所以能实现分布式锁呗。
-
-如何实现呢?这玩意其实跟选主基本一样,我们也可以利用临时节点的创建来实现。
-
-首先肯定是如何获取锁,因为创建节点的唯一性,我们可以让多个客户端同时创建一个临时节点,**创建成功的就说明获取到了锁** 。然后没有获取到锁的客户端也像上面选主的非主节点创建一个 `watcher` 进行节点状态的监听,如果这个互斥锁被释放了(可能获取锁的客户端宕机了,或者那个客户端主动释放了锁)可以调用回调函数重新获得锁。
-
-> `zk` 中不需要向 `redis` 那样考虑锁得不到释放的问题了,因为当客户端挂了,节点也挂了,锁也释放了。是不是很简单?
-
-那能不能使用 `zookeeper` 同时实现 **共享锁和独占锁** 呢?答案是可以的,不过稍微有点复杂而已。
-
-还记得 **有序的节点** 吗?
-
-这个时候我规定所有创建节点必须有序,当你是读请求(要获取共享锁)的话,如果 **没有比自己更小的节点,或比自己小的节点都是读请求** ,则可以获取到读锁,然后就可以开始读了。**若比自己小的节点中有写请求** ,则当前客户端无法获取到读锁,只能等待前面的写请求完成。
-
-如果你是写请求(获取独占锁),若 **没有比自己更小的节点** ,则表示当前客户端可以直接获取到写锁,对数据进行修改。若发现 **有比自己更小的节点,无论是读操作还是写操作,当前客户端都无法获取到写锁** ,等待所有前面的操作完成。
-
-这就很好地同时实现了共享锁和独占锁,当然还有优化的地方,比如当一个锁得到释放它会通知所有等待的客户端从而造成 **羊群效应** 。此时你可以通过让等待的节点只监听他们前面的节点。
-
-具体怎么做呢?其实也很简单,你可以让 **读请求监听比自己小的最后一个写请求节点,写请求只监听比自己小的最后一个节点** ,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自己去研究一下。
-
-### 命名服务
-
-如何给一个对象设置 ID,大家可能都会想到 `UUID`,但是 `UUID` 最大的问题就在于它太长了。。。(太长不一定是好事,嘿嘿嘿)。那么在条件允许的情况下,我们能不能使用 `zookeeper` 来实现呢?
-
-我们之前提到过 `zookeeper` 是通过 **树形结构** 来存储数据节点的,那也就是说,对于每个节点的 **全路径**,它必定是唯一的,我们可以使用节点的全路径作为命名方式了。而且更重要的是,路径是我们可以自己定义的,这对于我们对有些有语意的对象的 ID 设置可以更加便于理解。
-
-### 集群管理和注册中心
-
-看到这里是不是觉得 `zookeeper` 实在是太强大了,它怎么能这么能干!
-
-别急,它能干的事情还很多呢。可能我们会有这样的需求,我们需要了解整个集群中有多少机器在工作,我们想对集群中的每台机器的运行时状态进行数据采集,对集群中机器进行上下线操作等等。
-
-而 `zookeeper` 天然支持的 `watcher` 和 临时节点能很好的实现这些需求。我们可以为每条机器创建临时节点,并监控其父节点,如果子节点列表有变动(我们可能创建删除了临时节点),那么我们可以使用在其父节点绑定的 `watcher` 进行状态监控和回调。
-
-
-
-至于注册中心也很简单,我们同样也是让 **服务提供者** 在 `zookeeper` 中创建一个临时节点并且将自己的 `ip、port、调用方式` 写入节点,当 **服务消费者** 需要进行调用的时候会 **通过注册中心找到相应的服务的地址列表(IP 端口什么的)** ,并缓存到本地(方便以后调用),当消费者调用服务时,不会再去请求注册中心,而是直接通过负载均衡算法从地址列表中取一个服务提供者的服务器调用服务。
-
-当服务提供者的某台服务器宕机或下线时,相应的地址会从服务提供者地址列表中移除。同时,注册中心会将新的服务地址列表发送给服务消费者的机器并缓存在消费者本机(当然你可以让消费者进行节点监听,我记得 `Eureka` 会先试错,然后再更新)。
-
-
-
-## 总结
-
-看到这里的同学实在是太有耐心了 👍👍👍 不知道大家是否还记得我讲了什么 😒。
-
-
-
-这篇文章中我带大家入门了 `zookeeper` 这个强大的分布式协调框架。现在我们来简单梳理一下整篇文章的内容。
-
-- 分布式与集群的区别
-
-- `2PC`、`3PC` 以及 `paxos` 算法这些一致性框架的原理和实现。
-
-- `zookeeper` 专门的一致性算法 `ZAB` 原子广播协议的内容(`Leader` 选举、崩溃恢复、消息广播)。
-
-- `zookeeper` 中的一些基本概念,比如 `ACL`,数据节点,会话,`watcher`机制等等。
-
-- `zookeeper` 的典型应用场景,比如选主,注册中心等等。
-
- 如果忘了可以回去看看再次理解一下,如果有疑问和建议欢迎提出 🤝🤝🤝。
-
-
+To solve the data consistency problem, many consistency protocols
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
index fa4c83c743c..decdd90f1fe 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/distributed-transaction.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
---
-title: 分布式事务常见解决方案总结(付费)
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Solutions for Distributed Transactions (Paid)
+category: Distributed
---
-**分布式事务** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了《Java 面试指北》中。
+**Distributed Transactions** interview questions are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to view detailed information and joining methods) and have been organized into the "Java Interview Guide."

diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
index 36a2fa54d4a..eeb5fbb9193 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/cap-and-base-theorem.md
@@ -1,161 +1,161 @@
---
-title: CAP & BASE理论详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Explanation of CAP & BASE Theories
+category: Distributed Systems
tag:
- - 分布式理论
+ - Distributed Theory
---
-经历过技术面试的小伙伴想必对 CAP & BASE 这个两个理论已经再熟悉不过了!
+Those who have experienced technical interviews are likely very familiar with the CAP & BASE theories!
-我当年参加面试的时候,不夸张地说,只要问到分布式相关的内容,面试官几乎是必定会问这两个分布式相关的理论。一是因为这两个分布式基础理论是学习分布式知识的必备前置基础,二是因为很多面试官自己比较熟悉这两个理论(方便提问)。
+When I participated in interviews back then, I can say without exaggeration that as soon as distributed-related topics came up, interviewers almost invariably asked about these two distributed theories. This is partly because these two foundational theories are essential prerequisites for learning about distributed systems, and partly because many interviewers themselves are familiar with these theories (making it easier to ask questions).
-我们非常有必要将这两个理论搞懂,并且能够用自己的理解给别人讲出来。
+It is very necessary for us to understand these two theories and be able to explain them to others in our own words.
-## CAP 理论
+## CAP Theory
-[CAP 理论/定理](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86)起源于 2000 年,由加州大学伯克利分校的 Eric Brewer 教授在分布式计算原理研讨会(PODC)上提出,因此 CAP 定理又被称作 **布鲁尔定理(Brewer’s theorem)**
+[CAP Theorem](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86) originated in 2000, proposed by Professor Eric Brewer from the University of California, Berkeley at the Principles of Distributed Computing (PODC) symposium. Therefore, the CAP theorem is also known as **Brewer's theorem**.
-2 年后,麻省理工学院的 Seth Gilbert 和 Nancy Lynch 发表了布鲁尔猜想的证明,CAP 理论正式成为分布式领域的定理。
+Two years later, Seth Gilbert and Nancy Lynch from MIT published a proof of Brewer's conjecture, and the CAP theory officially became a theorem in the distributed field.
-### 简介
+### Introduction
-**CAP** 也就是 **Consistency(一致性)**、**Availability(可用性)**、**Partition Tolerance(分区容错性)** 这三个单词首字母组合。
+**CAP** is a combination of the first letters of **Consistency**, **Availability**, and **Partition Tolerance**.

-CAP 理论的提出者布鲁尔在提出 CAP 猜想的时候,并没有详细定义 **Consistency**、**Availability**、**Partition Tolerance** 三个单词的明确定义。
+When Brewer proposed the CAP conjecture, he did not provide a detailed definition of **Consistency**, **Availability**, and **Partition Tolerance**.
-因此,对于 CAP 的民间解读有很多,一般比较被大家推荐的是下面 👇 这种版本的解读。
+As a result, there are many informal interpretations of CAP, with the most commonly recommended interpretation being the one below 👇.
-在理论计算机科学中,CAP 定理(CAP theorem)指出对于一个分布式系统来说,当设计读写操作时,只能同时满足以下三点中的两个:
+In theoretical computer science, the CAP theorem states that for a distributed system, when designing read and write operations, it can only simultaneously satisfy two of the following three points:
-- **一致性(Consistency)** : 所有节点访问同一份最新的数据副本
-- **可用性(Availability)**: 非故障的节点在合理的时间内返回合理的响应(不是错误或者超时的响应)。
-- **分区容错性(Partition Tolerance)** : 分布式系统出现网络分区的时候,仍然能够对外提供服务。
+- **Consistency**: All nodes access the same up-to-date data copy.
+- **Availability**: Non-faulty nodes return reasonable responses (not errors or timeouts) within a reasonable time.
+- **Partition Tolerance**: The system continues to provide services despite network partitions.
-**什么是网络分区?**
+**What is a network partition?**
-分布式系统中,多个节点之间的网络本来是连通的,但是因为某些故障(比如部分节点网络出了问题)某些节点之间不连通了,整个网络就分成了几块区域,这就叫 **网络分区**。
+In a distributed system, multiple nodes are originally connected, but due to some faults (like issues with part of the node's network), some nodes become unreachable, and the entire network splits into several regions. This is called a **network partition**.

-### 不是所谓的“3 选 2”
+### Not a "choose 2 of 3"
-大部分人解释这一定律时,常常简单的表述为:“一致性、可用性、分区容忍性三者你只能同时达到其中两个,不可能同时达到”。实际上这是一个非常具有误导性质的说法,而且在 CAP 理论诞生 12 年之后,CAP 之父也在 2012 年重写了之前的论文。
+Most people simplistically explain this theorem by saying: "You can only achieve two of consistency, availability, and partition tolerance at the same time, and cannot achieve all three." This is actually a very misleading statement, and twelve years after the CAP theory was born, its father also rewrote his earlier paper in 2012.
-> **当发生网络分区的时候,如果我们要继续服务,那么强一致性和可用性只能 2 选 1。也就是说当网络分区之后 P 是前提,决定了 P 之后才有 C 和 A 的选择。也就是说分区容错性(Partition tolerance)我们是必须要实现的。**
+> **When a network partition occurs, if we are to continue providing services, then strong consistency and availability can only be chosen between 2 out of 1. In other words, when a network partition happens, P is the prerequisite, determining the choice of C or A thereafter. This means partition tolerance (P) is something we must implement.**
>
-> 简而言之就是:CAP 理论中分区容错性 P 是一定要满足的,在此基础上,只能满足可用性 A 或者一致性 C。
+> In short: In the CAP theory, partition tolerance P must be satisfied, and on this basis, we can only satisfy either availability A or consistency C.
-因此,**分布式系统理论上不可能选择 CA 架构,只能选择 CP 或者 AP 架构。** 比如 ZooKeeper、HBase 就是 CP 架构,Cassandra、Eureka 就是 AP 架构,Nacos 不仅支持 CP 架构也支持 AP 架构。
+Therefore, **theoretically, a distributed system cannot choose a CA architecture but can only choose a CP or AP architecture.** For example, ZooKeeper and HBase are CP architectures, while Cassandra and Eureka are AP architectures. Nacos supports both CP and AP architectures.
-**为啥不可能选择 CA 架构呢?** 举个例子:若系统出现“分区”,系统中的某个节点在进行写操作。为了保证 C, 必须要禁止其他节点的读写操作,这就和 A 发生冲突了。如果为了保证 A,其他节点的读写操作正常的话,那就和 C 发生冲突了。
+**Why is it impossible to choose a CA architecture?** For example: If a "partition" occurs in the system and a certain node is performing a write operation. To ensure C, we must prohibit other nodes’ read and write operations, which conflicts with A. Conversely, if we ensure A and allow other nodes to perform read and write operations, that would conflict with C.
-**选择 CP 还是 AP 的关键在于当前的业务场景,没有定论,比如对于需要确保强一致性的场景如银行一般会选择保证 CP 。**
+**The choice between CP and AP depends on the current business scenario, with no conclusive answer. For scenarios requiring strong consistency, such as banking, CP is generally chosen.**
-另外,需要补充说明的一点是:**如果网络分区正常的话(系统在绝大部分时候所处的状态),也就说不需要保证 P 的时候,C 和 A 能够同时保证。**
+Additionally, it should be noted that: **If the network partition is functioning normally (which is the state the system is in most of the time), that is, when P does not need to be ensured, C and A can be guaranteed simultaneously.**
-### CAP 实际应用案例
+### Practical Application of CAP
-我这里以注册中心来探讨一下 CAP 的实际应用。考虑到很多小伙伴不知道注册中心是干嘛的,这里简单以 Dubbo 为例说一说。
+I will explore the practical application of CAP using a registration center. Considering many may not know what a registration center is for, I will briefly explain it using Dubbo as an example.
-下图是 Dubbo 的架构图。**注册中心 Registry 在其中扮演了什么角色呢?提供了什么服务呢?**
+The following diagram is the architecture of Dubbo. **What role does the registration center play? What services does it provide?**
-注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互,注册中心不转发请求,压力较小。
+The registration center is responsible for the registration and discovery of service addresses, analogous to a directory service. Service providers and consumers only interact with the registration center upon starting, and the registration center does not forward requests, resulting in low pressure.

-常见的可以作为注册中心的组件有:ZooKeeper、Eureka、Nacos...。
+Common components that can serve as registration centers include: ZooKeeper, Eureka, Nacos...
-1. **ZooKeeper 保证的是 CP。** 任何时刻对 ZooKeeper 的读请求都能得到一致性的结果,但是, ZooKeeper 不保证每次请求的可用性比如在 Leader 选举过程中或者半数以上的机器不可用的时候服务就是不可用的。
-2. **Eureka 保证的则是 AP。** Eureka 在设计的时候就是优先保证 A (可用性)。在 Eureka 中不存在什么 Leader 节点,每个节点都是一样的、平等的。因此 Eureka 不会像 ZooKeeper 那样出现选举过程中或者半数以上的机器不可用的时候服务就是不可用的情况。 Eureka 保证即使大部分节点挂掉也不会影响正常提供服务,只要有一个节点是可用的就行了。只不过这个节点上的数据可能并不是最新的。
-3. **Nacos 不仅支持 CP 也支持 AP。**
+1. **ZooKeeper guarantees CP.** Any read request to ZooKeeper will provide a consistent result; however, ZooKeeper does not guarantee availability during events like Leader election or when more than half of the machines are unavailable—services would then be unavailable.
+1. **Eureka guarantees AP.** Eureka was designed with priority on A (availability). There is no Leader node in Eureka; each node is the same and equal. Thus, unlike ZooKeeper, Eureka does not face unavailability during election processes or when more than half of the machines are unavailable. Eureka ensures that as long as one node is available, normal services can continue, even if that node's data may not be the latest.
+1. **Nacos supports both CP and AP.**
-**🐛 修正(参见:[issue#1906](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1906))**:
+**🐛 Correction (see: [issue#1906](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/1906))**:
-ZooKeeper 通过可线性化(Linearizable)写入、全局 FIFO 顺序访问等机制来保障数据一致性。多节点部署的情况下, ZooKeeper 集群处于 Quorum 模式。Quorum 模式下的 ZooKeeper 集群, 是一组 ZooKeeper 服务器节点组成的集合,其中大多数节点必须同意任何变更才能被视为有效。
+ZooKeeper ensures data consistency through linearizable writes, global FIFO access, and other mechanisms. In a multi-node deployment, the ZooKeeper cluster operates in Quorum mode. In this mode, a group of ZooKeeper server nodes is formed, where the majority must agree to any changes for them to be considered valid.
-由于 Quorum 模式下的读请求不会触发各个 ZooKeeper 节点之间的数据同步,因此在某些情况下还是可能会存在读取到旧数据的情况,导致不同的客户端视图上看到的结果不同,这可能是由于网络延迟、丢包、重传等原因造成的。ZooKeeper 为了解决这个问题,提供了 Watcher 机制和版本号机制来帮助客户端检测数据的变化和版本号的变更,以保证数据的一致性。
+Due to the nature of Quorum mode, read requests do not trigger data synchronization between different ZooKeeper nodes, resulting in situations where outdated data may still be read, leading to inconsistent views on different clients due to reasons like network latency, packet loss, or retransmission. To address this, ZooKeeper provides a Watcher mechanism and versioning to help clients detect changes in data and version changes to ensure data consistency.
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-在进行分布式系统设计和开发时,我们不应该仅仅局限在 CAP 问题上,还要关注系统的扩展性、可用性等等
+In designing and developing distributed systems, we should not be limited to the CAP issue but also focus on aspects such as system scalability and availability.
-在系统发生“分区”的情况下,CAP 理论只能满足 CP 或者 AP。要注意的是,这里的前提是系统发生了“分区”
+In the event of a network "partition", the CAP theorem can only satisfy CP or AP. It is important to note that this assumes a "partition" has occurred.
-如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,节点间的网络连接通信正常的话,也就不存在 P 了。这个时候,我们就可以同时保证 C 和 A 了。
+If there is no "partition" in the system and the network communication among nodes is normal, P no longer exists. At that point, we can simultaneously ensure C and A.
-总结:**如果系统发生“分区”,我们要考虑选择 CP 还是 AP。如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,我们要思考如何保证 CA 。**
+In summary: **If a partition occurs in the system, we must consider whether to choose CP or AP. If there is no partition, we should think about how to ensure CA.**
-### 推荐阅读
+### Recommended Reading
-1. [CAP 定理简化](https://medium.com/@ravindraprasad/cap-theorem-simplified-28499a67eab4) (英文,有趣的案例)
-2. [神一样的 CAP 理论被应用在何方](https://juejin.im/post/6844903936718012430) (中文,列举了很多实际的例子)
-3. [请停止呼叫数据库 CP 或 AP](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2015/05/11/please-stop-calling-databases-cp-or-ap.html) (英文,带给你不一样的思考)
+1. [Simplifying the CAP Theorem](https://medium.com/@ravindraprasad/cap-theorem-simplified-28499a67eab4) (English, with interesting examples)
+1. [Where is the Amazing CAP Theory Applied](https://juejin.im/post/6844903936718012430) (Chinese, listing many practical examples)
+1. [Please Stop Calling Databases CP or AP](https://martin.kleppmann.com/2015/05/11/please-stop-calling-databases-cp-or-ap.html) (English, offering a different perspective)
-## BASE 理论
+## BASE Theory
-[BASE 理论](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1394127.1394128)起源于 2008 年, 由 eBay 的架构师 Dan Pritchett 在 ACM 上发表。
+[BASE Theory](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1394127.1394128) originated in 2008 and was published by eBay architect Dan Pritchett in ACM.
-### 简介
+### Introduction
-**BASE** 是 **Basically Available(基本可用)**、**Soft-state(软状态)** 和 **Eventually Consistent(最终一致性)** 三个短语的缩写。BASE 理论是对 CAP 中一致性 C 和可用性 A 权衡的结果,其来源于对大规模互联网系统分布式实践的总结,是基于 CAP 定理逐步演化而来的,它大大降低了我们对系统的要求。
+**BASE** is an acronym for **Basically Available**, **Soft-state**, and **Eventually Consistent**. The BASE theory is the result of the trade-offs between consistency (C) and availability (A) in CAP, arising from a summary of distributed practices in large-scale Internet systems. It has gradually evolved from the CAP theorem, significantly relaxing our requirements of the system.
-### BASE 理论的核心思想
+### Core Idea of BASE Theory
-即使无法做到强一致性,但每个应用都可以根据自身业务特点,采用适当的方式来使系统达到最终一致性。
+Even if strong consistency cannot be achieved, every application can adopt appropriate methods to achieve eventual consistency according to its business characteristics.
-> 也就是牺牲数据的一致性来满足系统的高可用性,系统中一部分数据不可用或者不一致时,仍需要保持系统整体“主要可用”。
+> This means sacrificing data consistency to ensure high system availability, wherein part of the system's data may be unavailable or inconsistent, yet the system overall still remains "mostly available".
-**BASE 理论本质上是对 CAP 的延伸和补充,更具体地说,是对 CAP 中 AP 方案的一个补充。**
+**The BASE theory is essentially an extension and supplement to CAP, specifically, it supplements the AP solution in CAP.**
-**为什么这样说呢?**
+**Why do I say this?**
-CAP 理论这节我们也说过了:
+As mentioned in the section on the CAP theory:
-> 如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,节点间的网络连接通信正常的话,也就不存在 P 了。这个时候,我们就可以同时保证 C 和 A 了。因此,**如果系统发生“分区”,我们要考虑选择 CP 还是 AP。如果系统没有发生“分区”的话,我们要思考如何保证 CA 。**
+> If the system has not undergone a "partition," and the network connections between nodes are functioning normally, then P does not exist. At that point, we can guarantee both C and A. Thus, **if a partition occurs in the system, we must consider choosing between CP or AP. If there is no "partition," we should think about how to ensure CA.**
-因此,AP 方案只是在系统发生分区的时候放弃一致性,而不是永远放弃一致性。在分区故障恢复后,系统应该达到最终一致性。这一点其实就是 BASE 理论延伸的地方。
+Therefore, the AP solution only sacrifices consistency during system partitions but does not permanently relinquish consistency. After recovering from partition faults, the system should achieve eventual consistency. This is, in fact, the essence of the extension provided by the BASE theory.
-### BASE 理论三要素
+### Three Elements of BASE Theory
-
+
-#### 基本可用
+#### Basically Available
-基本可用是指分布式系统在出现不可预知故障的时候,允许损失部分可用性。但是,这绝不等价于系统不可用。
+Basically available means that when unexpected failures occur in a distributed system, it allows some loss of availability. However, this does not equate to the system being unavailable.
-**什么叫允许损失部分可用性呢?**
+**What does it mean to allow loss of availability?**
-- **响应时间上的损失**: 正常情况下,处理用户请求需要 0.5s 返回结果,但是由于系统出现故障,处理用户请求的时间变为 3 s。
-- **系统功能上的损失**:正常情况下,用户可以使用系统的全部功能,但是由于系统访问量突然剧增,系统的部分非核心功能无法使用。
+- **Loss in response time**: Normally, it takes 0.5s to handle a user request, but due to system failures, the response time extends to 3s.
+- **Loss in system functionality**: Normally, users can access all features of the system, but due to a sudden surge in traffic, some non-core functionalities may become unavailable.
-#### 软状态
+#### Soft State
-软状态指允许系统中的数据存在中间状态(**CAP 理论中的数据不一致**),并认为该中间状态的存在不会影响系统的整体可用性,即允许系统在不同节点的数据副本之间进行数据同步的过程存在延时。
+Soft state refers to allowing data in the system to exist in intermediate states (**data inconsistency as described in the CAP theory**) while recognizing that the existence of this intermediate state will not affect the overall availability of the system. This means allowing delays in the synchronization process of data replicas between different nodes.
-#### 最终一致性
+#### Eventually Consistent
-最终一致性强调的是系统中所有的数据副本,在经过一段时间的同步后,最终能够达到一个一致的状态。因此,最终一致性的本质是需要系统保证最终数据能够达到一致,而不需要实时保证系统数据的强一致性。
+Eventually consistent emphasizes that all data replicas in the system can achieve a consistent state after a period of synchronization. Therefore, the essence of eventual consistency is that the system needs to ensure that the final data can achieve consistency, rather than requiring real-time strong consistency of the data.
-> 分布式一致性的 3 种级别:
+> The three levels of distributed consistency:
>
-> 1. **强一致性**:系统写入了什么,读出来的就是什么。
-> 2. **弱一致性**:不一定可以读取到最新写入的值,也不保证多少时间之后读取到的数据是最新的,只是会尽量保证某个时刻达到数据一致的状态。
-> 3. **最终一致性**:弱一致性的升级版,系统会保证在一定时间内达到数据一致的状态。
+> 1. **Strong consistency**: What is written in the system is exactly what is read.
+> 1. **Weak consistency**: It is not certain that the most recently written value can be read, nor is there a guarantee that the data read after a certain time will be the latest; it only aims to achieve data consistency at a given moment.
+> 1. **Eventual consistency**: This is an upgraded version of weak consistency, wherein the system guarantees that data will achieve consistency within a certain period.
>
-> **业界比较推崇是最终一致性级别,但是某些对数据一致要求十分严格的场景比如银行转账还是要保证强一致性。**
+> **The industry tends to commend the eventual consistency level, but in certain scenarios where data consistency is critically required, such as banking transactions, strong consistency must still be guaranteed.**
-那实现最终一致性的具体方式是什么呢? [《分布式协议与算法实战》](http://gk.link/a/10rZM) 中是这样介绍:
+What are the specific ways to achieve eventual consistency? In [《Distributed Protocols and Algorithms in Practice》](http://gk.link/a/10rZM), it is introduced as follows:
-> - **读时修复** : 在读取数据时,检测数据的不一致,进行修复。比如 Cassandra 的 Read Repair 实现,具体来说,在向 Cassandra 系统查询数据的时候,如果检测到不同节点的副本数据不一致,系统就自动修复数据。
-> - **写时修复** : 在写入数据,检测数据的不一致时,进行修复。比如 Cassandra 的 Hinted Handoff 实现。具体来说,Cassandra 集群的节点之间远程写数据的时候,如果写失败 就将数据缓存下来,然后定时重传,修复数据的不一致性。
-> - **异步修复** : 这个是最常用的方式,通过定时对账检测副本数据的一致性,并修复。
+> - **Read Repair**: During data reads, inconsistencies are detected and repaired. For example, Cassandra's Read Repair implementation automatically fixes data when inconsistencies are found among the replicas during a read query.
+> - **Write Repair**: During data writes, inconsistencies are detected and repaired. For example, Cassandra's Hinted Handoff implementation caches data that fails to write remotely between cluster nodes and retransmits it periodically to fix the inconsistencies.
+> - **Asynchronous Repair**: This is the most commonly used method, conducted through regular reconciliation checks to verify the consistency of replica data and repair it.
-比较推荐 **写时修复**,这种方式对性能消耗比较低。
+**Write Repair** is highly recommended as this method is less demanding on performance.
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-**ACID 是数据库事务完整性的理论,CAP 是分布式系统设计理论,BASE 是 CAP 理论中 AP 方案的延伸。**
+**ACID is a theory of transaction integrity in databases, CAP is a theory of distributed system design, and BASE is an extension of the AP solution in CAP theory.**
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
index 5590401a9b6..c6db7b9630f 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/gossip-protocl.md
@@ -1,145 +1,62 @@
---
-title: Gossip 协议详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Gossip Protocol
+category: Distributed
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithms
---
-## 背景
+## Background
-在分布式系统中,不同的节点进行数据/信息共享是一个基本的需求。
+In distributed systems, data/information sharing among different nodes is a fundamental requirement.
-一种比较简单粗暴的方法就是 **集中式发散消息**,简单来说就是一个主节点同时共享最新信息给其他所有节点,比较适合中心化系统。这种方法的缺陷也很明显,节点多的时候不光同步消息的效率低,还太依赖与中心节点,存在单点风险问题。
+A relatively simple and straightforward method is **centralized message dissemination**, which essentially involves a primary node sharing the latest information with all other nodes simultaneously, making it more suitable for centralized systems. The drawbacks of this method are also quite evident; when there are many nodes, not only is the efficiency of message synchronization low, but it also heavily relies on the central node, posing a single point of failure risk.
-于是,**分散式发散消息** 的 **Gossip 协议** 就诞生了。
+Thus, the **Gossip Protocol** for **decentralized message dissemination** was born.
-## Gossip 协议介绍
+## Introduction to the Gossip Protocol
-Gossip 直译过来就是闲话、流言蜚语的意思。流言蜚语有什么特点呢?容易被传播且传播速度还快,你传我我传他,然后大家都知道了。
+Gossip literally translates to idle talk or rumors. What are the characteristics of rumors? They are easily spread and propagate quickly; you tell me, I tell him, and then everyone knows.

-**Gossip 协议** 也叫 Epidemic 协议(流行病协议)或者 Epidemic propagation 算法(疫情传播算法),别名很多。不过,这些名字的特点都具有 **随机传播特性** (联想一下病毒传播、癌细胞扩散等生活中常见的情景),这也正是 Gossip 协议最主要的特点。
+The **Gossip Protocol** is also known as the Epidemic Protocol or Epidemic Propagation Algorithm, and it has many aliases. However, the common feature of these names is the **random propagation characteristic** (think of scenarios like virus transmission or cancer cell spread in everyday life), which is also the main feature of the Gossip Protocol.
-Gossip 协议最早是在 ACM 上的一篇 1987 年发表的论文 [《Epidemic Algorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance》](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/41840.41841)中被提出的。根据论文标题,我们大概就能知道 Gossip 协议当时提出的主要应用是在分布式数据库系统中各个副本节点同步数据。
+The Gossip Protocol was first proposed in a paper published in 1987 in ACM titled [“Epidemic Algorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance”](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/41840.41841). From the title of the paper, we can infer that the main application of the Gossip Protocol at that time was to synchronize data among various replica nodes in distributed database systems.
-正如 Gossip 协议其名一样,这是一种随机且带有传染性的方式将信息传播到整个网络中,并在一定时间内,使得系统内的所有节点数据一致。
+As the name suggests, the Gossip Protocol is a random and contagious way to disseminate information throughout the network, ensuring that all nodes in the system achieve data consistency within a certain time frame.
-在 Gossip 协议下,没有所谓的中心节点,每个节点周期性地随机找一个节点互相同步彼此的信息,理论上来说,各个节点的状态最终会保持一致。
+Under the Gossip Protocol, there is no so-called central node; each node periodically and randomly selects another node to synchronize information with each other. Theoretically, the states of all nodes will eventually remain consistent.
-下面我们来对 Gossip 协议的定义做一个总结:**Gossip 协议是一种允许在分布式系统中共享状态的去中心化通信协议,通过这种通信协议,我们可以将信息传播给网络或集群中的所有成员。**
+To summarize the definition of the Gossip Protocol: **The Gossip Protocol is a decentralized communication protocol that allows state sharing in distributed systems, enabling us to disseminate information to all members in a network or cluster.**
-## Gossip 协议应用
+## Applications of the Gossip Protocol
-NoSQL 数据库 Redis 和 Apache Cassandra、服务网格解决方案 Consul 等知名项目都用到了 Gossip 协议,学习 Gossip 协议有助于我们搞清很多技术的底层原理。
+Notable projects such as the NoSQL databases Redis and Apache Cassandra, as well as service mesh solutions like Consul, utilize the Gossip Protocol. Learning about the Gossip Protocol helps us understand the underlying principles of many technologies.
-我们这里以 Redis Cluster 为例说明 Gossip 协议的实际应用。
+Here, we will illustrate the practical application of the Gossip Protocol using Redis Cluster as an example.
-我们经常使用的分布式缓存 Redis 的官方集群解决方案(3.0 版本引入) Redis Cluster 就是基于 Gossip 协议来实现集群中各个节点数据的最终一致性。
+The official clustering solution for the distributed cache Redis (introduced in version 3.0), Redis Cluster, is based on the Gossip Protocol to achieve eventual consistency of data among various nodes in the cluster.
-
+
-Redis Cluster 是一个典型的分布式系统,分布式系统中的各个节点需要互相通信。既然要相互通信就要遵循一致的通信协议,Redis Cluster 中的各个节点基于 **Gossip 协议** 来进行通信共享信息,每个 Redis 节点都维护了一份集群的状态信息。
+Redis Cluster is a typical distributed system where various nodes need to communicate with each other. Since communication is required, a consistent communication protocol must be followed. The nodes in Redis Cluster communicate and share information based on the **Gossip Protocol**, with each Redis node maintaining a copy of the cluster's state information.
-Redis Cluster 的节点之间会相互发送多种 Gossip 消息:
+Nodes in Redis Cluster send various Gossip messages to each other:
-- **MEET**:在 Redis Cluster 中的某个 Redis 节点上执行 `CLUSTER MEET ip port` 命令,可以向指定的 Redis 节点发送一条 MEET 信息,用于将其添加进 Redis Cluster 成为新的 Redis 节点。
-- **PING/PONG**:Redis Cluster 中的节点都会定时地向其他节点发送 PING 消息,来交换各个节点状态信息,检查各个节点状态,包括在线状态、疑似下线状态 PFAIL 和已下线状态 FAIL。
-- **FAIL**:Redis Cluster 中的节点 A 发现 B 节点 PFAIL ,并且在下线报告的有效期限内集群中半数以上的节点将 B 节点标记为 PFAIL,节点 A 就会向集群广播一条 FAIL 消息,通知其他节点将故障节点 B 标记为 FAIL 。
+- **MEET**: Executing the `CLUSTER MEET ip port` command on a Redis node in Redis Cluster sends a MEET message to a specified Redis node, adding it as a new Redis node in the cluster.
+- **PING/PONG**: Nodes in Redis Cluster periodically send PING messages to other nodes to exchange status information, checking the status of each node, including online status, suspected offline status (PFAIL), and offline status (FAIL).
+- **FAIL**: If node A in Redis Cluster detects that node B is PFAIL, and more than half of the nodes in the cluster mark B as PFAIL within the validity period of the offline report, node A will broadcast a FAIL message to the cluster, notifying other nodes to mark the faulty node B as FAIL.
- ……
-下图就是主从架构的 Redis Cluster 的示意图,图中的虚线代表的就是各个节点之间使用 Gossip 进行通信 ,实线表示主从复制。
+The diagram below illustrates the master-slave architecture of Redis Cluster, where the dashed lines represent communication between nodes using Gossip, and the solid lines indicate master-slave replication.

-有了 Redis Cluster 之后,不需要专门部署 Sentinel 集群服务了。Redis Cluster 相当于是内置了 Sentinel 机制,Redis Cluster 内部的各个 Redis 节点通过 Gossip 协议共享集群内信息。
+With Redis Cluster, there is no need to deploy a separate Sentinel cluster service. Redis Cluster effectively has a built-in Sentinel mechanism, with the various Redis nodes internally sharing cluster information through the Gossip Protocol.
-关于 Redis Cluster 的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章 [Redis 集群详解(付费)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html) 。
+For a detailed introduction to Redis Cluster, you can refer to this article [Detailed Explanation of Redis Cluster (Paid)](https://javaguide.cn/database/redis/redis-cluster.html).
-## Gossip 协议消息传播模式
+## Gossip Protocol Message Propagation Modes
-Gossip 设计了两种可能的消息传播模式:**反熵(Anti-Entropy)** 和 **传谣(Rumor-Mongering)**。
-
-### 反熵(Anti-entropy)
-
-根据维基百科:
-
-> 熵的概念最早起源于[物理学](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/物理学),用于度量一个热力学系统的混乱程度。熵最好理解为不确定性的量度而不是确定性的量度,因为越随机的信源的熵越大。
-
-在这里,你可以把反熵中的熵理解为节点之间数据的混乱程度/差异性,反熵就是指消除不同节点中数据的差异,提升节点间数据的相似度,从而降低熵值。
-
-具体是如何反熵的呢?集群中的节点,每隔段时间就随机选择某个其他节点,然后通过互相交换自己的所有数据来消除两者之间的差异,实现数据的最终一致性。
-
-在实现反熵的时候,主要有推、拉和推拉三种方式:
-
-- 推方式,就是将自己的所有副本数据,推给对方,修复对方副本中的熵。
-- 拉方式,就是拉取对方的所有副本数据,修复自己副本中的熵。
-- 推拉就是同时修复自己副本和对方副本中的熵。
-
-伪代码如下:
-
-
-
-在我们实际应用场景中,一般不会采用随机的节点进行反熵,而是可以设计成一个闭环。这样的话,我们能够在一个确定的时间范围内实现各个节点数据的最终一致性,而不是基于随机的概率。像 InfluxDB 就是这样来实现反熵的。
-
-
-
-1. 节点 A 推送数据给节点 B,节点 B 获取到节点 A 中的最新数据。
-2. 节点 B 推送数据给 C,节点 C 获取到节点 A,B 中的最新数据。
-3. 节点 C 推送数据给 A,节点 A 获取到节点 B,C 中的最新数据。
-4. 节点 A 再推送数据给 B 形成闭环,这样节点 B 就获取到节点 C 中的最新数据。
-
-虽然反熵很简单实用,但是,节点过多或者节点动态变化的话,反熵就不太适用了。这个时候,我们想要实现最终一致性就要靠 **谣言传播(Rumor mongering)** 。
-
-### 谣言传播(Rumor mongering)
-
-谣言传播指的是分布式系统中的一个节点一旦有了新数据之后,就会变为活跃节点,活跃节点会周期性地联系其他节点向其发送新数据,直到所有的节点都存储了该新数据。
-
-如下图所示(下图来自于[INTRODUCTION TO GOSSIP](https://managementfromscratch.wordpress.com/2016/04/01/introduction-to-gossip/) 这篇文章):
-
-
-
-伪代码如下:
-
-
-
-谣言传播比较适合节点数量比较多的情况,不过,这种模式下要尽量避免传播的信息包不能太大,避免网络消耗太大。
-
-### 总结
-
-- 反熵(Anti-Entropy)会传播节点的所有数据,而谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)只会传播节点新增的数据。
-- 我们一般会给反熵设计一个闭环。
-- 谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)比较适合节点数量比较多或者节点动态变化的场景。
-
-## Gossip 协议优势和缺陷
-
-**优势:**
-
-1、相比于其他分布式协议/算法来说,Gossip 协议理解起来非常简单。
-
-2、能够容忍网络上节点的随意地增加或者减少,宕机或者重启,因为 Gossip 协议下这些节点都是平等的,去中心化的。新增加或者重启的节点在理想情况下最终是一定会和其他节点的状态达到一致。
-
-3、速度相对较快。节点数量比较多的情况下,扩散速度比一个主节点向其他节点传播信息要更快(多播)。
-
-**缺陷** :
-
-1、消息需要通过多个传播的轮次才能传播到整个网络中,因此,必然会出现各节点状态不一致的情况。毕竟,Gossip 协议强调的是最终一致,至于达到各个节点的状态一致需要多长时间,谁也无从得知。
-
-2、由于拜占庭将军问题,不允许存在恶意节点。
-
-3、可能会出现消息冗余的问题。由于消息传播的随机性,同一个节点可能会重复收到相同的消息。
-
-## 总结
-
-- Gossip 协议是一种允许在分布式系统中共享状态的通信协议,通过这种通信协议,我们可以将信息传播给网络或集群中的所有成员。
-- Gossip 协议被 Redis、Apache Cassandra、Consul 等项目应用。
-- 谣言传播(Rumor-Mongering)比较适合节点数量比较多或者节点动态变化的场景。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 一万字详解 Redis Cluster Gossip 协议:
-- 《分布式协议与算法实战》
-- 《Redis 设计与实现》
-
-
+Gossip has designed two possible message propagation modes: \*\*Anti-Entropy
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
index c820209f4a8..d1e5d437f71 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/paxos-algorithm.md
@@ -1,83 +1,83 @@
---
-title: Paxos 算法详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Paxos Algorithm
+category: Distributed
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithms
---
-## 背景
+## Background
-Paxos 算法是 Leslie Lamport([莱斯利·兰伯特](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/莱斯利·兰伯特))在 **1990** 年提出了一种分布式系统 **共识** 算法。这也是第一个被证明完备的共识算法(前提是不存在拜占庭将军问题,也就是没有恶意节点)。
+The Paxos algorithm is a consensus algorithm for distributed systems proposed by Leslie Lamport in **1990**. It is also the first consensus algorithm to be proven to be complete (under the assumption that the Byzantine Generals problem does not exist, meaning there are no malicious nodes).
-为了介绍 Paxos 算法,兰伯特专门写了一篇幽默风趣的论文。在这篇论文中,他虚拟了一个叫做 Paxos 的希腊城邦来更形象化地介绍 Paxos 算法。
+To introduce the Paxos algorithm, Lamport wrote a humorous and witty paper. In this paper, he created a fictional Greek city-state called Paxos to more vividly illustrate the Paxos algorithm.
-不过,审稿人并不认可这篇论文的幽默。于是,他们就给兰伯特说:“如果你想要成功发表这篇论文的话,必须删除所有 Paxos 相关的故事背景”。兰伯特一听就不开心了:“我凭什么修改啊,你们这些审稿人就是缺乏幽默细胞,发不了就不发了呗!”。
+However, the reviewers did not appreciate the humor in the paper. They told Lamport, "If you want to successfully publish this paper, you must remove all the background stories related to Paxos." Lamport was not pleased and replied, "Why should I make changes? You reviewers are simply lacking a sense of humor. If you can't publish it, then do not publish it!"
-于是乎,提出 Paxos 算法的那篇论文在当时并没有被成功发表。
+As a result, the paper proposing the Paxos algorithm was not successfully published at that time.
-直到 1998 年,系统研究中心 (Systems Research Center,SRC)的两个技术研究员需要找一些合适的分布式算法来服务他们正在构建的分布式系统,Paxos 算法刚好可以解决他们的部分需求。因此,兰伯特就把论文发给了他们。在看了论文之后,这俩大佬觉得论文还是挺不错的。于是,兰伯特在 **1998** 年重新发表论文 [《The Part-Time Parliament》](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/lamport-paxos.pdf)。
+It wasn't until **1998** that two technical researchers from the Systems Research Center (SRC) needed to find suitable distributed algorithms for the distributed system they were building, and the Paxos algorithm happened to fulfill some of their requirements. Lamport then sent the paper to them. After reviewing the paper, these two researchers found it to be quite impressive. Thus, Lamport republished his paper titled [“The Part-Time Parliament”](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/lamport-paxos.pdf) in **1998**.
-论文发表之后,各路学者直呼看不懂,言语中还略显调侃之意。这谁忍得了,在 **2001** 年的时候,兰伯特专门又写了一篇 [《Paxos Made Simple》](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/paxos-simple.pdf) 的论文来简化对 Paxos 的介绍,主要讲述两阶段共识协议部分,顺便还不忘嘲讽一下这群学者。
+After the paper was published, scholars around the world exclaimed that it was hard to understand, with a hint of mocking tone in their words. Who could stand that? In **2001**, Lamport specifically wrote another paper [“Paxos Made Simple”](http://lamport.azurewebsites.net/pubs/paxos-simple.pdf) to simplify the introduction of Paxos, mainly discussing the two-phase consensus protocol, while also taking a dig at those scholars.
-《Paxos Made Simple》这篇论文就 14 页,相比于 《The Part-Time Parliament》的 33 页精简了不少。最关键的是这篇论文的摘要就一句话:
+The paper "Paxos Made Simple" is only 14 pages long, considerably shorter than the 33 pages of "The Part-Time Parliament." The key point is that the abstract of this paper is just one sentence:

