前端应用、微服务的发展,使得模块化的概念越来越重要。 这也不可避免的会产生再不同的项目会有很多功能相似,甚至完全相同。所以跨应用的代码共享尤为重要,之前我们处理这种问题往往采用,
1、功能相似的页面直接赋值方便,不用费脑力直接复用。但这样就会导致项目中代码的复用性低,代码冗余多等问题出现。
2、微服务的出现,很多业务一般使用 npm 发布的形式管理公共包。我们 EDSP 前端项目也是用了 npm 插件形式;但在使用下来我们发现 npm 比较适合对业务逻辑耦合小,完全工具类的包。而对于业务逻辑比较繁重,更新频繁的模块,npm 包使用就会存在迭代需要更新版本的问题,。 并且 npm 包对于业务代码的拆分有工作量,维护成本相对较大,代码有一定质量要求,否则就会导致模块过大的问题。
3、Module Federation 解决了跨应用代码共享
Module federation (模块联邦)使 JavaScript 应用得以从另一个 JavaScript 应用中动态地加载代码 —— 同时共享依赖。
通过细化功能模块、组件复用、共享第三方库、runtime dependencies 线上加载 npm 包等,可以更好的服务于多页应用、微前端等开发模式。
Module Federation 整体是通过 ModuleFederationPlugin 这个插件串联起来的。
提供方配置示例
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
// 应用名称,调用方使用
name: 'vueAppOne',
// 调用方引用的文件名称
filename: 'app1.js',
library: { type: 'var', name: 'vueAppOne' },
exposes: {
//模块名称
'./untils': './src/untils/count.js',
},
})配置属性:
name,必须,唯一 ID,作为输出的模块名,使用的时通过 name/{name}/name/{expose} 的方式使用;
library,必须,其中这里的 name 为作为 umd 的 name;
remotes,可选,作为引用方最关键的配置项,用于声明需要引用的远程资源包的名称与模块名称,作为 Host 时,去消费哪些 Remote;
exposes,可选,表示作为 Remote 时,export 哪些属性被消费;
shared,可选若是配置了这个属性。webpack 在加载的时候会先判断本地应用是否存在对应的包,若是不存在,则加载远程应用的依赖包。 以 app1 来讲,由于它是一个远程应用,配置了["vue"] ,而它被 app1 所消费,因此 webpack 会先查找 app1 是否存在这个包,若是不存在就使用 app2 自带包。 app2(app2 之后会以案例的形式展现)里面一样申明了这两个参数,由于 app2 是本地应用,因此会直接用 app2 的依赖 在引用远程资源的项目中使用时,需要先远程资源入口文件引入,可以异步加载,也可以使用 script 标签引入。
消费方配置示例:
//-----webpack配置:-----
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
// 导入模块
remotes: {
// '导入别名':'远程应用名称/远程应用地址/导入文件的名称'
mfpVueAppOne: 'vueAppOne@http://localhost:3001/app1.js',
},
})
//-----vue项目中代码-----
//调用app1的模块
import('mfpVueAppOne/untils').then((res) => {
res.default(31, 2)
})1.创建两个 vue 项目
我们使用 webpack 单独部署两个 Vue 项目,目录结构如下:
Vue-app1 的 webpacl.config.js:
/*
* @Descripttion:
* @version:
* @Author: Jason chen
* @Date: 2021-08-18 14:09:16
* @LastEditors: sueRimn
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-19 18:16:41
*/
const { resolve } = require('path')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const VueLoaderPlugin = require('vue-loader/lib/plugin')
