diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 5199a3da..8c60a3f5 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
> ["For coding interview preparation, LeetCode is one of the best online resource providing a rich library of more than 300 real coding interview questions for you to practice from using one of the 7 supported languages - C, C++, Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, Ruby."](https://www.quora.com/How-effective-is-Leetcode-for-preparing-for-technical-interviews)
-* [SQL I](#sql-i)
* [Level 1](#level-1)
* [Level 2](#level-2)
* [Udemy](#udemy)
@@ -16,91 +15,7 @@
* [Programming Skills I](#programming-skills-i)
* [Programming Skills II](#programming-skills-ii)
* [Graph Theory I](#graph-theory-i)
-
-### SQL I
-
-#### Day 1 Select
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 0595 |[Big Countries](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries)| Easy | Database | 417 | 56.09
-| 1757 |[Recyclable and Low Fat Products](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1757_recyclable_and_low_fat_products)| Easy | Database | 1237 | 34.20
-| 0584 |[Find Customer Referee](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0584_find_customer_referee)| Easy | Database | 779 | 43.48
-| 0183 |[Customers Who Never Order](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0183_customers_who_never_order)| Easy | Database | 712 | 33.67
-
-#### Day 2 Select and Order
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 1873 |[Calculate Special Bonus](src/main/kotlin/g1801_1900/s1873_calculate_special_bonus)| Easy | Database | 1321 | 33.12
-| 0627 |[Swap Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary)| Easy | Database | 400 | 51.04
-| 0196 |[Delete Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 593 | 94.17
-
-#### Day 3 String Processing Functions
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 1667 |[Fix Names in a Table](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1667_fix_names_in_a_table)| Easy | Database | 1196 | 61.40
-| 1484 |[Group Sold Products By The Date](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 899 | 40.76
-| 1527 |[Patients With a Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition)| Easy | Database | 708 | 48.23
-
-#### Day 4 Union and Select
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 1965 |[Employees With Missing Information](src/main/kotlin/g1901_2000/s1965_employees_with_missing_information)| Easy | Database | 949 | 88.66
-| 1795 |[Rearrange Products Table](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1795_rearrange_products_table)| Easy | Database | 1027 | 67.57
-| 0608 |[Tree Node](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 794 | 48.38
-| 0176 |[Second Highest Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0176_second_highest_salary)| Medium | Database | 219 | 92.54
-
-#### Day 5 Union
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 0175 |[Combine Two Tables](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0175_combine_two_tables)| Easy | Database | 473 | 54.97
-| 1581 |[Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions)| Easy | Database | 2771 | 54.68
-| 1148 |[Article Views I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1148_article_views_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 806 | 54.41
-
-#### Day 6 Union
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 0197 |[Rising Temperature](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature)| Easy | Database | 394 | 94.15
-| 0607 |[Sales Person](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 2142 | 44.56
-
-#### Day 7 Function
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 1141 |[User Activity for the Past 30 Days I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1141_user_activity_for_the_past_30_days_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 790 | 87.11
-| 1693 |[Daily Leads and Partners](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1693_daily_leads_and_partners)| Easy | Database | 1115 | 52.84
-| 1729 |[Find Followers Count](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1729_find_followers_count)| Easy | Database | 1228 | 38.04
-
-#### Day 8 Function
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 0586 |[Customer Placing the Largest Number of Orders](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0586_customer_placing_the_largest_number_of_orders)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 768 | 44.85
-| 0511 |[Game Play Analysis I](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0511_game_play_analysis_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 790 | 45.04
-| 1890 |[The Latest Login in 2020](src/main/kotlin/g1801_1900/s1890_the_latest_login_in_2020)| Easy | Database | 1280 | 43.62
-| 1741 |[Find Total Time Spent by Each Employee](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1741_find_total_time_spent_by_each_employee)| Easy | Database | 1101 | 51.40
-
-#### Day 9 Control of Flow
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 1393 |[Capital Gain/Loss](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1393_capital_gainloss)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 990 | 47.36
-| 1407 |[Top Travellers](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1407_top_travellers)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 1394 | 98.43
-| 1158 |[Market Analysis I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1158_market_analysis_i)| Medium | Database | 2470 | 44.76
-
-#### Day 10 Where
-
-| | | | | |
-|-|-|-|-|-|-
-| 0182 |[Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0182_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 396 | 68.40
-| 1050 |[Actors and Directors Who Cooperated At Least Three Times](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1050_actors_and_directors_who_cooperated_at_least_three_times)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 629 | 81.02
-| 1587 |[Bank Account Summary II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii)| Easy | Database | 1582 | 52.96
-| 1084 |[Sales Analysis III](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1084_sales_analysis_iii)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 1881 | 79.36
+* [SQL I](#sql-i)
### Level 1
@@ -1812,10 +1727,119 @@
| 0886 |[Possible Bipartition](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find | 397 | 100.00
| 0785 |[Is Graph Bipartite?](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0785_is_graph_bipartite)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find | 215 | 82.35
+### SQL I
+
+#### Day 1 Select
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0595 |[Big Countries](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries)| Easy | Database | 417 | 56.09
+| 1757 |[Recyclable and Low Fat Products](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1757_recyclable_and_low_fat_products)| Easy | Database | 1237 | 34.20
+| 0584 |[Find Customer Referee](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0584_find_customer_referee)| Easy | Database | 779 | 43.48
+| 0183 |[Customers Who Never Order](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0183_customers_who_never_order)| Easy | Database | 712 | 33.67
+
+#### Day 2 Select and Order
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1873 |[Calculate Special Bonus](src/main/kotlin/g1801_1900/s1873_calculate_special_bonus)| Easy | Database | 1321 | 33.12
+| 0627 |[Swap Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary)| Easy | Database | 400 | 51.04
+| 0196 |[Delete Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 593 | 94.17
+
+#### Day 3 String Processing Functions
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1667 |[Fix Names in a Table](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1667_fix_names_in_a_table)| Easy | Database | 1196 | 61.40
+| 1484 |[Group Sold Products By The Date](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 899 | 40.76
+| 1527 |[Patients With a Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition)| Easy | Database | 708 | 48.23
+
+#### Day 4 Union and Select
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1965 |[Employees With Missing Information](src/main/kotlin/g1901_2000/s1965_employees_with_missing_information)| Easy | Database | 949 | 88.66
+| 1795 |[Rearrange Products Table](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1795_rearrange_products_table)| Easy | Database | 1027 | 67.57
+| 0608 |[Tree Node](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 794 | 48.38
+| 0176 |[Second Highest Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0176_second_highest_salary)| Medium | Database | 219 | 92.54
+
+#### Day 5 Union
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0175 |[Combine Two Tables](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0175_combine_two_tables)| Easy | Database | 473 | 54.97
+| 1581 |[Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions)| Easy | Database | 2771 | 54.68
+| 1148 |[Article Views I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1148_article_views_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 806 | 54.41
+
+#### Day 6 Union
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0197 |[Rising Temperature](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature)| Easy | Database | 394 | 94.15
+| 0607 |[Sales Person](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 2142 | 44.56
+
+#### Day 7 Function
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1141 |[User Activity for the Past 30 Days I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1141_user_activity_for_the_past_30_days_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 790 | 87.11
+| 1693 |[Daily Leads and Partners](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1693_daily_leads_and_partners)| Easy | Database | 1115 | 52.84
+| 1729 |[Find Followers Count](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1729_find_followers_count)| Easy | Database | 1228 | 38.04
+
+#### Day 8 Function
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0586 |[Customer Placing the Largest Number of Orders](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0586_customer_placing_the_largest_number_of_orders)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 768 | 44.85
+| 0511 |[Game Play Analysis I](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0511_game_play_analysis_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 790 | 45.04
+| 1890 |[The Latest Login in 2020](src/main/kotlin/g1801_1900/s1890_the_latest_login_in_2020)| Easy | Database | 1280 | 43.62
+| 1741 |[Find Total Time Spent by Each Employee](src/main/kotlin/g1701_1800/s1741_find_total_time_spent_by_each_employee)| Easy | Database | 1101 | 51.40
+
+#### Day 9 Control of Flow
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1393 |[Capital Gain/Loss](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1393_capital_gainloss)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 990 | 47.36
+| 1407 |[Top Travellers](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1407_top_travellers)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 1394 | 98.43
+| 1158 |[Market Analysis I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1158_market_analysis_i)| Medium | Database | 2470 | 44.76
+
+#### Day 10 Where
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0182 |[Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0182_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 396 | 68.40
+| 1050 |[Actors and Directors Who Cooperated At Least Three Times](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1050_actors_and_directors_who_cooperated_at_least_three_times)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 629 | 81.02