> The Paxos algorithm, when presented in plain English, is very simple.
-翻译过来的意思大概就是:当我用无修饰的英文来描述时,Paxos 算法真心简单!
+This roughly translates to: "When I describe it in straightforward English, the Paxos algorithm is genuinely simple!"
-有没有感觉到来自兰伯特大佬满满地嘲讽的味道?
+Do you sense the strong flavor of sarcasm from Lamport?
-## 介绍
+## Introduction
-Paxos 算法是第一个被证明完备的分布式系统共识算法。共识算法的作用是让分布式系统中的多个节点之间对某个提案(Proposal)达成一致的看法。提案的含义在分布式系统中十分宽泛,像哪一个节点是 Leader 节点、多个事件发生的顺序等等都可以是一个提案。
+The Paxos algorithm is the first proven comprehensive consensus algorithm for distributed systems. The role of a consensus algorithm is to reach a unanimous opinion among multiple nodes in a distributed system about a certain proposal (Proposal). The meaning of a proposal in a distributed system is quite broad, encompassing which node is the Leader, the order of multiple events, etc.
-兰伯特当时提出的 Paxos 算法主要包含 2 个部分:
+The Paxos algorithm proposed by Lamport actually comprises 2 parts:
-- **Basic Paxos 算法**:描述的是多节点之间如何就某个值(提案 Value)达成共识。
-- **Multi-Paxos 思想**:描述的是执行多个 Basic Paxos 实例,就一系列值达成共识。Multi-Paxos 说白了就是执行多次 Basic Paxos ,核心还是 Basic Paxos 。
+- **Basic Paxos Algorithm**: This describes how multiple nodes can reach a consensus on a certain value (proposed Value).
+- **Multi-Paxos Concept**: This describes executing multiple Basic Paxos instances to achieve consensus on a series of values. Multi-Paxos, simply put, entails executing Basic Paxos multiple times, with the core still being Basic Paxos.
-由于 Paxos 算法在国际上被公认的非常难以理解和实现,因此不断有人尝试简化这一算法。到了 2013 年才诞生了一个比 Paxos 算法更易理解和实现的共识算法—[Raft 算法](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/theorem&algorithm&protocol/raft-algorithm.html) 。更具体点来说,Raft 是 Multi-Paxos 的一个变种,其简化了 Multi-Paxos 的思想,变得更容易被理解以及工程实现。
+Due to the international consensus that the Paxos algorithm is particularly difficult to understand and implement, continuous attempts have been made to simplify this algorithm. It wasn't until 2013 that a consensus algorithm more understandable and implementable than Paxos—the [Raft algorithm](https://javaguide.cn/distributed-system/theorem&algorithm&protocol/raft-algorithm.html)—was born. More specifically, Raft is a variant of Multi-Paxos that simplifies the ideas behind Multi-Paxos, making it easier to understand and engineer.
-针对没有恶意节点的情况,除了 Raft 算法之外,当前最常用的一些共识算法比如 **ZAB 协议**、 **Fast Paxos** 算法都是基于 Paxos 算法改进的。
+For scenarios without malicious nodes, some commonly used consensus algorithms, like the **ZAB protocol**, **Fast Paxos**, are all improvements based on the Paxos algorithm.
-针对存在恶意节点的情况,一般使用的是 **工作量证明(POW,Proof-of-Work)**、 **权益证明(PoS,Proof-of-Stake )** 等共识算法。这类共识算法最典型的应用就是区块链,就比如说前段时间以太坊官方宣布其共识机制正在从工作量证明(PoW)转变为权益证明(PoS)。
+In cases with malicious nodes, consensus algorithms like **Proof-of-Work (PoW)** and **Proof-of-Stake (PoS)** are generally used. A typical application of such consensus algorithms is in blockchain technology. For example, recently, Ethereum's official announcement indicated that its consensus mechanism is transitioning from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
-区块链系统使用的共识算法需要解决的核心问题是 **拜占庭将军问题** ,这和我们日常接触到的 ZooKeeper、Etcd、Consul 等分布式中间件不太一样。
+The core problem that consensus algorithms used in blockchain systems need to solve is the **Byzantine Generals problem**, which is quite different from the distributed middleware we encounter in daily life, such as ZooKeeper, Etcd, and Consul.
-下面我们来对 Paxos 算法的定义做一个总结:
+Now, let's summarize the definition of the Paxos algorithm:
-- Paxos 算法是兰伯特在 **1990** 年提出了一种分布式系统共识算法。
-- 兰伯特当时提出的 Paxos 算法主要包含 2 个部分: Basic Paxos 算法和 Multi-Paxos 思想。
-- Raft 算法、ZAB 协议、 Fast Paxos 算法都是基于 Paxos 算法改进而来。
+- The Paxos algorithm is a consensus algorithm for distributed systems proposed by Lamport in **1990**.
+- The Paxos algorithm proposed by Lamport primarily consists of 2 parts: the Basic Paxos algorithm and the Multi-Paxos concept.
+- The Raft algorithm, ZAB protocol, and Fast Paxos algorithm are all derived from improvements over the Paxos algorithm.
-## Basic Paxos 算法
+## Basic Paxos Algorithm
-Basic Paxos 中存在 3 个重要的角色:
+The Basic Paxos algorithm involves 3 important roles:
-1. **提议者(Proposer)**:也可以叫做协调者(coordinator),提议者负责接受客户端的请求并发起提案。提案信息通常包括提案编号 (Proposal ID) 和提议的值 (Value)。
-2. **接受者(Acceptor)**:也可以叫做投票员(voter),负责对提议者的提案进行投票,同时需要记住自己的投票历史;
-3. **学习者(Learner)**:如果有超过半数接受者就某个提议达成了共识,那么学习者就需要接受这个提议,并就该提议作出运算,然后将运算结果返回给客户端。
+1. **Proposer**: Also known as the Coordinator, the proposer is responsible for accepting client requests and initiating proposals. Proposal information typically includes a proposal number (Proposal ID) and the proposed value (Value).
+1. **Acceptor**: Also referred to as a voter, the acceptor is responsible for voting on proposals from the proposer and must remember its voting history.
+1. **Learner**: If more than half of the acceptors reach a consensus on a certain proposal, the learner must accept that proposal, perform computations based on it, and then return the computation results to the client.

-为了减少实现该算法所需的节点数,一个节点可以身兼多个角色。并且,一个提案被选定需要被半数以上的 Acceptor 接受。这样的话,Basic Paxos 算法还具备容错性,在少于一半的节点出现故障时,集群仍能正常工作。
+To reduce the number of nodes required to implement this algorithm, a single node can take on multiple roles. Additionally, a proposal must be accepted by more than half of the acceptors to be chosen. This way, the Basic Paxos algorithm also possesses fault tolerance, allowing the cluster to operate normally even when less than half of the nodes fail.
-## Multi Paxos 思想
+## Multi-Paxos Concept
-Basic Paxos 算法的仅能就单个值达成共识,为了能够对一系列的值达成共识,我们需要用到 Multi Paxos 思想。
+The Basic Paxos algorithm can only reach consensus on a single value. To achieve consensus on a series of values, we need to employ the Multi-Paxos concept.
-⚠️**注意**:Multi-Paxos 只是一种思想,这种思想的核心就是通过多个 Basic Paxos 实例就一系列值达成共识。也就是说,Basic Paxos 是 Multi-Paxos 思想的核心,Multi-Paxos 就是多执行几次 Basic Paxos。
+⚠️**Note**: Multi-Paxos is merely a concept; the core of this concept is to reach consensus on a series of values through multiple Basic Paxos instances. In other words, Basic Paxos is at the heart of the Multi-Paxos concept, while Multi-Paxos simply entails executing Basic Paxos several times.
-由于兰伯特提到的 Multi-Paxos 思想缺少代码实现的必要细节(比如怎么选举领导者),所以在理解和实现上比较困难。
+Since the Multi-Paxos concept mentioned by Lamport lacks the essential details for code implementation (such as how to elect a leader), it can be somewhat challenging to understand and implement.
-不过,也不需要担心,我们并不需要自己实现基于 Multi-Paxos 思想的共识算法,业界已经有了比较出名的实现。像 Raft 算法就是 Multi-Paxos 的一个变种,其简化了 Multi-Paxos 的思想,变得更容易被理解以及工程实现,实际项目中可以优先考虑 Raft 算法。
+However, there's no need to worry; we do not need to implement a consensus algorithm based on the Multi-Paxos concept ourselves. The industry has already produced some notable implementations. For instance, the Raft algorithm is a variant of Multi-Paxos that simplifies its ideas, making it easier to understand and implement. In actual projects, Raft should be prioritized.
-## 参考
+## References
-
-- 分布式系统中的一致性与共识算法:
+- Consistency and Consensus Algorithms in Distributed Systems:
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
index 18d2c2eb0cb..aad8a9af1cf 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/protocol/raft-algorithm.md
@@ -1,167 +1,166 @@
---
-title: Raft 算法详解
-category: 分布式
+title: Detailed Explanation of the Raft Algorithm
+category: Distributed Systems
tag:
- - 分布式协议&算法
- - 共识算法
+ - Distributed Protocols & Algorithms
+ - Consensus Algorithm
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [Xieqijun](https://github.com/jun0315) 共同完成。
+> This article is jointly completed by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [Xieqijun](https://github.com/jun0315).
-## 1 背景
+## 1 Background
-当今的数据中心和应用程序在高度动态的环境中运行,为了应对高度动态的环境,它们通过额外的服务器进行横向扩展,并且根据需求进行扩展和收缩。同时,服务器和网络故障也很常见。
+Today’s data centers and applications operate in highly dynamic environments. To cope with such environments, they horizontally scale with additional servers and adjust resources based on demand. At the same time, server and network failures are quite common.
-因此,系统必须在正常操作期间处理服务器的上下线。它们必须对变故做出反应并在几秒钟内自动适应;对客户来说的话,明显的中断通常是不可接受的。
+Therefore, systems must handle server ups and downs during normal operations. They must react to incidents and adapt automatically within seconds; significant interruptions are usually unacceptable for customers.
-幸运的是,分布式共识可以帮助应对这些挑战。
+Fortunately, distributed consensus can help address these challenges.
-### 1.1 拜占庭将军
+### 1.1 Byzantine Generals
-在介绍共识算法之前,先介绍一个简化版拜占庭将军的例子来帮助理解共识算法。
+Before introducing consensus algorithms, let's first present a simplified example of Byzantine generals to help understand the consensus algorithm.
-> 假设多位拜占庭将军中没有叛军,信使的信息可靠但有可能被暗杀的情况下,将军们如何达成是否要进攻的一致性决定?
+> Suppose there are multiple Byzantine generals with no traitors, and the messenger's information is reliable but may get assassinated. How can the generals reach a consensus on whether to attack?
-解决方案大致可以理解成:先在所有的将军中选出一个大将军,用来做出所有的决定。
+The solution can be roughly understood as: first, select a general to be the Grand General among all the generals, who will make all the decisions.
-举例如下:假如现在一共有 3 个将军 A,B 和 C,每个将军都有一个随机时间的倒计时器,倒计时一结束,这个将军就把自己当成大将军候选人,然后派信使传递选举投票的信息给将军 B 和 C,如果将军 B 和 C 还没有把自己当作候选人(自己的倒计时还没有结束),并且没有把选举票投给其他人,它们就会把票投给将军 A,信使回到将军 A 时,将军 A 知道自己收到了足够的票数,成为大将军。在有了大将军之后,是否需要进攻就由大将军 A 决定,然后再去派信使通知另外两个将军,自己已经成为了大将军。如果一段时间还没收到将军 B 和 C 的回复(信使可能会被暗杀),那就再重派一个信使,直到收到回复。
+For example, suppose there are 3 generals A, B, and C. Each general has a countdown timer that runs for a random time. Once the timer reaches zero, that general declares themselves a candidate for Grand General and sends messages to generals B and C with details of the election vote. If generals B and C have not declared themselves candidates (their countdowners have not expired) and have not voted for anyone else, they will vote for general A. When messenger returns to general A, they will know they have received enough votes to become the Grand General. With the Grand General in place, whether to attack will be determined by Grand General A, who will then inform the other two generals about it. If there is still no response from generals B and C after a period of time (the messenger may have been assassinated), a new messenger will be dispatched until a response is received.
-### 1.2 共识算法
+### 1.2 Consensus Algorithm
-共识是可容错系统中的一个基本问题:即使面对故障,服务器也可以在共享状态上达成一致。
+Consensus is a fundamental problem in fault-tolerant systems: even in the presence of failures, servers must agree on a shared state.
-共识算法允许一组节点像一个整体一样一起工作,即使其中的一些节点出现故障也能够继续工作下去,其正确性主要是源于复制状态机的性质:一组`Server`的状态机计算相同状态的副本,即使有一部分的`Server`宕机了它们仍然能够继续运行。
+Consensus algorithms allow a group of nodes to work together as a whole, ensuring that the system can continue to function even if some nodes fail. Its correctness primarily stems from the properties of replicated state machines: a set of `Servers` computes replicas of the same state machine, which can continue to operate even if part of the `Servers` goes down.

-`图-1 复制状态机架构`
+`Figure 1: Replicated State Machine Architecture`
-一般通过使用复制日志来实现复制状态机。每个`Server`存储着一份包括命令序列的日志文件,状态机会按顺序执行这些命令。因为每个日志包含相同的命令,并且顺序也相同,所以每个状态机处理相同的命令序列。由于状态机是确定性的,所以处理相同的状态,得到相同的输出。
+Typically, replicated state machines are implemented using replicated logs. Each `Server` stores a log file that includes a sequence of commands; state machines execute these commands in order. Since each log contains the same commands executed in the same order, every state machine processes the same command sequence. As the state machine is deterministic, it produces the same output when processing the same state.
-因此共识算法的工作就是保持复制日志的一致性。服务器上的共识模块从客户端接收命令并将它们添加到日志中。它与其他服务器上的共识模块通信,以确保即使某些服务器发生故障。每个日志最终包含相同顺序的请求。一旦命令被正确地复制,它们就被称为已提交。每个服务器的状态机按照日志顺序处理已提交的命令,并将输出返回给客户端,因此,这些服务器形成了一个单一的、高度可靠的状态机。
+Thus, the job of the consensus algorithm is to maintain the consistency of the replicated logs. The consensus module on each server receives commands from clients and adds them to the log. It communicates with the consensus modules on other servers to ensure that all logs contain requests in the same order, even if some servers fail. Once commands are correctly replicated, they are said to be committed. The state machine of each server processes committed commands in log order and returns the output to the client; hence, these servers form a single, highly reliable state machine.
-适用于实际系统的共识算法通常具有以下特性:
+Consensus algorithms suitable for real systems typically have the following characteristics:
-- 安全。确保在非拜占庭条件(也就是上文中提到的简易版拜占庭)下的安全性,包括网络延迟、分区、包丢失、复制和重新排序。
-- 高可用。只要大多数服务器都是可操作的,并且可以相互通信,也可以与客户端进行通信,那么这些服务器就可以看作完全功能可用的。因此,一个典型的由五台服务器组成的集群可以容忍任何两台服务器端故障。假设服务器因停止而发生故障;它们稍后可能会从稳定存储上的状态中恢复并重新加入集群。
-- 一致性不依赖时序。错误的时钟和极端的消息延迟,在最坏的情况下也只会造成可用性问题,而不会产生一致性问题。
+- Safety. Ensures safety under non-Byzantine conditions (i.e., the simplified version of Byzantine mentioned above), including network delays, partitions, packet losses, and message reordering.
+- High availability. As long as a majority of servers are operational and can communicate with each other and with clients, these servers can be considered fully functional. Thus, a typical cluster of five servers can tolerate the failure of any two servers. If servers fail due to stoppage, they can later recover from stable storage and rejoin the cluster.
+- Consistency does not depend on timing. Erroneous clocks and extreme message delays will only cause availability issues in the worst case and will not result in consistency problems.
+- As long as the majority of servers respond in the cluster, commands can be completed without being affected by a few slow servers.
-- 在集群中大多数服务器响应,命令就可以完成,不会被少数运行缓慢的服务器来影响整体系统性能。
+## 2 Basics
-## 2 基础
+### 2.1 Node Types
-### 2.1 节点类型
+A Raft cluster consists of several servers. Taking a typical cluster of 5 servers as an example, at any given time, each server will be in one of the following three states:
-一个 Raft 集群包括若干服务器,以典型的 5 服务器集群举例。在任意的时间,每个服务器一定会处于以下三个状态中的一个:
+- `Leader`: Responsible for initiating heartbeats, responding to clients, creating logs, and synchronizing logs.
+- `Candidate`: A temporary role during the leader election process, transformed from Follower, initiating votes to participate in the election.
+- `Follower`: Accepts heartbeats and log synchronization data from the Leader, voting for the Candidate.
-- `Leader`:负责发起心跳,响应客户端,创建日志,同步日志。
-- `Candidate`:Leader 选举过程中的临时角色,由 Follower 转化而来,发起投票参与竞选。
-- `Follower`:接受 Leader 的心跳和日志同步数据,投票给 Candidate。
-
-在正常的情况下,只有一个服务器是 Leader,剩下的服务器是 Follower。Follower 是被动的,它们不会发送任何请求,只是响应来自 Leader 和 Candidate 的请求。
+Under normal conditions, only one server is the Leader, while the remaining servers are Followers. Followers are passive; they do not send requests but only respond to requests from the Leader and Candidates.

-`图-2:服务器的状态`
+`Figure 2: Server States`
-### 2.2 任期
+### 2.2 Terms

-`图-3:任期`
+`Figure 3: Terms`
-如图 3 所示,raft 算法将时间划分为任意长度的任期(term),任期用连续的数字表示,看作当前 term 号。每一个任期的开始都是一次选举,在选举开始时,一个或多个 Candidate 会尝试成为 Leader。如果一个 Candidate 赢得了选举,它就会在该任期内担任 Leader。如果没有选出 Leader,将会开启另一个任期,并立刻开始下一次选举。raft 算法保证在给定的一个任期最少要有一个 Leader。
+As shown in Figure 3, the Raft algorithm divides time into terms of arbitrary length, represented by consecutive numbers considered the current term number. The beginning of each term is an election; at the start of an election, one or more Candidates will attempt to become the Leader. If a Candidate wins the election, they will serve as the Leader for that term. If no Leader is elected, a new term will be initiated, and the next election will begin immediately. The Raft algorithm guarantees that there is at least one Leader in a given term.
-每个节点都会存储当前的 term 号,当服务器之间进行通信时会交换当前的 term 号;如果有服务器发现自己的 term 号比其他人小,那么他会更新到较大的 term 值。如果一个 Candidate 或者 Leader 发现自己的 term 过期了,他会立即退回成 Follower。如果一台服务器收到的请求的 term 号是过期的,那么它会拒绝此次请求。
+Each node stores the current term number, and during communication between servers, they exchange their current term numbers. If a server finds its term number is smaller than others, it will update to the larger term value. If a Candidate or Leader finds its term has expired, it will revert to Follower immediately. If a server receives a request with an expired term number, it will reject the request.
-### 2.3 日志
+### 2.3 Logs
-- `entry`:每一个事件成为 entry,只有 Leader 可以创建 entry。entry 的内容为``其中 cmd 是可以应用到状态机的操作。
-- `log`:由 entry 构成的数组,每一个 entry 都有一个表明自己在 log 中的 index。只有 Leader 才可以改变其他节点的 log。entry 总是先被 Leader 添加到自己的 log 数组中,然后再发起共识请求,获得同意后才会被 Leader 提交给状态机。Follower 只能从 Leader 获取新日志和当前的 commitIndex,然后把对应的 entry 应用到自己的状态机中。
+- `entry`: Each event becomes an entry, and only the Leader can create entries. The content of an entry is `` where cmd is an operation that can be applied to the state machine.
+- `log`: An array composed of entries, where each entry has an index indicating its position in the log. Only the Leader can change the logs of other nodes. Entries are always first added to the Leader's log array, and only after initiating a consensus request and obtaining agreement can they be committed to the state machine. Followers can only obtain new logs and the current commitIndex from the Leader and then apply the corresponding entries to their state machines.
-## 3 领导人选举
+## 3 Leader Election
-raft 使用心跳机制来触发 Leader 的选举。
+Raft uses a heartbeat mechanism to trigger Leader elections.
-如果一台服务器能够收到来自 Leader 或者 Candidate 的有效信息,那么它会一直保持为 Follower 状态,并且刷新自己的 electionElapsed,重新计时。
+If a server receives valid information from a Leader or Candidate, it will remain in the Follower state and refresh its electionElapsed timer.
-Leader 会向所有的 Follower 周期性发送心跳来保证自己的 Leader 地位。如果一个 Follower 在一个周期内没有收到心跳信息,就叫做选举超时,然后它就会认为此时没有可用的 Leader,并且开始进行一次选举以选出一个新的 Leader。
+The Leader periodically sends heartbeats to all Followers to ensure its leadership status. If a Follower does not receive heartbeat information within a cycle, it triggers an election timeout and assumes there is currently no available Leader, initiating an election to elect a new Leader.
-为了开始新的选举,Follower 会自增自己的 term 号并且转换状态为 Candidate。然后他会向所有节点发起 RequestVoteRPC 请求, Candidate 的状态会持续到以下情况发生:
+To start a new election, the Follower increments its term number and changes its state to Candidate. It will then send a RequestVoteRPC to all nodes, and the Candidate's state will persist until one of the following occurs:
-- 赢得选举
-- 其他节点赢得选举
-- 一轮选举结束,无人胜出
+- Wins the election
+- Other nodes win the election
+- One round of the election ends with no winner
-赢得选举的条件是:一个 Candidate 在一个任期内收到了来自集群内的多数选票`(N/2+1)`,就可以成为 Leader。
+The condition for winning the election is: a Candidate must receive votes from a majority of the cluster `(N/2+1)` in one term to become the Leader.
-在 Candidate 等待选票的时候,它可能收到其他节点声明自己是 Leader 的心跳,此时有两种情况:
+While waiting for votes, a Candidate may receive heartbeat messages from other nodes claiming to be the Leader, resulting in two situations:
-- 该 Leader 的 term 号大于等于自己的 term 号,说明对方已经成为 Leader,则自己回退为 Follower。
-- 该 Leader 的 term 号小于自己的 term 号,那么会拒绝该请求并让该节点更新 term。
+- The term number of that Leader is greater than or equal to its own; indicating that the other has become the Leader, it will revert to Follower.
+- The term number of that Leader is less than its own. In this case, the request is rejected, prompting that node to update its term.
-由于可能同一时刻出现多个 Candidate,导致没有 Candidate 获得大多数选票,如果没有其他手段来重新分配选票的话,那么可能会无限重复下去。
+As multiple Candidates may appear simultaneously without any means to redistribute votes, it could lead to an infinite loop of elections.
-raft 使用了随机的选举超时时间来避免上述情况。每一个 Candidate 在发起选举后,都会随机化一个新的选举超时时间,这种机制使得各个服务器能够分散开来,在大多数情况下只有一个服务器会率先超时;它会在其他服务器超时之前赢得选举。
+Raft uses a random election timeout to avoid the above situation. Each Candidate randomizes a new election timeout after initiating an election, allowing servers to spread apart; in most cases, only one server will timeout first, winning the election before others do.
-## 4 日志复制
+## 4 Log Replication
-一旦选出了 Leader,它就开始接受客户端的请求。每一个客户端的请求都包含一条需要被复制状态机(`Replicated State Machine`)执行的命令。
+Once a Leader is elected, it starts receiving client requests. Each client's request includes a command that needs to be executed by the replicated state machine (`Replicated State Machine`).
-Leader 收到客户端请求后,会生成一个 entry,包含``,再将这个 entry 添加到自己的日志末尾后,向所有的节点广播该 entry,要求其他服务器复制这条 entry。
+After the Leader receives the client request, it generates an entry containing ``, adds this entry to its log's end, and broadcasts it to all nodes, asking the other servers to replicate the entry.
-如果 Follower 接受该 entry,则会将 entry 添加到自己的日志后面,同时返回给 Leader 同意。
+If a Follower accepts the entry, it will append the entry to its log and return a consent response to the Leader.
-如果 Leader 收到了多数的成功响应,Leader 会将这个 entry 应用到自己的状态机中,之后可以称这个 entry 是 committed 的,并且向客户端返回执行结果。
+If the Leader receives a majority of successful responses, it will apply this entry to its state machine, and this entry can then be termed as committed, eventually returning the execution result to the client.
-raft 保证以下两个性质:
+Raft guarantees the following two properties:
-- 在两个日志里,有两个 entry 拥有相同的 index 和 term,那么它们一定有相同的 cmd
-- 在两个日志里,有两个 entry 拥有相同的 index 和 term,那么它们前面的 entry 也一定相同
+- Among two logs, if two entries have the same index and term, their cmds must also be the same.
+- Among two logs, if two entries have the same index and term, their preceding entries must also be the same.
-通过“仅有 Leader 可以生成 entry”来保证第一个性质,第二个性质需要一致性检查来进行保证。
+The first property is guaranteed by "only the Leader can generate entries," while the second property requires consistency checks to ensure.
-一般情况下,Leader 和 Follower 的日志保持一致,然后,Leader 的崩溃会导致日志不一样,这样一致性检查会产生失败。Leader 通过强制 Follower 复制自己的日志来处理日志的不一致。这就意味着,在 Follower 上的冲突日志会被领导者的日志覆盖。
+Generally, the logs of Leaders and Followers remain consistent; however, a Leader's crash may result in inconsistent logs, causing consistency checks to fail. The Leader handles log inconsistency by forcing Followers to replicate its logs, meaning any conflicting logs on Followers will be overwritten by the Leader's logs.
-为了使得 Follower 的日志和自己的日志一致,Leader 需要找到 Follower 与它日志一致的地方,然后删除 Follower 在该位置之后的日志,接着把这之后的日志发送给 Follower。
+To ensure Followers' logs align with its own, the Leader must find the point of consistency in the Follower's log and delete any log entries after that point, then send the missing logs from that position onward to the Follower.
-`Leader` 给每一个`Follower` 维护了一个 `nextIndex`,它表示 `Leader` 将要发送给该追随者的下一条日志条目的索引。当一个 `Leader` 开始掌权时,它会将 `nextIndex` 初始化为它的最新的日志条目索引数+1。如果一个 `Follower` 的日志和 `Leader` 的不一致,`AppendEntries` 一致性检查会在下一次 `AppendEntries RPC` 时返回失败。在失败之后,`Leader` 会将 `nextIndex` 递减然后重试 `AppendEntries RPC`。最终 `nextIndex` 会达到一个 `Leader` 和 `Follower` 日志一致的地方。这时,`AppendEntries` 会返回成功,`Follower` 中冲突的日志条目都被移除了,并且添加所缺少的上了 `Leader` 的日志条目。一旦 `AppendEntries` 返回成功,`Follower` 和 `Leader` 的日志就一致了,这样的状态会保持到该任期结束。
+The `Leader` maintains a `nextIndex` for each `Follower`, representing the index of the next log entry that the `Leader` will send to that Follower. When a `Leader` begins authority, it initializes `nextIndex` to the number of its latest log entry index + 1. If a `Follower`'s log is inconsistent with the `Leader`'s, the consistency check in `AppendEntries` will return a failure in the next `AppendEntries RPC`. After a failure, the `Leader` decrements `nextIndex` and retries `AppendEntries RPC`. Eventually, `nextIndex` reaches a point of consistency between the `Leader` and `Follower` logs. At that point, `AppendEntries` succeeds, and any conflicting log entries on the `Follower` are removed, with the missing log entries appended from the `Leader`. Once `AppendEntries` succeeds, the logs of `Follower` and `Leader` are consistent, maintaining this state until the end of the term.
-## 5 安全性
+## 5 Safety
-### 5.1 选举限制
+### 5.1 Election Constraints
-Leader 需要保证自己存储全部已经提交的日志条目。这样才可以使日志条目只有一个流向:从 Leader 流向 Follower,Leader 永远不会覆盖已经存在的日志条目。
+The Leader must ensure it stores all committed log entries. This assures that log entries have only one direction: from Leader to Follower; the Leader will never overwrite already existing log entries.
-每个 Candidate 发送 RequestVoteRPC 时,都会带上最后一个 entry 的信息。所有节点收到投票信息时,会对该 entry 进行比较,如果发现自己的更新,则拒绝投票给该 Candidate。
+Every Candidate sends a RequestVoteRPC with information on the last entry. When all nodes receive the voting information, they compare this entry against their own updates; if they find their logs more up-to-date, they refuse to vote for that Candidate.
-判断日志新旧的方式:如果两个日志的 term 不同,term 大的更新;如果 term 相同,更长的 index 更新。
+The way to determine the recency of logs: if the terms of the two logs differ, the log with the larger term updates; if the terms are the same, the longer index updates.
-### 5.2 节点崩溃
+### 5.2 Node Crashes
-如果 Leader 崩溃,集群中的节点在 electionTimeout 时间内没有收到 Leader 的心跳信息就会触发新一轮的选主,在选主期间整个集群对外是不可用的。
+If the Leader crashes, nodes in the cluster that do not receive heartbeat information from the Leader within the electionTimeout period will trigger a new round of leader election, during which the entire cluster becomes unavailable to outside requests.
-如果 Follower 和 Candidate 崩溃,处理方式会简单很多。之后发送给它的 RequestVoteRPC 和 AppendEntriesRPC 会失败。由于 raft 的所有请求都是幂等的,所以失败的话会无限的重试。如果崩溃恢复后,就可以收到新的请求,然后选择追加或者拒绝 entry。
+If Followers or Candidates crash, the process is much simpler. Subsequent RequestVoteRPCs and AppendEntriesRPCs sent to them will fail. Since all Raft requests are idempotent, failures will result in infinite retries. After recovery from a crash, they can receive new requests, choosing to append or reject entries.
-### 5.3 时间与可用性
+### 5.3 Time and Availability
-raft 的要求之一就是安全性不依赖于时间:系统不能仅仅因为一些事件发生的比预想的快一些或者慢一些就产生错误。为了保证上述要求,最好能满足以下的时间条件:
+One of Raft's requirements is that safety does not depend on time: the system cannot generate errors simply because some events occur faster or slower than expected. To ensure the above requirement, it is best to satisfy the following time conditions:
`broadcastTime << electionTimeout << MTBF`
-- `broadcastTime`:向其他节点并发发送消息的平均响应时间;
-- `electionTimeout`:选举超时时间;
-- `MTBF(mean time between failures)`:单台机器的平均健康时间;
+- `broadcastTime`: The average response time for concurrently sending messages to other nodes.
+- `electionTimeout`: The timeout for elections.
+- `MTBF(mean time between failures)`: The average healthy uptime of a single machine.
-`broadcastTime`应该比`electionTimeout`小一个数量级,为的是使`Leader`能够持续发送心跳信息(heartbeat)来阻止`Follower`开始选举;
+`broadcastTime` should be an order of magnitude smaller than `electionTimeout` to allow the `Leader` to continually send heartbeat messages to prevent `Follower` from initiating elections.
-`electionTimeout`也要比`MTBF`小几个数量级,为的是使得系统稳定运行。当`Leader`崩溃时,大约会在整个`electionTimeout`的时间内不可用;我们希望这种情况仅占全部时间的很小一部分。
+`electionTimeout` should also be several orders smaller than `MTBF` to keep the system running stably. When `Leader` crashes, the system will be unavailable for approximately the entire duration of `electionTimeout`; we wish for this situation to occupy only a small part of the total time.
-由于`broadcastTime`和`MTBF`是由系统决定的属性,因此需要决定`electionTimeout`的时间。
+Since `broadcastTime` and `MTBF` are system-determined properties, it is necessary to set the duration of `electionTimeout`.
-一般来说,broadcastTime 一般为 `0.5~20ms`,electionTimeout 可以设置为 `10~500ms`,MTBF 一般为一两个月。
+In general, `broadcastTime` is usually between `0.5-20ms`, while `electionTimeout` can be set to `10-500ms`, and `MTBF` is typically one to two months.
-## 6 参考
+## 6 References
-
-
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
index 3eaee38b50c..703d0f1f7d0 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/dubbo.md
@@ -1,461 +1,71 @@
---
-title: Dubbo常见问题总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Dubbo Issues
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
::: tip
-- Dubbo3 已经发布,这篇文章是基于 Dubbo2 写的。Dubbo3 基于 Dubbo2 演进而来,在保持原有核心功能特性的同时, Dubbo3 在易用性、超大规模微服务实践、云原生基础设施适配、安全设计等几大方向上进行了全面升级。
-- 本文中的很多链接已经失效,主要原因是因为 Dubbo 官方文档进行了修改导致 URL 失效。
+- Dubbo3 has been released, and this article is based on Dubbo2. Dubbo3 is evolved from Dubbo2, maintaining the original core functional characteristics while undergoing comprehensive upgrades in usability, large-scale microservice practices, cloud-native infrastructure adaptation, and security design.
+- Many links in this article are outdated, mainly due to changes in the official Dubbo documentation that have caused URL failures.
:::
-这篇文章是我根据官方文档以及自己平时的使用情况,对 Dubbo 所做的一个总结。欢迎补充!
+This article is a summary of Dubbo based on the official documentation and my own usage experience. Contributions are welcome!
-## Dubbo 基础
+## Dubbo Basics
-### 什么是 Dubbo?
+### What is Dubbo?
-
+
-[Apache Dubbo](https://github.com/apache/dubbo) |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源 WEB 和 RPC 框架。
+[Apache Dubbo](https://github.com/apache/dubbo) |ˈdʌbəʊ| is a high-performance, lightweight open-source WEB and RPC framework.
-根据 [Dubbo 官方文档](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/)的介绍,Dubbo 提供了六大核心能力
+According to the [official Dubbo documentation](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/), Dubbo provides six core capabilities:
-1. 面向接口代理的高性能 RPC 调用。
-2. 智能容错和负载均衡。
-3. 服务自动注册和发现。
-4. 高度可扩展能力。
-5. 运行期流量调度。
-6. 可视化的服务治理与运维。
+1. High-performance RPC calls oriented to interface proxies.
+1. Intelligent fault tolerance and load balancing.
+1. Automatic service registration and discovery.
+1. Highly extensible capabilities.
+1. Runtime traffic scheduling.
+1. Visual service governance and operation.
-
+
-简单来说就是:**Dubbo 不光可以帮助我们调用远程服务,还提供了一些其他开箱即用的功能比如智能负载均衡。**
+In simple terms: **Dubbo not only helps us call remote services but also provides other out-of-the-box features like intelligent load balancing.**
-Dubbo 目前已经有接近 34.4 k 的 Star 。
+Dubbo currently has nearly 34.4k stars.
-在 **2020 年度 OSC 中国开源项目** 评选活动中,Dubbo 位列开发框架和基础组件类项目的第 7 名。相比几年前来说,热度和排名有所下降。
+In the **2020 OSC China Open Source Project** selection event, Dubbo ranked 7th among development frameworks and basic component projects. Compared to a few years ago, its popularity and ranking have declined.