const ProgressBarPlugin = require('progress-bar-webpack-plugin')
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
const address = require('address')
const port = 3001
// 模块联邦的插件
const ModuleFederationPlugin =
require('webpack').container.ModuleFederationPlugin
const result = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: resolve(__dirname, 'output'),
filename: 'bundle.js',
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/i,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'],
},
{
test: /\.less$/i,
use: [
// compiles Less to CSS
'style-loader',
'css-loader',
'less-loader',
],
},
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
preserveWhitepace: true,
extractCSS: true,
cssModules: {},
//hotReload: false,//根据环境变量生成
},
},
],
},
devServer: {
contentBase: resolve(__dirname, 'output'),
port,
quiet: true, // necessary for FriendlyErrorsPlugin
},
plugins: [
new ProgressBarPlugin(),
new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({
compilationSuccessInfo: {
messages: [
` App running at:`,
` - Local: http://localhost:${port}`,
` - Network: http://${address.ip()}:${port}`,
],
},
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './public/index.html',
}),
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
// 应用名称,调用方使用
name: 'vueAppOne',
//调用放引用的文件名称
filename: 'app1.js',
exposes: {
//模块名称
'./untils': './src/untils/count.js',
'./appOneChildren': './src/App.vue',
},
}),
],
}
module.exports = resultVue-app2 的 webpacl.config.js:
/*
* @Descripttion:
* @version:
* @Author: Jason chen
* @Date: 2021-08-18 14:22:19
* @LastEditors: Jason chen
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-23 11:40:23
*/
const { resolve } = require('path')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const VueLoaderPlugin = require('vue-loader/lib/plugin')
const ProgressBarPlugin = require('progress-bar-webpack-plugin')
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const address = require('address')
// 模块联邦的插件
