>& rectangles) {
+ int ans = 0, mx = 0;
+ for (auto& e : rectangles) {
+ int x = min(e[0], e[1]);
+ if (mx < x) {
+ mx = x;
+ ans = 1;
+ } else if (mx == x) {
+ ++ans;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.go b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.go
index c65572904e834..13cbea30b0d00 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.go
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.go
@@ -1,15 +1,13 @@
-func countGoodRectangles(rectangles [][]int) int {
- ans, mx := 0, 0
- for _, r := range rectangles {
- t := r[0]
- if t > r[1] {
- t = r[1]
- }
- if mx < t {
- mx, ans = t, 1
- } else if mx == t {
+func countGoodRectangles(rectangles [][]int) (ans int) {
+ mx := 0
+ for _, e := range rectangles {
+ x := min(e[0], e[1])
+ if mx < x {
+ mx = x
+ ans = 1
+ } else if mx == x {
ans++
}
}
- return ans
+ return
}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.java b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.java
index e066b57fb7431..eda3cedcc5ee7 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.java
@@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
-class Solution {
- public int countGoodRectangles(int[][] rectangles) {
- int ans = 0, mx = 0;
- for (int[] r : rectangles) {
- int t = Math.min(r[0], r[1]);
- if (mx < t) {
- mx = t;
- ans = 1;
- } else if (mx == t) {
- ++ans;
- }
- }
- return ans;
- }
+class Solution {
+ public int countGoodRectangles(int[][] rectangles) {
+ int ans = 0, mx = 0;
+ for (var e : rectangles) {
+ int x = Math.min(e[0], e[1]);
+ if (mx < x) {
+ mx = x;
+ ans = 1;
+ } else if (mx == x) {
+ ++ans;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.py b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.py
index 8a1ee4eb1b232..bf0b05847b281 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.py
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.py
@@ -1,10 +1,11 @@
-class Solution:
- def countGoodRectangles(self, rectangles: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- ans = mx = 0
- for l, w in rectangles:
- t = min(l, w)
- if mx < t:
- mx, ans = t, 1
- elif mx == t:
- ans += 1
- return ans
+class Solution:
+ def countGoodRectangles(self, rectangles: List[List[int]]) -> int:
+ ans = mx = 0
+ for l, w in rectangles:
+ x = min(l, w)
+ if mx < x:
+ ans = 1
+ mx = x
+ elif mx == x:
+ ans += 1
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.ts b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.ts
index f5111a630c851..46ee5dcbbd6f5 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/Solution.ts
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
function countGoodRectangles(rectangles: number[][]): number {
- let maxLen = 0,
- ans = 0;
- for (let [l, w] of rectangles) {
- let k = Math.min(l, w);
- if (k == maxLen) {
- ans++;
- } else if (k > maxLen) {
- maxLen = k;
+ let [ans, mx] = [0, 0];
+ for (const [l, w] of rectangles) {
+ const x = Math.min(l, w);
+ if (mx < x) {
+ mx = x;
ans = 1;
+ } else if (mx === x) {
+ ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1732.Find the Highest Altitude/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1732.Find the Highest Altitude/README_EN.md
index 97eb331b25934..a6176f7dee71b 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1732.Find the Highest Altitude/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1732.Find the Highest Altitude/README_EN.md
@@ -36,6 +36,26 @@
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Prefix Sum (Difference Array)**
+
+We assume the altitude of each point is $h_i$. Since $gain[i]$ represents the altitude difference between the $i$th point and the $(i + 1)$th point, we have $gain[i] = h_{i + 1} - h_i$. Therefore:
+
+$$
+\sum_{i = 0}^{n-1} gain[i] = h_1 - h_0 + h_2 - h_1 + \cdots + h_n - h_{n - 1} = h_n - h_0 = h_n
+$$
+
+which implies:
+
+$$
+h_{i+1} = \sum_{j = 0}^{i} gain[j]
+$$
+
+We can see that the altitude of each point can be calculated through the prefix sum. Therefore, we only need to traverse the array once, find the maximum value of the prefix sum, which is the highest altitude.
+
+> In fact, the $gain$ array in the problem is a difference array. The prefix sum of the difference array gives the original altitude array. Then find the maximum value of the original altitude array.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(1)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the array `gain`.
+
### **Python3**
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1734.Decode XORed Permutation/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1734.Decode XORed Permutation/README_EN.md
index c51b9acf5ce5d..ffd79009ff24a 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1734.Decode XORed Permutation/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1734.Decode XORed Permutation/README_EN.md
@@ -37,6 +37,12 @@
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Bitwise Operation**
+
+We notice that the array $perm$ is a permutation of the first $n$ positive integers, so the XOR of all elements in $perm$ is $1 \oplus 2 \oplus \cdots \oplus n$, denoted as $a$. And $encode[i]=perm[i] \oplus perm[i+1]$, if we denote the XOR of all elements $encode[0],encode[2],\cdots,encode[n-3]$ as $b$, then $perm[n-1]=a \oplus b$. Knowing the last element of $perm$, we can find all elements of $perm$ by traversing the array $encode$ in reverse order.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array $perm$. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is $O(1)$.
+
### **Python3**
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1735.Count Ways to Make Array With Product/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1735.Count Ways to Make Array With Product/README_EN.md
index 6595be2308a49..692d66ed09b34 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1735.Count Ways to Make Array With Product/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1735.Count Ways to Make Array With Product/README_EN.md
@@ -37,6 +37,22 @@
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Prime Factorization + Combinatorial Mathematics**
+
+We can perform prime factorization on $k$, i.e., $k = p_1^{x_1} \times p_2^{x_2} \times \cdots \times p_m^{x_m}$, where $p_i$ is a prime number, and $x_i$ is the exponent of $p_i$. The problem is equivalent to: placing $x_1$ $p_1$s, $x_2$ $p_2$s, $\cdots$, $x_m$ $p_m$s into $n$ positions respectively, where a single position can be empty. The question is how many schemes are there.