-Dubbo 是由阿里开源,后来加入了 Apache 。正是由于 Dubbo 的出现,才使得越来越多的公司开始使用以及接受分布式架构。
+Dubbo was open-sourced by Alibaba and later joined Apache. It is the emergence of Dubbo that has led to more and more companies beginning to use and accept distributed architectures.
-### 为什么要用 Dubbo?
+### Why Use Dubbo?
-随着互联网的发展,网站的规模越来越大,用户数量越来越多。单一应用架构、垂直应用架构无法满足我们的需求,这个时候分布式服务架构就诞生了。
+With the development of the internet, websites are becoming larger, and the number of users is increasing. Single application architectures and vertical application architectures can no longer meet our needs, which is when distributed service architectures were born.
-分布式服务架构下,系统被拆分成不同的服务比如短信服务、安全服务,每个服务独立提供系统的某个核心服务。
+In a distributed service architecture, the system is split into different services, such as SMS service and security service, with each service independently providing a core service of the system.
-我们可以使用 Java RMI(Java Remote Method Invocation)、Hessian 这种支持远程调用的框架来简单地暴露和引用远程服务。但是!当服务越来越多之后,服务调用关系越来越复杂。当应用访问压力越来越大后,负载均衡以及服务监控的需求也迫在眉睫。我们可以用 F5 这类硬件来做负载均衡,但这样增加了成本,并且存在单点故障的风险。
+We can use frameworks that support remote calls, such as Java RMI (Java Remote Method Invocation) and Hessian, to simply expose and reference remote services. However! As the number of services increases, the relationships between service calls become increasingly complex. When application access pressure increases, the need for load balancing and service monitoring becomes urgent. We can use hardware like F5 for load balancing, but this increases costs and poses a risk of single points of failure.
-不过,Dubbo 的出现让上述问题得到了解决。**Dubbo 帮助我们解决了什么问题呢?**
+However, the emergence of Dubbo has solved the above problems. **What problems does Dubbo help us solve?**
-1. **负载均衡**:同一个服务部署在不同的机器时该调用哪一台机器上的服务。
-2. **服务调用链路生成**:随着系统的发展,服务越来越多,服务间依赖关系变得错踪复杂,甚至分不清哪个应用要在哪个应用之前启动,架构师都不能完整的描述应用的架构关系。Dubbo 可以为我们解决服务之间互相是如何调用的。
-3. **服务访问压力以及时长统计、资源调度和治理**:基于访问压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。
-4. ……
+1. **Load Balancing**: When the same service is deployed on different machines, which machine's service should be called?
+1. **Service Call Chain Generation**: As the system evolves, the number of services increases, and the dependencies between services become complex, making it difficult to determine which application should start before which. Even architects cannot fully describe the architectural relationships of applications. Dubbo can help us understand how services call each other.
+1. **Service Access Pressure and Duration Statistics, Resource Scheduling, and Governance**: Real-time management of cluster capacity based on access pressure to improve cluster utilization.
+1. ……
-
+
-另外,Dubbo 除了能够应用在分布式系统中,也可以应用在现在比较火的微服务系统中。不过,由于 Spring Cloud 在微服务中应用更加广泛,所以,我觉得一般我们提 Dubbo 的话,大部分是分布式系统的情况。
+Additionally, Dubbo can be applied not only in distributed systems but also in the currently popular microservice systems. However, since Spring Cloud is more widely used in microservices, I believe that when we mention Dubbo, it is mostly in the context of distributed systems.
-**我们刚刚提到了分布式这个概念,下面再给大家介绍一下什么是分布式?为什么要分布式?**
+**We just mentioned the concept of distribution, so let’s introduce what distribution is and why it is necessary.**
-## 分布式基础
+## Basics of Distribution
-### 什么是分布式?
+### What is Distribution?
-分布式或者说 SOA 分布式重要的就是面向服务,说简单的分布式就是我们把整个系统拆分成不同的服务然后将这些服务放在不同的服务器上减轻单体服务的压力提高并发量和性能。比如电商系统可以简单地拆分成订单系统、商品系统、登录系统等等,拆分之后的每个服务可以部署在不同的机器上,如果某一个服务的访问量比较大的话也可以将这个服务同时部署在多台机器上。
-
-
-
-### 为什么要分布式?
-
-从开发角度来讲单体应用的代码都集中在一起,而分布式系统的代码根据业务被拆分。所以,每个团队可以负责一个服务的开发,这样提升了开发效率。另外,代码根据业务拆分之后更加便于维护和扩展。
-
-另外,我觉得将系统拆分成分布式之后不光便于系统扩展和维护,更能提高整个系统的性能。你想一想嘛?把整个系统拆分成不同的服务/系统,然后每个服务/系统 单独部署在一台服务器上,是不是很大程度上提高了系统性能呢?
-
-## Dubbo 架构
-
-### Dubbo 架构中的核心角色有哪些?
-
-[官方文档中的框架设计章节](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/design/) 已经介绍的非常详细了,我这里把一些比较重要的点再提一下。
-
-
-
-上述节点简单介绍以及他们之间的关系:
-
-- **Container:** 服务运行容器,负责加载、运行服务提供者。必须。
-- **Provider:** 暴露服务的服务提供方,会向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。必须。
-- **Consumer:** 调用远程服务的服务消费方,会向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。必须。
-- **Registry:** 服务注册与发现的注册中心。注册中心会返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者。非必须。
-- **Monitor:** 统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的监控中心。服务消费者和提供者会定时发送统计数据到监控中心。 非必须。
-
-### Dubbo 中的 Invoker 概念了解么?
-
-`Invoker` 是 Dubbo 领域模型中非常重要的一个概念,你如果阅读过 Dubbo 源码的话,你会无数次看到这玩意。就比如下面我要说的负载均衡这块的源码中就有大量 `Invoker` 的身影。
-
-简单来说,`Invoker` 就是 Dubbo 对远程调用的抽象。
-
-
-
-按照 Dubbo 官方的话来说,`Invoker` 分为
-
-- 服务提供 `Invoker`
-- 服务消费 `Invoker`
-
-假如我们需要调用一个远程方法,我们需要动态代理来屏蔽远程调用的细节吧!我们屏蔽掉的这些细节就依赖对应的 `Invoker` 实现, `Invoker` 实现了真正的远程服务调用。
-
-### Dubbo 的工作原理了解么?
-
-下图是 Dubbo 的整体设计,从下至上分为十层,各层均为单向依赖。
-
-> 左边淡蓝背景的为服务消费方使用的接口,右边淡绿色背景的为服务提供方使用的接口,位于中轴线上的为双方都用到的接口。
-
-
-
-- **config 配置层**:Dubbo 相关的配置。支持代码配置,同时也支持基于 Spring 来做配置,以 `ServiceConfig`, `ReferenceConfig` 为中心
-- **proxy 服务代理层**:调用远程方法像调用本地的方法一样简单的一个关键,真实调用过程依赖代理类,以 `ServiceProxy` 为中心。
-- **registry 注册中心层**:封装服务地址的注册与发现。
-- **cluster 路由层**:封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以 `Invoker` 为中心。
-- **monitor 监控层**:RPC 调用次数和调用时间监控,以 `Statistics` 为中心。
-- **protocol 远程调用层**:封装 RPC 调用,以 `Invocation`, `Result` 为中心。
-- **exchange 信息交换层**:封装请求响应模式,同步转异步,以 `Request`, `Response` 为中心。
-- **transport 网络传输层**:抽象 mina 和 netty 为统一接口,以 `Message` 为中心。
-- **serialize 数据序列化层**:对需要在网络传输的数据进行序列化。
-
-### Dubbo 的 SPI 机制了解么? 如何扩展 Dubbo 中的默认实现?
-
-SPI(Service Provider Interface) 机制被大量用在开源项目中,它可以帮助我们动态寻找服务/功能(比如负载均衡策略)的实现。
-
-SPI 的具体原理是这样的:我们将接口的实现类放在配置文件中,我们在程序运行过程中读取配置文件,通过反射加载实现类。这样,我们可以在运行的时候,动态替换接口的实现类。和 IoC 的解耦思想是类似的。
-
-Java 本身就提供了 SPI 机制的实现。不过,Dubbo 没有直接用,而是对 Java 原生的 SPI 机制进行了增强,以便更好满足自己的需求。
-
-**那我们如何扩展 Dubbo 中的默认实现呢?**
-
-比如说我们想要实现自己的负载均衡策略,我们创建对应的实现类 `XxxLoadBalance` 实现 `LoadBalance` 接口或者 `AbstractLoadBalance` 类。
-
-```java
-package com.xxx;
-
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
-import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
-
-public class XxxLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
- public Invoker select(List> invokers, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
- // ...
- }
-}
-```
-
-我们将这个实现类的路径写入到`resources` 目录下的 `META-INF/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance`文件中即可。
-
-```java
-src
- |-main
- |-java
- |-com
- |-xxx
- |-XxxLoadBalance.java (实现LoadBalance接口)
- |-resources
- |-META-INF
- |-dubbo
- |-org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance (纯文本文件,内容为:xxx=com.xxx.XxxLoadBalance)
-```
-
-`org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance`
-
-```plain
-xxx=com.xxx.XxxLoadBalance
-```
-
-其他还有很多可供扩展的选择,你可以在[官方文档](https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/overview/home/)中找到。
-
-### Dubbo 的微内核架构了解吗?
-
-Dubbo 采用 微内核(Microkernel) + 插件(Plugin) 模式,简单来说就是微内核架构。微内核只负责组装插件。
-
-**何为微内核架构呢?** 《软件架构模式》 这本书是这样介绍的:
-
-> 微内核架构模式(有时被称为插件架构模式)是实现基于产品应用程序的一种自然模式。基于产品的应用程序是已经打包好并且拥有不同版本,可作为第三方插件下载的。然后,很多公司也在开发、发布自己内部商业应用像有版本号、说明及可加载插件式的应用软件(这也是这种模式的特征)。微内核系统可让用户添加额外的应用如插件,到核心应用,继而提供了可扩展性和功能分离的用法。
-
-微内核架构包含两类组件:**核心系统(core system)** 和 **插件模块(plug-in modules)**。
-
-
-
-核心系统提供系统所需核心能力,插件模块可以扩展系统的功能。因此, 基于微内核架构的系统,非常易于扩展功能。
-
-我们常见的一些 IDE,都可以看作是基于微内核架构设计的。绝大多数 IDE 比如 IDEA、VSCode 都提供了插件来丰富自己的功能。
-
-正是因为 Dubbo 基于微内核架构,才使得我们可以随心所欲替换 Dubbo 的功能点。比如你觉得 Dubbo 的序列化模块实现的不满足自己要求,没关系啊!你自己实现一个序列化模块就好了啊!
-
-通常情况下,微核心都会采用 Factory、IoC、OSGi 等方式管理插件生命周期。Dubbo 不想依赖 Spring 等 IoC 容器,也不想自己造一个小的 IoC 容器(过度设计),因此采用了一种最简单的 Factory 方式管理插件:**JDK 标准的 SPI 扩展机制** (`java.util.ServiceLoader`)。
-
-### 关于 Dubbo 架构的一些自测小问题
-
-#### 注册中心的作用了解么?
-
-注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互。
-
-#### 服务提供者宕机后,注册中心会做什么?
-
-注册中心会立即推送事件通知消费者。
-
-#### 监控中心的作用呢?
-
-监控中心负责统计各服务调用次数,调用时间等。
-
-#### 注册中心和监控中心都宕机的话,服务都会挂掉吗?
-
-不会。两者都宕机也不影响已运行的提供者和消费者,消费者在本地缓存了提供者列表。注册中心和监控中心都是可选的,服务消费者可以直连服务提供者。
-
-## Dubbo 的负载均衡策略
-
-### 什么是负载均衡?
-
-先来看一下稍微官方点的解释。下面这段话摘自维基百科对负载均衡的定义:
-
-> 负载均衡改善了跨多个计算资源(例如计算机,计算机集群,网络链接,中央处理单元或磁盘驱动)的工作负载分布。负载平衡旨在优化资源使用,最大化吞吐量,最小化响应时间,并避免任何单个资源的过载。使用具有负载平衡而不是单个组件的多个组件可以通过冗余提高可靠性和可用性。负载平衡通常涉及专用软件或硬件。
-
-**上面讲的大家可能不太好理解,再用通俗的话给大家说一下。**
-
-我们的系统中的某个服务的访问量特别大,我们将这个服务部署在了多台服务器上,当客户端发起请求的时候,多台服务器都可以处理这个请求。那么,如何正确选择处理该请求的服务器就很关键。假如,你就要一台服务器来处理该服务的请求,那该服务部署在多台服务器的意义就不复存在了。负载均衡就是为了避免单个服务器响应同一请求,容易造成服务器宕机、崩溃等问题,我们从负载均衡的这四个字就能明显感受到它的意义。
-
-### Dubbo 提供的负载均衡策略有哪些?
-
-在集群负载均衡时,Dubbo 提供了多种均衡策略,默认为 `random` 随机调用。我们还可以自行扩展负载均衡策略(参考 Dubbo SPI 机制)。
-
-在 Dubbo 中,所有负载均衡实现类均继承自 `AbstractLoadBalance`,该类实现了 `LoadBalance` 接口,并封装了一些公共的逻辑。
-
-```java
-public abstract class AbstractLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
-
- static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) {
- }
-
- @Override
- public Invoker select(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
- }
-
- protected abstract Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation);
-
-
- int getWeight(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) {
-
- }
-}
-```
-
-`AbstractLoadBalance` 的实现类有下面这些:
-
-
-
-官方文档对负载均衡这部分的介绍非常详细,推荐小伙伴们看看,地址:[https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#m-zhdocsv27devsourceloadbalance](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#m-zhdocsv27devsourceloadbalance) 。
-
-#### RandomLoadBalance
-
-根据权重随机选择(对加权随机算法的实现)。这是 Dubbo 默认采用的一种负载均衡策略。
-
-`RandomLoadBalance` 具体的实现原理非常简单,假如有两个提供相同服务的服务器 S1,S2,S1 的权重为 7,S2 的权重为 3。
-
-我们把这些权重值分布在坐标区间会得到:S1->[0, 7) ,S2->[7, 10)。我们生成[0, 10) 之间的随机数,随机数落到对应的区间,我们就选择对应的服务器来处理请求。
-
-
-
-`RandomLoadBalance` 的源码非常简单,简单花几分钟时间看一下。
-
-> 以下源码来自 Dubbo master 分支上的最新的版本 2.7.9。
-
-```java
-public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
-
- public static final String NAME = "random";
-
- @Override
- protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
-
- int length = invokers.size();
- boolean sameWeight = true;
- int[] weights = new int[length];
- int totalWeight = 0;
- // 下面这个for循环的主要作用就是计算所有该服务的提供者的权重之和 totalWeight(),
- // 除此之外,还会检测每个服务提供者的权重是否相同
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
- totalWeight += weight;
- weights[i] = totalWeight;
- if (sameWeight && totalWeight != weight * (i + 1)) {
- sameWeight = false;
- }
- }
- if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
- // 随机生成一个 [0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字
- int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
- // 判断会落在哪个服务提供者的区间
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- if (offset < weights[i]) {
- return invokers.get(i);
- }
- }
-
- return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
- }
-
-}
-
-```
-
-#### LeastActiveLoadBalance
-
-`LeastActiveLoadBalance` 直译过来就是**最小活跃数负载均衡**。
-
-这个名字起得有点不直观,不仔细看官方对活跃数的定义,你压根不知道这玩意是干嘛的。
-
-我这么说吧!初始状态下所有服务提供者的活跃数均为 0(每个服务提供者的中特定方法都对应一个活跃数,我在后面的源码中会提到),每收到一个请求后,对应的服务提供者的活跃数 +1,当这个请求处理完之后,活跃数 -1。
-
-因此,**Dubbo 就认为谁的活跃数越少,谁的处理速度就越快,性能也越好,这样的话,我就优先把请求给活跃数少的服务提供者处理。**
-
-**如果有多个服务提供者的活跃数相等怎么办?**
-
-很简单,那就再走一遍 `RandomLoadBalance` 。
-
-```java
-public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
-
- public static final String NAME = "leastactive";
-
- @Override
- protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
- int length = invokers.size();
- int leastActive = -1;
- int leastCount = 0;
- int[] leastIndexes = new int[length];
- int[] weights = new int[length];
- int totalWeight = 0;
- int firstWeight = 0;
- boolean sameWeight = true;
- // 这个 for 循环的主要作用是遍历 invokers 列表,找出活跃数最小的 Invoker
- // 如果有多个 Invoker 具有相同的最小活跃数,还会记录下这些 Invoker 在 invokers 集合中的下标,并累加它们的权重,比较它们的权重值是否相等
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- Invoker invoker = invokers.get(i);
- // 获取 invoker 对应的活跃(active)数
- int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
- int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
- weights[i] = afterWarmup;
- if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) {
- leastActive = active;
- leastCount = 1;
- leastIndexes[0] = i;
- totalWeight = afterWarmup;
- firstWeight = afterWarmup;
- sameWeight = true;
- } else if (active == leastActive) {
- leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i;
- totalWeight += afterWarmup;
- if (sameWeight && afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
- sameWeight = false;
- }
- }
- }
- // 如果只有一个 Invoker 具有最小的活跃数,此时直接返回该 Invoker 即可
- if (leastCount == 1) {
- return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]);
- }
- // 如果有多个 Invoker 具有相同的最小活跃数,但它们之间的权重不同
- // 这里的处理方式就和 RandomLoadBalance 一致了
- if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
- int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
- for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
- int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i];
- offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex];
- if (offsetWeight < 0) {
- return invokers.get(leastIndex);
- }
- }
- }
- return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]);
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-活跃数是通过 `RpcStatus` 中的一个 `ConcurrentMap` 保存的,根据 URL 以及服务提供者被调用的方法的名称,我们便可以获取到对应的活跃数。也就是说服务提供者中的每一个方法的活跃数都是互相独立的。
-
-```java
-public class RpcStatus {
-
- private static final ConcurrentMap> METHOD_STATISTICS =
- new ConcurrentHashMap>();
-
- public static RpcStatus getStatus(URL url, String methodName) {
- String uri = url.toIdentityString();
- ConcurrentMap map = METHOD_STATISTICS.computeIfAbsent(uri, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
- return map.computeIfAbsent(methodName, k -> new RpcStatus());
- }
- public int getActive() {
- return active.get();
- }
-
-}
-```
-
-#### ConsistentHashLoadBalance
-
-`ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 小伙伴们应该也不会陌生,在分库分表、各种集群中就经常使用这个负载均衡策略。
-
-`ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 即**一致性 Hash 负载均衡策略**。 `ConsistentHashLoadBalance` 中没有权重的概念,具体是哪个服务提供者处理请求是由你的请求的参数决定的,也就是说相同参数的请求总是发到同一个服务提供者。
-
-
-
-另外,Dubbo 为了避免数据倾斜问题(节点不够分散,大量请求落到同一节点),还引入了虚拟节点的概念。通过虚拟节点可以让节点更加分散,有效均衡各个节点的请求量。
-
-
-
-官方有详细的源码分析:[https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#23-consistenthashloadbalance](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/loadbalance/#23-consistenthashloadbalance) 。这里还有一个相关的 [PR#5440](https://github.com/apache/dubbo/pull/5440) 来修复老版本中 ConsistentHashLoadBalance 存在的一些 Bug。感兴趣的小伙伴,可以多花点时间研究一下。我这里不多分析了,这个作业留给你们!
-
-#### RoundRobinLoadBalance
-
-加权轮询负载均衡。
-
-轮询就是把请求依次分配给每个服务提供者。加权轮询就是在轮询的基础上,让更多的请求落到权重更大的服务提供者上。比如假如有两个提供相同服务的服务器 S1,S2,S1 的权重为 7,S2 的权重为 3。
-
-如果我们有 10 次请求,那么 7 次会被 S1 处理,3 次被 S2 处理。
-
-但是,如果是 `RandomLoadBalance` 的话,很可能存在 10 次请求有 9 次都被 S1 处理的情况(概率性问题)。
-
-Dubbo 中的 `RoundRobinLoadBalance` 的代码实现被修改重建了好几次,Dubbo-2.6.5 版本的 `RoundRobinLoadBalance` 为平滑加权轮询算法。
-
-## Dubbo 序列化协议
-
-### Dubbo 支持哪些序列化方式呢?
-
-
-
-Dubbo 支持多种序列化方式:JDK 自带的序列化、hessian2、JSON、Kryo、FST、Protostuff,ProtoBuf 等等。
-
-Dubbo 默认使用的序列化方式是 hessian2。
-
-### 谈谈你对这些序列化协议了解?
-
-一般我们不会直接使用 JDK 自带的序列化方式。主要原因有两个:
-
-1. **不支持跨语言调用** : 如果调用的是其他语言开发的服务的时候就不支持了。
-2. **性能差**:相比于其他序列化框架性能更低,主要原因是序列化之后的字节数组体积较大,导致传输成本加大。
-
-JSON 序列化由于性能问题,我们一般也不会考虑使用。
-
-像 Protostuff,ProtoBuf、hessian2 这些都是跨语言的序列化方式,如果有跨语言需求的话可以考虑使用。
-
-Kryo 和 FST 这两种序列化方式是 Dubbo 后来才引入的,性能非常好。不过,这两者都是专门针对 Java 语言的。Dubbo 官网的一篇文章中提到说推荐使用 Kryo 作为生产环境的序列化方式。
-
-Dubbo 官方文档中还有一个关于这些[序列化协议的性能对比图](https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/serialization/#m-zhdocsv27userserialization)可供参考。
-
-
-
-
+Distribution, or SOA, is fundamentally service-oriented. In simple terms, distribution means splitting the entire system into different services and placing these services on different servers to reduce the pressure on monolithic services and
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
index 35301d0bceb..ed51c28908d 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/http&rpc.md
@@ -1,196 +1,196 @@
---
-title: 有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?
-category: 分布式
+title: With HTTP Protocol, Why is RPC Still Needed?
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
-> 本文来自[小白 debug](https://juejin.cn/user/4001878057422087)投稿,原文: 。
+> This article is contributed by [Xiao Bai debug](https://juejin.cn/user/4001878057422087), original text: .
-我想起了我刚工作的时候,第一次接触 RPC 协议,当时就很懵,我 HTTP 协议用的好好的,为什么还要用 RPC 协议?
+I remember when I first started working and encountered RPC protocol for the first time. I was confused; I was using HTTP protocol just fine, so why do we need RPC protocol?
-于是就到网上去搜。
+So, I searched online.
-不少解释显得非常官方,我相信大家在各种平台上也都看到过,解释了又好像没解释,都在**用一个我们不认识的概念去解释另外一个我们不认识的概念**,懂的人不需要看,不懂的人看了还是不懂。
+Many explanations seemed very official. I'm sure everyone has seen them on various platforms, explaining but seemingly not explaining; they all used **one concept we don't understand to explain another concept we don't understand**. Those who understood didn't need to read it, and those who didn't understand remained confused.
-这种看了,又好像没看的感觉,云里雾里的很难受,**我懂**。
+That feeling of having read but not having grasped it is quite uncomfortable, **I understand**.
-为了避免大家有强烈的**审丑疲劳**,今天我们来尝试重新换个方式讲一讲。
+To avoid eliciting strong **aesthetic fatigue**, let's try to explain this in a different way today.
-## 从 TCP 聊起
+## Let's Start with TCP
-作为一个程序员,假设我们需要在 A 电脑的进程发一段数据到 B 电脑的进程,我们一般会在代码里使用 socket 进行编程。
+As a programmer, suppose we need to send some data from a process on computer A to a process on computer B, we typically use sockets in our code for programming.
-这时候,我们可选项一般也就**TCP 和 UDP 二选一。TCP 可靠,UDP 不可靠。** 除非是马总这种神级程序员(早期 QQ 大量使用 UDP),否则,只要稍微对可靠性有些要求,普通人一般无脑选 TCP 就对了。
+At this point, our options generally come down to **TCP or UDP**. TCP is reliable, while UDP is not. Unless someone like Ma Huateng, a legendary programmer (who heavily used UDP in early QQ), opts for UDP, most ordinary people tend to choose TCP without thinking if there's any requirement for reliability.
-类似下面这样。
+It looks something like this.
```ini
fd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
```
-其中`SOCK_STREAM`,是指使用**字节流**传输数据,说白了就是**TCP 协议**。
+Where `SOCK_STREAM` indicates the use of **byte stream** to transmit data, which simply means **TCP protocol**.
-在定义了 socket 之后,我们就可以愉快的对这个 socket 进行操作,比如用`bind()`绑定 IP 端口,用`connect()`发起建连。
+After defining the socket, we can happily perform operations on it, such as using `bind()` to bind the IP port and `connect()` to initiate a connection.
-
+
-在连接建立之后,我们就可以使用`send()`发送数据,`recv()`接收数据。
+Once the connection is established, we can use `send()` to send data and `recv()` to receive data.
-光这样一个纯裸的 TCP 连接,就可以做到收发数据了,那是不是就够了?
+A pure naked TCP connection can achieve data transmission; isn't that enough?
-不行,这么用会有问题。
+No, there are problems with using it this way.
-## 使用纯裸 TCP 会有什么问题
+## What are the Problems with Using Pure Naked TCP?
-八股文常背,TCP 是有三个特点,**面向连接**、**可靠**、基于**字节流**。
+It's often repeated that TCP has three characteristics: **connection-oriented**, **reliable**, and based on **byte stream**.
-
+
-这三个特点真的概括的 **非常精辟** ,这个八股文我们没白背。
+These three characteristics are indeed **very concise**; we didn’t memorize them for nothing.
-每个特点展开都能聊一篇文章,而今天我们需要关注的是 **基于字节流** 这一点。
+Each characteristic can be discussed in its own article, but today we need to focus on **byte stream**.
-字节流可以理解为一个双向的通道里流淌的二进制数据,也就是 **01 串** 。纯裸 TCP 收发的这些 01 串之间是 **没有任何边界** 的,你根本不知道到哪个地方才算一条完整消息。
+A byte stream can be understood as flowing binary data in a bidirectional channel, which is essentially a string of **01**. The 01 strings transmitted by pure naked TCP have **no boundaries** between them; you have no idea where a complete message starts and ends.
-
+
-正因为这个没有任何边界的特点,所以当我们选择使用 TCP 发送 **"夏洛"和"特烦恼"** 的时候,接收端收到的就是 **"夏洛特烦恼"** ,这时候接收端没发区分你是想要表达 **"夏洛"+"特烦恼"** 还是 **"夏洛特"+"烦恼"** 。
+Because of this lack of boundaries, when we choose to send **"Xia Luo" and "Te Fan Nao"** over TCP, the receiving end gets **"Xia Luo Te Fan Nao."** At this point, the receiver cannot distinguish whether you meant to express **"Xia Luo" + "Te Fan Nao"** or **"Xia Luo Te" + "Fan Nao."**
-
+
-这就是所谓的 **粘包问题**,之前也写过一篇专门的[文章](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0-YBxU1cSbDdzcZEZjmQYA)聊过这个问题。
+This is known as the **sticky packet problem**, and I have previously written a dedicated [article](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0-YBxU1cSbDdzcZEZjmQYA) discussing this issue.
-说这个的目的是为了告诉大家,纯裸 TCP 是不能直接拿来用的,你需要在这个基础上加入一些 **自定义的规则** ,用于区分 **消息边界** 。
+The point of mentioning this is to let everyone know that pure naked TCP cannot be used directly; you need to add some **custom rules** to distinguish **message boundaries.**
-于是我们会把每条要发送的数据都包装一下,比如加入 **消息头** ,消息头里写清楚一个完整的包长度是多少,根据这个长度可以继续接收数据,截取出来后它们就是我们真正要传输的 **消息体** 。
+So, we typically wrap each piece of data to be sent, such as adding a **message header** that clearly states the length of a complete packet. Based on this length, we can continue receiving data and extract it, which forms our actual **message body**.
-
+
-而这里头提到的 **消息头** ,还可以放各种东西,比如消息体是否被压缩过和消息体格式之类的,只要上下游都约定好了,互相都认就可以了,这就是所谓的 **协议。**
+The mentioned **message header** can also contain various pieces of information, such as whether the message body is compressed and the format of the message body. As long as both ends agree on the protocol, it's fine.
-每个使用 TCP 的项目都可能会定义一套类似这样的协议解析标准,他们可能 **有区别,但原理都类似**。
+Every project using TCP may define a set of parsing standards similar to this; they may **differ but the principles are similar.**
-**于是基于 TCP,就衍生了非常多的协议,比如 HTTP 和 RPC。**
+**Thus, many protocols have emerged based on TCP, such as HTTP and RPC.**
-## HTTP 和 RPC
+## HTTP and RPC
-### RPC 其实是一种调用方式
+### RPC is Essentially a Calling Method
-我们回过头来看网络的分层图。
+Let’s turn back to the network layering diagram.
-
+
-**TCP 是传输层的协议** ,而基于 TCP 造出来的 HTTP 和各类 RPC 协议,它们都只是定义了不同消息格式的 **应用层协议** 而已。
+**TCP is a transport layer protocol**, while HTTP and various RPC protocols built on TCP are merely **application layer protocols** that define different message formats.
-**HTTP**(**H**yper **T**ext **T**ransfer **P**rotocol)协议又叫做 **超文本传输协议** 。我们用的比较多,平时上网在浏览器上敲个网址就能访问网页,这里用到的就是 HTTP 协议。
+**HTTP** (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) is commonly known as the **hypertext transfer protocol**. We use it quite often; when browsing the internet, we can access a webpage by typing a URL in the browser, which utilizes the HTTP protocol.
-
+
-而 **RPC**(**R**emote **P**rocedure **C**all)又叫做 **远程过程调用**,它本身并不是一个具体的协议,而是一种 **调用方式** 。
+On the other hand, **RPC** (Remote Procedure Call) is also known as **remote procedure invocation**. It is not a specific protocol; it represents a **calling method**.
-举个例子,我们平时调用一个 **本地方法** 就像下面这样。
+For example, when we usually call a **local method**, it looks something like this.
```ini
- res = localFunc(req)
+res = localFunc(req)
```
-如果现在这不是个本地方法,而是个**远端服务器**暴露出来的一个方法`remoteFunc`,如果我们还能像调用本地方法那样去调用它,这样就可以**屏蔽掉一些网络细节**,用起来更方便,岂不美哉?
+If now this isn't a local method, but a method `remoteFunc` exposed by a **remote server**, and we can still call it just like a local method, it can **mask some network details**, making it more convenient, wouldn't that be great?
```ini
res = remoteFunc(req)
```
-
+
-基于这个思路,大佬们造出了非常多款式的 RPC 协议,比如比较有名的`gRPC`,`thrift`。
+Based on this idea, many different types of RPC protocols have been created, such as the well-known `gRPC` and `thrift`.
-值得注意的是,虽然大部分 RPC 协议底层使用 TCP,但实际上 **它们不一定非得使用 TCP,改用 UDP 或者 HTTP,其实也可以做到类似的功能。**
+It's important to note that although most RPC protocols use TCP underneath, in reality, **they don't have to use TCP; they could also use UDP or HTTP, achieving similar functionalities.**
-到这里,我们回到文章标题的问题。
+Now, let's return to the question posed in the article title.
-### 那既然有 RPC 了,为什么还要有 HTTP 呢?
+### If RPC Exists, Why is HTTP Still Needed?
-其实,TCP 是 **70 年** 代出来的协议,而 HTTP 是 **90 年代** 才开始流行的。而直接使用裸 TCP 会有问题,可想而知,这中间这么多年有多少自定义的协议,而这里面就有 **80 年代** 出来的`RPC`。
+In fact, TCP was a protocol developed in the **1970s**, while HTTP didn't begin to gain popularity until the **1990s**. Given that directly using naked TCP has its problems, it’s easy to see how many custom protocols have emerged over the years; and RPC was developed in the **1980s**.
-所以我们该问的不是 **既然有 HTTP 协议为什么要有 RPC** ,而是 **为什么有 RPC 还要有 HTTP 协议?**
+Therefore, we should not ask **why RPC exists alongside HTTP** but rather **why does HTTP still exist alongside RPC?**
-现在电脑上装的各种联网软件,比如 xx 管家,xx 卫士,它们都作为客户端(Client) 需要跟服务端(Server) 建立连接收发消息,此时都会用到应用层协议,在这种 Client/Server (C/S) 架构下,它们可以使用自家造的 RPC 协议,因为它只管连自己公司的服务器就 ok 了。
+Various networked applications installed on computers, such as xx Manager and xx Guardian, act as clients requiring connection to servers to send and receive messages; they utilize application layer protocols. In this Client/Server (C/S) architecture, they can use their own RPC protocols since they only need to connect to their company’s server.
-但有个软件不同,浏览器(Browser) ,不管是 Chrome 还是 IE,它们不仅要能访问自家公司的**服务器(Server)** ,还需要访问其他公司的网站服务器,因此它们需要有个统一的标准,不然大家没法交流。于是,HTTP 就是那个时代用于统一 **Browser/Server (B/S)** 的协议。
+However, one type of software is different: browsers (Browser). Whether it’s Chrome or IE, they need not only to access their own company’s **server** but also to reach websites hosted by other companies; therefore, they need a unified standard, otherwise, communication would be impossible. Consequently, HTTP serves as that standard for unifying **Browser/Server (B/S)** communication.
-也就是说在多年以前,**HTTP 主要用于 B/S 架构,而 RPC 更多用于 C/S 架构。但现在其实已经没分那么清了,B/S 和 C/S 在慢慢融合。** 很多软件同时支持多端,比如某度云盘,既要支持**网页版**,还要支持**手机端和 PC 端**,如果通信协议都用 HTTP 的话,那服务器只用同一套就够了。而 RPC 就开始退居幕后,一般用于公司内部集群里,各个微服务之间的通讯。
+In other words, many years ago, **HTTP was primarily used for B/S architecture, while RPC was more for C/S architecture. However, such distinctions have blurred over time; B/S and C/S are gradually merging.** Many applications now support multiple platforms, such as a certain cloud storage service needing both **web** and **mobile/PC** support. If communication protocols only used HTTP, the server would only need to deal with one set of protocols. Consequently, RPC has begun to take a backseat and is generally used for communication between various microservices within company internal clusters.
-那这么说的话,**都用 HTTP 得了,还用什么 RPC?**
+So that raises the question: **Why not just use HTTP; why use RPC at all?**
-仿佛又回到了文章开头的样子,那这就要从它们之间的区别开始说起。
+It feels like we're back at the beginning of the article, so we’ll need to discuss the differences between them.
-### HTTP 和 RPC 有什么区别
+### What Are the Differences Between HTTP and RPC?
-我们来看看 RPC 和 HTTP 区别比较明显的几个点。
+Let's look at a few points that clearly distinguish RPC from HTTP.
-#### 服务发现
+#### Service Discovery
-首先要向某个服务器发起请求,你得先建立连接,而建立连接的前提是,你得知道 **IP 地址和端口** 。这个找到服务对应的 IP 端口的过程,其实就是 **服务发现**。
+To initiate a request to a server, you must first establish a connection, and the prerequisite for establishing that connection is knowing the **IP address and port**. The process of finding the service's corresponding IP and port is known as **service discovery**.
-在 **HTTP** 中,你知道服务的域名,就可以通过 **DNS 服务** 去解析得到它背后的 IP 地址,默认 **80 端口**。
+In **HTTP**, if you know the domain name of the service, you can resolve the IP address behind it through **DNS services**, typically on the **default port 80**.
-而 **RPC** 的话,就有些区别,一般会有专门的中间服务去保存服务名和 IP 信息,比如 **Consul、Etcd、Nacos、ZooKeeper,甚至是 Redis**。想要访问某个服务,就去这些中间服务去获得 IP 和端口信息。由于 DNS 也是服务发现的一种,所以也有基于 DNS 去做服务发现的组件,比如 **CoreDNS**。
+In the case of **RPC**, there are some differences. Typically, there will be dedicated intermediary services responsible for storing service names and IP information, such as **Consul, Etcd, Nacos, ZooKeeper, or even Redis**. To access a certain service, you'd query these intermediary services to obtain the IP and port information. Since DNS also functions as a form of service discovery, there exist components that achieve service discovery based on DNS, such as **CoreDNS**.
-可以看出服务发现这一块,两者是有些区别,但不太能分高低。
+It's evident that the service discovery aspect does show some differences between the two, but they are not significantly superior or inferior to one another.
-#### 底层连接形式
+#### Underlying Connection Method
-以主流的 **HTTP1.1** 协议为例,其默认在建立底层 TCP 连接之后会一直保持这个连接(**keep alive**),之后的请求和响应都会复用这条连接。
+Taking the mainstream **HTTP/1.1** protocol as an example, its default behavior is to maintain a TCP connection once established (the **keep-alive** feature), allowing subsequent requests and responses to reuse this connection.
-而 **RPC** 协议,也跟 HTTP 类似,也是通过建立 TCP 长链接进行数据交互,但不同的地方在于,RPC 协议一般还会再建个 **连接池**,在请求量大的时候,建立多条连接放在池内,要发数据的时候就从池里取一条连接出来,用完放回去,下次再复用,可以说非常环保。
+On the other hand, **RPC protocols** also establish TCP long connections for data interactions, but unlike HTTP, RPC protocols typically create a **connection pool**. During times of high request volume, multiple connections are established and kept in the pool; when data needs to be sent, a connection is retrieved from the pool, used, and then returned for future reuse, which is quite efficient.
-
+
-由于连接池有利于提升网络请求性能,所以不少编程语言的网络库里都会给 HTTP 加个连接池,比如 Go 就是这么干的。
+Connection pools help improve network request performance, which is why many programming languages' network libraries introduce a connection pool for HTTP, as seen in Go.
-可以看出这一块两者也没太大区别,所以也不是关键。
+From this perspective, there isn’t a significant distinction in practices between them, so it’s not a key difference either.
-#### 传输的内容
+#### Content Being Transmitted
-基于 TCP 传输的消息,说到底,无非都是 **消息头 Header 和消息体 Body。**
+Messages transmitted using TCP ultimately consist of **header and body**.
-**Header** 是用于标记一些特殊信息,其中最重要的是 **消息体长度**。
+**Header** is used to denote certain special information, with the most important aspect being the **length of the message body**.
-**Body** 则是放我们真正需要传输的内容,而这些内容只能是二进制 01 串,毕竟计算机只认识这玩意。所以 TCP 传字符串和数字都问题不大,因为字符串可以转成编码再变成 01 串,而数字本身也能直接转为二进制。但结构体呢,我们得想个办法将它也转为二进制 01 串,这样的方案现在也有很多现成的,比如 **JSON,Protocol Buffers (Protobuf)** 。
+**Body** contains the actual content we need to transmit, which must be represented in binary as 01 strings since computers only recognize this format. Thus, TCP can handle strings and numbers without issue, because strings can be encoded as 01 strings, and numbers can be directly converted into binary. For structures, however, we need a method to convert them into binary 01 strings, and there are many existing solutions for this, such as **JSON** and **Protocol Buffers (Protobuf)**.
-这个将结构体转为二进制数组的过程就叫 **序列化** ,反过来将二进制数组复原成结构体的过程叫 **反序列化**。
+The process of converting a structure into a binary array is called **serialization**, while reverting a binary array back into a structure is called **deserialization**.
-
+
-对于主流的 HTTP1.1,虽然它现在叫超文本协议,支持音频视频,但 HTTP 设计 初是用于做网页文本展示的,所以它传的内容以字符串为主。Header 和 Body 都是如此。在 Body 这块,它使用 **JSON** 来 **序列化** 结构体数据。
+For mainstream HTTP/1.1, although it is referred to as a hypertext protocol—supporting audio and video—HTTP was originally designed primarily for displaying web text, so the content it transmits is predominantly string-based. Both the header and body follow this pattern. In the body section, it employs **JSON** to **serialize** structured data.
-我们可以随便截个图直观看下。
+We can capture a snapshot for a more intuitive view.
-
+
-可以看到这里面的内容非常多的冗余,显得非常啰嗦。最明显的,像 Header 里的那些信息,其实如果我们约定好头部的第几位是 `Content-Type`,就不需要每次都真的把 `Content-Type` 这个字段都传过来,类似的情况其实在 Body 的 JSON 结构里也特别明显。
+The content here exhibits significant redundancy and appears verbose. Most noticeably, information in the header (like `Content-Type`) could be effectively conveyed by agreeing on a specific bit's position in the header instead of transmitting the `Content-Type` field literally each time. Similar situations can also be observed in the body's JSON structure.
-而 RPC,因为它定制化程度更高,可以采用体积更小的 Protobuf 或其他序列化协议去保存结构体数据,同时也不需要像 HTTP 那样考虑各种浏览器行为,比如 302 重定向跳转啥的。**因此性能也会更好一些,这也是在公司内部微服务中抛弃 HTTP,选择使用 RPC 的最主要原因。**
+In contrast, RPC, due to its higher level of customization, can utilize smaller serialization formats like Protobuf to retain structured data, without needing to accommodate various browser behaviors (like 302 redirection). **Thus, its performance can be better, which is a major reason for opting for RPC instead of HTTP in internal microservice communications.**
-
+
-
+
-当然上面说的 HTTP,其实 **特指的是现在主流使用的 HTTP1.1**,`HTTP2`在前者的基础上做了很多改进,所以 **性能可能比很多 RPC 协议还要好**,甚至连`gRPC`底层都直接用的`HTTP2`。
+It’s worth noting that the HTTP referred to here specifically denotes the currently mainstream HTTP/1.1. `HTTP/2` has made many improvements on top of this, so **its performance may exceed many RPC protocols**, with `gRPC` directly utilizing `HTTP/2` at its core.
-那么问题又来了。
+This prompts yet another question.
-### 为什么既然有了 HTTP2,还要有 RPC 协议?
+### Why, Since We've Emerged with HTTP/2, Do We Still Need RPC Protocols?
-这个是由于 HTTP2 是 2015 年出来的。那时候很多公司内部的 RPC 协议都已经跑了好些年了,基于历史原因,一般也没必要去换了。
+The reason is that HTTP/2 was introduced in 2015, by which time many internal RPC protocols had already been running for several years; thus, due to historical reasons, there typically wasn’t a pressing need to shift to alternatives.
-## 总结
+## Conclusion
-- 纯裸 TCP 是能收发数据,但它是个无边界的数据流,上层需要定义消息格式用于定义 **消息边界** 。于是就有了各种协议,HTTP 和各类 RPC 协议就是在 TCP 之上定义的应用层协议。
-- **RPC 本质上不算是协议,而是一种调用方式**,而像 gRPC 和 Thrift 这样的具体实现,才是协议,它们是实现了 RPC 调用的协议。目的是希望程序员能像调用本地方法那样去调用远端的服务方法。同时 RPC 有很多种实现方式,**不一定非得基于 TCP 协议**。
-- 从发展历史来说,**HTTP 主要用于 B/S 架构,而 RPC 更多用于 C/S 架构。但现在其实已经没分那么清了,B/S 和 C/S 在慢慢融合。** 很多软件同时支持多端,所以对外一般用 HTTP 协议,而内部集群的微服务之间则采用 RPC 协议进行通讯。
-- RPC 其实比 HTTP 出现的要早,且比目前主流的 HTTP1.1 性能要更好,所以大部分公司内部都还在使用 RPC。
-- **HTTP2.0** 在 **HTTP1.1** 的基础上做了优化,性能可能比很多 RPC 协议都要好,但由于是这几年才出来的,所以也不太可能取代掉 RPC。
+- Pure naked TCP can send and receive data, but it is a borderless data stream, requiring the upper layers to define a message format to establish **message boundaries**. Thus, various application layer protocols, including HTTP and various RPC protocols, are defined on top of TCP.
+- **RPC is not essentially a protocol but a method of invocation**, while implementations like gRPC and Thrift are the protocols that realize RPC calls. The goal is to allow programmers to invoke remote service methods like local methods. Moreover, there are various ways to implement RPC, **and it does not have to be based on the TCP protocol**.
+- From a historical development perspective, **HTTP was primarily used for B/S architecture, while RPC was more oriented towards C/S architecture. However, now the distinction has become less clear as B/S and C/S are gradually merging.** Many applications support multiple platforms, making HTTP generally suitable for external communications, while RPC protocols are used for communication within internal clusters.
+- RPC actually predates HTTP and tends to perform better than the currently mainstream HTTP/1.1, which is why most companies still utilize RPC internally.
+- **HTTP/2** has been optimized upon **HTTP/1.1**, potentially outperforming many RPC protocols; however, it was introduced only in recent years, making it more challenging to replace RPC quickly.
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
index d2c5fb5e9c7..8d5e2801222 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/rpc/rpc-intro.md
@@ -1,141 +1,138 @@
---
-title: RPC基础知识总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Basic RPC Knowledge
+category: Distributed
tag:
- rpc
---
-这篇文章会简单介绍一下 RPC 相关的基础概念。
+This article will briefly introduce the basic concepts related to RPC.
-## RPC 是什么?
+## What is RPC?
-**RPC(Remote Procedure Call)** 即远程过程调用,通过名字我们就能看出 RPC 关注的是远程调用而非本地调用。
+**RPC (Remote Procedure Call)** refers to remote procedure calls, and from its name, we can see that RPC focuses on remote calls rather than local calls.
-**为什么要 RPC ?** 因为,两个不同的服务器上的服务提供的方法不在一个内存空间,所以,需要通过网络编程才能传递方法调用所需要的参数。并且,方法调用的结果也需要通过网络编程来接收。但是,如果我们自己手动网络编程来实现这个调用过程的话工作量是非常大的,因为,我们需要考虑底层传输方式(TCP 还是 UDP)、序列化方式等等方面。
+**Why use RPC?** Because the methods provided by services on two different servers do not share the same memory space, it is necessary to use network programming to pass the parameters required for the method call. Furthermore, the results of the method call also need to be received through network programming. However, if we were to manually implement this calling process through network programming, the workload would be extensive, as we need to consider various factors such as the underlying transmission method (TCP or UDP), serialization methods, and more.
-**RPC 能帮助我们做什么呢?** 简单来说,通过 RPC 可以帮助我们调用远程计算机上某个服务的方法,这个过程就像调用本地方法一样简单。并且!我们不需要了解底层网络编程的具体细节。
+**What can RPC help us with?** Simply put, RPC allows us to call a method from a service on a remote computer as easily as calling a local method. Moreover, we do not need to understand the specific details of underlying network programming.
-举个例子:两个不同的服务 A、B 部署在两台不同的机器上,服务 A 如果想要调用服务 B 中的某个方法的话就可以通过 RPC 来做。
+For example, if service A, deployed on one machine, wants to call a method from service B, deployed on another machine, it can do so via RPC.
-一言蔽之:**RPC 的出现就是为了让你调用远程方法像调用本地方法一样简单。**
+In short: **The purpose of RPC is to make calling remote methods as simple as calling local methods.**
-## RPC 的原理是什么?
+## What is the principle of RPC?
-为了能够帮助小伙伴们理解 RPC 原理,我们可以将整个 RPC 的 核心功能看作是下面 👇 5 个部分实现的:
+To help understand the principle of RPC, we can view the entire core functionality of RPC as being implemented in the following five parts:
-1. **客户端(服务消费端)**:调用远程方法的一端。
-1. **客户端 Stub(桩)**:这其实就是一代理类。代理类主要做的事情很简单,就是把你调用方法、类、方法参数等信息传递到服务端。
-1. **网络传输**:网络传输就是你要把你调用的方法的信息比如说参数啊这些东西传输到服务端,然后服务端执行完之后再把返回结果通过网络传输给你传输回来。网络传输的实现方式有很多种比如最基本的 Socket 或者性能以及封装更加优秀的 Netty(推荐)。
-1. **服务端 Stub(桩)**:这个桩就不是代理类了。我觉得理解为桩实际不太好,大家注意一下就好。这里的服务端 Stub 实际指的就是接收到客户端执行方法的请求后,去执行对应的方法然后返回结果给客户端的类。
-1. **服务端(服务提供端)**:提供远程方法的一端。
+1. **Client (Service Consumer)**: The end that calls the remote method.
+1. **Client Stub**: This is essentially a proxy class. Its main responsibility is to pass information about the method call, class, and method parameters to the server.
+1. **Network Transmission**: This involves sending the information regarding the method call, such as parameters, to the server. After the server completes execution, it sends the return result back to you via network transmission. There are many ways to implement network transmission; for example, the basic Socket or the more efficient and encapsulated Netty (recommended).
+1. **Server Stub**: This stub is not a proxy class. It's important to note here that the server stub refers to the class that receives the method execution request from the client, executes the corresponding method, and then returns the result to the client.
+1. **Server (Service Provider)**: The end that provides the remote method.
-具体原理图如下,后面我会串起来将整个 RPC 的过程给大家说一下。
+The detailed principle diagram is as follows, and later I will explain the entire RPC process to everyone.
-
+
-1. 服务消费端(client)以本地调用的方式调用远程服务;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub) 接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体(序列化):`RpcRequest`;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub) 找到远程服务的地址,并将消息发送到服务提供端;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)收到消息将消息反序列化为 Java 对象: `RpcRequest`;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)根据`RpcRequest`中的类、方法、方法参数等信息调用本地的方法;
-1. 服务端 Stub(桩)得到方法执行结果并将组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体:`RpcResponse`(序列化)发送至消费方;
-1. 客户端 Stub(client stub)接收到消息并将消息反序列化为 Java 对象:`RpcResponse` ,这样也就得到了最终结果。over!
+1. The service consumer (client) calls the remote service as if it were a local call;
+1. The client stub receives the call and is responsible for assembling the method, parameters, etc., into a message body for network transmission (serialization): `RpcRequest`;
+1. The client stub finds the address of the remote service and sends the message to the service provider;
+1. The server stub receives the message and deserializes it into a Java object: `RpcRequest`;
+1. The server stub invokes the local method based on the class, method, and method parameters in the `RpcRequest`;
+1. The server stub obtains the execution result and assembles it into a message body for network transmission: `RpcResponse` (serialization) to send back to the consumer;
+1. The client stub receives the message and deserializes it into a Java object: `RpcResponse`, thus obtaining the final result. Over!
-相信小伙伴们看完上面的讲解之后,已经了解了 RPC 的原理。
+I believe that after reading the explanation above, everyone understands the principle of RPC.
-虽然篇幅不多,但是基本把 RPC 框架的核心原理讲清楚了!另外,对于上面的技术细节,我会在后面的章节介绍到。
+Although the content is not extensive, it effectively clarifies the core principles of RPC frameworks! Additionally, I will introduce the technical details mentioned above in subsequent sections.
-**最后,对于 RPC 的原理,希望小伙伴不单单要理解,还要能够自己画出来并且能够给别人讲出来。因为,在面试中这个问题在面试官问到 RPC 相关内容的时候基本都会碰到。**
+**Finally, when it comes to the principles of RPC, I hope everyone not only understands but can also reproduce it and explain it to others. This is a common question you will encounter in interviews when the interviewer asks about RPC-related content.**
-## 有哪些常见的 RPC 框架?
+## What are some common RPC frameworks?
-我们这里说的 RPC 框架指的是可以让客户端直接调用服务端方法,就像调用本地方法一样简单的框架,比如我下面介绍的 Dubbo、Motan、gRPC 这些。 如果需要和 HTTP 协议打交道,解析和封装 HTTP 请求和响应。这类框架并不能算是“RPC 框架”,比如 Feign。
+The RPC frameworks we refer to here are those that allow clients to directly call server methods as easily as calling local methods, such as Dubbo, Motan, and gRPC that I will introduce below. If you need to interact with the HTTP protocol, parse, and encapsulate HTTP requests and responses, those frameworks cannot be classified as "RPC frameworks," such as Feign.
### Dubbo