const ModuleFederationPlugin =
require('webpack').container.ModuleFederationPlugin
const port = 3002
const result = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: resolve(__dirname, 'deploy'),
filename: '[name].js',
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/i,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'],
},
{
test: /\.less$/i,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'less-loader'],
},
{
test: /\.vue$/i,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
preserveWhitepace: true,
extractCSS: true,
cssModules: {},
//hotReload: false,//根据环境变量生成
},
},
],
},
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: resolve(__dirname, './public'),
to: '',
},
],
}),
new ProgressBarPlugin(),
new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({
compilationSuccessInfo: {
messages: [
` App running at:`,
` - Local: http://localhost:${port}`,
` - Network: http://${address.ip()}:${port}`,
],
},
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './/public/index.ejs',
}),
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
// 应用名称,调用方使用
name: 'vueAppTwo',
//调用放引用的文件名称
filename: 'app2.js',
// 导入模块
remotes: {
// '导入别名':'远程应用名称/远程应用地址/导入文件的名称'
mfpVueAppOne: 'vueAppOne@http://localhost:3001/app1.js',
// 'mfpVueAppOne': 'vueAppOne@http://localhost:3002/output/app1.js'
},
}),
],
devServer: {
quiet: true, // necessary for FriendlyErrorsPlugin
contentBase: resolve(__dirname, 'deploy'),
port,
},
}
module.exports = resultpackage.json(app1 与 app2 一致)
{
"name": "vue-app2",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development webpack serve",
"build": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack "
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"address": "^1.1.2",
"cross-env": "^7.0.3",
"css-loader": "^6.2.0",
"friendly-errors-webpack-plugin": "^1.7.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^5.3.2",
"less": "^4.1.1",
"less-loader": "^10.0.1",
"progress-bar-webpack-plugin": "^2.1.0",
"style-loader": "^3.2.1",