+
+According to combinatorial mathematics, there are two cases when we put $x$ balls into $n$ boxes:
+
+If the box cannot be empty, the number of schemes is $C_{x-1}^{n-1}$. This is using the partition method, i.e., there are a total of $x$ balls, and we insert $n-1$ partitions at $x-1$ positions, thereby dividing the $x$ balls into $n$ groups.
+
+If the box can be empty, we can add $n$ virtual balls, and then use the partition method, i.e., there are a total of $x+n$ balls, and we insert $n-1$ partitions at $x+n-1$ positions, thereby dividing the actual $x$ balls into $n$ groups and allowing the box to be empty. Therefore, the number of schemes is $C_{x+n-1}^{n-1}$.
+
+Therefore, for each query $queries[i]$, we can first perform prime factorization on $k$ to get the exponents $x_1, x_2, \cdots, x_m$, then calculate $C_{x_1+n-1}^{n-1}, C_{x_2+n-1}^{n-1}, \cdots, C_{x_m+n-1}^{n-1}$, and finally multiply all the scheme numbers.
+
+So, the problem is transformed into how to quickly calculate $C_m^n$. According to the formula $C_m^n = \frac{m!}{n!(m-n)!}$, we can pre-process $m!$, and then use the inverse element to quickly calculate $C_m^n$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(K \times \log \log K + N + m \times \log K)$, and the space complexity is $O(N)$.
+
### **Python3**
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1736.Latest Time by Replacing Hidden Digits/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1736.Latest Time by Replacing Hidden Digits/README_EN.md
index 1d657c3de3856..10b46b009f4c1 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1736.Latest Time by Replacing Hidden Digits/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1736.Latest Time by Replacing Hidden Digits/README_EN.md
@@ -43,6 +43,17 @@
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Greedy**
+
+We process each digit of the string in order, following these rules:
+
+1. First digit: If the value of the second digit is determined and falls within the range $[4, 9]$, then the first digit can only be $1$. Otherwise, the first digit can be up to $2$.
+1. Second digit: If the value of the first digit is determined and is $2$, then the second digit can be up to $3$. Otherwise, the second digit can be up to $9$.
+1. Third digit: The third digit can be up to $5$.
+1. Fourth digit: The fourth digit can be up to $9$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(1)$, and the space complexity is $O(1)$.
+
### **Python3**
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1737.Change Minimum Characters to Satisfy One of Three Conditions/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1737.Change Minimum Characters to Satisfy One of Three Conditions/README_EN.md
index 963dbfe40438d..db9f938f78ccb 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1737.Change Minimum Characters to Satisfy One of Three Conditions/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1737.Change Minimum Characters to Satisfy One of Three Conditions/README_EN.md
@@ -47,7 +47,17 @@ The best way was done in 2 operations (either condition 1 or condition 3).
## Solutions
-Prefix Sum
+**Solution 1: Counting + Enumeration**
+
+First, we count the number of occurrences of each letter in strings $a$ and $b$, denoted as $cnt_1$ and $cnt_2$.
+
+Then, we consider condition $3$, i.e., every letter in $a$ and $b$ is the same. We just need to enumerate the final letter $c$, and then count the number of letters in $a$ and $b$ that are not $c$. This is the number of characters that need to be changed.
+
+Next, we consider conditions $1$ and $2$, i.e., every letter in $a$ is less than every letter in $b$, or every letter in $b$ is less than every letter in $a$. For condition $1$, we make all characters in string $a$ less than character $c$, and all characters in string $b$ not less than $c$. We enumerate $c$ to find the smallest answer. Condition $2$ is similar.
+
+The final answer is the minimum of the above three cases.
+
+The time complexity is $O(m + n + C^2)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the lengths of strings $a$ and $b$ respectively, and $C$ is the size of the character set. In this problem, $C = 26$.