+| 1587 |[Bank Account Summary II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii)| Easy | Database | 1582 | 52.96
+| 1084 |[Sales Analysis III](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1084_sales_analysis_iii)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 1881 | 79.36
+
## Algorithms
| # | Title | Difficulty | Tag | Time, ms | Time, %
|------|----------------|-------------|-------------|----------|--------
+| 3213 |[Construct String with Minimum Cost](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost)| Hard | Array, String, Dynamic_Programming, Suffix_Array | 1176 | 46.67
+| 3212 |[Count Submatrices With Equal Frequency of X and Y](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y)| Medium | Array, Matrix, Prefix_Sum | 1009 | 78.95
+| 3211 |[Generate Binary Strings Without Adjacent Zeros](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros)| Medium | String, Bit_Manipulation, Recursion | 237 | 38.18
+| 3210 |[Find the Encrypted String](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string)| Easy | String | 170 | 62.69
+| 3209 |[Number of Subarrays With AND Value of K](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k)| Hard | Array, Binary_Search, Bit_Manipulation, Segment_Tree | 530 | 100.00
+| 3208 |[Alternating Groups II](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii)| Medium | Array, Sliding_Window | 449 | 97.62
+| 3207 |[Maximum Points After Enemy Battles](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles)| Medium | Array, Greedy | 470 | 100.00
+| 3206 |[Alternating Groups I](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i)| Easy | Array, Sliding_Window | 167 | 88.14
+| 3203 |[Find Minimum Diameter After Merging Two Trees](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees)| Hard | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Graph | 1156 | 100.00
+| 3202 |[Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence II](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 255 | 97.30
+| 3201 |[Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence I](src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 512 | 89.36
+| 3200 |[Maximum Height of a Triangle](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle)| Easy | Array, Enumeration | 136 | 81.36
+| 3197 |[Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones II](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii)| Hard | Array, Matrix, Enumeration | 216 | 100.00
+| 3196 |[Maximize Total Cost of Alternating Subarrays](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 496 | 73.81
+| 3195 |[Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones I](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i)| Medium | Array, Matrix | 1068 | 73.91
+| 3194 |[Minimum Average of Smallest and Largest Elements](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements)| Easy | Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 192 | 94.25
+| 3193 |[Count the Number of Inversions](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 243 | 94.74
+| 3192 |[Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One II](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 684 | 64.29
+| 3191 |[Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One I](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i)| Medium | Array, Bit_Manipulation, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window, Queue | 653 | 57.35
+| 3190 |[Find Minimum Operations to Make All Elements Divisible by Three](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three)| Easy | Array, Math | 153 | 87.95
+| 3187 |[Peaks in Array](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3187_peaks_in_array)| Hard | Array, Segment_Tree, Binary_Indexed_Tree | 1339 | 80.00
+| 3186 |[Maximum Total Damage With Spell Casting](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3186_maximum_total_damage_with_spell_casting)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Counting | 1106 | 92.73
+| 3185 |[Count Pairs That Form a Complete Day II](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3185_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_ii)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Counting | 578 | 78.33
+| 3184 |[Count Pairs That Form a Complete Day I](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3184_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_i)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Counting | 171 | 68.42
| 3181 |[Maximum Total Reward Using Operations II](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3181_maximum_total_reward_using_operations_ii)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation | 376 | 100.00
| 3180 |[Maximum Total Reward Using Operations I](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3180_maximum_total_reward_using_operations_i)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 183 | 100.00
| 3179 |[Find the N-th Value After K Seconds](src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3179_find_the_n_th_value_after_k_seconds)| Medium | Array, Math, Simulation, Prefix_Sum, Combinatorics | 175 | 100.00
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3184_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3184_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3d96d10a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3184_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3184\. Count Pairs That Form a Complete Day I
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `hours` representing times in **hours**, return an integer denoting the number of pairs `i`, `j` where `i < j` and `hours[i] + hours[j]` forms a **complete day**.
+
+A **complete day** is defined as a time duration that is an **exact** **multiple** of 24 hours.
+
+For example, 1 day is 24 hours, 2 days is 48 hours, 3 days is 72 hours, and so on.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** hours = [12,12,30,24,24]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The pairs of indices that form a complete day are `(0, 1)` and `(3, 4)`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** hours = [72,48,24,3]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The pairs of indices that form a complete day are `(0, 1)`, `(0, 2)`, and `(1, 2)`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= hours.length <= 100`
+* 1 <= hours[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countCompleteDayPairs(hours: IntArray): Int {
+ val modular = IntArray(26)
+ var ans = 0
+ for (hour in hours) {
+ val mod = hour % 24
+ ans += modular[24 - mod]
+ if (mod == 0) {
+ modular[24]++
+ } else {
+ modular[mod]++
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3185_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3185_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fd7f8cfb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3185_count_pairs_that_form_a_complete_day_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3185\. Count Pairs That Form a Complete Day II
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `hours` representing times in **hours**, return an integer denoting the number of pairs `i`, `j` where `i < j` and `hours[i] + hours[j]` forms a **complete day**.
+
+A **complete day** is defined as a time duration that is an **exact** **multiple** of 24 hours.
+
+For example, 1 day is 24 hours, 2 days is 48 hours, 3 days is 72 hours, and so on.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** hours = [12,12,30,24,24]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The pairs of indices that form a complete day are `(0, 1)` and `(3, 4)`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** hours = [72,48,24,3]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The pairs of indices that form a complete day are `(0, 1)`, `(0, 2)`, and `(1, 2)`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= hours.length <= 5 * 105
+* 1 <= hours[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countCompleteDayPairs(hours: IntArray): Long {
+ val hour = LongArray(24)
+ for (j in hours) {
+ hour[j % 24]++
+ }
+ var counter = hour[0] * (hour[0] - 1) / 2
+ counter += hour[12] * (hour[12] - 1) / 2
+ for (i in 1..11) {
+ counter += hour[i] * hour[24 - i]
+ }
+ return counter
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3186_maximum_total_damage_with_spell_casting/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3186_maximum_total_damage_with_spell_casting/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8bc427e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3186_maximum_total_damage_with_spell_casting/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3186\. Maximum Total Damage With Spell Casting
+
+Medium
+
+A magician has various spells.
+
+You are given an array `power`, where each element represents the damage of a spell. Multiple spells can have the same damage value.
+
+It is a known fact that if a magician decides to cast a spell with a damage of `power[i]`, they **cannot** cast any spell with a damage of `power[i] - 2`, `power[i] - 1`, `power[i] + 1`, or `power[i] + 2`.
+
+Each spell can be cast **only once**.
+
+Return the **maximum** possible _total damage_ that a magician can cast.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** power = [1,1,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The maximum possible damage of 6 is produced by casting spells 0, 1, 3 with damage 1, 1, 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** power = [7,1,6,6]
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The maximum possible damage of 13 is produced by casting spells 1, 2, 3 with damage 1, 6, 6.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= power.length <= 105
+* 1 <= power[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumTotalDamage(power: IntArray): Long {
+ var maxPower = 0
+ for (p in power) {
+ if (p > maxPower) {
+ maxPower = p
+ }
+ }
+ return if ((maxPower <= 1000000)) smallPower(power, maxPower) else bigPower(power)
+ }
+
+ private fun smallPower(power: IntArray, maxPower: Int): Long {
+ val counts = IntArray(maxPower + 6)
+ for (p in power) {
+ counts[p]++
+ }
+ val dp = LongArray(maxPower + 6)
+ dp[1] = counts[1].toLong()
+ dp[2] = max((counts[2] * 2L).toDouble(), dp[1].toDouble()).toLong()
+ for (i in 3..maxPower) {
+ dp[i] = max((counts[i] * i + dp[i - 3]).toDouble(), max(dp[i - 1].toDouble(), dp[i - 2].toDouble()))
+ .toLong()
+ }
+ return dp[maxPower]
+ }
+
+ private fun bigPower(power: IntArray): Long {
+ power.sort()
+ val n = power.size
+ val prevs = LongArray(4)
+ var curPower = power[0]
+ var count = 1
+ var result: Long = 0
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ val p = if ((i == n)) 1000000009 else power[i]
+ if (p == curPower) {
+ count++
+ } else {
+ val curVal = max(
+ (curPower.toLong() * count + prevs[3]).toDouble(),
+ max(prevs[1].toDouble(), prevs[2].toDouble())
+ )
+ .toLong()
+ val diff = min((p - curPower).toDouble(), (prevs.size - 1).toDouble()).toInt()
+ val nextCurVal =
+ if ((diff == 1)) 0 else max(prevs[3].toDouble(), max(curVal.toDouble(), prevs[2].toDouble()))
+ .toLong()
+ // Shift the values in prevs[].
+ var k = prevs.size - 1
+ if (diff < prevs.size - 1) {
+ while (k > diff) {
+ prevs[k] = prevs[k-- - diff]
+ }
+ prevs[k--] = curVal
+ }
+ while (k > 0) {
+ prevs[k--] = nextCurVal
+ }
+ curPower = p
+ count = 1
+ }
+ }
+ for (v in prevs) {
+ if (v > result) {
+ result = v
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3187_peaks_in_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3187_peaks_in_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b913c774
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3187_peaks_in_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3187\. Peaks in Array
+
+Hard
+
+A **peak** in an array `arr` is an element that is **greater** than its previous and next element in `arr`.