-Apache Dubbo 是一款微服务框架,为大规模微服务实践提供高性能 RPC 通信、流量治理、可观测性等解决方案,
-涵盖 Java、Golang 等多种语言 SDK 实现。
+Apache Dubbo is a microservice framework that provides high-performance RPC communication, traffic governance, observability, and other solutions for large-scale microservices practices, covering various language SDK implementations including Java and Golang.
-Dubbo 提供了从服务定义、服务发现、服务通信到流量管控等几乎所有的服务治理能力,支持 Triple 协议(基于 HTTP/2 之上定义的下一代 RPC 通信协议)、应用级服务发现、Dubbo Mesh (Dubbo3 赋予了很多云原生友好的新特性)等特性。
+Dubbo offers almost all service governance capabilities, from service definition, service discovery, service communication to traffic control, supporting the Triple protocol (the next generation RPC communication protocol defined over HTTP/2), application-level service discovery, and Dubbo Mesh (Dubbo3 has introduced many cloud-native friendly new features).

-Dubbo 是由阿里开源,后来加入了 Apache 。正是由于 Dubbo 的出现,才使得越来越多的公司开始使用以及接受分布式架构。
+Dubbo was open-sourced by Alibaba and later joined Apache. It is due to the emergence of Dubbo that more and more companies have begun to adopt and accept distributed architectures.
-Dubbo 算的是比较优秀的国产开源项目了,它的源码也是非常值得学习和阅读的!
+Dubbo is considered one of the more excellent domestic open-source projects, and its source code is worthy of study and reading!
-- GitHub:[https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo](https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo "https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo")
-- 官网:
+- GitHub: [https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo](https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo "https://github.com/apache/incubator-dubbo")
+- Official Website:
### Motan
-Motan 是新浪微博开源的一款 RPC 框架,据说在新浪微博正支撑着千亿次调用。不过笔者倒是很少看到有公司使用,而且网上的资料也比较少。
+Motan is an RPC framework open-sourced by Sina Weibo, reportedly supporting billions of calls at Sina Weibo. However, the author has rarely seen any companies using it, and there are also relatively few resources available online.
-很多人喜欢拿 Motan 和 Dubbo 作比较,毕竟都是国内大公司开源的。笔者在查阅了很多资料,以及简单查看了其源码之后发现:**Motan 更像是一个精简版的 Dubbo,可能是借鉴了 Dubbo 的思想,Motan 的设计更加精简,功能更加纯粹。**
+Many people like to compare Motan with Dubbo, as both are open-sourced by large domestic companies. After reviewing many materials and briefly checking the source code, I found that **Motan is more like a simplified version of Dubbo. It may have borrowed ideas from Dubbo, but its design is simpler and its functionality more refined.**
-不过,我不推荐你在实际项目中使用 Motan。如果你要是公司实际使用的话,还是推荐 Dubbo ,其社区活跃度以及生态都要好很多。
+However, I do not recommend using Motan in actual projects. If your company intends to use it, I still recommend Dubbo, as its community activity and ecosystem are much better.
-- 从 Motan 看 RPC 框架设计:[http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/](http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/ "http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/")
-- Motan 中文文档:[https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview](https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview "https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview")
+- Looking at RPC framework design from Motan: [http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/](http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/ "http://kriszhang.com/motan-rpc-impl/")
+- Motan Chinese Documentation: [https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview](https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview "https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_overview")
### gRPC

-gRPC 是 Google 开源的一个高性能、通用的开源 RPC 框架。其由主要面向移动应用开发并基于 HTTP/2 协议标准而设计(支持双向流、消息头压缩等功能,更加节省带宽),基于 ProtoBuf 序列化协议开发,并且支持众多开发语言。
+gRPC is a high-performance, open-source RPC framework developed by Google. It is primarily designed for mobile application development and is based on the HTTP/2 protocol standard (supporting bidirectional streaming, message header compression, etc., which saves bandwidth), and is developed based on the ProtoBuf serialization protocol, supporting many programming languages.
-**何谓 ProtoBuf?** [ProtoBuf( Protocol Buffer)](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) 是一种更加灵活、高效的数据格式,可用于通讯协议、数据存储等领域,基本支持所有主流编程语言且与平台无关。不过,通过 ProtoBuf 定义接口和数据类型还挺繁琐的,这是一个小问题。
+**What is ProtoBuf?** [ProtoBuf (Protocol Buffer)](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) is a more flexible and efficient data format that can be used in communication protocols, data storage, and other fields. It supports almost all mainstream programming languages and is platform-independent. However, defining interfaces and data types using ProtoBuf can be a bit cumbersome; that's a minor drawback.

-不得不说,gRPC 的通信层的设计还是非常优秀的,[Dubbo-go 3.0](https://dubbogo.github.io/) 的通信层改进主要借鉴了 gRPC。
+It must be said that the design of gRPC's communication layer is exceptionally well done, and the communication layer improvement of [Dubbo-go 3.0](https://dubbogo.github.io/) has heavily borrowed from gRPC.
-不过,gRPC 的设计导致其几乎没有服务治理能力。如果你想要解决这个问题的话,就需要依赖其他组件比如腾讯的 PolarisMesh(北极星)了。
+However, gRPC's design leads to almost no service governance capabilities. If you want to solve this problem, you will need to rely on other components, such as Tencent's PolarisMesh (North Star).
-- GitHub:[https://github.com/grpc/grpc](https://github.com/grpc/grpc "https://github.com/grpc/grpc")
-- 官网:[https://grpc.io/](https://grpc.io/ "https://grpc.io/")
+- GitHub: [https://github.com/grpc/grpc](https://github.com/grpc/grpc "https://github.com/grpc/grpc")
+- Official Website: [https://grpc.io/](https://grpc.io/ "https://grpc.io/")
### Thrift
-Apache Thrift 是 Facebook 开源的跨语言的 RPC 通信框架,目前已经捐献给 Apache 基金会管理,由于其跨语言特性和出色的性能,在很多互联网公司得到应用,有能力的公司甚至会基于 thrift 研发一套分布式服务框架,增加诸如服务注册、服务发现等功能。
+Apache Thrift is a cross-language RPC communication framework open-sourced by Facebook and is now managed by the Apache Foundation. Due to its cross-language features and excellent performance, it is applied in many internet companies. Capable companies may even develop a distributed service framework based on Thrift, adding features such as service registration and service discovery.
-`Thrift`支持多种不同的**编程语言**,包括`C++`、`Java`、`Python`、`PHP`、`Ruby`等(相比于 gRPC 支持的语言更多 )。
+`Thrift` supports various **programming languages**, including `C++`, `Java`, `Python`, `PHP`, `Ruby`, etc., and it supports more languages compared to gRPC.
-- 官网:[https://thrift.apache.org/](https://thrift.apache.org/ "https://thrift.apache.org/")
-- Thrift 简单介绍:[https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9")
+- Official Website: [https://thrift.apache.org/](https://thrift.apache.org/ "https://thrift.apache.org/")
+- Simple Introduction to Thrift: [https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f25d057a5a9")
-### 总结
+### Conclusion
-gRPC 和 Thrift 虽然支持跨语言的 RPC 调用,但是它们只提供了最基本的 RPC 框架功能,缺乏一系列配套的服务化组件和服务治理功能的支撑。
+Although gRPC and Thrift support cross-language RPC calls, they only provide the most basic RPC framework functionalities, lacking a series of supporting services and governance features.
-Dubbo 不论是从功能完善程度、生态系统还是社区活跃度来说都是最优秀的。而且,Dubbo 在国内有很多成功的案例比如当当网、滴滴等等,是一款经得起生产考验的成熟稳定的 RPC 框架。最重要的是你还能找到非常多的 Dubbo 参考资料,学习成本相对也较低。
+Dubbo is the most outstanding framework in terms of functionality completeness, ecosystem, and community activity. Moreover, there are many successful domestic cases of Dubbo, such as Dangdang, Didi, and others; it is a mature and stable RPC framework that has withstood practical tests. Most importantly, you can find a wealth of reference materials on Dubbo, making the learning curve relatively low.
-下图展示了 Dubbo 的生态系统。
+The following diagram shows Dubbo's ecosystem.

-Dubbo 也是 Spring Cloud Alibaba 里面的一个组件。
+Dubbo is also a component of Spring Cloud Alibaba.

-但是,Dubbo 和 Motan 主要是给 Java 语言使用。虽然,Dubbo 和 Motan 目前也能兼容部分语言,但是不太推荐。如果需要跨多种语言调用的话,可以考虑使用 gRPC。
+However, both Dubbo and Motan are mainly used for the Java language. Although they can currently also support some other languages, it's not highly recommended. If you need to call across multiple languages, consider using gRPC.
-综上,如果是 Java 后端技术栈,并且你在纠结选择哪一种 RPC 框架的话,我推荐你考虑一下 Dubbo。
+In summary, if you are in a Java backend tech stack and are conflicted about which RPC framework to choose, I recommend considering Dubbo.
-## 如何设计并实现一个 RPC 框架?
+## How to design and implement an RPC framework?
-**《手写 RPC 框架》** 是我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)的一个内部小册,我写了 12 篇文章来讲解如何从零开始基于 Netty+Kyro+Zookeeper 实现一个简易的 RPC 框架。
+**"Writing an RPC Framework"** is an internal booklet of my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html), where I wrote 12 articles explaining how to start from scratch and implement a simple RPC framework based on Netty+Kyro+Zookeeper.
-麻雀虽小五脏俱全,项目代码注释详细,结构清晰,并且集成了 Check Style 规范代码结构,非常适合阅读和学习。
+Although the project is compact, it covers all essential aspects, with detailed comments in the code, a clear structure, and integrated Check Style norms for code structure, making it very suitable for reading and learning.
-**内容概览**:
+**Content Overview**:

-## 既然有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?
+## Since there is an HTTP protocol, why is there still a need for RPC?
-关于这个问题的详细答案,请看这篇文章:[有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还要有 RPC ?](http&rpc.md) 。
-
-
+For a detailed answer to this question, please refer to this article: [Since there is an HTTP protocol, why is there still a need for RPC?](http&rpc.md).
diff --git a/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md b/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
index 1e6e86845af..e9f0103c590 100644
--- a/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
+++ b/docs/distributed-system/spring-cloud-gateway-questions.md
@@ -1,138 +1,138 @@
---
-title: Spring Cloud Gateway常见问题总结
-category: 分布式
+title: Summary of Common Issues with Spring Cloud Gateway
+category: Distributed
---
-> 本文重构完善自[6000 字 | 16 图 | 深入理解 Spring Cloud Gateway 的原理 - 悟空聊架构](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/XjFYsP1IUqNzWqXZdJn-Aw)这篇文章。
+> This article is a refined version of [6000 words | 16 images | In-depth Understanding of the Principles of Spring Cloud Gateway - Wukong Talks Architecture](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/XjFYsP1IUqNzWqXZdJn-Aw).
-## 什么是 Spring Cloud Gateway?
+## What is Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 属于 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,其诞生的目标是为了替代老牌网关 **Zuul**。准确点来说,应该是 Zuul 1.x。Spring Cloud Gateway 起步要比 Zuul 2.x 更早。
+Spring Cloud Gateway is a gateway in the Spring Cloud ecosystem, designed to replace the legacy gateway **Zuul**. More precisely, it aims to replace Zuul 1.x, as Spring Cloud Gateway was developed earlier than Zuul 2.x.
-为了提升网关的性能,Spring Cloud Gateway 基于 Spring WebFlux 。Spring WebFlux 使用 Reactor 库来实现响应式编程模型,底层基于 Netty 实现同步非阻塞的 I/O。
+To enhance gateway performance, Spring Cloud Gateway is built on Spring WebFlux. Spring WebFlux utilizes the Reactor library to implement a reactive programming model, and is based on Netty for synchronous non-blocking I/O at the core.

-Spring Cloud Gateway 不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,限流。
+Spring Cloud Gateway not only provides a unified routing method but also offers basic gateway functions based on a chain of filters, such as security, monitoring/metrics, and rate limiting.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 和 Zuul 2.x 的差别不大,也是通过过滤器来处理请求。不过,目前更加推荐使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 而非 Zuul,Spring Cloud 生态对其支持更加友好。
+The differences between Spring Cloud Gateway and Zuul 2.x are minimal, as both handle requests through filters. However, Spring Cloud Gateway is currently more recommended than Zuul, as the Spring Cloud ecosystem offers better support for it.
-- GitHub 地址:
-- 官网:
+- GitHub address:
+- Official website:
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程?
+## What is the workflow of Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程如下图所示:
+The workflow of Spring Cloud Gateway is illustrated in the following diagram:
-
+
-这是 Spring 官方博客中的一张图,原文地址:。
+This is an image from the official Spring blog, original text address: .
-具体的流程分析:
+Specific process analysis:
-1. **路由判断**:客户端的请求到达网关后,先经过 Gateway Handler Mapping 处理,这里面会做断言(Predicate)判断,看下符合哪个路由规则,这个路由映射后端的某个服务。
-2. **请求过滤**:然后请求到达 Gateway Web Handler,这里面有很多过滤器,组成过滤器链(Filter Chain),这些过滤器可以对请求进行拦截和修改,比如添加请求头、参数校验等等,有点像净化污水。然后将请求转发到实际的后端服务。这些过滤器逻辑上可以称作 Pre-Filters,Pre 可以理解为“在...之前”。
-3. **服务处理**:后端服务会对请求进行处理。
-4. **响应过滤**:后端处理完结果后,返回给 Gateway 的过滤器再次做处理,逻辑上可以称作 Post-Filters,Post 可以理解为“在...之后”。
-5. **响应返回**:响应经过过滤处理后,返回给客户端。
+1. **Route Determination**: Once the client's request reaches the gateway, it first passes through the Gateway Handler Mapping, where predicate assertions are evaluated to see which route rule applies. This route maps to a certain backend service.
+1. **Request Filtering**: The request then reaches the Gateway Web Handler, which has many filters that form a filter chain. These filters can intercept and modify requests, such as adding request headers, validating parameters, etc., akin to purifying wastewater. The request is then forwarded to the actual backend service. These filters are logically termed Pre-Filters, where Pre can be understood as "before...".
+1. **Service Processing**: The backend service processes the request.
+1. **Response Filtering**: After the backend has finished processing and returned the result, it is processed again by the Gateway's filters, logically termed Post-Filters, where Post can be understood as "after...".
+1. **Response Return**: After filtering, the response is returned to the client.
-总结:客户端的请求先通过匹配规则找到合适的路由,就能映射到具体的服务。然后请求经过过滤器处理后转发给具体的服务,服务处理后,再次经过过滤器处理,最后返回给客户端。
+In summary: the client's request first finds the appropriate route by matching rules, mapping it to a specific service. After passing through filter processing, the request is forwarded to the specific service, which is processed, filtered again, and ultimately returned to the client.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的断言是什么?
+## What are predicates in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-断言(Predicate)这个词听起来极其深奥,它是一种编程术语,我们生活中根本就不会用它。说白了它就是对一个表达式进行 if 判断,结果为真或假,如果为真则做这件事,否则做那件事。
+The term predicate might sound complex; it is a programming term that we do not commonly use in our daily life. Simply put, it refers to performing an if-judgment on an expression, yielding a true or false result. If true, an action is taken; if false, another action is executed.
-在 Gateway 中,如果客户端发送的请求满足了断言的条件,则映射到指定的路由器,就能转发到指定的服务上进行处理。
+In the Gateway, if the client's request meets the predicate's conditions, it maps to the specified router, enabling forwarding to the designated service for processing.
-断言配置的示例如下,配置了两个路由规则,有一个 predicates 断言配置,当请求 url 中包含 `api/thirdparty`,就匹配到了第一个路由 `route_thirdparty`。
+An example of predicate configuration is shown below, which configures two routing rules, with a predicates assertion that matches when the request URL contains `api/thirdparty`, corresponding to the first route `route_thirdparty`.
-
+
-常见的路由断言规则如下图所示:
+Common routing predicate rules are shown in the following diagram:
-
+
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的路由和断言是什么关系?
+## What is the relationship between routes and predicates in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-Route 路由和 Predicate 断言的对应关系如下::
+The correspondence between Route and Predicate is as follows:
-
+
-- **一对多**:一个路由规则可以包含多个断言。如上图中路由 Route1 配置了三个断言 Predicate。
-- **同时满足**:如果一个路由规则中有多个断言,则需要同时满足才能匹配。如上图中路由 Route2 配置了两个断言,客户端发送的请求必须同时满足这两个断言,才能匹配路由 Route2。
-- **第一个匹配成功**:如果一个请求可以匹配多个路由,则映射第一个匹配成功的路由。如上图所示,客户端发送的请求满足 Route3 和 Route4 的断言,但是 Route3 的配置在配置文件中靠前,所以只会匹配 Route3。
+- **One-to-Many**: One routing rule can contain multiple predicates. As shown in the image, Route1 is configured with three predicates.
+- **Simultaneous Satisfaction**: If a routing rule has multiple predicates, all must be satisfied for a match. In the image, for Route2, the client's request must satisfy both predicates to match Route2.
+- **First Match Success**: If a request can match multiple routes, the first successfully matching route is chosen. In the image, the client's request satisfies both Route3 and Route4's predicates, but since Route3's configuration appears earlier in the configuration file, it will only match Route3.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 如何实现动态路由?
+## How does Spring Cloud Gateway achieve dynamic routing?
-在使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 的时候,官方文档提供的方案总是基于配置文件或代码配置的方式。
+When using Spring Cloud Gateway, official documentation often provides solutions based on configuration files or code configurations.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 作为微服务的入口,需要尽量避免重启,而现在配置更改需要重启服务不能满足实际生产过程中的动态刷新、实时变更的业务需求,所以我们需要在 Spring Cloud Gateway 运行时动态配置网关。
+As the entry point for microservices, Spring Cloud Gateway should aim to avoid restarts. However, current configuration changes require server restarts, which cannot meet the dynamic refresh and real-time change demands in actual production. Thus, we need to dynamically configure the gateway during its runtime.
-实现动态路由的方式有很多种,其中一种推荐的方式是基于 Nacos 注册中心来做。 Spring Cloud Gateway 可以从注册中心获取服务的元数据(例如服务名称、路径等),然后根据这些信息自动生成路由规则。这样,当你添加、移除或更新服务实例时,网关会自动感知并相应地调整路由规则,无需手动维护路由配置。
+There are many ways to achieve dynamic routing, and one recommended method is based on the Nacos registry. Spring Cloud Gateway can retrieve service metadata (such as service name, path, etc.) from the registry and automatically generate routing rules based on this information. Thus, when you add, remove, or update service instances, the gateway will automatically perceive these changes and adjust the routing rules accordingly, eliminating the need for manual maintenance of routing configurations.
-其实这些复杂的步骤并不需要我们手动实现,通过 Nacos Server 和 Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config 即可实现配置的动态变更,官方文档地址: 。
+In fact, these complex steps do not require manual implementation since dynamic configuration changes can be achieved through Nacos Server and Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config. For the official documentation, visit: .
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 的过滤器有哪些?
+## What are the filters in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-过滤器 Filter 按照请求和响应可以分为两种:
+Filters can be categorized into two types based on requests and responses:
-- **Pre 类型**:在请求被转发到微服务之前,对请求进行拦截和修改,例如参数校验、权限校验、流量监控、日志输出以及协议转换等操作。
-- **Post 类型**:微服务处理完请求后,返回响应给网关,网关可以再次进行处理,例如修改响应内容或响应头、日志输出、流量监控等。
+- **Pre Type**: Intercepts and modifies requests before they are forwarded to microservices, including parameter validation, permission checks, traffic monitoring, logging, and protocol conversion.
+- **Post Type**: After the microservice processes the request and returns a response to the gateway, the gateway can perform further processing, such as modifying the response content or headers, logging, and traffic monitoring.
-另外一种分类是按照过滤器 Filter 作用的范围进行划分:
+Another classification divides filters based on their scope of action:
-- **GatewayFilter**:局部过滤器,应用在单个路由或一组路由上的过滤器。标红色表示比较常用的过滤器。
-- **GlobalFilter**:全局过滤器,应用在所有路由上的过滤器。
+- **GatewayFilter**: Local filters applied to a single route or a group of routes. The red-colored ones are commonly used filters.
+- **GlobalFilter**: Global filters applied across all routes.
-### 局部过滤器
+### Local Filters
-常见的局部过滤器如下图所示:
+Common local filters are illustrated in the following diagram:

-具体怎么用呢?这里有个示例,如果 URL 匹配成功,则去掉 URL 中的 “api”。
+How is it used? Here’s an example: if the URL matches successfully, it removes "api" from the URL.
```yaml
-filters: #过滤器
- - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # 将跳转路径中包含的 “api” 替换成空
+filters: # Filters
+ - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # Replace "api" in the redirection path with empty
```
-当然我们也可以自定义过滤器,本篇不做展开。
+Of course, we can also define custom filters, but this article does not elaborate on that.
-### 全局过滤器
+### Global Filters
-常见的全局过滤器如下图所示:
+Common global filters are illustrated in the following diagram:

-全局过滤器最常见的用法是进行负载均衡。配置如下所示:
+The most common use of global filters is for load balancing. The configuration is as follows:
```yaml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- - id: route_member # 第三方微服务路由规则
- uri: lb://passjava-member # 负载均衡,将请求转发到注册中心注册的 passjava-member 服务
- predicates: # 断言
- - Path=/api/member/** # 如果前端请求路径包含 api/member,则应用这条路由规则
- filters: #过滤器
- - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # 将跳转路径中包含的api替换成空
+ - id: route_member # Third-party microservice routing rule
+ uri: lb://passjava-member # Load balancing, forward requests to the registered passjava-member service in the registry
+ predicates: # Predicates
+ - Path=/api/member/** # If the frontend request path includes api/member, this routing rule applies
+ filters: # Filters
+ - RewritePath=/api/(?.*),/$\{segment} # Replace "api" in the redirection path with empty
```
-这里有个关键字 `lb`,用到了全局过滤器 `LoadBalancerClientFilter`,当匹配到这个路由后,会将请求转发到 passjava-member 服务,且支持负载均衡转发,也就是先将 passjava-member 解析成实际的微服务的 host 和 port,然后再转发给实际的微服务。
+Here we have a keyword `lb`, which utilizes the global filter `LoadBalancerClientFilter`. When this route matches, the request will be forwarded to the passjava-member service, supporting load-balanced forwarding, meaning it first resolves passjava-member to the actual microservice's host and port before forwarding it to the actual microservice.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 支持限流吗?
+## Does Spring Cloud Gateway support rate limiting?
-Spring Cloud Gateway 自带了限流过滤器,对应的接口是 `RateLimiter`,`RateLimiter` 接口只有一个实现类 `RedisRateLimiter` (基于 Redis + Lua 实现的限流),提供的限流功能比较简易且不易使用。
+Spring Cloud Gateway comes with a built-in rate limiting filter, corresponding to the interface `RateLimiter`. The `RateLimiter` interface has only one implementation class `RedisRateLimiter` (a rate limiter based on Redis + Lua), providing relatively simple and not very user-friendly rate limiting functionality.
-从 Sentinel 1.6.0 版本开始,Sentinel 引入了 Spring Cloud Gateway 的适配模块,可以提供两种资源维度的限流:route 维度和自定义 API 维度。也就是说,Spring Cloud Gateway 可以结合 Sentinel 实现更强大的网关流量控制。
+Starting from Sentinel version 1.6.0, Sentinel introduced an adaptation module for Spring Cloud Gateway that provides two dimensions for rate limiting: route dimension and custom API dimension. This means Spring Cloud Gateway can combine with Sentinel to achieve more powerful gateway traffic control.
-## Spring Cloud Gateway 如何自定义全局异常处理?
+## How do we customize global exception handling in Spring Cloud Gateway?
-在 SpringBoot 项目中,我们捕获全局异常只需要在项目中配置 `@RestControllerAdvice`和 `@ExceptionHandler`就可以了。不过,这种方式在 Spring Cloud Gateway 下不适用。
+In SpringBoot projects, we can capture global exceptions by simply configuring `@RestControllerAdvice` and `@ExceptionHandler`. However, this method is not applicable under Spring Cloud Gateway.
-Spring Cloud Gateway 提供了多种全局处理的方式,比较常用的一种是实现`ErrorWebExceptionHandler`并重写其中的`handle`方法。
+Spring Cloud Gateway provides various global handling methods, with a commonly used one being to implement `ErrorWebExceptionHandler` and override its `handle` method.
```java
@Order(-1)
@@ -148,10 +148,10 @@ public class GlobalErrorWebExceptionHandler implements ErrorWebExceptionHandler
}
```
-## 参考
+## References
-- Spring Cloud Gateway 官方文档:
-- Creating a custom Spring Cloud Gateway Filter:
-- 全局异常处理:
+- Official Spring Cloud Gateway documentation:
+- Creating a custom Spring Cloud Gateway Filter:
+- Global exception handling:
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md b/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
index 59725fa0521..34607fc1964 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/fallback-and-circuit-breaker.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
-title: 降级&熔断详解(付费)
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Downgrading & Circuit Breaking (Paid)
+category: High Availability
icon: circuit
---
-**降级&熔断** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html)中。
+The interview questions related to **Downgrading & Circuit Breaking** are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link to view detailed introduction and joining methods) and have been compiled in [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html).

diff --git a/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md b/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
index f461f93e99b..44f49e5dc56 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/high-availability-system-design.md
@@ -1,71 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 高可用系统设计指南
-category: 高可用
+title: High Availability System Design Guide
+category: High Availability
icon: design
---
-## 什么是高可用?可用性的判断标准是啥?
+## What is High Availability? What are the criteria for determining availability?
-高可用描述的是一个系统在大部分时间都是可用的,可以为我们提供服务的。高可用代表系统即使在发生硬件故障或者系统升级的时候,服务仍然是可用的。
+High availability describes a system that is available most of the time and can provide services to us. High availability means that the system remains available even during hardware failures or system upgrades.
-一般情况下,我们使用多少个 9 来评判一个系统的可用性,比如 99.9999% 就是代表该系统在所有的运行时间中只有 0.0001% 的时间是不可用的,这样的系统就是非常非常高可用的了!当然,也会有系统如果可用性不太好的话,可能连 9 都上不了。
+Generally, we use the number of nines to evaluate a system's availability. For example, 99.9999% means that the system is unavailable only 0.0001% of the time during all operational hours, making it extremely high availability! Of course, there are systems with poor availability that may not even reach a single nine.
-除此之外,系统的可用性还可以用某功能的失败次数与总的请求次数之比来衡量,比如对网站请求 1000 次,其中有 10 次请求失败,那么可用性就是 99%。
+In addition, the availability of a system can also be measured by the ratio of the number of failures of a certain function to the total number of requests. For example, if a website receives 1000 requests and 10 of them fail, the availability would be 99%.
-## 哪些情况会导致系统不可用?
+## What situations can lead to system unavailability?
-1. 黑客攻击;
-2. 硬件故障,比如服务器坏掉。
-3. 并发量/用户请求量激增导致整个服务宕掉或者部分服务不可用。
-4. 代码中的坏味道导致内存泄漏或者其他问题导致程序挂掉。
-5. 网站架构某个重要的角色比如 Nginx 或者数据库突然不可用。
-6. 自然灾害或者人为破坏。
-7. ……
+1. Hacker attacks;
+1. Hardware failures, such as server breakdowns.
+1. A surge in concurrent users/request volume causing the entire service to crash or parts of the service to become unavailable.
+1. Code smells leading to memory leaks or other issues causing the program to crash.
+1. An important component of the website architecture, such as Nginx or the database, suddenly becomes unavailable.
+1. Natural disasters or human destruction.
+1. ……
-## 有哪些提高系统可用性的方法?
+## What methods are there to improve system availability?
-### 注重代码质量,测试严格把关
+### Focus on Code Quality, Strict Testing
-我觉得这个是最最最重要的,代码质量有问题比如比较常见的内存泄漏、循环依赖都是对系统可用性极大的损害。大家都喜欢谈限流、降级、熔断,但是我觉得从代码质量这个源头把关是首先要做好的一件很重要的事情。如何提高代码质量?比较实际可用的就是 CodeReview,不要在乎每天多花的那 1 个小时左右的时间,作用可大着呢!
+I believe this is the most important aspect. Issues with code quality, such as common memory leaks and circular dependencies, can greatly harm system availability. Everyone likes to talk about rate limiting, degradation, and circuit breaking, but I think ensuring code quality from the source is a crucial first step. How can we improve code quality? A practical approach is Code Review; don't worry about spending an extra hour each day, as the benefits can be significant!
-另外,安利几个对提高代码质量有实际效果的神器:
+Additionally, here are a few tools that can effectively improve code quality:
- [Sonarqube](https://www.sonarqube.org/);
-- Alibaba 开源的 Java 诊断工具 [Arthas](https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/);
-- [阿里巴巴 Java 代码规范](https://github.com/alibaba/p3c)(Alibaba Java Code Guidelines);
-- IDEA 自带的代码分析等工具。
+- Alibaba's open-source Java diagnostic tool [Arthas](https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/);
+- [Alibaba Java Code Guidelines](https://github.com/alibaba/p3c);
+- Built-in code analysis tools in IDEA.
-### 使用集群,减少单点故障
+### Use Clusters to Reduce Single Points of Failure
-先拿常用的 Redis 举个例子!我们如何保证我们的 Redis 缓存高可用呢?答案就是使用集群,避免单点故障。当我们使用一个 Redis 实例作为缓存的时候,这个 Redis 实例挂了之后,整个缓存服务可能就挂了。使用了集群之后,即使一台 Redis 实例挂了,不到一秒就会有另外一台 Redis 实例顶上。
+Let's take the commonly used Redis as an example! How can we ensure our Redis cache is highly available? The answer is to use a cluster to avoid single points of failure. When we use a single Redis instance as a cache, if that instance goes down, the entire cache service may fail. With a cluster, even if one Redis instance fails, another instance will take over in less than a second.
-### 限流
+### Rate Limiting
-流量控制(flow control),其原理是监控应用流量的 QPS 或并发线程数等指标,当达到指定的阈值时对流量进行控制,以避免被瞬时的流量高峰冲垮,从而保障应用的高可用性。——来自 [alibaba-Sentinel](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel "Sentinel") 的 wiki。
+Flow control involves monitoring application traffic metrics such as QPS or concurrent thread counts. When a specified threshold is reached, traffic is controlled to avoid being overwhelmed by sudden traffic spikes, thereby ensuring high application availability. — From the [alibaba-Sentinel](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel "Sentinel") wiki.
-### 超时和重试机制设置
+### Timeout and Retry Mechanism Settings
-一旦用户请求超过某个时间的得不到响应,就抛出异常。这个是非常重要的,很多线上系统故障都是因为没有进行超时设置或者超时设置的方式不对导致的。我们在读取第三方服务的时候,尤其适合设置超时和重试机制。一般我们使用一些 RPC 框架的时候,这些框架都自带的超时重试的配置。如果不进行超时设置可能会导致请求响应速度慢,甚至导致请求堆积进而让系统无法再处理请求。重试的次数一般设为 3 次,再多次的重试没有好处,反而会加重服务器压力(部分场景使用失败重试机制会不太适合)。
+If a user request does not receive a response within a certain time, an exception should be thrown. This is very important; many online system failures occur due to the lack of timeout settings or incorrect timeout configurations. When reading from third-party services, it is especially suitable to set timeout and retry mechanisms. Generally, when using some RPC frameworks, these frameworks come with built-in timeout and retry configurations. Not setting a timeout can lead to slow response times and even request accumulation, making the system unable to process requests. The retry count is usually set to 3 times; retrying more than that is not beneficial and may increase server pressure (in some scenarios, using a failure retry mechanism may not be suitable).
-### 熔断机制
+### Circuit Breaker Mechanism
-超时和重试机制设置之外,熔断机制也是很重要的。 熔断机制说的是系统自动收集所依赖服务的资源使用情况和性能指标,当所依赖的服务恶化或者调用失败次数达到某个阈值的时候就迅速失败,让当前系统立即切换依赖其他备用服务。 比较常用的流量控制和熔断降级框架是 Netflix 的 Hystrix 和 alibaba 的 Sentinel。
+In addition to timeout and retry mechanism settings, the circuit breaker mechanism is also very important. The circuit breaker mechanism automatically collects resource usage and performance metrics of the dependent services. When the performance of the dependent service deteriorates or the number of failed calls reaches a certain threshold, it quickly fails, allowing the current system to switch to other backup services immediately. Commonly used flow control and circuit breaker frameworks include Netflix's Hystrix and Alibaba's Sentinel.
-### 异步调用
+### Asynchronous Calls
-异步调用的话我们不需要关心最后的结果,这样我们就可以用户请求完成之后就立即返回结果,具体处理我们可以后续再做,秒杀场景用这个还是蛮多的。但是,使用异步之后我们可能需要 **适当修改业务流程进行配合**,比如**用户在提交订单之后,不能立即返回用户订单提交成功,需要在消息队列的订单消费者进程真正处理完该订单之后,甚至出库后,再通过电子邮件或短信通知用户订单成功**。除了可以在程序中实现异步之外,我们常常还使用消息队列,消息队列可以通过异步处理提高系统性能(削峰、减少响应所需时间)并且可以降低系统耦合性。
-
-### 使用缓存
-
-如果我们的系统属于并发量比较高的话,如果我们单纯使用数据库的话,当大量请求直接落到数据库可能数据库就会直接挂掉。使用缓存缓存热点数据,因为缓存存储在内存中,所以速度相当地快!
-
-### 其他
-
-- **核心应用和服务优先使用更好的硬件**
-- **监控系统资源使用情况增加报警设置。**
-- **注意备份,必要时候回滚。**
-- **灰度发布:** 将服务器集群分成若干部分,每天只发布一部分机器,观察运行稳定没有故障,第二天继续发布一部分机器,持续几天才把整个集群全部发布完毕,期间如果发现问题,只需要回滚已发布的一部分服务器即可
-- **定期检查/更换硬件:** 如果不是购买的云服务的话,定期还是需要对硬件进行一波检查的,对于一些需要更换或者升级的硬件,要及时更换或者升级。
-- ……
-
-
+With asynchronous calls, we do not need to worry about the final result, allowing us to return results immediately after the user request is completed. The specific processing can be done later, which is quite common in flash sale scenarios. However, after using asynchronous calls, we may need to **appropriately modify the business process to accommodate** this, such as **not immediately returning a success message to the user after submitting an order. Instead, we should notify the user of the order success via email or SMS only after the order has been processed by the message queue's order consumer process, or even after it has been shipped**. In addition to implementing
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md b/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
index 41384457ccb..8d122a9b38f 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/idempotency.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
---
-title: 接口幂等方案总结(付费)
-category: 高可用
+title: Summary of Idempotency Solutions for APIs (Paid)
+category: High Availability
icon: security-fill
---
-**接口幂等** 相关的面试题为我的[知识星球](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)(点击链接即可查看详细介绍以及加入方法)专属内容,已经整理到了[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html)中。
+**Idempotency of APIs** related interview questions are exclusive content for my [Knowledge Planet](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html) (click the link for detailed introduction and joining methods), and have been compiled in [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html).