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README.md b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README.md
index f910a8aa316c9..0ccfd0aa5b3c3 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README.md
@@ -54,7 +54,23 @@
-二维前缀异或,然后求第 k 大的值即可。
+**方法一:二维前缀异或 + 排序或快速选择**
+
+我们定义一个二维前缀异或数组 $s$,其中 $s[i][j]$ 表示矩阵前 $i$ 行和前 $j$ 列的元素异或运算的结果,即:
+
+$$
+s[i][j] = \bigoplus_{0 \leq x \leq i, 0 \leq y \leq j} matrix[x][y]
+$$
+
+而 $s[i][j]$ 可以由 $s[i - 1][j]$, $s[i][j - 1]$ 和 $s[i - 1][j - 1]$ 三个元素计算得到,即:
+
+$$
+s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] \oplus s[i][j - 1] \oplus s[i - 1][j - 1] \oplus matrix[i - 1][j - 1]
+$$
+
+我们遍历矩阵,计算出所有的 $s[i][j]$,然后将其排序,最后返回第 $k$ 大的元素即可。如果不想使用排序,也可以使用快速选择算法,这样可以优化时间复杂度。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n))$ 或 $O(m \times n)$,空间复杂度 $O(m \times n)$。其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是矩阵的行数和列数。
@@ -81,7 +97,6 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
-
public int kthLargestValue(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] s = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
@@ -140,6 +155,25 @@ func kthLargestValue(matrix [][]int, k int) int {
}
```
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function kthLargestValue(matrix: number[][], k: number): number {
+ const m: number = matrix.length;
+ const n: number = matrix[0].length;
+ const s = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => 0));
+ const ans: number[] = [];
+ for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
+ for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ s[i + 1][j + 1] = s[i + 1][j] ^ s[i][j + 1] ^ s[i][j] ^ matrix[i][j];
+ ans.push(s[i + 1][j + 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ ans.sort((a, b) => b - a);
+ return ans[k - 1];
+}
+```
+
### **...**
```
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README_EN.md
index 6401b3710907b..079d29c94d819 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/README_EN.md
@@ -47,6 +47,24 @@
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Two-dimensional Prefix XOR + Sorting or Quick Selection**
+
+We define a two-dimensional prefix XOR array $s$, where $s[i][j]$ represents the XOR result of the elements in the first $i$ rows and the first $j$ columns of the matrix, i.e.,
+
+$$
+s[i][j] = \bigoplus_{0 \leq x \leq i, 0 \leq y \leq j} matrix[x][y]
+$$
+
+And $s[i][j]$ can be calculated from the three elements $s[i - 1][j]$, $s[i][j - 1]$ and $s[i - 1][j - 1]$, i.e.,
+
+$$
+s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] \oplus s[i][j - 1] \oplus s[i - 1][j - 1] \oplus matrix[i - 1][j - 1]
+$$
+
+We traverse the matrix, calculate all $s[i][j]$, then sort them, and finally return the $k$th largest element. If you don't want to use sorting, you can also use the quick selection algorithm, which can optimize the time complexity.
+
+The time complexity is $O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n))$ or $O(m \times n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Here, $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the matrix, respectively.
+
### **Python3**
@@ -68,7 +86,6 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
-
public int kthLargestValue(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] s = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
@@ -127,6 +144,25 @@ func kthLargestValue(matrix [][]int, k int) int {
}
```
+### **TypeScript**
+
+```ts
+function kthLargestValue(matrix: number[][], k: number): number {
+ const m: number = matrix.length;
+ const n: number = matrix[0].length;
+ const s = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => 0));
+ const ans: number[] = [];
+ for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
+ for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ s[i + 1][j + 1] = s[i + 1][j] ^ s[i][j + 1] ^ s[i][j] ^ matrix[i][j];
+ ans.push(s[i + 1][j + 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ ans.sort((a, b) => b - a);
+ return ans[k - 1];
+}
+```
+
### **...**
```
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/Solution.ts b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..cb4b51977f0d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1738.Find Kth Largest XOR Coordinate Value/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+function kthLargestValue(matrix: number[][], k: number): number {
+ const m: number = matrix.length;
+ const n: number = matrix[0].length;
+ const s = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => 0));
+ const ans: number[] = [];
+ for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
+ for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
+ s[i + 1][j + 1] = s[i + 1][j] ^ s[i][j + 1] ^ s[i][j] ^ matrix[i][j];
+ ans.push(s[i + 1][j + 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ ans.sort((a, b) => b - a);
+ return ans[k - 1];
+}
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README.md b/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README.md
index c29f0a7060c7a..c8147d435fd47 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README.md
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@
如果此时盒子还有剩余,那么可以从最低一层继续摆放,假设摆放 $i$ 个,那么累计可摆放的盒子个数为 $1+2+\cdots+i$。
-时间复杂度 $O(\sqrt{n})$,空间复杂度 $O(1)$。其中 $n$ 为题目给定的盒子数量。
+时间复杂度 $O(\sqrt{n})$,其中 $n$ 为题目给定的盒子数量。空间复杂度 $O(1)$。
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README_EN.md
index 9008d66e0fdc9..346766ad96fc3 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1739.Building Boxes/README_EN.md
@@ -55,6 +55,16 @@ These boxes are placed in the corner of the room, where the corner is on the bac
## Solutions
+**Solution 1: Mathematical Rule**
+
+According to the problem description, the box with the highest number of layers needs to be placed in the corner of the wall, and the arrangement of the boxes is in a step-like shape, which can minimize the number of boxes touching the ground.
+
+Assume that the boxes are arranged in $k$ layers. From top to bottom, if each layer is filled, then the number of boxes in each layer is $1, 1+2, 1+2+3, \cdots, 1+2+\cdots+k$.
+
+If there are still remaining boxes at this point, they can continue to be placed from the lowest layer. Assume that $i$ boxes are placed, then the cumulative number of boxes that can be placed is $1+2+\cdots+i$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(\sqrt{n})$, where $n$ is the number of boxes given in the problem. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
+
### **Python3**
diff --git a/solution/2500-2599/2563.Count the Number of Fair Pairs/README.md b/solution/2500-2599/2563.Count the Number of Fair Pairs/README.md
index 36cd9486017e0..e16d4de115741 100644
--- a/solution/2500-2599/2563.Count the Number of Fair Pairs/README.md
+++ b/solution/2500-2599/2563.Count the Number of Fair Pairs/README.md
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@
输入:nums = [1,7,9,2,5], lower = 11, upper = 11
输出:1
-解释:只有单个公平数对:(2,3) 。
+解释:只有单个公平数对:(2,9) 。
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2693.Call Function with Custom Context/README_EN.md b/solution/2600-2699/2693.Call Function with Custom Context/README_EN.md
index 5b7890dec324a..97c0eebb69fce 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2693.Call Function with Custom Context/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2693.Call Function with Custom Context/README_EN.md
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ args = [{"item": "burger"}, 10, 1.1]
Constraints:
-
+
typeof args[0] == 'object' and args[0] != null1 <= args.length <= 1002 <= JSON.stringify(args[0]).length <= 105Write a function that accepts two deeply nested objects or arrays obj1 and obj2 and returns a new object representing their differences.