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` and a 2D integer array `queries`.
+
+You have to process queries of two types:
+
+* queries[i] = [1, li, ri], determine the count of **peak** elements in the subarray nums[li..ri].
+* queries[i] = [2, indexi, vali], change nums[indexi] to vali.
+
+Return an array `answer` containing the results of the queries of the first type in order.
+
+**Notes:**
+
+* The **first** and the **last** element of an array or a subarray **cannot** be a peak.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,4,2,5], queries = \[\[2,3,4],[1,0,4]]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+First query: We change `nums[3]` to 4 and `nums` becomes `[3,1,4,4,5]`.
+
+Second query: The number of peaks in the `[3,1,4,4,5]` is 0.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,1,4,2,1,5], queries = \[\[2,2,4],[1,0,2],[1,0,4]]
+
+**Output:** [0,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+First query: `nums[2]` should become 4, but it is already set to 4.
+
+Second query: The number of peaks in the `[4,1,4]` is 0.
+
+Third query: The second 4 is a peak in the `[4,1,4,2,1]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 105
+* `queries[i][0] == 1` or `queries[i][0] == 2`
+* For all `i` that:
+ * `queries[i][0] == 1`: `0 <= queries[i][1] <= queries[i][2] <= nums.length - 1`
+ * `queries[i][0] == 2`: `0 <= queries[i][1] <= nums.length - 1`, 1 <= queries[i][2] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun countOfPeaks(nums: IntArray, queries: Array): List {
+ val peaks = BooleanArray(nums.size)
+ val binaryIndexedTree = IntArray(Integer.highestOneBit(peaks.size) * 2 + 1)
+ for (i in 1 until peaks.size - 1) {
+ if (nums[i] > max(nums[i - 1], nums[i + 1])) {
+ peaks[i] = true
+ update(binaryIndexedTree, i + 1, 1)
+ }
+ }
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (query in queries) {
+ if (query[0] == 1) {
+ val leftIndex = query[1]
+ val rightIndex = query[2]
+ result.add(computeRangeSum(binaryIndexedTree, leftIndex + 2, rightIndex))
+ } else {
+ val index = query[1]
+ val value = query[2]
+ nums[index] = value
+ for (i in -1..1) {
+ val affected = index + i
+ if (affected >= 1 && affected <= nums.size - 2) {
+ val peak =
+ nums[affected] > max(nums[affected - 1], nums[affected + 1])
+ if (peak != peaks[affected]) {
+ if (peak) {
+ update(binaryIndexedTree, affected + 1, 1)
+ } else {
+ update(binaryIndexedTree, affected + 1, -1)
+ }
+ peaks[affected] = peak
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun computeRangeSum(binaryIndexedTree: IntArray, beginIndex: Int, endIndex: Int): Int {
+ return if (beginIndex <= endIndex) query(binaryIndexedTree, endIndex) - query(binaryIndexedTree, beginIndex - 1)
+ else 0
+ }
+
+ private fun query(binaryIndexedTree: IntArray, index: Int): Int {
+ var index = index
+ var result = 0
+ while (index != 0) {
+ result += binaryIndexedTree[index]
+ index -= index and -index
+ }
+
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun update(binaryIndexedTree: IntArray, index: Int, delta: Int) {
+ var index = index
+ while (index < binaryIndexedTree.size) {
+ binaryIndexedTree[index] += delta
+ index += index and -index
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc793b53
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3190_find_minimum_operations_to_make_all_elements_divisible_by_three/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3190\. Find Minimum Operations to Make All Elements Divisible by Three
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`. In one operation, you can add or subtract 1 from **any** element of `nums`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations to make all elements of `nums` divisible by 3.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All array elements can be made divisible by 3 using 3 operations:
+
+* Subtract 1 from 1.
+* Add 1 to 2.
+* Subtract 1 from 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,6,9]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 50`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] % 3 != 0) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9164702b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3191_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3191\. Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a binary array `nums`.
+
+You can do the following operation on the array **any** number of times (possibly zero):
+
+* Choose **any** 3 **consecutive** elements from the array and **flip** **all** of them.
+
+**Flipping** an element means changing its value from 0 to 1, and from 1 to 0.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make all elements in `nums` equal to 1. If it is impossible, return -1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,1,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operations:
+
+* Choose the elements at indices 0, 1 and 2. The resulting array is nums = [**1**,**0**,**0**,1,0,0].
+* Choose the elements at indices 1, 2 and 3. The resulting array is nums = [1,**1**,**1**,**0**,0,0].
+* Choose the elements at indices 3, 4 and 5. The resulting array is nums = [1,1,1,**1**,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+ It is impossible to make all elements equal to 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var ans = 0
+ // Iterate through the array up to the third-last element
+ for (i in 0 until nums.size - 2) {
+ // If the current element is 0, perform an operation
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ ans++
+ // Flip the current element and the next two elements
+ nums[i] = 1
+ nums[i + 1] = if (nums[i + 1] == 0) 1 else 0
+ nums[i + 2] = if (nums[i + 2] == 0) 1 else 0
+ }
+ }
+ // Check the last two elements if they are 0, return -1 as they cannot be flipped
+ for (i in nums.size - 2 until nums.size) {
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6c68a4f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3192_minimum_operations_to_make_binary_array_elements_equal_to_one_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3192\. Minimum Operations to Make Binary Array Elements Equal to One II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a binary array `nums`.
+
+You can do the following operation on the array **any** number of times (possibly zero):
+
+* Choose **any** index `i` from the array and **flip** **all** the elements from index `i` to the end of the array.
+
+**Flipping** an element means changing its value from 0 to 1, and from 1 to 0.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make all elements in `nums` equal to 1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operations:
+
+* Choose the index `i = 1`. The resulting array will be nums = [0,**0**,**0**,**1**,**0**].
+* Choose the index `i = 0`. The resulting array will be nums = [**1**,**1**,**1**,**0**,**1**].
+* Choose the index `i = 4`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,1,0,**0**].
+* Choose the index `i = 3`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,1,1,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,0,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+ We can do the following operation:
+
+* Choose the index `i = 1`. The resulting array will be nums = [1,**1**,**1**,**1**].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var a = 0
+ var c = 1
+ for (x in nums) {
+ if (x != c) {
+ a++
+ c = c xor 1
+ }
+ }
+ return a
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3eaba983
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3193_count_the_number_of_inversions/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3193\. Count the Number of Inversions
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `n` and a 2D array `requirements`, where requirements[i] = [endi, cnti] represents the end index and the **inversion** count of each requirement.
+
+A pair of indices `(i, j)` from an integer array `nums` is called an **inversion** if:
+
+* `i < j` and `nums[i] > nums[j]`
+
+Return the number of permutations `perm` of `[0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1]` such that for **all** `requirements[i]`, perm[0..endi] has exactly cnti inversions.
+
+Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, requirements = \[\[2,2],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The two permutations are:
+
+* `[2, 0, 1]`
+ * Prefix `[2, 0, 1]` has inversions `(0, 1)` and `(0, 2)`.
+ * Prefix `[2]` has 0 inversions.
+* `[1, 2, 0]`
+ * Prefix `[1, 2, 0]` has inversions `(0, 2)` and `(1, 2)`.
+ * Prefix `[1]` has 0 inversions.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, requirements = \[\[2,2],[1,1],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only satisfying permutation is `[2, 0, 1]`:
+
+* Prefix `[2, 0, 1]` has inversions `(0, 1)` and `(0, 2)`.
+* Prefix `[2, 0]` has an inversion `(0, 1)`.
+* Prefix `[2]` has 0 inversions.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, requirements = \[\[0,0],[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only satisfying permutation is `[0, 1]`:
+
+* Prefix `[0]` has 0 inversions.
+* Prefix `[0, 1]` has an inversion `(0, 1)`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 300`
+* `1 <= requirements.length <= n`
+* requirements[i] = [endi, cnti]
+* 0 <= endi <= n - 1
+* 0 <= cnti <= 400
+* The input is generated such that there is at least one `i` such that endi == n - 1.