diff --git a/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md b/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
index 22db662eedf..c45eafd8b55 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/limit-request.md
@@ -1,298 +1,63 @@
---
-title: 服务限流详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Rate Limiting
+category: High Availability
icon: limit_rate
---
-针对软件系统来说,限流就是对请求的速率进行限制,避免瞬时的大量请求击垮软件系统。毕竟,软件系统的处理能力是有限的。如果说超过了其处理能力的范围,软件系统可能直接就挂掉了。
+For software systems, rate limiting refers to the restriction of request rates to prevent a sudden influx of requests from overwhelming the system. After all, the processing capacity of a software system is limited. If the number of requests exceeds its processing capacity, the software system may crash.
-限流可能会导致用户的请求无法被正确处理或者无法立即被处理,不过,这往往也是权衡了软件系统的稳定性之后得到的最优解。
+Rate limiting may result in user requests not being processed correctly or not being processed immediately; however, this is often the optimal solution after weighing the stability of the software system.
-现实生活中,处处都有限流的实际应用,就比如排队买票是为了避免大量用户涌入购票而导致售票员无法处理。
+In real life, there are many practical applications of rate limiting. For example, queuing to buy tickets is intended to prevent a large number of users from flooding in and overwhelming the ticket seller.
-## 常见限流算法有哪些?
+## What are the Common Rate Limiting Algorithms?
-简单介绍 4 种非常好理解并且容易实现的限流算法!
+Here’s a brief introduction to four very understandable and easy-to-implement rate limiting algorithms!
-> 图片来源于 InfoQ 的一篇文章[《分布式服务限流实战,已经为你排好坑了》](https://www.infoq.cn/article/Qg2tX8fyw5Vt-f3HH673)。
+> Image source: An article from InfoQ [“Practical Distributed Service Rate Limiting, Already Prepared for You”](https://www.infoq.cn/article/Qg2tX8fyw5Vt-f3HH673).
-### 固定窗口计数器算法
+### Fixed Window Counter Algorithm
-固定窗口其实就是时间窗口,其原理是将时间划分为固定大小的窗口,在每个窗口内限制请求的数量或速率,即固定窗口计数器算法规定了系统单位时间处理的请求数量。
+A fixed window is essentially a time window. Its principle is to divide time into fixed-size windows, limiting the number of requests or the rate within each window. The fixed window counter algorithm specifies the number of requests the system can handle in a unit of time.
-假如我们规定系统中某个接口 1 分钟只能被访问 33 次的话,使用固定窗口计数器算法的实现思路如下:
+For example, if we specify that a certain interface in the system can only be accessed 33 times in one minute, the implementation idea of the fixed window counter algorithm is as follows:
-- 将时间划分固定大小窗口,这里是 1 分钟一个窗口。
-- 给定一个变量 `counter` 来记录当前接口处理的请求数量,初始值为 0(代表接口当前 1 分钟内还未处理请求)。
-- 1 分钟之内每处理一个请求之后就将 `counter+1` ,当 `counter=33` 之后(也就是说在这 1 分钟内接口已经被访问 33 次的话),后续的请求就会被全部拒绝。
-- 等到 1 分钟结束后,将 `counter` 重置 0,重新开始计数。
+- Divide time into fixed-size windows, here it is one window per minute.
+- Set a variable `counter` to record the number of requests processed by the current interface, with an initial value of 0 (indicating that no requests have been processed in the current minute).
+- For each request processed within one minute, increment `counter` by 1. Once `counter=33` (meaning the interface has been accessed 33 times in this minute), all subsequent requests will be rejected.
+- At the end of one minute, reset `counter` to 0 and start counting again.
-
+
-优点:实现简单,易于理解。
+Advantages: Simple to implement and easy to understand.
-缺点:
+Disadvantages:
-- 限流不够平滑。例如,我们限制某个接口每分钟只能访问 30 次,假设前 30 秒就有 30 个请求到达的话,那后续 30 秒将无法处理请求,这是不可取的,用户体验极差!
-- 无法保证限流速率,因而无法应对突然激增的流量。例如,我们限制某个接口 1 分钟只能访问 1000 次,该接口的 QPS 为 500,前 55s 这个接口 1 个请求没有接收,后 1s 突然接收了 1000 个请求。然后,在当前场景下,这 1000 个请求在 1s 内是没办法被处理的,系统直接就被瞬时的大量请求给击垮了。
+- Rate limiting is not smooth enough. For example, if we limit a certain interface to only 30 accesses per minute, and 30 requests arrive in the first 30 seconds, then no requests can be processed in the following 30 seconds, which is undesirable and results in a poor user experience!
+- It cannot guarantee the rate limiting speed, thus unable to cope with sudden surges in traffic. For instance, if we limit a certain interface to only 1000 accesses per minute, and the QPS of that interface is 500, if no requests are received in the first 55 seconds, but suddenly 1000 requests arrive in the last second, these 1000 requests cannot be processed in that second, and the system will be overwhelmed by the sudden influx of requests.
-### 滑动窗口计数器算法
+### Sliding Window Counter Algorithm
-**滑动窗口计数器算法** 算的上是固定窗口计数器算法的升级版,限流的颗粒度更小。
+**The sliding window counter algorithm** can be considered an upgraded version of the fixed window counter algorithm, with finer granularity for rate limiting.
-滑动窗口计数器算法相比于固定窗口计数器算法的优化在于:**它把时间以一定比例分片** 。
+The optimization of the sliding window counter algorithm compared to the fixed window counter algorithm is that **it divides time into segments at a certain ratio**.
-例如我们的接口限流每分钟处理 60 个请求,我们可以把 1 分钟分为 60 个窗口。每隔 1 秒移动一次,每个窗口一秒只能处理不大于 `60(请求数)/60(窗口数)` 的请求, 如果当前窗口的请求计数总和超过了限制的数量的话就不再处理其他请求。
+For example, if our interface limits processing to 60 requests per minute, we can divide one minute into 60 windows. Each window can only handle no more than `60(requests)/60(window)` requests per second. If the total request count in the current window exceeds the limit, no further requests will be processed.
-很显然, **当滑动窗口的格子划分的越多,滑动窗口的滚动就越平滑,限流的统计就会越精确。**
+Clearly, **the more segments the sliding window is divided into, the smoother the sliding window's movement will be, and the more accurate the rate limiting statistics will be.**
-
+
-优点:
+Advantages:
-- 相比于固定窗口算法,滑动窗口计数器算法可以应对突然激增的流量。
-- 相比于固定窗口算法,滑动窗口计数器算法的颗粒度更小,可以提供更精确的限流控制。
+- Compared to the fixed window algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm can handle sudden surges in traffic.
+- Compared to the fixed window algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm has finer granularity, allowing for more precise rate limiting control.
-缺点:
+Disadvantages:
-- 与固定窗口计数器算法类似,滑动窗口计数器算法依然存在限流不够平滑的问题。
-- 相比较于固定窗口计数器算法,滑动窗口计数器算法实现和理解起来更复杂一些。
+- Similar to the fixed window counter algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm still suffers from the issue of insufficiently smooth rate limiting.
+- Compared to the fixed window counter algorithm, the sliding window counter algorithm is more complex to implement and understand.
-### 漏桶算法
+### Leaky Bucket Algorithm
-我们可以把发请求的动作比作成注水到桶中,我们处理请求的过程可以比喻为漏桶漏水。我们往桶中以任意速率流入水,以一定速率流出水。当水超过桶流量则丢弃,因为桶容量是不变的,保证了整体的速率。
-
-如果想要实现这个算法的话也很简单,准备一个队列用来保存请求,然后我们定期从队列中拿请求来执行就好了(和消息队列削峰/限流的思想是一样的)。
-
-
-
-优点:
-
-- 实现简单,易于理解。
-- 可以控制限流速率,避免网络拥塞和系统过载。
-
-缺点:
-
-- 无法应对突然激增的流量,因为只能以固定的速率处理请求,对系统资源利用不够友好。
-- 桶流入水(发请求)的速率如果一直大于桶流出水(处理请求)的速率的话,那么桶会一直是满的,一部分新的请求会被丢弃,导致服务质量下降。
-
-实际业务场景中,基本不会使用漏桶算法。
-
-### 令牌桶算法
-
-令牌桶算法也比较简单。和漏桶算法算法一样,我们的主角还是桶(这限流算法和桶过不去啊)。不过现在桶里装的是令牌了,请求在被处理之前需要拿到一个令牌,请求处理完毕之后将这个令牌丢弃(删除)。我们根据限流大小,按照一定的速率往桶里添加令牌。如果桶装满了,就不能继续往里面继续添加令牌了。
-
-
-
-优点:
-
-- 可以限制平均速率和应对突然激增的流量。
-- 可以动态调整生成令牌的速率。
-
-缺点:
-
-- 如果令牌产生速率和桶的容量设置不合理,可能会出现问题比如大量的请求被丢弃、系统过载。
-- 相比于其他限流算法,实现和理解起来更复杂一些。
-
-## 针对什么来进行限流?
-
-实际项目中,还需要确定限流对象,也就是针对什么来进行限流。常见的限流对象如下:
-
-- IP :针对 IP 进行限流,适用面较广,简单粗暴。
-- 业务 ID:挑选唯一的业务 ID 以实现更针对性地限流。例如,基于用户 ID 进行限流。
-- 个性化:根据用户的属性或行为,进行不同的限流策略。例如, VIP 用户不限流,而普通用户限流。根据系统的运行指标(如 QPS、并发调用数、系统负载等),动态调整限流策略。例如,当系统负载较高的时候,控制每秒通过的请求减少。
-
-针对 IP 进行限流是目前比较常用的一个方案。不过,实际应用中需要注意用户真实 IP 地址的正确获取。常用的真实 IP 获取方法有 X-Forwarded-For 和 TCP Options 字段承载真实源 IP 信息。虽然 X-Forwarded-For 字段可能会被伪造,但因为其实现简单方便,很多项目还是直接用的这种方法。
-
-除了我上面介绍到的限流对象之外,还有一些其他较为复杂的限流对象策略,比如阿里的 Sentinel 还支持 [基于调用关系的限流](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/流量控制#基于调用关系的流量控制)(包括基于调用方限流、基于调用链入口限流、关联流量限流等)以及更细维度的 [热点参数限流](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/热点参数限流)(实时的统计热点参数并针对热点参数的资源调用进行流量控制)。
-
-另外,一个项目可以根据具体的业务需求选择多种不同的限流对象搭配使用。
-
-## 单机限流怎么做?
-
-单机限流针对的是单体架构应用。
-
-单机限流可以直接使用 Google Guava 自带的限流工具类 `RateLimiter` 。 `RateLimiter` 基于令牌桶算法,可以应对突发流量。
-
-> Guava 地址:
-
-除了最基本的令牌桶算法(平滑突发限流)实现之外,Guava 的`RateLimiter`还提供了 **平滑预热限流** 的算法实现。
-
-平滑突发限流就是按照指定的速率放令牌到桶里,而平滑预热限流会有一段预热时间,预热时间之内,速率会逐渐提升到配置的速率。
-
-我们下面通过两个简单的小例子来详细了解吧!
-
-我们直接在项目中引入 Guava 相关的依赖即可使用。
-
-```xml
-
- com.google.guava
- guava
- 31.0.1-jre
-
-```
-
-下面是一个简单的 Guava 平滑突发限流的 Demo。
-
-```java
-import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
-
-/**
- * 微信搜 JavaGuide 回复"面试突击"即可免费领取个人原创的 Java 面试手册
- *
- * @author Guide哥
- * @date 2021/10/08 19:12
- **/
-public class RateLimiterDemo {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 1s 放 5 个令牌到桶里也就是 0.2s 放 1个令牌到桶里
- RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5);
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- double sleepingTime = rateLimiter.acquire(1);
- System.out.printf("get 1 tokens: %ss%n", sleepingTime);
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-输出:
-
-```bash
-get 1 tokens: 0.0s
-get 1 tokens: 0.188413s
-get 1 tokens: 0.197811s
-get 1 tokens: 0.198316s
-get 1 tokens: 0.19864s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199363s
-get 1 tokens: 0.193997s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199623s
-get 1 tokens: 0.199357s
-get 1 tokens: 0.195676s
-```
-
-下面是一个简单的 Guava 平滑预热限流的 Demo。
-
-```java
-import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
-import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
-/**
- * 微信搜 JavaGuide 回复"面试突击"即可免费领取个人原创的 Java 面试手册
- *
- * @author Guide哥
- * @date 2021/10/08 19:12
- **/
-public class RateLimiterDemo {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // 1s 放 5 个令牌到桶里也就是 0.2s 放 1个令牌到桶里
- // 预热时间为3s,也就说刚开始的 3s 内发牌速率会逐渐提升到 0.2s 放 1 个令牌到桶里
- RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
- double sleepingTime = rateLimiter.acquire(1);
- System.out.printf("get 1 tokens: %sds%n", sleepingTime);
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-输出:
-
-```bash
-get 1 tokens: 0.0s
-get 1 tokens: 0.561919s
-get 1 tokens: 0.516931s
-get 1 tokens: 0.463798s
-get 1 tokens: 0.41286s
-get 1 tokens: 0.356172s
-get 1 tokens: 0.300489s
-get 1 tokens: 0.252545s
-get 1 tokens: 0.203996s
-get 1 tokens: 0.198359s
-```
-
-另外,**Bucket4j** 是一个非常不错的基于令牌/漏桶算法的限流库。
-
-> Bucket4j 地址:
-
-相对于,Guava 的限流工具类来说,Bucket4j 提供的限流功能更加全面。不仅支持单机限流和分布式限流,还可以集成监控,搭配 Prometheus 和 Grafana 使用。
-
-不过,毕竟 Guava 也只是一个功能全面的工具类库,其提供的开箱即用的限流功能在很多单机场景下还是比较实用的。
-
-Spring Cloud Gateway 中自带的单机限流的早期版本就是基于 Bucket4j 实现的。后来,替换成了 **Resilience4j**。
-
-Resilience4j 是一个轻量级的容错组件,其灵感来自于 Hystrix。自[Netflix 宣布不再积极开发 Hystrix](https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/commit/a7df971cbaddd8c5e976b3cc5f14013fe6ad00e6) 之后,Spring 官方和 Netflix 都更推荐使用 Resilience4j 来做限流熔断。
-
-> Resilience4j 地址:
-
-一般情况下,为了保证系统的高可用,项目的限流和熔断都是要一起做的。
-
-Resilience4j 不仅提供限流,还提供了熔断、负载保护、自动重试等保障系统高可用开箱即用的功能。并且,Resilience4j 的生态也更好,很多网关都使用 Resilience4j 来做限流熔断的。
-
-因此,在绝大部分场景下 Resilience4j 或许会是更好的选择。如果是一些比较简单的限流场景的话,Guava 或者 Bucket4j 也是不错的选择。
-
-## 分布式限流怎么做?
-
-分布式限流针对的分布式/微服务应用架构应用,在这种架构下,单机限流就不适用了,因为会存在多种服务,并且一种服务也可能会被部署多份。
-
-分布式限流常见的方案:
-
-- **借助中间件限流**:可以借助 Sentinel 或者使用 Redis 来自己实现对应的限流逻辑。
-- **网关层限流**:比较常用的一种方案,直接在网关层把限流给安排上了。不过,通常网关层限流通常也需要借助到中间件/框架。就比如 Spring Cloud Gateway 的分布式限流实现`RedisRateLimiter`就是基于 Redis+Lua 来实现的,再比如 Spring Cloud Gateway 还可以整合 Sentinel 来做限流。
-
-如果你要基于 Redis 来手动实现限流逻辑的话,建议配合 Lua 脚本来做。
-
-**为什么建议 Redis+Lua 的方式?** 主要有两点原因:
-
-- **减少了网络开销**:我们可以利用 Lua 脚本来批量执行多条 Redis 命令,这些 Redis 命令会被提交到 Redis 服务器一次性执行完成,大幅减小了网络开销。
-- **原子性**:一段 Lua 脚本可以视作一条命令执行,一段 Lua 脚本执行过程中不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令同时执行,保证了操作不会被其他指令插入或打扰。
-
-我这里就不放具体的限流脚本代码了,网上也有很多现成的优秀的限流脚本供你参考,就比如 Apache 网关项目 ShenYu 的 RateLimiter 限流插件就基于 Redis + Lua 实现了令牌桶算法/并发令牌桶算法、漏桶算法、滑动窗口算法。
-
-> ShenYu 地址:
-
-
-
-另外,如果不想自己写 Lua 脚本的话,也可以直接利用 Redisson 中的 `RRateLimiter` 来实现分布式限流,其底层实现就是基于 Lua 代码+令牌桶算法。
-
-Redisson 是一个开源的 Java 语言 Redis 客户端,提供了很多开箱即用的功能,比如 Java 中常用的数据结构实现、分布式锁、延迟队列等等。并且,Redisson 还支持 Redis 单机、Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster 等多种部署架构。
-
-`RRateLimiter` 的使用方式非常简单。我们首先需要获取一个`RRateLimiter`对象,直接通过 Redisson 客户端获取即可。然后,设置限流规则就好。
-
-```java
-// 创建一个 Redisson 客户端实例
-RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create();
-// 获取一个名为 "javaguide.limiter" 的限流器对象
-RRateLimiter rateLimiter = redissonClient.getRateLimiter("javaguide.limiter");
-// 尝试设置限流器的速率为每小时 100 次
-// RateType 有两种,OVERALL是全局限流,ER_CLIENT是单Client限流(可以认为就是单机限流)
-rateLimiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 100, 1, RateIntervalUnit.HOURS);
-```
-
-接下来我们调用`acquire()`方法或`tryAcquire()`方法即可获取许可。
-
-```java
-// 获取一个许可,如果超过限流器的速率则会等待
-// acquire()是同步方法,对应的异步方法:acquireAsync()
-rateLimiter.acquire(1);
-// 尝试在 5 秒内获取一个许可,如果成功则返回 true,否则返回 false
-// tryAcquire()是同步方法,对应的异步方法:tryAcquireAsync()
-boolean res = rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
-```
-
-## 总结
-
-这篇文章主要介绍了常见的限流算法、限流对象的选择以及单机限流和分布式限流分别应该怎么做。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 服务治理之轻量级熔断框架 Resilience4j:
-- 超详细的 Guava RateLimiter 限流原理解析:
-- 实战 Spring Cloud Gateway 之限流篇 👍:
-- 详解 Redisson 分布式限流的实现原理:
-- 一文详解 Java 限流接口实现 - 阿里云开发者:
-- 分布式限流方案的探索与实践 - 腾讯云开发者:
-
-
+We can compare the action of sending requests to pouring water into a bucket, while the process of handling requests can be likened to water leaking from the bucket. We can pour water into the bucket at any rate, and it leaks out at a certain rate. If the water exceeds the bucket's capacity, it will
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md b/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
index 47201441d7e..0cb09454396 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/performance-test.md
@@ -1,178 +1,178 @@
---
-title: 性能测试入门
-category: 高可用
+title: Introduction to Performance Testing
+category: High Availability
icon: et-performance
---
-性能测试一般情况下都是由测试这个职位去做的,那还需要我们开发学这个干嘛呢?了解性能测试的指标、分类以及工具等知识有助于我们更好地去写出性能更好的程序,另外作为开发这个角色,如果你会性能测试的话,相信也会为你的履历加分不少。
+Performance testing is generally conducted by testers, so why should developers learn about it? Understanding performance testing metrics, classifications, and tools helps us write better-performing programs. Furthermore, if you as a developer possess performance testing skills, it will undoubtedly enhance your resume.
-这篇文章是我会结合自己的实际经历以及在测试这里取的经所得,除此之外,我还借鉴了一些优秀书籍,希望对你有帮助。
+This article combines my personal experiences and insights from testing, along with references to some excellent books, hoping to be of help to you.
-## 不同角色看网站性能
+## Perspectives on Website Performance from Different Roles
-### 用户
+### Users
-当用户打开一个网站的时候,最关注的是什么?当然是网站响应速度的快慢。比如我们点击了淘宝的主页,淘宝需要多久将首页的内容呈现在我的面前,我点击了提交订单按钮需要多久返回结果等等。
+When a user opens a website, what do they pay the most attention to? Certainly, it is the website's response speed. For instance, when we click on the homepage of Taobao, how long does it take for Taobao to display the content? How long does it take to return a result after clicking the "submit order" button, etc.
-所以,用户在体验我们系统的时候往往根据你的响应速度的快慢来评判你的网站的性能。
+Therefore, when users experience our system, they often judge the performance of your website based on its response speed.
-### 开发人员
+### Developers
-用户与开发人员都关注速度,这个速度实际上就是我们的系统**处理用户请求的速度**。
+Both users and developers focus on speed, which truly refers to our system's **processing speed of user requests**.
-开发人员一般情况下很难直观的去评判自己网站的性能,我们往往会根据网站当前的架构以及基础设施情况给一个大概的值,比如:
+Developers generally find it challenging to intuitively assess the performance of their website. We often provide an approximate value based on the current architecture and infrastructure of the website, for instance:
-1. 项目架构是分布式的吗?
-2. 用到了缓存和消息队列没有?
-3. 高并发的业务有没有特殊处理?
-4. 数据库设计是否合理?
-5. 系统用到的算法是否还需要优化?
-6. 系统是否存在内存泄露的问题?
-7. 项目使用的 Redis 缓存多大?服务器性能如何?用的是机械硬盘还是固态硬盘?
-8. ……
+1. Is the project architecture distributed?
+1. Are caching and messaging queues utilized?
+1. Are there any special handling for high-concurrency business?
+1. Is the database design reasonable?
+1. Do the algorithms used in the system need optimization?
+1. Does the system have memory leak issues?
+1. How large is the Redis cache used in the project? What is the server performance like? Is it using a mechanical hard disk or a solid-state drive?
+1. ……
-### 测试人员
+### Testers
-测试人员一般会根据性能测试工具来测试,然后一般会做出一个表格。这个表格可能会涵盖下面这些重要的内容:
+Testers typically conduct tests according to performance testing tools and usually create a table. This table might cover important contents like:
-1. 响应时间;
-2. 请求成功率;
-3. 吞吐量;
-4. ……
+1. Response time;
+1. Request success rate;
+1. Throughput;
+1. ……
-### 运维人员
+### Operations Personnel
-运维人员会倾向于根据基础设施和资源的利用率来判断网站的性能,比如我们的服务器资源使用是否合理、数据库资源是否存在滥用的情况、当然,这是传统的运维人员,现在 Devops 火起来后,单纯干运维的很少了。我们这里暂且还保留有这个角色。
+Operations personnel tend to evaluate the website's performance based on infrastructure and resource utilization rates. For instance, they might analyze whether resource usage on our servers is reasonable or whether there is abuse of database resources. Of course, this is the traditional role of operations personnel. With the rise of DevOps, pure operations roles are less common now, although we still acknowledge this role for the time being.
-## 性能测试需要注意的点
+## Key Points to Note in Performance Testing
-几乎没有文章在讲性能测试的时候提到这个问题,大家都会讲如何去性能测试,有哪些性能测试指标这些东西。
+Few articles address this issue when discussing performance testing. Most articles focus on how to conduct performance tests and what performance testing metrics exist.
-### 了解系统的业务场景
+### Understanding the Business Context of the System
-**性能测试之前更需要你了解当前的系统的业务场景。** 对系统业务了解的不够深刻,我们很容易犯测试方向偏执的错误,从而导致我们忽略了对系统某些更需要性能测试的地方进行测试。比如我们的系统可以为用户提供发送邮件的功能,用户配置成功邮箱后只需输入相应的邮箱之后就能发送,系统每天大概能处理上万次发邮件的请求。很多人看到这个可能就直接开始使用相关工具测试邮箱发送接口,但是,发送邮件这个场景可能不是当前系统的性能瓶颈,这么多人用我们的系统发邮件, 还可能有很多人一起发邮件,单单这个场景就这么人用,那用户管理可能才是性能瓶颈吧!
+**Before performance testing, it is crucial to comprehend the business context of the current system.** If our understanding of the system's business is not deep enough, we easily make biased testing direction mistakes, leading us to overlook certain areas of the system that need performance testing. For example, if our system provides users with the ability to send emails, after setting up a successful email address, users can simply input the corresponding email to send, and the system can handle thousands of email-sending requests daily. Many would immediately begin using relevant tools to test the email-sending interface, but sending emails may not currently be the performance bottleneck of the system. With so many users sending emails, there might be many others sending emails simultaneously, so user management could be the actual performance bottleneck!
-### 历史数据非常有用
+### Historical Data is Very Useful
-当前系统所留下的历史数据非常重要,一般情况下,我们可以通过相应的些历史数据初步判定这个系统哪些接口调用的比较多、哪些服务承受的压力最大,这样的话,我们就可以针对这些地方进行更细致的性能测试与分析。
+The historical data left by the current system is very important. Generally, we can use relevant historical data to initially determine which interfaces are being called frequently and which services are under the most pressure. This allows us to conduct more detailed performance testing and analysis targeted at these areas.
-另外,这些地方也就像这个系统的一个短板一样,优化好了这些地方会为我们的系统带来质的提升。
+Moreover, these areas are like weak points in the system; optimizing them can result in a significant qualitative improvement for our system.
-## 常见性能指标
+## Common Performance Metrics
-### 响应时间
+### Response Time
-**响应时间 RT(Response-time)就是用户发出请求到用户收到系统处理结果所需要的时间。**
+**Response Time RT (Response-time) is the time taken from when a user issues a request to when the user receives the system's processed result.**
-RT 是一个非常重要且直观的指标,RT 数值大小直接反应了系统处理用户请求速度的快慢。
+RT is a very important and intuitive metric. The size of the RT value directly reflects how quickly the system processes user requests.
-### 并发数
+### Concurrent Users
-**并发数可以简单理解为系统能够同时供多少人访问使用也就是说系统同时能处理的请求数量。**
+**Concurrent users can be simply understood as the number of people the system can support to access and use simultaneously, meaning the number of requests the system can handle at the same time.**
-并发数反应了系统的负载能力。
+The number of concurrent users reflects the system's load capacity.
-### QPS 和 TPS
+### QPS and TPS
-- **QPS(Query Per Second)** :服务器每秒可以执行的查询次数;
-- **TPS(Transaction Per Second)** :服务器每秒处理的事务数(这里的一个事务可以理解为客户发出请求到收到服务器的过程);
+- **QPS (Queries Per Second)**: The number of queries the server can execute per second;
+- **TPS (Transactions Per Second)**: The number of transactions processed by the server per second (a transaction can be understood as the process from when a customer issues a request to when they receive a response from the server).
-书中是这样描述 QPS 和 TPS 的区别的。
+The book describes the difference between QPS and TPS as follows:
-> QPS vs TPS:QPS 基本类似于 TPS,但是不同的是,对于一个页面的一次访问,形成一个 TPS;但一次页面请求,可能产生多次对服务器的请求,服务器对这些请求,就可计入“QPS”之中。如,访问一个页面会请求服务器 2 次,一次访问,产生一个“T”,产生 2 个“Q”。
+> QPS vs TPS: QPS is quite similar to TPS, but the difference lies in that one access to a page counts as one TPS; however, a single page request may generate multiple requests to the server, which can be counted as "QPS." For example, if accessing a page generates 2 requests to the server, one access would result in one "T" and two "Q".
-### 吞吐量
+### Throughput
-**吞吐量指的是系统单位时间内系统处理的请求数量。**
+**Throughput refers to the number of requests processed by the system within a unit of time.**
-一个系统的吞吐量与请求对系统的资源消耗等紧密关联。请求对系统资源消耗越多,系统吞吐能力越低,反之则越高。
+The throughput of a system is closely related to the resource consumption of requests. The more resources a request consumes from the system, the lower the system's throughput capability, and vice versa.
-TPS、QPS 都是吞吐量的常用量化指标。
+TPS and QPS are commonly used quantitative metrics for throughput.
-- **QPS(TPS)** = 并发数/平均响应时间(RT)
-- **并发数** = QPS \* 平均响应时间(RT)
+- **QPS (TPS)** = Concurrent Users / Average Response Time (RT)
+- **Concurrent Users** = QPS * Average Response Time (RT)
-## 系统活跃度指标
+## System Activity Indicators
-### PV(Page View)
+### PV (Page View)
-访问量, 即页面浏览量或点击量,衡量网站用户访问的网页数量;在一定统计周期内用户每打开或刷新一个页面就记录 1 次,多次打开或刷新同一页面则浏览量累计。UV 从网页打开的数量/刷新的次数的角度来统计的。
+Page Views refer to website traffic or click counts, measuring the number of pages visited by users; each time a user opens or refreshes a page within a specific statistical period, it records one instance; multiple openings or refreshes of the same page accumulate the view count. UV is counted from the perspective of the number of pages opened/refreshed.
-### UV(Unique Visitor)
+### UV (Unique Visitor)
-独立访客,统计 1 天内访问某站点的用户数。1 天内相同访客多次访问网站,只计算为 1 个独立访客。UV 是从用户个体的角度来统计的。
+Unique Visitors refer to the count of users visiting a site within one day. If the same visitor accesses the site multiple times in one day, they are only counted as one unique visitor. UV is counted from the perspective of individual users.
-### DAU(Daily Active User)
+### DAU (Daily Active Users)
-日活跃用户数量。
+The number of daily active users.
-### MAU(monthly active users)
+### MAU (Monthly Active Users)
-月活跃用户人数。
+The number of monthly active users.
-举例:某网站 DAU 为 1200w, 用户日均使用时长 1 小时,RT 为 0.5s,求并发量和 QPS。
+For example, if a website has a DAU of 12 million, with an average usage time of 1 hour per day, and an RT of 0.5s, we can calculate the concurrent user load and QPS.
-平均并发量 = DAU(1200w)\* 日均使用时长(1 小时,3600 秒) /一天的秒数(86400)=1200w/24 = 50w
+Average concurrent users = DAU (12 million) * Average usage time (1 hour, 3600 seconds) / Seconds in a day (86400) = 12 million / 24 = 500,000
-真实并发量(考虑到某些时间段使用人数比较少) = DAU(1200w)\* 日均使用时长(1 小时,3600 秒) /一天的秒数-访问量比较小的时间段假设为 8 小时(57600)=1200w/16 = 75w
+Real concurrent users (considering lower usage during certain periods) = DAU (12 million) * Average usage time (1 hour, 3600 seconds) / Seconds in a day - assume 8 hours (57600) for low access time = 12 million / 16 = 750,000
-峰值并发量 = 平均并发量 \* 6 = 300w
+Peak concurrent users = Average concurrent users * 6 = 3 million
-QPS = 真实并发量/RT = 75W/0.5=150w/s
+QPS = Real concurrent users / RT = 750,000 / 0.5 = 1.5 million/s
-## 性能测试分类
+## Classification of Performance Testing
-### 性能测试
+### Performance Testing
-性能测试方法是通过测试工具模拟用户请求系统,目的主要是为了测试系统的性能是否满足要求。通俗地说,这种方法就是要在特定的运行条件下验证系统的能力状态。
+Performance testing methods simulate user requests to the system using testing tools, primarily to verify whether the system's performance meets the requirements. Simply put, this method aims to validate the system's capacity under specific operating conditions.
-性能测试是你在对系统性能已经有了解的前提之后进行的,并且有明确的性能指标。
+Performance testing is carried out after you have some understanding of system performance, with clear performance metrics.
-### 负载测试
+### Load Testing
-对被测试的系统继续加大请求压力,直到服务器的某个资源已经达到饱和了,比如系统的缓存已经不够用了或者系统的响应时间已经不满足要求了。
+Continuously increasing request pressure on the tested system until some resource on the server reaches saturation, such as when system caching is insufficient or the response time is no longer acceptable.
-负载测试说白点就是测试系统的上限。
+In simpler terms, load testing tests the limits of the system.
-### 压力测试
+### Stress Testing
-不去管系统资源的使用情况,对系统继续加大请求压力,直到服务器崩溃无法再继续提供服务。
+Pressuring the system with requests regardless of resource utilization until the server crashes and can no longer provide services.
-### 稳定性测试
+### Stability Testing
-模拟真实场景,给系统一定压力,看看业务是否能稳定运行。
+Simulating real scenarios by applying a certain amount of pressure on the system to see if the business can operate stably.
-## 常用性能测试工具
+## Commonly Used Performance Testing Tools
-### 后端常用
+### Common Backend Tools
-既然系统设计涉及到系统性能方面的问题,那在面试的时候,面试官就很可能会问:**你是如何进行性能测试的?**
+Since system design involves performance-related issues, interviewers are likely to ask, **How do you conduct performance testing?**
-推荐 4 个比较常用的性能测试工具:
+Here are four commonly used performance testing tools:
-1. **Jmeter** :Apache JMeter 是 JAVA 开发的性能测试工具。
-2. **LoadRunner**:一款商业的性能测试工具。
-3. **Galtling** :一款基于 Scala 开发的高性能服务器性能测试工具。
-4. **ab** :全称为 Apache Bench 。Apache 旗下的一款测试工具,非常实用。
+1. **JMeter**: Apache JMeter is a performance testing tool developed in Java.
+1. **LoadRunner**: A commercial performance testing tool.
+1. **Gatling**: A high-performance server performance testing tool developed in Scala.
+1. **ab**: Full name is Apache Bench. It is a testing tool under the Apache umbrella and is very practical.
-没记错的话,除了 **LoadRunner** 其他几款性能测试工具都是开源免费的。
+If I remember correctly, all the performance testing tools mentioned, except for **LoadRunner**, are open-source and free.
-### 前端常用
+### Common Frontend Tools
-1. **Fiddler**:抓包工具,它可以修改请求的数据,甚至可以修改服务器返回的数据,功能非常强大,是 Web 调试的利器。
-2. **HttpWatch**: 可用于录制 HTTP 请求信息的工具。
+1. **Fiddler**: A packet capturing tool that can modify request data, and even server response data, with powerful features; it's an essential tool for web debugging.
+1. **HttpWatch**: A tool for recording HTTP request information.
-## 常见的性能优化策略
+## Common Performance Optimization Strategies
-性能优化之前我们需要对请求经历的各个环节进行分析,排查出可能出现性能瓶颈的地方,定位问题。
+Before performance optimization, we need to analyze each stage of the requests to identify potential performance bottlenecks and locate issues.
-下面是一些性能优化时,我经常拿来自问的一些问题:
+Here are some questions I often ask myself during performance optimization:
-1. 系统是否需要缓存?
-2. 系统架构本身是不是就有问题?
-3. 系统是否存在死锁的地方?
-4. 系统是否存在内存泄漏?(Java 的自动回收内存虽然很方便,但是,有时候代码写的不好真的会造成内存泄漏)
-5. 数据库索引使用是否合理?
-6. ……
+1. Does the system require caching?
+1. Does the system architecture itself have problems?
+1. Are there deadlock situations in the system?
+1. Does the system have memory leaks? (While Java’s automatic memory recovery is very convenient, poorly written code can sometimes lead to memory leaks.)
+1. Is the database indexing reasonable?
+1. ……
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md b/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
index 9d14d726675..1f40115ee83 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/redundancy.md
@@ -1,47 +1,45 @@
---
-title: 冗余设计详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Detailed Explanation of Redundant Design
+category: High Availability
icon: cluster
---
-冗余设计是保证系统和数据高可用的最常的手段。
+Redundant design is the most common means to ensure high availability of systems and data.
-对于服务来说,冗余的思想就是相同的服务部署多份,如果正在使用的服务突然挂掉的话,系统可以很快切换到备份服务上,大大减少系统的不可用时间,提高系统的可用性。
+For services, the idea of redundancy is to deploy multiple instances of the same service. If the currently used service suddenly fails, the system can quickly switch to a backup service, significantly reducing downtime and improving system availability.
-对于数据来说,冗余的思想就是相同的数据备份多份,这样就可以很简单地提高数据的安全性。
+For data, the idea of redundancy is to have multiple backups of the same data, which can easily enhance data security.
-实际上,日常生活中就有非常多的冗余思想的应用。
+In fact, there are many applications of redundancy in daily life.
-拿我自己来说,我对于重要文件的保存方法就是冗余思想的应用。我日常所使用的重要文件都会同步一份在 GitHub 以及个人云盘上,这样就可以保证即使电脑硬盘损坏,我也可以通过 GitHub 或者个人云盘找回自己的重要文件。
+For example, my method of saving important files is an application of redundancy. I synchronize important files I use daily to both GitHub and my personal cloud storage, ensuring that even if my computer's hard drive fails, I can retrieve my important files from GitHub or my personal cloud.
-高可用集群(High Availability Cluster,简称 HA Cluster)、同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活和异地多活是冗余思想在高可用系统设计中最典型的应用。
+High Availability Cluster (HA Cluster), local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, and remote active-active are the most typical applications of redundancy in high availability system design.
-- **高可用集群** : 同一份服务部署两份或者多份,当正在使用的服务突然挂掉的话,可以切换到另外一台服务,从而保证服务的高可用。
-- **同城灾备**:一整个集群可以部署在同一个机房,而同城灾备中相同服务部署在同一个城市的不同机房中。并且,备用服务不处理请求。这样可以避免机房出现意外情况比如停电、火灾。
-- **异地灾备**:类似于同城灾备,不同的是,相同服务部署在异地(通常距离较远,甚至是在不同的城市或者国家)的不同机房中
-- **同城多活**:类似于同城灾备,但备用服务可以处理请求,这样可以充分利用系统资源,提高系统的并发。
-- **异地多活** : 将服务部署在异地的不同机房中,并且,它们可以同时对外提供服务。
+- **High Availability Cluster**: The same service is deployed in two or more instances. If the currently used service suddenly fails, it can switch to another service, ensuring high availability.
+- **Local Disaster Recovery**: An entire cluster can be deployed in the same data center, while in local disaster recovery, the same service is deployed in different data centers within the same city. Additionally, the backup service does not handle requests. This helps avoid unexpected situations in the data center, such as power outages or fires.
+- **Remote Disaster Recovery**: Similar to local disaster recovery, but the same service is deployed in different data centers in remote locations (usually far apart, even in different cities or countries).
+- **Local Active-Active**: Similar to local disaster recovery, but the backup service can handle requests, allowing for better utilization of system resources and increased concurrency.
+- **Remote Active-Active**: Services are deployed in different data centers in remote locations, and they can provide services simultaneously.
-高可用集群单纯是服务的冗余,并没有强调地域。同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活和异地多活实现了地域上的冗余。
+High Availability Clusters focus solely on service redundancy without emphasizing geographic location. Local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, and remote active-active achieve geographic redundancy.
-同城和异地的主要区别在于机房之间的距离。异地通常距离较远,甚至是在不同的城市或者国家。
+The main difference between local and remote is the distance between data centers. Remote locations are usually farther apart, even in different cities or countries.
-和传统的灾备设计相比,同城多活和异地多活最明显的改变在于“多活”,即所有站点都是同时在对外提供服务的。异地多活是为了应对突发状况比如火灾、地震等自然或者人为灾害。
+Compared to traditional disaster recovery design, the most significant change in local active-active and remote active-active is the "active-active" aspect, meaning all sites are simultaneously providing services. Remote active-active is designed to respond to emergencies such as fires, earthquakes, or other natural or man-made disasters.
-光做好冗余还不够,必须要配合上 **故障转移** 才可以! 所谓故障转移,简单来说就是实现不可用服务快速且自动地切换到可用服务,整个过程不需要人为干涉。
+Simply having redundancy is not enough; it must be paired with **failover**! Failover, in simple terms, is the ability to quickly and automatically switch from an unavailable service to an available one without human intervention.
-举个例子:哨兵模式的 Redis 集群中,如果 Sentinel(哨兵) 检测到 master 节点出现故障的话, 它就会帮助我们实现故障转移,自动将某一台 slave 升级为 master,确保整个 Redis 系统的可用性。整个过程完全自动,不需要人工介入。我在[《Java 面试指北》](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7)的「技术面试题篇」中的数据库部分详细介绍了 Redis 集群相关的知识点&面试题,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
+For example, in a Redis cluster using Sentinel mode, if the Sentinel detects a failure in the master node, it will help us achieve failover by automatically promoting one of the slaves to master, ensuring the availability of the entire Redis system. The entire process is fully automated and requires no manual intervention. I have detailed the relevant knowledge and interview questions about Redis clusters in the database section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7), which interested readers can check out.
-再举个例子:Nginx 可以结合 Keepalived 来实现高可用。如果 Nginx 主服务器宕机的话,Keepalived 可以自动进行故障转移,备用 Nginx 主服务器升级为主服务。并且,这个切换对外是透明的,因为使用的虚拟 IP,虚拟 IP 不会改变。我在[《Java 面试指北》](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7)的「技术面试题篇」中的「服务器」部分详细介绍了 Nginx 相关的知识点&面试题,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看。
+Another example: Nginx can be combined with Keepalived to achieve high availability. If the primary Nginx server goes down, Keepalived can automatically perform failover, promoting the backup Nginx server to primary. Moreover, this switch is transparent to external users because a virtual IP is used, which does not change. I have detailed the relevant knowledge and interview questions about Nginx in the "Servers" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/f37fc804-bfe6-4b0d-b373-9c462188fec7), which interested readers can check out.
-异地多活架构实施起来非常难,需要考虑的因素非常多。本人不才,实际项目中并没有实践过异地多活架构,我对其了解还停留在书本知识。
+Implementing a remote active-active architecture is very challenging, with many factors to consider. I have not personally practiced remote active-active architecture in actual projects, and my understanding remains at the theoretical level.
-如果你想要深入学习异地多活相关的知识,我这里推荐几篇我觉得还不错的文章:
+If you want to delve deeper into knowledge related to remote active-active, I recommend a few articles that I find quite good:
-- [搞懂异地多活,看这篇就够了- 水滴与银弹 - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/T6mMDdtTfBuIiEowCpqu6Q)
-- [四步构建异地多活](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hMD-IS__4JE5_nQhYPYSTg)
-- [《从零开始学架构》— 28 | 业务高可用的保障:异地多活架构](http://gk.link/a/10pKZ)
+- [Understanding Remote Active-Active, This Article is Enough - Water Droplets and Silver Bullets - 2021](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/T6mMDdtTfBuIiEowCpqu6Q)
+- [Building Remote Active-Active in Four Steps](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hMD-IS__4JE5_nQhYPYSTg)
+- [“Learning Architecture from Scratch” — 28 | Ensuring Business High Availability: Remote Active-Active Architecture](http://gk.link/a/10pKZ)
-不过,这些文章大多也都是在介绍概念知识。目前,网上还缺少真正介绍具体要如何去实践落地异地多活架构的资料。
-
-
+However, most of these articles mainly introduce conceptual knowledge. Currently, there is
diff --git a/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md b/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
index 3c7ba1ac9cd..8b5f3a4a161 100644
--- a/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
+++ b/docs/high-availability/timeout-and-retry.md
@@ -1,86 +1,58 @@
---
-title: 超时&重试详解
-category: 高可用
+title: Timeout & Retry Explained
+category: High Availability
icon: retry
---
-由于网络问题、系统或者服务内部的 Bug、服务器宕机、操作系统崩溃等问题的不确定性,我们的系统或者服务永远不可能保证时刻都是可用的状态。
+Due to uncertainties such as network issues, internal bugs in systems or services, server crashes, and operating system failures, our systems or services can never guarantee constant availability.
-为了最大限度的减小系统或者服务出现故障之后带来的影响,我们需要用到的 **超时(Timeout)** 和 **重试(Retry)** 机制。
+To minimize the impact of failures in systems or services, we need to utilize **Timeout** and **Retry** mechanisms.
-想要把超时和重试机制讲清楚其实很简单,因为它俩本身就不是什么高深的概念。
+Explaining the timeout and retry mechanisms is actually quite simple, as they are not complex concepts.
-虽然超时和重试机制的思想很简单,但是它俩是真的非常实用。你平时接触到的绝大部分涉及到远程调用的系统或者服务都会应用超时和重试机制。尤其是对于微服务系统来说,正确设置超时和重试非常重要。单体服务通常只涉及数据库、缓存、第三方 API、中间件等的网络调用,而微服务系统内部各个服务之间还存在着网络调用。
+Although the ideas behind timeout and retry mechanisms are straightforward, they are indeed very practical. Most systems or services you encounter that involve remote calls will apply timeout and retry mechanisms. This is especially important for microservices systems, where correctly setting timeouts and retries is crucial. Monolithic services typically only involve network calls to databases, caches, third-party APIs, and middleware, while microservices systems also involve network calls between various services.
-## 超时机制
+## Timeout Mechanism
-### 什么是超时机制?
+### What is the Timeout Mechanism?
-超时机制说的是当一个请求超过指定的时间(比如 1s)还没有被处理的话,这个请求就会直接被取消并抛出指定的异常或者错误(比如 `504 Gateway Timeout`)。
+The timeout mechanism refers to the cancellation of a request if it exceeds a specified time (e.g., 1 second) without being processed, resulting in a specified exception or error being thrown (e.g., `504 Gateway Timeout`).
-我们平时接触到的超时可以简单分为下面 2 种:
+Timeouts can generally be categorized into the following two types:
-- **连接超时(ConnectTimeout)**:客户端与服务端建立连接的最长等待时间。
-- **读取超时(ReadTimeout)**:客户端和服务端已经建立连接,客户端等待服务端处理完请求的最长时间。实际项目中,我们关注比较多的还是读取超时。
+- **Connect Timeout**: The maximum wait time for the client to establish a connection with the server.
+- **Read Timeout**: The maximum time the client waits for the server to complete processing the request after a connection has been established. In practical projects, we often focus more on read timeouts.
-一些连接池客户端框架中可能还会有获取连接超时和空闲连接清理超时。
+Some connection pool client frameworks may also have connection acquisition timeouts and idle connection cleanup timeouts.
-如果没有设置超时的话,就可能会导致服务端连接数爆炸和大量请求堆积的问题。
+If timeouts are not set, it can lead to an explosion of server connections and a backlog of requests.
-这些堆积的连接和请求会消耗系统资源,影响新收到的请求的处理。严重的情况下,甚至会拖垮整个系统或者服务。
+These accumulated connections and requests consume system resources, affecting the processing of new incoming requests. In severe cases, it can even bring down the entire system or service.
-我之前在实际项目就遇到过类似的问题,整个网站无法正常处理请求,服务器负载直接快被拉满。后面发现原因是项目超时设置错误加上客户端请求处理异常,导致服务端连接数直接接近 40w+,这么多堆积的连接直接把系统干趴了。
+I encountered a similar issue in a previous project where the entire website could not process requests normally, and the server load was nearly maxed out. The cause was found to be incorrect timeout settings combined with exceptions in client request handling, leading to server connections approaching 400,000+. Such a backlog of connections directly caused the system to crash.
-### 超时时间应该如何设置?
+### How Should Timeout Values Be Set?
-超时到底设置多长时间是一个难题!超时值设置太高或者太低都有风险。如果设置太高的话,会降低超时机制的有效性,比如你设置超时为 10s 的话,那设置超时就没啥意义了,系统依然可能会出现大量慢请求堆积的问题。如果设置太低的话,就可能会导致在系统或者服务在某些处理请求速度变慢的情况下(比如请求突然增多),大量请求重试(超时通常会结合重试)继续加重系统或者服务的压力,进而导致整个系统或者服务被拖垮的问题。
+Determining the appropriate timeout duration is a challenge! Setting the timeout value too high or too low both carry risks. If set too high, it reduces the effectiveness of the timeout mechanism; for example, if you set the timeout to 10 seconds, then the timeout becomes meaningless, and the system may still experience a backlog of slow requests. If set too low, it may lead to a situation where, under certain conditions (e.g., a sudden increase in requests), a large number of requests are retried (timeouts are usually combined with retries), further increasing the pressure on the system or service, potentially leading to a complete system failure.
-通常情况下,我们建议读取超时设置为 **1500ms** ,这是一个比较普适的值。如果你的系统或者服务对于延迟比较敏感的话,那读取超时值可以适当在 **1500ms** 的基础上进行缩短。反之,读取超时值也可以在 **1500ms** 的基础上进行加长,不过,尽量还是不要超过 **1500ms** 。连接超时可以适当设置长一些,建议在 **1000ms ~ 5000ms** 之内。
+In general, we recommend setting the read timeout to **1500ms**, which is a relatively universal value. If your system or service is sensitive to latency, the read timeout can be shortened from the **1500ms** baseline. Conversely, it can also be extended, but it is best not to exceed **1500ms**. The connect timeout can be set a bit longer, ideally within **1000ms to 5000ms**.
-没有银弹!超时值具体该设置多大,还是要根据实际项目的需求和情况慢慢调整优化得到。
+There is no silver bullet! The specific timeout value should be adjusted and optimized based on the actual project requirements and conditions.
-更上一层,参考[美团的 Java 线程池参数动态配置](https://tech.meituan.com/2020/04/02/java-pooling-pratice-in-meituan.html)思想,我们也可以将超时弄成可配置化的参数而不是固定的,比较简单的一种办法就是将超时的值放在配置中心中。这样的话,我们就可以根据系统或者服务的状态动态调整超时值了。
+Furthermore, referring to [Meituan's dynamic configuration of Java thread pool parameters](https://tech.meituan.com/2020/04/02/java-pooling-pratice-in-meituan.html), we can also make timeouts configurable parameters rather than fixed values. A simple approach is to place the timeout values in a configuration center. This way, we can dynamically adjust the timeout values based on the state of the system or service.
-## 重试机制
+## Retry Mechanism
-### 什么是重试机制?
+### What is the Retry Mechanism?
-重试机制一般配合超时机制一起使用,指的是多次发送相同的请求来避免瞬态故障和偶然性故障。
+The retry mechanism is generally used in conjunction with the timeout mechanism, referring to the repeated sending of the same request to avoid transient and occasional failures.
-瞬态故障可以简单理解为某一瞬间系统偶然出现的故障,并不会持久。偶然性故障可以理解为哪些在某些情况下偶尔出现的故障,频率通常较低。
+Transient failures can be simply understood as faults that occur momentarily in the system and are not persistent. Occasional failures can be understood as faults that occur infrequently under certain conditions.
-重试的核心思想是通过消耗服务器的资源来尽可能获得请求更大概率被成功处理。由于瞬态故障和偶然性故障是很少发生的,因此,重试对于服务器的资源消耗几乎是可以被忽略的。
+The core idea of retrying is to consume server resources to maximize the probability of successfully processing a request. Since transient and occasional failures are rare, the resource consumption from retries is almost negligible.
-### 常见的重试策略有哪些?
+### What Are Common Retry Strategies?
-常见的重试策略有两种:
+There are two common retry strategies:
-1. **固定间隔时间重试**:每次重试之间都使用相同的时间间隔,比如每隔 1.5 秒进行一次重试。这种重试策略的优点是实现起来比较简单,不需要考虑重试次数和时间的关系,也不需要维护额外的状态信息。但是这种重试策略的缺点是可能会导致重试过于频繁或过于稀疏,从而影响系统的性能和效率。如果重试间隔太短,可能会对目标系统造成过大的压力,导致雪崩效应;如果重试间隔太长,可能会导致用户等待时间过长,影响用户体验。
-2. **梯度间隔重试**:根据重试次数的增加去延长下次重试时间,比如第一次重试间隔为 1 秒,第二次为 2 秒,第三次为 4 秒,以此类推。这种重试策略的优点是能够有效提高重试成功的几率(随着重试次数增加,但是重试依然不成功,说明目标系统恢复时间比较长,因此可以根据重试次数延长下次重试时间),也能通过柔性化的重试避免对下游系统造成更大压力。但是这种重试策略的缺点是实现起来比较复杂,需要考虑重试次数和时间的关系,以及设置合理的上限和下限值。另外,这种重试策略也可能会导致用户等待时间过长,影响用户体验。
-
-这两种适合的场景各不相同。固定间隔时间重试适用于目标系统恢复时间比较稳定和可预测的场景,比如网络波动或服务重启。梯度间隔重试适用于目标系统恢复时间比较长或不可预测的场景,比如网络故障和服务故障。
-
-### 重试的次数如何设置?
-
-重试的次数不宜过多,否则依然会对系统负载造成比较大的压力。
-
-重试的次数通常建议设为 3 次。大部分情况下,我们还是更建议使用梯度间隔重试策略,比如说我们要重试 3 次的话,第 1 次请求失败后,等待 1 秒再进行重试,第 2 次请求失败后,等待 2 秒再进行重试,第 3 次请求失败后,等待 3 秒再进行重试。
-
-### 什么是重试幂等?
-
-超时和重试机制在实际项目中使用的话,需要注意保证同一个请求没有被多次执行。
-
-什么情况下会出现一个请求被多次执行呢?客户端等待服务端完成请求完成超时但此时服务端已经执行了请求,只是由于短暂的网络波动导致响应在发送给客户端的过程中延迟了。
-
-举个例子:用户支付购买某个课程,结果用户支付的请求由于重试的问题导致用户购买同一门课程支付了两次。对于这种情况,我们在执行用户购买课程的请求的时候需要判断一下用户是否已经购买过。这样的话,就不会因为重试的问题导致重复购买了。
-
-### Java 中如何实现重试?
-
-如果要手动编写代码实现重试逻辑的话,可以通过循环(例如 while 或 for 循环)或者递归实现。不过,一般不建议自己动手实现,有很多第三方开源库提供了更完善的重试机制实现,例如 Spring Retry、Resilience4j、Guava Retrying。
-
-## 参考
-
-- 微服务之间调用超时的设置治理:
-- 超时、重试和抖动回退:
-
-
+1. **Fixed Interval Retry**: Each retry uses the same time interval, such as retrying every 1.5 seconds. The advantage of this strategy is its simplicity; there is no need to consider the relationship between retry count and time, nor maintain additional state information. However, the downside is that it may lead to retries being too frequent or too sparse, affecting system performance and efficiency. If the retry interval is too short, it may put excessive pressure on the target system, leading to
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/cdn.md b/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
index f4ca0eab5f2..417a6a70b4f 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/cdn.md
@@ -1,135 +1,135 @@
---
-title: CDN工作原理详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of How CDN Works
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: CDN,内容分发网络
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: CDN, Content Delivery Network
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.
---
-## 什么是 CDN ?
+## What is CDN?
-**CDN** 全称是 Content Delivery Network/Content Distribution Network,翻译过的意思是 **内容分发网络** 。
+**CDN** stands for Content Delivery Network, which translates to **Content Distribution Network**.
-我们可以将内容分发网络拆开来看:
+We can break down the concept of a content distribution network:
-- 内容:指的是静态资源比如图片、视频、文档、JS、CSS、HTML。
-- 分发网络:指的是将这些静态资源分发到位于多个不同的地理位置机房中的服务器上,这样,就可以实现静态资源的就近访问比如北京的用户直接访问北京机房的数据。
+- Content: Refers to static resources such as images, videos, documents, JS, CSS, and HTML.
+- Distribution Network: Refers to distributing these static resources to servers located in different geographic locations, allowing for nearby access to static resources, such as a user in Beijing directly accessing data from the Beijing data center.
-所以,简单来说,**CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。**
+So, simply put, **CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.**
-类似于京东建立的庞大的仓储运输体系,京东物流在全国拥有非常多的仓库,仓储网络几乎覆盖全国所有区县。这样的话,用户下单的第一时间,商品就从距离用户最近的仓库,直接发往对应的配送站,再由京东小哥送到你家。
+Similar to the massive warehousing and transportation system established by JD.com, JD logistics has many warehouses across the country, with a storage network covering almost all districts and counties in the country. This way, when a user places an order, the product is sent directly from the nearest warehouse to the corresponding distribution station, and then delivered to your home by JD couriers.
-
+
-你可以将 CDN 看作是服务上一层的特殊缓存服务,分布在全国各地,主要用来处理静态资源的请求。
+You can think of CDN as a special caching service on top of the server, distributed across the country, primarily used to handle requests for static resources.
-
+
-我们经常拿全站加速和内容分发网络做对比,不要把两者搞混了!全站加速(不同云服务商叫法不同,腾讯云叫 ECDN、阿里云叫 DCDN)既可以加速静态资源又可以加速动态资源,内容分发网络(CDN)主要针对的是 **静态资源** 。
+We often compare full-site acceleration with content delivery networks; do not confuse the two! Full-site acceleration (known as ECDN by Tencent Cloud and DCDN by Alibaba Cloud) can accelerate both static and dynamic resources, whereas content delivery network (CDN) mainly targets **static resources**.
-
+
-绝大部分公司都会在项目开发中使用 CDN 服务,但很少会有自建 CDN 服务的公司。基于成本、稳定性和易用性考虑,建议直接选择专业的云厂商(比如阿里云、腾讯云、华为云、青云)或者 CDN 厂商(比如网宿、蓝汛)提供的开箱即用的 CDN 服务。
+Most companies will use CDN services in their project development, but very few will build their own CDN services. Considering cost, stability, and usability, it is advisable to choose ready-to-use CDN services offered by professional cloud vendors (such as Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, QingCloud) or CDN providers (such as Wangsu, Blue boolean).
-很多朋友可能要问了:**既然是就近访问,为什么不直接将服务部署在多个不同的地方呢?**
+Many friends may ask: **Since it's about nearby access, why not deploy services directly in multiple different places?**
-- 成本太高,需要部署多份相同的服务。
-- 静态资源通常占用空间比较大且经常会被访问到,如果直接使用服务器或者缓存来处理静态资源请求的话,对系统资源消耗非常大,可能会影响到系统其他服务的正常运行。
+- The cost is too high, as multiple identical services need to be deployed.
+- Static resources usually take up a lot of space and are frequently accessed. If we use servers or caches to handle static resource requests directly, it consumes a lot of system resources, potentially affecting the normal operation of other system services.
-同一个服务在在多个不同的地方部署多份(比如同城灾备、异地灾备、同城多活、异地多活)是为了实现系统的高可用而不是就近访问。
+Deploying the same service in multiple different locations (such as local disaster recovery, remote disaster recovery, local active-active, remote active-active) is for achieving high availability of the system, not for nearby access.
-## CDN 工作原理是什么?
+## What is the Working Principle of CDN?
-搞懂下面 3 个问题也就搞懂了 CDN 的工作原理:
+Understanding the following three questions will help you grasp the working principle of CDN:
-1. 静态资源是如何被缓存到 CDN 节点中的?
-2. 如何找到最合适的 CDN 节点?
-3. 如何防止静态资源被盗用?
+1. How are static resources cached to CDN nodes?
+1. How to find the most suitable CDN node?
+1. How to prevent static resources from being misused?
-### 静态资源是如何被缓存到 CDN 节点中的?
+### How are static resources cached to CDN nodes?
-你可以通过 **预热** 的方式将源站的资源同步到 CDN 的节点中。这样的话,用户首次请求资源可以直接从 CDN 节点中取,无需回源。这样可以降低源站压力,提升用户体验。
+You can synchronize the origin server's resources to the CDN nodes through **warming**. This way, users requesting resources for the first time can directly retrieve them from the CDN node without needing to go back to the origin, reducing the pressure on the origin server and improving user experience.
-如果不预热的话,你访问的资源可能不在 CDN 节点中,这个时候 CDN 节点将请求源站获取资源,这个过程是大家经常说的 **回源**。
+If resources are not warmed, the requested resources may not be present at the CDN node. In this case, the CDN node will fetch the resources from the origin server, which is often referred to as **back to source**.
-> - 回源:当 CDN 节点上没有用户请求的资源或该资源的缓存已经过期时,CDN 节点需要从原始服务器获取最新的资源内容,这个过程就是回源。当用户请求发生回源的话,会导致该请求的响应速度比未使用 CDN 还慢,因为相比于未使用 CDN 还多了一层 CDN 的调用流程。
-> - 预热:预热是指在 CDN 上提前将内容缓存到 CDN 节点上。这样当用户在请求这些资源时,能够快速地从最近的 CDN 节点获取到而不需要回源,进而减少了对源站的访问压力,提高了访问速度。
+> - Back to Source: When the CDN node does not have the requested resource or the resource's cache has expired, the CDN node needs to retrieve the latest resource content from the original server. This process is known as back to source. When a user request undergoes back to source, it results in a response speed slower than without using CDN, as it adds an extra layer of CDN call process.
+> - Warming: Warming refers to caching content in advance at the CDN nodes. This allows users to quickly retrieve resources from the nearest CDN node without going back to the origin, thereby reducing the access pressure on the origin server and improving access speed.
-
+
-如果资源有更新的话,你也可以对其 **刷新** ,删除 CDN 节点上缓存的旧资源,并强制 CDN 节点回源站获取最新资源。
+If there are updates to resources, you can also **refresh** them by deleting the old cached resources on the CDN node and forcing the CDN node to go back to the origin server to fetch the latest resources.
-几乎所有云厂商提供的 CDN 服务都具备缓存的刷新和预热功能(下图是阿里云 CDN 服务提供的相应功能):
+Almost all cloud providers' CDN services offer cache refresh and warming functions (the following image shows the corresponding functions provided by Alibaba Cloud CDN):
-
+
-**命中率** 和 **回源率** 是衡量 CDN 服务质量两个重要指标。命中率越高越好,回源率越低越好。
+**Hit Rate** and **Back to Source Rate** are two important indicators for measuring the quality of CDN services. The higher the hit rate, the better, and the lower the back to source rate, the better.
-### 如何找到最合适的 CDN 节点?
+### How to find the most suitable CDN node?
-GSLB (Global Server Load Balance,全局负载均衡)是 CDN 的大脑,负责多个 CDN 节点之间相互协作,最常用的是基于 DNS 的 GSLB。
+GSLB (Global Server Load Balance) is the brain of the CDN, responsible for the cooperation among multiple CDN nodes. The most commonly used is DNS-based GSLB.
-CDN 会通过 GSLB 找到最合适的 CDN 节点,更具体点来说是下面这样的:
+CDN uses GSLB to find the most suitable CDN node, specifically as follows:
-1. 浏览器向 DNS 服务器发送域名请求;
-2. DNS 服务器向根据 CNAME( Canonical Name ) 别名记录向 GSLB 发送请求;
-3. GSLB 返回性能最好(通常距离请求地址最近)的 CDN 节点(边缘服务器,真正缓存内容的地方)的地址给浏览器;
-4. 浏览器直接访问指定的 CDN 节点。
+1. The browser sends a domain name request to the DNS server;
+1. The DNS server sends a request to GSLB based on the CNAME (Canonical Name) alias record;
+1. GSLB returns the address of the best-performing (usually the nearest to the request address) CDN node (edge server, the actual caching location) to the browser;
+1. The browser directly accesses the specified CDN node.
-
+
-为了方便理解,上图其实做了一点简化。GSLB 内部可以看作是 CDN 专用 DNS 服务器和负载均衡系统组合。CDN 专用 DNS 服务器会返回负载均衡系统 IP 地址给浏览器,浏览器使用 IP 地址请求负载均衡系统进而找到对应的 CDN 节点。
+To facilitate understanding, the above diagram simplifies certain aspects. Internally, GSLB can be viewed as a combination of a CDN-specific DNS server and a load-balancing system. The CDN-specific DNS server returns the IP address of the load-balancing system to the browser, which then uses this IP address to request the load-balancing system to find the corresponding CDN node.
-**GSLB 是如何选择出最合适的 CDN 节点呢?** GSLB 会根据请求的 IP 地址、CDN 节点状态(比如负载情况、性能、响应时间、带宽)等指标来综合判断具体返回哪一个 CDN 节点的地址。
+**How does GSLB choose the most suitable CDN node?** GSLB comprehensively judges which CDN node’s address to return based on metrics such as the request's IP address, the status of the CDN node (such as load status, performance, response time, bandwidth), etc.
-### 如何防止资源被盗刷?
+### How to prevent misuse of resources?
-如果我们的资源被其他用户或者网站非法盗刷的话,将会是一笔不小的开支。
+If our resources are illegally accessed or scraped by other users or websites, it could result in significant expenses.
-解决这个问题最常用最简单的办法设置 **Referer 防盗链**,具体来说就是根据 HTTP 请求的头信息里面的 Referer 字段对请求进行限制。我们可以通过 Referer 字段获取到当前请求页面的来源页面的网站地址,这样我们就能确定请求是否来自合法的网站。
+The most common and straightforward solution to this problem is to set up **Referer anti-hotlinking**. Specifically, this limits requests based on the Referer field in the HTTP request headers. By utilizing the Referer field, we can determine the originating website address of the current request and ascertain whether it comes from a legitimate website.
-CDN 服务提供商几乎都提供了这种比较基础的防盗链机制。
+Almost all CDN service providers offer this basic anti-hotlinking mechanism.
-
+
-不过,如果站点的防盗链配置允许 Referer 为空的话,通过隐藏 Referer,可以直接绕开防盗链。
+However, if the site's anti-hotlinking configuration allows a blank Referer, it is possible to bypass the anti-hotlinking by hiding the Referer.
-通常情况下,我们会配合其他机制来确保静态资源被盗用,一种常用的机制是 **时间戳防盗链** 。相比之下,**时间戳防盗链** 的安全性更强一些。时间戳防盗链加密的 URL 具有时效性,过期之后就无法再被允许访问。
+Usually, we combine other mechanisms to ensure the static resources are not misused. A commonly used mechanism is **timestamp anti-hotlinking**. Compared to the simple Referer-based approach, **timestamp anti-hotlinking** offers stronger security. The encrypted URL in timestamp anti-hotlinking is time-sensitive, and once it expires, access is no longer permitted.
-时间戳防盗链的 URL 通常会有两个参数一个是签名字符串,一个是过期时间。签名字符串一般是通过对用户设定的加密字符串、请求路径、过期时间通过 MD5 哈希算法取哈希的方式获得。
+The URL for timestamp anti-hotlinking typically includes two parameters: a signature string and an expiration time. The signature string is generally obtained by executing an MD5 hash on a user-defined encrypted string, request path, and expiration time.
-时间戳防盗链 URL 示例:
+Example URL for timestamp anti-hotlinking:
```plain
-http://cdn.wangsu.com/4/123.mp3? wsSecret=79aead3bd7b5db4adeffb93a010298b5&wsTime=1601026312
+http://cdn.wangsu.com/4/123.mp3?wsSecret=79aead3bd7b5db4adeffb93a010298b5&wsTime=1601026312
```
-- `wsSecret`:签名字符串。
-- `wsTime`: 过期时间。
+- `wsSecret`: Signature string.
+- `wsTime`: Expiration time.