"url-loader": "^4.1.1",
"vue": "^2.6.14",
"vue-loader": "^15.9.8",
"vue-template-compiler": "^2.6.14",
"webpack": "^5.50.0",
"webpack-cli": "^4.8.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^3.11.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"copy-webpack-plugin": "^9.0.1",
"vue-i18n": "^8.25.0"
}
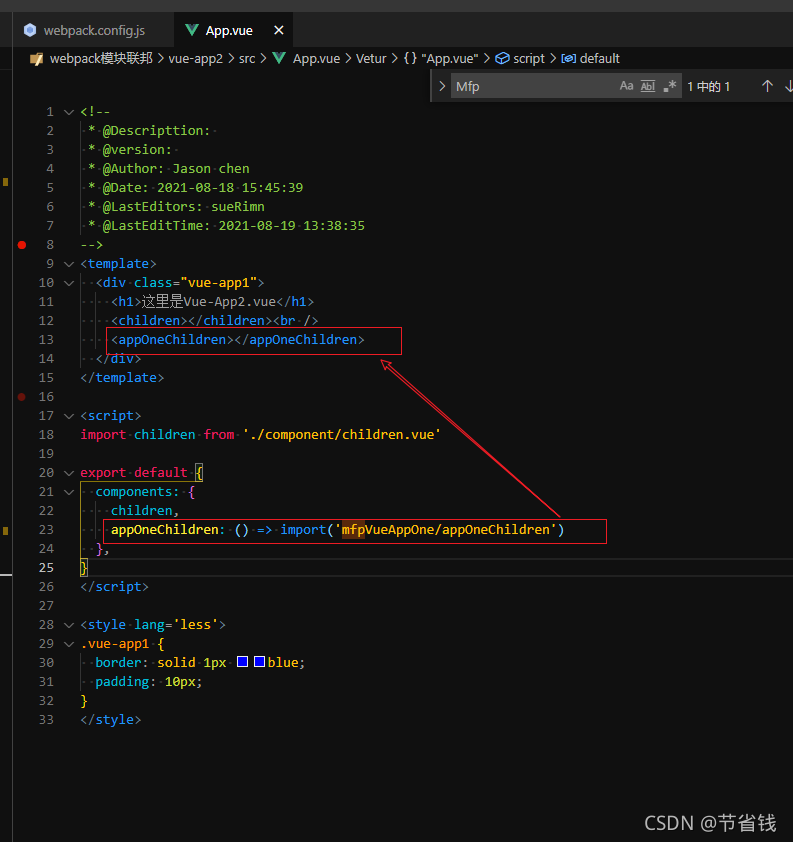
}我们在 app2 中引入 app1 共享的 appOneChildren 组件:
分别在 app1 和 app2 的终端中执行:
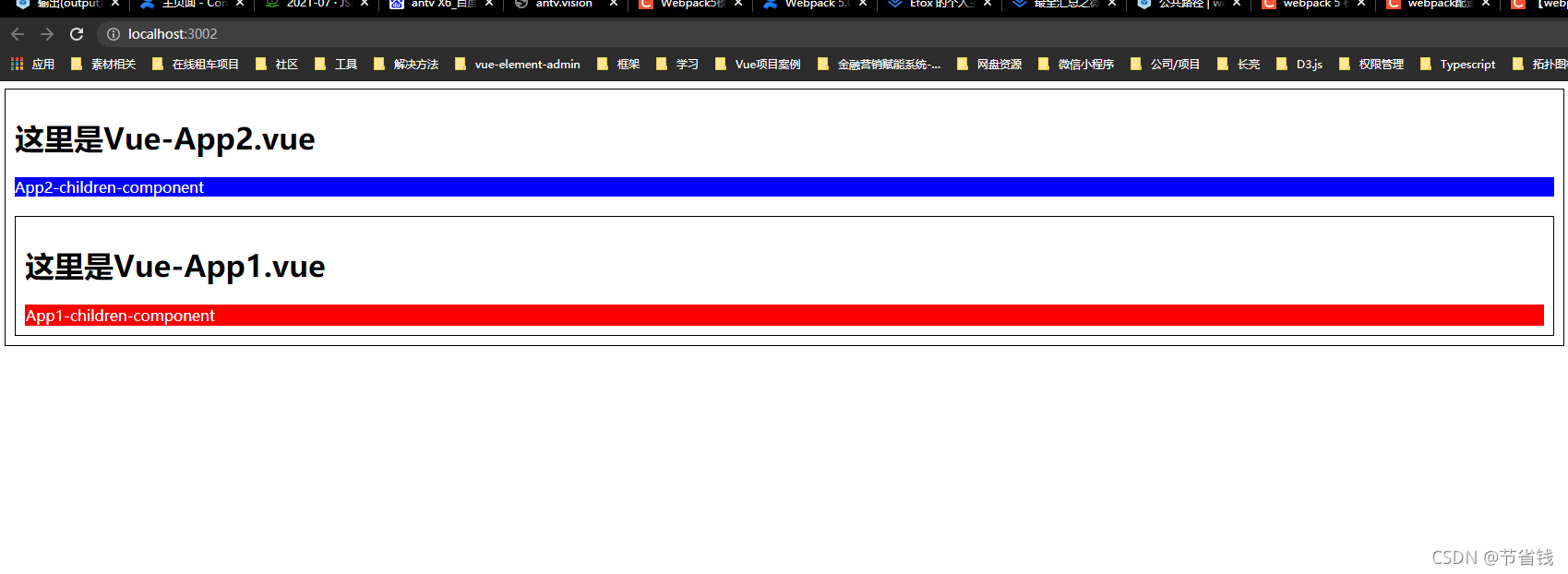
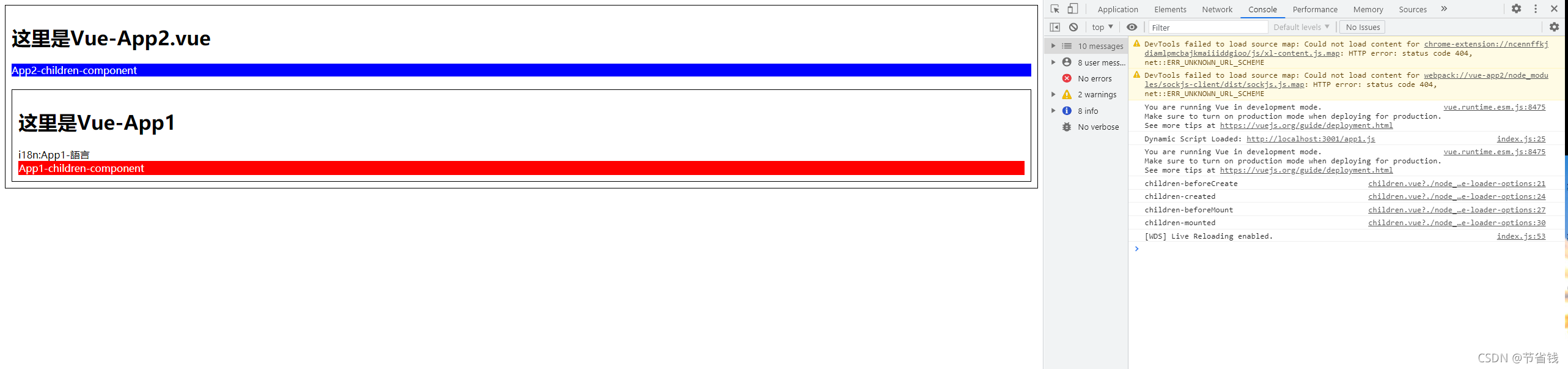
yarn devapp2 运行效果:
这样我们就成功从 app2 成功引用了 app1 共享出来的代码,并成功运用到 app2 中了
如上述所说我们通过 webpack-dev-serve 启动了两个前端项目,并且通过模块联邦共享出来了他们各自的代码模块,但是我们能否实现在前端项目打包后,实现模块联邦呢?
操作步骤:
1.我们先将 app1 进行打包,我们在 app1 目录中执行
webpack2.我们先将 app1 打包生成的 output 目录复制到 app2 中的 public 目录中(让 app2 通过 webpack-dev-serve 跑起来时可以拿到 app1 打包后的资源)
3.1 我们先单独将 app2 前端用 webpack-dev-serve 跑起来,看看是否能拿得到 public 中的 app1 资源:
前置工作:因为我们在 app2 中是要获取 app1 共享出来的代码的,而现在 app1 打包后的代码保存在 app2 的 public 目录中,所以 app2 的 webpack 中消费 app1 的地址需要修改为 app2 它自己的地址
'mfpVueAppOne': vueAppOne@http://localhost:${port}/output/app1.js
运行 app2:
由图可见,此方案是可以行的,我们只需要可以访问 app1 的资源即可使用 app1 通过模块联邦分享过来的代码了
1.我们 app2 项目在线时可以拿到 app1 的资源了;现在我们尝试打包 app2
前置工作:因为我们在 app2 中是要获取 app1 共享出来的代码的,而现在 app1 打包后的代码保存在 app2 的 public 目录中,所以 app2 的 webpack 中消费 app1 的地址需要修改为 app2 它自己的地址
'mfpVueAppOne': vueAppOne@./output/app1.js
2.在 app2 根目录执行
webpack4.我们在 app2 中跑一个本地的 node 服务访问 deploy 中的 index.html 看看是否正常:
web-serve/index.js 文件:
/*
* @Descripttion:
* @version:
* @Author: Jason chen
* @Date: 2021-08-20 15:31:00
* @LastEditors: Jason chen
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-23 13:52:39
*/
const express = require('express')
const expressStaticGzip = require('express-static-gzip')
const app = express()
app.use(
expressStaticGzip('../', {
maxAge: '3d',
setHeaders: setCustomCacheControl,
})
)
function setCustomCacheControl(res, currentFilePath, stat) {
if (currentFilePath.match(/\index\.html$/)) {
// Custom Cache-Control for HTML files
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-cache')