+* The input is generated such that all endi are unique.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfPermutations(n: Int, r: Array): Int {
+ r.sortWith { o1: IntArray, o2: IntArray -> o1[0] - o2[0] }
+ if (r[0][0] == 0 && r[0][1] > 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var ri = if (r[0][0] == 0) 1 else 0
+ var a: Long = 1
+ var t: Long
+ val m = Array(n) { IntArray(401) }
+ m[0][0] = 1
+ for (i in 1 until m.size) {
+ m[i][0] = m[i - 1][0]
+ for (j in 1..i) {
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i][j - 1]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i - 1][j]) % MOD
+ }
+ for (j in i + 1..r[ri][1]) {
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i][j - 1]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + m[i - 1][j]) % MOD
+ m[i][j] = (m[i][j] - m[i - 1][j - i - 1])
+ if (m[i][j] < 0) {
+ m[i][j] += MOD
+ }
+ }
+ if (r[ri][0] == i) {
+ t = m[i][r[ri][1]].toLong()
+ if (t == 0L) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ m[i].fill(0)
+ m[i][r[ri][1]] = 1
+ a = (a * t) % MOD
+ ri++
+ }
+ }
+ return a.toInt()
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD = 1000000007
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1c5fe0cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3194_minimum_average_of_smallest_and_largest_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3194\. Minimum Average of Smallest and Largest Elements
+
+Easy
+
+You have an array of floating point numbers `averages` which is initially empty. You are given an array `nums` of `n` integers where `n` is even.
+
+You repeat the following procedure `n / 2` times:
+
+* Remove the **smallest** element, `minElement`, and the **largest** element `maxElement`, from `nums`.
+* Add `(minElement + maxElement) / 2` to `averages`.
+
+Return the **minimum** element in `averages`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [7,8,3,4,15,13,4,1]
+
+**Output:** 5.5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|------------------|------------|
+| 0 | [7,8,3,4,15,13,4,1] | [] |
+| 1 | [7,8,3,4,13,4] | [8] |
+| 2 | [7,8,4,4] | [8, 8] |
+| 3 | [7,4] | [8, 8, 6] |
+| 4 | [] | [8, 8, 6, 5.5] |
+
+The smallest element of averages, 5.5, is returned.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,9,8,3,10,5]
+
+**Output:** 5.5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|----------------|------------|
+| 0 | [1,9,8,3,10,5] | [] |
+| 1 | [9,8,3,5] | [5.5] |
+| 2 | [8,5] | [5.5, 6] |
+| 3 | [] | [5.5, 6, 6.5] |
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,7,8,9]
+
+**Output:** 5.0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Step | nums | averages |
+|------|----------------|------------|
+| 0 | [1,2,3,7,8,9] | [] |
+| 1 | [2,3,7,8] | [5] |
+| 2 | [3,7] | [5, 5] |
+| 3 | [] | [5, 5, 5] |
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n == nums.length <= 50`
+* `n` is even.
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumAverage(nums: IntArray): Double {
+ nums.sort()
+ var m = 102.0
+ var i = 0
+ val l = nums.size
+ while (i < l / 2) {
+ m = min(m, nums[i] + nums[l - i - 1].toDouble())
+ i++
+ }
+ return m / 2.0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fd2613d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3195_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3195\. Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones I
+
+Medium
+
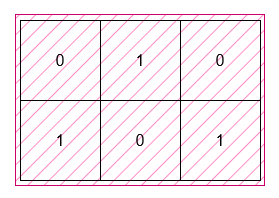
+You are given a 2D **binary** array `grid`. Find a rectangle with horizontal and vertical sides with the **smallest** area, such that all the 1's in `grid` lie inside this rectangle.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible area of the rectangle.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,1,0],[1,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The smallest rectangle has a height of 2 and a width of 3, so it has an area of `2 * 3 = 6`.
+
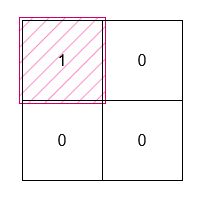
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The smallest rectangle has both height and width 1, so its area is `1 * 1 = 1`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 1000`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either 0 or 1.
+* The input is generated such that there is at least one 1 in `grid`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumArea(grid: Array): Int {
+ var xmin = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var xmax = -1
+ var ymin = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var ymax = -1
+ var i = 0
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ while (i < m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
+ xmin = min(xmin, i)
+ xmax = max(xmax, i)
+ ymin = min(ymin, j)
+ ymax = max(ymax, j)
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return (xmax - xmin + 1) * (ymax - ymin + 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..101137b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3196_maximize_total_cost_of_alternating_subarrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3196\. Maximize Total Cost of Alternating Subarrays
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` with length `n`.
+
+The **cost** of a subarray `nums[l..r]`, where `0 <= l <= r < n`, is defined as:
+
+cost(l, r) = nums[l] - nums[l + 1] + ... + nums[r] * (−1)r − l
+
+Your task is to **split** `nums` into subarrays such that the **total** **cost** of the subarrays is **maximized**, ensuring each element belongs to **exactly one** subarray.
+
+Formally, if `nums` is split into `k` subarrays, where `k > 1`, at indices i1, i2, ..., ik − 1, where 0 <= i1 < i2 < ... < ik - 1 < n - 1, then the total cost will be:
+
+cost(0, i1) + cost(i1 + 1, i2) + ... + cost(ik − 1 + 1, n − 1)
+
+Return an integer denoting the _maximum total cost_ of the subarrays after splitting the array optimally.
+
+**Note:** If `nums` is not split into subarrays, i.e. `k = 1`, the total cost is simply `cost(0, n - 1)`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+One way to maximize the total cost is by splitting `[1, -2, 3, 4]` into subarrays `[1, -2, 3]` and `[4]`. The total cost will be `(1 + 2 + 3) + 4 = 10`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-1,1,-1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+One way to maximize the total cost is by splitting `[1, -1, 1, -1]` into subarrays `[1, -1]` and `[1, -1]`. The total cost will be `(1 + 1) + (1 + 1) = 4`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We cannot split the array further, so the answer is 0.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Selecting the whole array gives a total cost of `1 + 1 = 2`, which is the maximum.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumTotalCost(nums: IntArray): Long {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var addResult = nums[0].toLong()
+ var subResult = nums[0].toLong()
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ val tempAdd = (max(addResult.toDouble(), subResult.toDouble()) + nums[i]).toLong()
+ val tempSub = addResult - nums[i]
+ addResult = tempAdd
+ subResult = tempSub
+ }
+ return max(addResult, subResult)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f353a199
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3197_find_the_minimum_area_to_cover_all_ones_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3197\. Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones II
+
+Hard
+
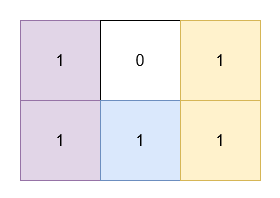
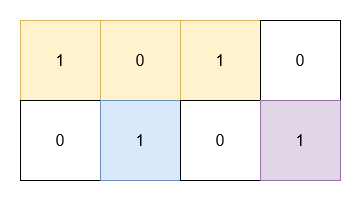
+You are given a 2D **binary** array `grid`. You need to find 3 **non-overlapping** rectangles having **non-zero** areas with horizontal and vertical sides such that all the 1's in `grid` lie inside these rectangles.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible sum of the area of these rectangles.
+
+**Note** that the rectangles are allowed to touch.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The 1's at `(0, 0)` and `(1, 0)` are covered by a rectangle of area 2.
+* The 1's at `(0, 2)` and `(1, 2)` are covered by a rectangle of area 2.
+* The 1 at `(1, 1)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The 1's at `(0, 0)` and `(0, 2)` are covered by a rectangle of area 3.
+* The 1 at `(1, 1)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+* The 1 at `(1, 3)` is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 30`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either 0 or 1.
+* The input is generated such that there are at least three 1's in `grid`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ // rectangle unit count
+ private lateinit var ruc: Array
+ private var height = 0
+ private var width = 0
+
+ // r0, c0 incl., r1, c1 excl.