-The function should compare the properties of the two objects and identify any changes. The returned object should only contains keys where the value is different from obj1 to obj2. For each changed key, the value should be represented as an array [obj1 value, obj2 value]. Keys that exist in one object but not in the other should not be included in the returned object. When comparing two arrays, the indices of the arrays are considered to be their keys. The end result should be a deeply nested object where each leaf value is a difference array.
+The function should compare the properties of the two objects and identify any changes. The returned object should only contains keys where the value is different from obj1 to obj2.
+
+For each changed key, the value should be represented as an array [obj1 value, obj2 value]. Keys that exist in one object but not in the other should not be included in the returned object. When comparing two arrays, the indices of the arrays are considered to be their keys. The end result should be a deeply nested object where each leaf value is a difference array.
You may assume that both objects are the output of JSON.parse.
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2715.Timeout Cancellation/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2715.Timeout Cancellation/README_EN.md
index 423d1c91a44d1..4a4cd7e96a77e 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2715.Timeout Cancellation/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2715.Timeout Cancellation/README_EN.md
@@ -24,26 +24,8 @@ setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs)
Output: [{"time": 20, "returned": 10}]
Explanation:
const cancelTimeMs = 50;
-const result = [];
-
-const fn = (x) => x * 5;
-
-const start = performance.now();
-
-const log = (...argsArr) => {
- const diff = Math.floor(performance.now() - start);
- result.push({"time": diff, "returned": fn(...argsArr)});
-}
-
-const cancel = cancellable(log, [2], 20);
-
-const maxT = Math.max(t, 50);
-
-setTimeout(cancel, cancelTimeMs);
-
-setTimeout(() => {
- console.log(result); // [{"time":20,"returned":10}]
-}, maxT + 15);
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x) => x * 5, [2], 20);
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs);
The cancellation was scheduled to occur after a delay of cancelTimeMs (50ms), which happened after the execution of fn(2) at 20ms.
@@ -55,6 +37,9 @@ The cancellation was scheduled to occur after a delay of cancelTimeMs (50ms), wh
Output: []
Explanation:
const cancelTimeMs = 50;
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x) => x**2, [2], 100);
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs);
+
The cancellation was scheduled to occur after a delay of cancelTimeMs (50ms), which happened before the execution of fn(2) at 100ms, resulting in fn(2) never being called.
@@ -65,6 +50,9 @@ The cancellation was scheduled to occur after a delay of cancelTimeMs (50ms), wh
Output: [{"time": 30, "returned": 8}]
Explanation:
const cancelTimeMs = 100;
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x1, x2) => x1 * x2, [2,4], 30);
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs);
+
The cancellation was scheduled to occur after a delay of cancelTimeMs (100ms), which happened after the execution of fn(2,4) at 30ms.
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2724.Sort By/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2724.Sort By/README_EN.md
index 64b2f73b8b791..00feabdacc972 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2724.Sort By/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2724.Sort By/README_EN.md
@@ -37,8 +37,8 @@
Constraints:
- arr is a valid JSON arrayfn is a function that returns a numberarr is a valid JSON arrayfn is a function that returns a number1 <= arr.length <= 5 * 105
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2725.Interval Cancellation/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2725.Interval Cancellation/README_EN.md
index 80222d6de91fe..9c9b6af7f9989 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2725.Interval Cancellation/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2725.Interval Cancellation/README_EN.md
@@ -23,23 +23,9 @@
{"time": 175, "returned": 8}
]
Explanation:
-const result = [];
-const fn = (x) => x * 2;
const cancelTimeMs = 190;
-
-const start = performance.now();
-
-const log = (...argsArr) => {
- const diff = Math.floor(performance.now() - start);
- result.push({"time": diff, "returned": fn(...argsArr)});
-}
-
-const cancel = cancellable(log, [4], 35);
-setTimeout(cancel, cancelTimeMs);
-
-setTimeout(() => {
- console.log(result); // Output
- }, cancelTimeMs + 50)
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x) => x * 2, [4], 35);
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs);
Every 35ms, fn(4) is called. Until t=190ms, then it is cancelled.
1st fn call is at 0ms. fn(4) returns 8.
@@ -65,7 +51,9 @@ Cancelled at 190ms
{"time": 150, "returned": 10}
]
Explanation:
-const cancelTimeMs = 165;
+const cancelTimeMs = 165;
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x1, x2) => (x1 * x2), [2, 5], 30)
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs)
Every 30ms, fn(2, 5) is called. Until t=165ms, then it is cancelled.
1st fn call is at 0ms
@@ -90,6 +78,8 @@ Cancelled at 165ms
]
Explanation:
const cancelTimeMs = 180;
+const cancelFn = cancellable((x1, x2, x3) => (x1 + x2 + x3), [5, 1, 3], 50)
+setTimeout(cancelFn, cancelTimeMs)
Every 50ms, fn(5, 1, 3) is called. Until t=180ms, then it is cancelled.