}
}
app.use(express.static('../deploy'))
app.listen(9901, (req, res) => {
console.log(req, res)
console.log('启动成功,请通过localhost:9901访问')
})5.在 web-serve 目录中执行
node index.js- 运行效果
由图可见,此方案是可以行的,及时 app2 项目已经被打包成静态资源了,app2 中只需要可以访问 app1 的资源即可使用 app1 通过模块联邦分享过来的代码了
1.我们在 app1 中使用 vue-i18n,app2 中不开启 vue-i18n,查看效果
app1 中国际化使用正常
2.app2 中暂不使用 vue-i18n 并在 app2 中引入 app1 通过模块联邦分享的代码
3.我们发现 app2 中报错了,$t 未定义,所以 app2 在 app1 中运行时,所使用的插件或其他依赖是需要消费方提供的,
3.1 我们在 app2 中安装 vue-i18n 并注册
3.2 并且 app1 它也把自己用到的国际化文件也导出并合到 app2 的 vue-i18n 的语言库里去
除了前面提到的模块引入和模块暴露相关的配置外,还有个 shared 配置,主要是用来避免项目出现多个公共依赖。
例如,我们当前的 app1,已经引入了一个 vue-i18n 和 Vue,而 app2 暴露的组件也依赖了 vue-i18n 和 Vue。如果不解决这个问题,app1 就会加载两个 vue-i18n 和 Vue 库。影响页面性能。
所以,我们在使用 Module Federation 的时候一定要记得,将公共依赖配置到 shared 中。
4.1 接下来,我们在浏览器打开 app1,在 Chrome 的 network 面板中,可以看到 app1 直接使用了项目 B 的 vue-i18n。
4.2 我们在 app1 处配置 shared:
4.3 重新运行 app1 项目,在 app2 页面中查看 netWork:
我们可以看到如果提供方应用配置了 shared 之后,消费方就不会去下载 vue-i18n 和 Vue 这两个库了
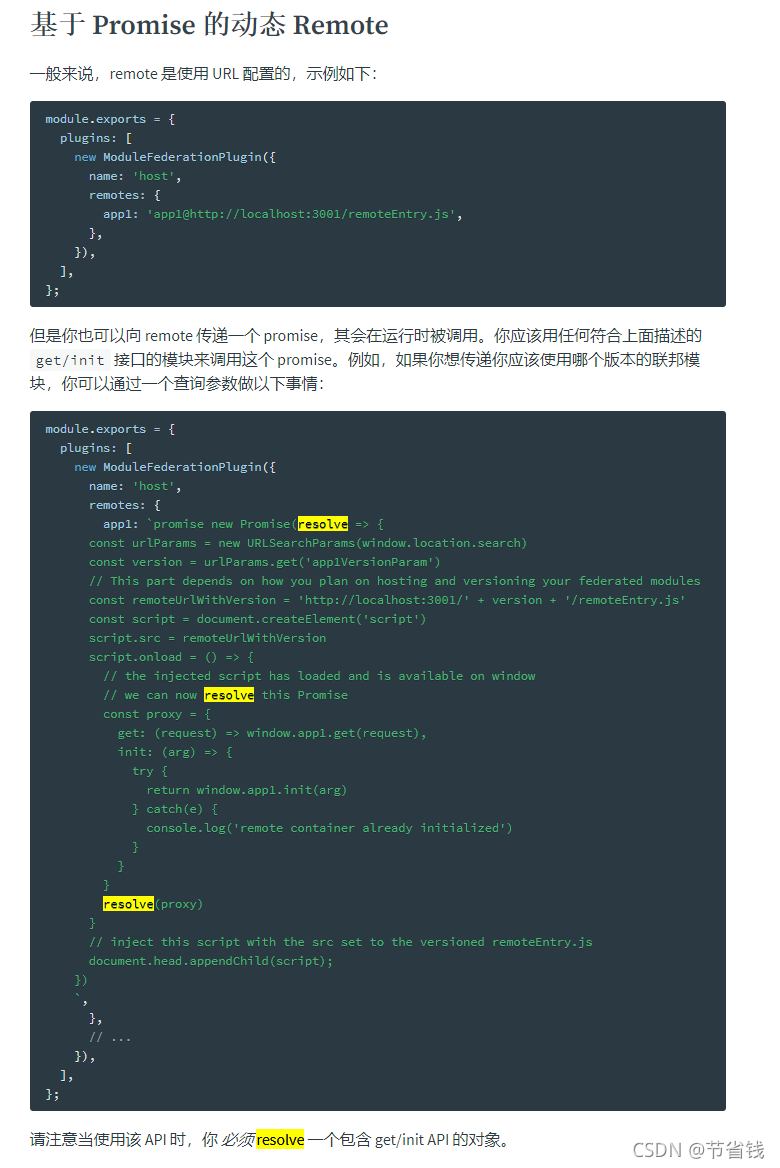
第一步:我们在 webpack 的官网文档中可以看到,我们模块联邦可以动态的加载远端的代码资源:
关键代码:
new Promise((resolve) => {
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search)
const version = urlParams.get('app1VersionParam')
// 这一部分取决于您计划如何托管和版本化您的联邦模块
const remoteUrlWithVersion =
'http://localhost:3001/' + version + '/remoteEntry.js'
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = remoteUrlWithVersion
script.onload = () => {
//注入的脚本已加载,可在Windows上使用
const proxy = {
get: (request) => window.app1.get(request),
init: (arg) => {
try {
return window.app1.init(arg)
} catch (e) {
console.log('remote container already initialized')
}
},
}
resolve(proxy)
}
// 将 script设置为 versioned 注入此脚本 remoteEntry.js
document.head.appendChild(script)
})这一步使我们通过 script 标签成功注入远端联邦模块的入口 remoteEntry.js ,
第二步:我们需要加载远端联邦模块的组件(容器):
关键代码:
function loadComponent(scope, module) {
return async () => {
// 初始化共享作用域(shared scope)用提供的已知此构建和所有远程的模块填充它
await __webpack_init_sharing__('default')
const container = window[scope] // 或从其他地方获取容器