+ private fun unitsInRectangle(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int): Int {
+ return ruc[r1][c1] - ruc[r0][c1] - ruc[r1][c0] + ruc[r0][c0]
+ }
+
+ private fun minArea(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int): Int {
+ if (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var minRow = r0
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, minRow + 1, c1) == 0) {
+ minRow++
+ }
+ var maxRow = r1 - 1
+ while (unitsInRectangle(maxRow, c0, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ maxRow--
+ }
+ var minCol = c0
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, c0, r1, minCol + 1) == 0) {
+ minCol++
+ }
+ var maxCol = c1 - 1
+ while (unitsInRectangle(r0, maxCol, r1, c1) == 0) {
+ maxCol--
+ }
+ return (maxRow - minRow + 1) * (maxCol - minCol + 1)
+ }
+
+ private fun minSum2(r0: Int, c0: Int, r1: Int, c1: Int, splitVertical: Boolean): Int {
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ if (splitVertical) {
+ for (c in c0 + 1 until c1) {
+ val a1 = minArea(r0, c0, r1, c)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val a2 = minArea(r0, c, r1, c1)
+ if (a2 != 0) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (r in r0 + 1 until r1) {
+ val a1 = minArea(r0, c0, r, c1)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val a2 = minArea(r, c0, r1, c1)
+ if (a2 != 0) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return min
+ }
+
+ private fun minSum3(
+ firstSplitVertical: Boolean,
+ takeLower: Boolean,
+ secondSplitVertical: Boolean
+ ): Int {
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ if (firstSplitVertical) {
+ for (c in 1 until width) {
+ var a1: Int
+ var a2: Int
+ if (takeLower) {
+ a1 = minArea(0, 0, height, c)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, c, height, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ } else {
+ a1 = minArea(0, c, height, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, 0, height, c, secondSplitVertical)
+ }
+ if (a2 != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (r in 1 until height) {
+ var a1: Int
+ var a2: Int
+ if (takeLower) {
+ a1 = minArea(0, 0, r, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(r, 0, height, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ } else {
+ a1 = minArea(r, 0, height, width)
+ if (a1 == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ a2 = minSum2(0, 0, r, width, secondSplitVertical)
+ }
+ if (a2 != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ min = min(min, (a1 + a2))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return min
+ }
+
+ fun minimumSum(grid: Array): Int {
+ height = grid.size
+ width = grid[0].size
+ ruc = Array(height + 1) { IntArray(width + 1) }
+ for (i in 0 until height) {
+ val gRow = grid[i]
+ val cRow0 = ruc[i]
+ val cRow1 = ruc[i + 1]
+ var c = 0
+ for (j in 0 until width) {
+ c += gRow[j]
+ cRow1[j + 1] = cRow0[j + 1] + c
+ }
+ }
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, true, true))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, true, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(true, false, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, true, true))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, true, false))
+ min = min(min, minSum3(false, false, true))
+ return min
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..10925b16
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3101_3200/s3200_maximum_height_of_a_triangle/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3200\. Maximum Height of a Triangle
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two integers `red` and `blue` representing the count of red and blue colored balls. You have to arrange these balls to form a triangle such that the 1st row will have 1 ball, the 2nd row will have 2 balls, the 3rd row will have 3 balls, and so on.
+
+All the balls in a particular row should be the **same** color, and adjacent rows should have **different** colors.
+
+Return the **maximum** _height of the triangle_ that can be achieved.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
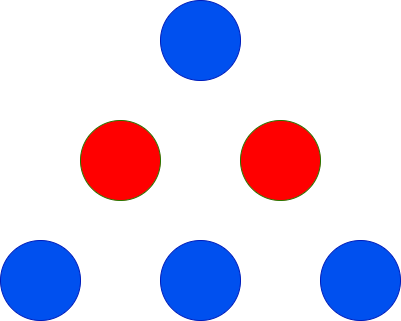
+**Input:** red = 2, blue = 4
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** red = 2, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+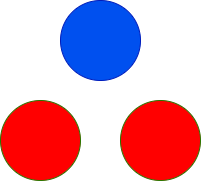
+ The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** red = 1, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** red = 10, blue = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+ The only possible arrangement is shown above.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= red, blue <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ private fun count(v1: Int, v2: Int): Int {
+ var v1 = v1
+ var v2 = v2
+ var ct = 1
+ var flag = true
+ while (true) {
+ if (flag) {
+ if (ct <= v1) {
+ v1 -= ct
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (ct <= v2) {
+ v2 -= ct
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ ct++
+ flag = !flag
+ }
+ return ct - 1
+ }
+
+ fun maxHeightOfTriangle(red: Int, blue: Int): Int {
+ return max(count(red, blue), count(blue, red))
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..adaa0865
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3201_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3201\. Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`.
+
+A subsequence `sub` of `nums` with length `x` is called **valid** if it satisfies:
+
+* `(sub[0] + sub[1]) % 2 == (sub[1] + sub[2]) % 2 == ... == (sub[x - 2] + sub[x - 1]) % 2.`
+
+Return the length of the **longest** **valid** subsequence of `nums`.
+
+A **subsequence** is an array that can be derived from another array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 3, 4]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,1,1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2]`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 3]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 2 * 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 107
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumLength(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var alter = 1
+ var odd = 0
+ var even = 0
+ if (nums[0] % 2 == 0) {
+ even++
+ } else {