1st fn call is at 0ms
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2754.Bind Function to Context/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2754.Bind Function to Context/README_EN.md
index 61640ed6fadce..c20407dfad9ad 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2754.Bind Function to Context/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2754.Bind Function to Context/README_EN.md
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ boundFunc(); // "My name is Kathy"
Constraints:
- obj is a non-null objectobj is a non-null object0 <= inputs.length <= 100
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2756.Query Batching/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2756.Query Batching/README_EN.md
index c97a5c2e2adae..723d839c0a163 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2756.Query Batching/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2756.Query Batching/README_EN.md
@@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
-
-
Example 1:
@@ -119,7 +117,7 @@ queryMultiple(['f']) is called at t=350ms, it is resolved at 450ms
0 <= t <= 10000 <= calls.length <= 101 <= key.length <= 100all keys are unique- All keys are unique
## Solutions
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md"
similarity index 97%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md"
index 964ab6057909c..cacf01ce645b3 100644
--- "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md"
+++ "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README.md"
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# [2764. 数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/is-array-a-preorder-of-some-binary-tree)
-[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+[English Version](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
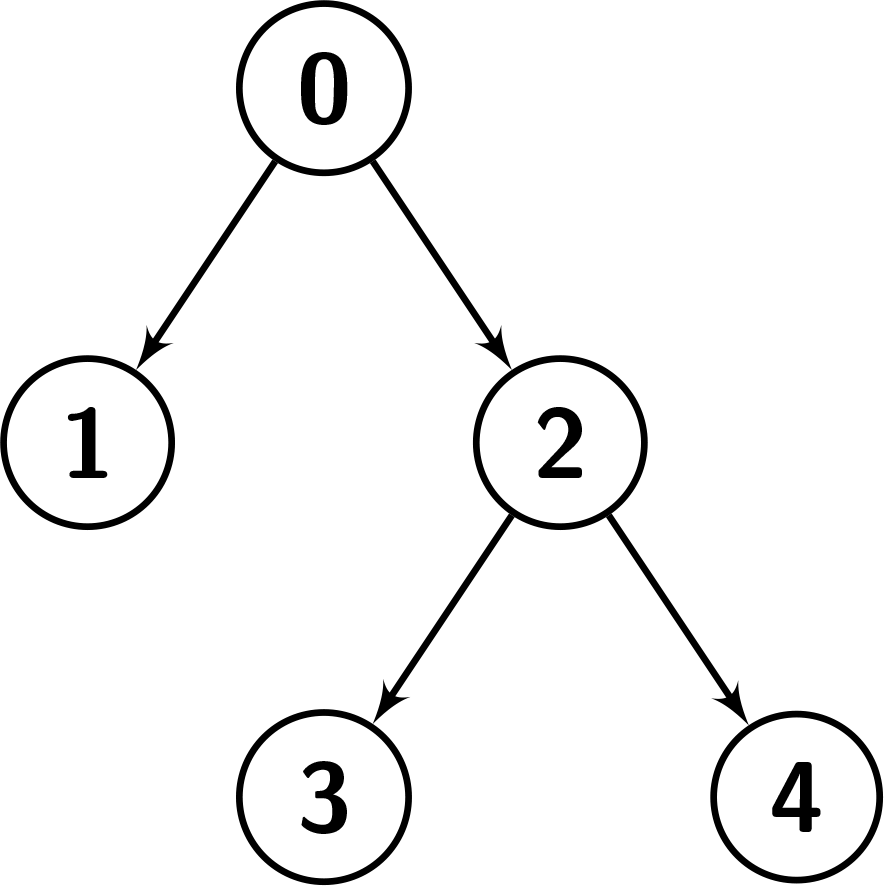
我们可以验证这是树的前序遍历,首先访问节点 0,然后对左子节点进行前序遍历,即 [1] ,然后对右子节点进行前序遍历,即 [2,3,4] 。
-
+
示例 2:
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
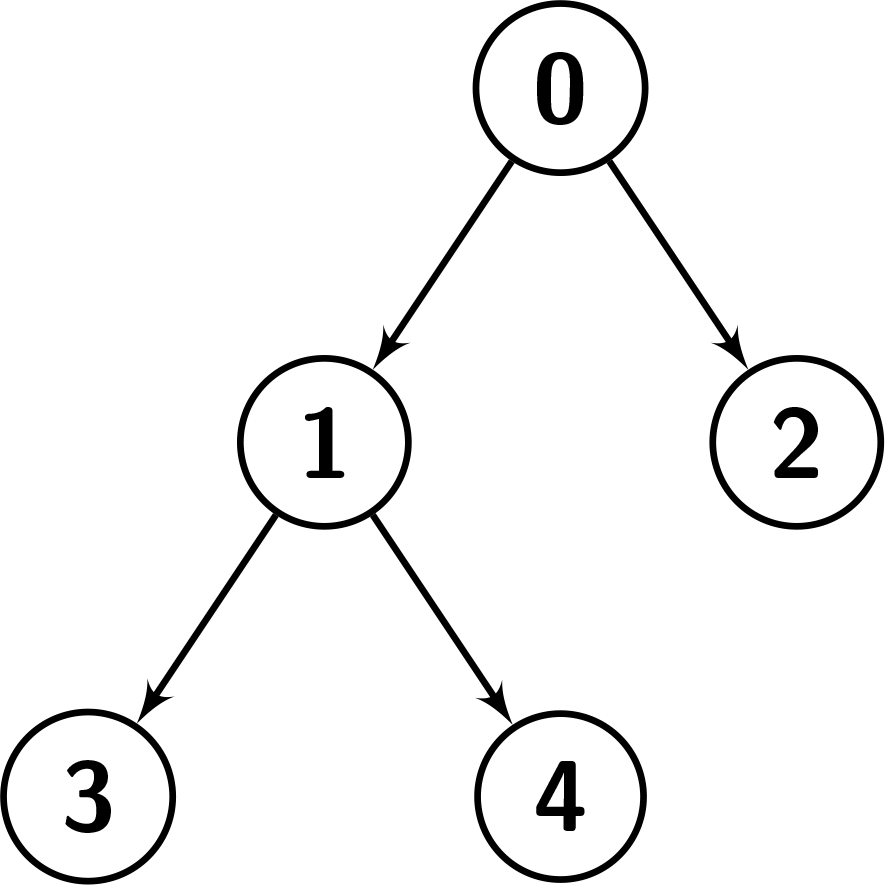
对于前序遍历,首先访问节点 0,然后对左子节点进行前序遍历,即 [1,3,4],但是我们可以看到在给定的顺序中,2 位于 1 和 3 之间,因此它不是树的前序遍历。
-
+
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md"
similarity index 93%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md"
index 09610786d812e..f6bc683163e36 100644
--- "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md"
+++ "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/README_EN.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-# [2764. is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/is-array-a-preorder-of-some-binary-tree)
+# [2764. Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/is-array-a-preorder-of-some-binary-tree)
-[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+[中文文档](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
## Description
Given a 0-indexed integer 2D array nodes, your task is to determine if the given array represents the preorder traversal of some binary tree.