-时间戳防盗链的实现也比较简单,并且可靠性较高,推荐使用。并且,绝大部分 CDN 服务提供商都提供了开箱即用的时间戳防盗链机制。
+The implementation of timestamp anti-hotlinking is relatively simple and highly reliable, making it a recommended option. Additionally, most CDN service providers offer plug-and-play timestamp anti-hotlinking mechanisms.
-
+
-除了 Referer 防盗链和时间戳防盗链之外,你还可以 IP 黑白名单配置、IP 访问限频配置等机制来防盗刷。
+In addition to Referer anti-hotlinking and timestamp anti-hotlinking, you can also utilize IP black and white list configurations, IP access rate limiting configurations, and other mechanisms to prevent misuse.
-## 总结
+## Summary
-- CDN 就是将静态资源分发到多个不同的地方以实现就近访问,进而加快静态资源的访问速度,减轻服务器以及带宽的负担。
-- 基于成本、稳定性和易用性考虑,建议直接选择专业的云厂商(比如阿里云、腾讯云、华为云、青云)或者 CDN 厂商(比如网宿、蓝汛)提供的开箱即用的 CDN 服务。
-- GSLB (Global Server Load Balance,全局负载均衡)是 CDN 的大脑,负责多个 CDN 节点之间相互协作,最常用的是基于 DNS 的 GSLB。CDN 会通过 GSLB 找到最合适的 CDN 节点。
-- 为了防止静态资源被盗用,我们可以利用 **Referer 防盗链** + **时间戳防盗链** 。
+- CDN is the distribution of static resources to multiple different places to achieve nearby access, thereby speeding up the access speed of static resources and reducing the burden on servers and bandwidth.
+- Considering cost, stability, and usability, it is advisable to choose ready-to-use CDN services offered by professional cloud vendors (such as Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, QingCloud) or CDN providers (such as Wangsu, Blue boolean).
+- GSLB (Global Server Load Balance) is the brain of the CDN, responsible for the cooperation among multiple CDN nodes. The most common implementation is DNS-based GSLB. CDN utilizes GSLB to find the most suitable CDN node.
+- To prevent the misuse of static resources, we can use **Referer anti-hotlinking** combined with **timestamp anti-hotlinking**.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 时间戳防盗链 - 七牛云 CDN:
-- CDN 是个啥玩意?一文说个明白:
-- 《透视 HTTP 协议》- 37 | CDN:加速我们的网络服务:
+- Timestamp Anti-Hotlinking - Qiniu Cloud CDN:
+- What on Earth is CDN? A Clear Explanation:
+- "Understanding HTTP Protocol" - 37 | CDN: Accelerating Our Network Services:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md b/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
index d7ae70c2bfd..436b68af621 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/data-cold-hot-separation.md
@@ -1,68 +1,56 @@
---
-title: 数据冷热分离详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of Data Hot and Cold Separation
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: 数据冷热分离,冷数据迁移,冷数据存储
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 数据冷热分离是指根据数据的访问频率和业务重要性,将数据分为冷数据和热数据,冷数据一般存储在存储在低成本、低性能的介质中,热数据高性能存储介质中。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Data hot and cold separation, cold data migration, cold data storage
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: Data hot and cold separation refers to dividing data into cold and hot data based on access frequency and business importance. Cold data is generally stored in low-cost, low-performance media, while hot data is stored in high-performance media.
---
-## 什么是数据冷热分离?
+## What is Data Hot and Cold Separation?
-数据冷热分离是指根据数据的访问频率和业务重要性,将数据分为冷数据和热数据,冷数据一般存储在存储在低成本、低性能的介质中,热数据高性能存储介质中。
+Data hot and cold separation refers to dividing data into cold and hot data based on access frequency and business importance. Cold data is generally stored in low-cost, low-performance media, while hot data is stored in high-performance media.
-### 冷数据和热数据
+### Cold Data and Hot Data
-热数据是指经常被访问和修改且需要快速访问的数据,冷数据是指不经常访问,对当前项目价值较低,但需要长期保存的数据。
+Hot data refers to data that is frequently accessed and modified and requires quick access, while cold data refers to data that is infrequently accessed, has lower current project value, but needs to be stored for the long term.
-冷热数据到底如何区分呢?有两个常见的区分方法:
+How do we distinguish between hot and cold data? There are two common methods of distinction:
-1. **时间维度区分**:按照数据的创建时间、更新时间、过期时间等,将一定时间段内的数据视为热数据,超过该时间段的数据视为冷数据。例如,订单系统可以将 1 年前的订单数据作为冷数据,1 年内的订单数据作为热数据。这种方法适用于数据的访问频率和时间有较强的相关性的场景。
-2. **访问频率区分**:将高频访问的数据视为热数据,低频访问的数据视为冷数据。例如,内容系统可以将浏览量非常低的文章作为冷数据,浏览量较高的文章作为热数据。这种方法需要记录数据的访问频率,成本较高,适合访问频率和数据本身有较强的相关性的场景。
+1. **Time Dimension Distinction**: Data is classified as hot or cold based on its creation time, update time, expiration time, etc. Data within a certain time frame is considered hot, while data beyond that time frame is considered cold. For example, an order system might classify order data from one year ago as cold data and order data within the last year as hot data. This method is suitable for scenarios where access frequency is strongly correlated with time.
+1. **Access Frequency Distinction**: Data that is accessed frequently is considered hot, while data that is accessed infrequently is considered cold. For example, a content system might classify articles with very low views as cold data and articles with higher views as hot data. This method requires tracking data access frequency, which can be costly, and is suitable for scenarios where access frequency is strongly correlated with the data itself.
-几年前的数据并不一定都是冷数据,例如一些优质文章发表几年后依然有很多人访问,大部分普通用户新发表的文章却基本没什么人访问。
+Data from a few years ago is not necessarily all cold data; for instance, some high-quality articles may still receive many visits years after publication, while most newly published articles by ordinary users may hardly be accessed.
-这两种区分冷热数据的方法各有优劣,实际项目中,可以将两者结合使用。
+Both methods of distinguishing hot and cold data have their pros and cons, and in actual projects, they can be used in combination.
-### 冷热分离的思想
+### The Concept of Hot and Cold Separation
-冷热分离的思想非常简单,就是对数据进行分类,然后分开存储。冷热分离的思想可以应用到很多领域和场景中,而不仅仅是数据存储,例如:
+The concept of hot and cold separation is quite simple: classify data and then store it separately. This concept can be applied in many fields and scenarios, not just data storage, such as:
-- 邮件系统中,可以将近期的比较重要的邮件放在收件箱,将比较久远的不太重要的邮件存入归档。
-- 日常生活中,可以将常用的物品放在显眼的位置,不常用的物品放入储藏室或者阁楼。
-- 图书馆中,可以将最受欢迎和最常借阅的图书单独放在一个显眼的区域,将较少借阅的书籍放在不起眼的位置。
+- In an email system, important recent emails can be placed in the inbox, while less important older emails can be archived.
+- In daily life, frequently used items can be placed in prominent locations, while less frequently used items can be stored in a storage room or attic.
+- In a library, the most popular and frequently borrowed books can be placed in a prominent area, while less borrowed books can be placed in less noticeable locations.
- ……
-### 数据冷热分离的优缺点
+### Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Hot and Cold Separation
-- 优点:热数据的查询性能得到优化(用户的绝大部分操作体验会更好)、节约成本(可以冷热数据的不同存储需求,选择对应的数据库类型和硬件配置,比如将热数据放在 SSD 上,将冷数据放在 HDD 上)
-- 缺点:系统复杂性和风险增加(需要分离冷热数据,数据错误的风险增加)、统计效率低(统计的时候可能需要用到冷库的数据)。
+- Advantages: The query performance of hot data is optimized (the user experience for most operations will be better), and costs are saved (different storage requirements for hot and cold data allow for the selection of appropriate database types and hardware configurations, such as placing hot data on SSDs and cold data on HDDs).
+- Disadvantages: Increased system complexity and risk (the need to separate hot and cold data increases the risk of data errors), and lower statistical efficiency (cold storage data may be needed for statistics).
-## 冷数据如何迁移?
+## How to Migrate Cold Data?
-冷数据迁移方案:
+Cold data migration solutions:
-1. 业务层代码实现:当有对数据进行写操作时,触发冷热分离的逻辑,判断数据是冷数据还是热数据,冷数据就入冷库,热数据就入热库。这种方案会影响性能且冷热数据的判断逻辑不太好确定,还需要修改业务层代码,因此一般不会使用。
-2. 任务调度:可以利用 xxl-job 或者其他分布式任务调度平台定时去扫描数据库,找出满足冷数据条件的数据,然后批量地将其复制到冷库中,并从热库中删除。这种方法修改的代码非常少,非常适合按照时间区分冷热数据的场景。
-3. 监听数据库的变更日志 binlog :将满足冷数据条件的数据从 binlog 中提取出来,然后复制到冷库中,并从热库中删除。这种方法可以不用修改代码,但不适合按照时间维度区分冷热数据的场景。
+1. **Business Layer Code Implementation**: When there is a write operation on the data, trigger the logic for hot and cold separation to determine whether the data is cold or hot. Cold data goes to cold storage, while hot data goes to hot storage. This solution can impact performance, and the logic for determining hot and cold data can be difficult to establish, plus it requires modifying business layer code, so it is generally not used.
+1. **Task Scheduling**: You can use xxl-job or other distributed task scheduling platforms to periodically scan the database, identify data that meets the cold data criteria, and then batch copy it to cold storage while deleting it from hot storage. This method requires very little code modification and is very suitable for scenarios where cold and hot data are distinguished by time.
+1. **Listening to Database Change Logs (binlog)**: Extract data that meets the cold data criteria from the binlog, then copy it to cold storage and delete it from hot storage. This method does not require code modification but is not suitable for scenarios where hot and cold data are distinguished by time.
-如果你的公司有 DBA 的话,也可以让 DBA 进行冷数据的人工迁移,一次迁移完成冷数据到冷库。然后,再搭配上面介绍的方案实现后续冷数据的迁移工作。
+If your company has a DBA, you can also have the DBA perform manual migration of cold data to cold storage in one go. Then, you can use the solutions mentioned above to implement subsequent cold data migration work.
-## 冷数据如何存储?
+## How to Store Cold Data?
-冷数据的存储要求主要是容量大,成本低,可靠性高,访问速度可以适当牺牲。
-
-冷数据存储方案:
-
-- 中小厂:直接使用 MySQL/PostgreSQL 即可(不改变数据库选型和项目当前使用的数据库保持一致),比如新增一张表来存储某个业务的冷数据或者使用单独的冷库来存放冷数据(涉及跨库查询,增加了系统复杂性和维护难度)
-- 大厂:Hbase(常用)、RocksDB、Doris、Cassandra
-
-如果公司成本预算足的话,也可以直接上 TiDB 这种分布式关系型数据库,直接一步到位。TiDB 6.0 正式支持数据冷热存储分离,可以降低 SSD 使用成本。使用 TiDB 6.0 的数据放置功能,可以在同一个集群实现海量数据的冷热存储,将新的热数据存入 SSD,历史冷数据存入 HDD。
-
-## 案例分享
-
-- [如何快速优化几千万数据量的订单表 - 程序员济癫 - 2023](https://www.cnblogs.com/fulongyuanjushi/p/17910420.html)
-- [海量数据冷热分离方案与实践 - 字节跳动技术团队 - 2022](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZKRkZP6rLHuTE1wvnqmAPQ)
+The storage requirements for cold data mainly include large capacity, low cost, high
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md b/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
index 0d39e627cef..4aaf6a61f15 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/deep-pagination-optimization.md
@@ -1,140 +1,140 @@
---
-title: 深度分页介绍及优化建议
-category: 高性能
+title: Introduction to Deep Pagination and Optimization Suggestions
+category: High Performance
head:
- - - meta
- - name: keywords
- content: 深度分页
- - - meta
- - name: description
- content: 查询偏移量过大的场景我们称为深度分页,这会导致查询性能较低。深度分页可以采用范围查询、子查询、INNER JOIN 延迟关联、覆盖索引等方法进行优化。
+ - - meta
+ - name: keywords
+ content: Deep Pagination
+ - - meta
+ - name: description
+ content: The scenario where the query offset is excessively large is referred to as deep pagination, which leads to lower query performance. Deep pagination can be optimized using techniques such as range queries, subqueries, INNER JOIN lazy association, and covering indexes.
---
-## 深度分页介绍
+## Introduction to Deep Pagination
-查询偏移量过大的场景我们称为深度分页,这会导致查询性能较低,例如:
+The scenario where the query offset is excessively large is referred to as deep pagination, which leads to lower query performance. For example:
```sql
-# MySQL 在无法利用索引的情况下跳过1000000条记录后,再获取10条记录
+# MySQL skips 1,000,000 records without utilizing the index, then retrieves 10 records.
SELECT * FROM t_order ORDER BY id LIMIT 1000000, 10
```
-## 深度分页问题的原因
+## Reasons for Deep Pagination Issues
-当查询偏移量过大时,MySQL 的查询优化器可能会选择全表扫描而不是利用索引来优化查询。这是因为扫描索引和跳过大量记录可能比直接全表扫描更耗费资源。
+When the query offset is too large, the MySQL query optimizer may choose a full table scan instead of using the index to optimize the query. This is because scanning the index and skipping a large number of records may be more resource-intensive than performing a direct full table scan.
-
+
-不同机器上这个查询偏移量过大的临界点可能不同,取决于多个因素,包括硬件配置(如 CPU 性能、磁盘速度)、表的大小、索引的类型和统计信息等。
+The critical point for this excessively large query offset may vary between different machines, depending on multiple factors, including hardware configuration (such as CPU performance, disk speed), table size, index types, and statistical information.
-
+
-MySQL 的查询优化器采用基于成本的策略来选择最优的查询执行计划。它会根据 CPU 和 I/O 的成本来决定是否使用索引扫描或全表扫描。如果优化器认为全表扫描的成本更低,它就会放弃使用索引。不过,即使偏移量很大,如果查询中使用了覆盖索引(covering index),MySQL 仍然可能会使用索引,避免回表操作。
+MySQL’s query optimizer employs a cost-based strategy to select the optimal query execution plan. It determines whether to use index scanning or full table scanning based on the costs of CPU and I/O. If the optimizer decides that the cost of a full table scan is lower, it will forgo using the index. However, even with a large offset, if a covering index is used in the query, MySQL might still utilize the index, avoiding the need to access the data rows again.
-## 深度分页优化建议
+## Optimization Suggestions for Deep Pagination
-这里以 MySQL 数据库为例介绍一下如何优化深度分页。
+Taking the MySQL database as an example, here are some ways to optimize deep pagination.
-### 范围查询
+### Range Query
-当可以保证 ID 的连续性时,根据 ID 范围进行分页是比较好的解决方案:
+When continuity of IDs can be ensured, using ID ranges for pagination is a good solution:
```sql
-# 查询指定 ID 范围的数据
+# Query data within a specified ID range
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id > 100000 AND id <= 100010 ORDER BY id
-# 也可以通过记录上次查询结果的最后一条记录的ID进行下一页的查询:
+# You can also query the next page using the ID of the last record from the previous query:
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id > 100000 LIMIT 10
```
-这种基于 ID 范围的深度分页优化方式存在很大限制:
+This ID range-based deep pagination optimization method has significant limitations:
-1. **ID 连续性要求高**: 实际项目中,数据库自增 ID 往往因为各种原因(例如删除数据、事务回滚等)导致 ID 不连续,难以保证连续性。
-2. **排序问题**: 如果查询需要按照其他字段(例如创建时间、更新时间等)排序,而不是按照 ID 排序,那么这种方法就不再适用。
-3. **并发场景**: 在高并发场景下,单纯依赖记录上次查询的最后一条记录的 ID 进行分页,容易出现数据重复或遗漏的问题。
+1. **High Requirement for ID Continuity**: In actual projects, database auto-increment IDs often become non-continuous for various reasons (such as data deletion, transaction rollbacks), making it difficult to ensure continuity.
+1. **Sorting Issues**: If the query needs to be sorted by other fields (such as creation time, update time, etc.) instead of sorting by ID, then this method is no longer applicable.
+1. **Concurrent Scenarios**: In high concurrency scenarios, relying solely on the ID of the last record from the previous query for pagination can easily lead to data duplication or omission issues.
-### 子查询
+### Subquery
-我们先查询出 limit 第一个参数对应的主键值,再根据这个主键值再去过滤并 limit,这样效率会更快一些。
+We can first retrieve the primary key values corresponding to the first parameter of limit, and then filter and limit based on this primary key value, which will be more efficient.
-阿里巴巴《Java 开发手册》中也有对应的描述:
+The Alibaba "Java Development Handbook" also describes this:
-> 利用延迟关联或者子查询优化超多分页场景。
+> Use lazy association or subqueries to optimize excessive pagination scenarios.
>
> 
```sql
-# 通过子查询来获取 id 的起始值,把 limit 1000000 的条件转移到子查询
+# Use a subquery to get the starting value of id, transferring the LIMIT 1000000 condition to the subquery
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= (SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1) LIMIT 10;
```
-**工作原理**:
+**How It Works**:
-1. 子查询 `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1)` 会利用主键索引快速定位到第 1000001 条记录,并返回其 ID 值。
-2. 主查询 `SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= ... LIMIT 10` 将子查询返回的起始 ID 作为过滤条件,使用 `id >=` 获取从该 ID 开始的后续 10 条记录。
+1. The subquery `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 limit 1)` quickly locates the 1,000,001st record using the primary key index and returns its ID value.
+1. The main query `SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE id >= ... LIMIT 10` uses the starting ID returned from the subquery as a filter condition, using `id >=` to retrieve the subsequent 10 records starting from that ID.
-不过,子查询的结果会产生一张新表,会影响性能,应该尽量避免大量使用子查询。并且,这种方法只适用于 ID 是正序的。在复杂分页场景,往往需要通过过滤条件,筛选到符合条件的 ID,此时的 ID 是离散且不连续的。
+However, the result of the subquery generates a temporary table, which can impact performance. Therefore, large-scale use of subqueries should be avoided. Moreover, this method is only suitable when IDs are in ascending order. In complex pagination scenarios, filtering conditions may be needed to identify matching IDs, resulting in discrete and non-continuous IDs.
-当然,我们也可以利用子查询先去获取目标分页的 ID 集合,然后再根据 ID 集合获取内容,但这种写法非常繁琐,不如使用 INNER JOIN 延迟关联。
+Of course, we can also use subqueries to retrieve the target page's set of IDs and then fetch content based on this ID set, but this approach is very cumbersome compared to using INNER JOIN for lazy association.
-### 延迟关联
+### Lazy Association
-延迟关联与子查询的优化思路类似,都是通过将 `LIMIT` 操作转移到主键索引树上,减少回表次数。相比直接使用子查询,延迟关联通过 `INNER JOIN` 将子查询结果集成到主查询中,避免了子查询可能产生的临时表。在执行 `INNER JOIN` 时,MySQL 优化器能够利用索引进行高效的连接操作(如索引扫描或其他优化策略),因此在深度分页场景下,性能通常优于直接使用子查询。
+Lazy association is similar to the optimization idea of subqueries, where `LIMIT` operations are moved to the primary key index tree to reduce the number of back-table operations. Compared to directly using subqueries, lazy association integrates the subquery results into the main query through `INNER JOIN`, avoiding the potential creation of temporary tables by subqueries. When executing `INNER JOIN`, the MySQL optimizer can utilize indexes for efficient join operations (like index scanning or other optimization strategies), thus usually achieving better performance in deep pagination scenarios than directly using subqueries.
```sql
--- 使用 INNER JOIN 进行延迟关联
+-- Use INNER JOIN for lazy association
SELECT t1.*
FROM t_order t1
INNER JOIN (SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10) t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;
```
-**工作原理**:
+**How It Works**:
-1. 子查询 `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10)` 利用主键索引快速定位目标分页的 10 条记录的 ID。
-2. 通过 `INNER JOIN` 将子查询结果与主表 `t_order` 关联,获取完整的记录数据。
+1. The subquery `(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10)` quickly locates the IDs of the 10 target records using the primary key index.
+1. Using `INNER JOIN`, the subquery results are associated with the main table `t_order`, retrieving complete record data.
-除了使用 INNER JOIN 之外,还可以使用逗号连接子查询。
+In addition to using INNER JOIN, you can also connect subqueries with commas.
```sql
--- 使用逗号进行延迟关联
+-- Use a comma for lazy association
SELECT t1.* FROM t_order t1,
(SELECT id FROM t_order where id > 1000000 LIMIT 10) t2
WHERE t1.id = t2.id;
```
-**注意**: 虽然逗号连接子查询也能实现类似的效果,但为了代码可读性和可维护性,建议使用更规范的 `INNER JOIN` 语法。
+[!NOTE]
+Although connecting subqueries with commas can achieve similar effects, it is recommended to use the more standardized `INNER JOIN` syntax for code readability and maintainability.
+### Covering Index
-### 覆盖索引
+A query method where all required fields are included in the index is known as a covering index.
-索引中已经包含了所有需要获取的字段的查询方式称为覆盖索引。
+**Benefits of Covering Index**:
-**覆盖索引的好处:**
-
-- **避免 InnoDB 表进行索引的二次查询,也就是回表操作:** InnoDB 是以聚集索引的顺序来存储的,对于 InnoDB 来说,二级索引在叶子节点中所保存的是行的主键信息,如果是用二级索引查询数据的话,在查找到相应的键值后,还要通过主键进行二次查询才能获取我们真实所需要的数据。而在覆盖索引中,二级索引的键值中可以获取所有的数据,避免了对主键的二次查询(回表),减少了 IO 操作,提升了查询效率。
-- **可以把随机 IO 变成顺序 IO 加快查询效率:** 由于覆盖索引是按键值的顺序存储的,对于 IO 密集型的范围查找来说,对比随机从磁盘读取每一行的数据 IO 要少的多,因此利用覆盖索引在访问时也可以把磁盘的随机读取的 IO 转变成索引查找的顺序 IO。
+- **Avoids InnoDB tables from performing second index queries, which is a back-table operation**: InnoDB stores data in the order of the clustered index. For InnoDB, the secondary index stores the primary key information in its leaf nodes. If data is queried using the secondary index, after finding the corresponding key value, a secondary query via the primary key is still required to retrieve the actual data we need. However, in covering indexes, all data can be accessed from the secondary index's key values, avoiding the need for a secondary query (back-table access), thereby reducing I/O operations and improving query efficiency.
+- **Transforms random I/O into sequential I/O, speeding up query efficiency**: Since covering indexes are stored in key value order, for I/O intensive range queries, it significantly reduces the I/O involved in randomly reading each row of data from disk, thus making disk random reads into index lookups in sequential order.
```sql
-# 如果只需要查询 id, code, type 这三列,可建立 code 和 type 的覆盖索引
+# If only the id, code, and type columns are needed, a covering index can be established for code and type
SELECT id, code, type FROM t_order
ORDER BY code
LIMIT 1000000, 10;
```
-**⚠️注意**:
+**⚠️Note**:
-- 当查询的结果集占表的总行数的很大一部分时,MySQL 查询优化器可能选择放弃使用索引,自动转换为全表扫描。
-- 虽然可以使用 `FORCE INDEX` 强制查询优化器走索引,但这种方式可能会导致查询优化器无法选择更优的执行计划,效果并不总是理想。
+- When the result set of a query accounts for a large proportion of the total rows in the table, MySQL’s query optimizer may opt to forgo using the index, automatically switching to a full table scan.
+- While you can use `FORCE INDEX` to compel the query optimizer to use the index, this might lead to the optimizer being unable to select a better execution plan, and the outcome may not always be ideal.
-## 总结
+## Conclusion
-本文总结了几种常见的深度分页优化方案:
+This article summarizes several common optimization schemes for deep pagination:
-1. **范围查询**: 基于 ID 连续性进行分页,通过记录上一页最后一条记录的 ID 来获取下一页数据。适合 ID 连续且按 ID 查询的场景,但在 ID 不连续或需要按其他字段排序时存在局限。
-2. **子查询**: 先通过子查询获取分页的起始主键值,再根据主键进行筛选分页。利用主键索引提高效率,但子查询会生成临时表,复杂场景下性能不佳。
-3. **延迟关联 (INNER JOIN)**: 使用 `INNER JOIN` 将分页操作转移到主键索引上,减少回表次数。相比子查询,延迟关联的性能更优,适合大数据量的分页查询。
-4. **覆盖索引**: 通过索引直接获取所需字段,避免回表操作,减少 IO 开销,适合查询特定字段的场景。但当结果集较大时,MySQL 可能会选择全表扫描。
+1. **Range Query**: Pagination based on ID continuity, using the ID of the last record from the previous page to fetch data for the next page. Suitable for scenarios where IDs are continuous and queries are sorted by ID, but limited in cases where IDs are non-continuous or sorted by other fields.
+1. **Subquery**: First, the starting primary key value for pagination is retrieved through a subquery, then filtered based on the primary key for pagination. It utilizes primary key indexing to improve efficiency, but subqueries create temporary tables, which may lead to poor performance in complex scenarios.
+1. **Lazy Association (INNER JOIN)**: Utilizing `INNER JOIN` to shift pagination operations to the primary key index, reducing the incidence of back-table operations. Lazy association typically performs better than subqueries, making it suitable for pagination queries involving large data volumes.
+1. **Covering Index**: Directly retrieving required fields through an index, avoiding back-table operations and minimizing I/O overhead, suitable for queries that target specific fields. However, when the result set is large, MySQL may choose a full table scan.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 聊聊如何解决 MySQL 深分页问题 - 捡田螺的小男孩:
-- 数据库深分页介绍及优化方案 - 京东零售技术:
-- MySQL 深分页优化 - 得物技术:
+- Discussing how to solve MySQL deep pagination issues - A Boy Who Picks Snails:
+- Introduction to deep pagination in databases and optimization schemes - JD Retail Technology:
+- MySQL deep pagination optimization - Dewu Technology:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md b/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
index 619df980574..50b4db93623 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/load-balancing.md
@@ -1,208 +1,208 @@
---
-title: 负载均衡原理及算法详解
-category: 高性能
+title: Detailed Explanation of Load Balancing Principles and Algorithms
+category: High Performance
head:
- - meta
- name: keywords
- content: 客户端负载均衡,服务负载均衡,Nginx,负载均衡算法,七层负载均衡,DNS解析
+ content: Client-side Load Balancing, Server-side Load Balancing, Nginx, Load Balancing Algorithms, Layer 7 Load Balancing, DNS Resolution
- - meta
- name: description
- content: 负载均衡指的是将用户请求分摊到不同的服务器上处理,以提高系统整体的并发处理能力。负载均衡可以简单分为服务端负载均衡和客户端负载均衡 这两种。服务端负载均衡涉及到的知识点更多,工作中遇到的也比较多,因为,我会花更多时间来介绍。
+ content: Load balancing refers to distributing user requests across different servers to improve the overall concurrency and reliability of the system. Load balancing can be simply divided into two types: server-side load balancing and client-side load balancing. Server-side load balancing involves more knowledge points and is encountered more frequently in work, thus, I will spend more time introducing it.
---
-## 什么是负载均衡?
+## What is Load Balancing?
-**负载均衡** 指的是将用户请求分摊到不同的服务器上处理,以提高系统整体的并发处理能力以及可靠性。负载均衡服务可以有由专门的软件或者硬件来完成,一般情况下,硬件的性能更好,软件的价格更便宜(后文会详细介绍到)。
+**Load balancing** refers to distributing user requests across different servers to enhance the overall concurrency capacity and reliability of a system. Load balancing services can be implemented by specialized software or hardware. Generally, hardware has better performance, while software is cheaper (which will be discussed in detail later).
-下图是[《Java 面试指北》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247519384&idx=1&sn=bc7e71af75350b755f04ca4178395b1a&chksm=cea1c353f9d64a458f797696d4144b4d6e58639371a4612b8e4d106d83a66d2289e7b2cd7431&token=660789642&lang=zh_CN&scene=21#wechat_redirect) 「高并发篇」中的一篇文章的配图,从图中可以看出,系统的商品服务部署了多份在不同的服务器上,为了实现访问商品服务请求的分流,我们用到了负载均衡。
+The following image is from an article in the "High Concurrency" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2OTA0Njk0OA==&mid=2247519384&idx=1&sn=bc7e71af75350b755f04ca4178395b1a&chksm=cea1c353f9d64a458f797696d4144b4d6e58639371a4612b8e4d106d83a66d2289e7b2cd7431&token=660789642&lang=zh_CN&scene=21#wechat_redirect). From the image, we can see that the system's product service is deployed across multiple servers, and to achieve request sharding for accessing the product service, we utilize load balancing.
-
+
-负载均衡是一种比较常用且实施起来较为简单的提高系统并发能力和可靠性的手段,不论是单体架构的系统还是微服务架构的系统几乎都会用到。
+Load balancing is a commonly used and relatively simple means of enhancing system concurrency and reliability. It is utilized in nearly all systems, whether they are monolithic architectures or microservice architectures.
-## 负载均衡分为哪几种?
+## What Types of Load Balancing Are There?
-负载均衡可以简单分为 **服务端负载均衡** 和 **客户端负载均衡** 这两种。
+Load balancing can be simply divided into **server-side load balancing** and **client-side load balancing**.
-服务端负载均衡涉及到的知识点更多,工作中遇到的也比较多,因此,我会花更多时间来介绍。
+Server-side load balancing involves more knowledge points and is encountered more frequently in work, hence I will spend more time introducing it.
-### 服务端负载均衡
+### Server-side Load Balancing
-**服务端负载均衡** 主要应用在 **系统外部请求** 和 **网关层** 之间,可以使用 **软件** 或者 **硬件** 实现。
+**Server-side load balancing** is mainly applied between **external system requests** and the **gateway layer** and can be implemented using **software** or **hardware**.
-下图是我画的一个简单的基于 Nginx 的服务端负载均衡示意图:
+The following diagram illustrates a simple server-side load balancing setup based on Nginx:
-
+
-**硬件负载均衡** 通过专门的硬件设备(比如 **F5、A10、Array** )实现负载均衡功能。
+**Hardware load balancing** is achieved via specialized hardware devices (such as **F5, A10, Array**).
-硬件负载均衡的优势是性能很强且稳定,缺点就是实在是太贵了。像基础款的 F5 最低也要 20 多万,绝大部分公司是根本负担不起的,业务量不大的话,真没必要非要去弄个硬件来做负载均衡,用软件负载均衡就足够了!
+The advantage of hardware load balancing is its strong and stable performance; however, the downside is that it is quite expensive. For instance, a basic model of F5 starts from over 200,000 yuan, which most companies cannot afford. If the business volume is not high, it is unnecessary to invest in hardware for load balancing; software load balancing suffices!
-在我们日常开发中,一般很难接触到硬件负载均衡,接触的比较多的还是 **软件负载均衡** 。软件负载均衡通过软件(比如 **LVS、Nginx、HAproxy** )实现负载均衡功能,性能虽然差一些,但价格便宜啊!像基础款的 Linux 服务器也就几千,性能好一点的 2~3 万的就很不错了。
+In our daily development, we generally have limited exposure to hardware load balancing, as we encounter **software load balancing** more frequently. Software load balancing uses software (such as **LVS, Nginx, HAProxy**) to implement load balancing functionality; while its performance is slightly lower, it is more cost-effective! For instance, a basic Linux server can be just a few thousand yuan, and a slightly better one might cost around 20,000 to 30,000 yuan.
-根据 OSI 模型,服务端负载均衡还可以分为:
+According to the OSI model, server-side load balancing can also be categorized into:
-- 二层负载均衡
-- 三层负载均衡
-- 四层负载均衡
-- 七层负载均衡
+- Layer 2 Load Balancing
+- Layer 3 Load Balancing
+- Layer 4 Load Balancing
+- Layer 7 Load Balancing
-最常见的是四层和七层负载均衡,因此,本文也是重点介绍这两种负载均衡。
+The most common types are Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing, thus this article will primarily focus on these two types.
-> Nginx 官网对四层负载和七层负载均衡均衡做了详细介绍,感兴趣的可以看看。
+> The Nginx official website provides a detailed introduction to Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing. If you're interested, you can check it out.
>
> - [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/)
> - [What Is Layer 7 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-7-load-balancing/)
-
+
-- **四层负载均衡** 工作在 OSI 模型第四层,也就是传输层,这一层的主要协议是 TCP/UDP,负载均衡器在这一层能够看到数据包里的源端口地址以及目的端口地址,会基于这些信息通过一定的负载均衡算法将数据包转发到后端真实服务器。也就是说,四层负载均衡的核心就是 IP+端口层面的负载均衡,不涉及具体的报文内容。
-- **七层负载均衡** 工作在 OSI 模型第七层,也就是应用层,这一层的主要协议是 HTTP 。这一层的负载均衡比四层负载均衡路由网络请求的方式更加复杂,它会读取报文的数据部分(比如说我们的 HTTP 部分的报文),然后根据读取到的数据内容(如 URL、Cookie)做出负载均衡决策。也就是说,七层负载均衡器的核心是报文内容(如 URL、Cookie)层面的负载均衡,执行第七层负载均衡的设备通常被称为 **反向代理服务器** 。
+- **Layer 4 load balancing** operates at the fourth layer of the OSI model, which is the transport layer. The main protocols at this layer are TCP/UDP. The load balancer at this layer can see the source and destination port addresses in the data packets and will forward the packets to the backend real servers based on this information using specific load balancing algorithms. In other words, the core of Layer 4 load balancing is IP + port level load balancing without involving the actual content of the messages.
+- **Layer 7 load balancing** functions at the seventh layer of the OSI model, which is the application layer. The main protocol at this layer is HTTP. The load balancing at this layer is more complex than at Layer 4, as it reads the message data section (for instance, the HTTP portion of messages), and makes load balancing decisions based on the content read (such as URL, Cookie). In other words, the core of Layer 7 load balancers is load balancing at the message content level (such as URL, Cookie), and devices performing Layer 7 load balancing are usually referred to as **reverse proxy servers**.
-七层负载均衡比四层负载均衡会消耗更多的性能,不过,也相对更加灵活,能够更加智能地路由网络请求,比如说你可以根据请求的内容进行优化如缓存、压缩、加密。
+Layer 7 load balancing consumes more performance than Layer 4 load balancing, but it is also relatively more flexible and capable of routing network requests more intelligently. For example, you can optimize based on request content, such as caching, compression, and encryption.
-简单来说,**四层负载均衡性能很强,七层负载均衡功能更强!** 不过,对于绝大部分业务场景来说,四层负载均衡和七层负载均衡的性能差异基本可以忽略不计的。
+In short, **Layer 4 load balancing has strong performance, while Layer 7 load balancing has more powerful functionalities!** However, for most business scenarios, the performance difference between Layer 4 and Layer 7 load balancing can generally be negligible.
-下面这段话摘自 Nginx 官网的 [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/) 这篇文章。
+The following excerpt is from the Nginx official article [What Is Layer 4 Load Balancing?](https://www.nginx.com/resources/glossary/layer-4-load-balancing/).
> Layer 4 load balancing was a popular architectural approach to traffic handling when commodity hardware was not as powerful as it is now, and the interaction between clients and application servers was much less complex. It requires less computation than more sophisticated load balancing methods (such as Layer 7), but CPU and memory are now sufficiently fast and cheap that the performance advantage for Layer 4 load balancing has become negligible or irrelevant in most situations.
>
> 第 4 层负载平衡是一种流行的流量处理体系结构方法,当时商用硬件没有现在这么强大,客户端和应用程序服务器之间的交互也不那么复杂。它比更复杂的负载平衡方法(如第 7 层)需要更少的计算量,但是 CPU 和内存现在足够快和便宜,在大多数情况下,第 4 层负载平衡的性能优势已经变得微不足道或无关紧要。
-在工作中,我们通常会使用 **Nginx** 来做七层负载均衡,LVS(Linux Virtual Server 虚拟服务器, Linux 内核的 4 层负载均衡)来做四层负载均衡。
+In practice, we usually use **Nginx** for Layer 7 load balancing and LVS (Linux Virtual Server, a Layer 4 load balancer in the Linux kernel) for Layer 4 load balancing.
-关于 Nginx 的常见知识点总结,[《Java 面试指北》](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html) 中「技术面试题篇」中已经有对应的内容了,感兴趣的小伙伴可以去看看。
+For a summary of common knowledge about Nginx, corresponding content is already available in the "Technical Interview Questions" section of [“Java Interview Guide”](https://javaguide.cn/zhuanlan/java-mian-shi-zhi-bei.html). Interested readers can take a look.