+ odd++
+ }
+ var lastodd = nums[0] % 2 != 0
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ val flag = nums[i] % 2 == 0
+ if (flag) {
+ if (lastodd) {
+ alter++
+ lastodd = false
+ }
+ even++
+ } else {
+ if (!lastodd) {
+ alter++
+ lastodd = true
+ }
+ odd++
+ }
+ }
+ return max(alter, max(odd, even))
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ab83c478
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3202_find_the_maximum_length_of_valid_subsequence_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3202\. Find the Maximum Length of Valid Subsequence II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` and a **positive** integer `k`.
+
+A subsequence `sub` of `nums` with length `x` is called **valid** if it satisfies:
+
+* `(sub[0] + sub[1]) % k == (sub[1] + sub[2]) % k == ... == (sub[x - 2] + sub[x - 1]) % k.`
+
+Return the length of the **longest** **valid** subsequence of `nums`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,4,2,3,1,4], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The longest valid subsequence is `[1, 4, 1, 4]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 103
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 107
+* 1 <= k <= 103
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumLength(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ // dp array to store the index against each possible modulo
+ val dp = Array(nums.size + 1) { IntArray(k + 1) }
+ var longest = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ for (j in 0 until i) {
+ // Checking the modulo with each previous number
+ val `val` = (nums[i] + nums[j]) % k
+ // storing the number of pairs that have the same modulo.
+ // it would be one more than the number of pairs with the same modulo at the last
+ // index
+ dp[i][`val`] = dp[j][`val`] + 1
+ // Calculating the max seen till now
+ longest = max(longest, dp[i][`val`])
+ }
+ }
+ // total number of elements in the subsequence would be 1 more than the number of pairs
+ return longest + 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..60664cb8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3203_find_minimum_diameter_after_merging_two_trees/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3203\. Find Minimum Diameter After Merging Two Trees
+
+Hard
+
+There exist two **undirected** trees with `n` and `m` nodes, numbered from `0` to `n - 1` and from `0` to `m - 1`, respectively. You are given two 2D integer arrays `edges1` and `edges2` of lengths `n - 1` and `m - 1`, respectively, where edges1[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the first tree and edges2[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the second tree.
+
+You must connect one node from the first tree with another node from the second tree with an edge.
+
+Return the **minimum** possible **diameter** of the resulting tree.
+
+The **diameter** of a tree is the length of the _longest_ path between any two nodes in the tree.
+
+**Example 1:**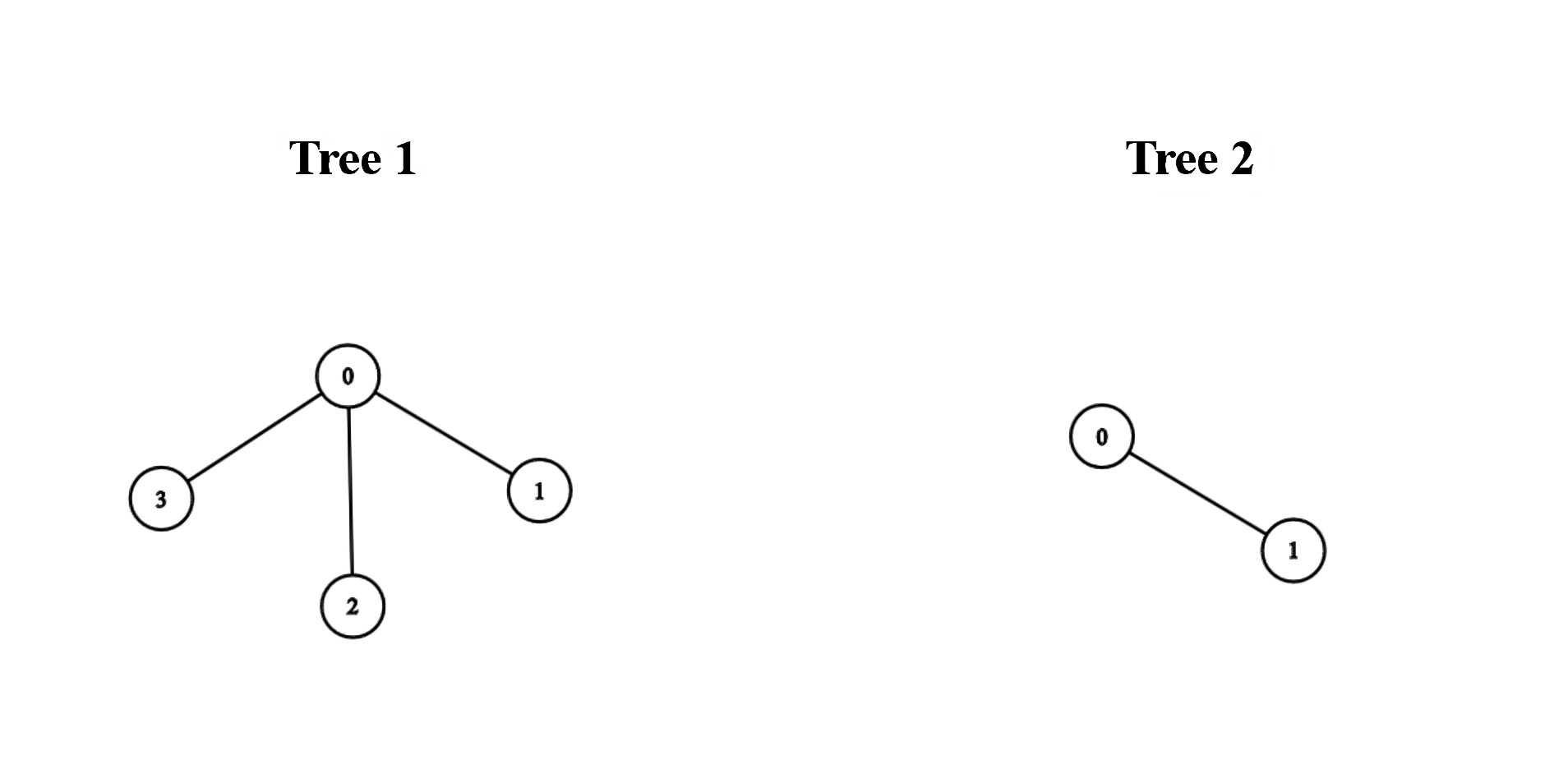
+
+**Input:** edges1 = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], edges2 = \[\[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can obtain a tree of diameter 3 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with any node from the second tree.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+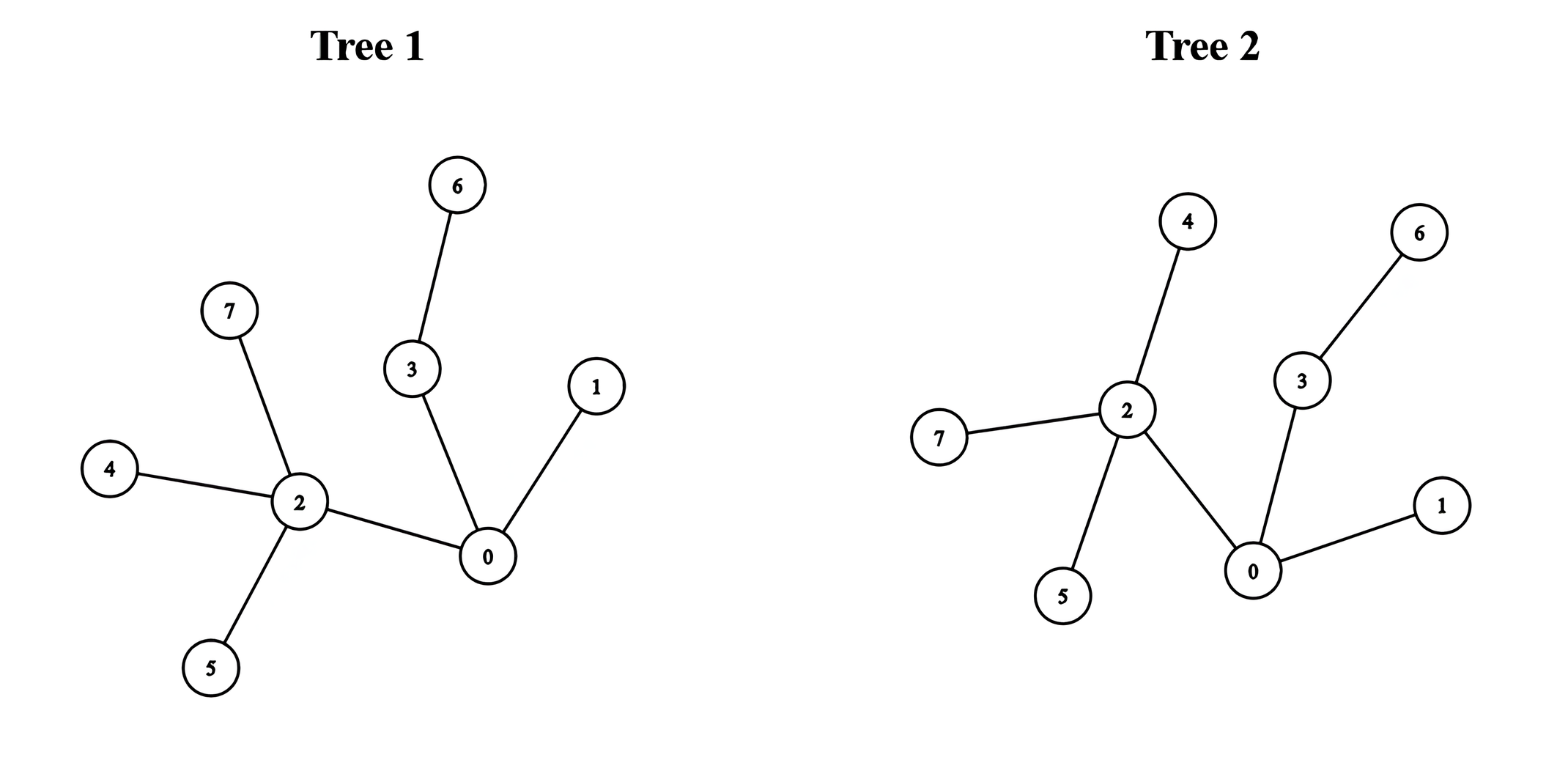
+
+**Input:** edges1 = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]], edges2 = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can obtain a tree of diameter 5 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with node 0 from the second tree.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n, m <= 105
+* `edges1.length == n - 1`
+* `edges2.length == m - 1`
+* `edges1[i].length == edges2[i].length == 2`
+* edges1[i] = [ai, bi]
+* 0 <= ai, bi < n
+* edges2[i] = [ui, vi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi < m
+* The input is generated such that `edges1` and `edges2` represent valid trees.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumDiameterAfterMerge(edges1: Array, edges2: Array): Int {
+ val n = edges1.size + 1
+ val g = packU(n, edges1)
+ val m = edges2.size + 1
+ val h = packU(m, edges2)
+ val d1 = diameter(g)
+ val d2 = diameter(h)
+ var ans = max(d1[0], d2[0])
+ ans = max(
+ ((d1[0] + 1) / 2 + ((d2[0] + 1) / 2) + 1),
+ ans
+ )
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun diameter(g: Array): IntArray {
+ val n = g.size
+ val f0: Int
+ val f1: Int
+ val d01: Int
+ val q = IntArray(n)
+ val ved = BooleanArray(n)
+ var qp = 0
+ q[qp++] = 0
+ ved[0] = true
+ run {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < qp) {
+ val cur = q[i]
+ for (e in g[cur]!!) {
+ if (!ved[e]) {
+ ved[e] = true
+ q[qp++] = e
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ f0 = q[n - 1]
+ val d = IntArray(n)
+ qp = 0
+ ved.fill(false)
+ q[qp++] = f0
+ ved[f0] = true
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < qp) {
+ val cur = q[i]
+ for (e in g[cur]!!) {
+ if (!ved[e]) {
+ ved[e] = true
+ q[qp++] = e
+ d[e] = d[cur] + 1
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ f1 = q[n - 1]
+ d01 = d[f1]
+ return intArrayOf(d01, f0, f1)
+ }
+
+ private fun packU(n: Int, ft: Array): Array {
+ val g = arrayOfNulls(n)
+ val p = IntArray(n)
+ for (u in ft) {
+ p[u[0]]++
+ p[u[1]]++
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ g[i] = IntArray(p[i])
+ }
+ for (u in ft) {
+ g[u[0]]!![--p[u[0]]] = u[1]
+ g[u[1]]!![--p[u[1]]] = u[0]
+ }
+ return g
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..814bee47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3206_alternating_groups_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3206\. Alternating Groups I
+
+Easy
+
+There is a circle of red and blue tiles. You are given an array of integers `colors`. The color of tile `i` is represented by `colors[i]`:
+
+* `colors[i] == 0` means that tile `i` is **red**.
+* `colors[i] == 1` means that tile `i` is **blue**.
+
+Every 3 contiguous tiles in the circle with **alternating** colors (the middle tile has a different color from its **left** and **right** tiles) is called an **alternating** group.
+
+Return the number of **alternating** groups.