-For each index i, nodes[i] = [id, parentId], where id is the id of the node at the index i and parentId is the id of its parent in the tree (if the node has no parent, then parentId = -1).
+For each index i, nodes[i] = [id, parentId], where id is the id of the node at the index i and parentId is the id of its parent in the tree (if the node has no parent, then parentId == -1).
-Return true if the given array represents the preorder traversal of some tree, and false otherwise.
+Return true if the given array represents the preorder traversal of some tree, and false otherwise.
Note: the preorder traversal of a tree is a recursive way to traverse a tree in which we first visit the current node, then we do the preorder traversal for the left child, and finally, we do it for the right child.
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
We can show that this is the preorder traversal of the tree, first we visit node 0, then we do the preorder traversal of the right child which is [1], then we do the preorder traversal of the left child which is [2,3,4].
-
+
Example 2:
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ We can show that this is the preorder traversal of the tree, first we visit node
For the preorder traversal, first we visit node 0, then we do the preorder traversal of the right child which is [1,3,4], but we can see that in the given order, 2 comes between 1 and 3, so, it's not the preorder traversal of the tree.
-
+
Constraints:
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.cpp" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.cpp"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.cpp"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.cpp"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.go" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.go"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.go"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.go"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.java" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.java"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.java"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.java"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.py" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.py"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.py"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.py"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.ts" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.ts"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.ts"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/Solution.ts"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/1.png" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/1.png"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/1.png"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/1.png"
diff --git "a/solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/2.png" "b/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/2.png"
similarity index 100%
rename from "solution/2700-2799/2764.is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/2.png"
rename to "solution/2700-2799/2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some \342\200\214Binary Tree/images/2.png"
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2774.Array Upper Bound/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2774.Array Upper Bound/README_EN.md
index 8e06c07a1108f..6d6d17e5247f8 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2774.Array Upper Bound/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2774.Array Upper Bound/README_EN.md
@@ -39,6 +39,9 @@
nums is sorted in ascending order.
+
+Follow up: Can you write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity?
+
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2776.Convert Callback Based Function to Promise Based Function/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2776.Convert Callback Based Function to Promise Based Function/README_EN.md
index fe35ce8c098ee..269e80ba8a88c 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2776.Convert Callback Based Function to Promise Based Function/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2776.Convert Callback Based Function to Promise Based Function/README_EN.md
@@ -6,7 +6,9 @@
Write a function that accepts another function fn and converts the callback-based function into a promise-based function.
-The promisify function takes in a function fn that accepts a callback as its first argument and also any additional arguments. It returns a new function that returns a promise instead. The returned promise should resolve with the result of the original function when the callback is called with a successful response, and reject with the error when the callback is called with an error. The returned promise-based function should accept the additional arguments as inputs.
+The function fn takes a callback as its first argument, along with any additional arguments args passed as separate inputs.
+
+The promisify function returns a new function that should return a promise. The promise should resolve with the argument passed as the first parameter of the callback when the callback is invoked without error, and reject with the error when the callback is called with an error as the second argument.
The following is an example of a function that could be passed into promisify.