-不过,LVS 这个绝大部分公司真用不上,像阿里、百度、腾讯、eBay 等大厂才会使用到,用的最多的还是 Nginx。
+However, most companies do not need to use LVS; it is typically used by large companies like Alibaba, Baidu, Tencent, eBay, etc. The most commonly used solution remains Nginx.
-### 客户端负载均衡
+### Client-side Load Balancing
-**客户端负载均衡** 主要应用于系统内部的不同的服务之间,可以使用现成的负载均衡组件来实现。
+**Client-side load balancing** is mainly applied between different services within the system and can be implemented using existing load balancing components.
-在客户端负载均衡中,客户端会自己维护一份服务器的地址列表,发送请求之前,客户端会根据对应的负载均衡算法来选择具体某一台服务器处理请求。
+In client-side load balancing, the client maintains its own list of server addresses. Before sending a request, the client selects a specific server to handle the request based on the corresponding load balancing algorithm.
-客户端负载均衡器和服务运行在同一个进程或者说 Java 程序里,不存在额外的网络开销。不过,客户端负载均衡的实现会受到编程语言的限制,比如说 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 就只能用于 Java 语言。
+The client load balancer and the services run within the same process or Java program, eliminating additional network overhead. However, the implementation of client-side load balancing may be constrained by the programming language; for instance, Spring Cloud Load Balancer can only be used with Java.
-Java 领域主流的微服务框架 Dubbo、Spring Cloud 等都内置了开箱即用的客户端负载均衡实现。Dubbo 属于是默认自带了负载均衡功能,Spring Cloud 是通过组件的形式实现的负载均衡,属于可选项,比较常用的是 Spring Cloud Load Balancer(官方,推荐) 和 Ribbon(Netflix,已被弃用)。
+Mainstream microservice frameworks in the Java field, such as Dubbo and Spring Cloud, come with out-of-the-box client-side load balancing implementations. Dubbo has load balancing functionality built in by default, while Spring Cloud implements load balancing through components; it is optional, with Spring Cloud Load Balancer (official, recommended) and Ribbon (Netflix, deprecated) being the more commonly used options.
-下图是我画的一个简单的基于 Spring Cloud Load Balancer(Ribbon 也类似) 的客户端负载均衡示意图:
+The following diagram illustrates a simple client-side load balancing setup based on Spring Cloud Load Balancer (Ribbon is similar):

-## 负载均衡常见的算法有哪些?
+## What Are the Common Algorithms for Load Balancing?
-### 随机法
+### Random Method
-**随机法** 是最简单粗暴的负载均衡算法。
+**Random method** is the simplest and most brute-force load balancing algorithm.
-如果没有配置权重的话,所有的服务器被访问到的概率都是相同的。如果配置权重的话,权重越高的服务器被访问的概率就越大。
+If weights are not configured, all servers have the same probability of being accessed. If weights are configured, servers with higher weights are more likely to be accessed.
-未加权重的随机算法适合于服务器性能相近的集群,其中每个服务器承载相同的负载。加权随机算法适合于服务器性能不等的集群,权重的存在可以使请求分配更加合理化。
+The unweighted random algorithm is suitable for clusters with similar server performance, where each server bears the same load. The weighted random algorithm is suitable for clusters with unequal server performance, where the presence of weights allows for a more rational request distribution.
-不过,随机算法有一个比较明显的缺陷:部分机器在一段时间之内无法被随机到,毕竟是概率算法,就算是大家权重一样, 也可能会出现这种情况。
+However, the random algorithm has a notable flaw: some machines may not be randomly selected for a period of time due to the nature of probability algorithms. Even if everyone has the same weight, such situations can still occur.
-于是,**轮询法** 来了!
+Thus, the **Round Robin method** comes into play!
-### 轮询法
+### Round Robin Method
-轮询法是挨个轮询服务器处理,也可以设置权重。
+The Round Robin method involves polling each server for processing, and weights can also be set.
-如果没有配置权重的话,每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的服务器处理。如果配置权重的话,权重越高的服务器被访问的次数就越多。
+If weights are not configured, each request is distributed sequentially to different servers based on time. If weights are configured, the server with the higher weight will be accessed more frequently.
-未加权重的轮询算法适合于服务器性能相近的集群,其中每个服务器承载相同的负载。加权轮询算法适合于服务器性能不等的集群,权重的存在可以使请求分配更加合理化。
+The unweighted round robin algorithm is suitable for clusters with similar server performance, where each server bears the same load. The weighted round robin algorithm is suitable for clusters with unequal server performance, where the presence of weights allows for a more rational request distribution.
-在加权轮询的基础上,还有进一步改进得到的负载均衡算法,比如平滑的加权轮训算法。
+On the basis of weighted round robin, further improved load balancing algorithms may arise, such as the smooth weighted round robin algorithm.
-平滑的加权轮训算法最早是在 Nginx 中被实现,可以参考这个 commit:。如果你认真学习过 Dubbo 负载均衡策略的话,就会发现 Dubbo 的加权轮询就借鉴了该算法实现并进一步做了优化。
+The smooth weighted round robin algorithm was first implemented in Nginx; you can refer to this commit: . If you have studied Dubbo's load balancing strategies seriously, you will find that Dubbo's weighted round robin borrowed from this algorithm and further optimized it.
-
+
-### 两次随机法
+### Two-time Random Method
-两次随机法在随机法的基础上多增加了一次随机,多选出一个服务器。随后再根据两台服务器的负载等情况,从其中选择出一个最合适的服务器。
+The two-time random method adds an additional round of randomness on the basis of the random method by selecting an extra server. Then, based on the load conditions of these two servers, one is chosen as the most suitable for processing.
-两次随机法的好处是可以动态地调节后端节点的负载,使其更加均衡。如果只使用一次随机法,可能会导致某些服务器过载,而某些服务器空闲。
+The benefit of the two-time random method is that it can dynamically adjust the load of backend nodes to achieve better balance. Relying solely on the single random method may lead to certain servers being overloaded while others remain idle.
-### 哈希法
+### Hash Method
-将请求的参数信息通过哈希函数转换成一个哈希值,然后根据哈希值来决定请求被哪一台服务器处理。
+The request parameters are transformed into a hash value using a hash function, and the request is then directed to the server based on this hash value.
-在服务器数量不变的情况下,相同参数的请求总是发到同一台服务器处理,比如同个 IP 的请求、同一个用户的请求。
+When the number of servers remains the same, requests with the same parameters will always be sent to the same server, such as requests from the same IP address or requests from the same user.
-### 一致性 Hash 法
+### Consistent Hash Method
-和哈希法类似,一致性 Hash 法也可以让相同参数的请求总是发到同一台服务器处理。不过,它解决了哈希法存在的一些问题。
+Similar to the hash method, the consistent hash method also allows requests with the same parameters to be consistently sent to the same server. However, it addresses some issues present in the hash method.
-常规哈希法在服务器数量变化时,哈希值会重新落在不同的服务器上,这明显违背了使用哈希法的本意。而一致性哈希法的核心思想是将数据和节点都映射到一个哈希环上,然后根据哈希值的顺序来确定数据属于哪个节点。当服务器增加或删除时,只影响该服务器的哈希,而不会导致整个服务集群的哈希键值重新分布。
+Conventional hash methods reassign hash values to different servers when the number of servers changes, which clearly defeats the purpose of using the hash method. The core idea of consistent hashing is to map both data and nodes onto a hash ring and determine the respective nodes based on the order of hash values. When servers are added or removed, only the hash of the related servers is affected, without causing a complete redistribution of the hash keys across the service cluster.
-### 最小连接法
+### Least Connections Method
-当有新的请求出现时,遍历服务器节点列表并选取其中连接数最小的一台服务器来响应当前请求。相同连接的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+When a new request arrives, the load balancer traverses the server node list and selects the one with the least number of connections to handle the current request. In the case of equal connections, weighted random methods may be employed.
-最少连接数基于一个服务器连接数越多,负载就越高这一理想假设。然而, 实际情况是连接数并不能代表服务器的实际负载,有些连接耗费系统资源更多,有些连接不怎么耗费系统资源。
+The least connected method is based on the ideal assumption that a higher number of connections indicates a higher load on the server. In practice, however, the number of connections does not accurately represent the server's actual load, as some connections may consume more system resources than others.
-### 最少活跃法
+### Least Active Method
-最少活跃法和最小连接法类似,但要更科学一些。最少活跃法以活动连接数为标准,活动连接数可以理解为当前正在处理的请求数。活跃数越低,说明处理能力越强,这样就可以使处理能力强的服务器处理更多请求。相同活跃数的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+The least active method is similar to the least connections method but is more scientific. The least active method uses the number of active connections as the standard; active connections could be understood as the current number of requests being processed. The lower the active connection count, the stronger the processing capacity, allowing more requests to be handled by stronger servers. In the case of the same number of active connections, weighted random methods can be employed.
-### 最快响应时间法
+### Fastest Response Time Method
-不同于最小连接法和最少活跃法,最快响应时间法以响应时间为标准来选择具体是哪一台服务器处理。客户端会维持每个服务器的响应时间,每次请求挑选响应时间最短的。相同响应时间的情况下,可以进行加权随机。
+Differing from the least connections and least active methods, the fastest response time method selects the appropriate server based on the response time. The client maintains the response times for each server and chooses the one with the shortest response time for each request. In the case of equal response times, weighted random methods may be employed.
-这种算法可以使得请求被更快处理,但可能会造成流量过于集中于高性能服务器的问题。
+This algorithm ensures that requests are processed more quickly, but it may lead to an excessive concentration of traffic on high-performance servers.
-## 七层负载均衡可以怎么做?
+## How Can Layer 7 Load Balancing Be Achieved?
-简单介绍两种项目中常用的七层负载均衡解决方案:DNS 解析和反向代理。
+Let’s briefly introduce two commonly used Layer 7 load balancing solutions: DNS resolution and reverse proxy.
-除了我介绍的这两种解决方案之外,HTTP 重定向等手段也可以用来实现负载均衡,不过,相对来说,还是 DNS 解析和反向代理用的更多一些,也更推荐一些。
+Apart from the two solutions introduced, other methods such as HTTP redirection can also achieve load balancing; however, DNS resolution and reverse proxy are generally used more and are recommended.
-### DNS 解析
+### DNS Resolution
-DNS 解析是比较早期的七层负载均衡实现方式,非常简单。
+DNS resolution is an early implementation of Layer 7 load balancing; it is very simple.
-DNS 解析实现负载均衡的原理是这样的:在 DNS 服务器中为同一个主机记录配置多个 IP 地址,这些 IP 地址对应不同的服务器。当用户请求域名的时候,DNS 服务器采用轮询算法返回 IP 地址,这样就实现了轮询版负载均衡。
+The principle of DNS resolution for achieving load balancing is as follows: Multiple IP addresses corresponding to different servers are configured in the DNS server for the same host record. When a user requests a domain name, the DNS server uses a round-robin algorithm to return an IP address, thereby achieving round-robin load balancing.

-现在的 DNS 解析几乎都支持 IP 地址的权重配置,这样的话,在服务器性能不等的集群中请求分配会更加合理化。像我自己目前正在用的阿里云 DNS 就支持权重配置。
+Most modern DNS resolutions support the configuration of weight for IP addresses, making request distribution in clusters with unequal server performance more rational. For instance, Alibaba Cloud DNS, which I am currently using, supports weight configuration.

-### 反向代理
+### Reverse Proxy
-客户端将请求发送到反向代理服务器,由反向代理服务器去选择目标服务器,获取数据后再返回给客户端。对外暴露的是反向代理服务器地址,隐藏了真实服务器 IP 地址。反向代理“代理”的是目标服务器,这一个过程对于客户端而言是透明的。
+Clients send requests to the reverse proxy server, which then selects the target server. After obtaining the data, it is returned to the client. The external address exposed is the reverse proxy server's address, concealing the real server IP addresses. The reverse proxy "proxies" the target server, and this process is transparent to the client.
-Nginx 就是最常用的反向代理服务器,它可以将接收到的客户端请求以一定的规则(负载均衡策略)均匀地分配到这个服务器集群中所有的服务器上。
+Nginx is the most commonly used reverse proxy server, capable of evenly distributing incoming client requests across all servers in the server cluster based on certain rules (load balancing strategies).
-反向代理负载均衡同样属于七层负载均衡。
+Reverse proxy load balancing also falls under Layer 7 load balancing.

-## 客户端负载均衡通常是怎么做的?
+## How Is Client-side Load Balancing Usually Implemented?
-我们上面也说了,客户端负载均衡可以使用现成的负载均衡组件来实现。
+As mentioned earlier, client-side load balancing can be implemented using existing load balancing components.
-**Netflix Ribbon** 和 **Spring Cloud Load Balancer** 就是目前 Java 生态最流行的两个负载均衡组件。
+**Netflix Ribbon** and **Spring Cloud Load Balancer** are currently the two most popular load balancing components in the Java ecosystem.
-Ribbon 是老牌负载均衡组件,由 Netflix 开发,功能比较全面,支持的负载均衡策略也比较多。 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 是 Spring 官方为了取代 Ribbon 而推出的,功能相对更简单一些,支持的负载均衡也少一些。
+Ribbon is an established load balancing component developed by Netflix, offering comprehensive features and supporting various load balancing strategies. Spring Cloud Load Balancer is launched by Spring as a replacement for Ribbon, featuring a relatively simpler function set and fewer supported load balancing strategies.
-Ribbon 支持的 7 种负载均衡策略:
+The 7 load balancing strategies supported by Ribbon include:
-- `RandomRule`:随机策略。
-- `RoundRobinRule`(默认):轮询策略
-- `WeightedResponseTimeRule`:权重(根据响应时间决定权重)策略
-- `BestAvailableRule`:最小连接数策略
-- `RetryRule`:重试策略(按照轮询策略来获取服务,如果获取的服务实例为 null 或已经失效,则在指定的时间之内不断地进行重试来获取服务,如果超过指定时间依然没获取到服务实例则返回 null)
-- `AvailabilityFilteringRule`:可用敏感性策略(先过滤掉非健康的服务实例,然后再选择连接数较小的服务实例)
-- `ZoneAvoidanceRule`:区域敏感性策略(根据服务所在区域的性能和服务的可用性来选择服务实例)
+- `RandomRule`: Random strategy.
+- `RoundRobinRule` (default): Round-robin strategy
+- `WeightedResponseTimeRule`: Weighted strategy (determining weights based on response time)
+- `BestAvailableRule`: Least connections strategy
+- `RetryRule`: Retry strategy (fetching services based on round-robin strategy; if the obtained service instance is null or already invalid, it keeps retrying within the specified time; if it still cannot fetch a service instance beyond the specified time, it returns null)
+- `AvailabilityFilteringRule`: Availability sensitivity strategy (first filtering out unhealthy service instances, then choosing the one with a lesser number of connections)
+- `ZoneAvoidanceRule`: Zone sensitivity strategy (selecting service instances based on performance and availability of the service's operating zone)
-Spring Cloud Load Balancer 支持的 2 种负载均衡策略:
+The 2 load balancing strategies supported by Spring Cloud Load Balancer include:
-- `RandomLoadBalancer`:随机策略
-- `RoundRobinLoadBalancer`(默认):轮询策略
+- `RandomLoadBalancer`: Random strategy
+- `RoundRobinLoadBalancer` (default): Round-robin strategy
```java
public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
@@ -218,16 +218,16 @@ public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
}
```
-不过,Spring Cloud Load Balancer 支持的负载均衡策略其实不止这两种,`ServiceInstanceListSupplier` 的实现类同样可以让其支持类似于 Ribbon 的负载均衡策略。这个应该是后续慢慢完善引入的,不看官方文档还真发现不了,所以说阅读官方文档真的很重要!
+However, the load balancing strategies supported by Spring Cloud Load Balancer extend beyond just these two; the implementation class of `ServiceInstanceListSupplier` can also be configured to support loading balancing strategies similar to those of Ribbon. This should be gradually improved and introduced in future updates. Without looking at the official documentation, one might not realize this, which underscores the importance of reading official documentation!
-这里举两个官方的例子:
+Here are two official examples:
-- `ZonePreferenceServiceInstanceListSupplier`:实现基于区域的负载平衡
-- `HintBasedServiceInstanceListSupplier`:实现基于 hint 提示的负载均衡
+- `ZonePreferenceServiceInstanceListSupplier`: Implements region-based load balancing
+- `HintBasedServiceInstanceListSupplier`: Implements hint-based load balancing
```java
public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
- // 使用基于区域的负载平衡方法
+ // Using region-based loading balancing method
@Bean
public ServiceInstanceListSupplier discoveryClientServiceInstanceListSupplier(
ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
@@ -240,28 +240,28 @@ public class CustomLoadBalancerConfiguration {
}
```
-关于 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 更详细更新的介绍,推荐大家看看官方文档: ,一切以官方文档为主。
+For a more detailed and updated introduction to Spring Cloud Load Balancer, I recommend checking the official documentation: , everything is based on the official documentation.
-轮询策略基本可以满足绝大部分项目的需求,我们的实际项目中如果没有特殊需求的话,通常使用的就是默认的轮询策略。并且,Ribbon 和 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 都支持自定义负载均衡策略。
+The round-robin strategy can meet the needs of the vast majority of projects. In our actual projects, if there are no special requirements, we usually just use the default round-robin strategy. Moreover, both Ribbon and Spring Cloud Load Balancer support custom load balancing strategies.
-个人建议如非必需 Ribbon 某个特有的功能或者负载均衡策略的话,就优先选择 Spring 官方提供的 Spring Cloud Load Balancer。
+Personally, I suggest opting for Spring Cloud Load Balancer first unless you specifically need a unique feature or load balancing strategy from Ribbon.
-最后再说说为什么我不太推荐使用 Ribbon 。
+Lastly, let's discuss why I do not recommend using Ribbon much.
-Spring Cloud 2020.0.0 版本移除了 Netflix 除 Eureka 外的所有组件。Spring Cloud Hoxton.M2 是第一个支持 Spring Cloud Load Balancer 来替代 Netfix Ribbon 的版本。
+Spring Cloud 2020.0.0 version removed all Netflix components except for Eureka. Spring Cloud Hoxton.M2 was the first version to support Spring Cloud Load Balancer in place of Netflix Ribbon.
-我们早期学习微服务,肯定接触过 Netflix 公司开源的 Feign、Ribbon、Zuul、Hystrix、Eureka 等知名的微服务系统构建所必须的组件,直到现在依然有非常非常多的公司在使用这些组件。不夸张地说,Netflix 公司引领了 Java 技术栈下的微服务发展。
+When we were learning about microservices, we certainly came across well-known components necessary for building microservices systems, such as Feign, Ribbon, Zuul, Hystrix, and Eureka from Netflix. Even now, many companies are still using these components. It is not an exaggeration to say that Netflix has led the development of microservices in the Java technology stack.