+
+**Note** that since `colors` represents a **circle**, the **first** and the **last** tiles are considered to be next to each other.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
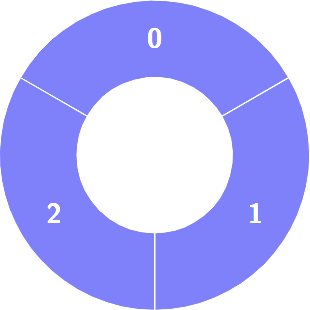
+**Input:** colors = [1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Example 2:**
+
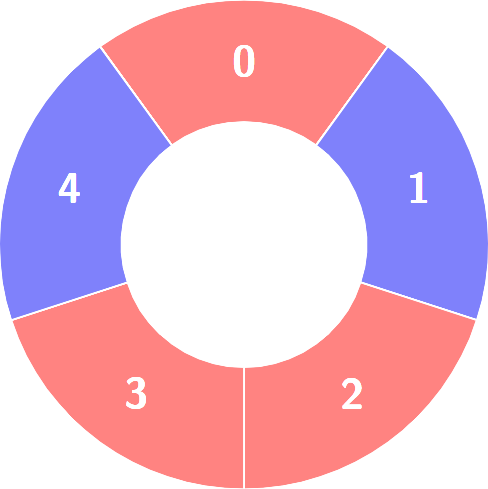
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+Alternating groups:
+
+**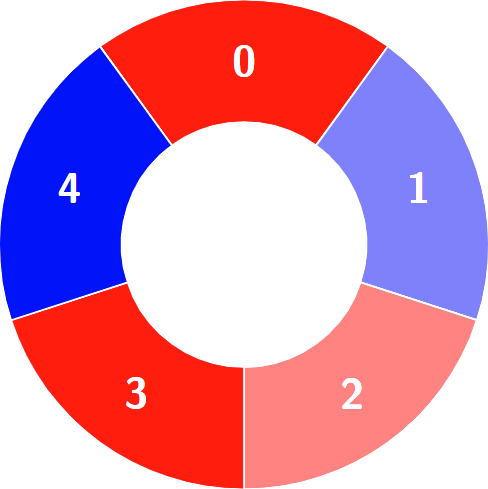**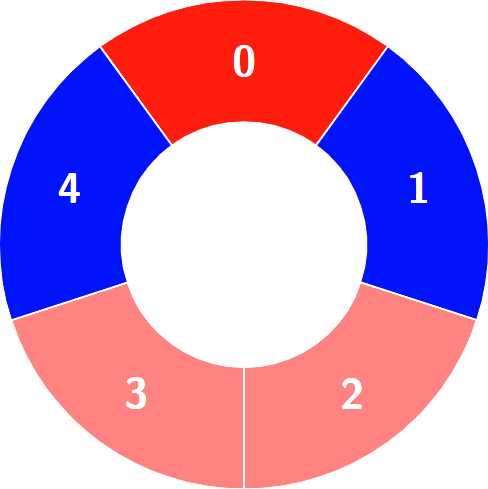**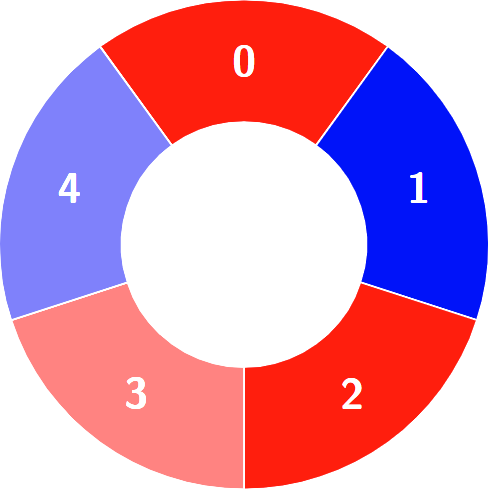**
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= colors.length <= 100`
+* `0 <= colors[i] <= 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = colors.size
+ var count = 0
+ if (colors[n - 1] != colors[0] && colors[0] != colors[1]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ if (colors[n - 1] != colors[0] && colors[n - 1] != colors[n - 2]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until n - 1) {
+ if (colors[i] != colors[i - 1] && colors[i] != colors[i + 1]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..32a78c68
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3207_maximum_points_after_enemy_battles/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3207\. Maximum Points After Enemy Battles
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `enemyEnergies` denoting the energy values of various enemies.
+
+You are also given an integer `currentEnergy` denoting the amount of energy you have initially.
+
+You start with 0 points, and all the enemies are unmarked initially.
+
+You can perform **either** of the following operations **zero** or multiple times to gain points:
+
+* Choose an **unmarked** enemy, `i`, such that `currentEnergy >= enemyEnergies[i]`. By choosing this option:
+ * You gain 1 point.
+ * Your energy is reduced by the enemy's energy, i.e. `currentEnergy = currentEnergy - enemyEnergies[i]`.
+* If you have **at least** 1 point, you can choose an **unmarked** enemy, `i`. By choosing this option:
+ * Your energy increases by the enemy's energy, i.e. `currentEnergy = currentEnergy + enemyEnergies[i]`.
+ * The enemy `i` is **marked**.
+
+Return an integer denoting the **maximum** points you can get in the end by optimally performing operations.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** enemyEnergies = [3,2,2], currentEnergy = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The following operations can be performed to get 3 points, which is the maximum:
+
+* First operation on enemy 1: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 1`, and `currentEnergy = 0`.
+* Second operation on enemy 0: `currentEnergy` increases by 3, and enemy 0 is marked. So, `points = 1`, `currentEnergy = 3`, and marked enemies = `[0]`.
+* First operation on enemy 2: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 2`, `currentEnergy = 1`, and marked enemies = `[0]`.
+* Second operation on enemy 2: `currentEnergy` increases by 2, and enemy 2 is marked. So, `points = 2`, `currentEnergy = 3`, and marked enemies = `[0, 2]`.
+* First operation on enemy 1: `points` increases by 1, and `currentEnergy` decreases by 2. So, `points = 3`, `currentEnergy = 1`, and marked enemies = `[0, 2]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** enemyEnergies = [2], currentEnergy = 10
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Performing the first operation 5 times on enemy 0 results in the maximum number of points.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= enemyEnergies.length <= 105
+* 1 <= enemyEnergies[i] <= 109
+* 0 <= currentEnergy <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumPoints(enemyEnergies: IntArray, currentEnergy: Int): Long {
+ val n = enemyEnergies.size
+ var min = enemyEnergies[0]
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ min = min(min.toDouble(), enemyEnergies[i].toDouble()).toInt()
+ }
+ if (currentEnergy == 0 || currentEnergy < min) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var sum = currentEnergy.toLong()
+ for (i in n - 1 downTo 0) {
+ sum += enemyEnergies[i].toLong()
+ }
+ sum -= min.toLong()
+ return sum / min
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a60f210e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3208_alternating_groups_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3208\. Alternating Groups II
+
+Medium
+
+There is a circle of red and blue tiles. You are given an array of integers `colors` and an integer `k`. The color of tile `i` is represented by `colors[i]`:
+
+* `colors[i] == 0` means that tile `i` is **red**.
+* `colors[i] == 1` means that tile `i` is **blue**.
+
+An **alternating** group is every `k` contiguous tiles in the circle with **alternating** colors (each tile in the group except the first and last one has a different color from its **left** and **right** tiles).
+
+Return the number of **alternating** groups.
+
+**Note** that since `colors` represents a **circle**, the **first** and the **last** tiles are considered to be next to each other.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
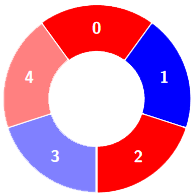
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,1,0], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**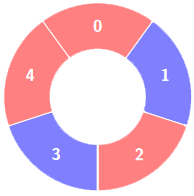**
+
+Alternating groups:
+
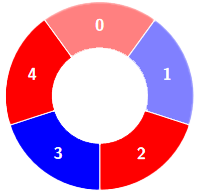
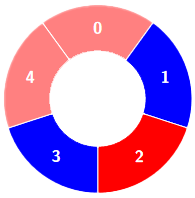
+
+
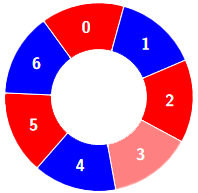
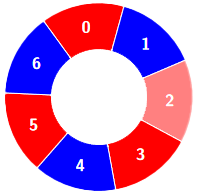
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**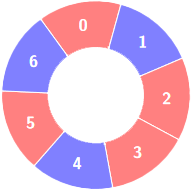**
+
+Alternating groups:
+
+
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [1,1,0,1], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= colors.length <= 105
+* `0 <= colors[i] <= 1`
+* `3 <= k <= colors.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var i = 0
+ var len = 0
+ var total = 0
+ while (i < colors.size - 1) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ if (colors[j] != colors[i]) {
+ len = 2
+ j++
+ while (j < colors.size && colors[j] != colors[j - 1]) {
+ j++
+ len++
+ }
+ if (j == colors.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ total += max(0, (len - k + 1))
+ }
+ i = j
+ len = 0
+ }
+ if (colors[0] != colors[colors.size - 1]) {
+ len = if (len == 0) 2 else len + 1
+ var j = 1
+ while (j < colors.size && colors[j] != colors[j - 1]) {
+ j++
+ len++
+ }
+ if (j >= k) {
+ len -= (j - k + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ total += max(0, (len - k + 1))
+ return total
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dbb445b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3209_number_of_subarrays_with_and_value_of_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3209\. Number of Subarrays With AND Value of K
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `k`, return the number of subarrays of `nums` where the bitwise `AND` of the elements of the subarray equals `k`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All subarrays contain only 1's.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,2], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Subarrays having an `AND` value of 1 are: [**1**,1,2], [1,**1**,2], [**1,1**,2].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Subarrays having an `AND` value of 2 are: [1,**2**,3], [1,**2,3**].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 0 <= nums[i], k <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countSubarrays(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
+ var ans: Long = 0
+ var left = 0
+ var right = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ val x = nums[i]
+ var j = i - 1
+ while (j >= 0 && (nums[j] and x) != nums[j]) {
+ nums[j] = nums[j] and x
+ j--
+ }
+ while (left <= i && nums[left] < k) {
+ left++
+ }
+ while (right <= i && nums[right] <= k) {
+ right++
+ }
+ ans += (right - left).toLong()
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..be165af5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3210_find_the_encrypted_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3210\. Find the Encrypted String
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` and an integer `k`. Encrypt the string using the following algorithm:
+
+* For each character `c` in `s`, replace `c` with the kth character after `c` in the string (in a cyclic manner).