diff --git a/solution/2700-2799/2796.Repeat String/README_EN.md b/solution/2700-2799/2796.Repeat String/README_EN.md
index 5557e88d77a17..6262e1a4d35e7 100644
--- a/solution/2700-2799/2796.Repeat String/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2700-2799/2796.Repeat String/README_EN.md
@@ -37,8 +37,7 @@
Constraints:
- 1 <= str.length <= 10001 <= times <= 10001 <= str.length, times <= 105
## Solutions
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README.md b/solution/DATABASE_README.md
index c07f1614bd397..6ee852dec4315 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README.md
@@ -250,4 +250,15 @@
## 版权
-著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+
+## 联系我们
+
+欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
+
+|  |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
index aad41ef999334..07fb8ec7a3df1 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
@@ -248,4 +248,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|
|
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
index aad41ef999334..07fb8ec7a3df1 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
@@ -248,4 +248,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|  |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
index e24d9b431fc61..c95287c9c0c86 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
@@ -80,4 +80,15 @@
## 版权
-著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+
+## 联系我们
+
+欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
+
+|
|
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
index e24d9b431fc61..c95287c9c0c86 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
@@ -80,4 +80,15 @@
## 版权
-著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+
+## 联系我们
+
+欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
+
+|  |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
index 6d0c0dbc0b136..e6781d310ba50 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
@@ -78,4 +78,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|
|
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
index 6d0c0dbc0b136..e6781d310ba50 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
@@ -78,4 +78,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|  |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index b2fd88bdf9cdb..aea51e28c1ce8 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2774,7 +2774,7 @@
| 2761 | [和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`枚举`,`数论` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2762 | [不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md) | `队列`,`数组`,`有序集合`,`滑动窗口`,`单调队列`,`堆(优先队列)` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2763 | [所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`有序集合` | 困难 | 第 352 场周赛 |
-| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md) | `数组`,`枚举` | 简单 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2766 | [重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`排序`,`模拟` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2767 | [将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md) | `哈希表`,`字符串`,`动态规划`,`回溯` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
@@ -2989,8 +2989,4 @@
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
|
|
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index b2fd88bdf9cdb..aea51e28c1ce8 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2774,7 +2774,7 @@
| 2761 | [和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`枚举`,`数论` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2762 | [不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md) | `队列`,`数组`,`有序集合`,`滑动窗口`,`单调队列`,`堆(优先队列)` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2763 | [所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`有序集合` | 困难 | 第 352 场周赛 |
-| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md) | `数组`,`枚举` | 简单 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2766 | [重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`排序`,`模拟` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2767 | [将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md) | `哈希表`,`字符串`,`动态规划`,`回溯` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
@@ -2989,8 +2989,4 @@
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
|  |
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
-
-## 许可证
-
-知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
\ No newline at end of file
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 840750846244b..fbaba2fd8a2cf 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2772,7 +2772,7 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
| 2761 | [Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Math`,`Enumeration`,`Number Theory` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2762 | [Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Queue`,`Array`,`Ordered Set`,`Sliding Window`,`Monotonic Queue`,`Heap (Priority Queue)` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2763 | [Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Ordered Set` | Hard | Weekly Contest 352 |
-| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Enumeration` | Easy | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2766 | [Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Sorting`,`Simulation` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2767 | [Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md) | `Hash Table`,`String`,`Dynamic Programming`,`Backtracking` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
@@ -2991,4 +2991,4 @@ We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), wit
## License
-This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index c0c71264c584e..78016bbc0885b 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md)
- [2762.不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2763.所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md)
- - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+ - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
- [2765.最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
- [2766.重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
- [2767.将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 8ca362264e6c1..4a4cb39a6461a 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md)
- [2762.Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2763.Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- - [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+ - [2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
- [2765.Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
- [2766.Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
- [2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/template.md b/solution/template.md
index b139c1832a136..4a83ccc7df5a8 100644
--- a/solution/template.md
+++ b/solution/template.md
@@ -23,6 +23,10 @@
|
|
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
-
-## 许可证
-
-知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
\ No newline at end of file
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 840750846244b..fbaba2fd8a2cf 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2772,7 +2772,7 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
| 2761 | [Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Math`,`Enumeration`,`Number Theory` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2762 | [Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Queue`,`Array`,`Ordered Set`,`Sliding Window`,`Monotonic Queue`,`Heap (Priority Queue)` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2763 | [Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Ordered Set` | Hard | Weekly Contest 352 |
-| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Enumeration` | Easy | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2766 | [Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Sorting`,`Simulation` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2767 | [Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md) | `Hash Table`,`String`,`Dynamic Programming`,`Backtracking` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
@@ -2991,4 +2991,4 @@ We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), wit
## License
-This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index c0c71264c584e..78016bbc0885b 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md)
- [2762.不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2763.所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md)
- - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+ - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
- [2765.最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
- [2766.重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
- [2767.将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 8ca362264e6c1..4a4cb39a6461a 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md)
- [2762.Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2763.Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- - [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+ - [2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
- [2765.Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
- [2766.Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
- [2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/template.md b/solution/template.md
index b139c1832a136..4a83ccc7df5a8 100644
--- a/solution/template.md
+++ b/solution/template.md
@@ -23,6 +23,10 @@
|  |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
+
---
|
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
+
---









 |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
index aad41ef999334..07fb8ec7a3df1 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
@@ -248,4 +248,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|
|
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
index aad41ef999334..07fb8ec7a3df1 100644
--- a/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md
@@ -248,4 +248,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|  |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
index e24d9b431fc61..c95287c9c0c86 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
@@ -80,4 +80,15 @@
## 版权
-著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+
+## 联系我们
+
+欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
+
+|
|
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
index e24d9b431fc61..c95287c9c0c86 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README.md
@@ -80,4 +80,15 @@
## 版权
-著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
+
+## 联系我们
+
+欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
+
+|  |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
index 6d0c0dbc0b136..e6781d310ba50 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
@@ -78,4 +78,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|
|
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
diff --git a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
index 6d0c0dbc0b136..e6781d310ba50 100644
--- a/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md
@@ -78,4 +78,15 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
## Copyright
-[@Doocs](https://github.com/doocs)
+The copyright of this project belongs to [Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) community. For commercial reprints, please contact [@yanglbme](mailto:contact@yanglibin.info) for authorization. For non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
+
+## Contact Us
+
+We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), with the note "leetcode". In the future, we will create algorithm and technology related discussion groups, where we can learn and share experiences together, and make progress together.