-**那为什么 Spring Cloud 这么急着移除 Netflix 的组件呢?** 主要是因为在 2018 年的时候,Netflix 宣布其开源的核心组件 Hystrix、Ribbon、Zuul、Eureka 等进入维护状态,不再进行新特性开发,只修 BUG。于是,Spring 官方不得不考虑移除 Netflix 的组件。
+**So why is Spring Cloud so eager to remove Netflix components?** The main reason is that in 2018, Netflix announced that its core open-source components such as Hystrix, Ribbon, Zuul, and Eureka would enter maintenance mode, ceasing new feature developments and focusing solely on bug fixes. Therefore, Spring had to consider removing Netflix components.
-**Spring Cloud Alibaba** 是一个不错的选择,尤其是对于国内的公司和个人开发者来说。
+**Spring Cloud Alibaba** is a good choice, especially for domestic companies and individual developers.
-## 参考
+## References
-- 干货 | eBay 的 4 层软件负载均衡实现:
-- HTTP Load Balancing(Nginx 官方文档):
-- 深入浅出负载均衡 - vivo 互联网技术:
+- Practical Guide | eBay's Layer 4 Software Load Balancing Implementation:
+- HTTP Load Balancing (Nginx Official Documentation):
+- In-depth Understanding of Load Balancing - Vivo Internet Technology:
diff --git a/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md b/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
index 1881f6c2c79..ca3185ec15f 100644
--- a/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
+++ b/docs/high-performance/message-queue/disruptor-questions.md
@@ -1,140 +1,140 @@
---
-title: Disruptor常见问题总结
-category: 高性能
+title: Summary of Common Questions About Disruptor
+category: High Performance
tag:
- - 消息队列
+ - Message Queue
---
-Disruptor 是一个相对冷门一些的知识点,不过,如果你的项目经历中用到了 Disruptor 的话,那面试中就很可能会被问到。
+Disruptor is a relatively niche topic, but if you've used Disruptor in your project experience, it's likely you'll be asked about it in an interview.
-一位球友之前投稿的面经(社招)中就涉及一些 Disruptor 的问题,文章传送门:[圆梦!顺利拿到字节、淘宝、拼多多等大厂 offer!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/C5QMjwEb6pzXACqZsyqC4A) 。
+A fellow player previously submitted an interview experience (for external recruitment) that included some Disruptor-related questions. You can find the article here: [Achieved my dream! Successfully received offers from major companies like ByteDance, Taobao, and Pinduoduo!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/C5QMjwEb6pzXACqZsyqC4A).

-这篇文章可以看作是对 Disruptor 做的一个简单总结,每个问题都不会扯太深入,主要针对面试或者速览 Disruptor。
+This article can be seen as a simple summary of Disruptor. Each question does not delve too deeply and is mainly focused on interviews or a quick overview of Disruptor.
-## Disruptor 是什么?
+## What is Disruptor?
-Disruptor 是一个开源的高性能内存队列,诞生初衷是为了解决内存队列的性能和内存安全问题,由英国外汇交易公司 LMAX 开发。
+Disruptor is an open-source high-performance memory queue, originally developed to solve performance and memory safety issues associated with memory queues by LMAX, a foreign exchange trading company in the UK.
-根据 Disruptor 官方介绍,基于 Disruptor 开发的系统 LMAX(新的零售金融交易平台),单线程就能支撑每秒 600 万订单。Martin Fowler 在 2011 年写的一篇文章 [The LMAX Architecture](https://martinfowler.com/articles/lmax.html) 中专门介绍过这个 LMAX 系统的架构,感兴趣的可以看看这篇文章。。
+According to the official introduction of Disruptor, the LMAX system developed based on Disruptor (a new retail financial trading platform) can support 6 million orders per second with a single thread. Martin Fowler wrote an article in 2011 [The LMAX Architecture](https://martinfowler.com/articles/lmax.html) specifically introducing the architecture of this LMAX system, which may be of interest.
-LMAX 公司 2010 年在 QCon 演讲后,Disruptor 获得了业界关注,并获得了 2011 年的 Oracle 官方的 Duke's Choice Awards(Duke 选择大奖)。
+After LMAX’s presentation at QCon in 2010, Disruptor received attention from the industry and won the Oracle official Duke's Choice Award in 2011.

-> “Duke 选择大奖”旨在表彰过去一年里全球个人或公司开发的、最具影响力的 Java 技术应用,由甲骨文公司主办。含金量非常高!
+> The "Duke's Choice Award" aims to recognize the most influential Java technology applications developed by individuals or companies worldwide in the past year, and is hosted by Oracle. It holds significant value!
-我专门找到了 Oracle 官方当年颁布获得 Duke's Choice Awards 项目的那篇文章(文章地址: 。从文中可以看出,同年获得此大奖荣誉的还有大名鼎鼎的 Netty、JRebel 等项目。
+I specifically found the Oracle official article announcing the Duke's Choice Award winners that year (article link: ). From the text, it can be seen that other well-known projects such as Netty and JRebel also received this award that year.
-
+
-Disruptor 提供的功能优点类似于 Kafka、RocketMQ 这类分布式队列,不过,其作为范围是 JVM(内存)。
+The capabilities provided by Disruptor are similar to those of distributed queues like Kafka and RocketMQ, but its scope is JVM (memory).
-- Github 地址:
-- 官方教程:
+- GitHub link:
+- Official tutorial:
-关于如何在 Spring Boot 项目中使用 Disruptor,可以看这篇文章:[Spring Boot + Disruptor 实战入门](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0iG5brK3bYF0BgSjX4jRiA) 。
+To learn how to use Disruptor in a Spring Boot project, you can refer to this article: [Spring Boot + Disruptor Practical Introduction](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0iG5brK3bYF0BgSjX4jRiA).
-## 为什么要用 Disruptor?
+## Why Use Disruptor?
-Disruptor 主要解决了 JDK 内置线程安全队列的性能和内存安全问题。
+Disruptor mainly addresses the performance and memory safety issues of the JDK's built-in thread-safe queues.
-**JDK 中常见的线程安全的队列如下**:
+**The commonly used thread-safe queues in the JDK are as follows**:
-| 队列名字 | 锁 | 是否有界 |
-| ----------------------- | ----------------------- | -------- |
-| `ArrayBlockingQueue` | 加锁(`ReentrantLock`) | 有界 |
-| `LinkedBlockingQueue` | 加锁(`ReentrantLock`) | 有界 |
-| `LinkedTransferQueue` | 无锁(`CAS`) | 无界 |
-| `ConcurrentLinkedQueue` | 无锁(`CAS`) | 无界 |
+| Queue Name | Lock | Bounded/Unbounded |
+| ----------------------- | ------------------------ | ----------------- |
+| `ArrayBlockingQueue` | Locked (`ReentrantLock`) | Bounded |
+| `LinkedBlockingQueue` | Locked (`ReentrantLock`) | Bounded |
+| `LinkedTransferQueue` | Lock-Free (`CAS`) | Unbounded |
+| `ConcurrentLinkedQueue` | Lock-Free (`CAS`) | Unbounded |
-从上表中可以看出:这些队列要不就是加锁有界,要不就是无锁无界。而加锁的的队列势必会影响性能,无界的队列又存在内存溢出的风险。
+As can be seen from the table above, these queues are either bounded and locked or unbounded and lock-free. The locked queues inevitably affect performance, while unbounded queues face the risk of memory overflow.
-因此,一般情况下,我们都是不建议使用 JDK 内置线程安全队列。
+Therefore, in general, we do not recommend using the JDK's built-in thread-safe queues.
-**Disruptor 就不一样了!它在无锁的情况下还能保证队列有界,并且还是线程安全的。**
+**Disruptor is different! It guarantees that the queue is bounded while being lock-free, and it is still thread-safe.**
-下面这张图是 Disruptor 官网提供的 Disruptor 和 ArrayBlockingQueue 的延迟直方图对比。
+The following image is a comparison of latency histograms between Disruptor and ArrayBlockingQueue provided by the Disruptor official website.

-Disruptor 真的很快,关于它为什么这么快这个问题,会在后文介绍到。
+Disruptor is indeed very fast, and we will introduce why it is so fast later.
-此外,Disruptor 还提供了丰富的扩展功能比如支持批量操作、支持多种等待策略。
+Additionally, Disruptor also provides a rich set of extension capabilities, such as supporting batch operations and multiple wait strategies.
-## Kafka 和 Disruptor 什么区别?
+## What Are the Differences Between Kafka and Disruptor?
-- **Kafka**:分布式消息队列,一般用在系统或者服务之间的消息传递,还可以被用作流式处理平台。
-- **Disruptor**:内存级别的消息队列,一般用在系统内部中线程间的消息传递。
+- **Kafka**: A distributed message queue typically used for message transmission between systems or services and can also be used as a stream processing platform.
+- **Disruptor**: A memory-level message queue commonly used for message transmission between threads within a system.
-## 哪些组件用到了 Disruptor?
+## Which Components Use Disruptor?
-用到 Disruptor 的开源项目还是挺多的,这里简单举几个例子:
+There are quite a few open-source projects that utilize Disruptor. Here are a few examples:
-- **Log4j2**:Log4j2 是一款常用的日志框架,它基于 Disruptor 来实现异步日志。
-- **SOFATracer**:SOFATracer 是蚂蚁金服开源的分布式应用链路追踪工具,它基于 Disruptor 来实现异步日志。
-- **Storm** : Storm 是一个开源的分布式实时计算系统,它基于 Disruptor 来实现工作进程内发生的消息传递(同一 Storm 节点上的线程间,无需网络通信)。
-- **HBase**:HBase 是一个分布式列存储数据库系统,它基于 Disruptor 来提高写并发性能。
+- **Log4j2**: Log4j2 is a commonly used logging framework that implements asynchronous logging based on Disruptor.
+- **SOFATracer**: SOFATracer is an open-source distributed application tracing tool developed by Ant Financial, which uses Disruptor for asynchronous logging.
+- **Storm**: Storm is an open-source distributed real-time computation system that uses Disruptor for message passing within the same worker process (between threads on the same Storm node, without the need for network communication).
+- **HBase**: HBase is a distributed column storage database system that uses Disruptor to improve write concurrency performance.
- ……
-## Disruptor 核心概念有哪些?
+## What Are the Core Concepts of Disruptor?
-- **Event**:你可以把 Event 理解为存放在队列中等待消费的消息对象。
-- **EventFactory**:事件工厂用于生产事件,我们在初始化 `Disruptor` 类的时候需要用到。
-- **EventHandler**:Event 在对应的 Handler 中被处理,你可以将其理解为生产消费者模型中的消费者。
-- **EventProcessor**:EventProcessor 持有特定消费者(Consumer)的 Sequence,并提供用于调用事件处理实现的事件循环(Event Loop)。
-- **Disruptor**:事件的生产和消费需要用到 `Disruptor` 对象。
-- **RingBuffer**:RingBuffer(环形数组)用于保存事件。
-- **WaitStrategy**:等待策略。决定了没有事件可以消费的时候,事件消费者如何等待新事件的到来。
-- **Producer**:生产者,只是泛指调用 `Disruptor` 对象发布事件的用户代码,Disruptor 没有定义特定接口或类型。
-- **ProducerType**:指定是单个事件发布者模式还是多个事件发布者模式(发布者和生产者的意思类似,我个人比较喜欢用发布者)。
-- **Sequencer**:Sequencer 是 Disruptor 的真正核心。此接口有两个实现类 `SingleProducerSequencer`、`MultiProducerSequencer` ,它们定义在生产者和消费者之间快速、正确地传递数据的并发算法。
+- **Event**: You can think of an Event as a message object that is stored in the queue waiting to be consumed.
+- **EventFactory**: The event factory is used to produce events that we need when initializing the `Disruptor` class.
+- **EventHandler**: Events are processed in the corresponding Handler, which can be understood as the consumer in the producer-consumer model.
+- **EventProcessor**: EventProcessor holds the sequence of a specific consumer and provides an event loop for invoking the implementation of event processing.
+- **Disruptor**: The production and consumption of events require the `Disruptor` object.
+- **RingBuffer**: RingBuffer (circular array) is used to store events.
+- **WaitStrategy**: The wait strategy determines how the event consumers wait for new events to arrive when there are no events to consume.
+- **Producer**: The producer refers generically to user code that calls the `Disruptor` object to publish events; Disruptor does not define a specific interface or type.
+- **ProducerType**: Specifies whether it is a single event publisher mode or multiple event publisher mode (the term publisher is similar to producer, and I personally prefer to use publisher).
+- **Sequencer**: The Sequencer is the true core of Disruptor. This interface has two implementation classes: `SingleProducerSequencer` and `MultiProducerSequencer`, which define a concurrent algorithm for fast and correct data transmission between producers and consumers.
-下面这张图摘自 Disruptor 官网,展示了 LMAX 系统使用 Disruptor 的示例。
+The following image is extracted from the Disruptor official website and shows an example of using Disruptor in the LMAX system.
-
+
-## Disruptor 等待策略有哪些?
+## What Are the Wait Strategies of Disruptor?
-**等待策略(WaitStrategy)** 决定了没有事件可以消费的时候,事件消费者如何等待新事件的到来。
+**WaitStrategy** determines how event consumers wait for new events to arrive when there are no events to consume.
-常见的等待策略有下面这些:
+Common wait strategies include the following:
-
+
-- `BlockingWaitStrategy`:基于 `ReentrantLock`+`Condition` 来实现等待和唤醒操作,实现代码非常简单,是 Disruptor 默认的等待策略。虽然最慢,但也是 CPU 使用率最低和最稳定的选项生产环境推荐使用;
-- `BusySpinWaitStrategy`:性能很好,存在持续自旋的风险,使用不当会造成 CPU 负载 100%,慎用;
-- `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`:基于 `BlockingWaitStrategy` 的轻量级等待策略,在没有锁竞争的时候会省去唤醒操作,但是作者说测试不充分,因此不建议使用;
-- `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`:带超时的等待策略,超时后会执行业务指定的处理逻辑;
-- `LiteTimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`:基于`TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`的策略,当没有锁竞争的时候会省去唤醒操作;
-- `SleepingWaitStrategy`:三段式策略,第一阶段自旋,第二阶段执行 Thread.yield 让出 CPU,第三阶段睡眠执行时间,反复的睡眠;
-- `YieldingWaitStrategy`:二段式策略,第一阶段自旋,第二阶段执行 Thread.yield 交出 CPU;
-- `PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy`:四段式策略,第一阶段自旋指定次数,第二阶段自旋指定时间,第三阶段执行 `Thread.yield` 交出 CPU,第四阶段调用成员变量的`waitFor`方法,该成员变量可以被设置为`BlockingWaitStrategy`、`LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`、`SleepingWaitStrategy`三个中的一个。
+- `BlockingWaitStrategy`: Implemented using `ReentrantLock` + `Condition` for waiting and waking operations. The implementation code is quite simple and is the default wait strategy of Disruptor. Although it is the slowest, it is also the option with the lowest and most stable CPU usage and is recommended for production environments.
+- `BusySpinWaitStrategy`: Provides good performance but has the risk of continuous spinning, which can cause the CPU load to reach 100% if used improperly, so caution is advised.
+- `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`: A lightweight wait strategy based on `BlockingWaitStrategy` that skips the waking operation when there is no lock contention, but the author mentions that testing is insufficient and therefore it's not recommended for use.
+- `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`: A wait strategy with a timeout that executes specified processing logic after the timeout.
+- `LiteTimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy`: A strategy based on `TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy` that skips wakening operations when there is no lock contention.
+- `SleepingWaitStrategy`: A three-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins; in the second phase, it executes Thread.yield to give up the CPU; in the third phase, it sleeps for a specific time, repeating the sleep.
+- `YieldingWaitStrategy`: A two-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins; in the second phase, it executes Thread.yield to yield the CPU.
+- `PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy`: A four-phase strategy — in the first phase, it spins a specified number of times; in the second phase, it spins for a specified duration; in the third phase, it executes `Thread.yield` to yield the CPU; in the fourth phase, it calls the member variable's `waitFor` method, which can be set to one of `BlockingWaitStrategy`, `LiteBlockingWaitStrategy`, or `SleepingWaitStrategy`.
-## Disruptor 为什么这么快?
+## Why is Disruptor So Fast?
-- **RingBuffer(环形数组)** : Disruptor 内部的 RingBuffer 是通过数组实现的。由于这个数组中的所有元素在初始化时一次性全部创建,因此这些元素的内存地址一般来说是连续的。这样做的好处是,当生产者不断往 RingBuffer 中插入新的事件对象时,这些事件对象的内存地址就能够保持连续,从而利用 CPU 缓存的局部性原理,将相邻的事件对象一起加载到缓存中,提高程序的性能。这类似于 MySQL 的预读机制,将连续的几个页预读到内存里。除此之外,RingBuffer 基于数组还支持批量操作(一次处理多个元素)、还可以避免频繁的内存分配和垃圾回收(RingBuffer 是一个固定大小的数组,当向数组中添加新元素时,如果数组已满,则新元素将覆盖掉最旧的元素)。
-- **避免了伪共享问题**:CPU 缓存内部是按照 Cache Line(缓存行)管理的,一般的 Cache Line 大小在 64 字节左右。Disruptor 为了确保目标字段独占一个 Cache Line,会在目标字段前后增加字节填充(前 56 个字节和后 56 个字节),这样可以避免 Cache Line 的伪共享(False Sharing)问题。同时,为了让 RingBuffer 存放数据的数组独占缓存行,数组的设计为 无效填充(128 字节)+ 有效数据。
-- **无锁设计**:Disruptor 采用无锁设计,避免了传统锁机制带来的竞争和延迟。Disruptor 的无锁实现起来比较复杂,主要是基于 CAS、内存屏障(Memory Barrier)、RingBuffer 等技术实现的。
+- **RingBuffer (Circular Array)**: The internal RingBuffer of Disruptor is implemented via an array. Since all elements of this array are created at once during initialization, these element memory addresses are generally continuous. The benefit of this is that as the producer continuously inserts new event objects into the RingBuffer, the memory addresses of these event objects can remain contiguous, thus utilizing the locality principle of CPU caches and loading adjacent event objects into the cache together to improve program performance. This is similar to MySQL's pre-read mechanism, which pre-loads several continuous pages into memory. Additionally, the RingBuffer, based on the array, supports batch operations (processing multiple elements at once) and avoids frequent memory allocation and garbage collection (the RingBuffer is a fixed-size array, so when a new element is added to the array, if the array is full, the new element will overwrite the oldest element).
+- **Avoided False Sharing Issues**: CPU caches are managed according to Cache Lines, with a typical Cache Line size around 64 bytes. Disruptor ensures that the target field occupies a single Cache Line by adding byte padding (56 bytes before and after the target field), thereby avoiding the false sharing problem. Additionally, to ensure that the array storing the data in the RingBuffer occupies a cache line, the design of the array includes invalid padding (128 bytes) plus valid data.
+- **Lock-Free Design**: Disruptor employs a lock-free design, eliminating the competition and delays associated with traditional locking mechanisms. The lock-free implementation of Disruptor is relatively complex and is primarily based on technologies such as CAS, memory barriers, and RingBuffer.
-综上所述,Disruptor 之所以能够如此快,是基于一系列优化策略的综合作用,既充分利用了现代 CPU 缓存结构的特点,又避免了常见的并发问题和性能瓶颈。
+In summary, the rapid performance of Disruptor stems from a comprehensive series of optimization strategies, effectively utilizing the characteristics of modern CPU cache structures while avoiding common concurrency issues and performance bottlenecks.
-关于 Disruptor 高性能队列原理的详细介绍,可以查看这篇文章:[Disruptor 高性能队列原理浅析](https://qin.news/disruptor/) (参考了美团技术团队的[高性能队列——Disruptor](https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html)这篇文章)。
+For a detailed introduction to the principles of Disruptor's high-performance queue, refer to this article: [Analysis of Disruptor High-Performance Queue Principles](https://qin.news/disruptor/) (which references the Meituan tech team's article on [High-Performance Queue - Disruptor](https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html)).
-🌈 这里额外补充一点:**数组中对象元素地址连续为什么可以提高性能?**
+🌈 As an additional note: **Why does having contiguous memory addresses for object elements in an array improve performance?**
-CPU 缓存是通过将最近使用的数据存储在高速缓存中来实现更快的读取速度,并使用预取机制提前加载相邻内存的数据以利用局部性原理。
+CPU caches enable faster reading speeds by storing recently used data in high-speed caches and using prefetching mechanisms to load adjacent memory data ahead of time, leveraging the principle of locality.
-在计算机系统中,CPU 主要访问高速缓存和内存。高速缓存是一种速度非常快、容量相对较小的内存,通常被分为多级缓存,其中 L1、L2、L3 分别表示一级缓存、二级缓存、三级缓存。越靠近 CPU 的缓存,速度越快,容量也越小。相比之下,内存容量相对较大,但速度较慢。
+In computer systems, the CPU primarily accesses high-speed caches and memory. Caches are very fast and relatively small in capacity, usually organized into multiple levels, denoted as L1, L2, and L3 (representing levels of cache). The closer the cache is to the CPU, the faster and smaller its capacity tends to be. In contrast, memory has a relatively large capacity but slower speeds.
-
+
-为了加速数据的读取过程,CPU 会先将数据从内存中加载到高速缓存中,如果下一次需要访问相同的数据,就可以直接从高速缓存中读取,而不需要再次访问内存。这就是所谓的 **缓存命中** 。另外,为了利用 **局部性原理** ,CPU 还会根据之前访问的内存地址预取相邻的内存数据,因为在程序中,连续的内存地址通常会被频繁访问到,这样做可以提高数据的缓存命中率,进而提高程序的性能。
+To accelerate data reading, the CPU first loads data from memory into the cache; if the same data needs to be accessed again, it can be read directly from the cache without needing to access memory again. This is known as a **cache hit**. Additionally, to utilize **locality**, the CPU will prefetch adjacent memory data based on previously accessed memory addresses, as consecutive memory addresses are usually accessed frequently in programs; this increases the cache hit rate and, consequently, improves program performance.
-## 参考
+## References
-- Disruptor 高性能之道-等待策略:< 高性能之道-等待策略/>
-- 《Java 并发编程实战》- 40 | 案例分析(三):高性能队列 Disruptor: +
+ 
 ](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
+> I recommend reading through online reading websites for a better experience and faster speed!
+> 📚 Address: [javaguide.cn](https://javaguide.cn/)
+
+[
](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
+> I recommend reading through online reading websites for a better experience and faster speed!
+> 📚 Address: [javaguide.cn](https://javaguide.cn/)
+
+[ ](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
](https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html)
 +
+ 
 -
-每种方式都有各自的优势,根据实际场景选择最合适的才是王道。下面再对这三种方式做一个简单的对比,以供大家实际开发中选择正确的存放时间的数据类型:
-
-| 类型 | 存储空间 | 日期格式 | 日期范围 | 是否带时区信息 |
-| ------------ | -------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------- |
-| DATETIME | 5~8 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1000-01-01 00:00:00[.000000] ~ 9999-12-31 23:59:59[.999999] | 否 |
-| TIMESTAMP | 4~7 字节 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.fraction] | 1970-01-01 00:00:01[.000000] ~ 2038-01-19 03:14:07[.999999] | 是 |
-| 数值型时间戳 | 4 字节 | 全数字如 1578707612 | 1970-01-01 00:00:01 之后的时间 | 否 |
-
-**选择建议小结:**
-
-- `TIMESTAMP` 的核心优势在于其内建的时区处理能力。数据库负责 UTC 存储和基于会话时区的自动转换,简化了需要处理多时区应用的开发。如果应用需要处理多时区,或者希望数据库能自动管理时区转换,`TIMESTAMP` 是自然的选择(注意其时间范围限制,也就是 2038 年问题)。
-- 如果应用场景不涉及时区转换,或者希望应用程序完全控制时区逻辑,并且需要表示 2038 年之后的时间,`DATETIME` 是更稳妥的选择。
-- 如果极度关注比较性能,或者需要频繁跨系统传递时间数据,并且可以接受可读性的牺牲(或总是在应用层转换),数值时间戳是一个强大的选项。
-
-
+Insert a
diff --git a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
index 52ad40f4a47..46b60051291 100644
--- a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
+++ b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
@@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
---
-title: MySQL事务隔离级别详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of MySQL Transaction Isolation Levels
+category: Database
tag:
- MySQL
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [guang19](https://github.com/guang19) 共同完成。
+> This article is co-authored by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [guang19](https://github.com/guang19).
-关于事务基本概览的介绍,请看这篇文章的介绍:[MySQL 常见知识点&面试题总结](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-事务)
+For an overview of transactions, please refer to this article: [Summary of Common MySQL Knowledge Points & Interview Questions](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-%E4%BA%8B%E5%8A%A1)
-## 事务隔离级别总结
+## Summary of Transaction Isolation Levels
-SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别:
+The SQL standard defines four isolation levels:
-- **READ-UNCOMMITTED(读取未提交)** :最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读。
-- **READ-COMMITTED(读取已提交)** :允许读取并发事务已经提交的数据,可以阻止脏读,但是幻读或不可重复读仍有可能发生。
-- **REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)** :对同一字段的多次读取结果都是一致的,除非数据是被本身事务自己所修改,可以阻止脏读和不可重复读,但幻读仍有可能发生。
-- **SERIALIZABLE(可串行化)** :最高的隔离级别,完全服从 ACID 的隔离级别。所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。
+- **READ-UNCOMMITTED**: The lowest isolation level, allowing reading of uncommitted data changes, which may lead to dirty reads, phantom reads, or non-repeatable reads.
+- **READ-COMMITTED**: Allows reading of data that has been committed by concurrent transactions, preventing dirty reads, but phantom reads or non-repeatable reads may still occur.
+- **REPEATABLE-READ**: Ensures that multiple reads of the same field yield consistent results unless the data is modified by the transaction itself. It prevents dirty reads and non-repeatable reads, but phantom reads may still occur.
+- **SERIALIZABLE**: The highest isolation level, fully compliant with the ACID isolation level. All transactions are executed sequentially, preventing any interference between transactions, meaning this level can prevent dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads.
----
+______________________________________________________________________
-| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
-| :--------------: | :--: | :--------: | :--: |
-| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
-| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
-| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
-| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
+| Isolation Level | Dirty Read | Non-repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
+| :--------------: | :--------: | :-----------------: | :----------: |
+| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
+| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
+| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
+| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
-MySQL InnoDB 存储引擎的默认支持的隔离级别是 **REPEATABLE-READ(可重读)**。我们可以通过`SELECT @@tx_isolation;`命令来查看,MySQL 8.0 该命令改为`SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
+The default isolation level supported by the MySQL InnoDB storage engine is **REPEATABLE-READ**. We can check this using the command `SELECT @@tx_isolation;`, which in MySQL 8.0 has changed to `SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
```sql
MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
@@ -38,78 +38,34 @@ MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
```
-从上面对 SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别的介绍可以看出,标准的 SQL 隔离级别定义里,REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)是不可以防止幻读的。
+From the introduction above regarding the four isolation levels defined by the SQL standard, it can be seen that the standard SQL isolation level definition does not prevent phantom reads for REPEATABLE-READ.
-但是!InnoDB 实现的 REPEATABLE-READ 隔离级别其实是可以解决幻读问题发生的,主要有下面两种情况:
+However! The REPEATABLE-READ isolation level implemented by InnoDB can actually resolve the issue of phantom reads, mainly in the following two situations:
-- **快照读**:由 MVCC 机制来保证不出现幻读。
-- **当前读**:使用 Next-Key Lock 进行加锁来保证不出现幻读,Next-Key Lock 是行锁(Record Lock)和间隙锁(Gap Lock)的结合,行锁只能锁住已经存在的行,为了避免插入新行,需要依赖间隙锁。
+- **Snapshot Read**: Ensured by the MVCC mechanism to prevent phantom reads.
+- **Current Read**: Uses Next-Key Lock for locking to prevent phantom reads. Next-Key Lock is a combination of row locks (Record Lock) and gap locks (Gap Lock). Row locks can only lock existing rows, and to prevent the insertion of new rows, gap locks are relied upon.
-因为隔离级别越低,事务请求的锁越少,所以大部分数据库系统的隔离级别都是 **READ-COMMITTED** ,但是你要知道的是 InnoDB 存储引擎默认使用 **REPEATABLE-READ** 并不会有任何性能损失。
+Since lower isolation levels require fewer locks for transaction requests, most database systems use **READ-COMMITTED** as the default isolation level. However, it is important to note that the InnoDB storage engine's default use of **REPEATABLE-READ** does not incur any performance loss.
-InnoDB 存储引擎在分布式事务的情况下一般会用到 SERIALIZABLE 隔离级别。
+In distributed transactions, the InnoDB storage engine generally uses the SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
-《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎(第 2 版)》7.7 章这样写到:
+Chapter 7.7 of "MySQL Internals: InnoDB Storage Engine (2nd Edition)" states:
-> InnoDB 存储引擎提供了对 XA 事务的支持,并通过 XA 事务来支持分布式事务的实现。分布式事务指的是允许多个独立的事务资源(transactional resources)参与到一个全局的事务中。事务资源通常是关系型数据库系统,但也可以是其他类型的资源。全局事务要求在其中的所有参与的事务要么都提交,要么都回滚,这对于事务原有的 ACID 要求又有了提高。另外,在使用分布式事务时,InnoDB 存储引擎的事务隔离级别必须设置为 SERIALIZABLE。
+> The InnoDB storage engine provides support for XA transactions and uses XA transactions to support the implementation of distributed transactions. Distributed transactions allow multiple independent transactional resources to participate in a global transaction. Transactional resources are typically relational database systems, but can also include other types of resources. A global transaction requires that all participating transactions either commit or roll back, which raises the original ACID requirements for transactions. Additionally, when using distributed transactions, the transaction isolation level of the InnoDB storage engine must be set to SERIALIZABLE.
-## 实际情况演示
+## Practical Demonstration
-在下面我会使用 2 个命令行 MySQL ,模拟多线程(多事务)对同一份数据的脏读问题。
+Below, I will use two MySQL command line instances to simulate the dirty read problem with multiple threads (multiple transactions) on the same data.
-MySQL 命令行的默认配置中事务都是自动提交的,即执行 SQL 语句后就会马上执行 COMMIT 操作。如果要显式地开启一个事务需要使用命令:`START TRANSACTION`。
+In the default configuration of the MySQL command line, transactions are automatically committed, meaning that after executing an SQL statement, a COMMIT operation is immediately performed. To explicitly start a transaction, the command `START TRANSACTION` is used.
-我们可以通过下面的命令来设置隔离级别。
+We can set the isolation level using the following command:
```sql
SET [SESSION|GLOBAL] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL [READ UNCOMMITTED|READ COMMITTED|REPEATABLE READ|SERIALIZABLE]
```
-我们再来看一下我们在下面实际操作中使用到的一些并发控制语句:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` |`BEGIN`:显式地开启一个事务。
-- `COMMIT`:提交事务,使得对数据库做的所有修改成为永久性。
-- `ROLLBACK`:回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的修改。
-
-### 脏读(读未提交)
-
-。
-- 如果应用场景不涉及时区转换,或者希望应用程序完全控制时区逻辑,并且需要表示 2038 年之后的时间,`DATETIME` 是更稳妥的选择。
-- 如果极度关注比较性能,或者需要频繁跨系统传递时间数据,并且可以接受可读性的牺牲(或总是在应用层转换),数值时间戳是一个强大的选项。
-
-
+Insert a
diff --git a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
index 52ad40f4a47..46b60051291 100644
--- a/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
+++ b/docs/database/mysql/transaction-isolation-level.md
@@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
---
-title: MySQL事务隔离级别详解
-category: 数据库
+title: Detailed Explanation of MySQL Transaction Isolation Levels
+category: Database
tag:
- MySQL
---
-> 本文由 [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) 和 [guang19](https://github.com/guang19) 共同完成。
+> This article is co-authored by [SnailClimb](https://github.com/Snailclimb) and [guang19](https://github.com/guang19).
-关于事务基本概览的介绍,请看这篇文章的介绍:[MySQL 常见知识点&面试题总结](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-事务)
+For an overview of transactions, please refer to this article: [Summary of Common MySQL Knowledge Points & Interview Questions](./mysql-questions-01.md#MySQL-%E4%BA%8B%E5%8A%A1)
-## 事务隔离级别总结
+## Summary of Transaction Isolation Levels
-SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别:
+The SQL standard defines four isolation levels:
-- **READ-UNCOMMITTED(读取未提交)** :最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读。
-- **READ-COMMITTED(读取已提交)** :允许读取并发事务已经提交的数据,可以阻止脏读,但是幻读或不可重复读仍有可能发生。
-- **REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)** :对同一字段的多次读取结果都是一致的,除非数据是被本身事务自己所修改,可以阻止脏读和不可重复读,但幻读仍有可能发生。
-- **SERIALIZABLE(可串行化)** :最高的隔离级别,完全服从 ACID 的隔离级别。所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。
+- **READ-UNCOMMITTED**: The lowest isolation level, allowing reading of uncommitted data changes, which may lead to dirty reads, phantom reads, or non-repeatable reads.
+- **READ-COMMITTED**: Allows reading of data that has been committed by concurrent transactions, preventing dirty reads, but phantom reads or non-repeatable reads may still occur.
+- **REPEATABLE-READ**: Ensures that multiple reads of the same field yield consistent results unless the data is modified by the transaction itself. It prevents dirty reads and non-repeatable reads, but phantom reads may still occur.
+- **SERIALIZABLE**: The highest isolation level, fully compliant with the ACID isolation level. All transactions are executed sequentially, preventing any interference between transactions, meaning this level can prevent dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads.
----
+______________________________________________________________________
-| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
-| :--------------: | :--: | :--------: | :--: |
-| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
-| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
-| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
-| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
+| Isolation Level | Dirty Read | Non-repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
+| :--------------: | :--------: | :-----------------: | :----------: |
+| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
+| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
+| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
+| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
-MySQL InnoDB 存储引擎的默认支持的隔离级别是 **REPEATABLE-READ(可重读)**。我们可以通过`SELECT @@tx_isolation;`命令来查看,MySQL 8.0 该命令改为`SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
+The default isolation level supported by the MySQL InnoDB storage engine is **REPEATABLE-READ**. We can check this using the command `SELECT @@tx_isolation;`, which in MySQL 8.0 has changed to `SELECT @@transaction_isolation;`
```sql
MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
@@ -38,78 +38,34 @@ MySQL> SELECT @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
```
-从上面对 SQL 标准定义了四个隔离级别的介绍可以看出,标准的 SQL 隔离级别定义里,REPEATABLE-READ(可重复读)是不可以防止幻读的。
+From the introduction above regarding the four isolation levels defined by the SQL standard, it can be seen that the standard SQL isolation level definition does not prevent phantom reads for REPEATABLE-READ.
-但是!InnoDB 实现的 REPEATABLE-READ 隔离级别其实是可以解决幻读问题发生的,主要有下面两种情况:
+However! The REPEATABLE-READ isolation level implemented by InnoDB can actually resolve the issue of phantom reads, mainly in the following two situations:
-- **快照读**:由 MVCC 机制来保证不出现幻读。
-- **当前读**:使用 Next-Key Lock 进行加锁来保证不出现幻读,Next-Key Lock 是行锁(Record Lock)和间隙锁(Gap Lock)的结合,行锁只能锁住已经存在的行,为了避免插入新行,需要依赖间隙锁。
+- **Snapshot Read**: Ensured by the MVCC mechanism to prevent phantom reads.
+- **Current Read**: Uses Next-Key Lock for locking to prevent phantom reads. Next-Key Lock is a combination of row locks (Record Lock) and gap locks (Gap Lock). Row locks can only lock existing rows, and to prevent the insertion of new rows, gap locks are relied upon.
-因为隔离级别越低,事务请求的锁越少,所以大部分数据库系统的隔离级别都是 **READ-COMMITTED** ,但是你要知道的是 InnoDB 存储引擎默认使用 **REPEATABLE-READ** 并不会有任何性能损失。
+Since lower isolation levels require fewer locks for transaction requests, most database systems use **READ-COMMITTED** as the default isolation level. However, it is important to note that the InnoDB storage engine's default use of **REPEATABLE-READ** does not incur any performance loss.
-InnoDB 存储引擎在分布式事务的情况下一般会用到 SERIALIZABLE 隔离级别。
+In distributed transactions, the InnoDB storage engine generally uses the SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
-《MySQL 技术内幕:InnoDB 存储引擎(第 2 版)》7.7 章这样写到:
+Chapter 7.7 of "MySQL Internals: InnoDB Storage Engine (2nd Edition)" states:
-> InnoDB 存储引擎提供了对 XA 事务的支持,并通过 XA 事务来支持分布式事务的实现。分布式事务指的是允许多个独立的事务资源(transactional resources)参与到一个全局的事务中。事务资源通常是关系型数据库系统,但也可以是其他类型的资源。全局事务要求在其中的所有参与的事务要么都提交,要么都回滚,这对于事务原有的 ACID 要求又有了提高。另外,在使用分布式事务时,InnoDB 存储引擎的事务隔离级别必须设置为 SERIALIZABLE。
+> The InnoDB storage engine provides support for XA transactions and uses XA transactions to support the implementation of distributed transactions. Distributed transactions allow multiple independent transactional resources to participate in a global transaction. Transactional resources are typically relational database systems, but can also include other types of resources. A global transaction requires that all participating transactions either commit or roll back, which raises the original ACID requirements for transactions. Additionally, when using distributed transactions, the transaction isolation level of the InnoDB storage engine must be set to SERIALIZABLE.
-## 实际情况演示
+## Practical Demonstration
-在下面我会使用 2 个命令行 MySQL ,模拟多线程(多事务)对同一份数据的脏读问题。
+Below, I will use two MySQL command line instances to simulate the dirty read problem with multiple threads (multiple transactions) on the same data.
-MySQL 命令行的默认配置中事务都是自动提交的,即执行 SQL 语句后就会马上执行 COMMIT 操作。如果要显式地开启一个事务需要使用命令:`START TRANSACTION`。
+In the default configuration of the MySQL command line, transactions are automatically committed, meaning that after executing an SQL statement, a COMMIT operation is immediately performed. To explicitly start a transaction, the command `START TRANSACTION` is used.
-我们可以通过下面的命令来设置隔离级别。
+We can set the isolation level using the following command:
```sql
SET [SESSION|GLOBAL] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL [READ UNCOMMITTED|READ COMMITTED|REPEATABLE READ|SERIALIZABLE]
```
-我们再来看一下我们在下面实际操作中使用到的一些并发控制语句:
-
-- `START TRANSACTION` |`BEGIN`:显式地开启一个事务。
-- `COMMIT`:提交事务,使得对数据库做的所有修改成为永久性。
-- `ROLLBACK`:回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的修改。
-
-### 脏读(读未提交)
-
-![](