+
+Return the _encrypted string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "dart", k = 3
+
+**Output:** "tdar"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* For `i = 0`, the 3rd character after `'d'` is `'t'`.
+* For `i = 1`, the 3rd character after `'a'` is `'d'`.
+* For `i = 2`, the 3rd character after `'r'` is `'a'`.
+* For `i = 3`, the 3rd character after `'t'` is `'r'`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaa", k = 1
+
+**Output:** "aaa"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+As all the characters are the same, the encrypted string will also be the same.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* 1 <= k <= 104
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun getEncryptedString(s: String, k: Int): String {
+ var k = k
+ val n = s.length
+ k %= n
+ val str = StringBuilder(s.substring(k, n))
+ str.append(s.substring(0, k))
+ return str.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43dcc82a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3211_generate_binary_strings_without_adjacent_zeros/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3211\. Generate Binary Strings Without Adjacent Zeros
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a positive integer `n`.
+
+A binary string `x` is **valid** if all substrings of `x` of length 2 contain **at least** one `"1"`.
+
+Return all **valid** strings with length `n`**,** in _any_ order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** ["010","011","101","110","111"]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The valid strings of length 3 are: `"010"`, `"011"`, `"101"`, `"110"`, and `"111"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** ["0","1"]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The valid strings of length 1 are: `"0"` and `"1"`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 18`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun validStrings(n: Int): List {
+ val strings: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ dfs(n, StringBuilder(), strings)
+ return strings
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(n: Int, build: StringBuilder, strings: MutableList) {
+ if (build.length == n) {
+ strings.add(build.toString())
+ return
+ }
+ // need to add a one
+ if (build.isNotEmpty() && build[build.length - 1] == '0') {
+ build.append('1')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ // undo for backtracking
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ return
+ }
+ // choose to append a one
+ build.append('1')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ // choose to append a zero
+ build.append('0')
+ dfs(n, build, strings)
+ build.setLength(build.length - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7209ad18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3212_count_submatrices_with_equal_frequency_of_x_and_y/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3212\. Count Submatrices With Equal Frequency of X and Y
+
+Medium
+
+Given a 2D character matrix `grid`, where `grid[i][j]` is either `'X'`, `'Y'`, or `'.'`, return the number of submatrices that contains:
+
+* `grid[0][0]`
+* an **equal** frequency of `'X'` and `'Y'`.
+* **at least** one `'X'`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\["X","Y","."],["Y",".","."]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**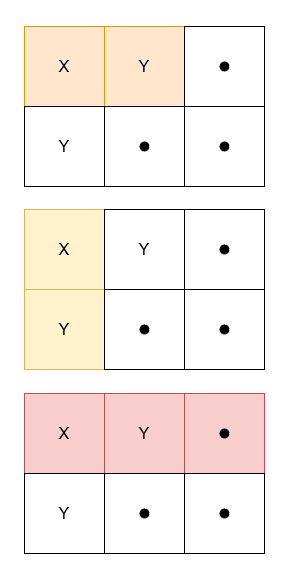**
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\["X","X"],["X","Y"]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No submatrix has an equal frequency of `'X'` and `'Y'`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[".","."],[".","."]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No submatrix has at least one `'X'`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 1000`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either `'X'`, `'Y'`, or `'.'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfSubmatrices(grid: Array): Int {
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ var ans = 0
+ val row = Array(n) { IntArray(2) }
+ for (chars in grid) {
+ val count = IntArray(2)
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (chars[j] != '.') {
+ count[chars[j].code - 'X'.code]++
+ }
+ row[j][0] += count[0]
+ row[j][1] += count[1]
+ if (row[j][0] > 0 && row[j][0] == row[j][1]) {
+ ans++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c14d31ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3213_construct_string_with_minimum_cost/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3213\. Construct String with Minimum Cost
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a string `target`, an array of strings `words`, and an integer array `costs`, both arrays of the same length.
+
+Imagine an empty string `s`.
+
+You can perform the following operation any number of times (including **zero**):
+
+* Choose an index `i` in the range `[0, words.length - 1]`.
+* Append `words[i]` to `s`.
+* The cost of operation is `costs[i]`.
+
+Return the **minimum** cost to make `s` equal to `target`. If it's not possible, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = "abcdef", words = ["abdef","abc","d","def","ef"], costs = [100,1,1,10,5]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The minimum cost can be achieved by performing the following operations:
+
+* Select index 1 and append `"abc"` to `s` at a cost of 1, resulting in `s = "abc"`.
+* Select index 2 and append `"d"` to `s` at a cost of 1, resulting in `s = "abcd"`.
+* Select index 4 and append `"ef"` to `s` at a cost of 5, resulting in `s = "abcdef"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = "aaaa", words = ["z","zz","zzz"], costs = [1,10,100]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+It is impossible to make `s` equal to `target`, so we return -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= target.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= words.length == costs.length <= 5 * 104
+* `1 <= words[i].length <= target.length`
+* The total sum of `words[i].length` is less than or equal to 5 * 104.
+* `target` and `words[i]` consist only of lowercase English letters.
+* 1 <= costs[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ private class ACAutomaton {
+ class Node {
+ var key: Char = 0.toChar()
+ var `val`: Int? = null
+ var len: Int = 0
+ val next: Array = arrayOfNulls(26)
+ var suffix: Node? = null
+ var output: Node? = null
+ var parent: Node? = null
+ }
+
+ fun build(patterns: Array, values: IntArray): Node {
+ val root = Node()
+ root.suffix = root
+ root.output = root
+ for (i in patterns.indices) {
+ put(root, patterns[i], values[i])
+ }
+ for (i in root.next.indices) {
+ if (root.next[i] == null) {
+ root.next[i] = root
+ } else {
+ root.next[i]!!.suffix = root
+ }
+ }
+ return root
+ }
+
+ private fun put(root: Node, s: String, `val`: Int) {
+ var node: Node? = root
+ for (c in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (node!!.next[c.code - 'a'.code] == null) {
+ node.next[c.code - 'a'.code] = Node()
+ node.next[c.code - 'a'.code]!!.parent = node
+ node.next[c.code - 'a'.code]!!.key = c
+ }
+ node = node.next[c.code - 'a'.code]
+ }
+ if (node!!.`val` == null || node.`val`!! > `val`) {
+ node.`val` = `val`
+ node.len = s.length
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun getOutput(node: Node?): Node? {
+ if (node!!.output == null) {
+ val suffix = getSuffix(node)
+ node.output = if (suffix!!.`val` != null) suffix else getOutput(suffix)
+ }
+ return node.output
+ }
+
+ fun go(node: Node?, c: Char): Node? {
+ if (node!!.next[c.code - 'a'.code] == null) {
+ node.next[c.code - 'a'.code] = go(getSuffix(node), c)
+ }
+ return node.next[c.code - 'a'.code]
+ }
+
+ private fun getSuffix(node: Node?): Node? {
+ if (node!!.suffix == null) {
+ node.suffix = go(getSuffix(node.parent), node.key)
+ if (node.suffix!!.`val` != null) {
+ node.output = node.suffix
+ } else {
+ node.output = node.suffix!!.output
+ }
+ }
+ return node.suffix
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun minimumCost(target: String, words: Array, costs: IntArray): Int {
+ val ac = ACAutomaton()
+ val root = ac.build(words, costs)
+ val dp = IntArray(target.length + 1)
+ dp.fill(Int.MAX_VALUE / 2)
+ dp[0] = 0
+ var node: ACAutomaton.Node? = root
+ for (i in 1 until dp.size) {
+ node = ac.go(node, target[i - 1])
+ var temp = node
+ while (temp != null && temp !== root) {
+ if (temp.`val` != null && dp[i - temp.len] < Int.MAX_VALUE / 2) {
+ dp[i] = min(dp[i], (dp[i - temp.len] + temp.`val`!!))
+ }
+ temp = ac.getOutput(temp)
+ }
+ }
+ return if (dp[dp.size - 1] >= Int.MAX_VALUE / 2) -1 else dp[dp.size - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file