+
+|  |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index b2fd88bdf9cdb..aea51e28c1ce8 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2774,7 +2774,7 @@
| 2761 | [和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`枚举`,`数论` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2762 | [不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md) | `队列`,`数组`,`有序集合`,`滑动窗口`,`单调队列`,`堆(优先队列)` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2763 | [所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`有序集合` | 困难 | 第 352 场周赛 |
-| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md) | `数组`,`枚举` | 简单 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2766 | [重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`排序`,`模拟` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2767 | [将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md) | `哈希表`,`字符串`,`动态规划`,`回溯` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
@@ -2989,8 +2989,4 @@
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
|
|
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+
+## License
+
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index b2fd88bdf9cdb..aea51e28c1ce8 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2774,7 +2774,7 @@
| 2761 | [和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md) | `数组`,`数学`,`枚举`,`数论` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2762 | [不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md) | `队列`,`数组`,`有序集合`,`滑动窗口`,`单调队列`,`堆(优先队列)` | 中等 | 第 352 场周赛 |
| 2763 | [所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`有序集合` | 困难 | 第 352 场周赛 |
-| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md) | `栈`,`树`,`深度优先搜索`,`二叉树` | 中等 | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md) | `数组`,`枚举` | 简单 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2766 | [重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md) | `数组`,`哈希表`,`排序`,`模拟` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
| 2767 | [将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md) | `哈希表`,`字符串`,`动态规划`,`回溯` | 中等 | 第 108 场双周赛 |
@@ -2989,8 +2989,4 @@
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
|  |
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
-
-## 许可证
-
-知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
\ No newline at end of file
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 840750846244b..fbaba2fd8a2cf 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2772,7 +2772,7 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
| 2761 | [Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Math`,`Enumeration`,`Number Theory` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2762 | [Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Queue`,`Array`,`Ordered Set`,`Sliding Window`,`Monotonic Queue`,`Heap (Priority Queue)` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2763 | [Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Ordered Set` | Hard | Weekly Contest 352 |
-| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Enumeration` | Easy | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2766 | [Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Sorting`,`Simulation` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2767 | [Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md) | `Hash Table`,`String`,`Dynamic Programming`,`Backtracking` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
@@ -2991,4 +2991,4 @@ We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), wit
## License
-This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index c0c71264c584e..78016bbc0885b 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md)
- [2762.不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2763.所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md)
- - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+ - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
- [2765.最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
- [2766.重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
- [2767.将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 8ca362264e6c1..4a4cb39a6461a 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md)
- [2762.Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2763.Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- - [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+ - [2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
- [2765.Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
- [2766.Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
- [2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/template.md b/solution/template.md
index b139c1832a136..4a83ccc7df5a8 100644
--- a/solution/template.md
+++ b/solution/template.md
@@ -23,6 +23,10 @@
|
|
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
-
-## 许可证
-
-知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
\ No newline at end of file
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 840750846244b..fbaba2fd8a2cf 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2772,7 +2772,7 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
| 2761 | [Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Math`,`Enumeration`,`Number Theory` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2762 | [Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Queue`,`Array`,`Ordered Set`,`Sliding Window`,`Monotonic Queue`,`Heap (Priority Queue)` | Medium | Weekly Contest 352 |
| 2763 | [Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Ordered Set` | Hard | Weekly Contest 352 |
-| 2764 | [is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
+| 2764 | [Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md) | `Stack`,`Tree`,`Depth-First Search`,`Binary Tree` | Medium | 🔒 |
| 2765 | [Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Enumeration` | Easy | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2766 | [Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md) | `Array`,`Hash Table`,`Sorting`,`Simulation` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
| 2767 | [Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md) | `Hash Table`,`String`,`Dynamic Programming`,`Backtracking` | Medium | Biweekly Contest 108 |
@@ -2991,4 +2991,4 @@ We welcome everyone to add @yanglbme's personal WeChat (WeChat ID: YLB0109), wit
## License
-This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
+This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index c0c71264c584e..78016bbc0885b 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.和等于目标值的质数对](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README.md)
- [2762.不间断子数组](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README.md)
- [2763.所有子数组中不平衡数字之和](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README.md)
- - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
+ - [2764.数组是否表示某二叉树的前序遍历](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README.md)
- [2765.最长交替子序列](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README.md)
- [2766.重新放置石块](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README.md)
- [2767.将字符串分割为最少的美丽子字符串](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 8ca362264e6c1..4a4cb39a6461a 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -2817,7 +2817,7 @@
- [2761.Prime Pairs With Target Sum](/solution/2700-2799/2761.Prime%20Pairs%20With%20Target%20Sum/README_EN.md)
- [2762.Continuous Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2762.Continuous%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- [2763.Sum of Imbalance Numbers of All Subarrays](/solution/2700-2799/2763.Sum%20of%20Imbalance%20Numbers%20of%20All%20Subarrays/README_EN.md)
- - [2764.is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
+ - [2764.Is Array a Preorder of Some Binary Tree](/solution/2700-2799/2764.Is%20Array%20a%20Preorder%20of%20Some%20%E2%80%8CBinary%20Tree/README_EN.md)
- [2765.Longest Alternating Subarray](/solution/2700-2799/2765.Longest%20Alternating%20Subarray/README_EN.md)
- [2766.Relocate Marbles](/solution/2700-2799/2766.Relocate%20Marbles/README_EN.md)
- [2767.Partition String Into Minimum Beautiful Substrings](/solution/2700-2799/2767.Partition%20String%20Into%20Minimum%20Beautiful%20Substrings/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/template.md b/solution/template.md
index b139c1832a136..4a83ccc7df5a8 100644
--- a/solution/template.md
+++ b/solution/template.md
@@ -23,6 +23,10 @@
|  |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
+
---
|
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+## 许可证
+
+知识共享 版权归属-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 公共许可证
+
---
 -[Gitpod.io](https://www.gitpod.io) 是一个免费的在线开发环境,你也可以使用它参与本项目。
-
-
-[Gitpod.io](https://www.gitpod.io) 是一个免费的在线开发环境,你也可以使用它参与本项目。
-
-