// 初始化容器 它可能提供共享模块
await container.init(__webpack_share_scopes__.default)
const factory = await window[scope].get(module)
const Module = factory()
return Module
}
}第一步和第二步汇总:
export async function loadRemoteComponent(config) {
return loadScript(config).then(() => loadComponentByWebpack(config))
}
function loadScript(config) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = config.url
script.type = 'text/javascript'
script.async = true
script.onload = () => {
console.log(`Dynamic Script Loaded: ${config.url}`)
document.head.removeChild(script)
resolve()
}
script.onerror = () => {
console.error(`Dynamic Script Error: ${config.url}`)
document.head.removeChild(script)
reject()
}
document.head.appendChild(script)
})
}
async function loadComponent({ scope, module }) {
// 初始化共享作用域,这将使用此构建和所有远程提供的已知模块填充它
await __webpack_init_sharing__('default')
const container = window[scope] // 获取容器
// 初始化容器,它可以提供共享模块
await container.init(__webpack_share_scopes__.default)
const factory = await window[scope].get(module)
return factory()
}我们先观察到这个 loadRemoteComponent 方法,它内部 return 了获取到的远程组件的数据,往下看这个 loadScript 方法,它返回了一个 Promise,内部的代码我们稍微瞄一眼就知道这里是在使用 js 动态创建 script 标签的方式来加载一个远程 js 文件,当加载完毕时,将这个标签从页面中移除,然后结束。
当 js 文件加载完毕之后,页面中就拿到了远程项目暴露的组件信息,这个时候,我们就能使用 loadComponent 来加载指定的组件了,这个函数中主要就是初始化远程组件所需的环境,并根据我们传入的 module,从相关作用域中查到到对应的模块进行返回;
在 vue2 中使用:
<template>
<div class="vue-app1">
<h1>这里是Vue-App2.vue</h1>
<children ref="children"></children><br />
<appOneChildren></appOneChildren>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import children from './component/children.vue'
import { loadRemoteComponent } from './untils/index.js'
export default {
components: {
children,
appOneChildren: async () => {
const app1 = await loadRemoteComponent({
url: 'http://localhost:3001/app1.js',
scope: 'vueAppOne',
module: './appOneChildren',
})
return app1
},
},
}
</script>效果:
简单理解:
url:就是我们模块联邦提供方的入口文件的地址;
scope:就是我们提供方模块联邦中 name 的值;
module:就是提供方在模块联邦中 exposes 中的 key;
如下是 app1(提供方)中的模块联邦的配置: